Exam 1
1/223
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
224 Terms
catalase and peroxidase
-convert H2O2 to O2 and H2O
microorganisms
-oldest forms of life
-major fraction of Earth's biomass
microbial applications
-animal health, human health, ecosystem health, water and waste, agriculture, natural resources, food, biotechnology, industry, bioenergy
common structure of all cells
-cytoplasmic membrane: barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment
-cytoplasm: aqueous mixture of macromolecules, small organics, ions, and ribosomes inside the cell
-ribosomes: protein-synthesizing structures
-cell wall: present in some microbes: confers to structural strength
prokaryotes
-bacteria and archaea
-no organelles and nucleus
eukaryotes
-plants, animals, algae, protozoa, fungi
-contain organelles
-DNA in nucleus (membrane bound)
-mitochondria and chloroplasts
properties of all cells
-structure, metabolism, growth, evolution
properties of some cells
-differentiation, communication, motility, horizontal gene transfer
prokaryotes size
-0.2-600+ μm range
-
eukaryote size
- 5- 100 μm
surface area and volume
-the smaller you are then the relatively larger your surface area is
-larger surface area encourages the highest diffusion efficiency
-greater nutrient and waste product exchange per unit cell
-surface area: 4pi x r^2
-volume: (4/3) pi x r^3
-surface/volume = 3r
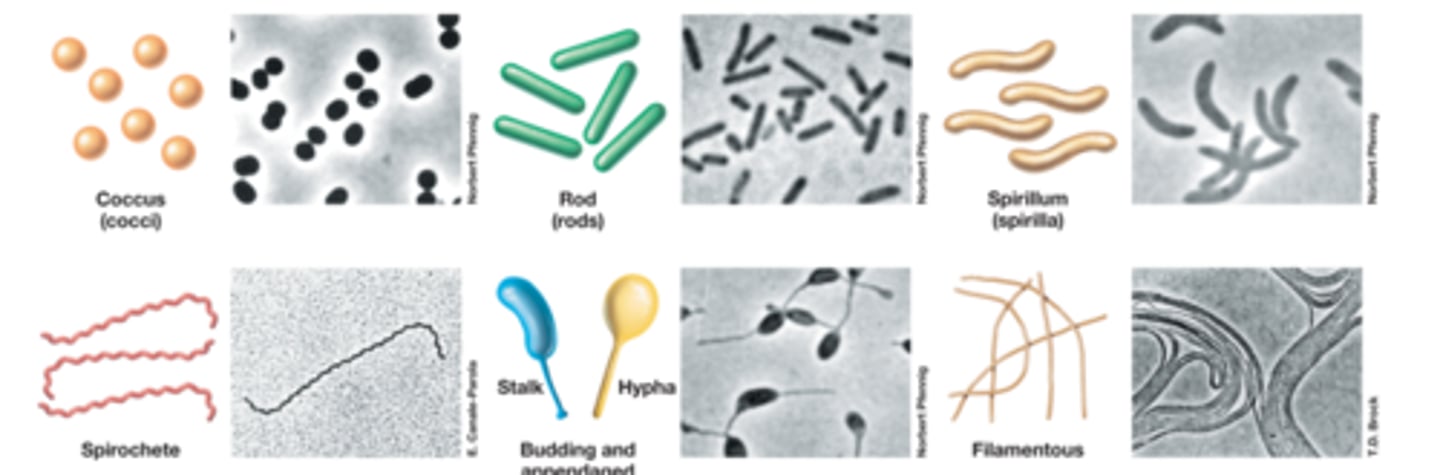
Cell morphologies
-coccus: spherical or ovoid
-rod/bacillus: cylindrical
-spirillum: flexible spiral
Bacteria
-prokaryotes
-undifferentiated single cells
-80+ phylogenetic lineages
Archaea
-prokaryotes
-associated with extreme environments (extremophiles)
-lack parasites or pathogens for plants/animals
Eukarya
-plants, animals, fungi
-first were unicellular
-vary dramatically
viruses
-obligate parasites that only replicate within host cells
-not cells
-small genomes
-do not carry out metabolism
percent global biomass
-70-80% of all P and N concentrated within microbial biomass
