Ch 33-34: Plant Transport
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What happens in the absence of essential elements
their abesence severely disrupts plant growth & reproduction
Essential elements: micronutrients (7)
Fe, Cl, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni, Mo
needed in small quantities
Essential elements: macronutrients (6)
N, P, K, Ca, S, Mg
Why do plants need water? (4)
Photosynthesis, cooling, transporting solutes, internal pressure for support
Water & ions move into the root thru ___ & ___
Apoplast (intercellular) & symplast (extracellular)
Plants regulate…
nutrient uptake
What do soils provide?
anchorage for mechanical supprt
mineral nutrients & water from soil solution
minerals dissolved as ions in water
O2 for root respiration from air spaces between soil particles
services of soil organisms: bacteria, fungi, protists, earthworms, arthropods
Soils develop a soil profile of horizontal layers called ______
horizons
A Horizon
Topsoil
most living/dead organic matter
B Horizon
Subsoil
accumulates materials from topsoil & parent rock
C Horizon
parent rock from which soil arises
Soil fertility
ability to support plant growth
What is soil fertility determined by?
particle size
soil composition
soil organic matter (humus)
cation exchange capacity
What soil composition is most ideal?
loam
Xylem vessel
1-way
carries water & mineral
thick walls stiffened w lignin
no end walls between cells
Phloem vessels
2-way flow
carries water & food
cells have end walls w perforations
How do root cells take up water?
osmosis
What is the water potential of pure water?
0
What is water potential?
tendency of water molecules to move in response to pressure & solute concentration gradients
What does a more negative water potential mean?
greater driving force for water movement across membrane
Water enters cells until what happens?
pressure potential balances solute potential
Turgor pressure
Positive pressure potential
maintains structure of many plants
What happens to a plant when pressure potential drops?
the plant wilts
Water moves from cell to cell along a gradient of _____ _____
Water potential thru xylem vessels
Passive transport
no energy required
bulk flow
aquaporins
Bulk flow
movement of water from higher pressure potential to lower pressure potential
What in cell membranes allows water to diffuse rapidly?
aquaporins & tonoplasts (vacuole membrane)
Active transport
energy required
ion channels & pumps
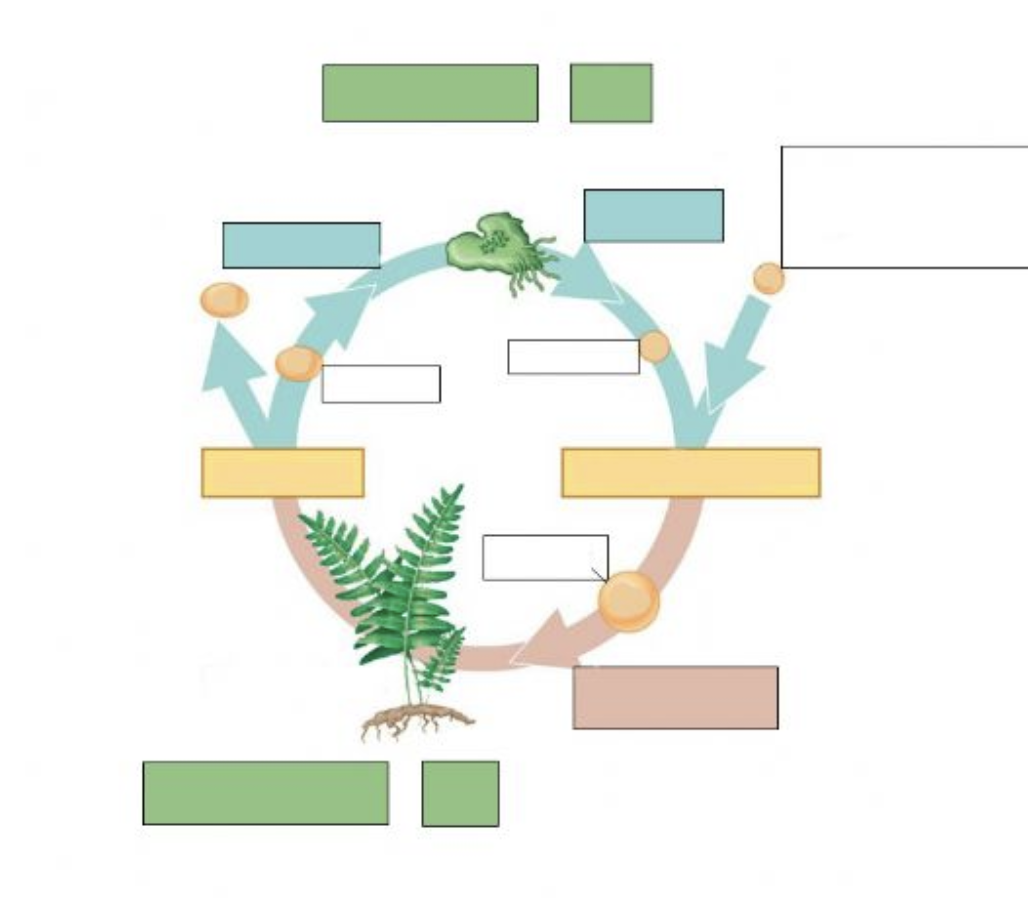
Label
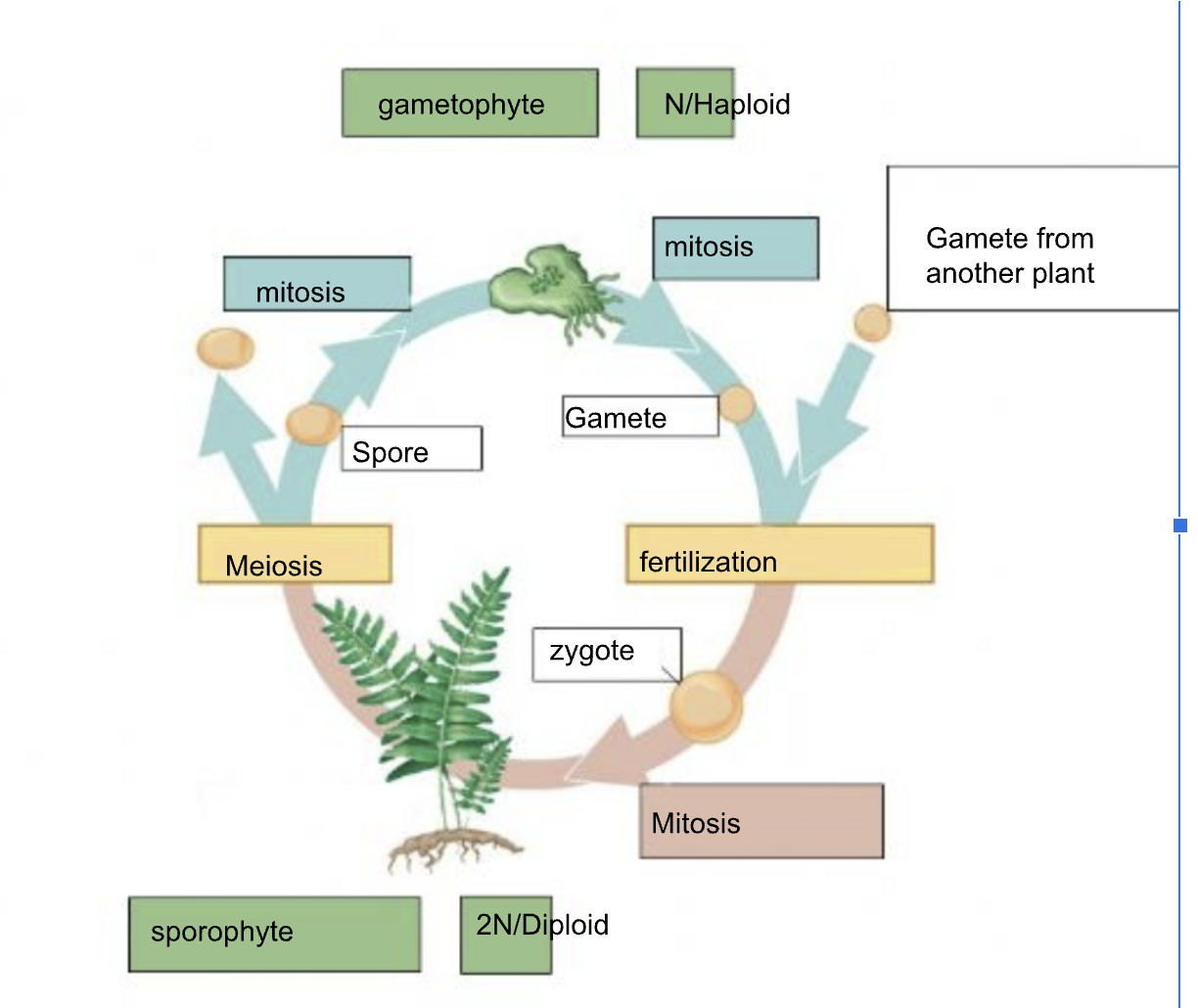
Label the adaptations
How does xylem move water up?
