Pathophysiology Week 1 - Lesson 1 and 2
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
What are cellular changes?
Adaptations that cells undergo in response to various conditions.
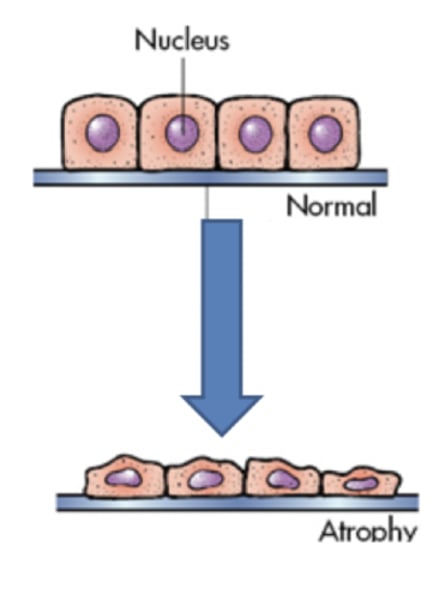
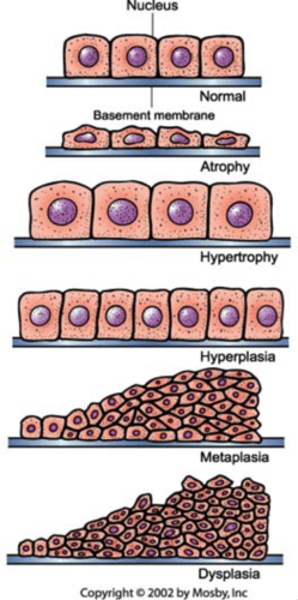
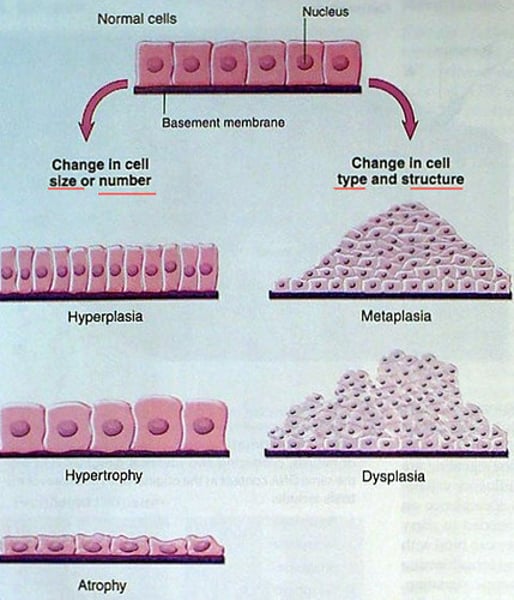
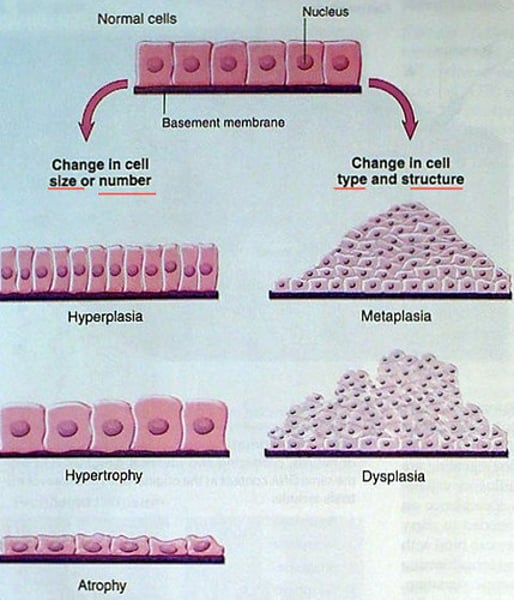
What is Atrophy?
Decrease in cell size due to disuse, malnutrition, or loss of nerve supply.
What is Hypertrophy?
Increase in cell size often seen in exercising or in response to heart workload.