-80% C is in plants biomass
extremophiles
-cellsthat live in extreme environments.
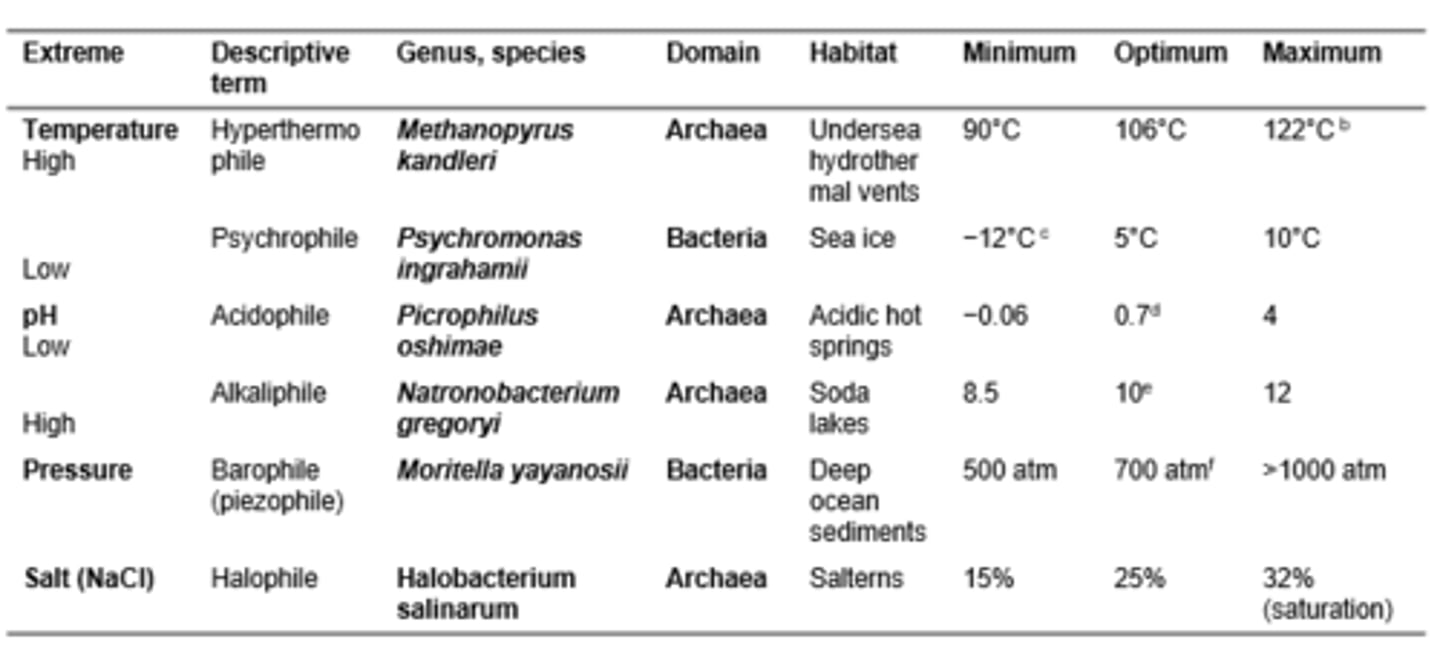
Death rates for leading causes of death in the United States
Industrial Microbiology
-wastewater treatment: microbes are used to clean wastewater
-bioremediation: microbes are used to clean contaminated environments
-biofilms: microbes grow on surfaces and can foul pipes and pipelines
-biotechnology: microbes can be genetically modified to produce high-value products such as pharmaceuticals and enzymes
-fermentation: microbes are used at industrial scale to make chemicals, solvents, enzymes, and pharmaceuticals
-biofuels: microbes are used to convert biomass into ethanol and wastes into natural gas
Robert Hooke
-first to observe microbes
-illustrated the fruiting structures of molds
Antoni can Leeuwenhoek
-first to see bacteria
-used a light microscope
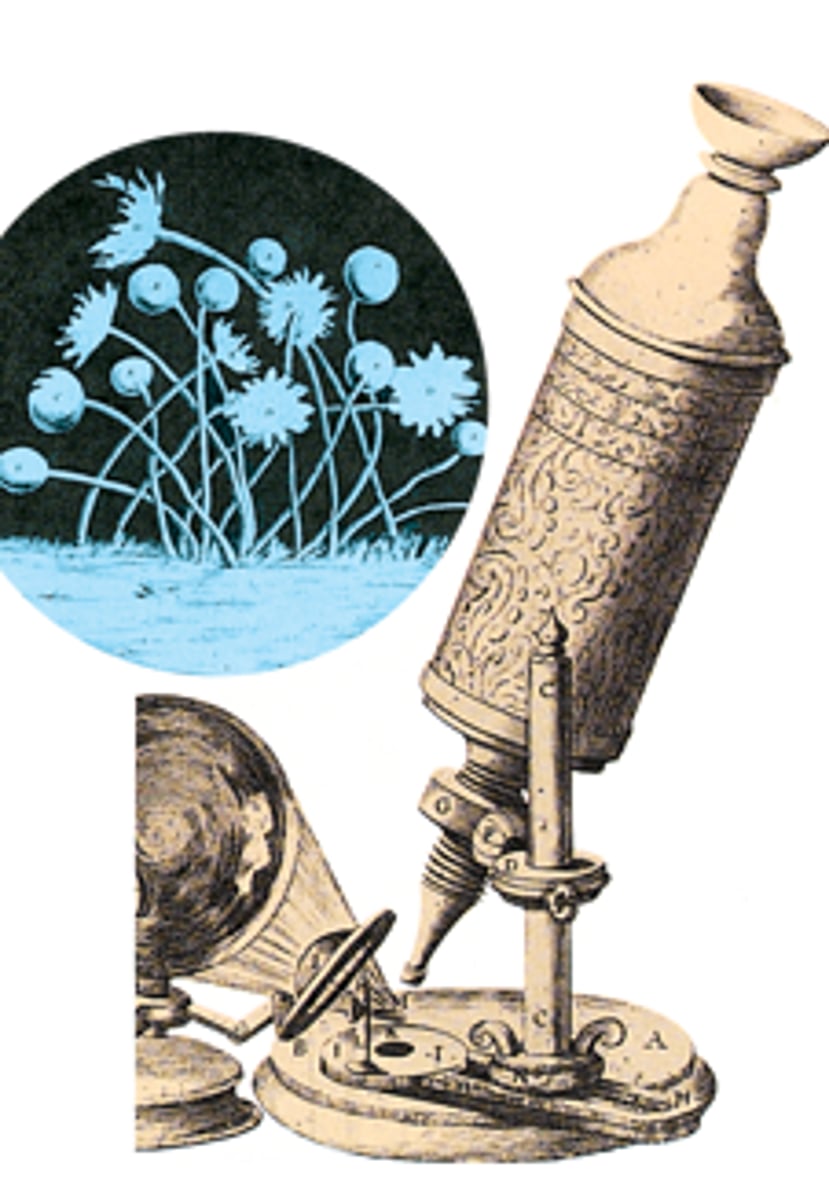

Bright field scope
-Specimens are visualized because of differences in contrast (density) between specimen and surroundings
-pigments add contrast
basic dyes
-positively charged , bind strongly to negatively charged cell components
differential stains
-render different kinds of cells different colors
Procedure for gram staining
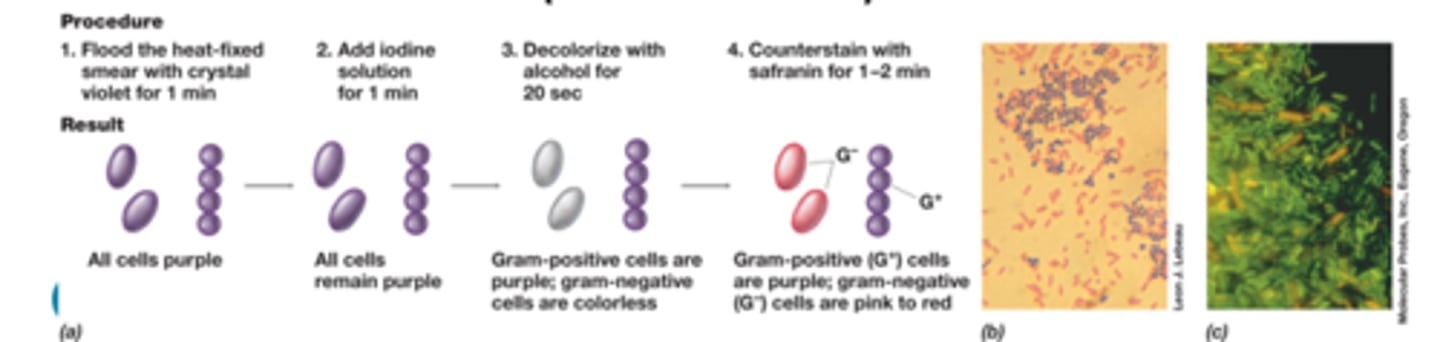
gram positive
-appear purple-violet
gram negative
-appear pink
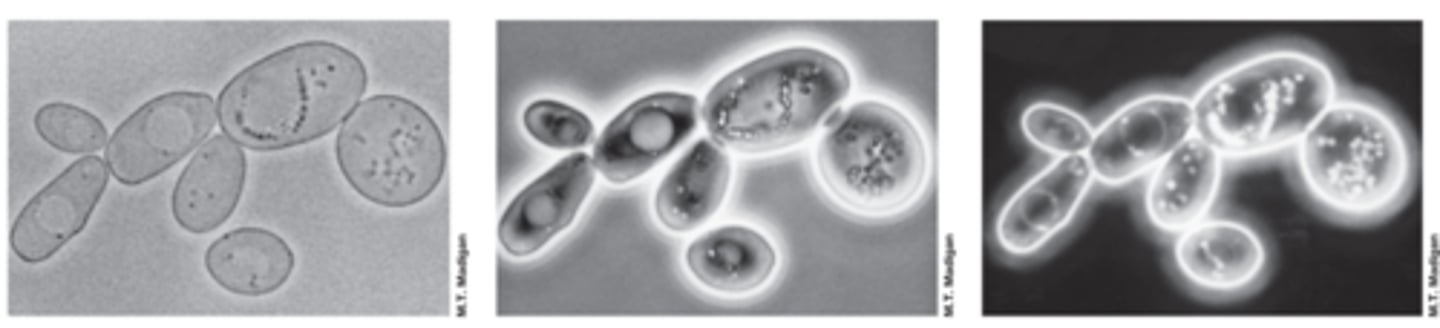
phase contrast microscopy
-improves image contrast of unstained live cells
-phase ring amplifies differences in the refractive index of cell and surroundings
dark field microscopy
-light reaches specimen from the sides
-only light scattered by specimen reaches the lens
-image appears light on a dark background
-better resolution than light microscopy and better for motility
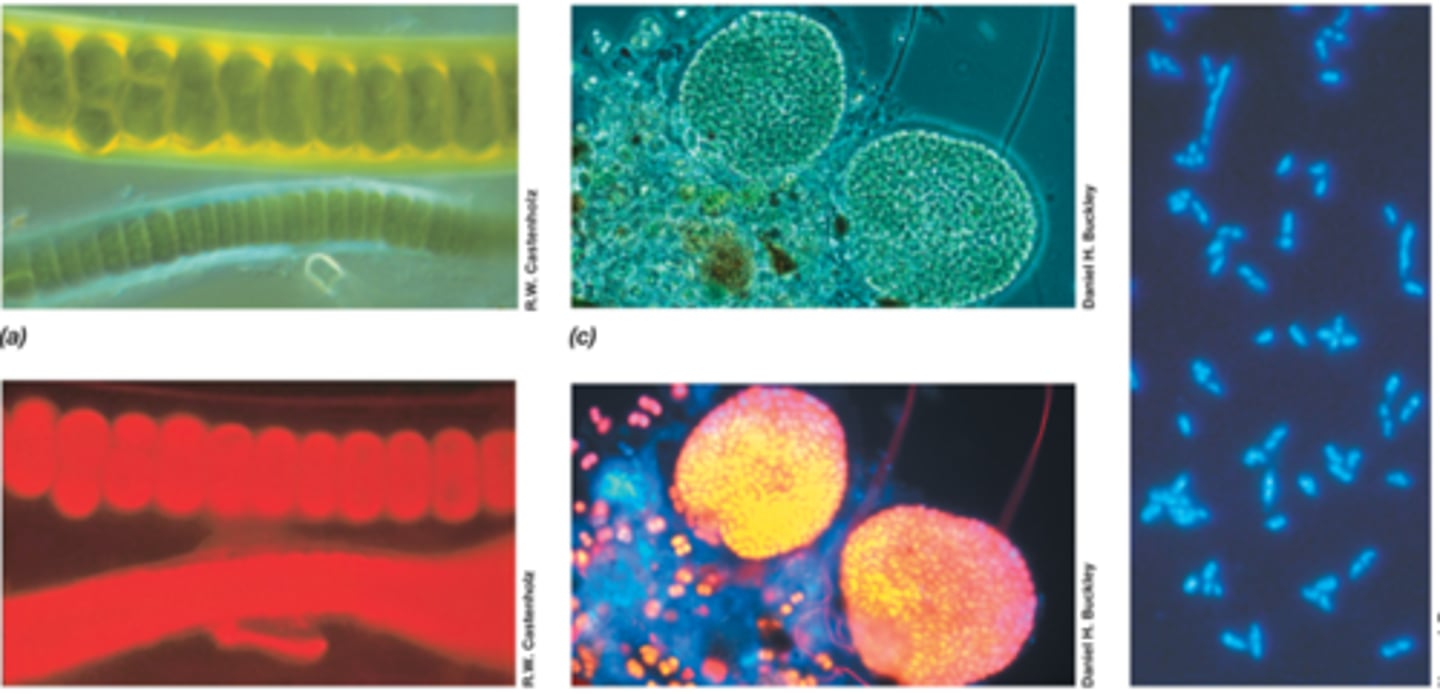
fluorescence microscopy
-used to visualize specimens that fluoresce
-cells appear to glow on black background
-dye: DAPI
