HSC 214 exit quiz 11
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Pericardial sac
Description: Sac composed of the fibrous and parietal pericardium that anchors the heart to the diaphragm and sternum
Relationship: N/A
Fibrous pericardium
Description: Fibrous connective tissue on the outer surface of the pericardial sac
Relationship: Usually covered in adipose tissue
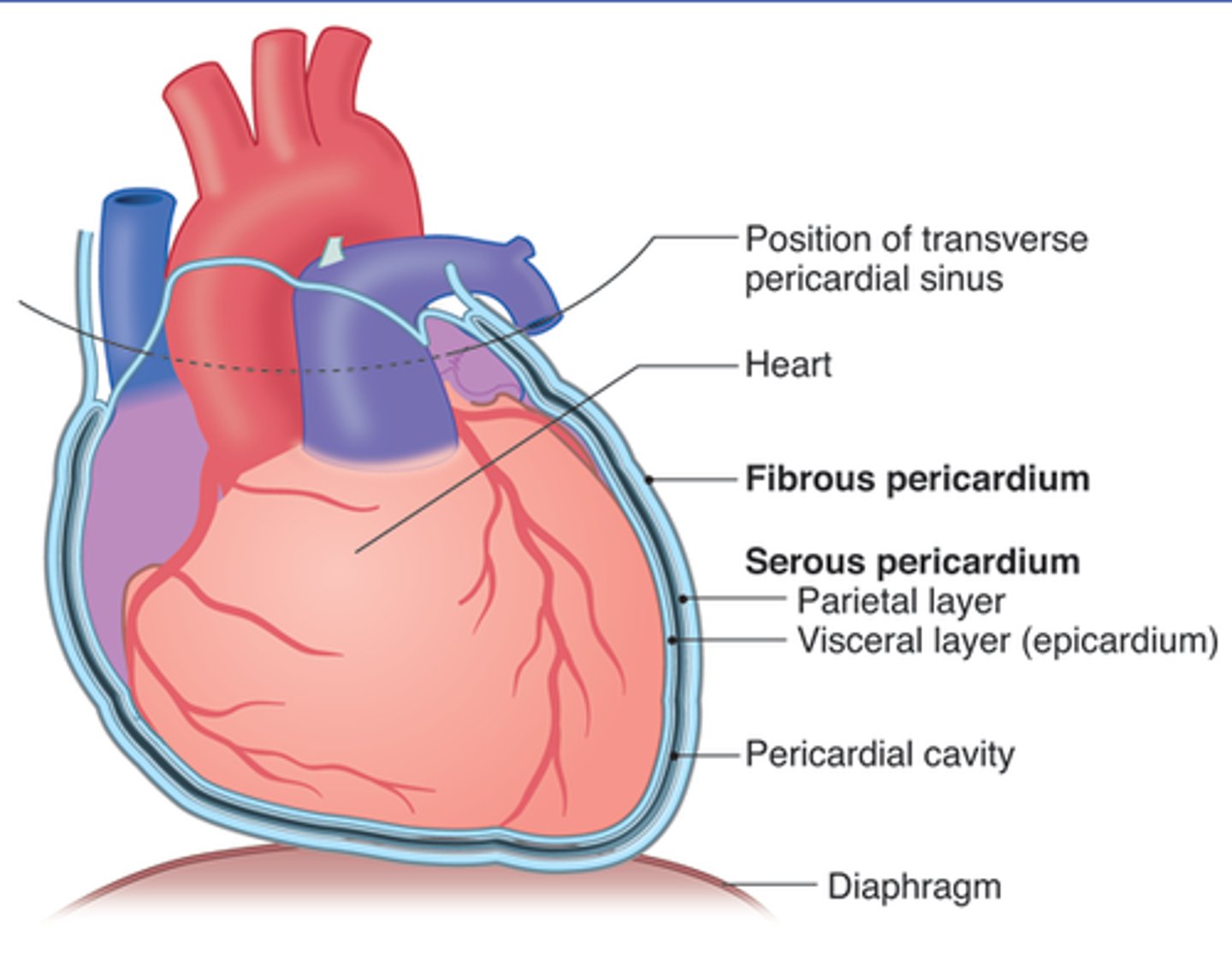
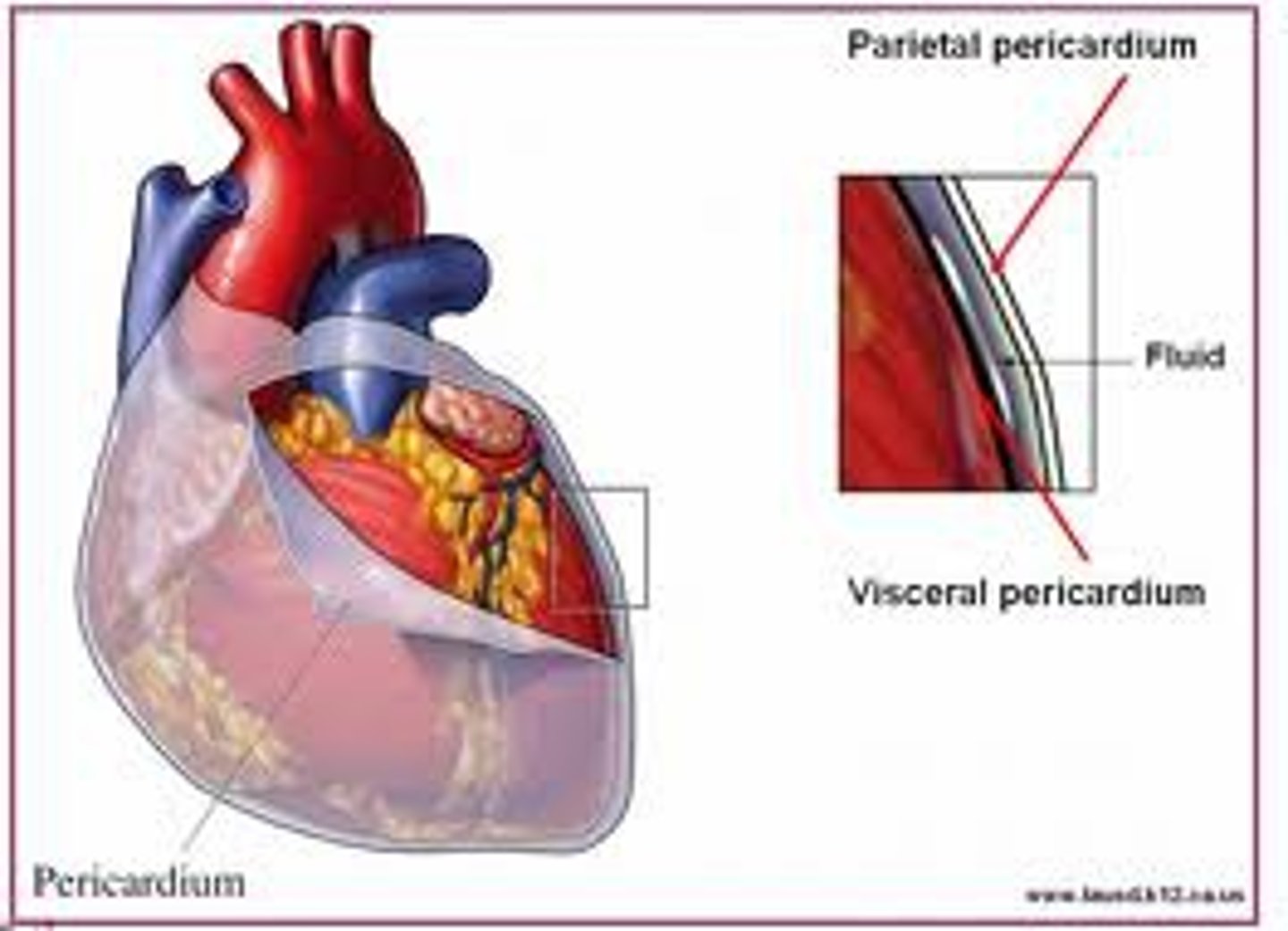
Parietal pericardium
Description: Thin, serous membrane fused to the inner surface of the fibrous pericardium
Relationship: Shiny and smooth inner layer of the pericardial sac
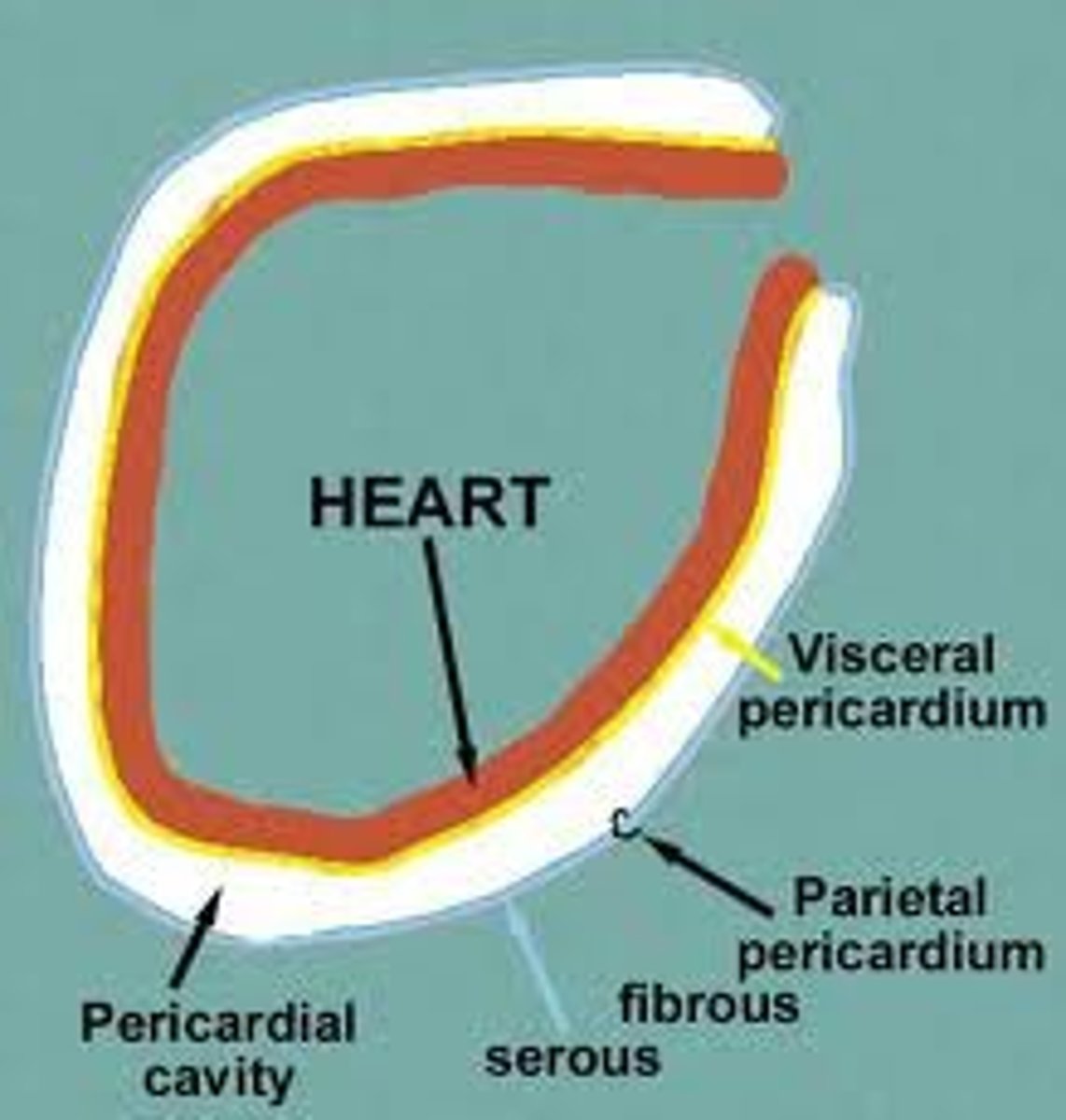
Pericardial cavity
Description: Potential space between the parietal pericardium and visceral pericardium (epicardium)
Relationship: Parietal and visceral pericardium (epicardium) membranes are lined with serous fluid
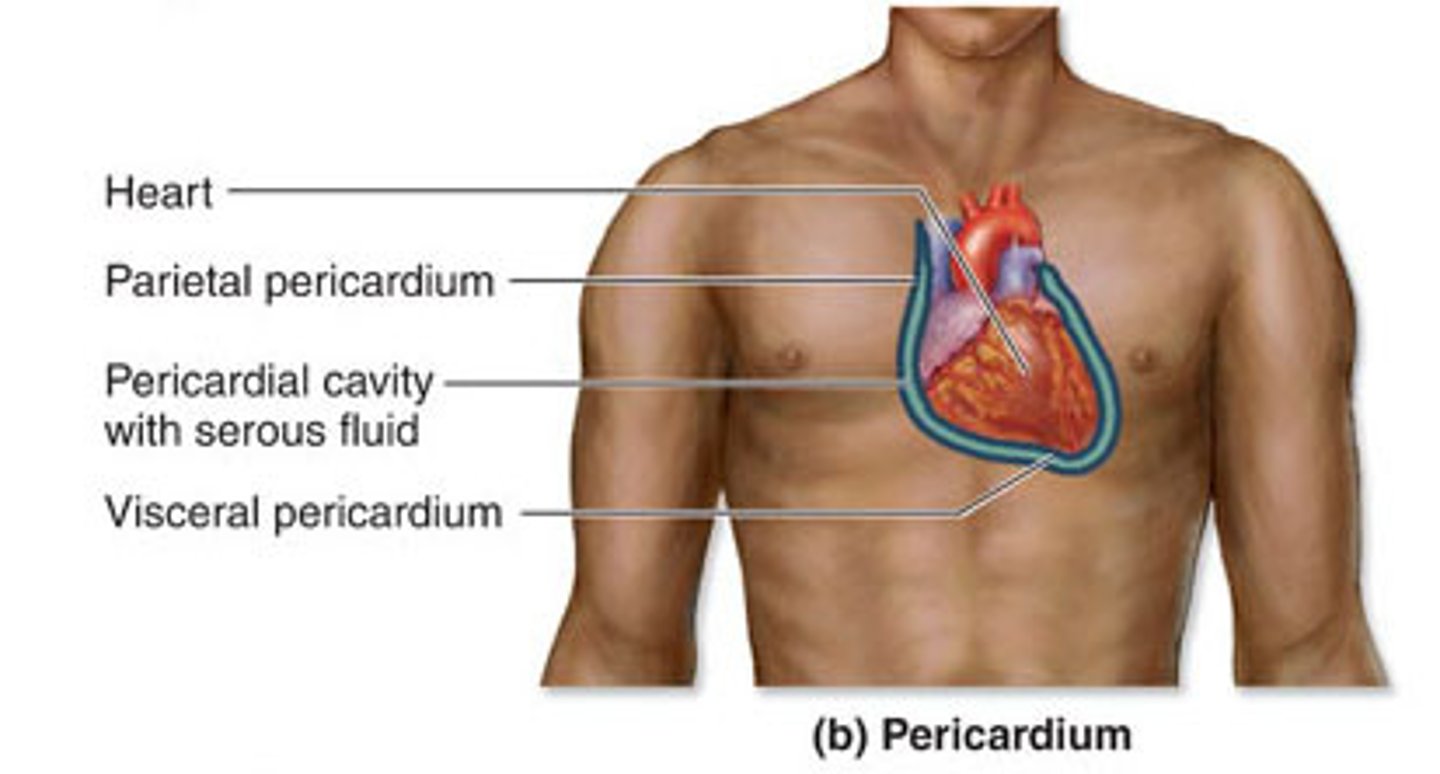
Visceral pericardium (epicardium)
Description: Thin serous membrane fused to the surface of the heart
Relationship: Directly on the surface of the heart
Myocardium
Description: Thick, middle muscular layer between the endocardium and epicardium
Relationship: Muscle (myo-) of the heart-cardiac muscle
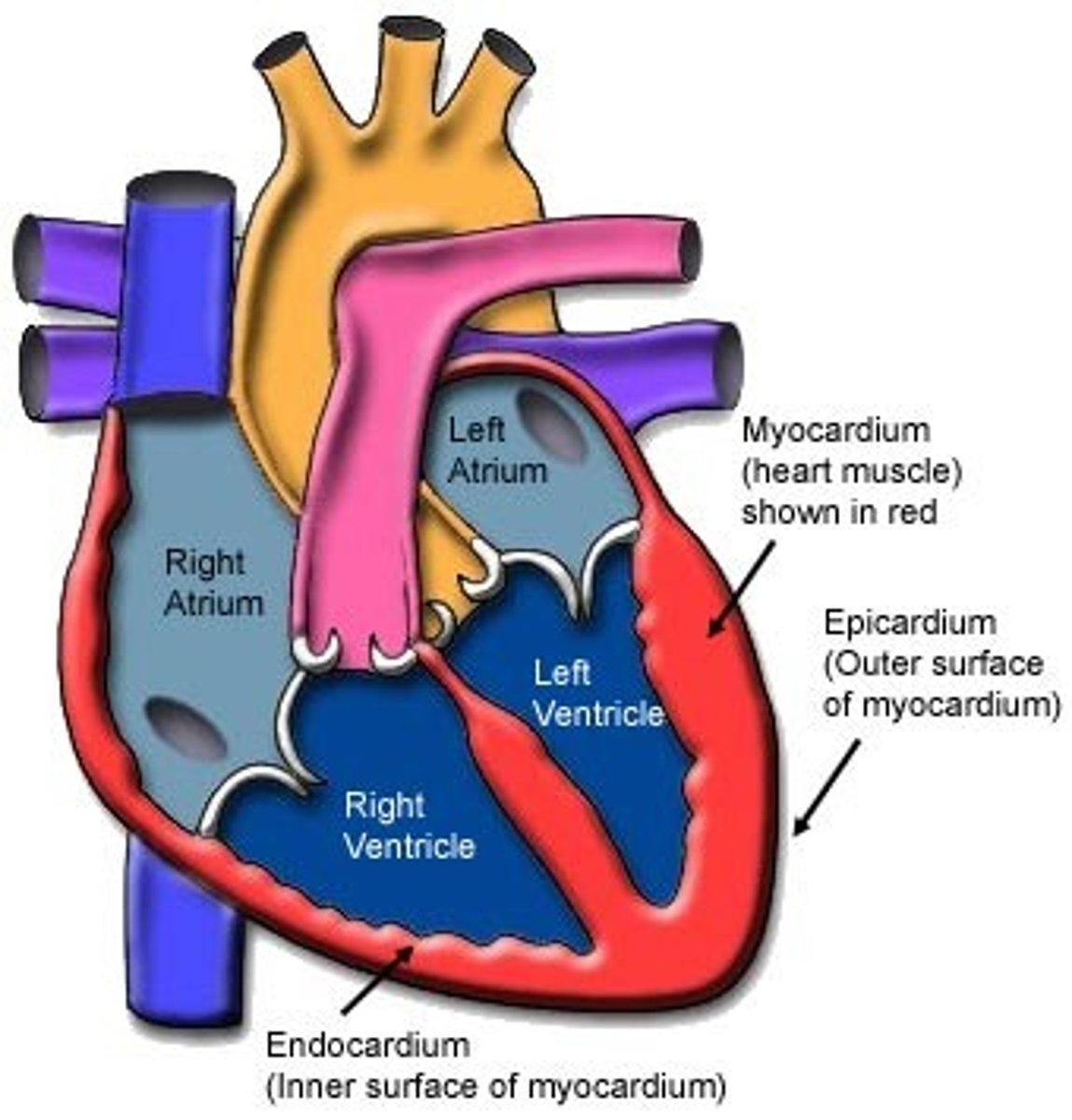
Endocardium
Description: Thin, internal layer of the heart
Relationship: Walls of all heart chambers are lined with endocardium
Base of heart
Description: Superior aspect of the heart
Relationship: Where great blood vessels enter and exit the heart (aorta/superior vena cava/pulmonary trunk)
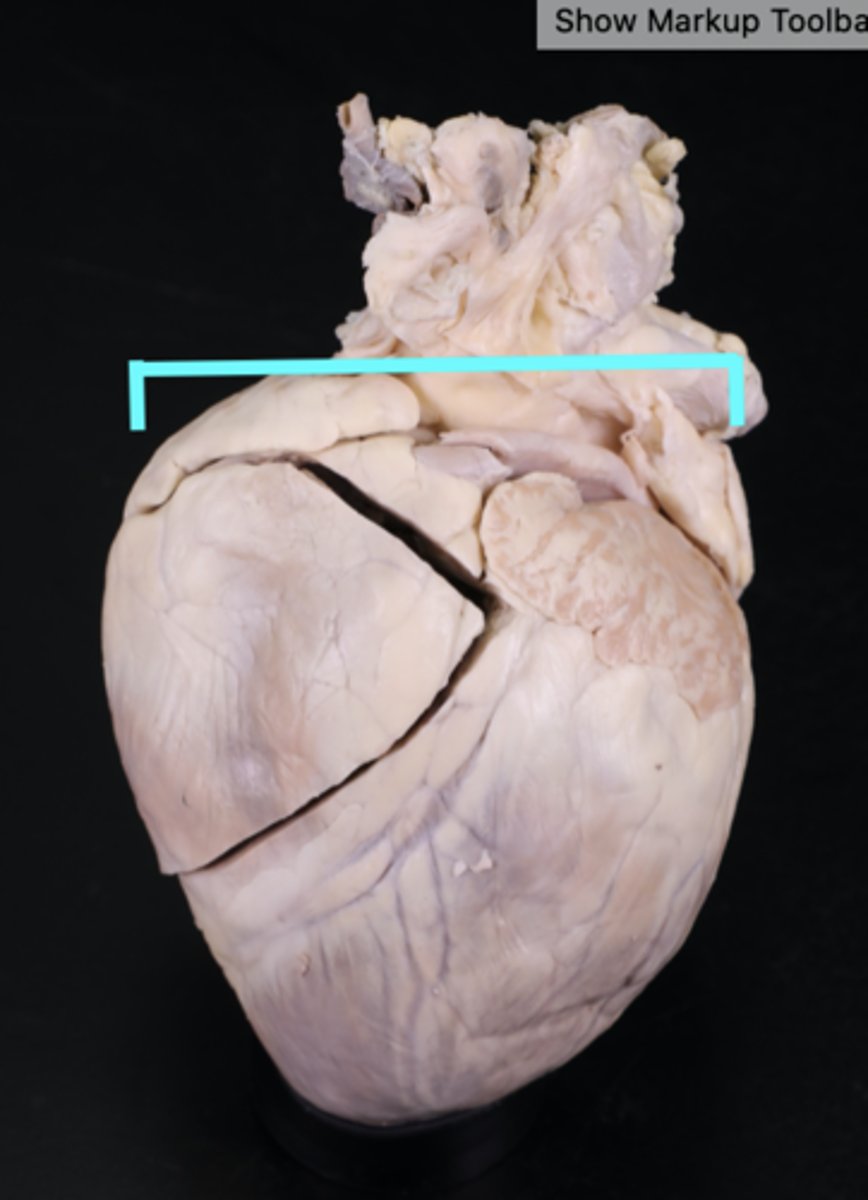
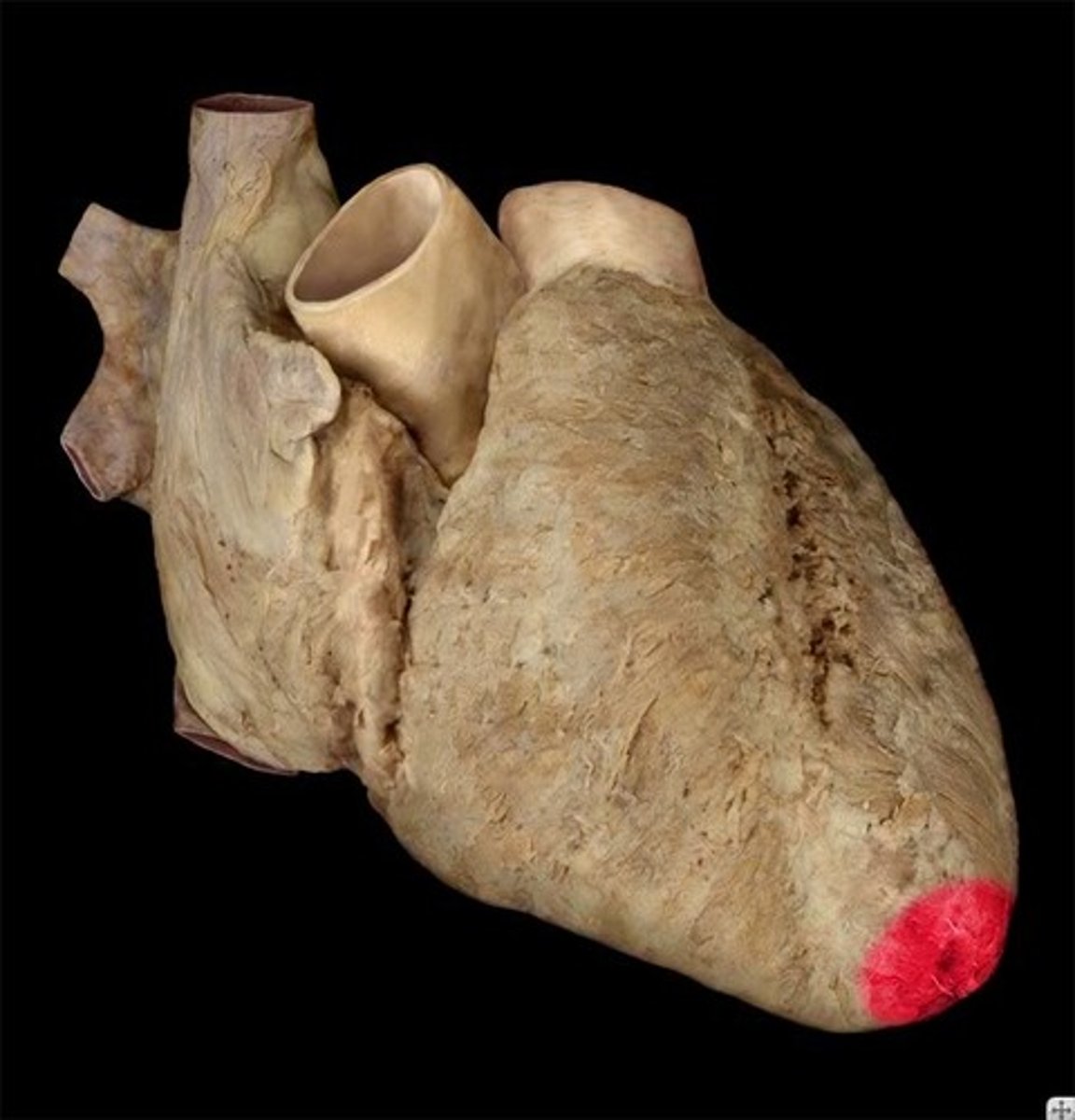
Apex of heart
Description: Blunt tip of the left ventricle
Relationship: Surface projection at the left 5h intercostal space along the mid-clavicular line. Best place of hear and palpate heart beat.