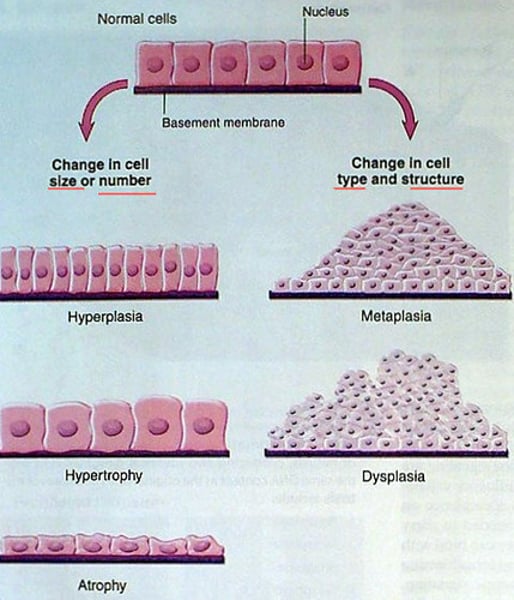
What is Hyperplasia?
Increase in cell number, observed in the human uterus during pregnancy.
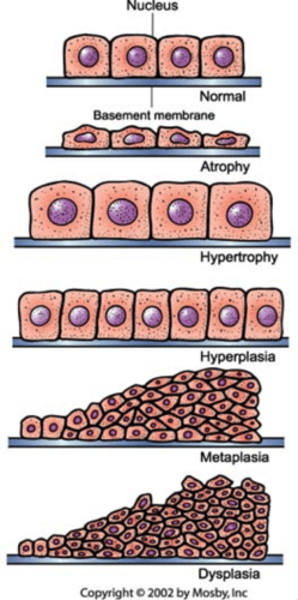
What is Metaplasia?
Replacement of one mature cell type with another mature cell type, often linked to smoking.
What can cellular changes lead to?
Diseases, including cancer.
What happens when cells are damaged?
Altered metabolic reactions and loss of function,
causing cells to swell with water and lipids,
and increasing in size.
What are the potential outcomes if cell damage continues after initial damage occurs?
Cells may recover or die, potentially causing inflammation and damage to nearby cells.
What can severe cell damage result in?
Cell death, lysis, and dissolution by lysosomal enzymes.
What are the consequences of severe cell damage?
Inflammation and tissue damage.
What is necrosis?
Unplanned cellular damage, distinct from apoptosis.
What are the types of necrosis?
Liquefaction Necrosis and Coagulative Necrosis.
What happens in Liquefaction Necrosis?
Dead cells release enzymes and the tissue becomes creamy yellow-blue.
What happens in Coagulative Necrosis?
Altered or denatured cell proteins cause the tissue to become dry, hard, and white, with a gel-like appearance.
What is Dry Gangrene?
Caused by whole-hydrotic necrosis, tissue becomes dry and black and resembles mummification.
What is Wet Gangrene?
Fluid and pus-producing, resulting from impaired venous supply.
What is Gas Gangrene (Emphysematous Gangrene)?
Gas-producing bacteria invade dead tissue, forming gas bubbles and making the tissue feel crackly.
What does 'patho' mean in Pathophysiology?
Disease.
What does 'physis' mean in Pathophysiology?
Nature.
What does 'logos' mean in Pathophysiology?
Science.
What is pathophysiology?
science of disease, studying functional changes in the body
What is pathology?
study of cause and effect of disease using laboratory study of cell and tissue changes
What is a Medical History?
comprehensive record of a person's past and current health conditions, treatments, surgeries, medications, allergies, and family medical background, used by healthcare providers to guide diagnosis and treatment decisions
What is the purpose of a Medical History?
To guide diagnosis and treatment decisions by healthcare providers.
What is Etiology?
The causative factor in a disease.
What is a Prognosis?
The probability or likelihood of recovery.
What is Cancer?
A proliferation of cells.
What does Idiopathic mean?
When the underlying cause or origin of a condition is uncertain.
What are Gross changes?
Alterations that happen in the tissues, organs, or systems that are visible or microscopic.
What is a Biopsy?
An excision of a small amount of living tissue.
What does Nosocomial mean?
A disease originating in the healthcare facility.
What is Acute onset?
Sudden and obvious presence of disease
What is Chronic onset?
Gradual progression with vague or mild signs, lengthy illness, or disease process
What is Subclinical state?
Pathological change that occurs but has no obvious manifestations
What are Latent stages?
No symptoms or clinical signs
What is Exacerbation?
Sudden worsening or increase in the severity of symptoms or a disease
What are Complications?
New secondary or additional problems
What is Therapy?
Treatment measure to promote recovery
What is Epidemiology?
Science of identifying causative factors and tracking the pattern or occurrence of disease
Homeostasis definition
Maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment regardless of external changes
What is ischemia?