-used in clinical diagnostic microbiology and microbial ecology
transmission electron microscopy
-much greater resolving power than light microscopy
-visualization of structures at the molecular level
-needs to be stained with high atomic weight substances that scatter e-
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
-specimen coated with a thin film of heavy metal
-electron beam scans the object
-scattered electrons collected to project the image
-very large specimens
-only surface
confocal laser scanning microscope
-uses computerized fluorescent microscope coupled with a laser source to generate a 3D image
-can focus the laser of single layers
-different layers compiled for 3D image
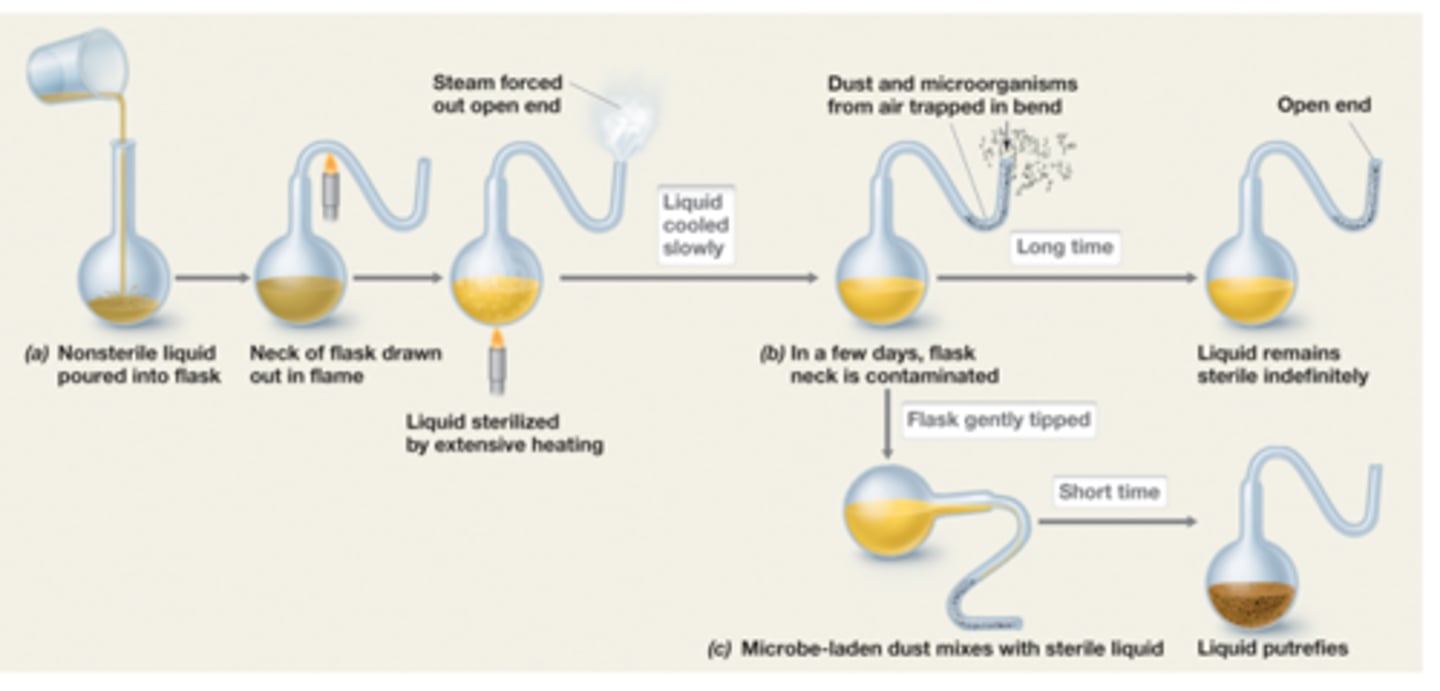
Pasteur
-disproved spontaneous generation
-led to sterilization methods and food preservation
-vaccines for anthrax, fowl cholera, and rabies
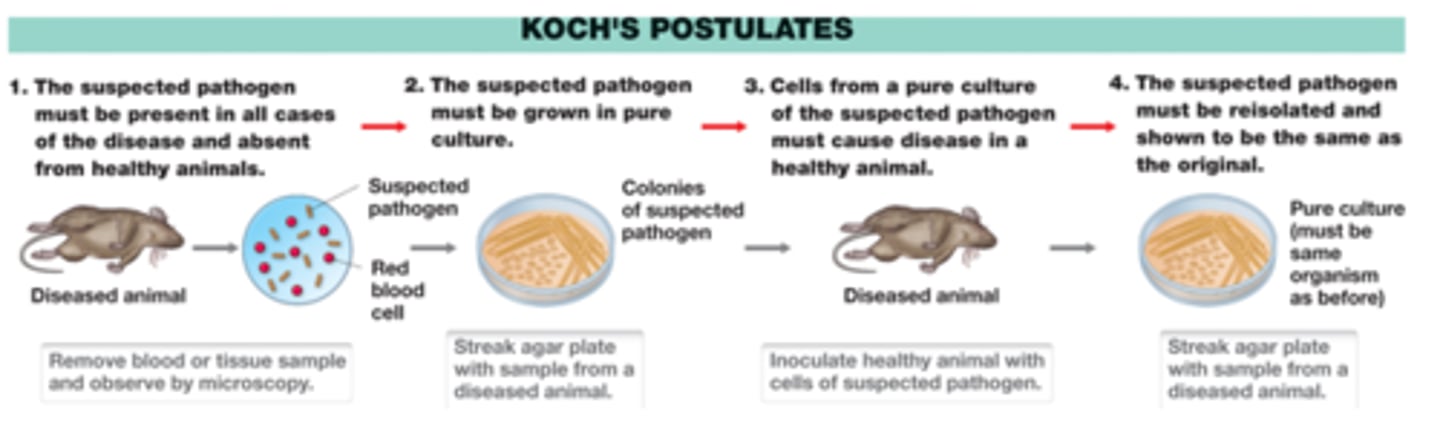
Koch
-demonstrated a link between microbes and infectious diseases
-developed solid media for obtaining pure cultures of microbes
microbial diversity
-focuses on nonmedical aspects of microbiology in soil and water
Sergei Winogradsky
-demonstrated that specific bacteria are linked to specific biogeochemical transformations
-Beggiatoa (sulfur oxidizers)
-concept of chemolithotrophy: oxidation of only inorganic compounds to yield energy
-first to demonstrate nitrogen fixation (Clostridium pasteurianum) and nitrification
Martinus Beijerinck
-developed enrichment culture technique which selectively encourages growth of specific bacterium
-isolated Azotobacter (aerobic nitrogen fixing)
-first to observe a virus (tobacco mosaic virus)
Frederick Griffith
-Discovered transformation in pneumonia-causing bacteria
James Watson, Francis Crick, Rosalind Franklin
-discovered the structure of DNA
Emile Zuckerland and Linus Pauling
-scientists that discovered molecular sequences and evolutionary relationships
Carl Woese
-three domain based on r RNA (eukarya, bacteria, archaea)