Sternocostal surface
Description: Anterior surface of the heart
Relationship: Surface of the heart in contact with the sternum
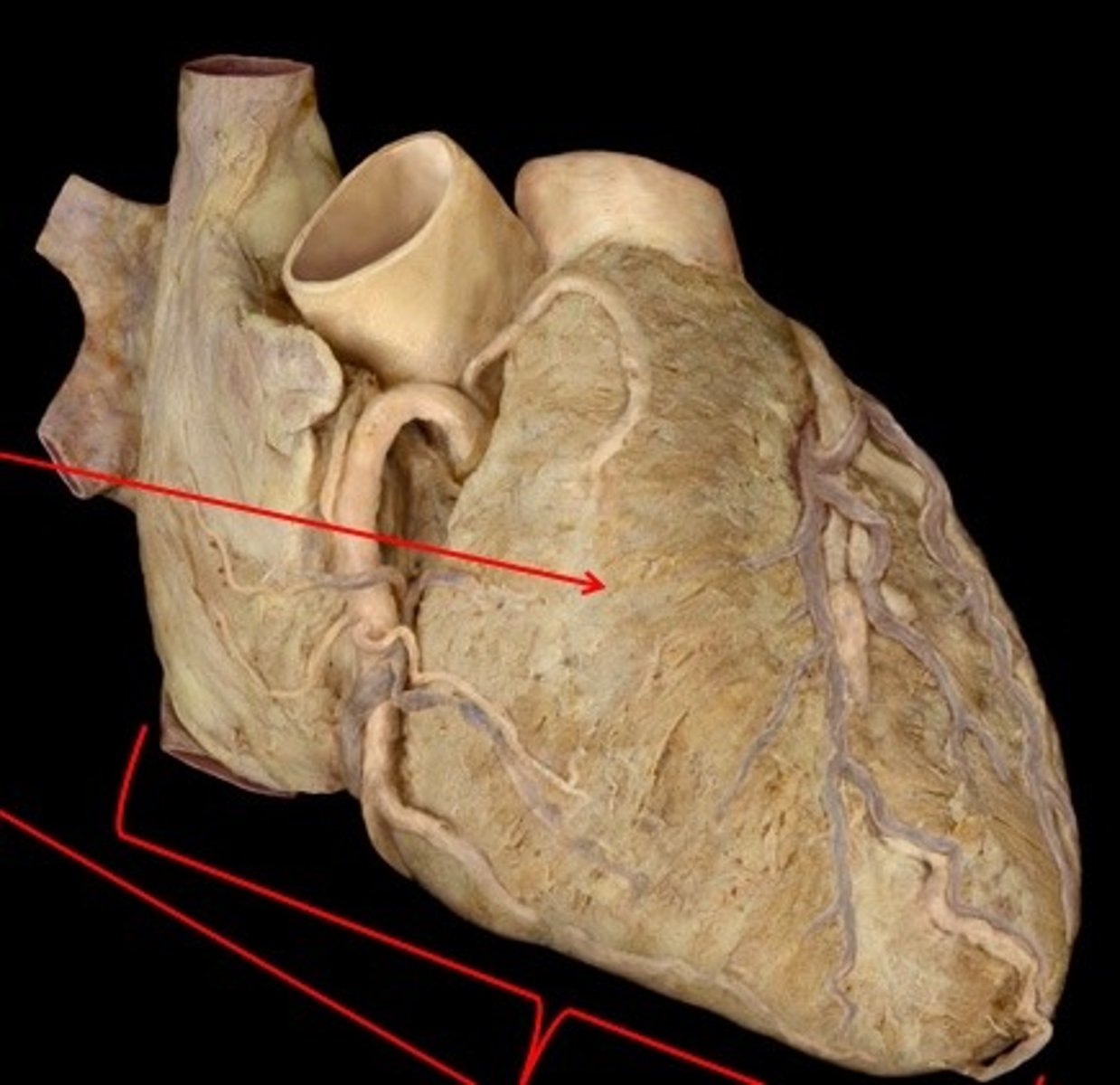
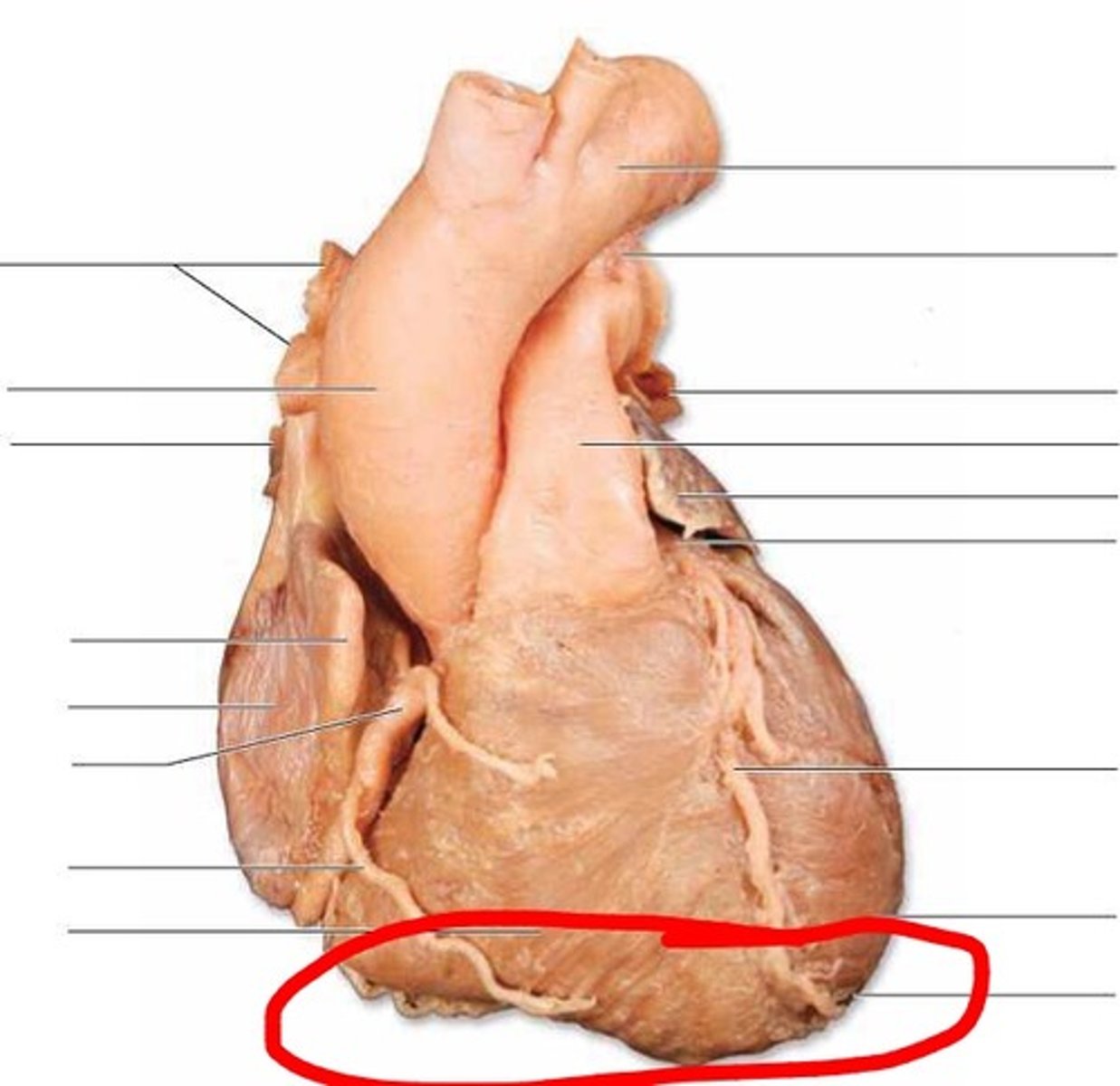
Diaphragmatic surface
Description: Posterior and inferior surface of the heart
Relationship: Surface of the heart in contact with the diaphragm
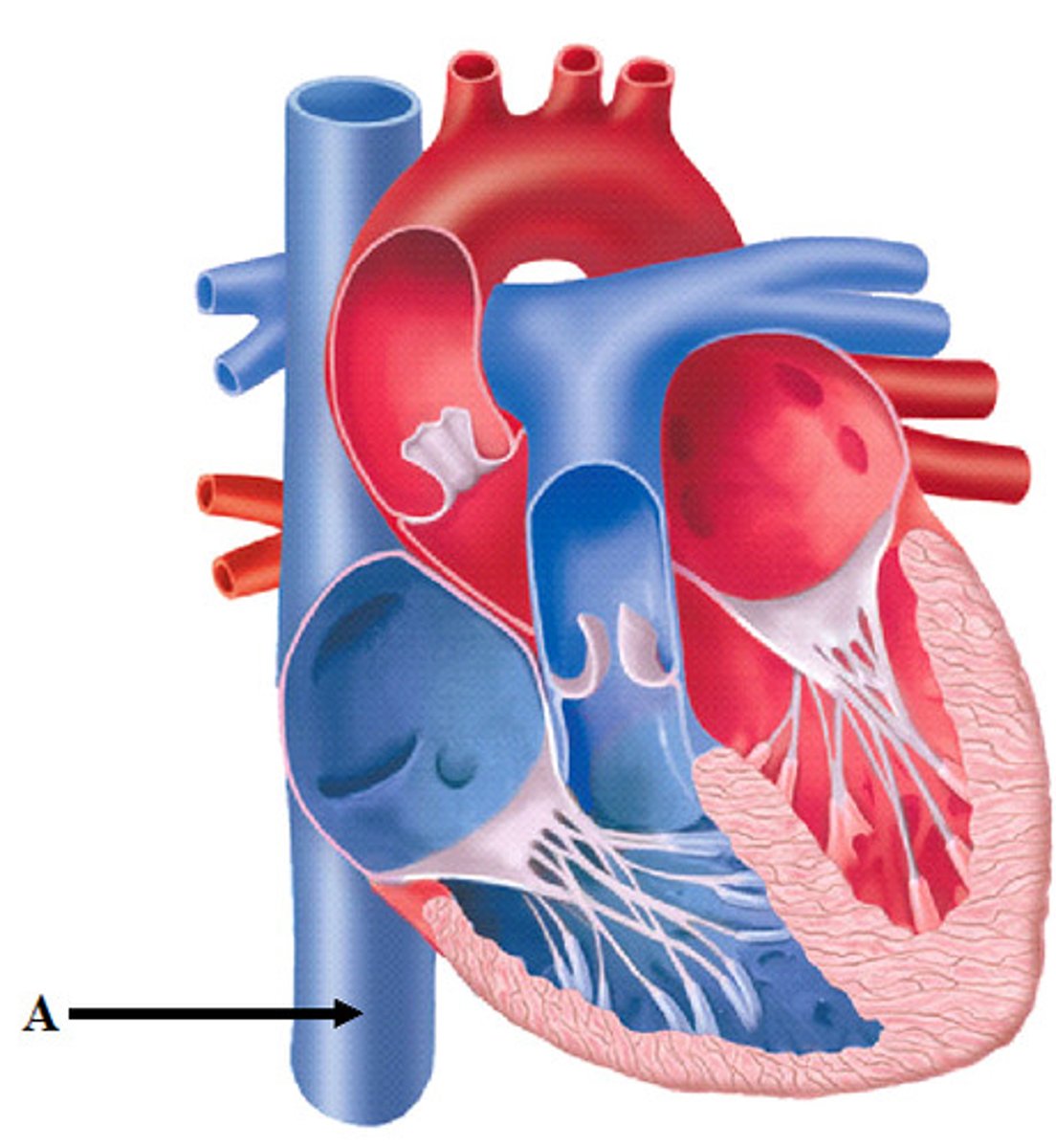
Inferior vena cava
Description: Vein draining blood from everything inferior of the diaphragm into the heart
Relationship: Terminates into the right atrium. Largest vein of the body
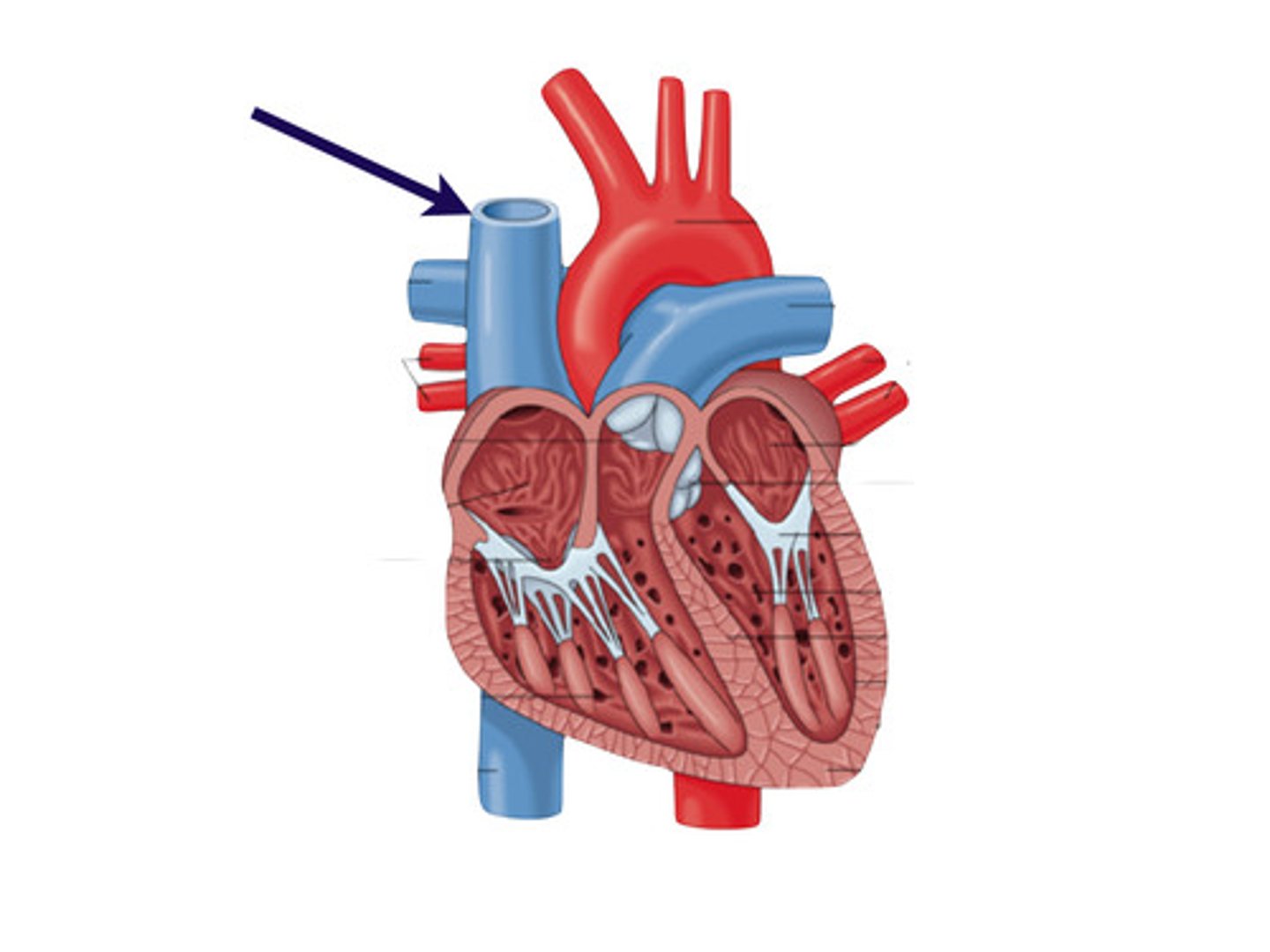
Superior vena cava
Description: Vein draining blood from the head and upper limbs into the heart
Relationship: Terminates into the right atrium. Formed by the union of the right and left brachiocephalic veins
Ascending aorta
Description: Artery extending from the left ventricle where the coronary blood vessels originate.
Relationship: Continues as the arch of the aorta. Located posterior to the pulmonary trunk.
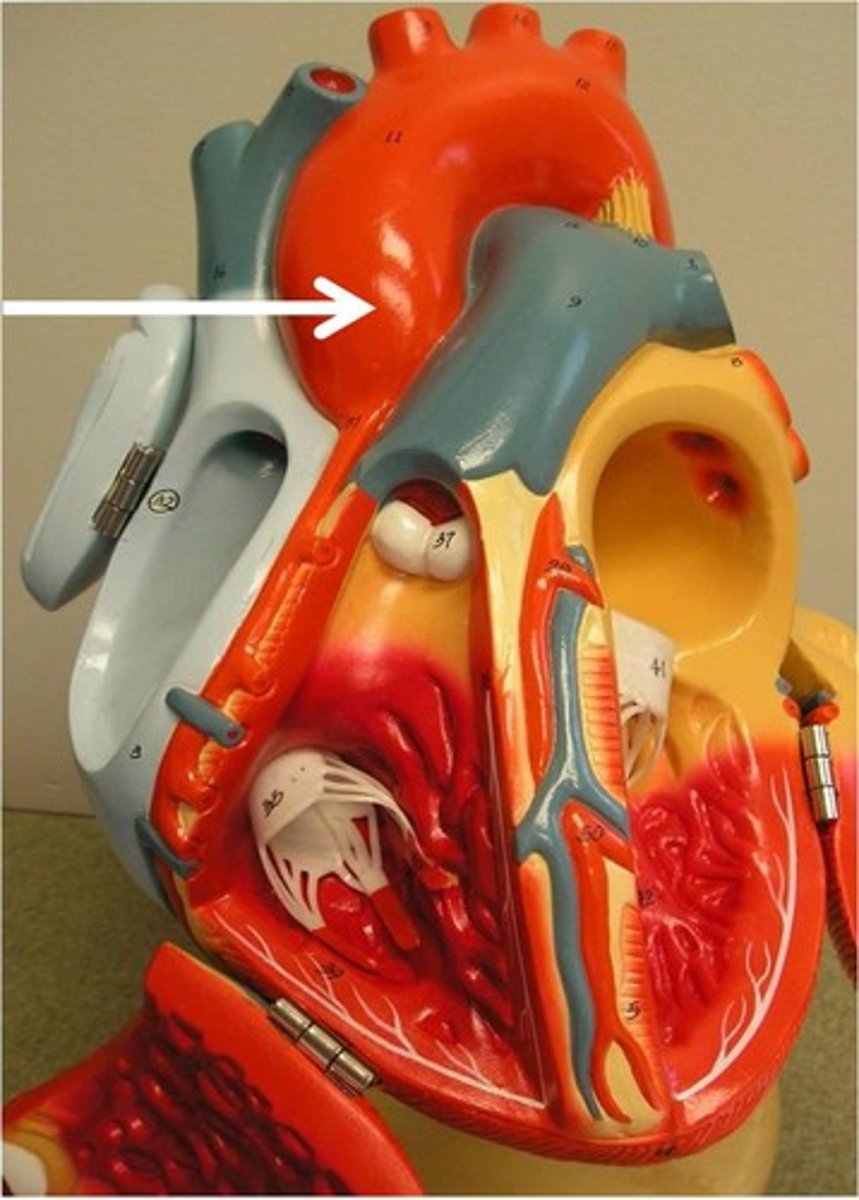
Pulmonary trunk
Description: Carries low oxygen blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
Relationship: Terminates into the pulmonary arteries. Located anterior to the ascending aorta.
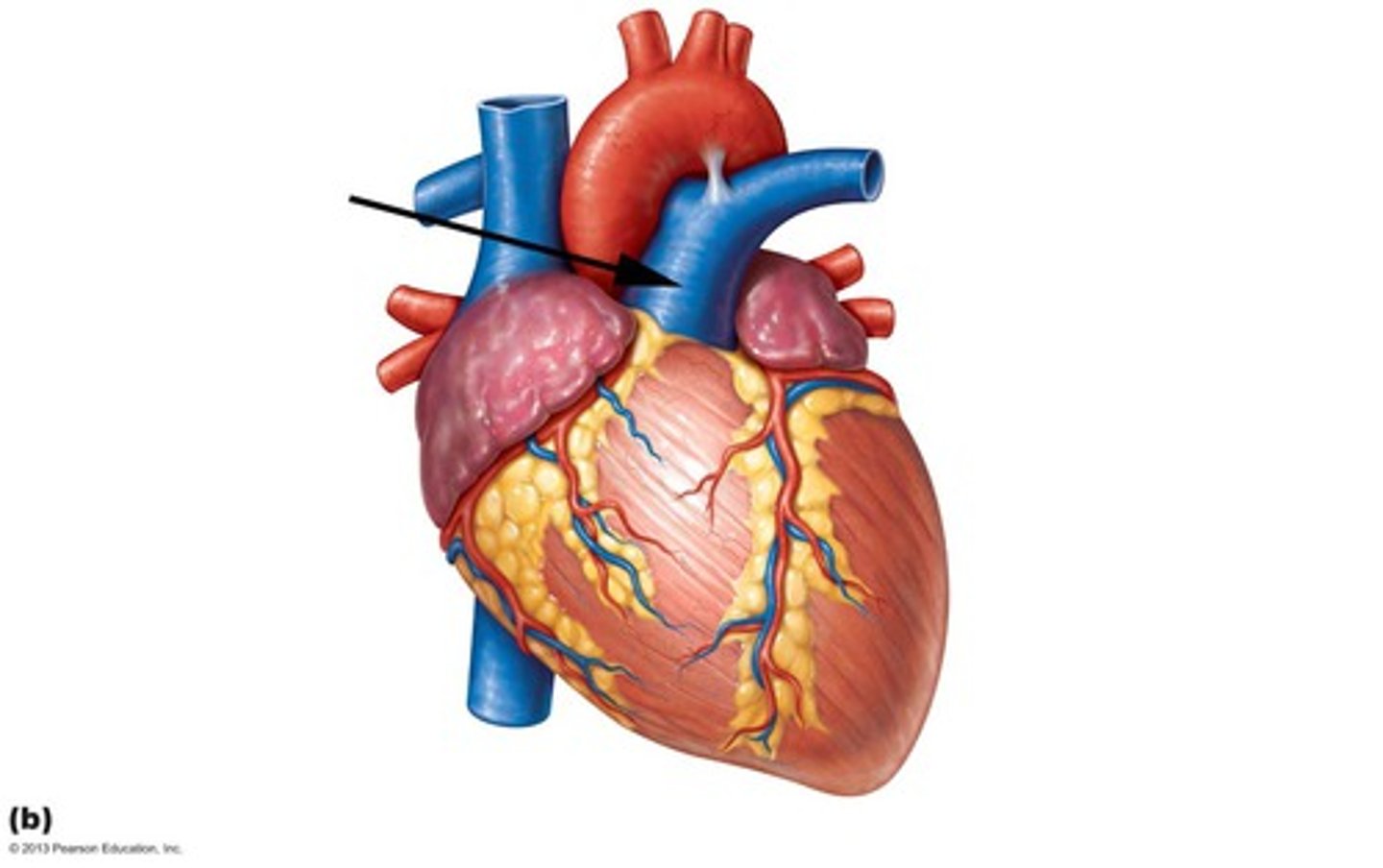
Pulmonary arteries
Description: Vessels taking low oxygen blood to the lungs from the pulmonary trunk
Relationship: Carries deoxygenated blood to lungs
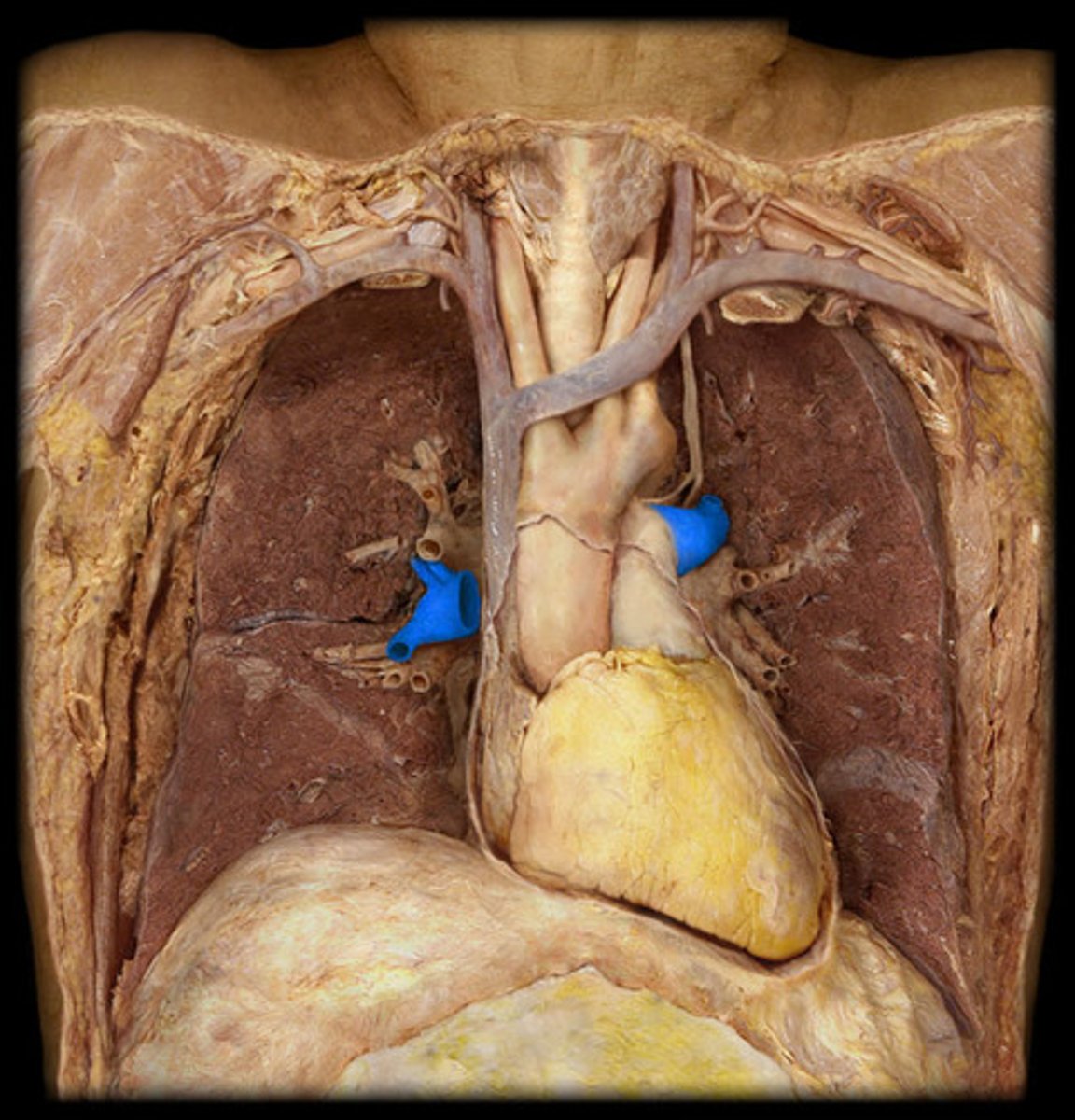
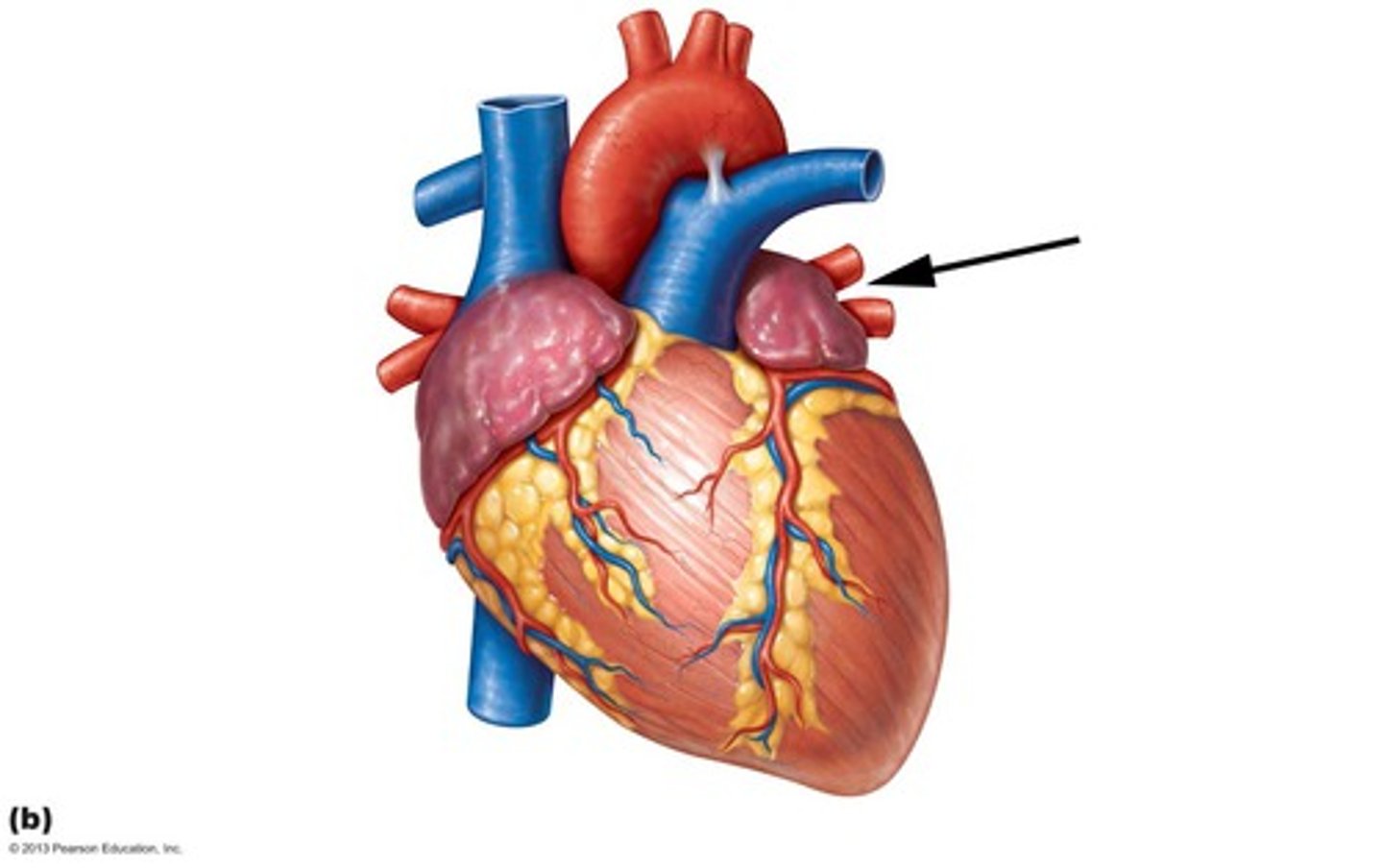
Pulmonary veins
Description: Vessels bringing high oxygen blood from the lungs to the left atrium
Relationship: Carries oxygenated blood back to heart
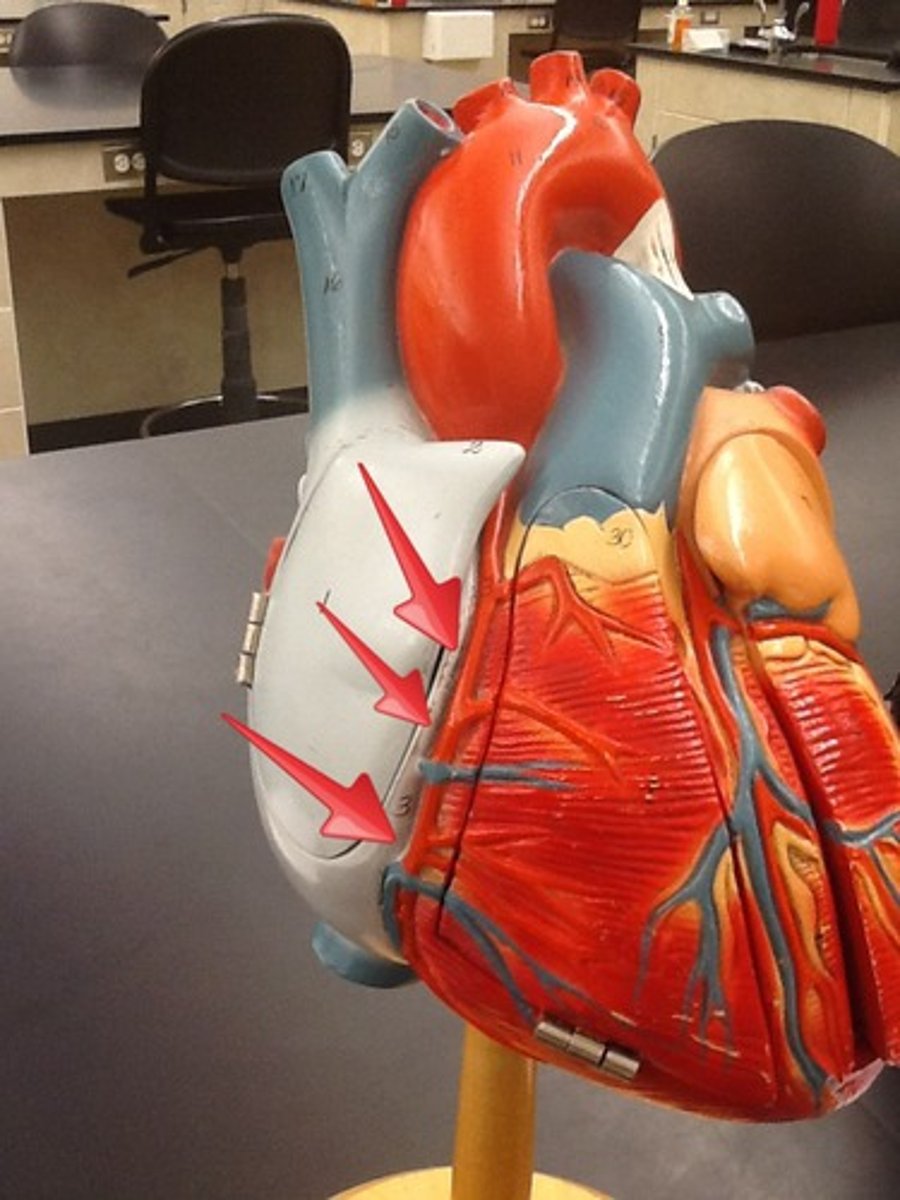
Auricle of heart
Description: Lumpy and wrinkled flap (ear-like extensions) of the atria
Relationship: Allows for the atria to expand when filling with blood
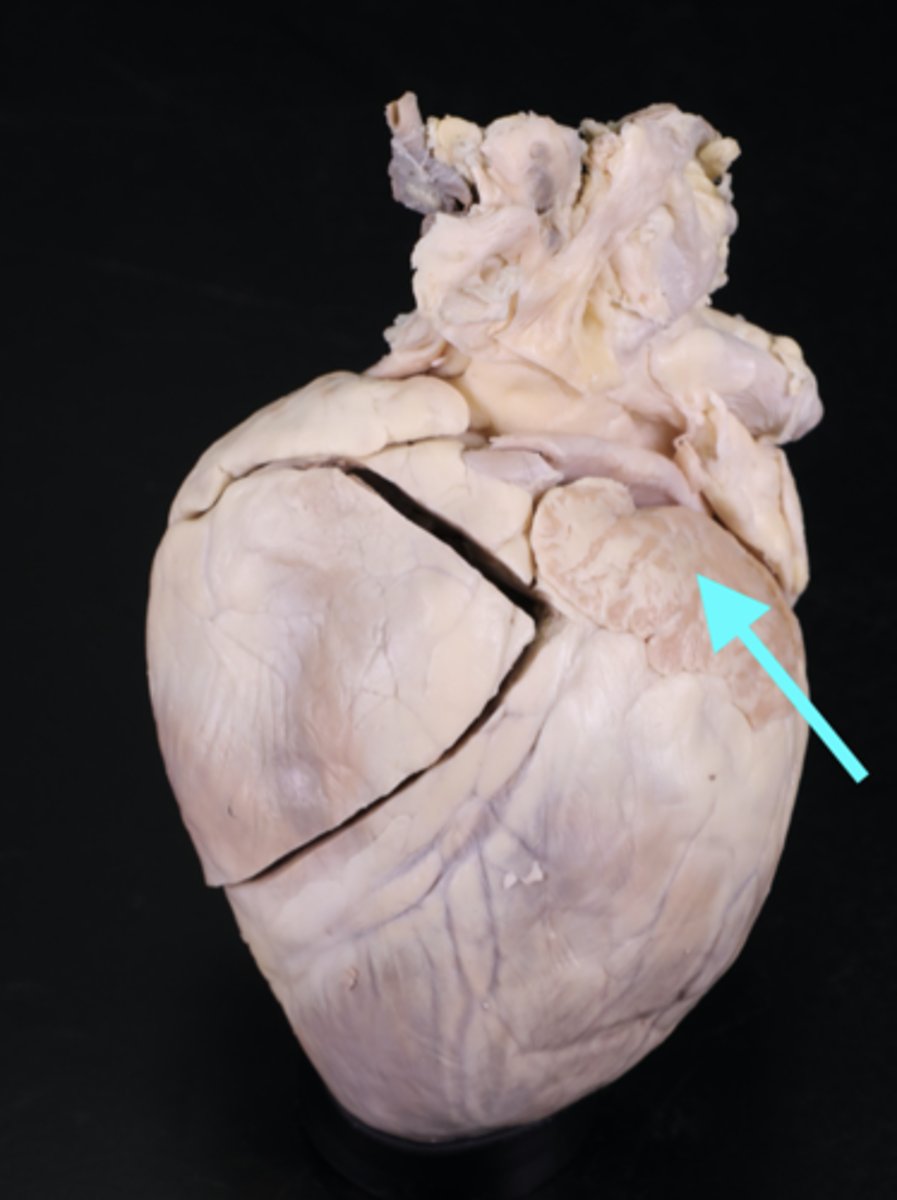
Anterior interventricular sulcus
Description: Groove on the anterior surface of the heart between the left and right ventricles
Relationship: Contains the anterior interventricular artery and great cardiac vein
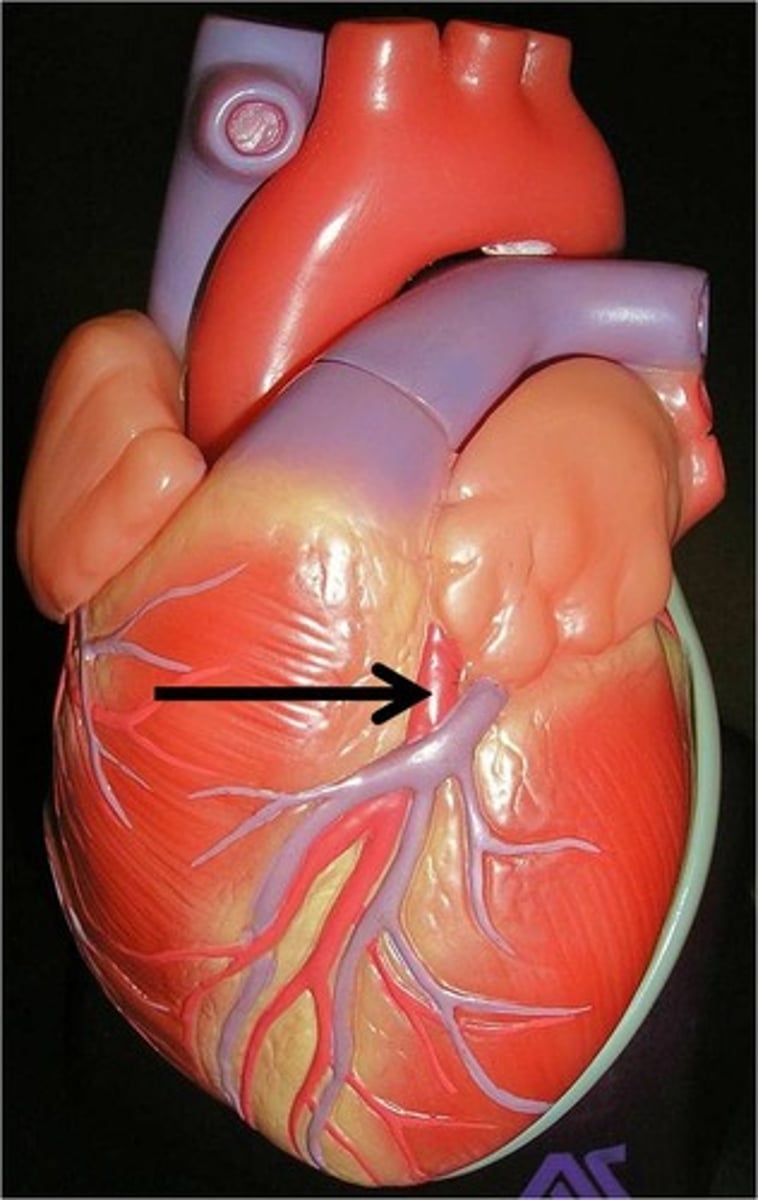
Posterior interventricular sulcus
