Physiology Final Exam Cumulative
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
The following is a list of several levels of organization that make up the human body.
1) Tissue
2) Cell
3) Organ
4) Molecule
5) Organism
6) Organ system
The correct order from the smallest to largest is...
4, 2, 1, 3, 6, 5
Homeostasis is the ability of the body to...
quickly restore changed conditions to normal
If you see a molecule that has a name ending in "-ose" it is most likely...
carbohydrate
In lipids, "unsaturated" refers to
the presence of double bonds between adjacent carbon atoms in the fatty acid tail
A nucleotide containing the base cytosine would base pair with which of the following?
guanine
An energy-transferring compound in a cell is a nucleotide known as
adenosine triphosphate
Which of the following is NOT a function of membrane proteins?
anchor or stabilize the cell membrane
create junctions between cells
respond to extracellular molecules
produce energy
produce energy
When a chemical reaction is in equilibrium, then...
there is no net change in the amount of substrates or products
The addition of a phosphate group to a substrate is called ______. The enzyme that catalyzes this reaction is referred to as a ______.
phosphorylation, kinase

What reaction is this?
endergonic
Which body fluid compartment contains high levels of K+?
intracellular fluid
The resting membrane potential in most cells is about ...
-70mV
In a sodium potassium pump (Na+/K+), how many ions are typically exchanged?
3 Na+ released, and 2 K+ brought in to cell
Endocytosis is a form of _______ transport.
active
What is the longest form of chemical signaling?
endocrine
Neurotransmitters and neurohormones both...
are released by neurons
usually bind to receptors inside the cytoplasm or nucleus
Lipophilic hormones
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) activates...
protein kinase A
most rapid, often ion flow
channel receptor
most signal transduction
GPCR
described as catalytic
enzyme receptor
most interaction with the ECM
Integrin receptor
what are prostaglandins associated with?
pain response
The majority of hormones in the body are…
peptide hormones
The posterior pituitary gland secretes…
Vasopressin (ADH)
The term for two hormones that have greater thanadditive effects is…
synergistic
The binding of lipophilic messengers such as steroid hormones to their receptors triggers...
gene transcription
True or False: The example discussed in class of uterine contractions causing the brain to secrete oxytocin, and oxytocin causing uterine contraction is a negative feedback loop.
False. This is a positive feedback loop
the nervous system is broken down in the CNS and the PNS. What is true of the somatic nervous system in the PNS?
associated with voluntary movements
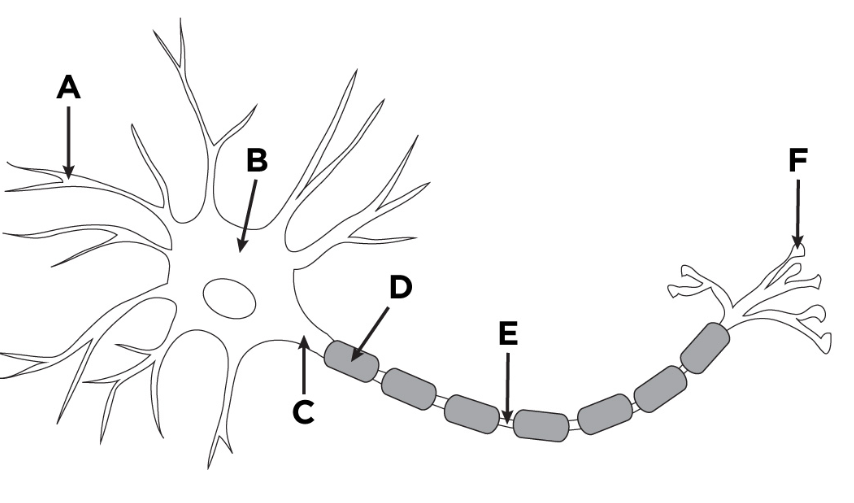
What part of this diagram indicates to the dendrites of a neuron?
A
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding receptor-specific channels in the synapse?
They are often slower
They can bind general types of ions (more than one)
They are often called ionotropic
They do not include GPCRs
they are often slower
neurons that bind this neurotransmitter are called cholinergic
Acetylcholine
an example receptor is called a NMDA receptor
amino acid
often associated with opiods and endorphins
peptide
very excitable, often associated with ATP
purine
often diffuses freely, like nitric oxide
gas
known to bind cannabinoid receptors
lipid
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are often…
depolarizing
Which ion is primarily responsible for neurotransmitter release?