-found evolutionary relationships between all living cells could be revealed with RNA analysis to create a tree of life
-16 S in prokaryotes or 18 S / 23 S RNA in eukaryotes
-not viruses
-discovered archaea when studying methanogens
E. Haeckel
-first to attempt to put all the living organisms on the same tree of life
-5 kingdoms
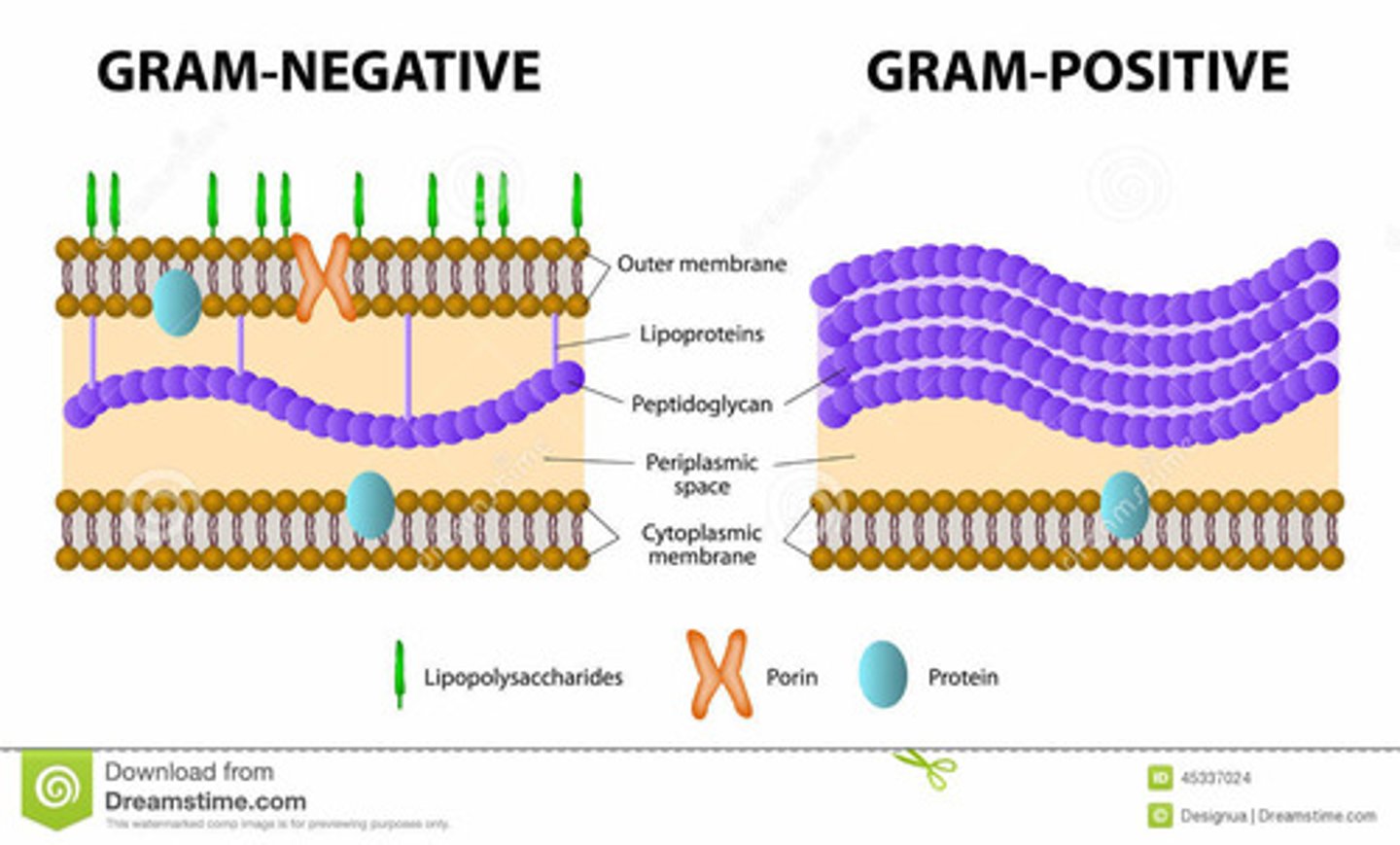
Gram Positive
-large layer of peptidoglycan
-have Teichoic acid and Lipoteichoic acid
-glycosidic bonds on the outside
-dark purple when stained
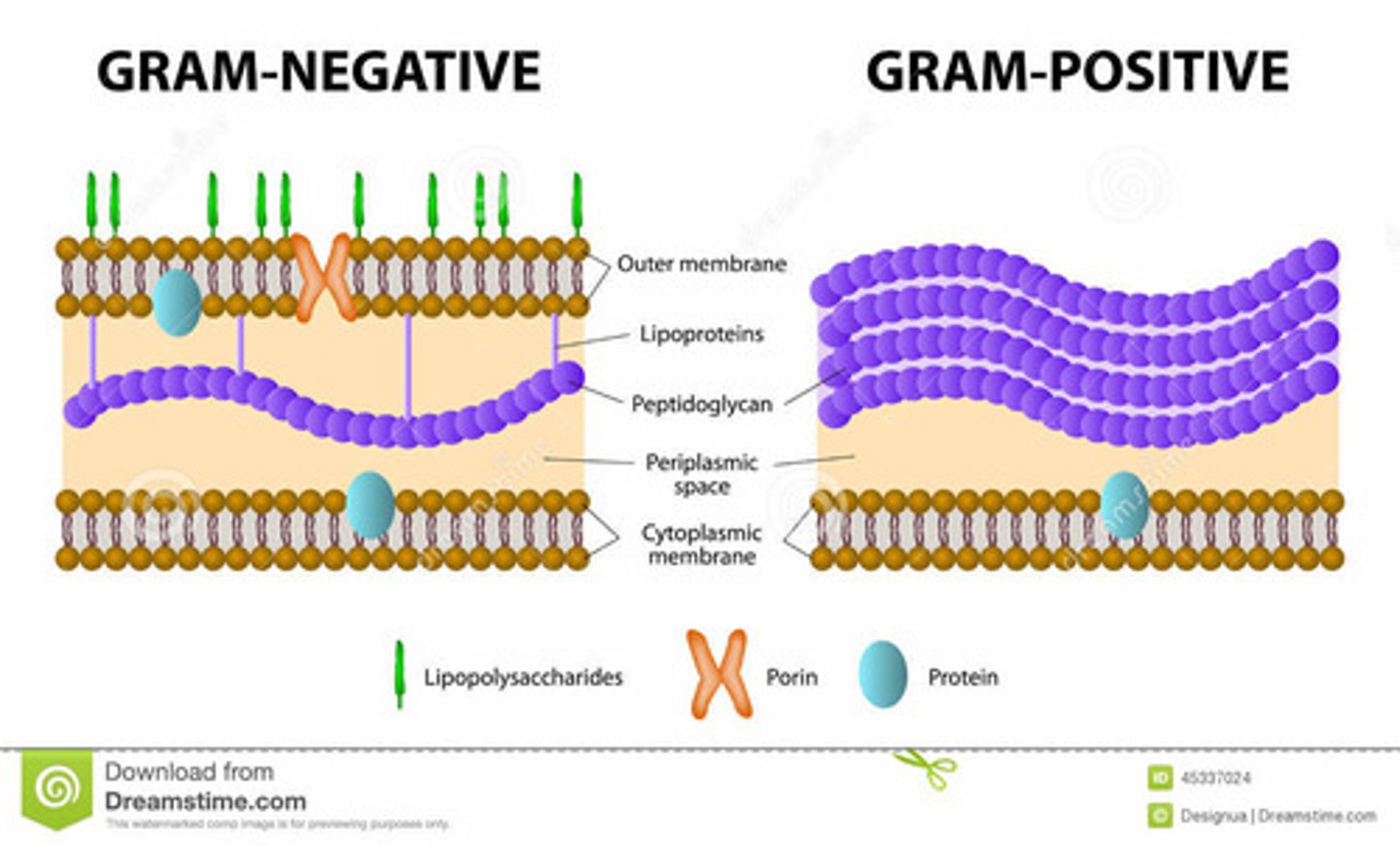
Gram Negative
-second lipid bilayer external to the cell wall
-outer membrane contains polysaccharides covalently bound to lipids
-contains porins (transmembrane transport proteins)
-small layer of peptidoglycan
-pink when stained
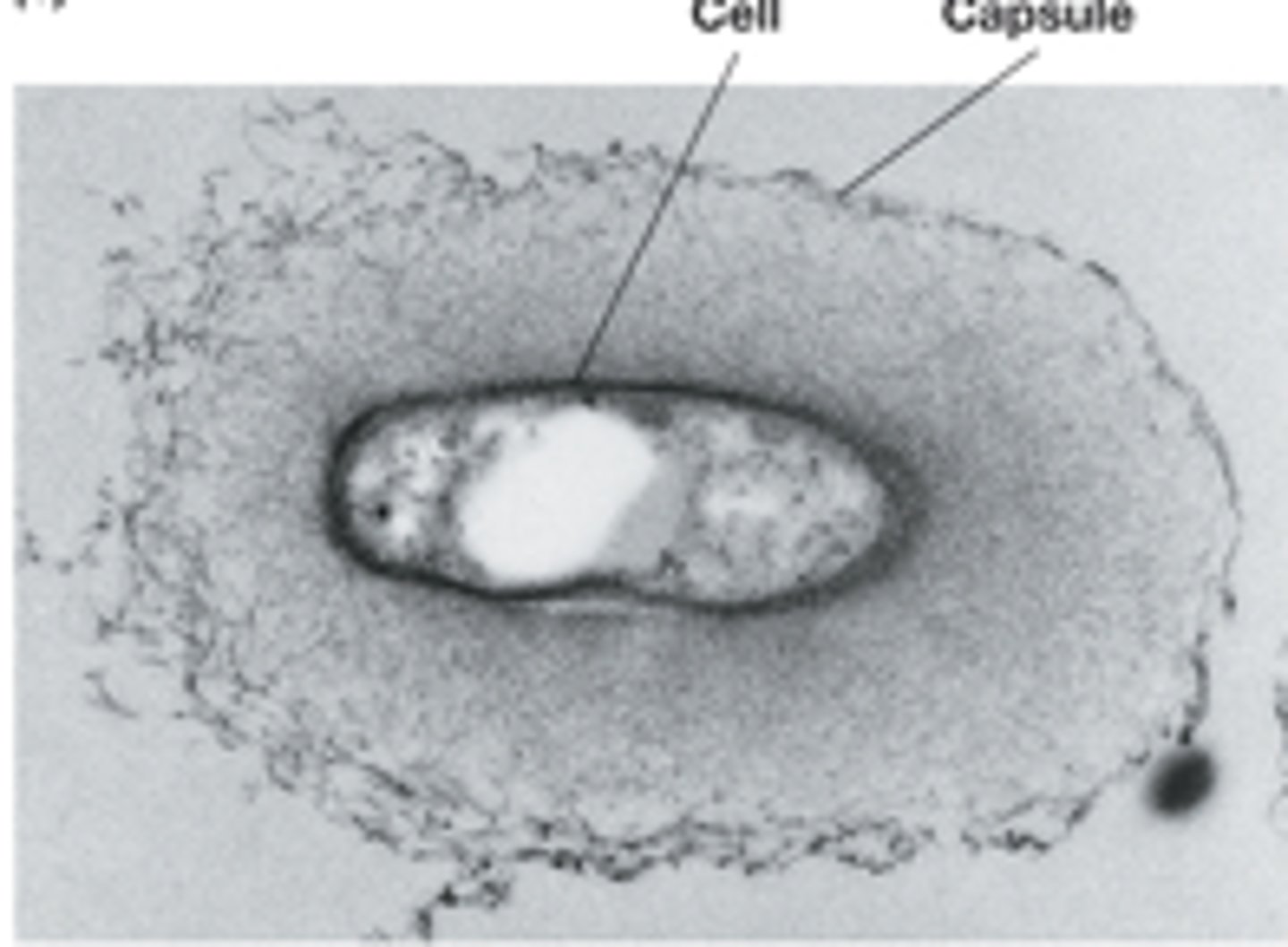
Capsule cell surface
-if tightly attached, tight matrix; visible if treated with India ink
-assist in attachment to surfaces
-role in development and maintenance of biofilms
-contribute to infectivity
-prevent dehydration/desiccation
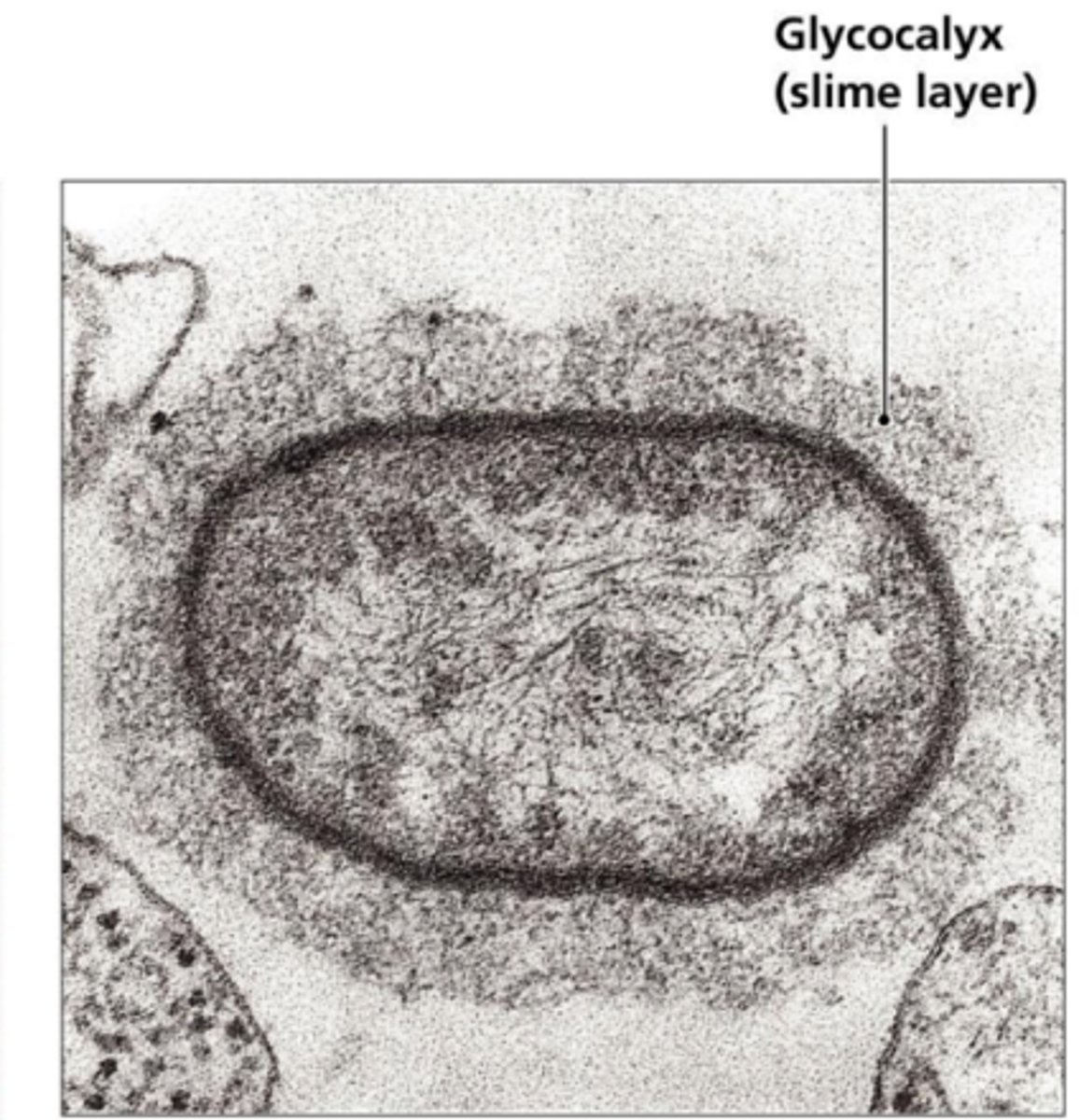
Slime layer surface
-loosely attached, easily deformed
-sticky polysaccharide coat outside cell envelope
-assist in attachment to surfaces
-role in development and maintenance of biofilms
-contribute to infectivity
-prevent dehydration/desiccation
Fimbriae
-extensions of the cell surface
-pili: thin long filamentous protein structures; shorter than flagellum; longer than a fimbria
-made by all gram-negative and many gram-positives
-sex pili: facilitate genetic exchange between cells through conjugation
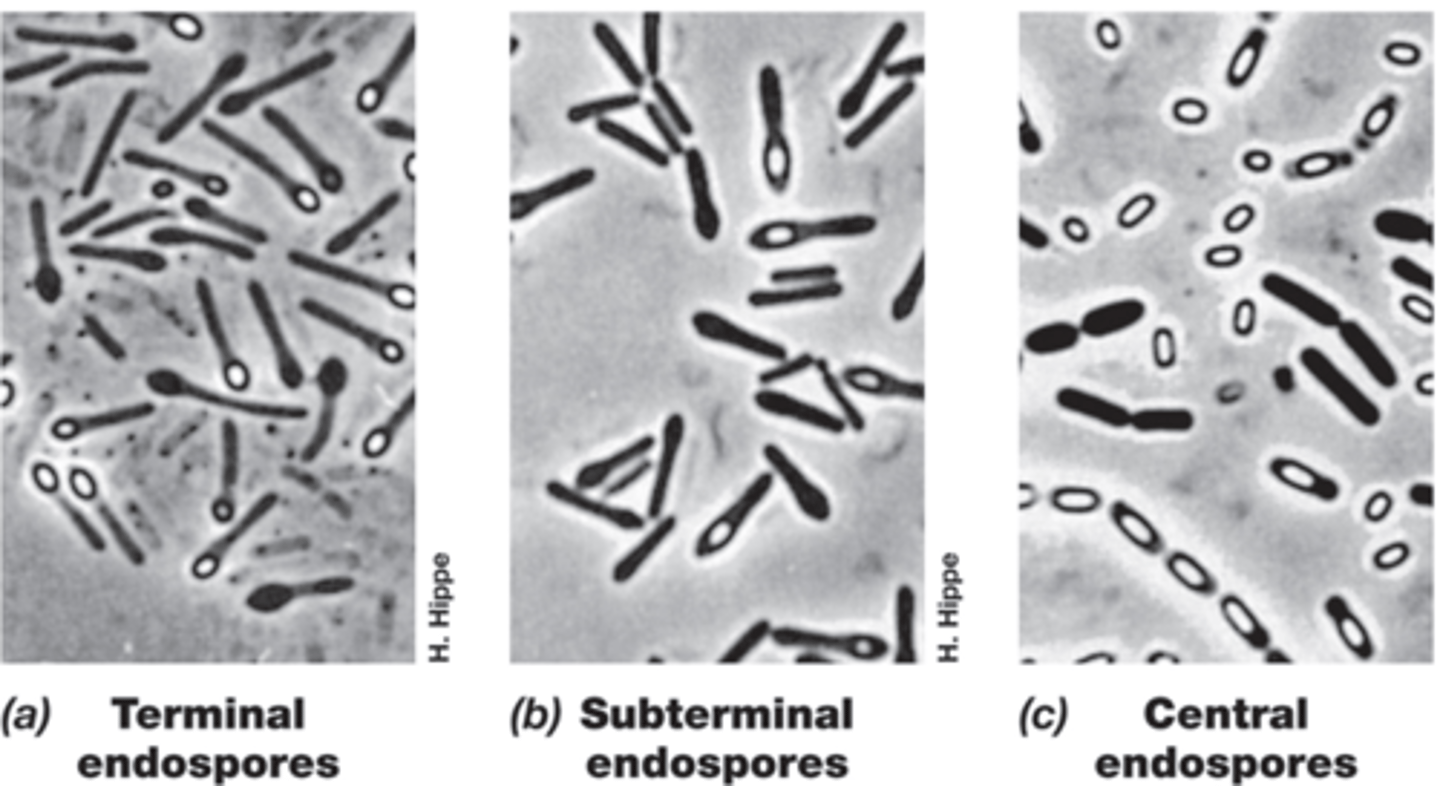
Endospores
-malachite green to stain
-highly specialized spores
-highly differentiated, dormant cells resistant to heat, radiation, chemical exposure, drying, lack of nutrients
-only present in some gram positive bacteria (Bacillales and Clostridiales)
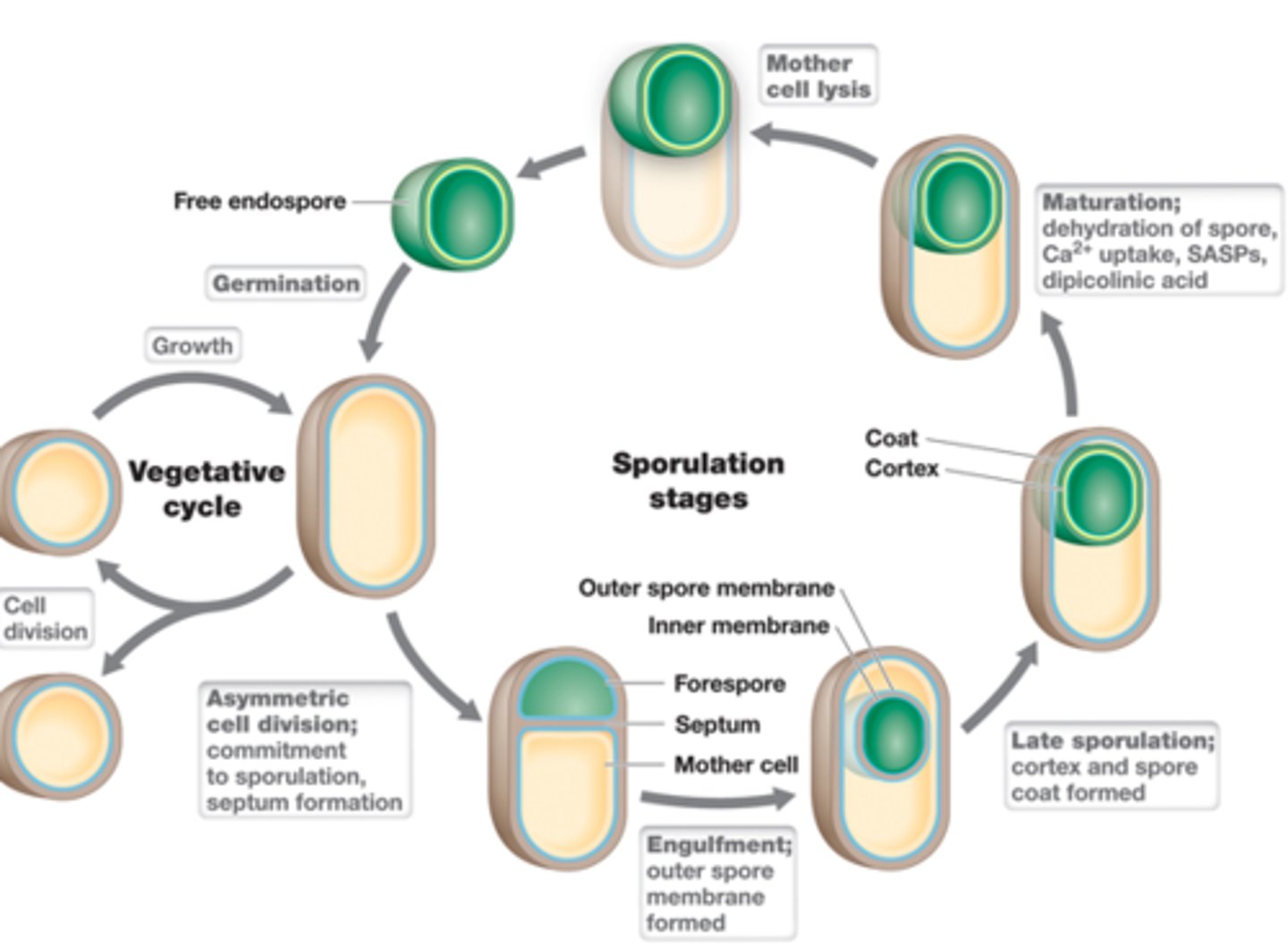
-Vegetative->Endospore->Vegetative
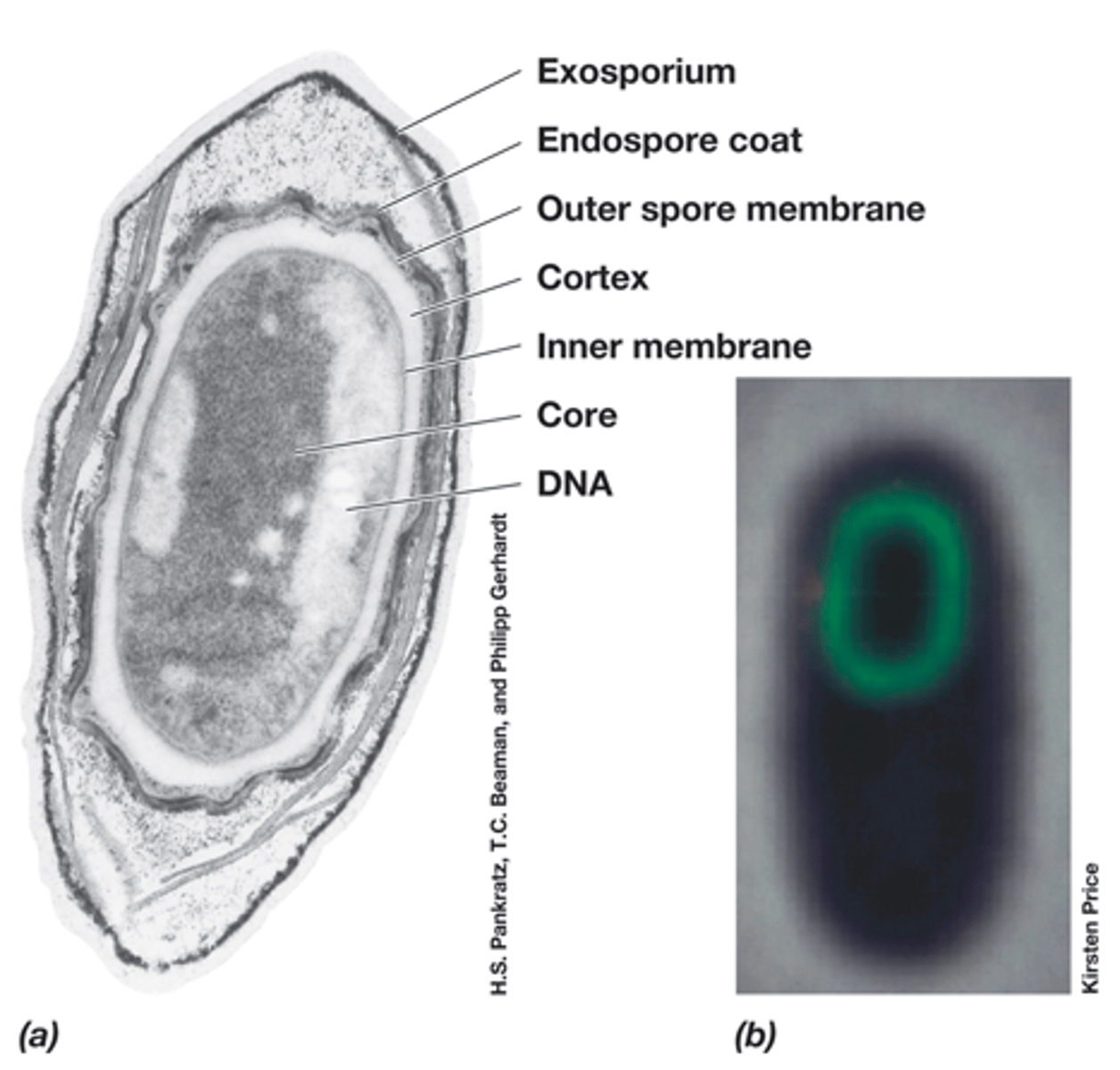