Description: Groove on the posterior surface of the heart between the left and right ventricles
Relationship: Contains the posterior interventricular artery and middle cardiac vein
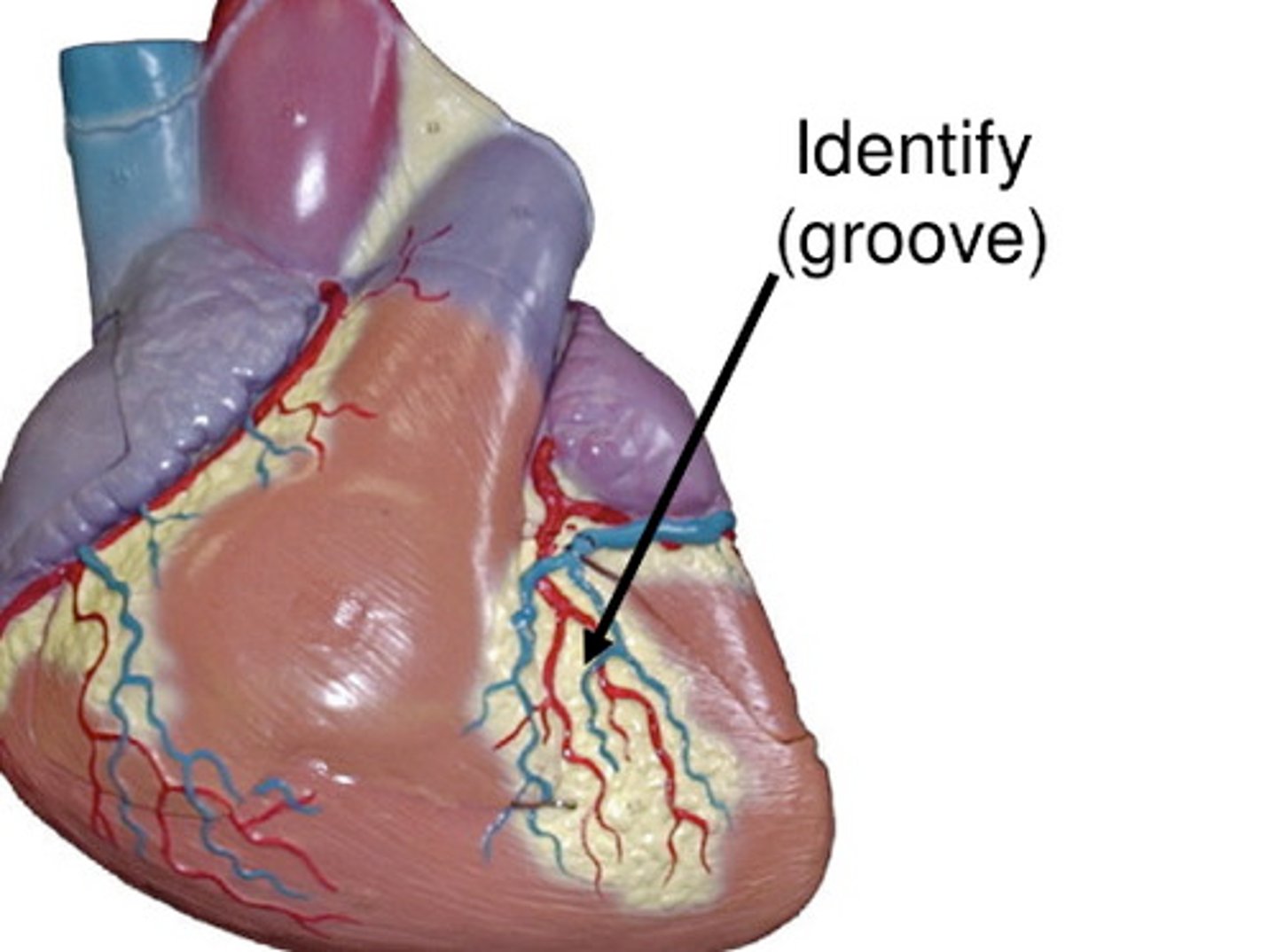
Coronary (atriventricular) sulcus
Description: Groove separating the atria from the ventricles
Relationship: Contains the right and left coronary arteries, circumflex artery, and coronary sinus
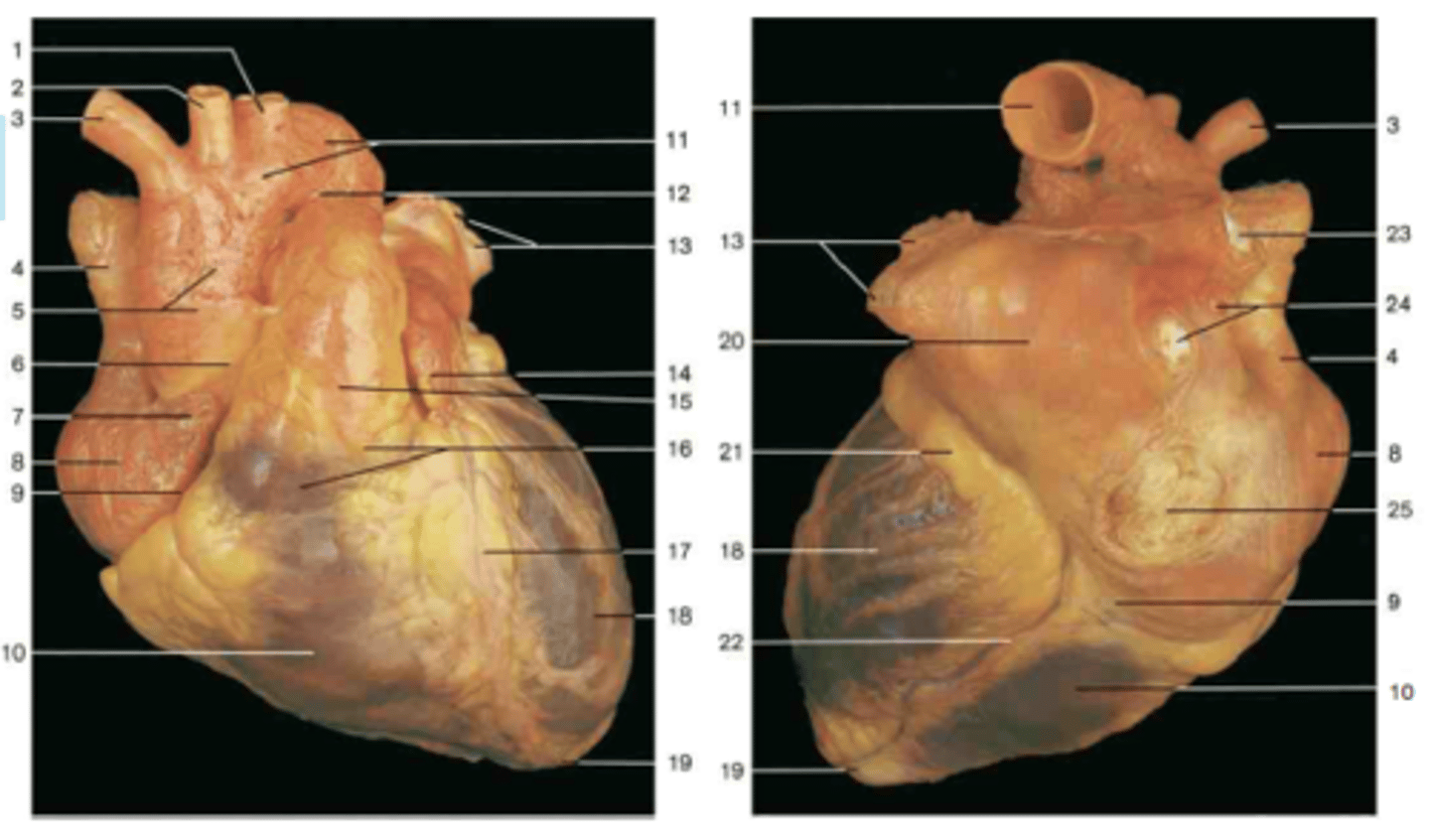
Left coronary artery
Description: Arises from the ascending aorta and passes between the pulmonary trunk and left auricle
Relationship: Lies in the coronary sulcus
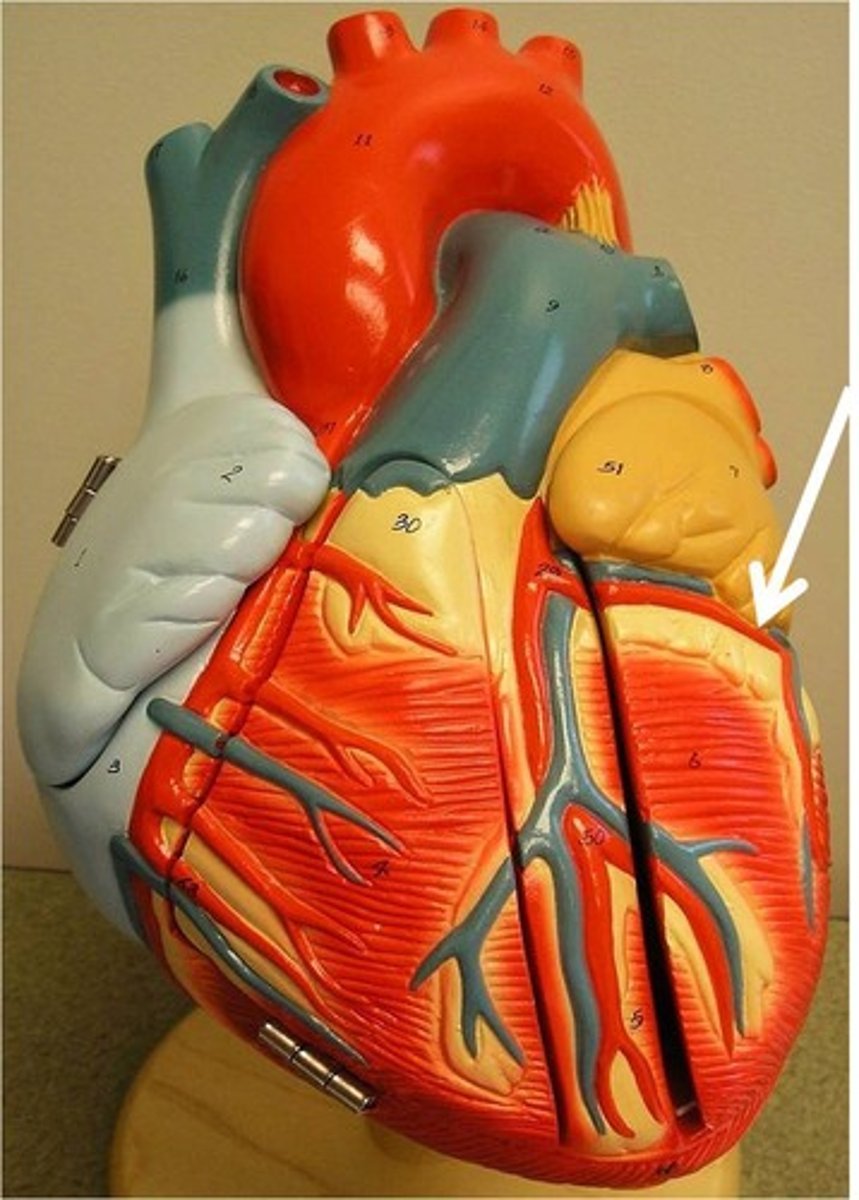
Anterior interventricular (descending) artery (LAD)
Description: Passes between the left and right ventricle in the anterior interventricular sulcus toward the apex of the heart
Relationship: Supplies the right and left ventricles and two thirds of the interventricular septum
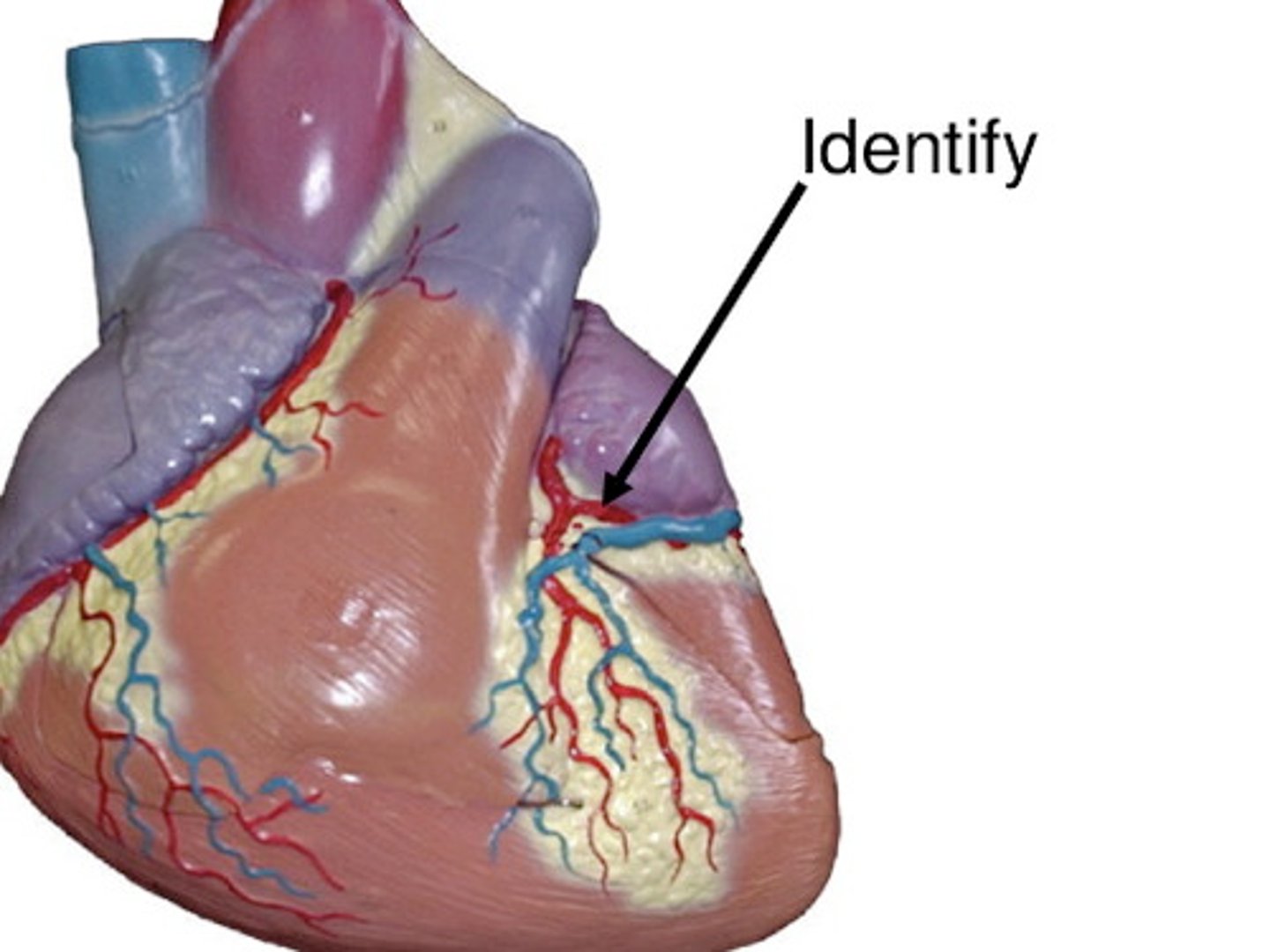
Circumflex artery
Description: Passes from the anterior to posterior surface of the heart in the coronary sulcus
Relationship: To bend (-flex) around (circum-). Supplies the posterior surface of the left atrium and left ventricle
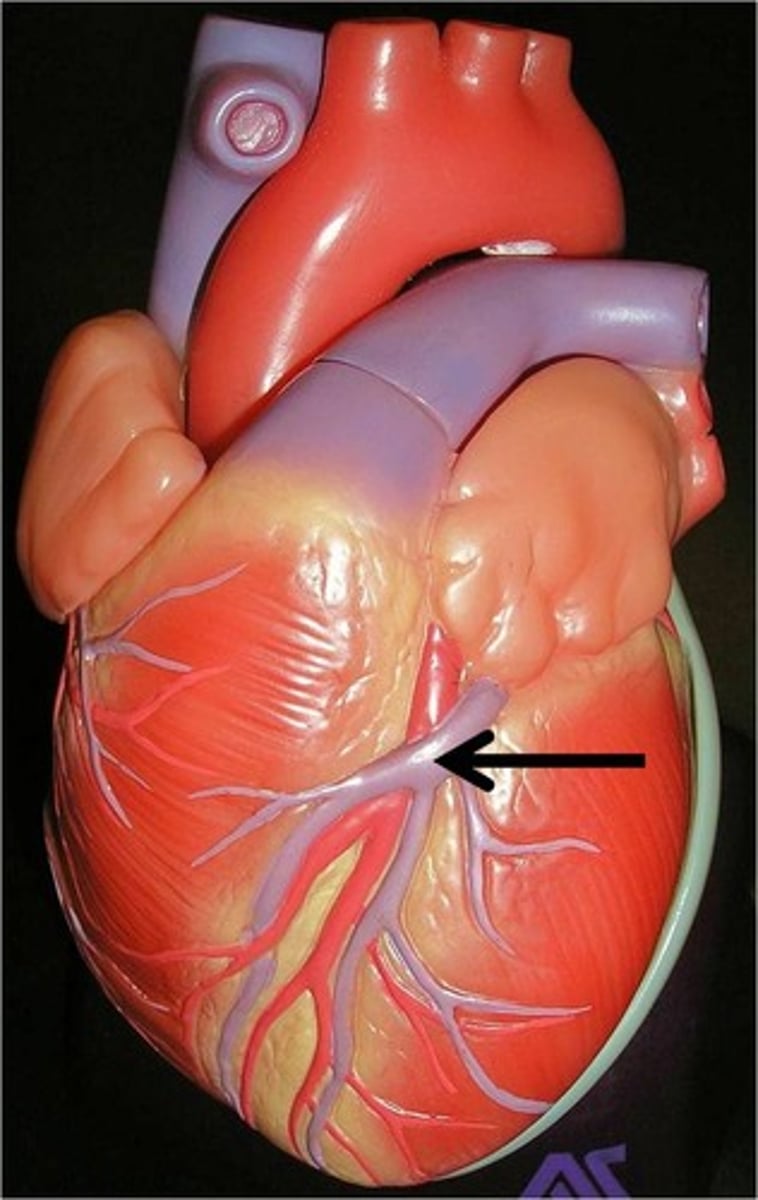
Right coronary artery
Description: Arises from the ascending aorta and passes between the pulmonary trunk and right auricle
Relationship: Lies in the coronary sulcus
Posterior interventricular (descending) artery (PAD)
Description: Branch of the right coronary artery traveling between the left and right ventricle in the posterior interventricular sulcus
Relationship: Supplies the left and right ventricles and interventricular septum
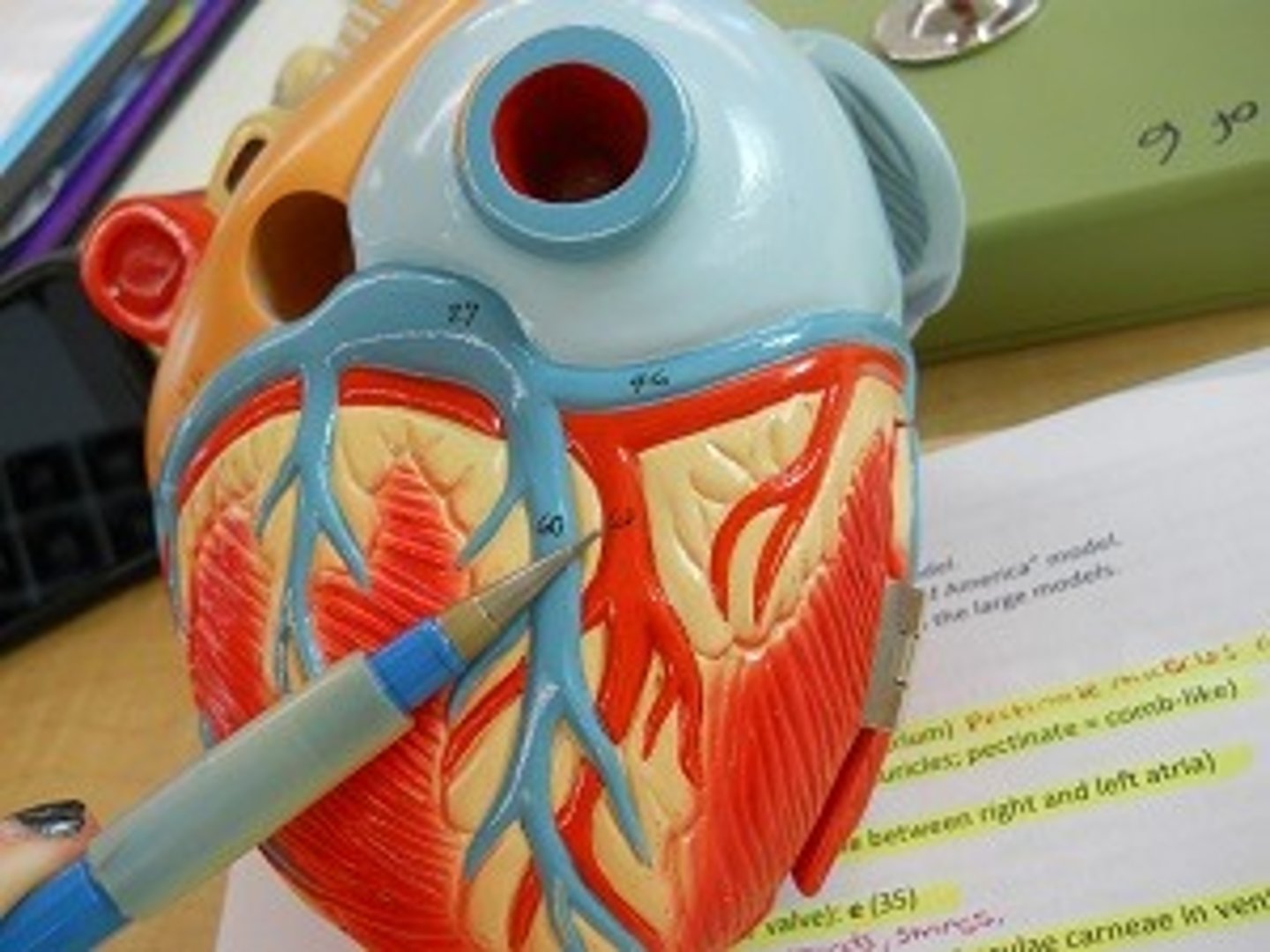
Right marginal artery
Description: Branch of the right coronary artery on the anterior surface of the right ventricle extending toward the apex
Relationship: Supplies the right ventricle
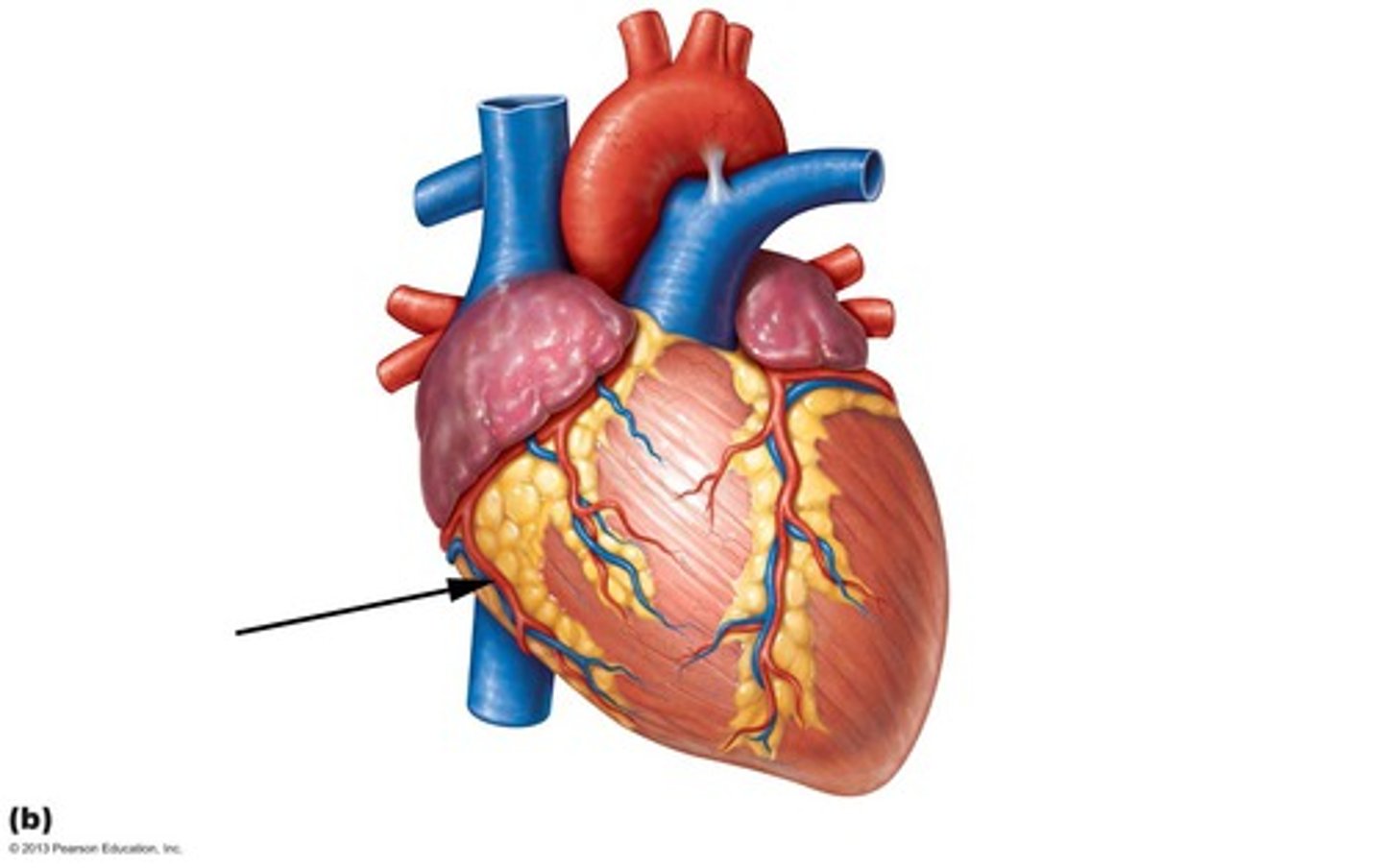
Coronary sinus
Description: Major vein draining the heart located on the posterior surface in the coronary sulcus
Relationship: Drains all coronary veins into the right atrium
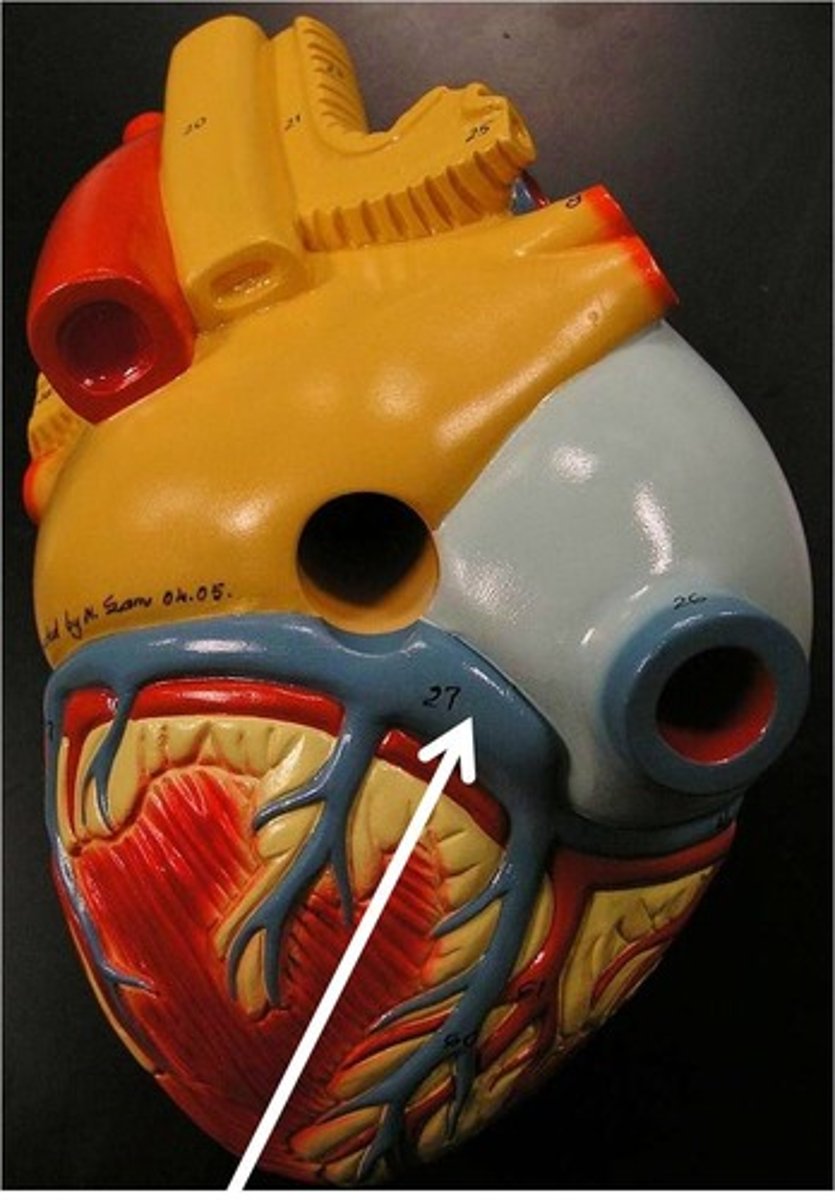
Great cardiac vein