Lack of oxygen supply to cells.
What is Metaplasia often linked to?
Smoking.
What are predisposing factors?
Tendencies that promote development of a disease in an individual
What is prophylaxis?
Measures to prevent disease spread and preserve health.
What is the prophylactic treatment for myocardial infarction?
Daily baby aspirin for high-risk patients.
What is prevention?
Measures to avoid the development of a specific disease.
Vaccinations, dietary/lifestyle modifications, removal of harmful materials, and cessation of harmful activities are all examples of?
Preventive measures.
What is pathogenesis?
The development and sequence of events in a disease process.
What is an acute disease?
A disease with sudden and obvious onset.
What is an insidious disease?
A disease with gradual onset and vague/mild signs.
What is a chronic disease?
A condition that develops gradually, persists for a long time, and causes permanent tissue damage.
Kidney damage progressing to advanced renal failure without symptoms is an example of?
A subclinical state.
What is an incubation period?
The time between exposure to a microorganism and the onset of signs/symptoms.
How long can an incubation period last?
It can last for a day, weeks, or even longer.
What is a prodromal period?
The early stage of a disease when non-specific changes are noticed.
What does it mean if a manifestation is local?
It is found at the site of the problem.
What are systemic signs and symptoms?
General indicators of illness affecting the whole body.
What is a syndrome?
A collection of signs and symptoms, often affecting more than one organ.
What is convalescence?
The period of recovery and return to the normal healthy state.
What is prognosis?
The probability or likelihood for recovery or other outcomes.
What is epidemiology?
The science of tracking the pattern or occurrence of disease.
What is a pandemic?
When there are higher numbers of cases in many regions of the globe.
What is an autopsy?
A post mortem examination performed after death to determine the exact cause of death or the course of the illness and effectiveness of treatment.
What is dysplasia?
Abnormal tissue growth with variable cell size and shape.
What is anaplasia?
Undifferentiated cells with abnormal structures.
What is cellular neoplasia?
New growth, commonly referred to as a tumor.
What are some ways cells can be injured?
Ischemia,
physical agents,
mechanical damage,
chemical toxins,
microorganisms,
abnormal metabolites,
nutritional deficits,
fluid or electrolyte imbalances.
What are exogenous chemicals?
Chemicals from the environment.
What are endogenous chemicals?
Chemicals produced within the body.
What is caseous necrosis?
Form of coagulative necrosis in which a thick, yellowish, cheesy substance forms, often seen in tuberculosis (TB).
What is infarction?
Term applied to an area of dead cells resulting from lack of oxygen.
people who suffer from paralysis as a result of a stroke is an example of?
A complication.
What is exacerbation?
A sudden worsening or increase in the severity of symptoms or a disease.
What is homeostasis?
Maintenance of stable internal environment despite external changes
What is diagnosis?
Identification of a specific disease based on signs and symptoms
What is etiology?
Cause of disease
What does idiopathic mean?
No known cause
What does iatrogenic mean?
Disease caused by treatment, procedure, or error
What is an acute illness?
Short-term illness that develops quickly
What is a chronic condition?
Milder condition that develops gradually and persists for a long time
What is a subclinical state?
Pathologic changes without obvious manifestations
What does latent mean?
No clinical signs are evident
What is the incubation period?
Time between exposure to microorganism and onset of signs/symptoms
What is the prodromal period?
Early period with mild non-specific symptoms before disease fully develops
What is meant by non-specific signs?
Awareness of a change in the body without specific indications
Define manifestations of disease.
Clinical evidence or effects of disease
What does 'local' refer to?
Found at the site of the problem
What are systemic signs?
Common signs of significant infections in any area
What are signs?
Objective indicators of disease
What are symptoms?
Subjective feelings experienced by the patient
What is a lesion?
An abnormality in the structure of a tissue or organ
Define syndrome.
A group of signs and symptoms characteristic of a specific disorder
What are diagnostic tests?
Laboratory tests that assist in the diagnosis of a specific disease
What is remission?
Subsiding of disease manifestations
What is an exacerbation?
Worsening in severity of the disease
What is a precipitating factor?
A condition that triggers an acute episode
What are complications?
New additional problems that arise after the original disease begins
What is therapy?
Treatment used to promote recovery or slow disease progress
What are sequelae?
Potential unwanted outcomes of the primary condition
Define convalescence.
Period of recovery and return to normal healthy state