-many layers: core, inner membrane, cortex, outer membrane, endospore coat, exosporium
-dipicolinic acid with Ca2+
-small acid-soluble spore proteins which bind and protect DNA and function as carbon and energy source for growth
Structure of endospores
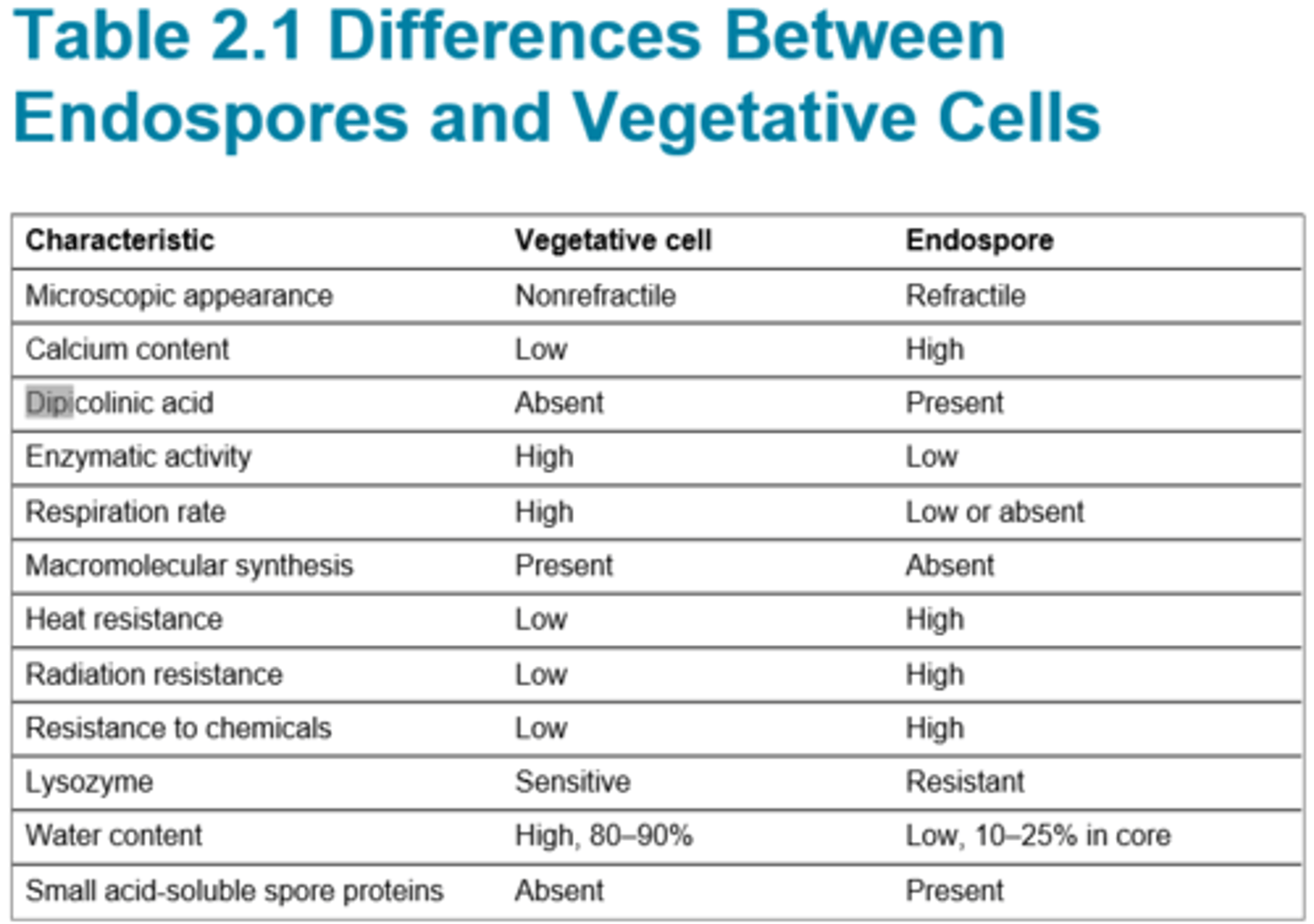
Difference between endospores and vegetative cells
Formation of endospores
Flagella/archaella
-structure that assists in swimming in Bacteria and Archaea
-long, thin appendages anchored in a cell at one end
-peritrichous, polar, lophotrichous
-powered by proton motive force
-filament, book, basal body
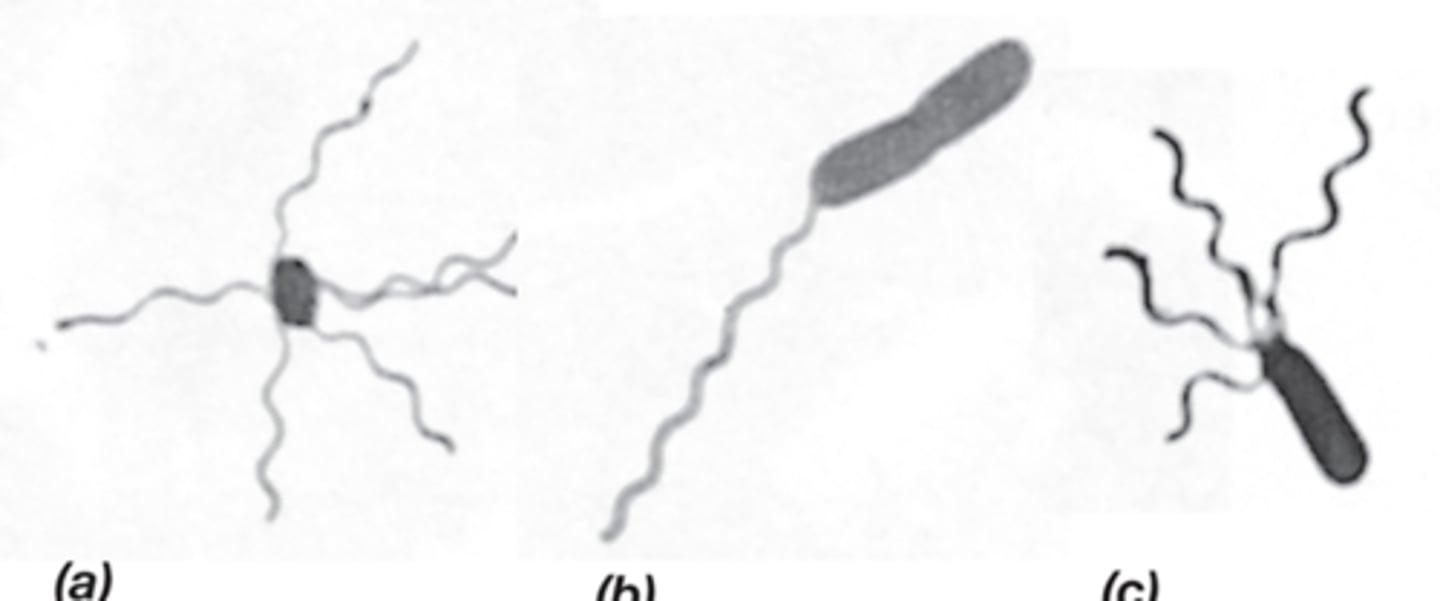
Movement in peritrichously and polarly flagellated prokaryotic cells
Twitching motility
- requires type IV pili
- extend from one cell pole, attach to surface, retract to pull cell forward
- energy from ATP hydrolysis
-e.g. Pseudomonas and myxobacteria
Gliding motility
-smooth, continuous motion along long axis without external structures
-only bacteria so far (e.g. Myxococcus)
-helical intracellular protein track + gliding motors and adhesion proteins
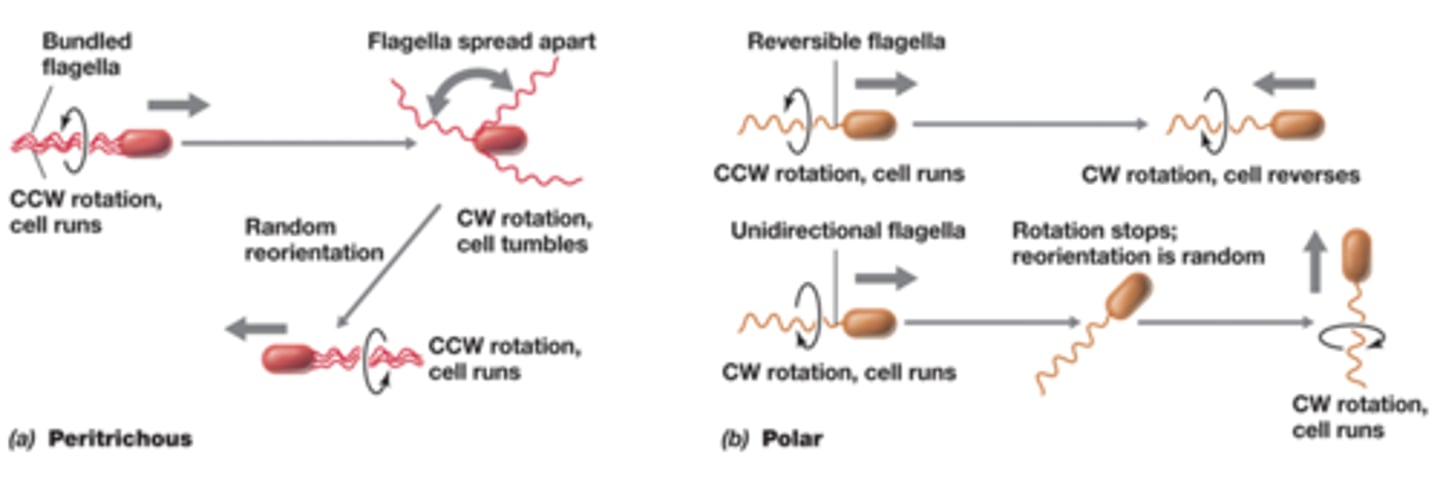
Chemotaxis
-cell movement in response to chemicals
-run: smooth forward motion, flagellar motor rotates counterclockwise
-tumble: bacteria stops and jiggles because flagellar motor rotates
-run and tumble caused by different types of rotation of the flagella
-measured with capillary tube that has decreasing concentration far from tip
Other forms of taxis
-osmotaxis: response to ionic strength
-hydrotaxis: response to water
-aerotaxis: response to O2
-phototaxis: response to light
Nucleus
-contains the chromosomes
-DNA wound around histones forming nucleosomes that are organized into chromosomes
-archaea contain histones and nucleosomes
-nucleolus: inside nucleus and site of ribosomal RNA synthesis
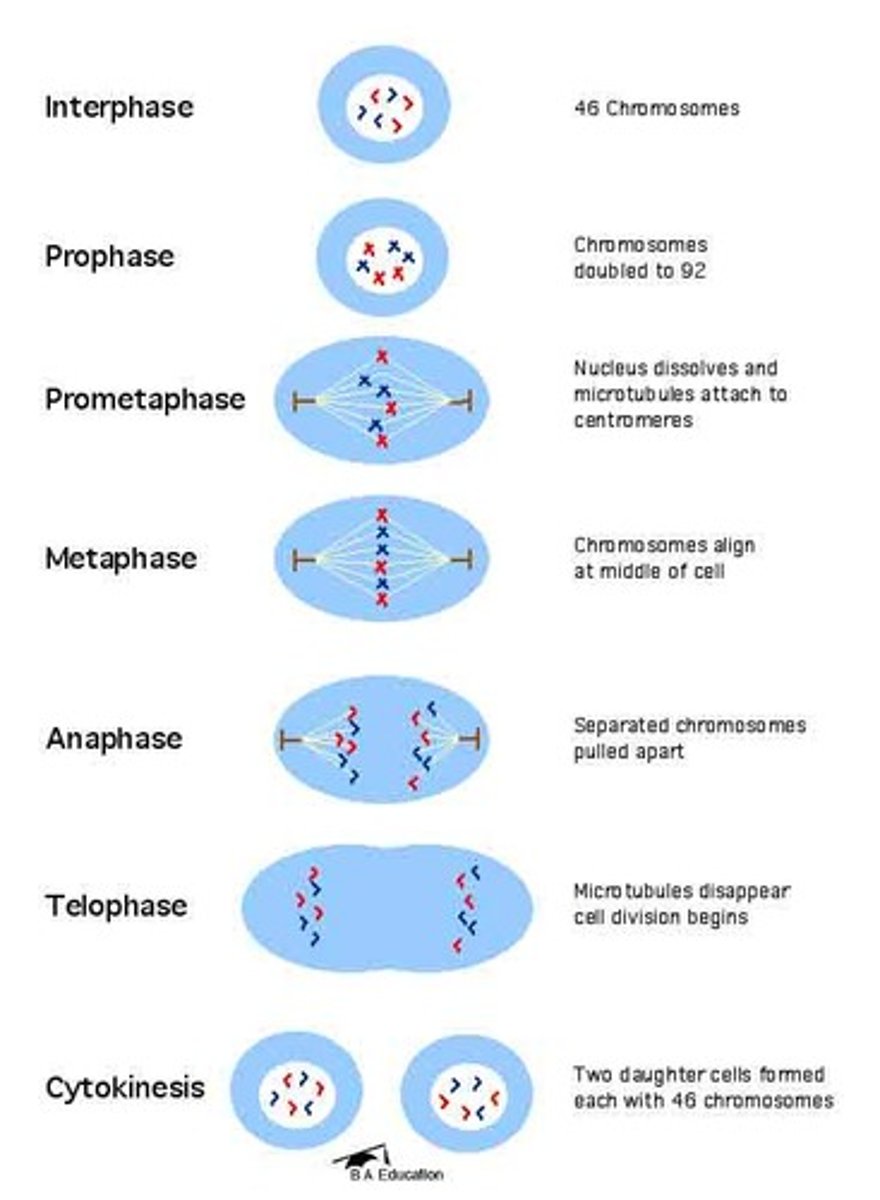
Mitosis
-results in two diploid (two copies of each chromosome) daughter cells
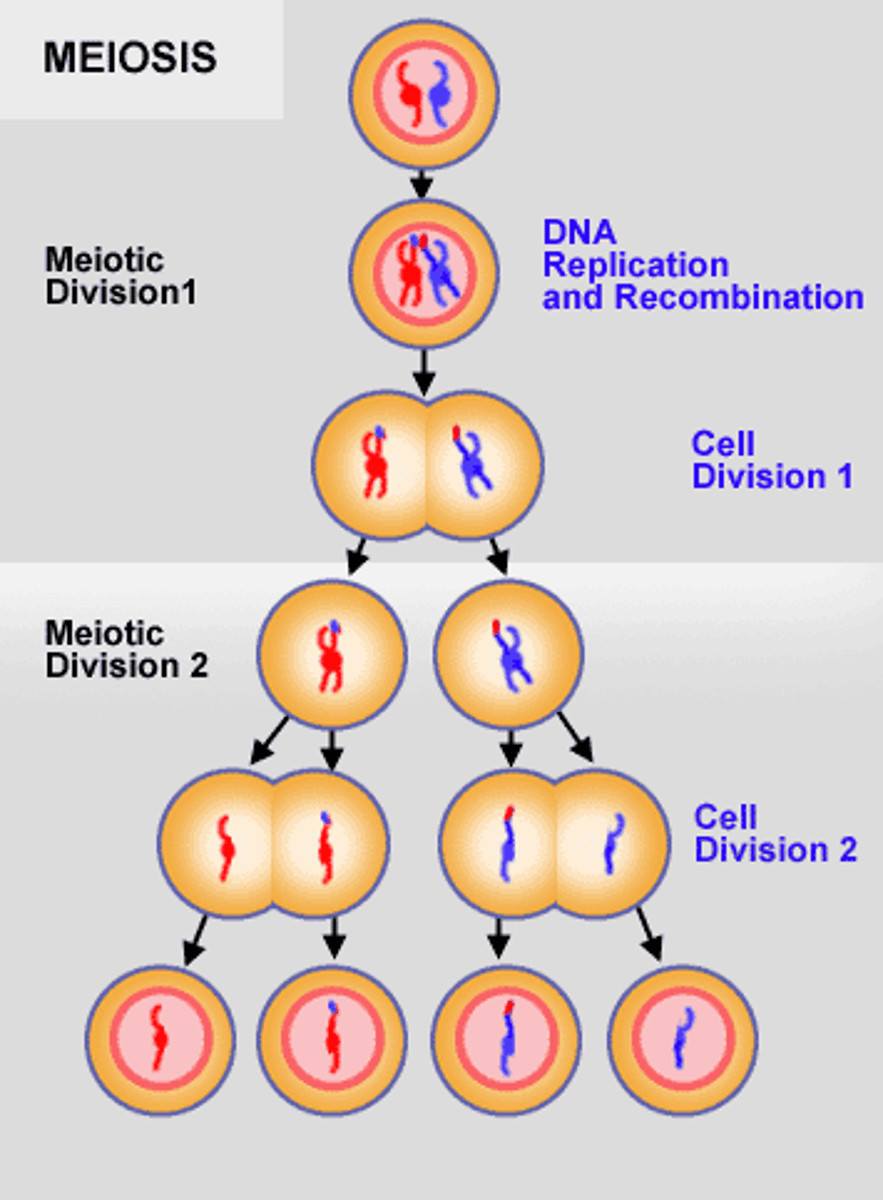