Description: Vein traveling from the apex of the heart with the anterior interventricular artery to the coronary sinus
Relationship: Drains the left and right ventricles and left atrium
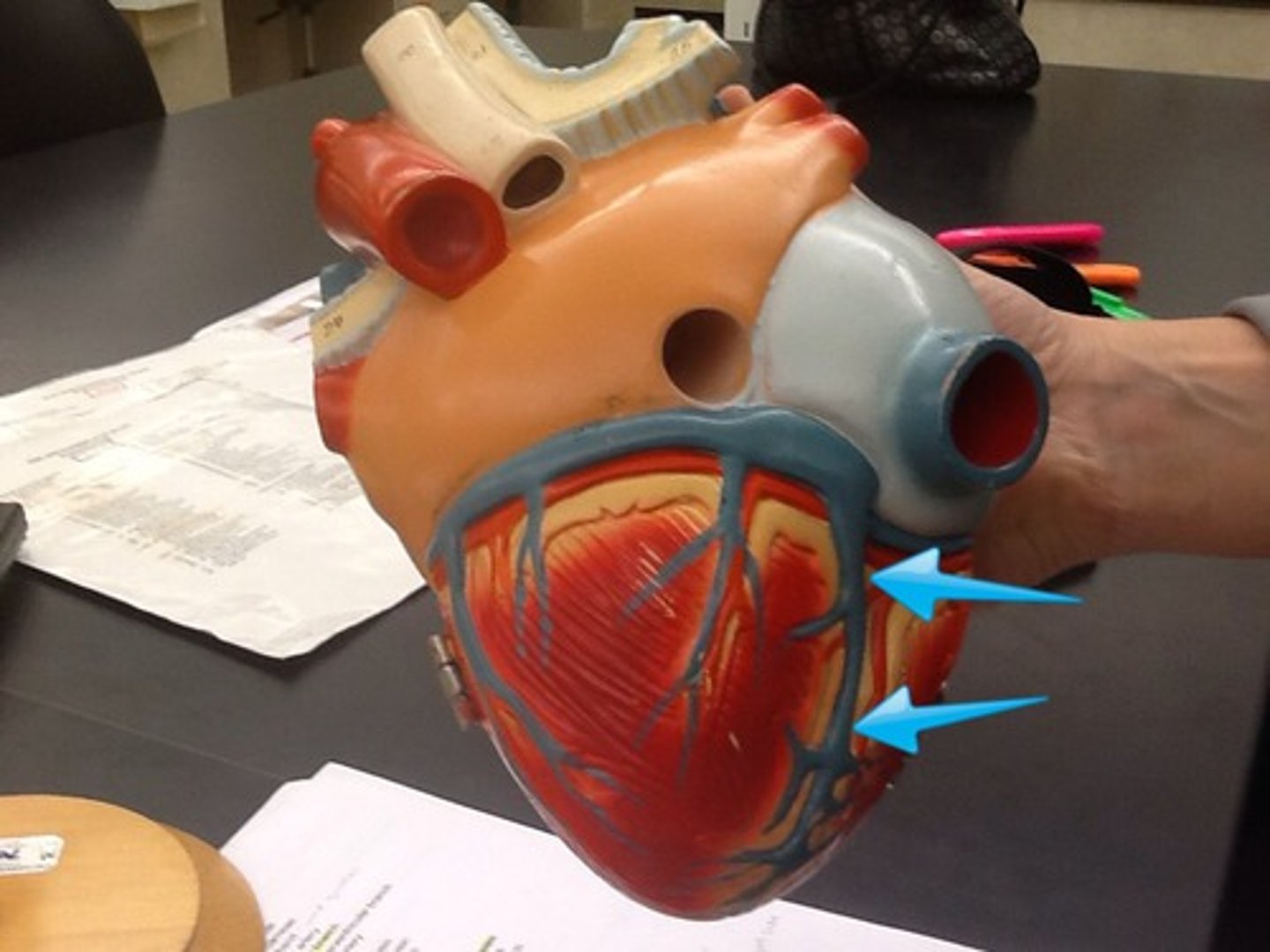
Atria
Description: Thin, smooth walled chambers that carry blood to the ventricles
Relationship: Superior to the coronary sinus
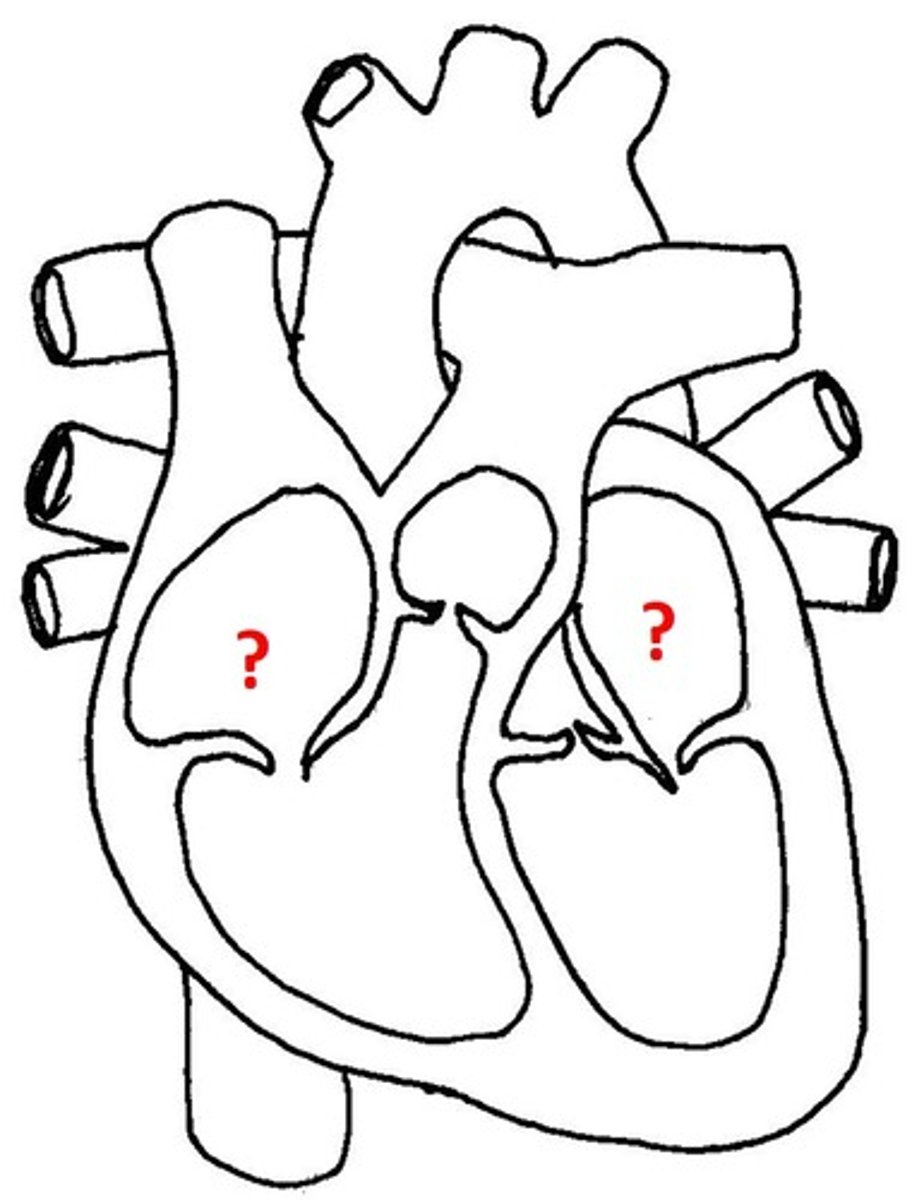
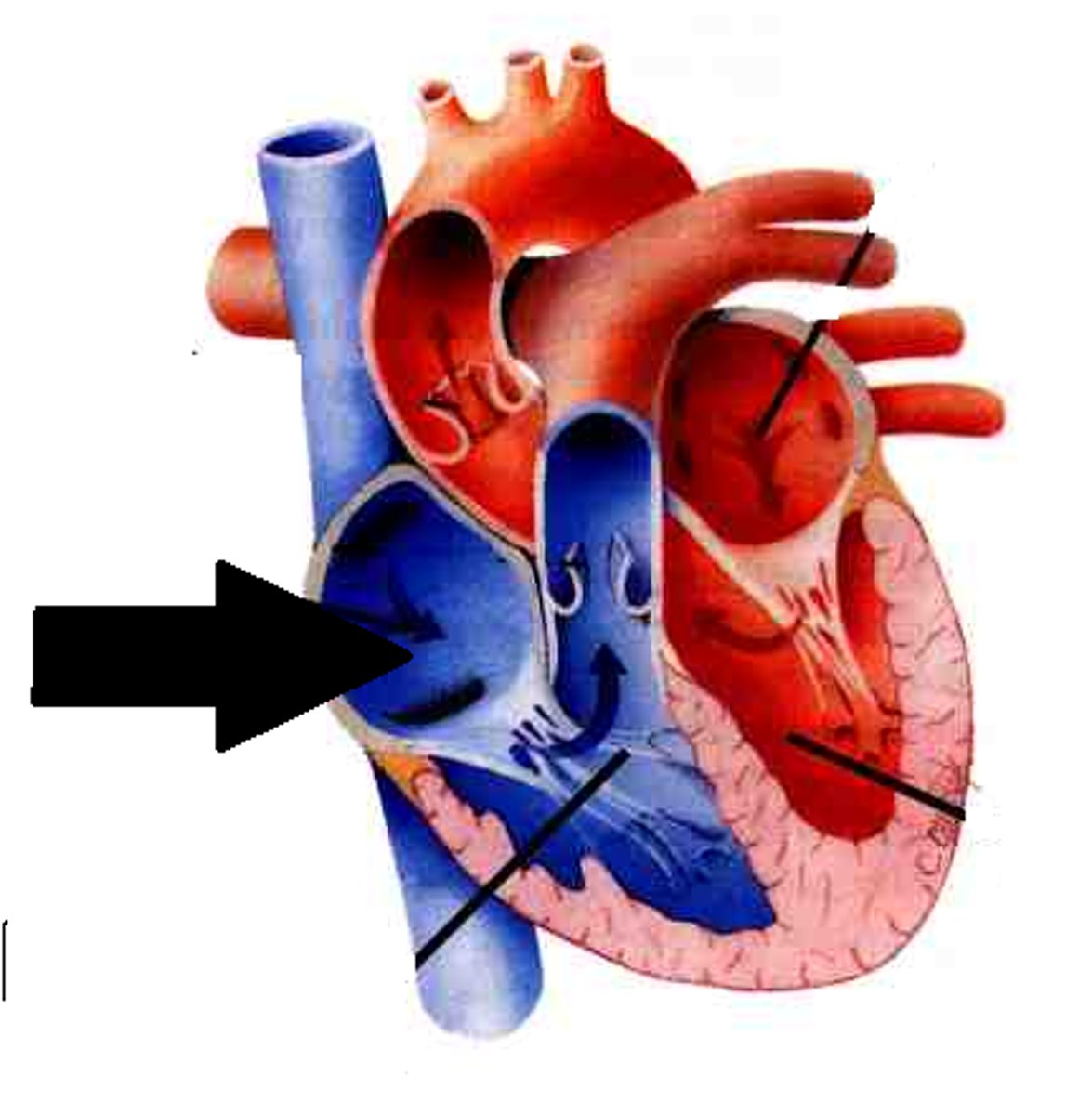
Right atrium
Description: Chamber forming the right, superior margin of the heart
Relationship: Receives blood from the superior and inferior vena cava and the coronary sinus
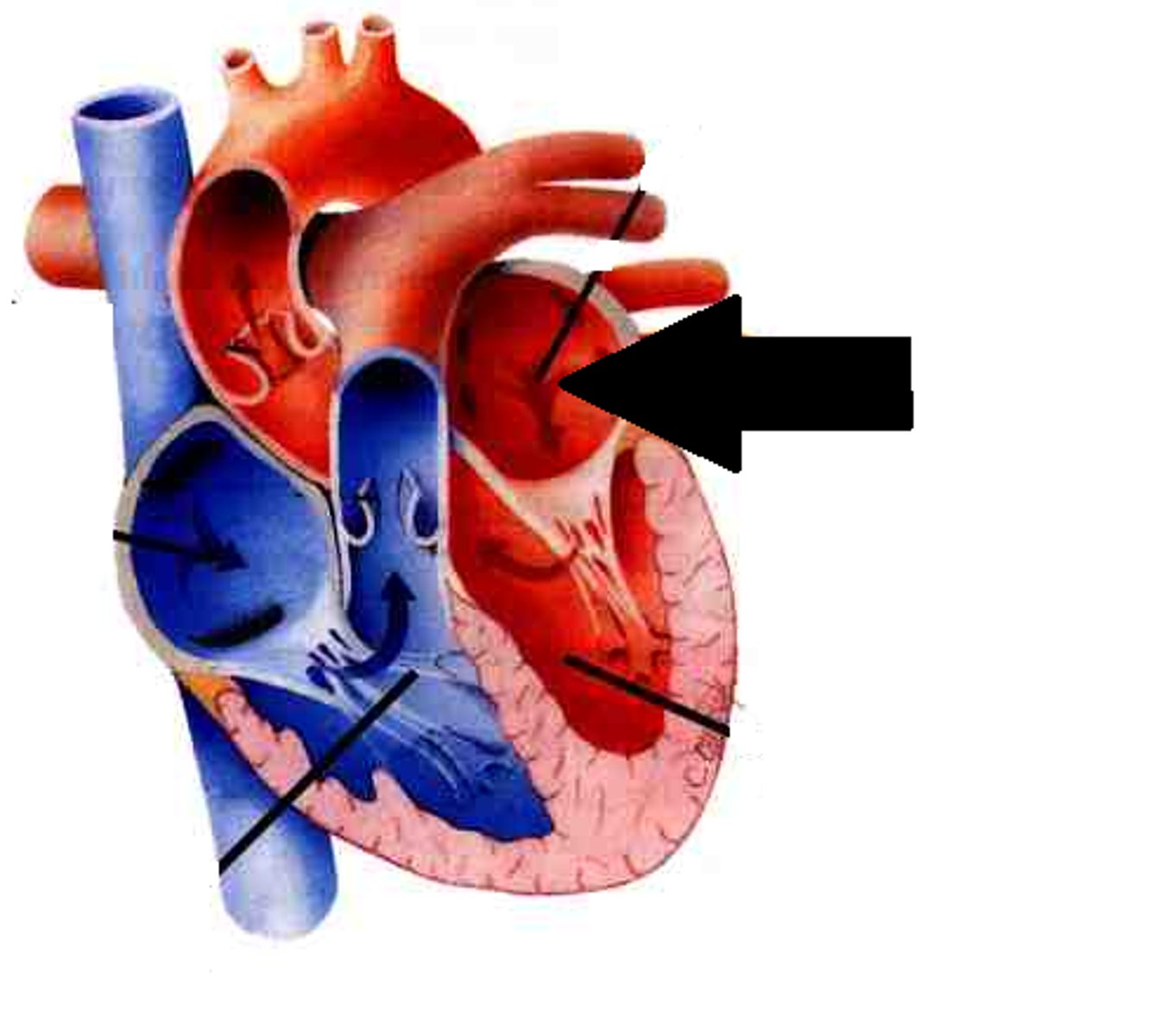
Left atrium
Description: Chamber forming the left, posterior margin of the heart
Relationship: Receives blood from the pulmonary veins
Ventricles
Description: Thicker, muscular walled chambers that pump blood to the pulmonary and systemic circuits
Relationship: Inferior to the coronary sulcus
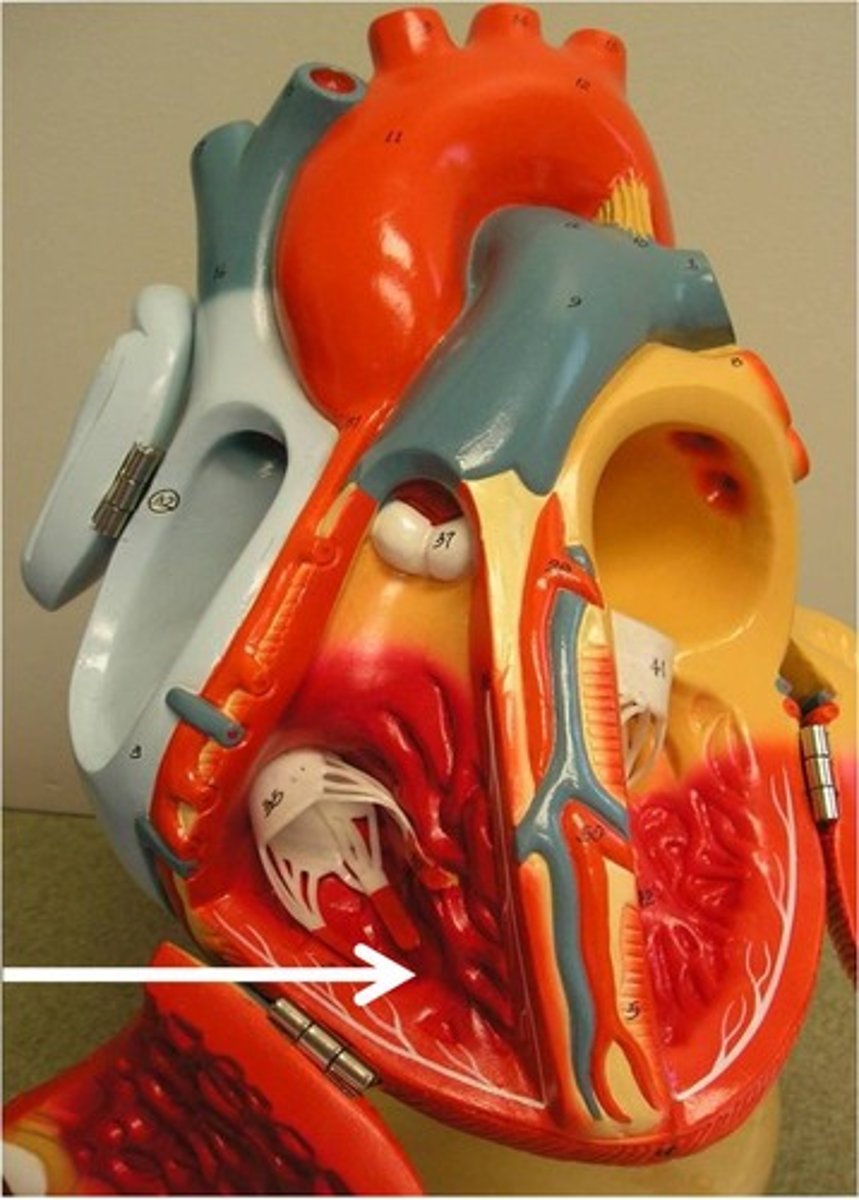
Right ventricle
Description: Chamber forming the right, inferior margin of the heart
Relationship: Pumps deoxygenated blood from the heart to the pulmonary circuit (lungs)
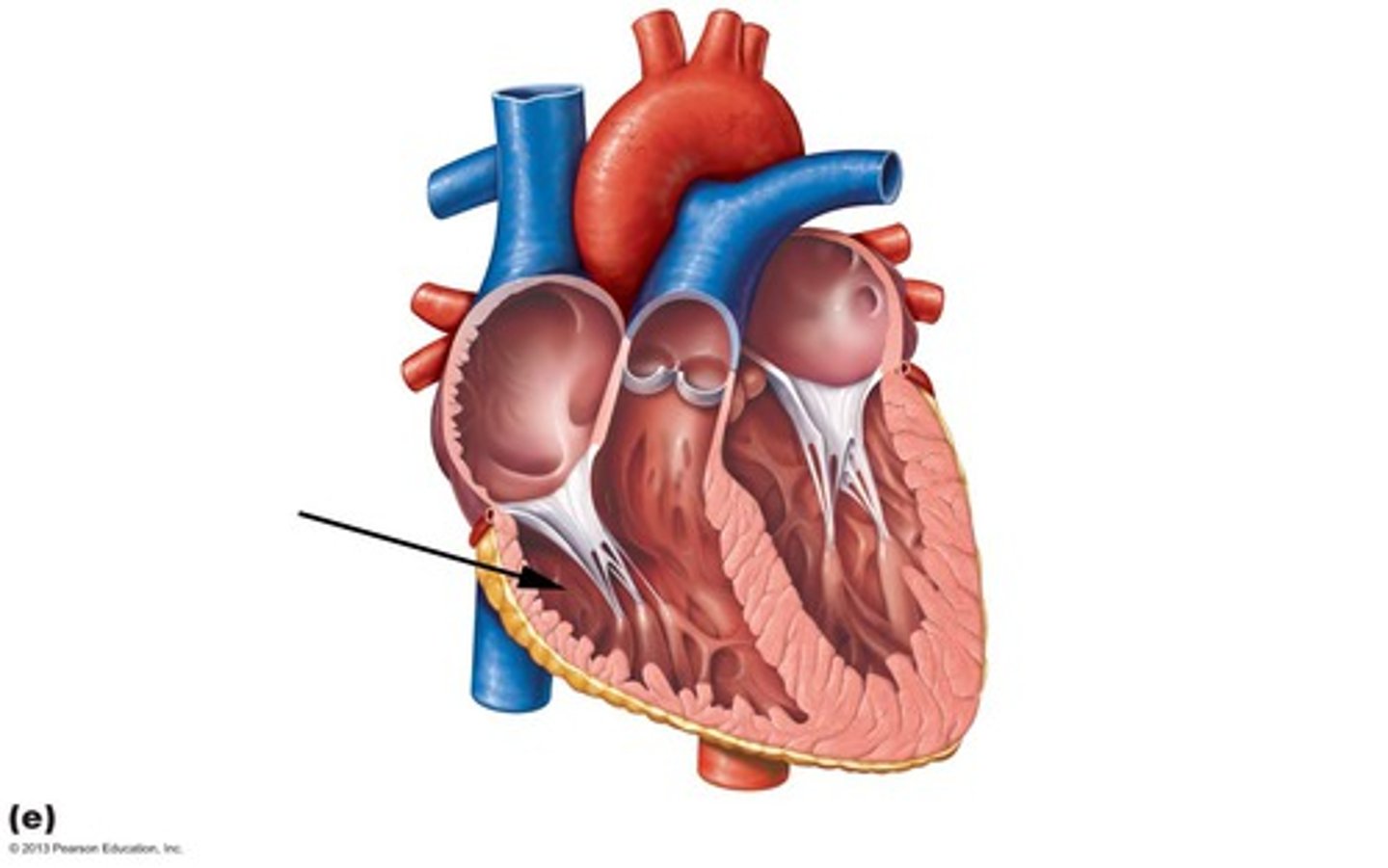
Left ventricle
Description: Chamber forming the left, apex margin of the heart
Relationship: Pumps oxygenated blood from the heart into the aorta and systemic circuit
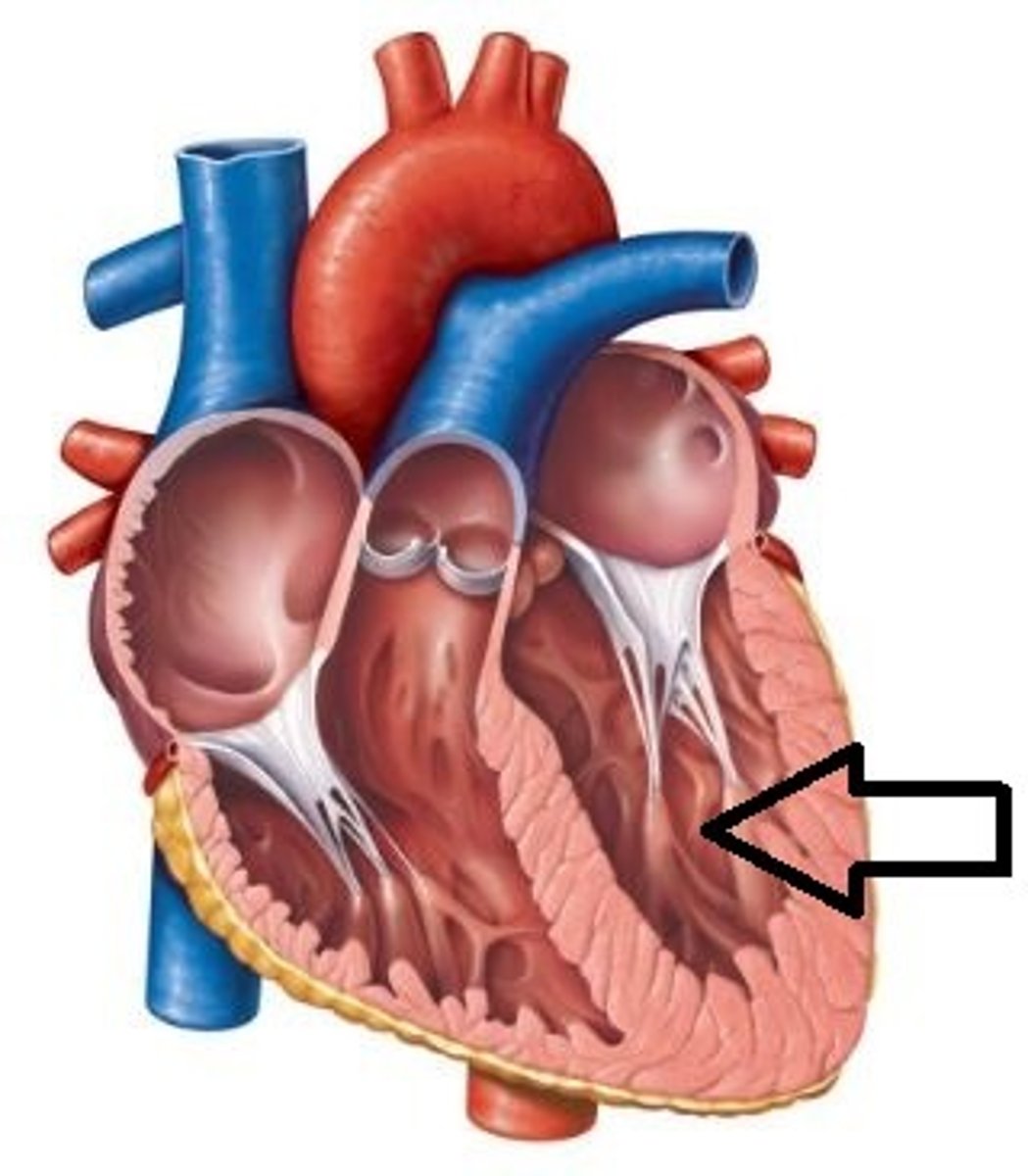
Interventricular septum
Description: Thick, muscular partition separating the left and right ventricles
Relationship: N/A
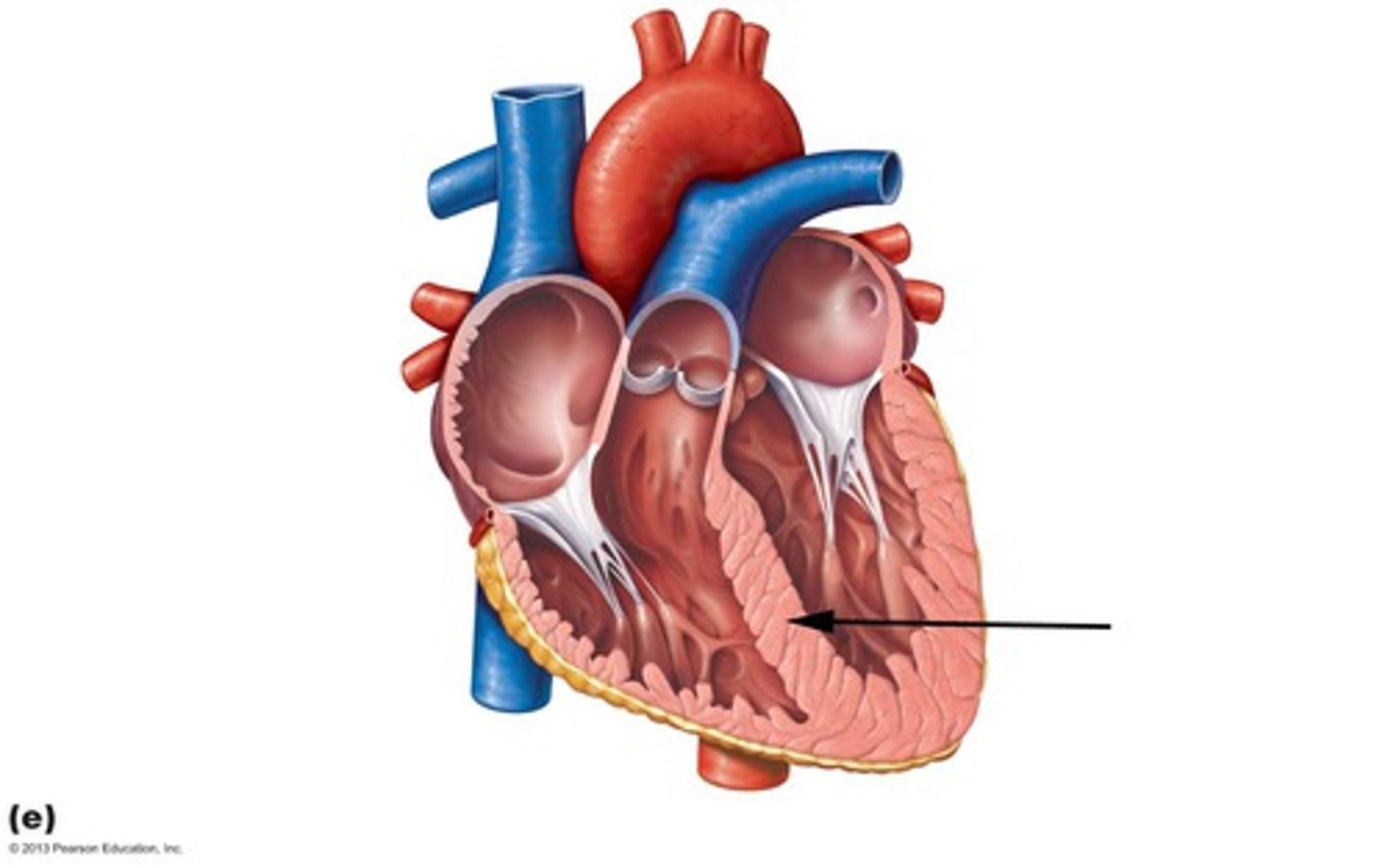
Chordae tendineae
Description: Fibrous strands that attach the atrioventricular valve cusps to the papillary muscles
Relationship: "Heart strings" that prevent the atrioventricular valve cusps from being forced into the atria during ventricular contraction
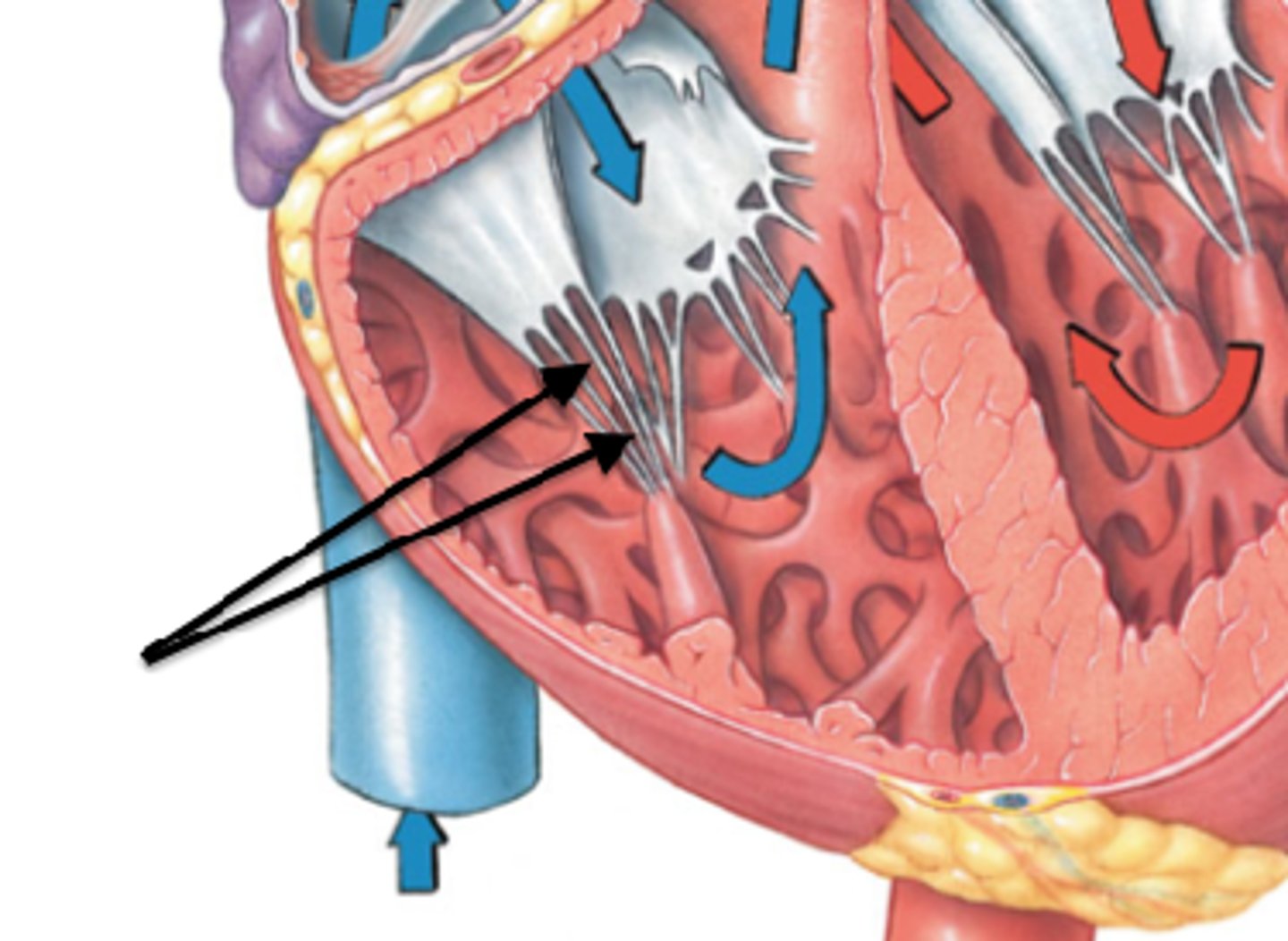
Papillary muscle
Description: Cone shaped muscular projections attaching the chordae tendineae to the walls of the ventricles
Relationship: Helps to assure proper closure of the atrioventricular valves and prevents backflow (regurgitation) of blood into the atria
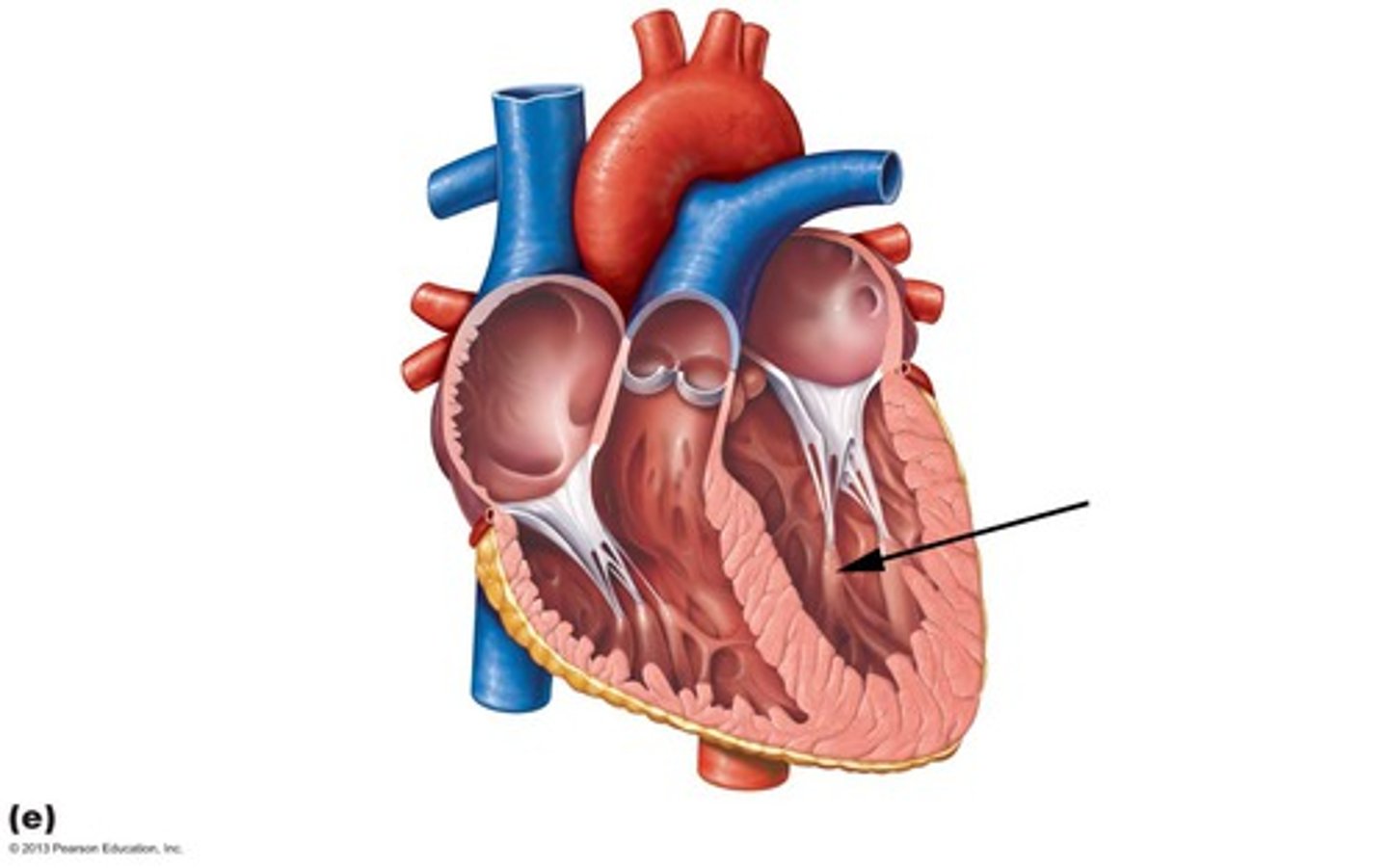
Trabeculae carneae