Ca2+
True/False: All animals haves brains.
false
loosely connected to inner membrane but makes space between the two layers
arachnoid membrane
cushion against force to the head, less pressure on the brain, selective in what can transport into the brain, physical and chemical protection
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
The oldest and most primitive region of the brain is the....
brain stem
What section of the brain is responsible for the behavioral drives like hunger?
hypothalamus
what side of the brain deals with detail orientation
left hemisphere
What side of the brain deals with big picture
right hemisphere
what are the somatic senses?
touch, proprioception, temperature, pain, itch
what are the special senses?
vision, hearing, equilibrium, smell, taste
A mechanoreceptor would respond best to which of the following stimuli?
sound
When discussing lateral inhibition, or the ability of one sensory receptor to inhibit neighboring receptors, we are most likely talking about which property of a stimulus?
location
Initially smelling a strong perfume but then not noticing it over time
phasic receptor
The final destination for a sensory related signal is the ....
somatosensory cortex
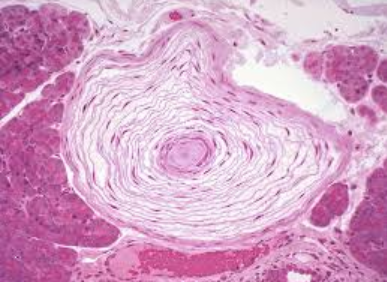
What type of touch receptor is this?
Pacinian corpuscle
Thermoreceptors on the skin generally only work on temperatures between…
20-45 degrees C
There are different types of fibers found in pain receptors. One common type of fiber is called Alpha Delta. What type of pain is this fiber associated with?
cold,fast pain
When someone suffers from a heart attack, they often describe feeling pain not only in their chest, but also down their left arm, in their neck, and even in their jaw. What type of pain would this be described as?
refferred pain
What pain fibers are utilized during the gate control theory?
Alpha beta
What two senses have been found to be closely related?
smell and taste
Olfactory (or smell) signal transduction is often a mechanism of....
a GPCR
Sound is measured by…
frequency and amplitude
appropriate order of skeletal muscle components from smallest to largest?
Muscle Fascicles
Myofibrils
Actin
Skeletal Muscle
Muscle Fibers
Actin<Myofibrils<Muscle Fibers<Muscle Fascicles<Skeletal Muscle
H zone contains only…
thick filaments
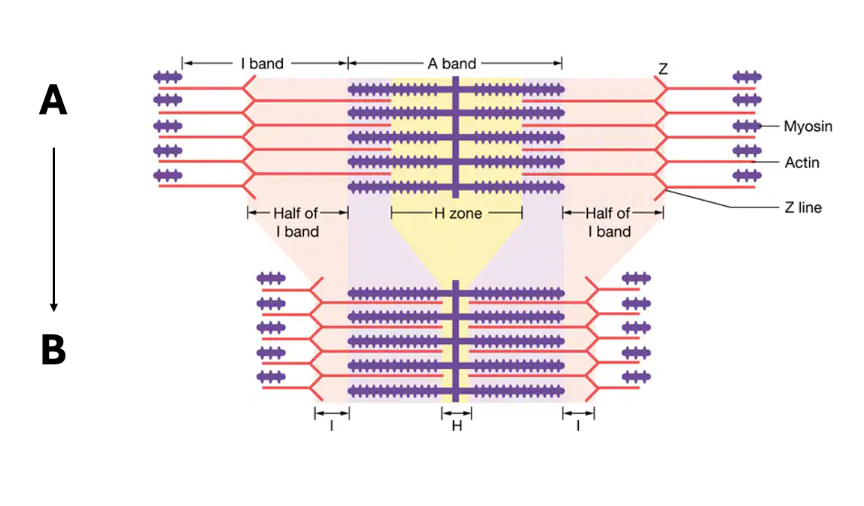
What is happening in the diagram below from A to B?
the muscle is contracting
In the steps of muscle contraction, what chemical/ion is responsible for the very beginning of this process?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
During muscle contraction, ________ is the calcium-binding complex that helps control position, while ________ helps align the actin and myosin.
troponin, tropomyosin
Based on the sliding filament theory, what happens to z regarding the contraction of the muscle?
Z disks move closer together
During the steps of contractions, specifically during the power stroke, which chemical/ion is responsible for the regulation of the movement?
calcium (Ca2+)
characteristics of slow-twitch fibers?
more myoglobin, slower contraction
Both smooth and skeletal muscle require…
calcium (Ca2+) regulation
What is a characteristic of smooth muscle and NOT skeletal muscle?
Smooth muscle uses less energy
Which of the following does NOT happen during the relaxation of smooth muscle?
Increase ATPase activity
Calmodulin is unbound from calcium
Dephosphorylation occurs
Decrease Ca2+
Increase ATPase activity
What type of muscle is ths\is?
skeletal
The muscle disorder, Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), is often caused by an _________ of the gene dystrophin.
underexpression
The knee-jerk reflex can be described as a...
Spinal reflex, Monosynaptic reflex, Innate reflex, Somatic reflex
what is the correct pairing of neuron to muscle fiber?
Alpha motor neurons activate extrafusal muscle fibers
There are 3 sensory receptors of the skeletal muscle reflexes that we discussed in lecture. whatis the best explanation for Golgi tendon organs (GTOs)?