Meiosis
-converts diploid into haploid cells
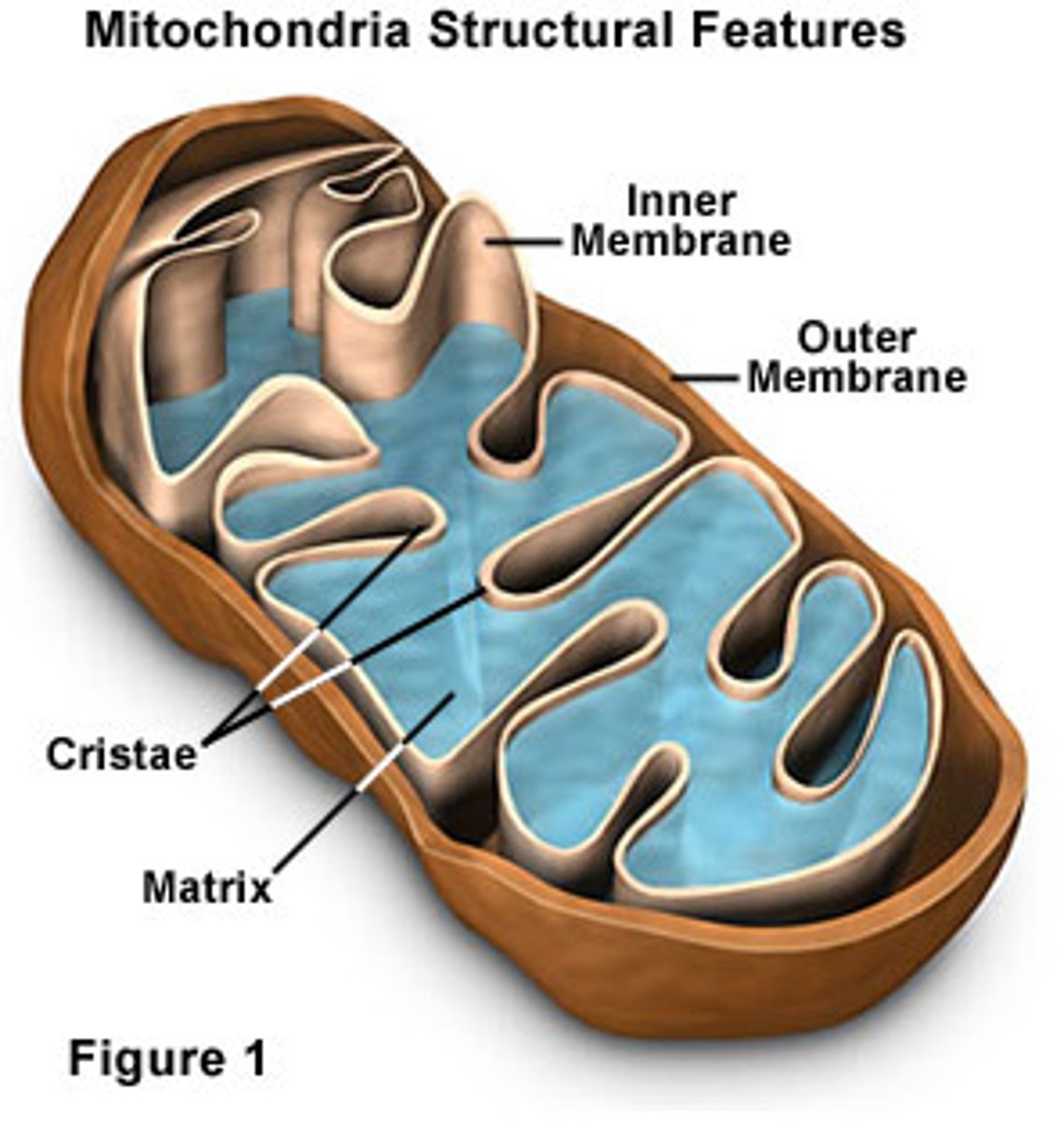
Mitochondria
-respiration and oxidative phosphorylation for aerobic eukaryotes
-cristae: folded internal membranes
-matrix: innermost area of mitochondrion
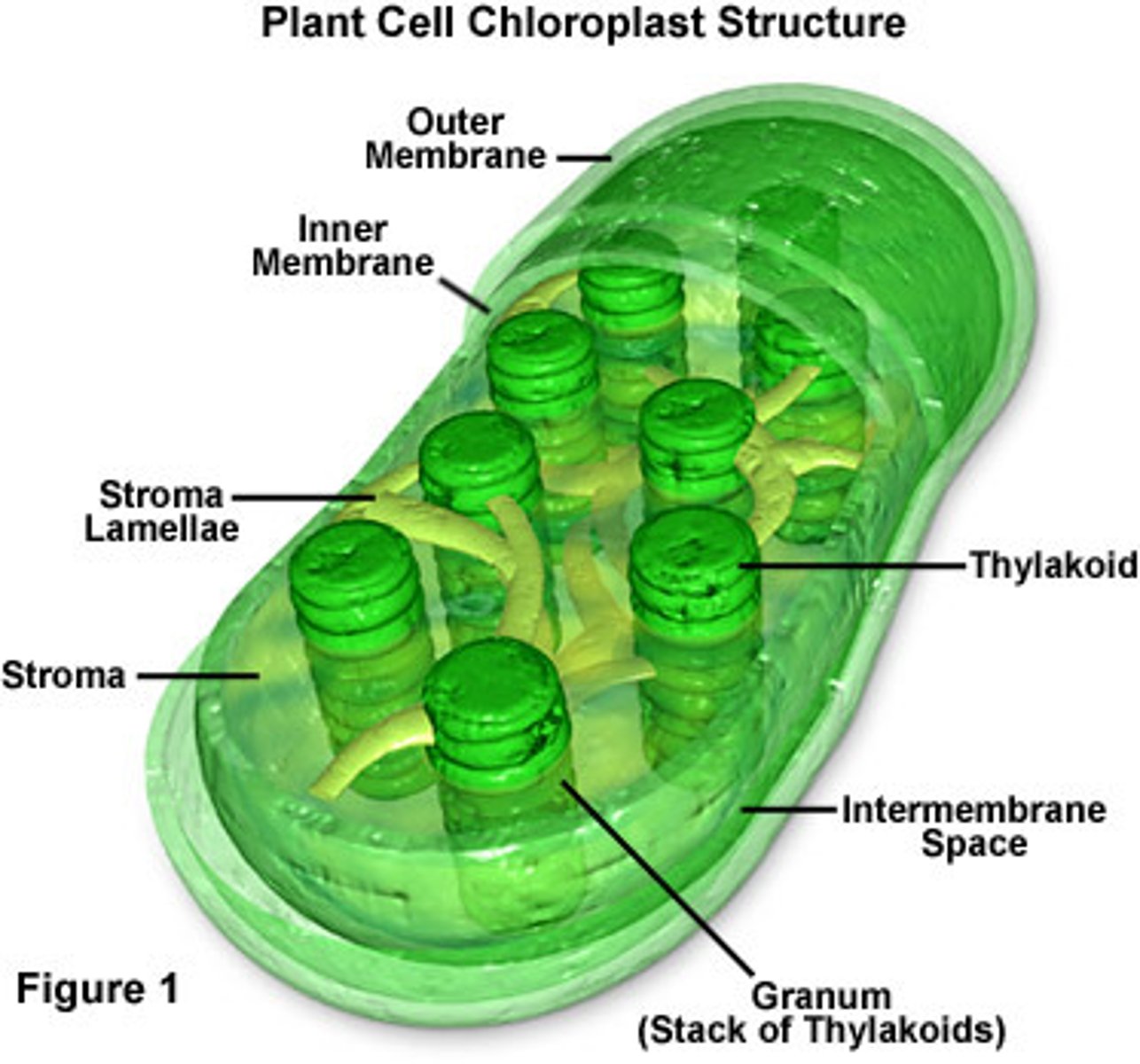
Chloroplasts
-chlorophyll containing organelle found in phototrophic eukaryotes
-site of photosynthesis with two membranes
-inner membrane surrounds stroma
-stroma contains large amounts of RuBisCO which is the key enzyme for the Calvin cycle
-thylakoids: flattened membrane discs contain chlorophyll and ATP synthetic components, form proton motive force
Cytoskeleton
-microtubules: maintain cell shape, facilitate motility; move chromosomes and organelles
-microfilaments: maintain and change cell shape; involved in amoeboid motility and cell division
-intermediate filaments: maintain cell shapes and position organelles
endoplasmic reticulum
-network of membranes continuous with nuclear membrane
-smooth: participates in the synthesis of lipids and carbohydrate metabolism
-rough: produces glycoproteins and new membrane material
golgi complex
-stacks of membrane-bound sacs modifying ER products
lysosomes
-membrane-enclosed compartments containing digestive enzymes and recycling cell components
first law of thermodynamics
-energy is neither created nor destroyed
free energy
-energy available to do work
reducing power
-an ability to donate electrons
-requires a compound that serves as a source of electrons
-reduction potential: tendency to donate electrons
exergonic reactions
-reactions with negative deltaG that release free energy
endergonic reactions
-reactions with positive deltaG that require energy
catabolic pathways
-generate free energy
-coupled to ATP synthesis to conserve free E
-breaking down of metabolic compounds
-degradation of glucose linked to production of ATP
anabolic pathways
-use up free energy
-coupled to ATP degradation reaction
-creating of different metabolic compounds