Description: Irregular ridges of cardiac muscle on the inner walls of the ventricles
Relationship: Web-like appearance
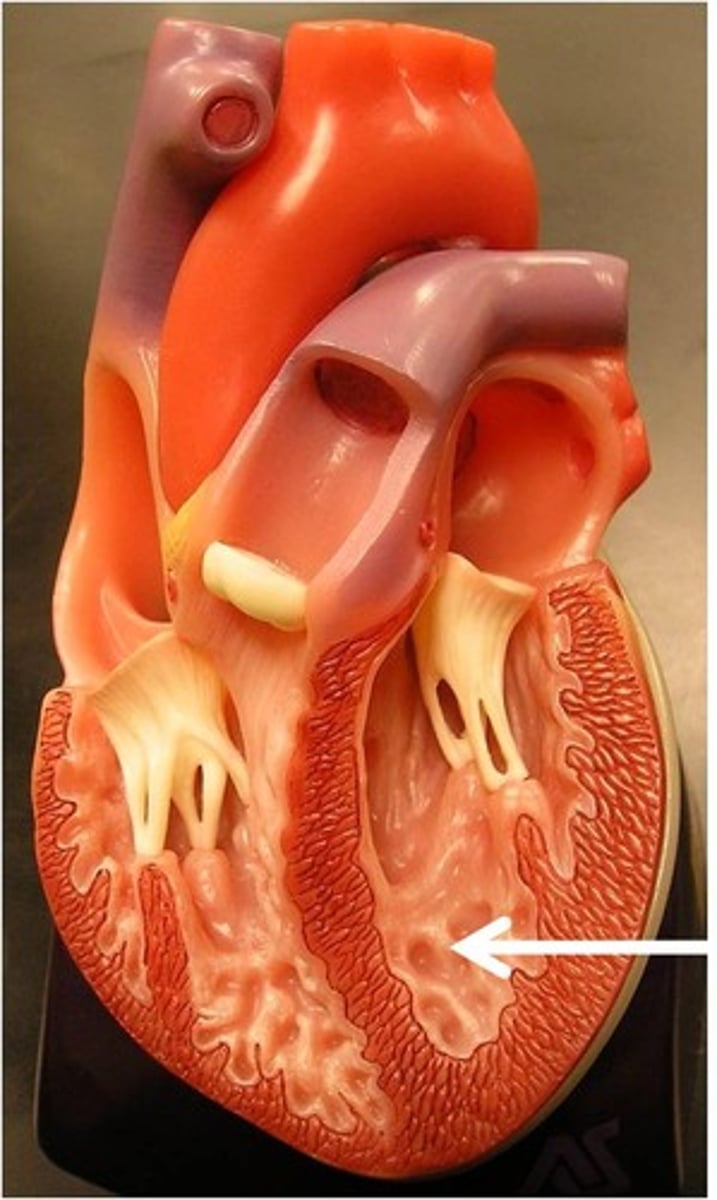
Fossa ovalis
Description: Oval shaped depression in the intra atrial septum of the right atrium
Relationship: Fetal remnant of the foramen ovale which shunted blood from the right to left atrium in order to bypass lungs
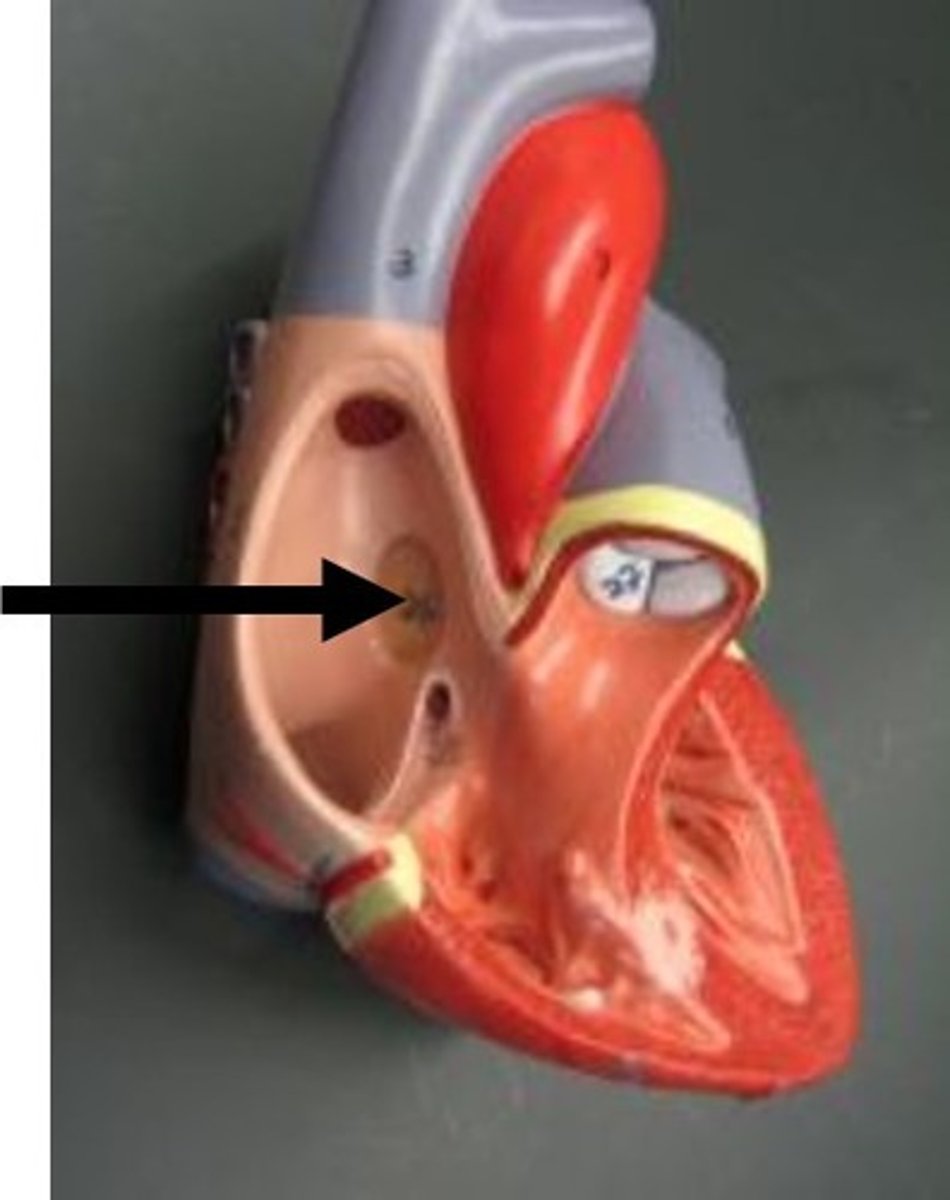
Ligamentum arteriosum
Description: Fibrous cord connecting the arch of the aorta and pulmonary trunk
Relationship: Fetal remnant of the ductus arteriosus that shunted blood from the pulmonary trunk to the aortic arch in order to bypass the lungs
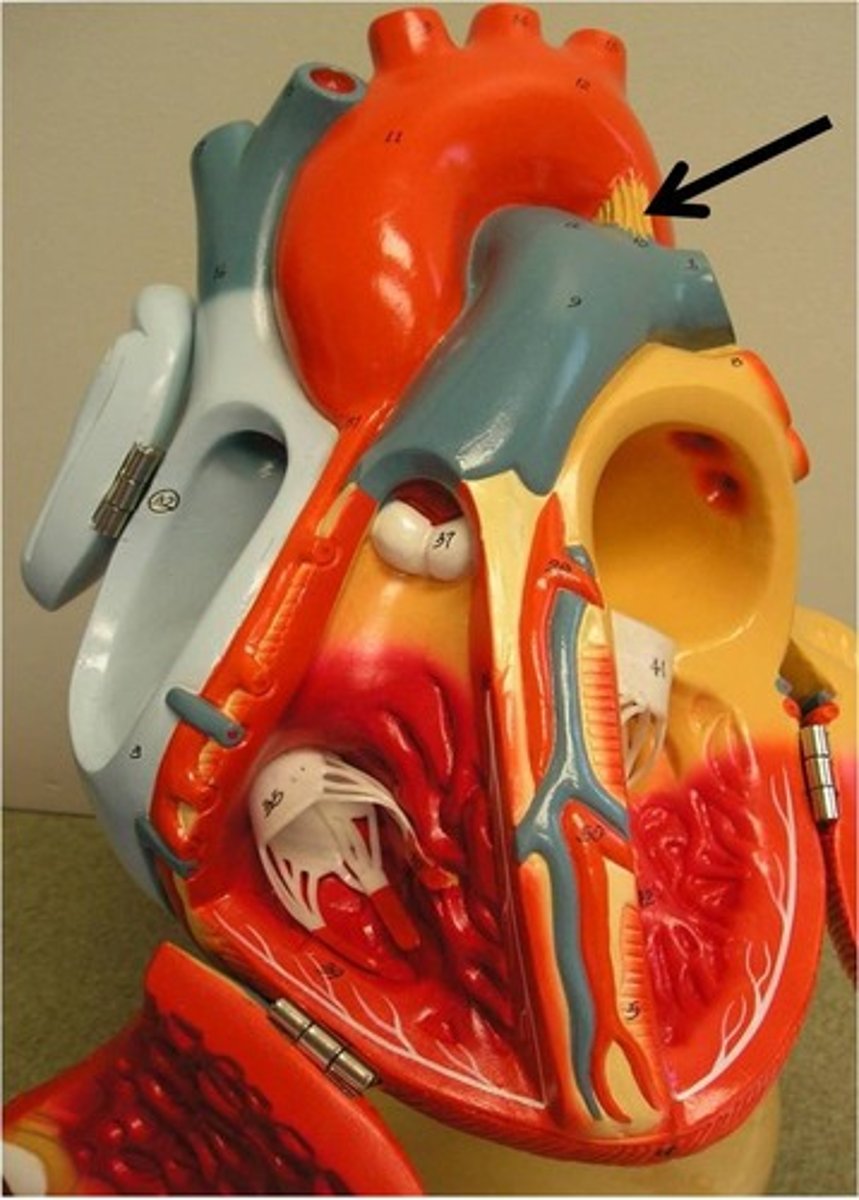
Right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve
Description: Valve with three cusps between the right atrium and ventricle
Relationship: Atrioventricular valves are open during ventricular diastole (filling)
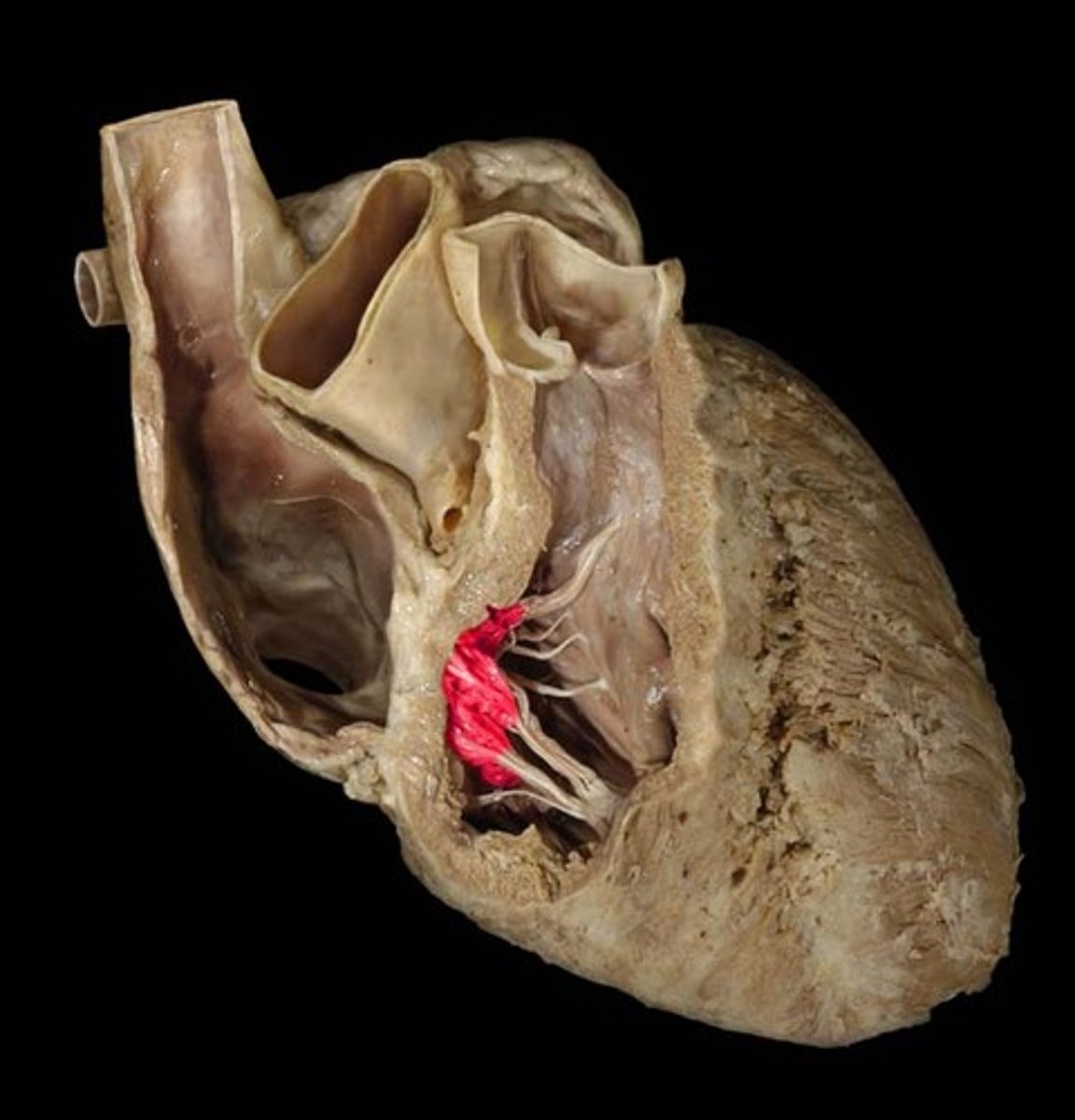
Left atrioventricular (bicuspid or mitral) valve
Description: Valve with two cusps between the left atrium and ventricle
Relationship: The order of the Tricuspid and Bicuspid valves can be remembered by "Try before you Buy"
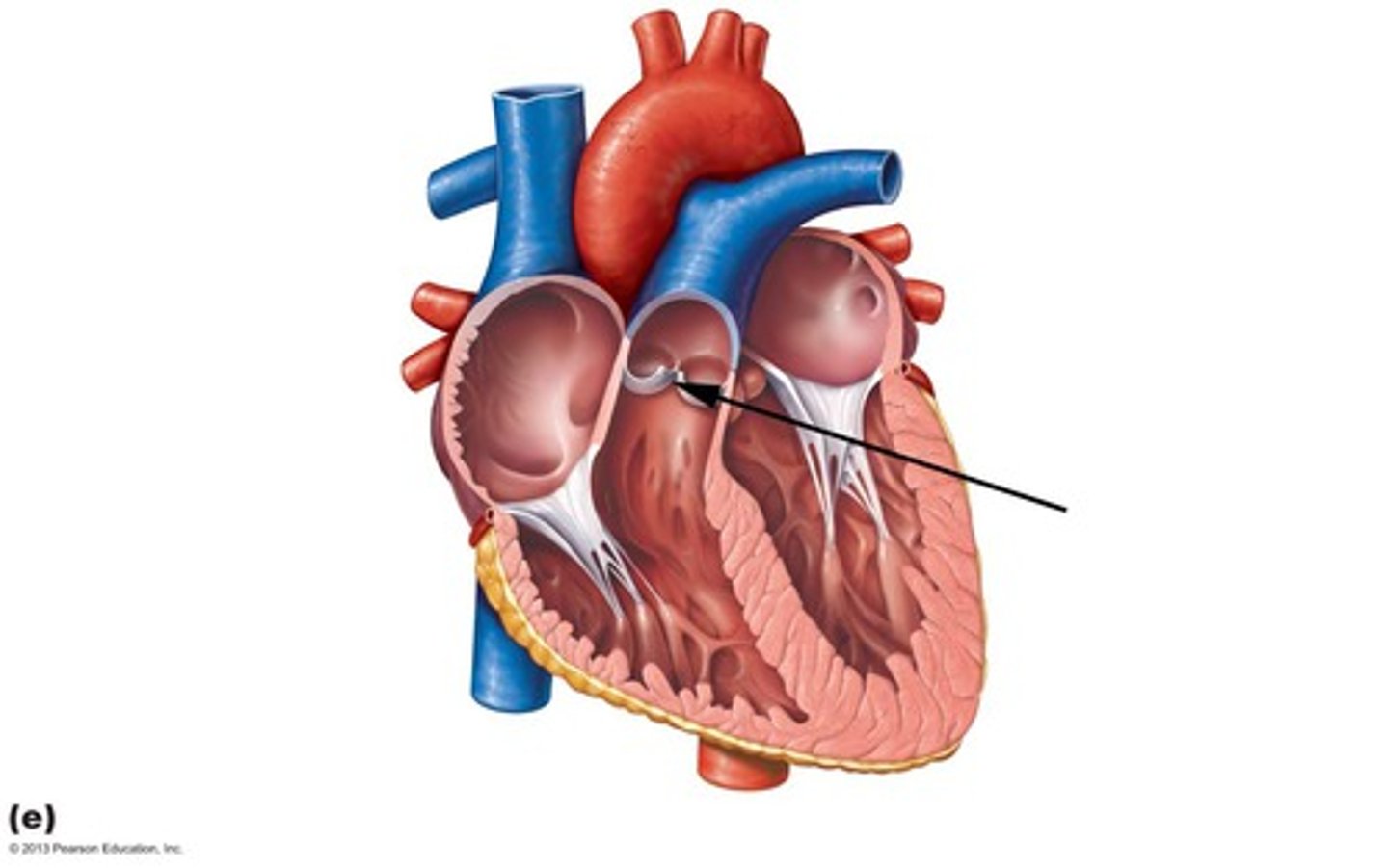
Pulmonary semilunar valve
Description: Valve with three cusps at the base of the pulmonary trunk
Relationship: Semilunar valves are closed during ventricular diastole (filling)
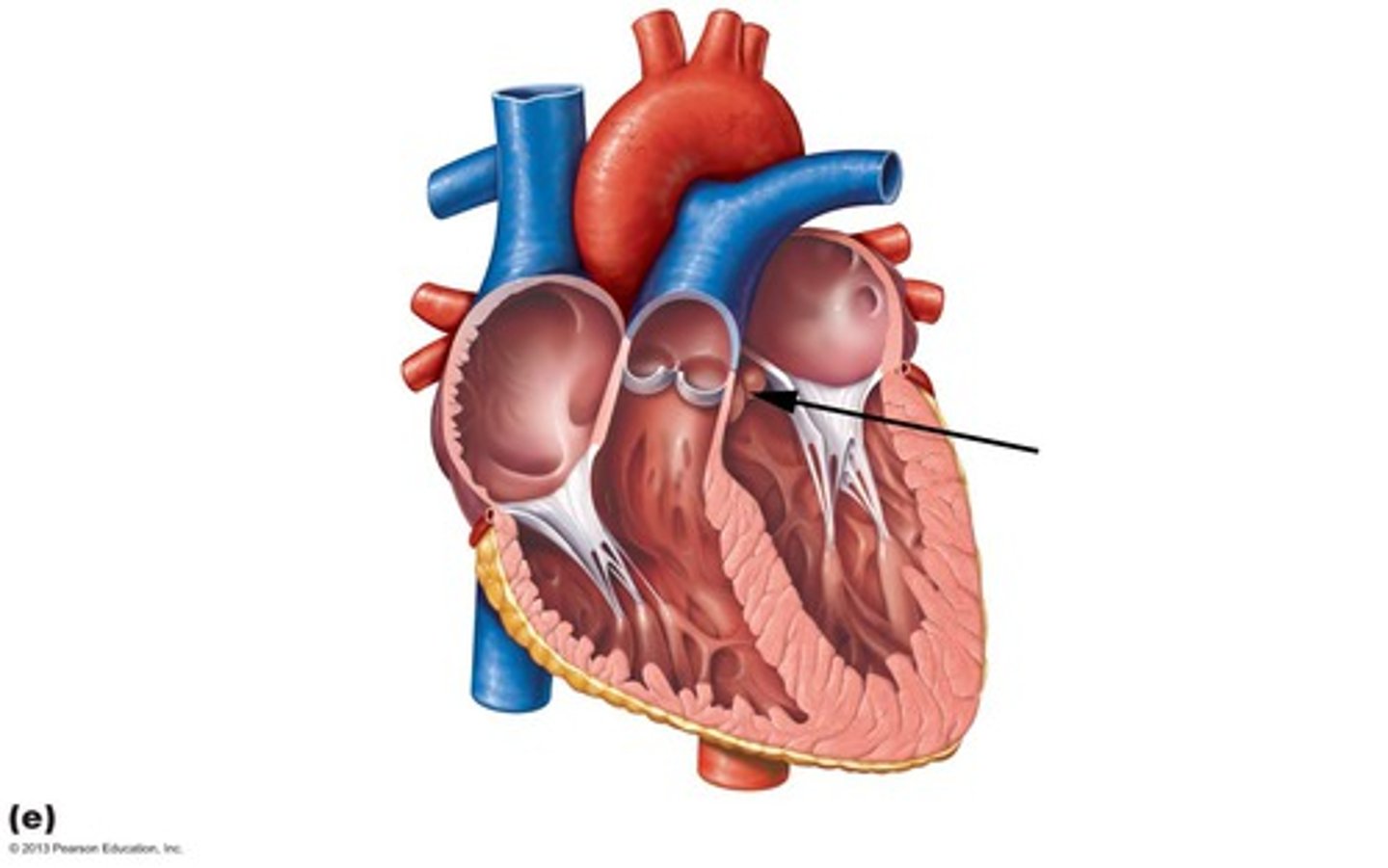
Aortic semilunar valve
Description: Valve with three cusps at the base of the ascending aorta
Relationship: Named semilunar because the valve cusps are moon (lunar) shaped
Sinoatrial (SA) node
Description: Specialized cells in the roof of the right atrium near the entrance of the superior vena cava
Relationship: "Pacemaker" of the heart
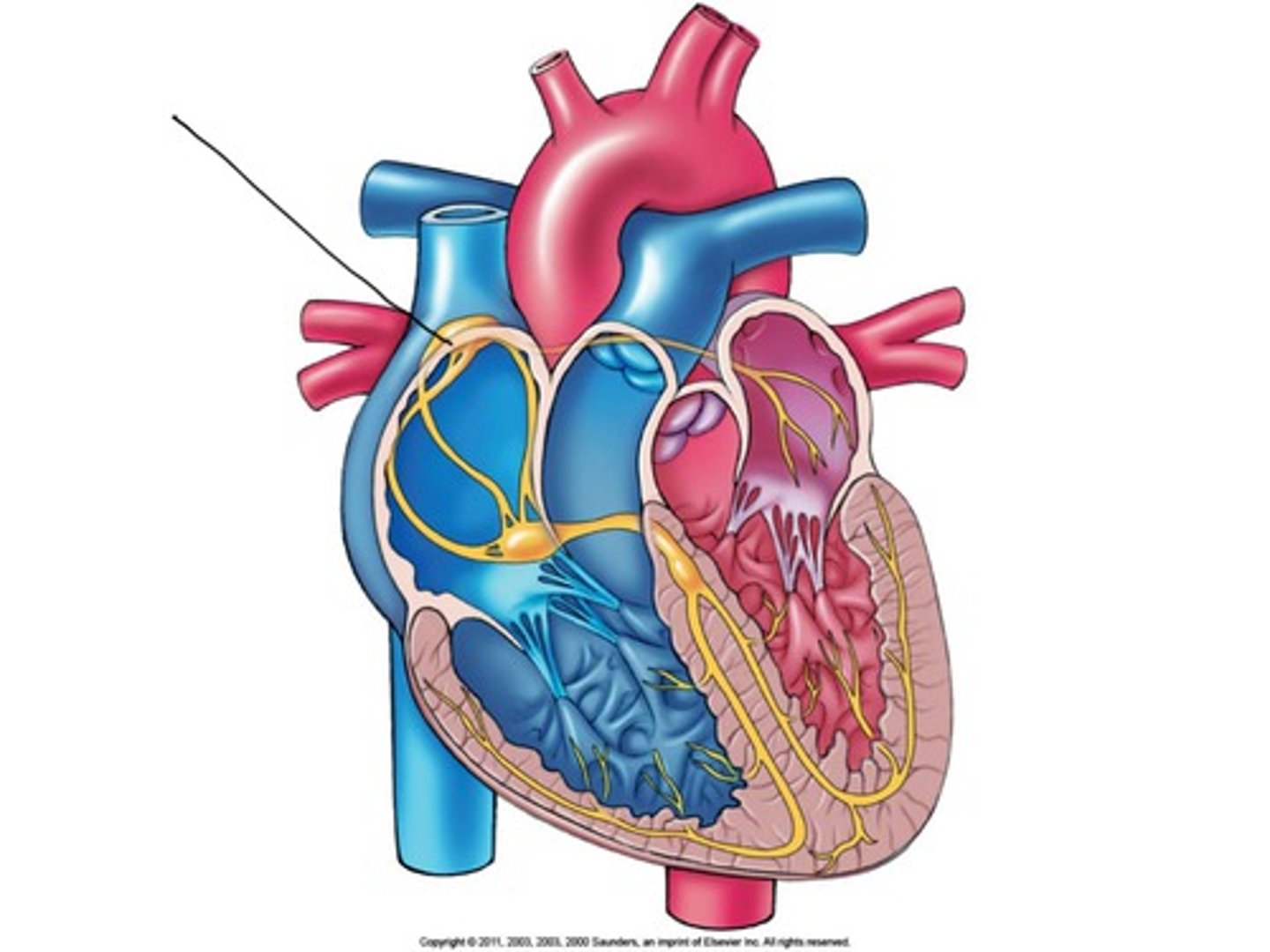
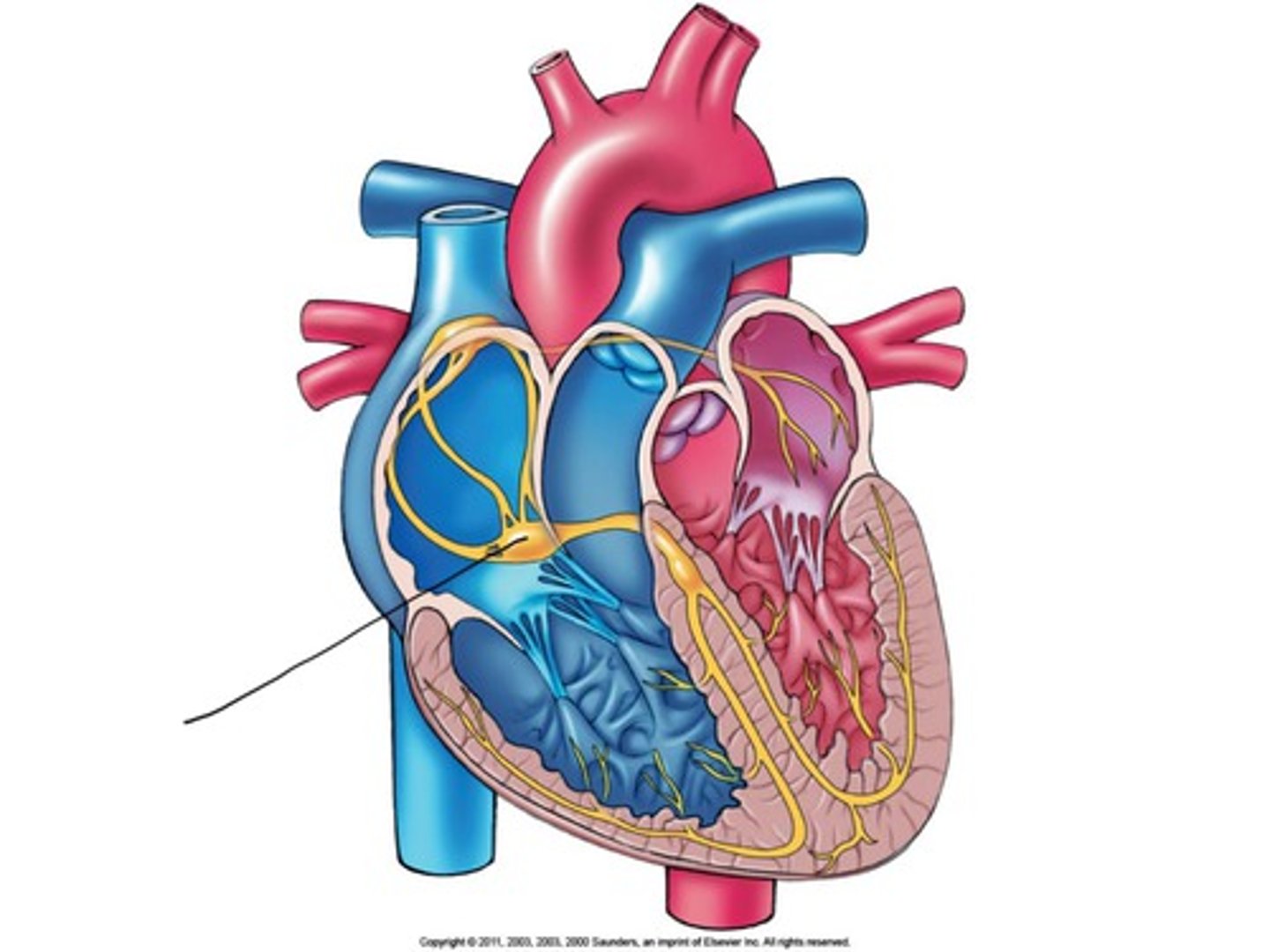
Atrioventricular (AV) node
Description: Specialized cells in the floor of the right atrium near the opening of the coronary sinus
Relationship: Delays electrical impulse allowing the atria time to contract and the ventricles to completely fill with blood
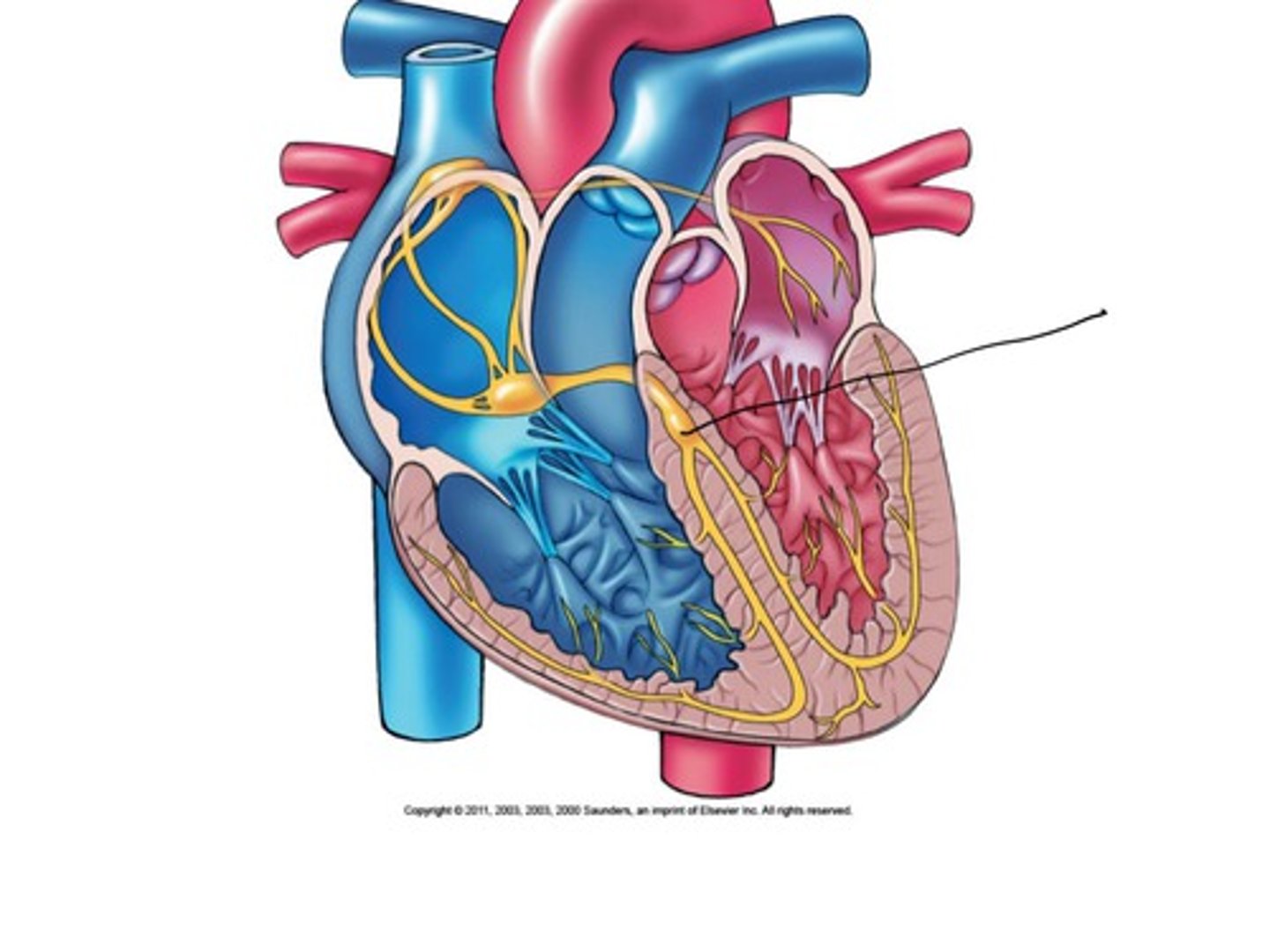
AV bundle (bundle of his)