Found at the junction of tendons and the muscle fibers, can be associated with tension and stretch
Alpha motor neurons and gamma motor neurons are often activated…
At the same time
When would a flexion reflex be triggered?
exposure to danger or pain
The lowest pressure in the cardiovascular system is found in the....
venae cavae
what would INCREASE resistance in blood vessels?
a smaller radius of the vessel
Which tissue layer of the heart contains the cardiomyocytes or muscle cells?
myocardium
What makes the action potential of a cardiac muscle cell different from the previous action potentials we have discussed?
During the plateau phase there is a brief pause in repolarization due to Ca2+
What happens once If channels reach their threshold?
Ca2+ flows in
The majority of calcium (Ca2+) used in the EC coupling of cardiac muscle comes from calcium entering the cell via
the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Electrical signals that coordinate contraction in the heart often originate in the SA node of the heart. Specifically, pacemaker cells found in the ____________ are the main regulators of cardiac contraction.
right atrium
When analyzing an ECG, what is often known to happen during the T wave?
repolarization of the ventricles
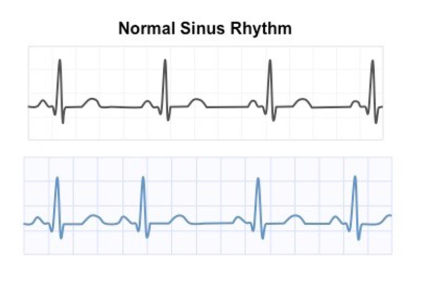
Compared to the normal rhythm shown first, what is most likely happening in the second ECG?
an irregular heartbeat
The atria and the ventricles contract and relax at ______ times.
different
At what stage of the cardiac cycle do we often get the end-systolic volume (ESV) measurement?
Ventricle ejection
what measurements takes heart rate into consideration when calculating?
Cardiac Output (CO)
Ventilation is also known as....
breathing
The upper respiratory system includes all of the following EXCEPT
the sinuses
the mouth
the larynx
the lungs
the lungs
The site of gas exchange in the lungs is found in the....
alveoli
What type of alveolar cells are more commonly found in the alveoli
Type 1
Boyle's Law states that gas volume is
inversely proportional to pressure
most accurate way to describe the pressure and volume in our lungs
As we breathe in, the chest volume increases and the alveolar pressure decreases
Pulmonary blood pressure is ______ in the lungs than in other part of our body.
lower
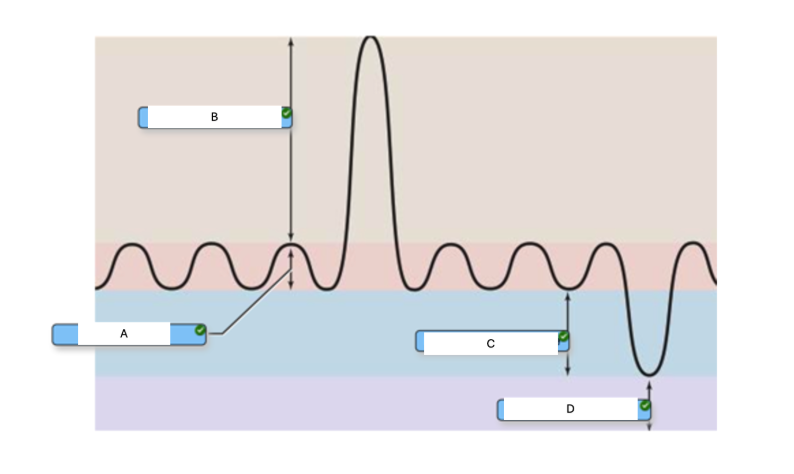
In the graph below of a respiratory cycle, which letter corresponds to the residual volume?
D
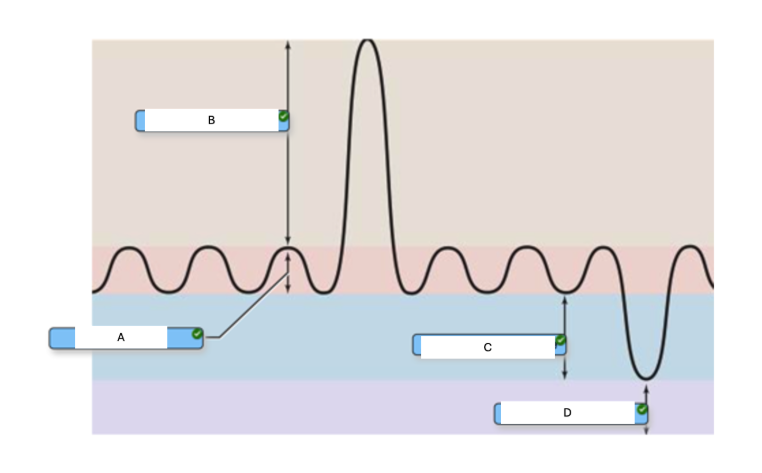
In the graph below of the respiratory cycle, what is the best definition of what is happening at letter A?
volume of air moved during a single "quiet" breathe
When measuring lung volumes and capacity, which value can be the largest?
IRV