electron donor
-transfers electrons (oxidized)
electron acceptor
-adds electrons (reduced)
phototrophs
-obtain energy from light
-oxygenic (O2 produced) and anoxygenic (no O2 produced) photosynthesis
-oxidative phosphorylation
chemotrophs
-obtain energy from chemical reaction
-chemoautotrophs: energy source is inorganic
-chemoorganotrophs: energy source is organic (fatty acid e.g.)
-aerobic reactions require O2 as electron acceptor
-anaerobic reactions use anything other than O2 as electron acceptor
redox tower
-Represents the range of possible reduction potentials
-The reduced substance at the top of the tower donates electrons
-The oxidized substance at the bottom of the tower accepts electrons
-The farther the electrons "drop" the greater the amount of energy released
NAD+/NADH
-soluble electron carriers
-coenzymes
-coupled value is -0.32 V
-NADH good electron donor and can also donate hydrogens
-NAD+ weak electron acceptor

calculating deltaG
-Δ G0 = −n F Δ E0ʹ
-Δ E0ʹ : change in reduction potential
-can also be found by finding the difference between free energy of formation of products and reactants
substrate-level phosphorylation
-energy-rich substrate bond hydrolyzed directly to drive ATP formation (e.g., hydrolysis of phosphoenolpyruvate)
oxidative phosphorylation
-movement of electrons generates a proton motive force (electrochemical gradient) used to synthesize ATP
photophosphorylation
-light used to form proton motive force
enzymes
-prosthetic groups: tightly bound, usually covalently and permanently
-coenzymes: loose and transiently bound with most being derivatives of vitamins
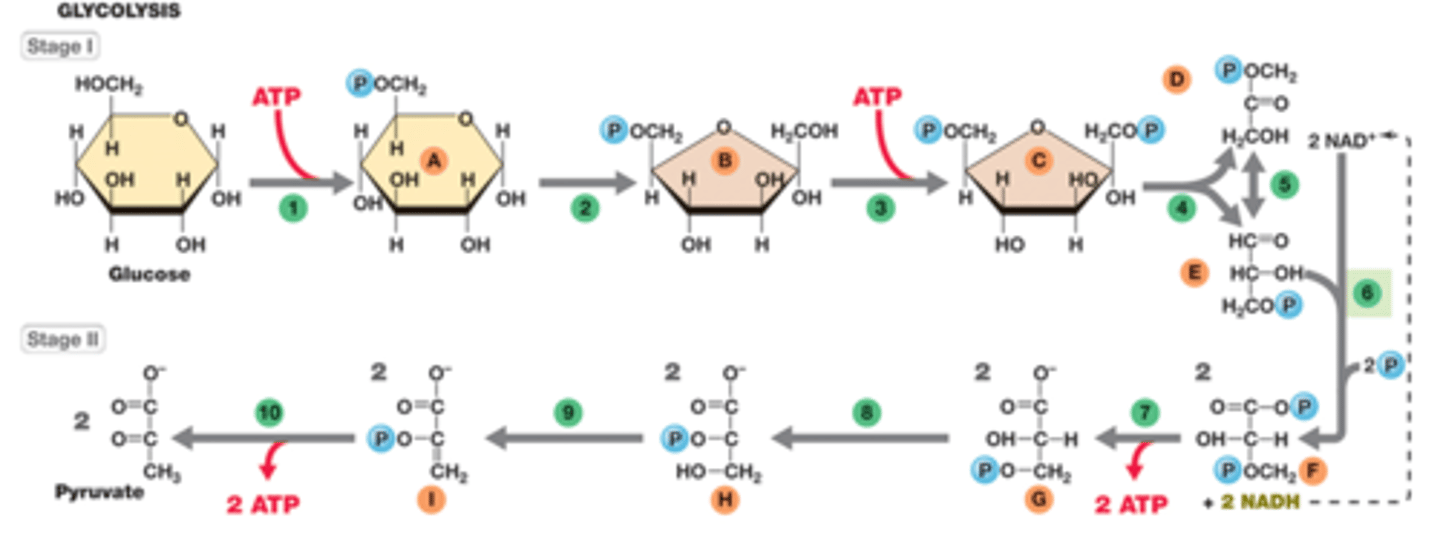
Glycolysis
-stage 1: energy investing or preparatory, forming G3P intermediate
-stage 2: energy producing, redox, energy conserved, 2 pyruvates formed
-net is 2 ATPs, 2 NADHs, 2 pyruvates per glucose
Citric Acid Cycle
-2 CO2, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP formed per each pyruvate being oxidized