Description: Massive bundle of conducting fibers located in the superior aspect of the interventricular septum
Relationship: N/A
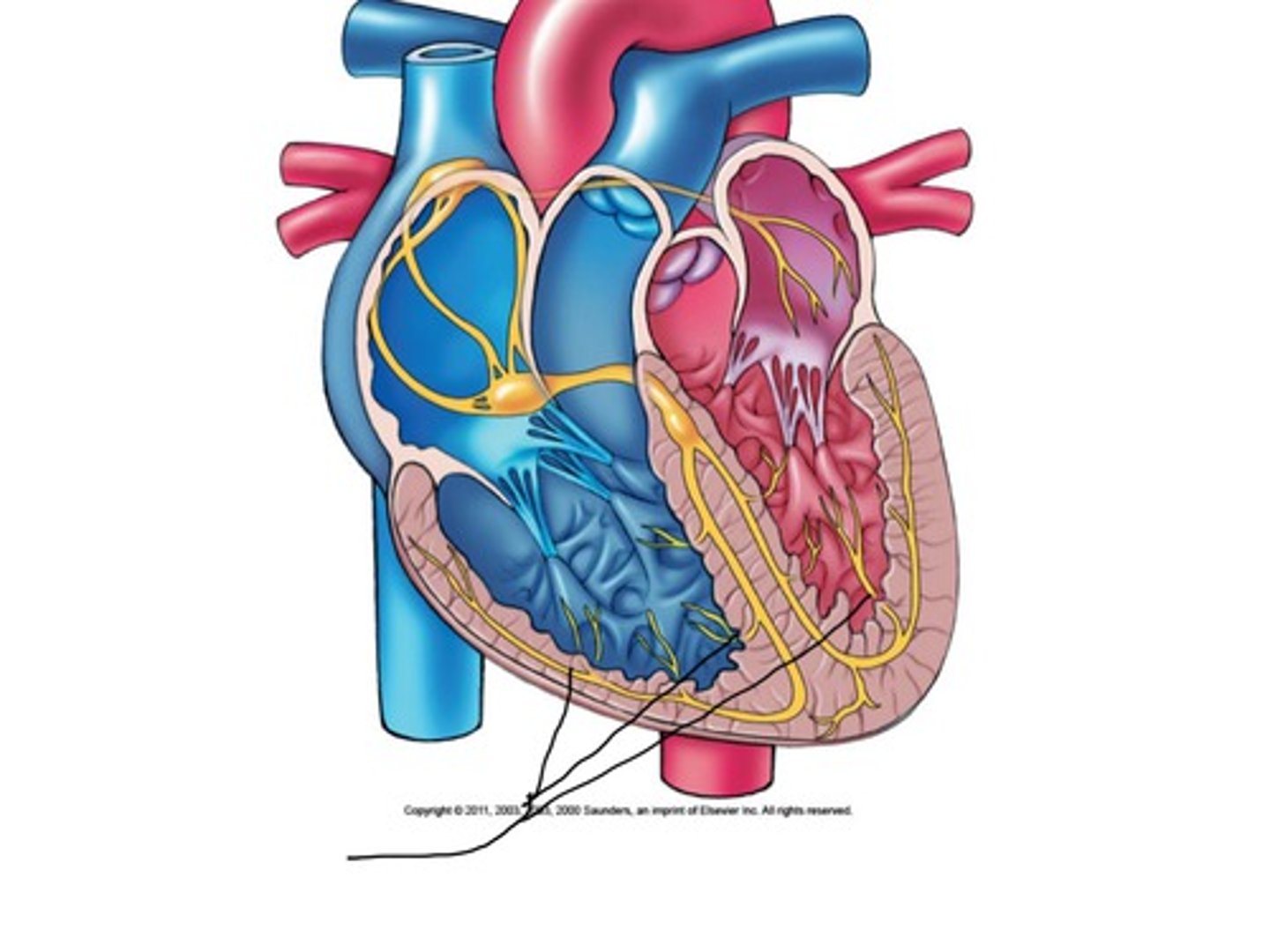
Bundle branches (R/L)
Description: Right and left branches of the AV bundle in the interventricular septum for their respective ventricles
Relationship: N/A
Purkinje fibers
Description: Rapid contractile cells in the ventricular myocardium
Relationship: End of the conduction system
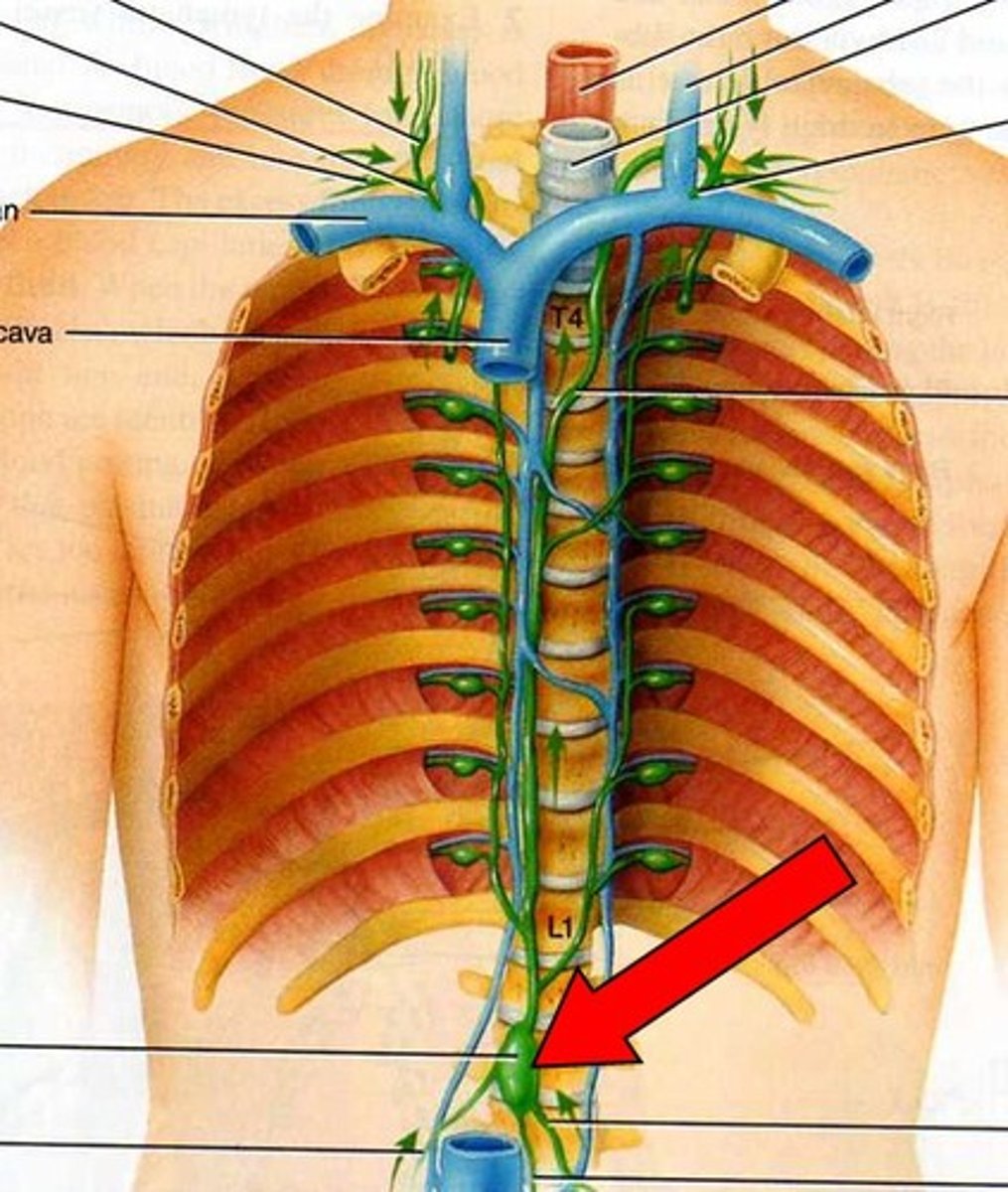
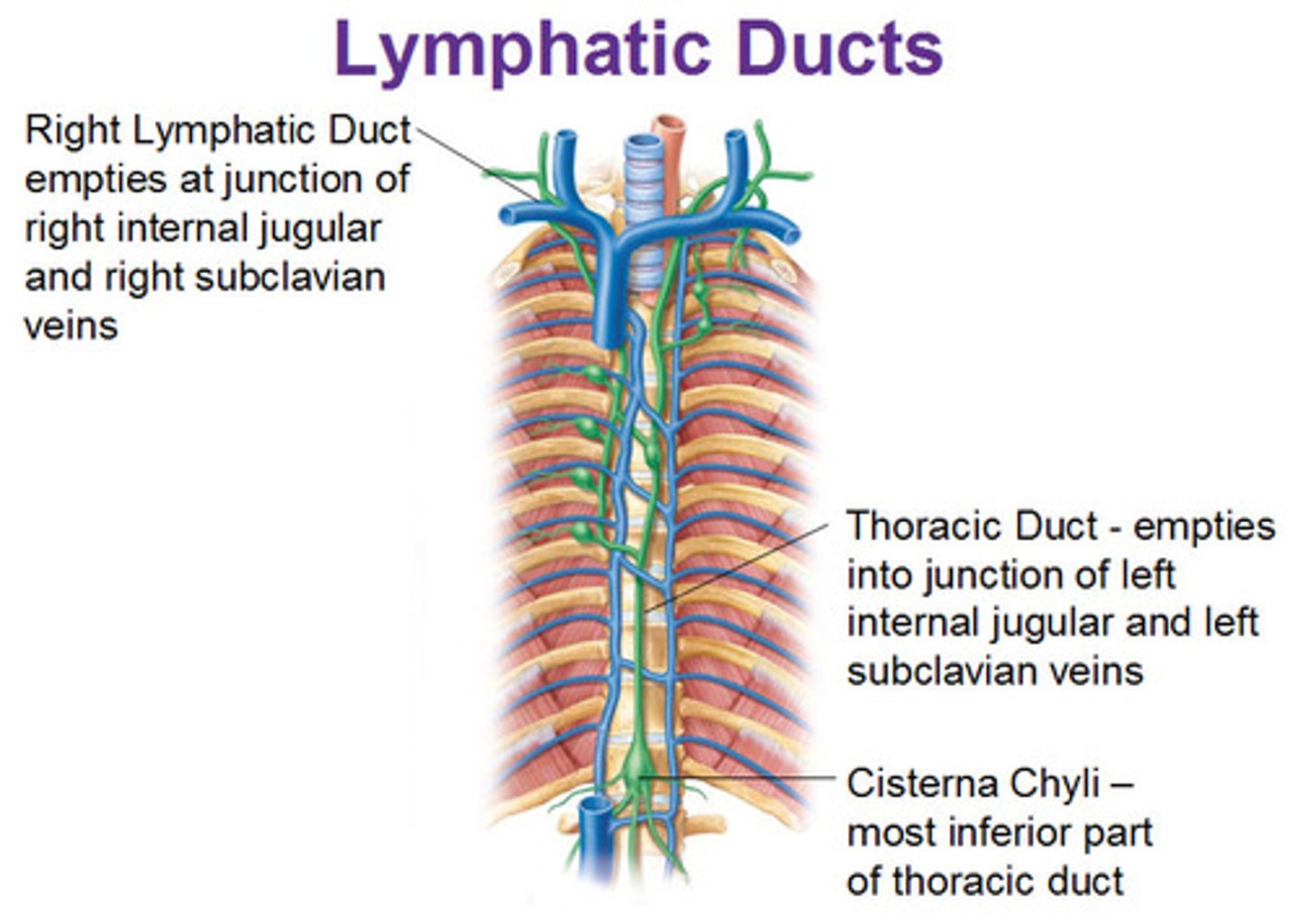
Thoracic (Left lymphatic) duct
Location: Long duct that originates in the superior abdomen (cisterna chyli) and ascends through the posterior mediastinum along the thoracic aorta
Description: Receives lymph from the left side of the thorax, left upper limb, left side of the head and neck, and all structures inferior to the diaphragm. Empties into the venous system at junction of the left internal jugular and left subclavian veins.
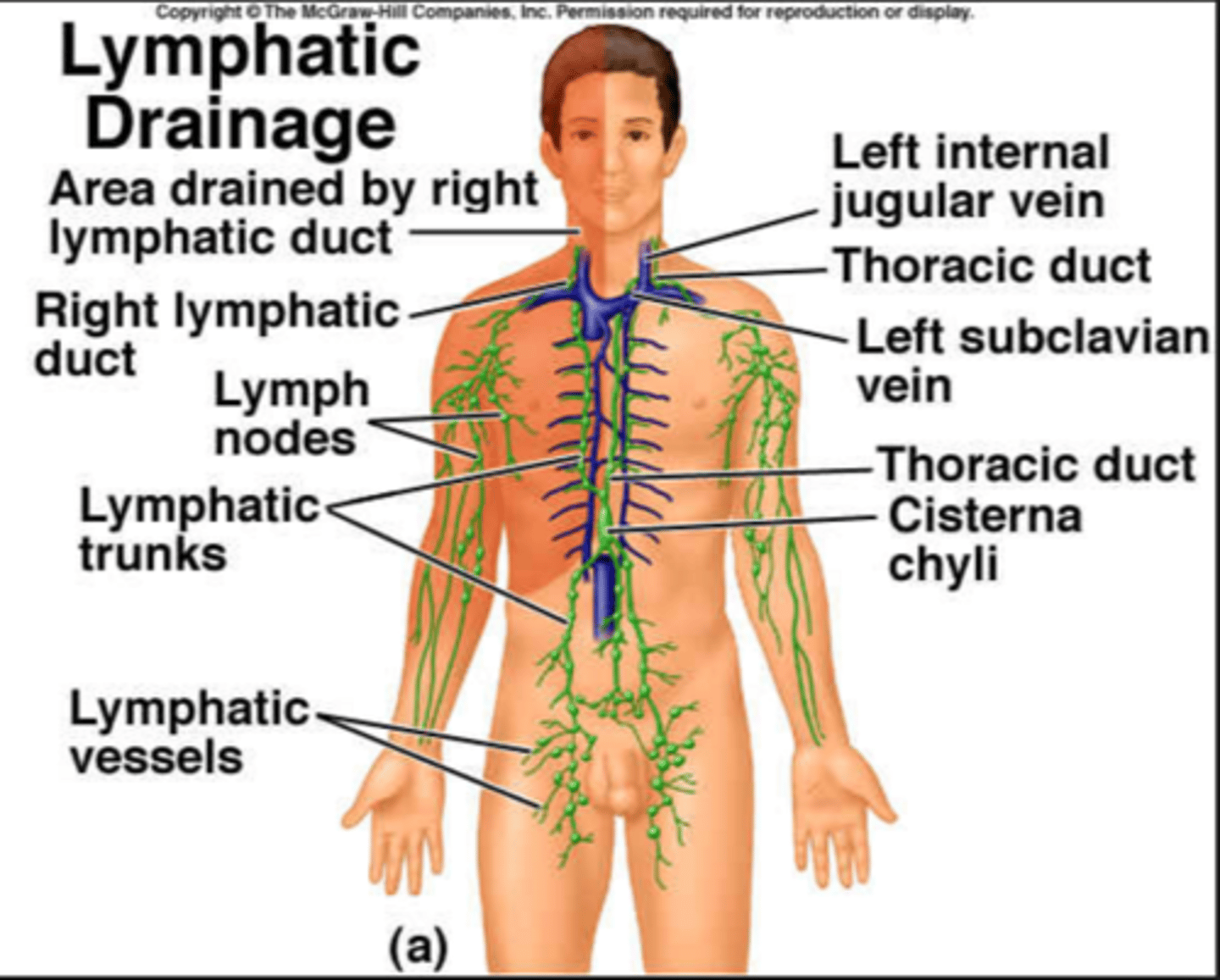
Cisterna chyli
Location: Irregular shaped sac in the posterior, superior abdomen
Description: Origin of the thoracic duct. Receives lymph from the abdomen, pelvis, and lower limbs
Right lymphatic duct
Location: Small collecting duct in the clavicular region
Description: Receives lymph from the right side of the thorax, right upper limb, and right side of head and neck. Empties into the venous system at the junction of the right subclavian vein and internal jugular veins.
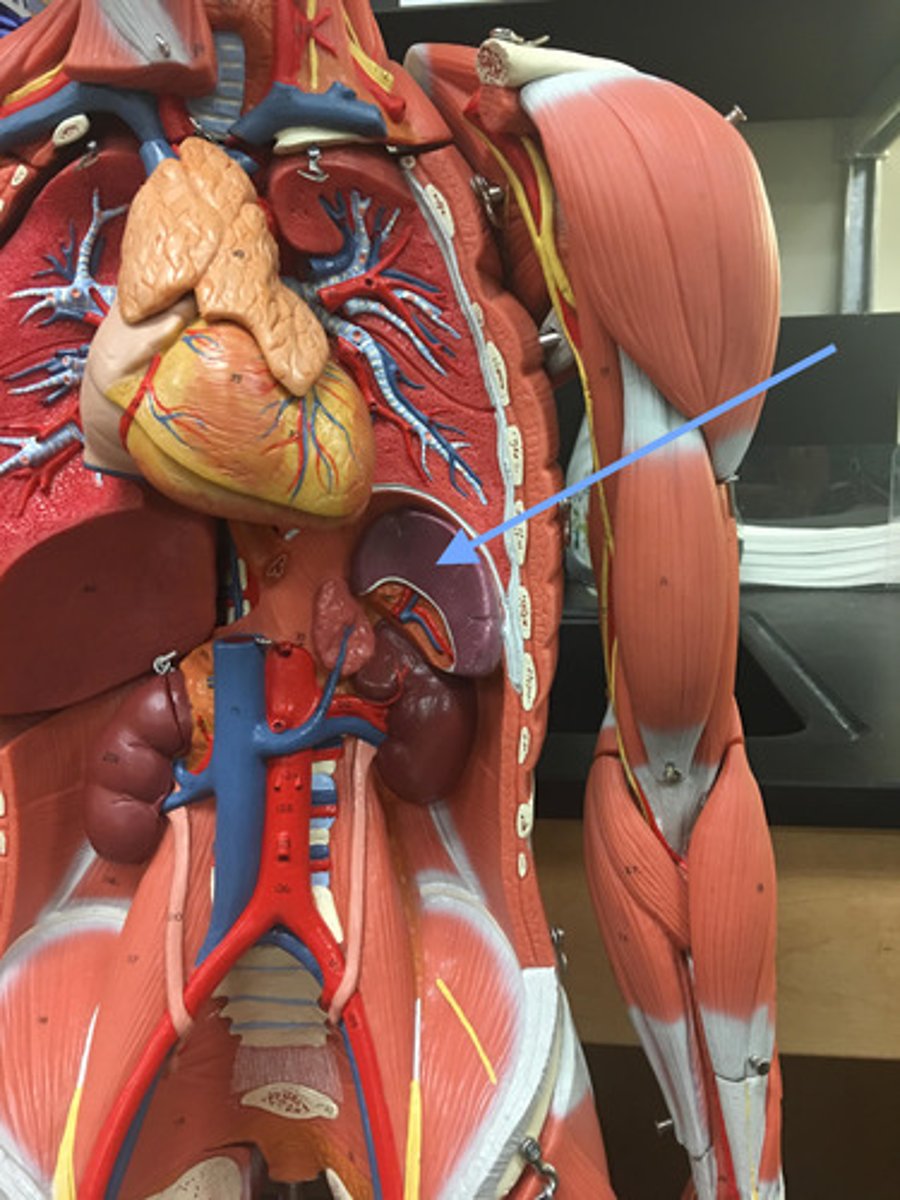
Spleen
Location: Large purple lymphatic organ located left of the stomach and inferior to the diaphragm
Description: Largest lymphatic organ of the body. Functions to initiate the immune response, removal of bacteria, and storage of red and white blood cells.
Palatine tonsils
Location: Lateral walls of the oropharynx
Description: Inflammation of the tonsils is known as tonsilitis
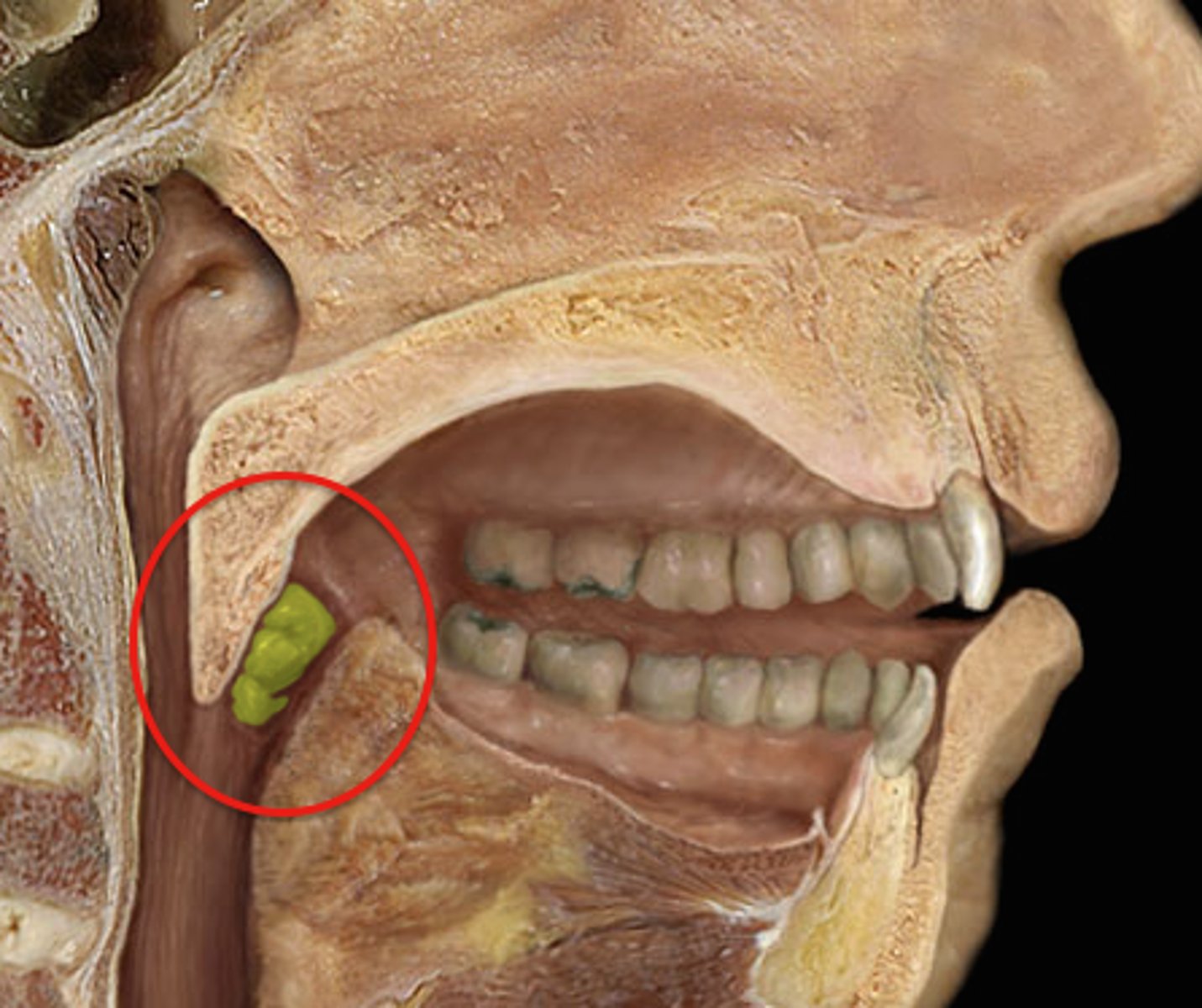
Lingual tonsils
Location: Base of the tongue
Description: N/A
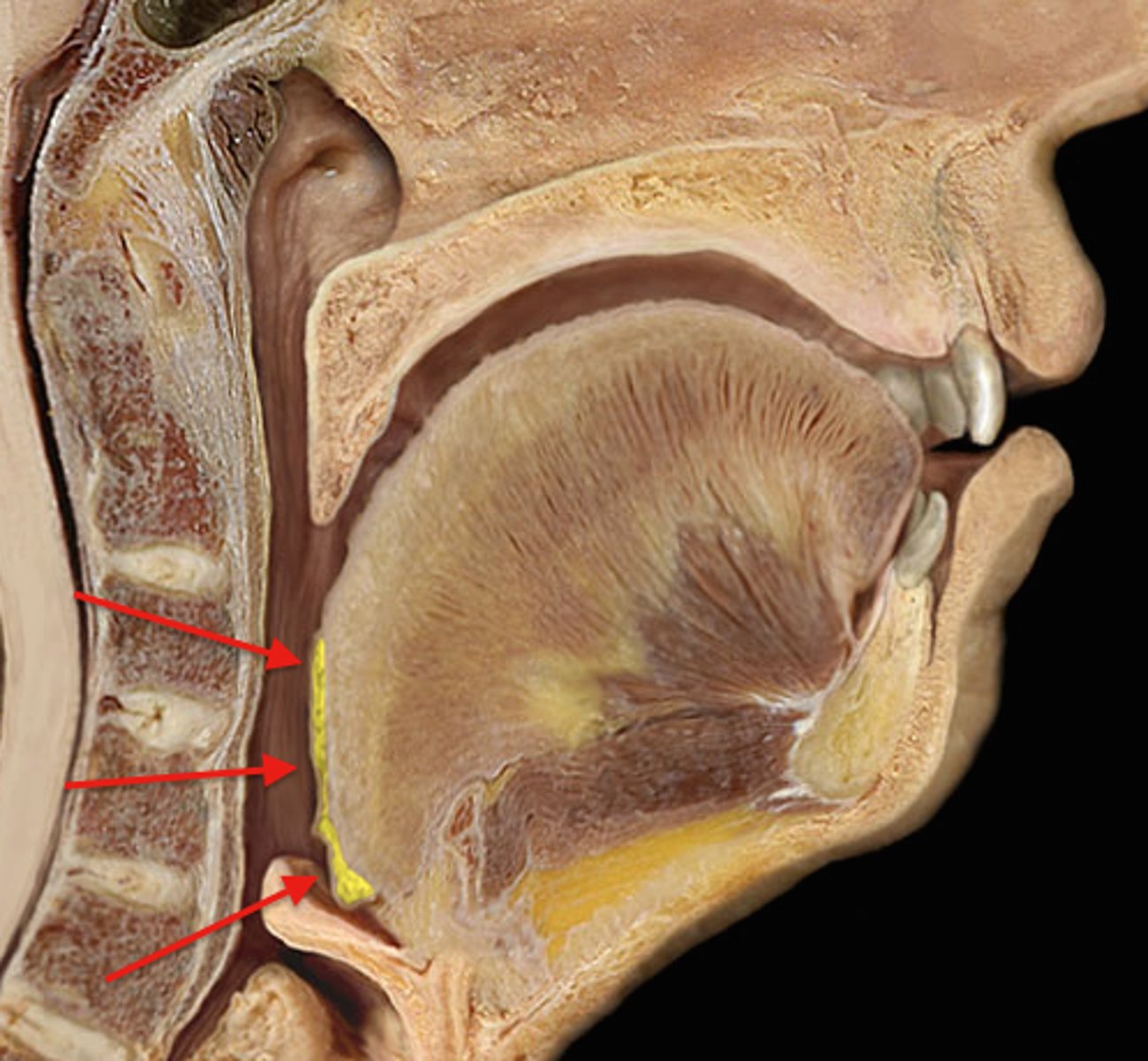
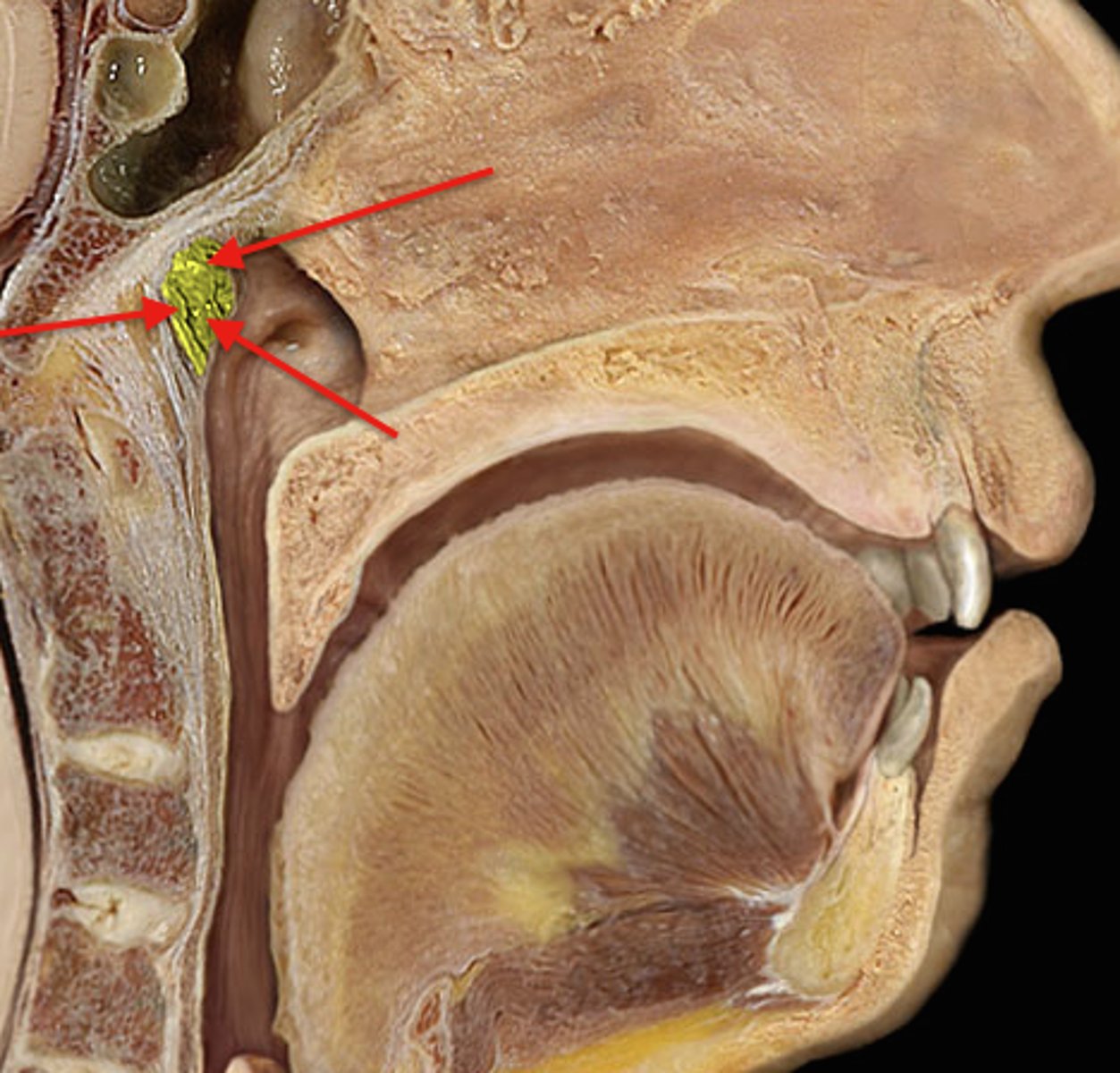
Pharyngeal tonsils
Location: Superior, posterior wall of the nasopharynx
Description: Known as adenoids when infected or inflamed