Transpiration
cohesion
tension
adhesion
What does the stomata do? (4)
manage water loss
allow CO2 to enter by diffusion
waxy cuticle - minimize water loss
guard cells control the opening & closing
How are solutes transported in the phloem?
solutes transported upward/downward
translocation
What does the phloem carry?
sugars & waters
What is translocation?
movement of carbohydrates & other solutes thru the phloem
Products of photosynthesis are called ______
photosynthates
What is the content of the phloem?
phloem sap
How does the phloem carry photosynthates & solutes
from source to sink thru bulk flow
What are sources?
organs that produce more sugars than they require (leaf)
What are sinks?
sinks consume sugars for growth or storage
True or false? Organs & tissues can switch between sources & sinks sometimes.
True
What do the phloem conducting tubes have?
sieve tube elements that meet end-to-end
have walls between different segments
pores allow for movement
What is the driving force for bulk flow, site of bulk flow, & pressure potential in sap flow for the phloem & xylem
Phloem
driving force: transpiration from leaves
site: nonliving vessel elements & tracheids
potential: negative (pull from top, tension)
Xylem
driving force: active transport of sucrose at source & sink
site: living sieve tube elements
potential: positive (push from source, pressure)
What are nutrients?
elements required to build macromolecules
Where do the nutrients carbon, nitrogen, & hydrogen come from?
Carbon - CO2
Hydrogen - water
Nitrogen - soil
Plants ______ nutrient uptake
regulate
How do polar molecules & nutrient ions enter epidermal cells?
transport protein
What are the 3 ways to replenish nutrients? Define.
Shifting agriculture - when soil is depleted, move to another location & let natural processes replenish soil
organic fertilizer - humus used as food source by soil organisms, which releases simpler molecules to the soil solution
inorganic fertilizers - supply mineral nutrients in forms that are easily used
NPK percentages - produced in manufacturing that uses lots of energy
1g of soil contains _____ many bacterial species & up to ___ meters of fungal hyphae
6,000-50,000 & 200 meters
What are exudates? What do they influence?
Exidates are compounds that plants actively secrete, they influence organisms living in nearby in the region called rhizosphere
__ percent of plants have symbiotic relationships with bacteria & fungi
90%
What does mycorrhizal fungi do?
expand the surface area, increasing amount of soil plants can explore for nutrients
mainly obtains phosphorus
Can plants use N2?
no
What do bacteria with nitrogenase do?
convert N2 to NH3 thru nitrogen fixation
What reaction is nitrogen fixation?
reduction reaction that requires lots of energy
Formation of nitrogen-fixing nodules
legume plants form symbiois w rhizobia bacteria
these roots release flavenoids & other signals to attract rhizobia
Purpose of legumes in crop rotations
clover or alfalfa to increase available nitrogen in soil
Why are industrial nitrogen fertilizers produced?
because bacterial N fixation may not be sufficient to support agriculture
How do carnivorous plants get nutrients? Where are they found?
get nutrients by capturing & digesting insects
they get nitrogen by capturing animals & digesting proteins
Live in boggy habitats that are nutrient deficient & acidic
How do parasitic plants get nutrients?
they get minerals, nutrients, or photosynthate from bodies of other plants
Hemiparasites
can photosynthesize but get water & mineral nutrients from living plants
mistletoe
Holoparasites
completely parasitic, n