-oxaloacetate is regenerated so the cycle is repeated
glyoxylate cycle
-plants and bacteria
-acetyl-coA --> carbohydrates
fermentation
-conserve energy (produce ATP)
-restore redox balance (regenerate NADH)
-need to produce compounds containing high energy bonds for ATP synthesis
respiration
-electrons transferred from reduced electron donors to external electron acceptors
-reoxidation occurs during the electron transport chain
-occurs in cytoplasmic membrane due to electrochemical gradient that conserves energy through ATP synthesis
-arranged with increasingly more positive reduction potential
NADH dehydrogenase
-active site binds NADH, accepts two electrons and two protons that are transferred to flavoproteins, regenerating NAD+
Flavoproteins
-contain derivative of riboflavin as prosthetic group that accepts two electrons and two protons but only donate electrons
cytochromes
-proteins that contain heme prosthetic groups
-oxidized or reduced by 1 electron via the iron atom
nonheme iron proteins
-contains cluster of iron and sulfur
quinones
-small hydrophobic nonprotein redox molecules
-can move within membrane
-ubiquinone (coenzyme Q) and menaquinone are the most common
ATP synthase
-oxidative phosphorylation from respiratory electrons
-photophosphorylation from light energy
-uses energy from proton motive force to form ATP
-38 ATP in aerobic respiration and 2 ATP in lactic acid fermentation
respiration in Escherichia coli
-versatile chemoorganotroph with electron transport similar to Paracoccus denitrificans
-grows by aerobic respiration, fermentation, anaerobic respiration (nitrate)
-no O2, then E. coli uses nitrate reductase as a terminal reductase
chemolithography
-use inorganic chemicals as inorganic electron donors
-use reverse electron transport for proton motive force
calvin cycle
-reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugars
-requires CO2, a CO2 acceptor (RuBP), NADPH, ATP, ribulose bisphophate carboxylase (RubisCO), and phosphoribulokinase