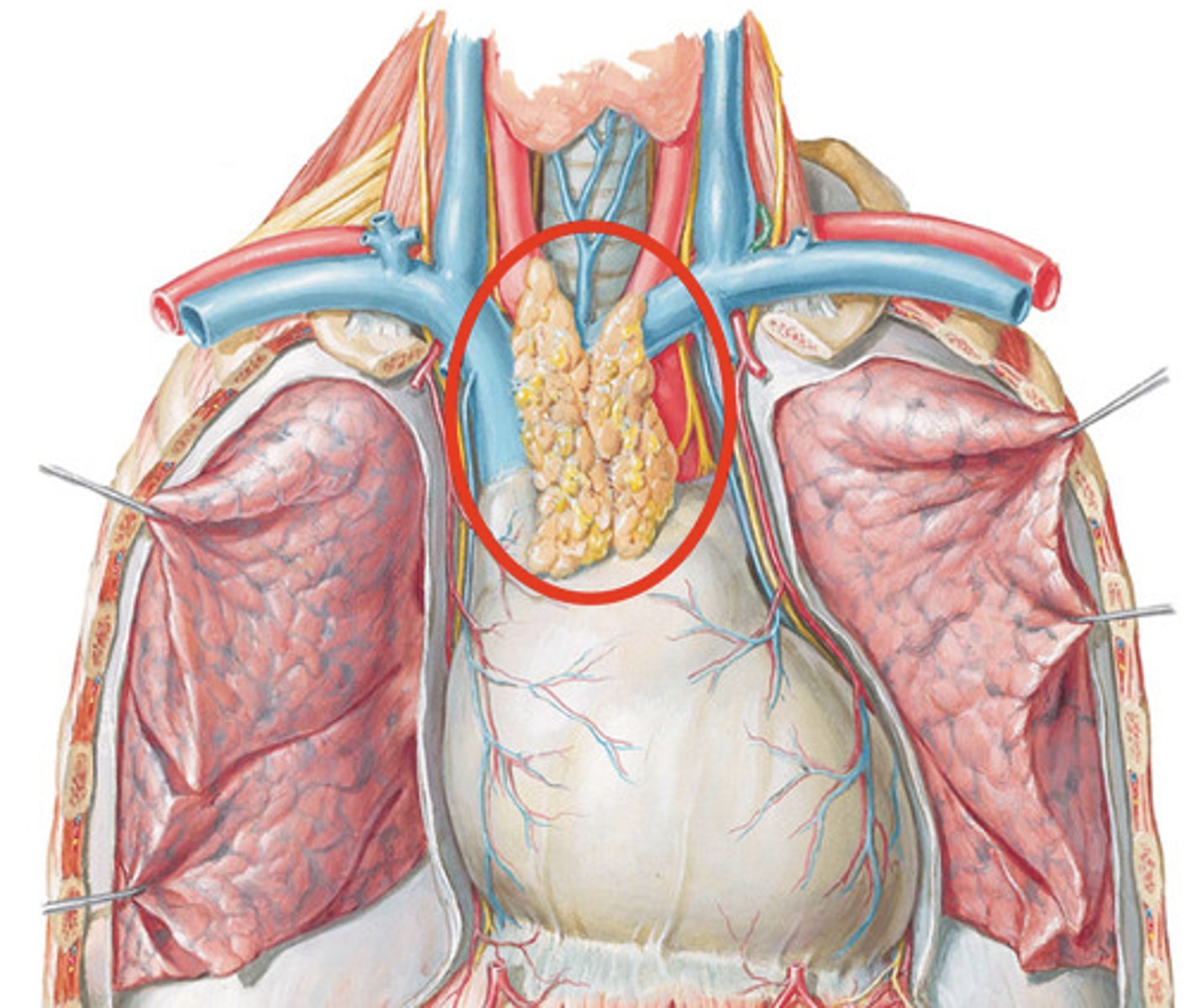
Thymus
Location: Large lobulated tissue between sternum and aorta in childhood
Description: In the thoracic cavity superior to heart. Shrinks in size from childhood to adulthood. Helps in immunity
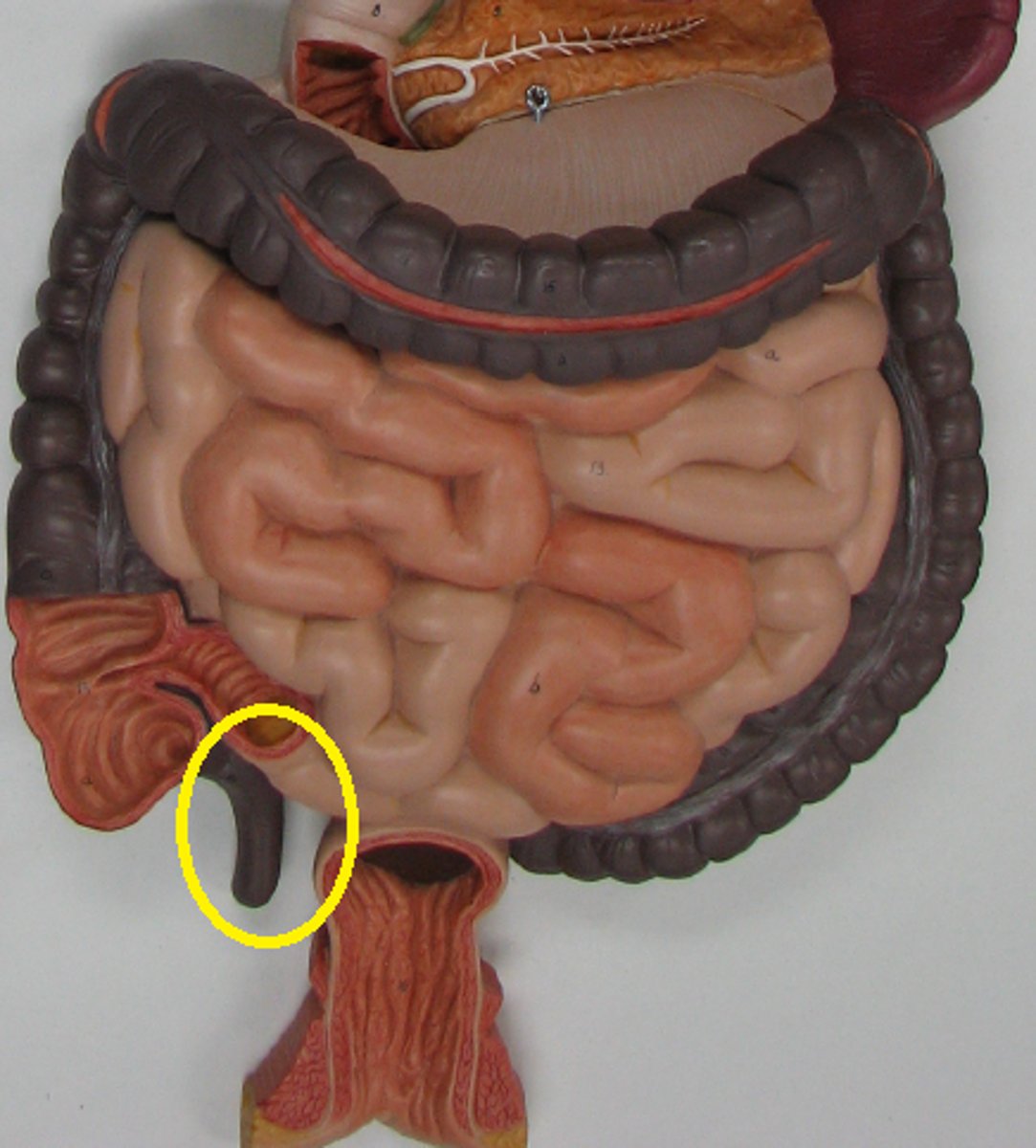
Appendix
Location: Worm-shaped flap connected to the cecum near the junction of the small and large intestines
Description: Contains collections of lymph nodes
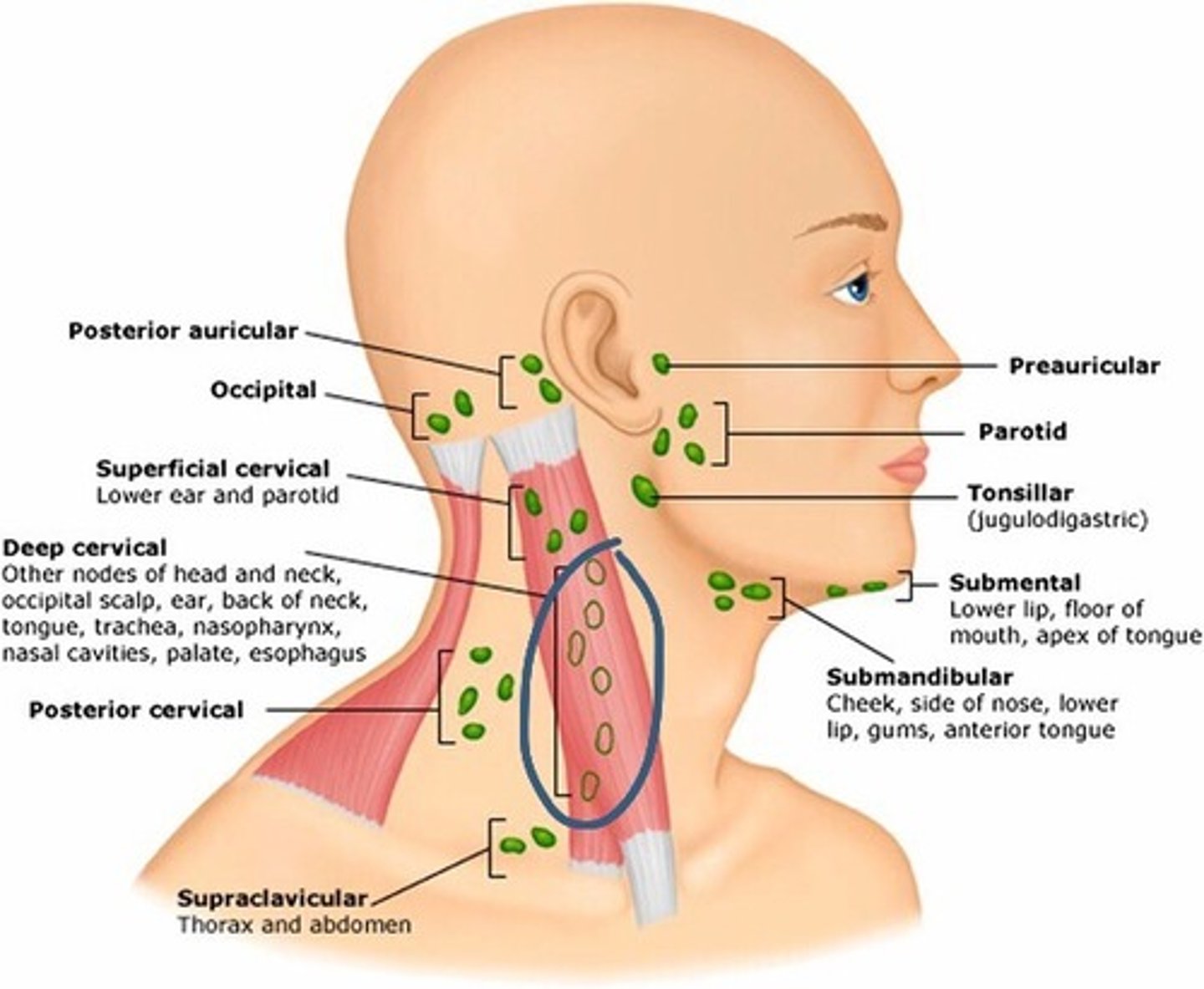
Superficial cervical lymph nodes
Location: Superficial to the sternocleidomastoid muscle along the external jugular vein
Description: Receives lymph from the inferior ear, parotid gland regions, scalp, and skin of head and neck.
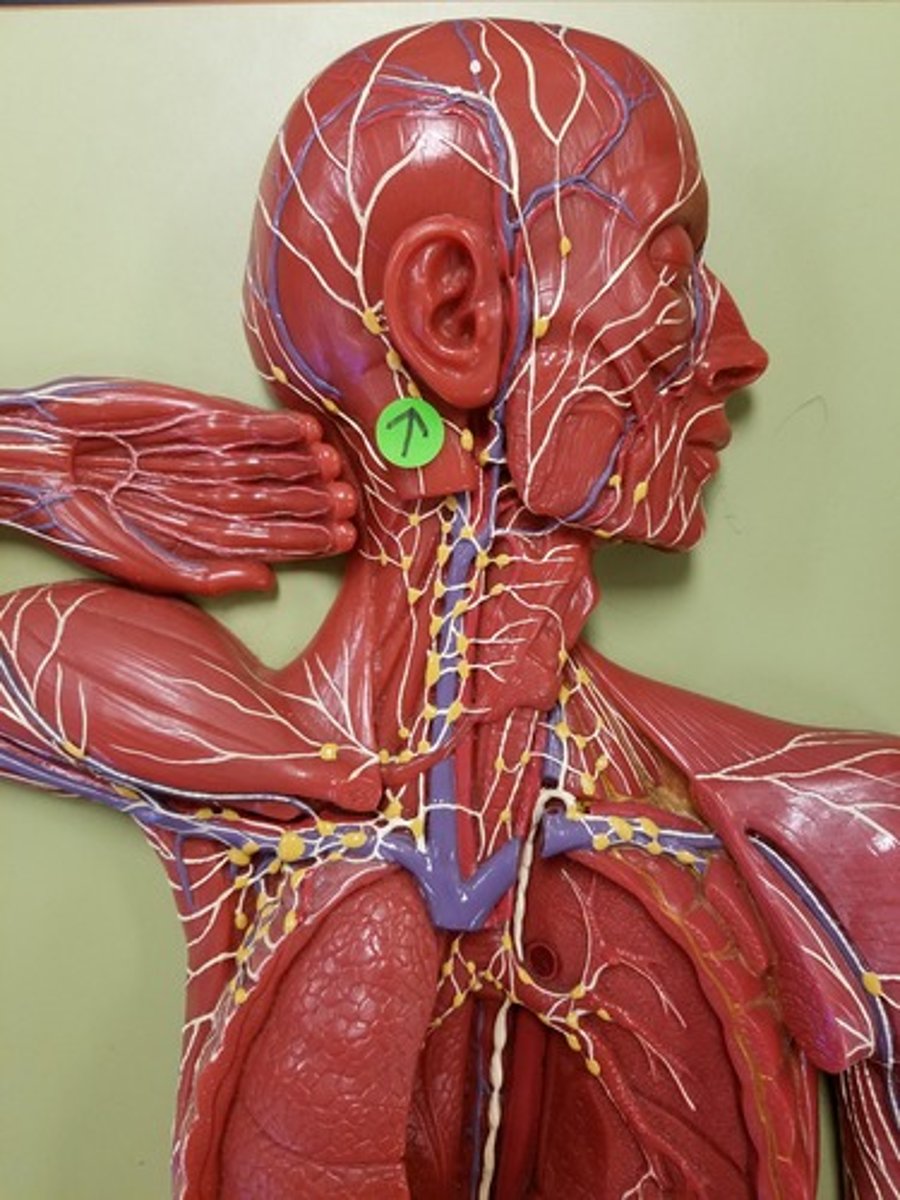
Deep cervical lymph nodes
Location: Deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle along the internal jugular vein
Description: Receives lymph from the posterior head, neck, and mouth region
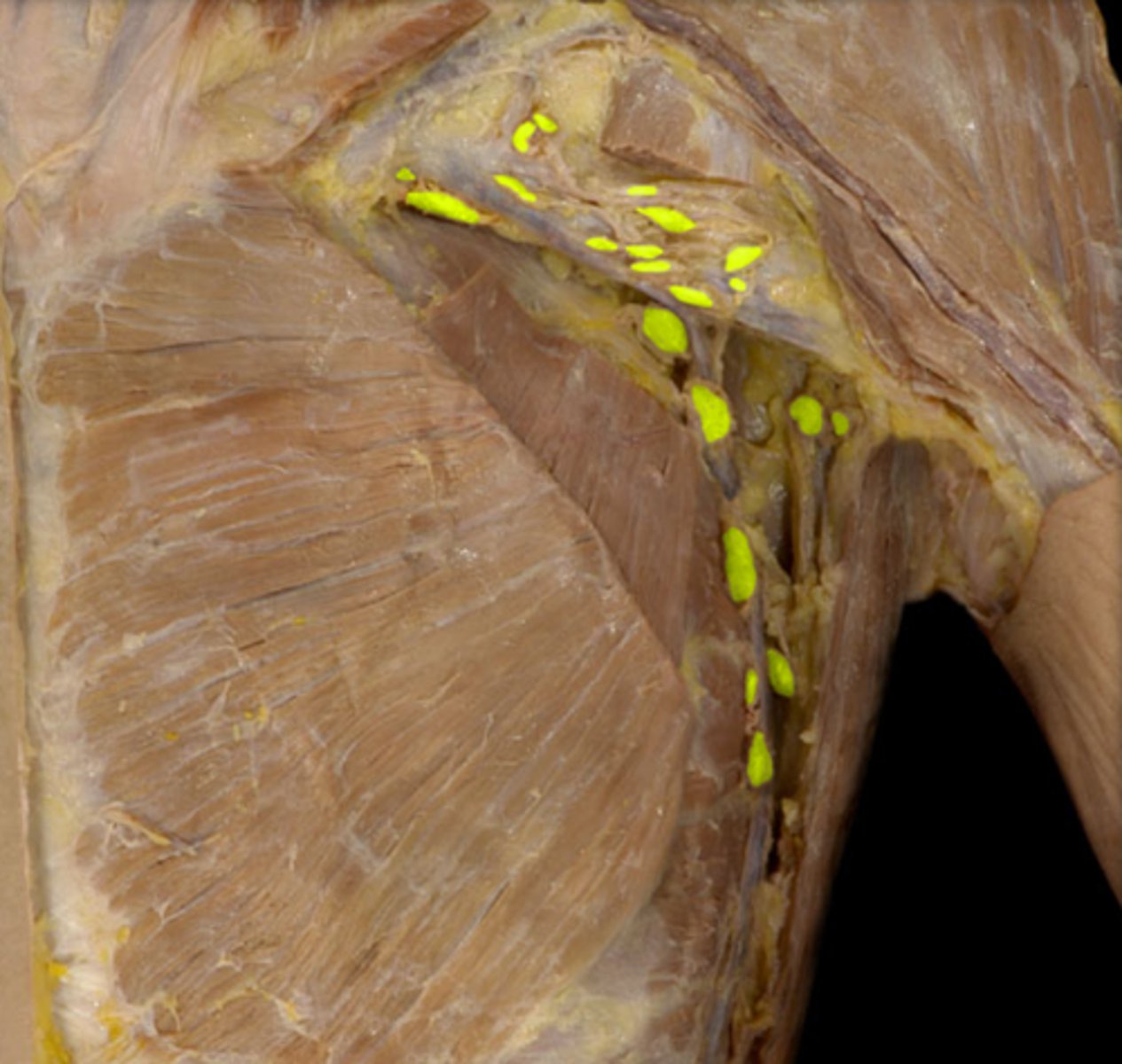
Axillary lymph nodes
Location: Large tissues in the axilla (armpit)
Description: Receives lymph from the upper limbs
Pectoral lymph nodes
Location: Along the pectoralis minor muscle
Description: Receives lymph from the skin and muscles of the anterior thorax
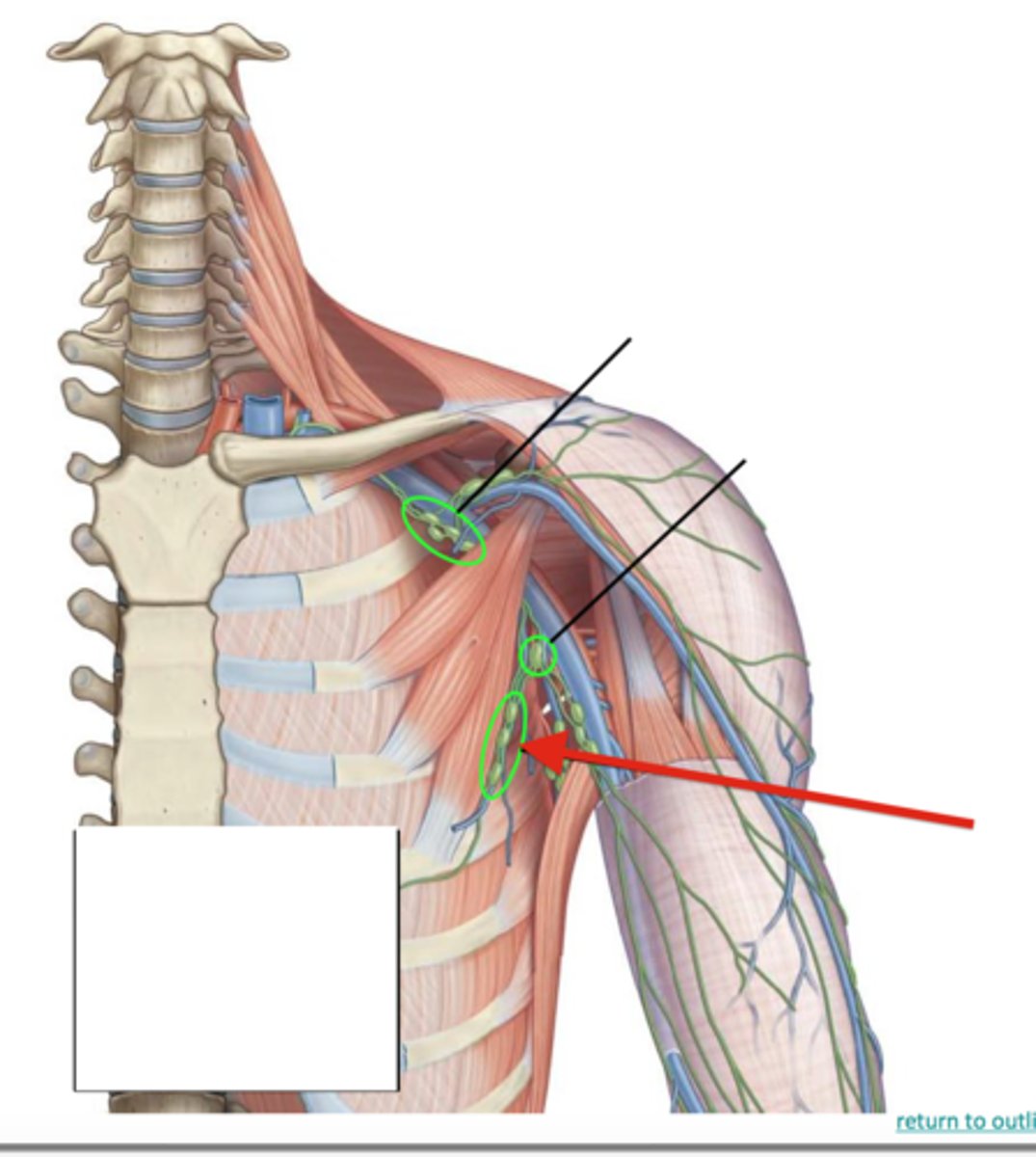
Common iliac lymph nodes
Location: Along the common iliac blood vessels
Description: Receives lymph from the pelvic viscera
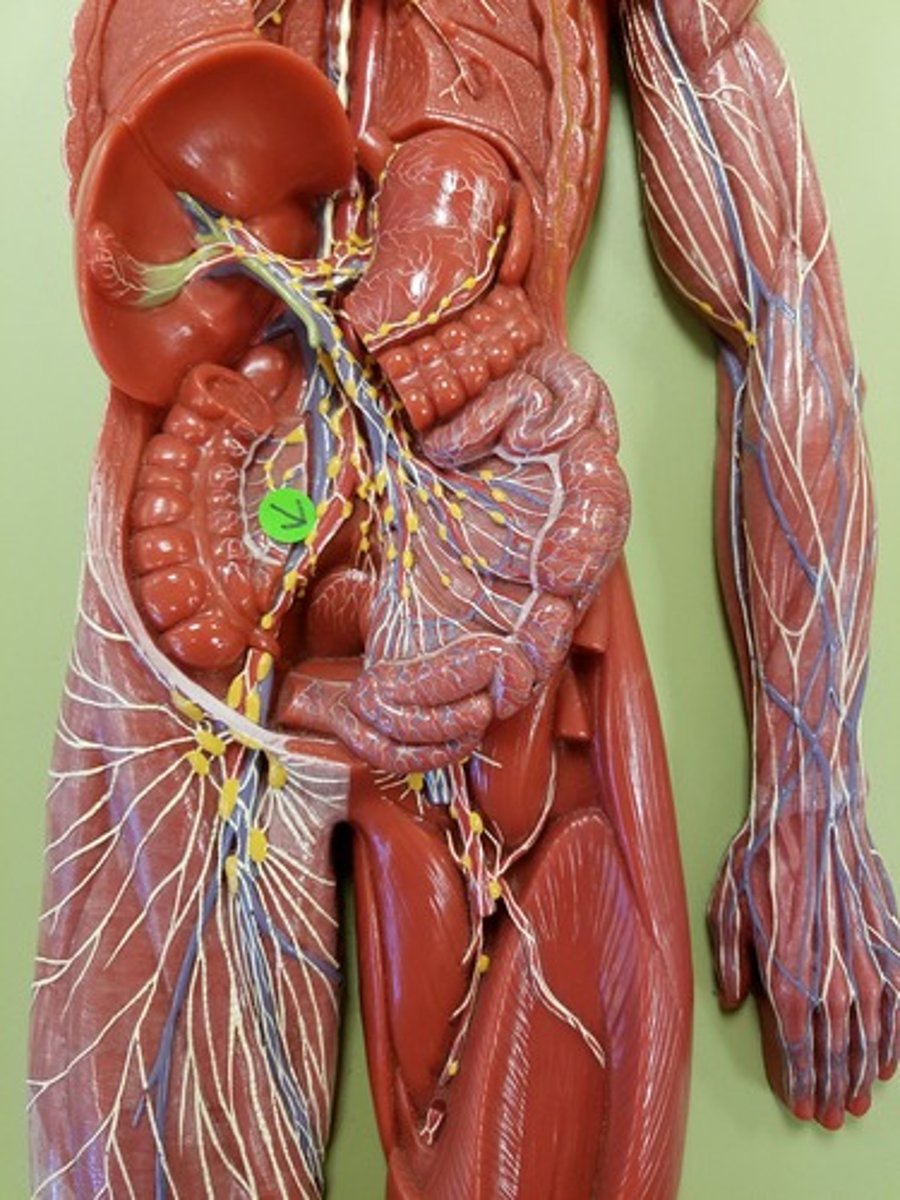
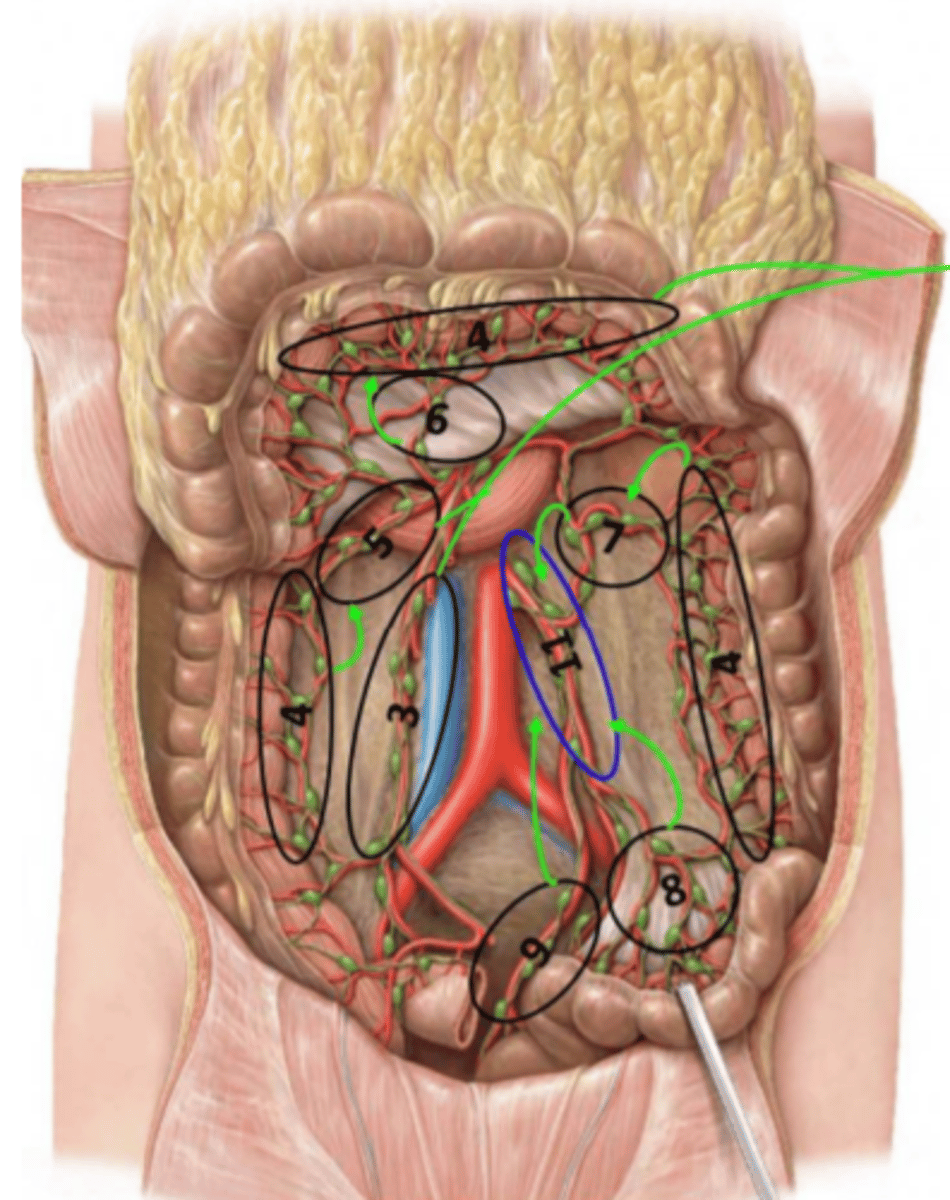
Mesenteric lymph nodes
Location: Along the large and small intestines within the mesentery proper and their blood vessels
Description: Receives lymph from the large and small intestines
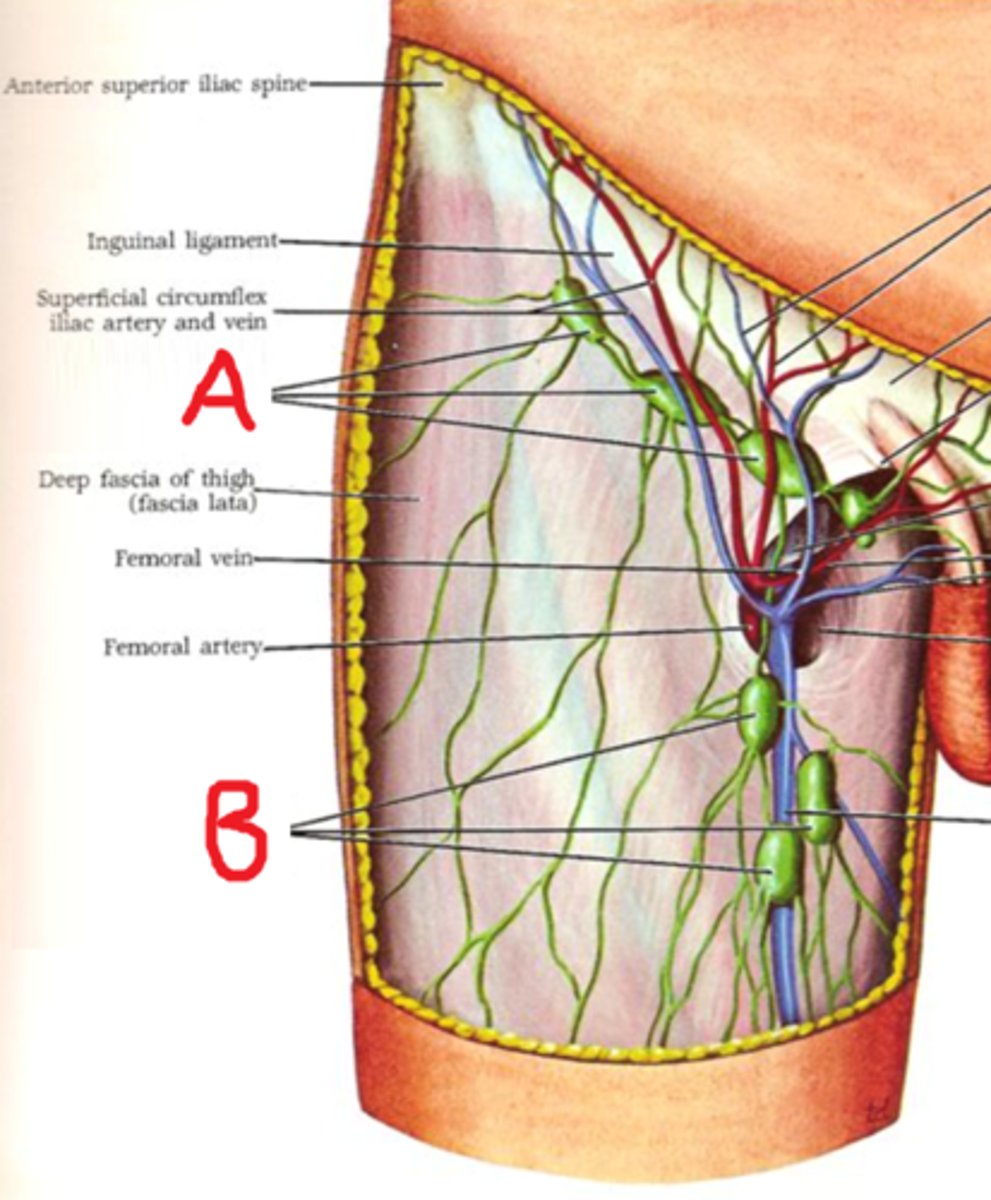
Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
Location: Superficial and lateral to the femoral vein
Description: Receives lymph from the abdominal wall and gluteal region
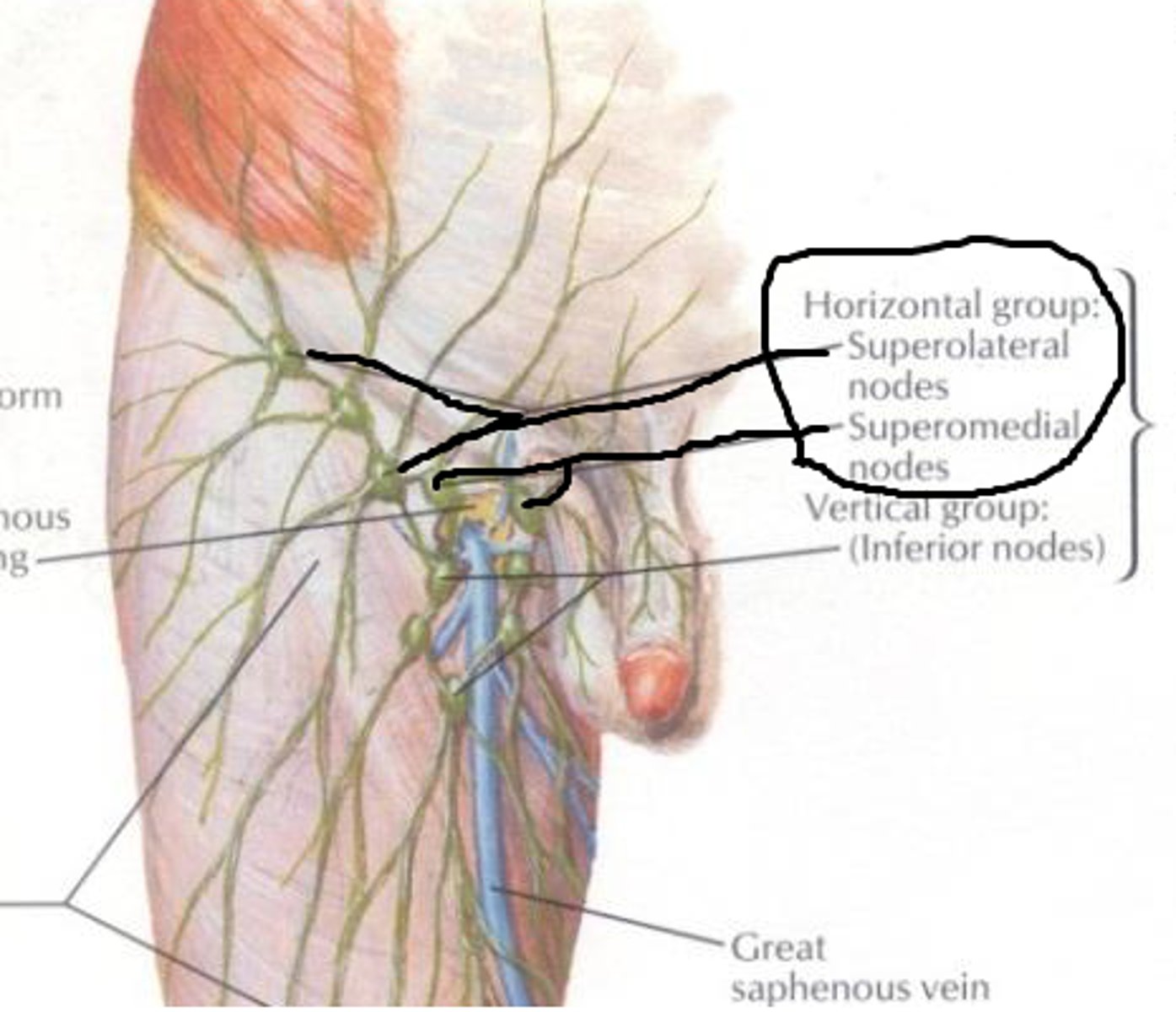
Deep inguinal lymph nodes
Location: Deep and medial to the femoral vein
Description: Receives lymph grom the deep lower limb and reproductive organs
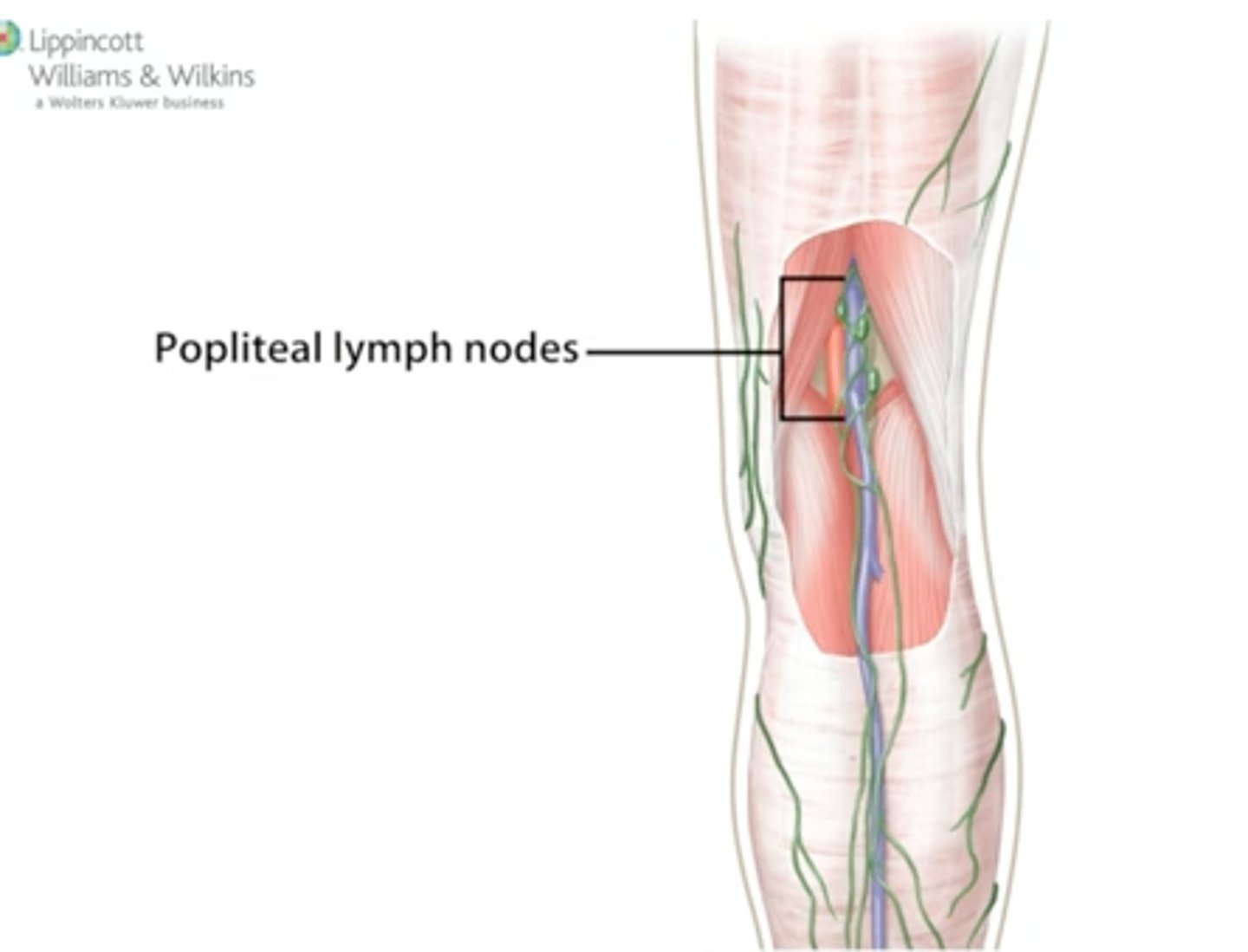
Popliteal lymph nodes
Location: Popliteal fossa in the posterior knee along popliteal vein.
Description: Receives lymph from the knee, leg, and foot regions
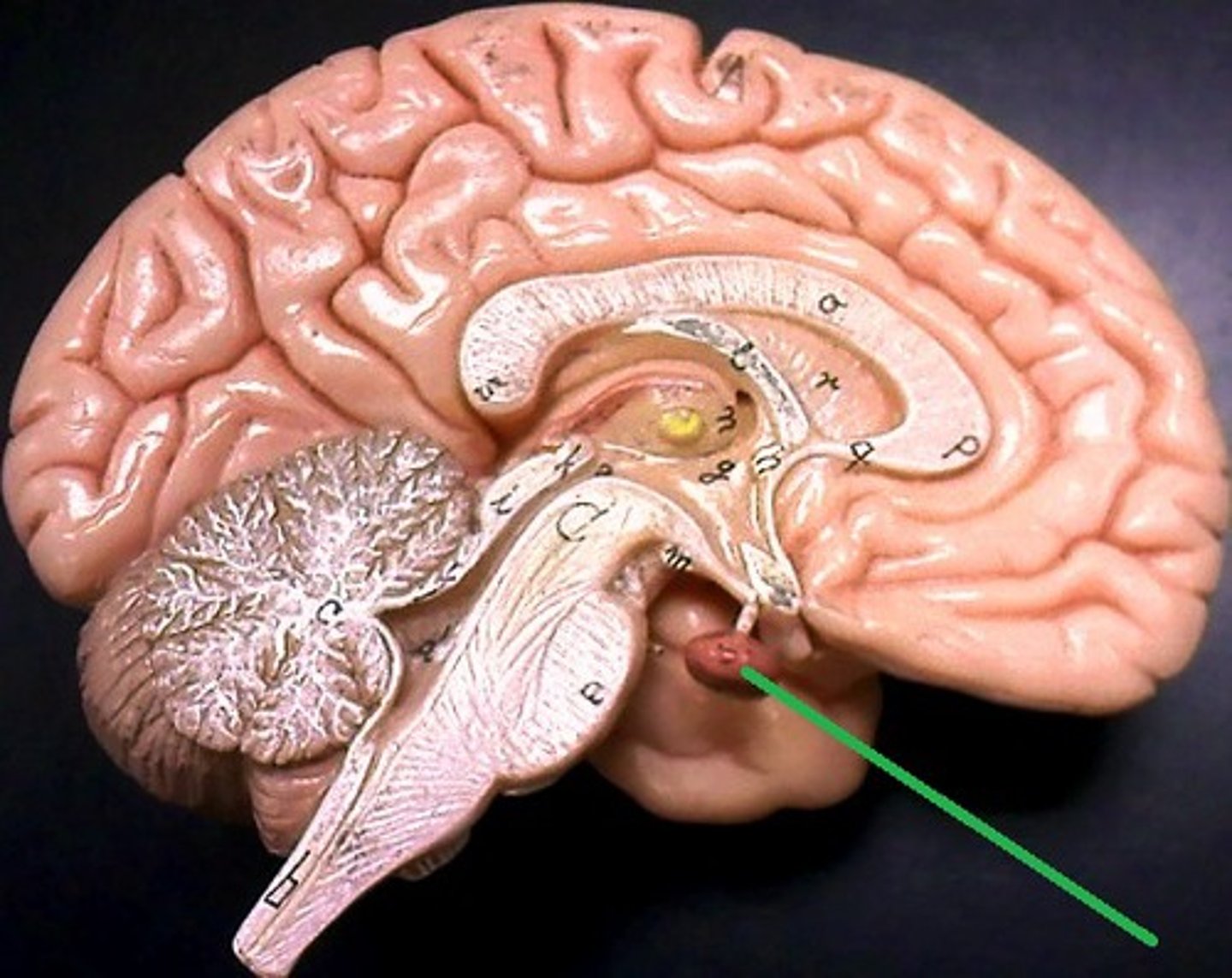
Pituitary gland (hypophysis)
Description: Small projection from the inferior portion of the brain
Location: Sits in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bonem inferior to thalamus of the brain
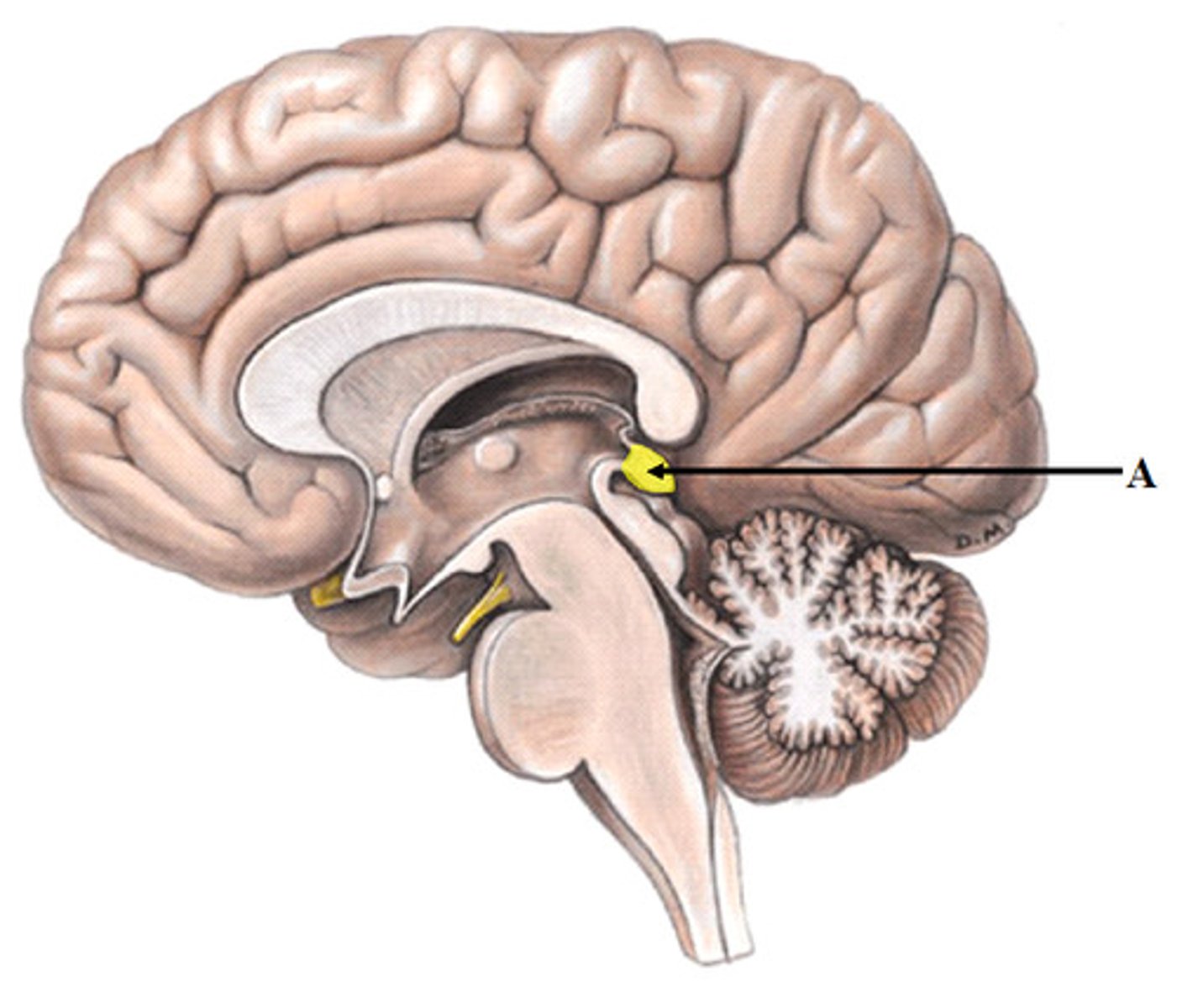
Pineal gland
Description: Small, pine cone shaped tissue
Location: Posterior and inferior aspect of the corpus callosum of the brain
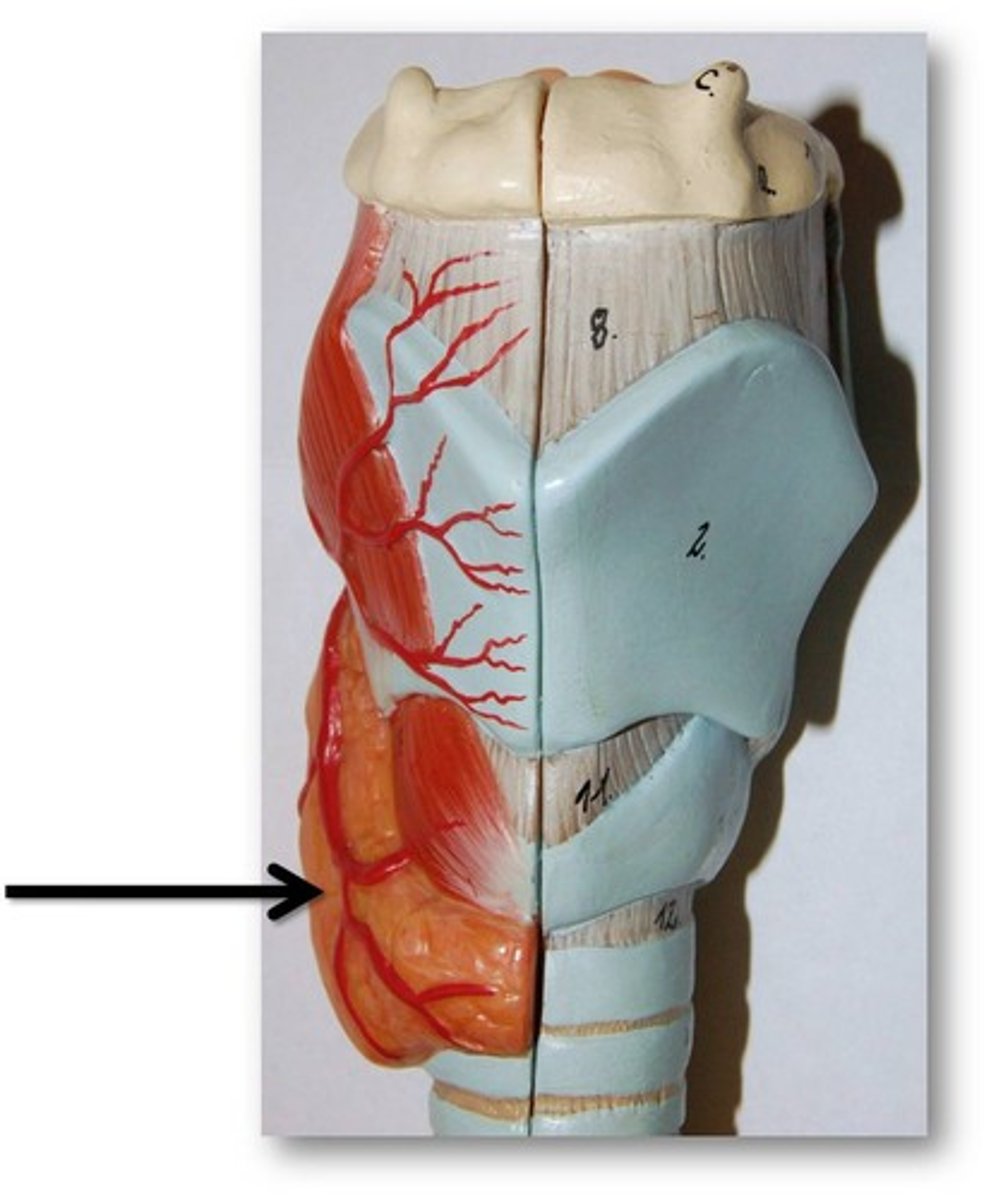
Thyroid gland
Description: Butterfly-shaped (two lobes) tissue
Location: Immediately inferior the thyroid cartilage of the larynx and anterior to the trachea
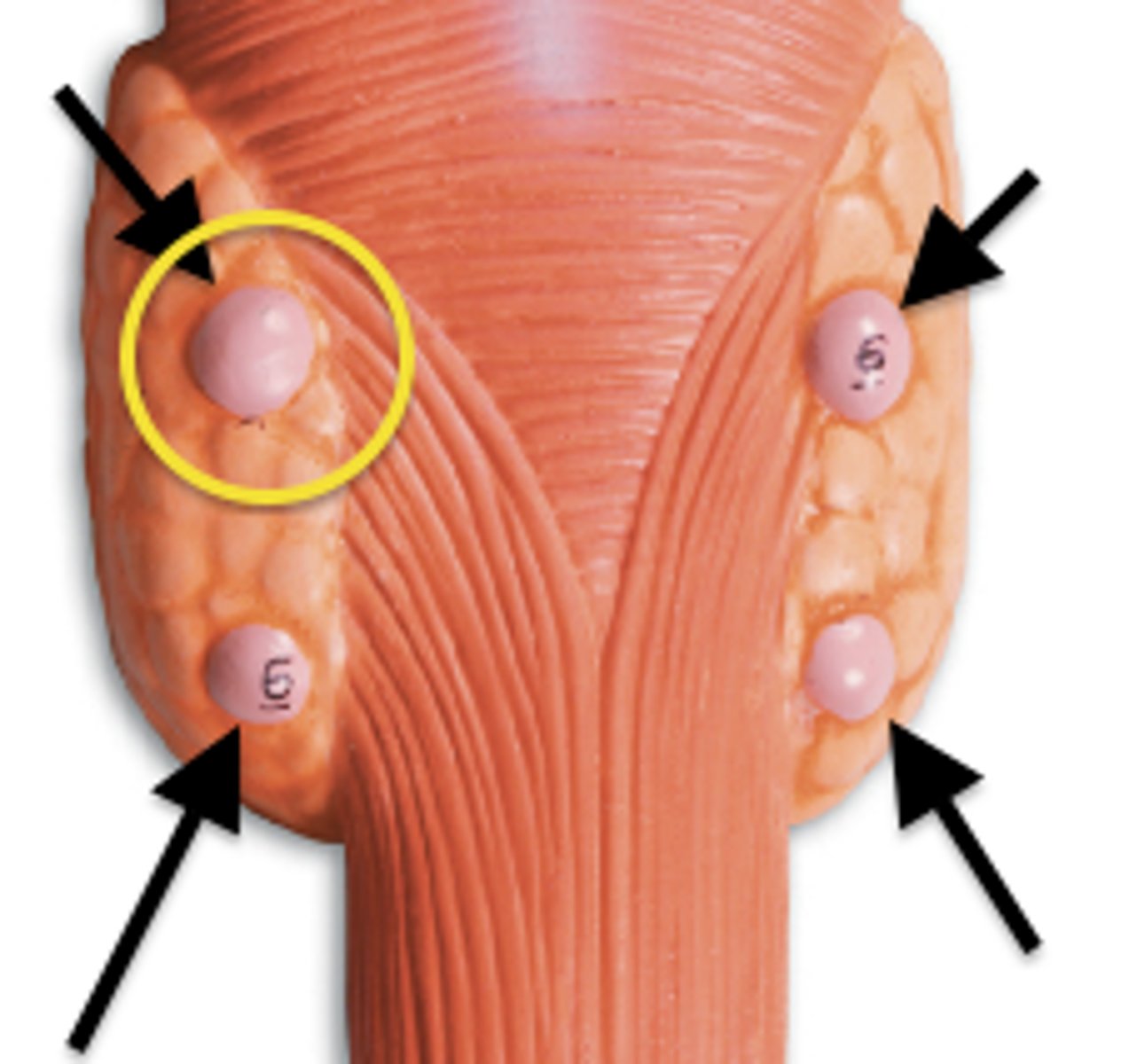
Parathyroid glands
Description: Four smallest endocrine tissues
Location: On the posterior side of the thyroid gland
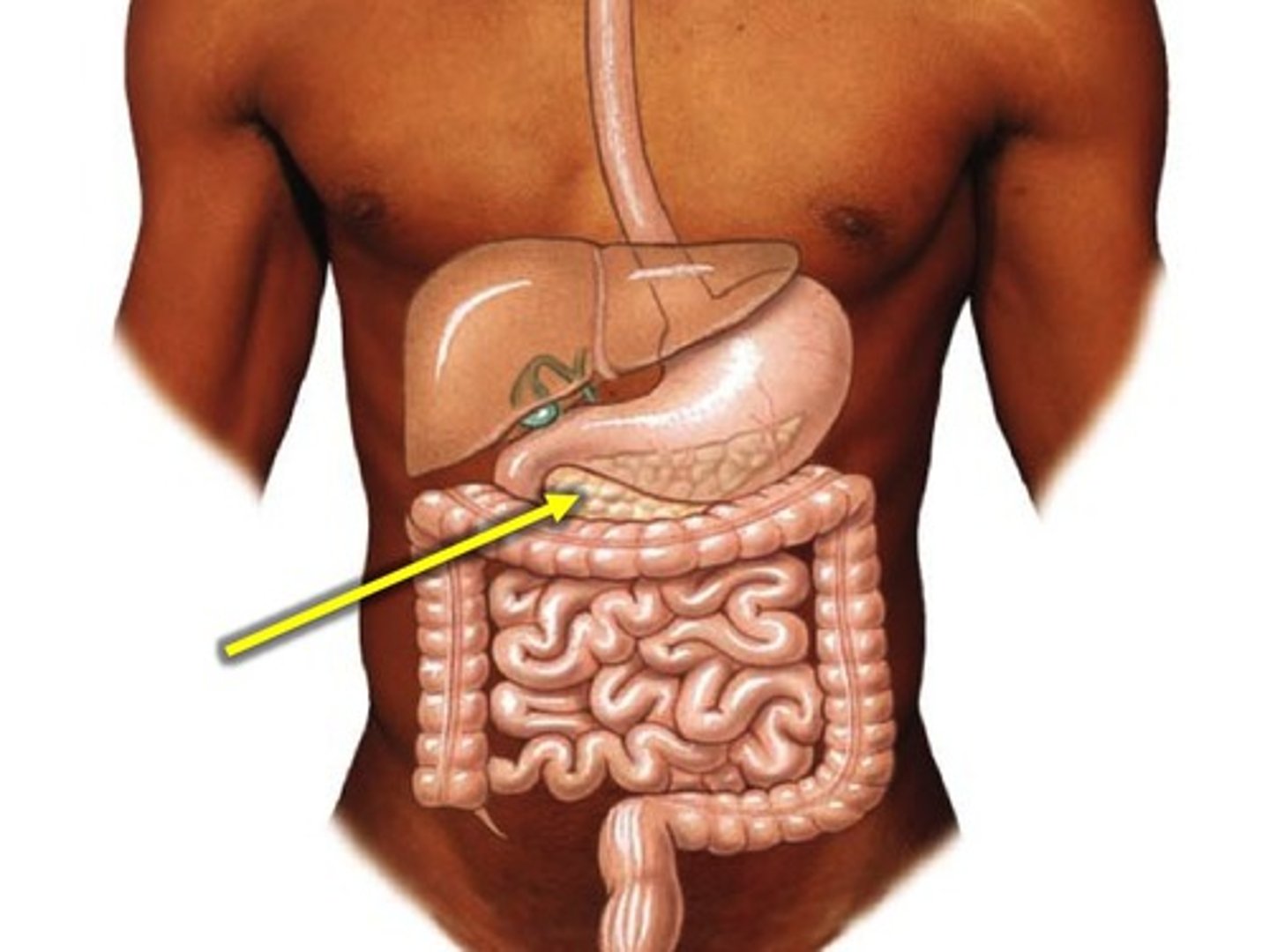
Pancreas
Description: Elongated, lumpy tissue about 5-6 inches long
Location: Head of the pancreas lies in the C loop of the duodenum. Lies inferior and posterior to the stomach. Tail of the pancreas touches the spleen
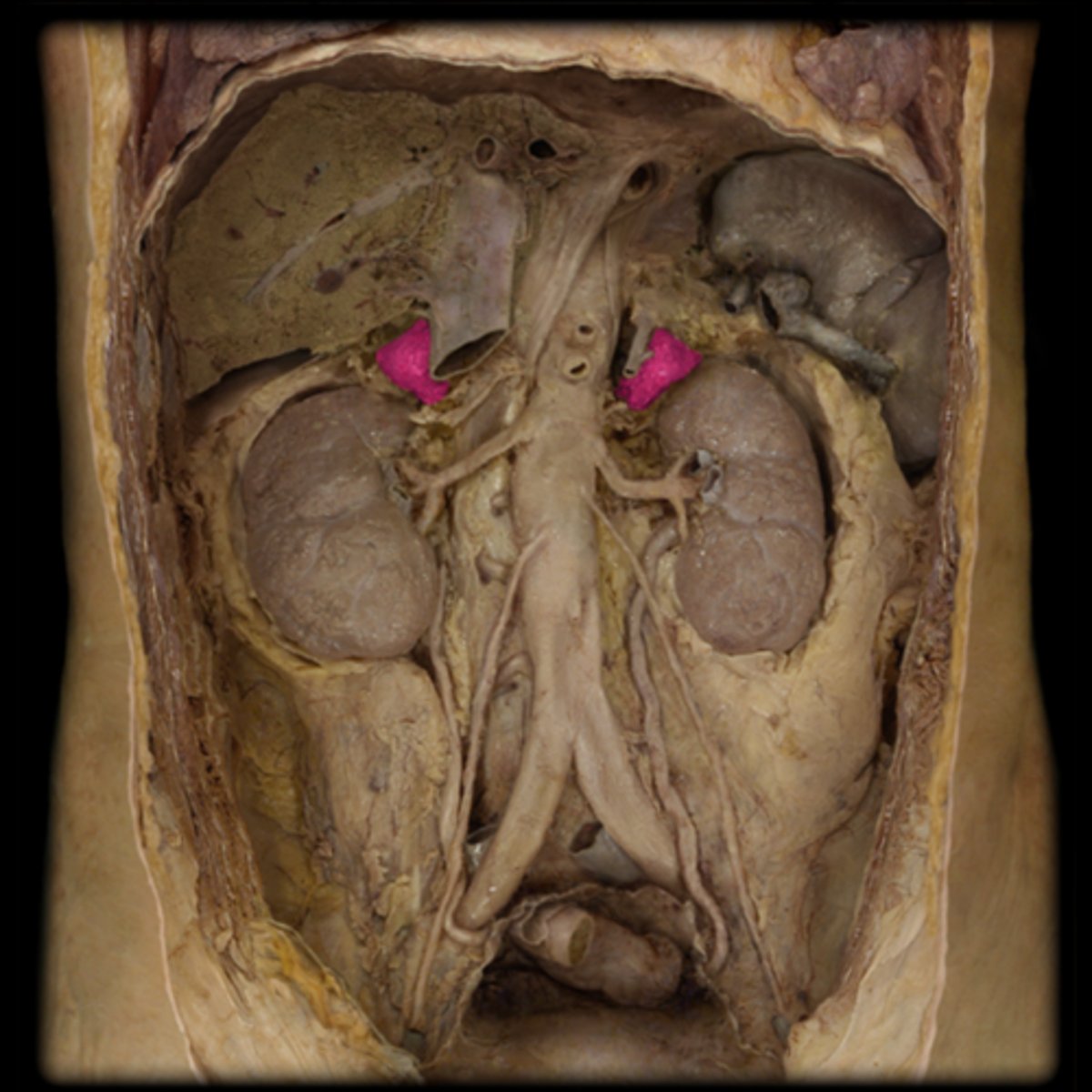
Adrenal (suprarenal) glands
Description: Small, pyramidal-shaped tissues with a bumpy texture
Location: Located on the superior aspect of kidneys
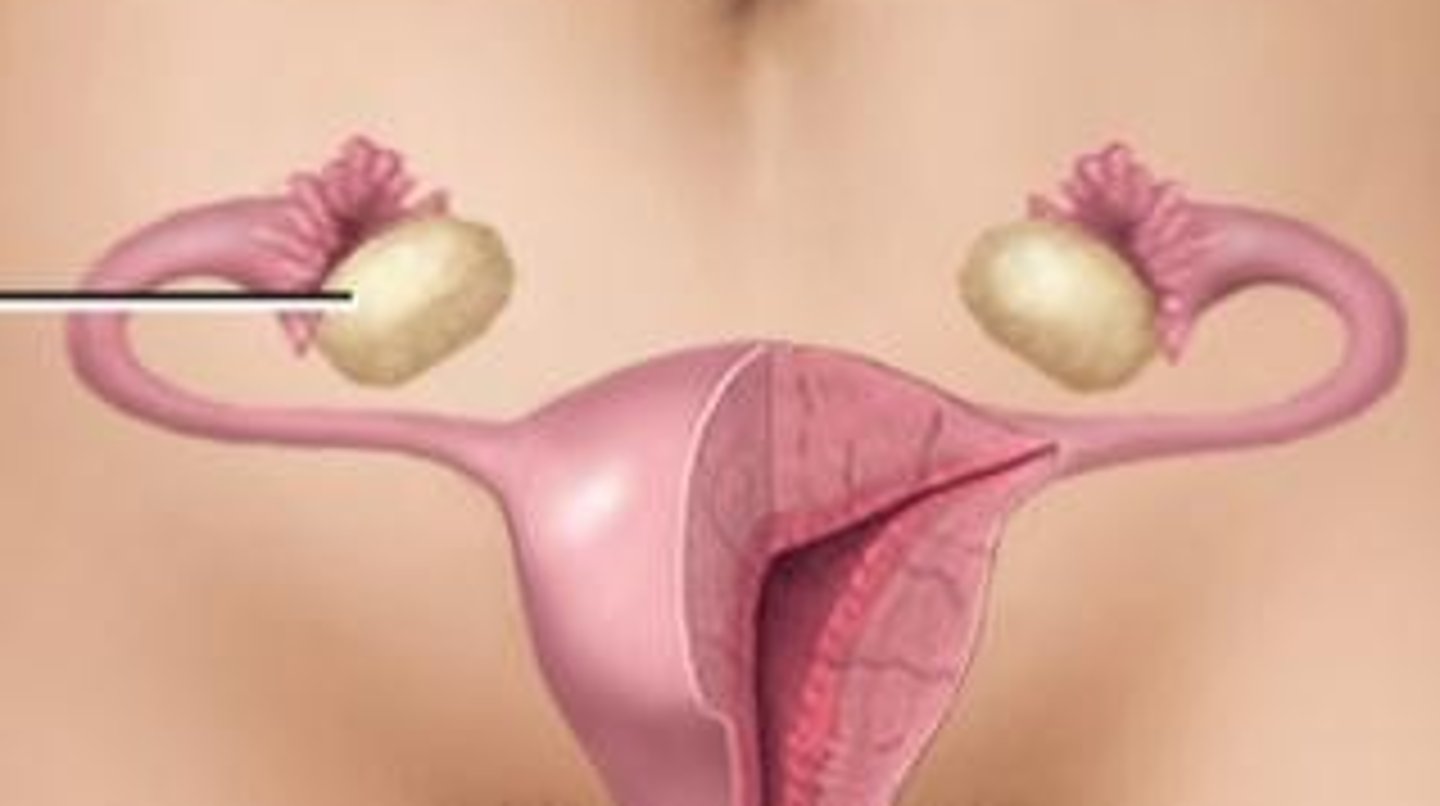
Ovaries
Description: Pair of oval-shaped bodies in females
Location: Within the pelvic cavity
Testes
Description: Pair of oval gonads in males
Location: Within the scrotum