Long Term Potentiation (exam 3)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:57 PM on 4/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
1
New cards
Associative Learning
•Linkage of two or more unrelated stimuli to elicit a behavioral response
2
New cards
Long-term Potentiation (LTP)
•In response to stimulation at a synapse, changed amplitude of an excitatory postsynaptic potential that lasts for hours to days or longer
•Plays a part in associative learning
•Plays a part in associative learning
3
New cards
•When researchers applied a **tetanus** to the hippocampus, response of postsynaptic neurons changed—
larger EPSPs.
4
New cards
\
•**Long-term potentiation** (**LTP**)—
•**Long-term potentiation** (**LTP**)—
a stable and enduring increase in the effectiveness of synapses.
•Weakening of synaptic efficacy—termed long-term depression—can also encode information.
•Weakening of synaptic efficacy—termed long-term depression—can also encode information.
5
New cards
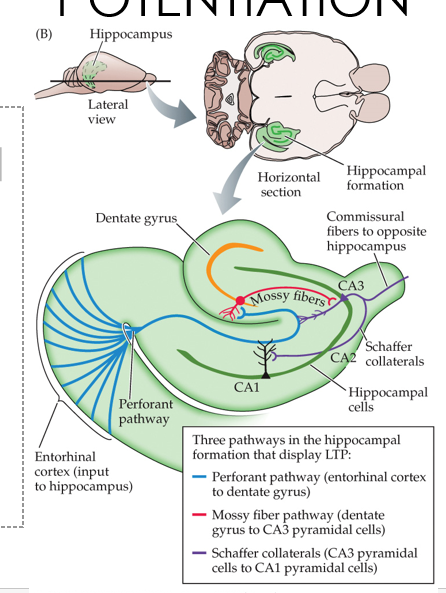
•The hippocampal formation consists of two interlocking C-shaped structures
•Hippocampus
•CA1
•CA2
•CA3
Dentate gyrus
•CA1
•CA2
•CA3
Dentate gyrus
6
New cards
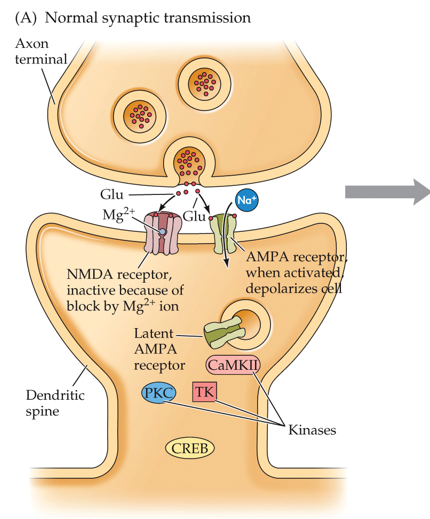
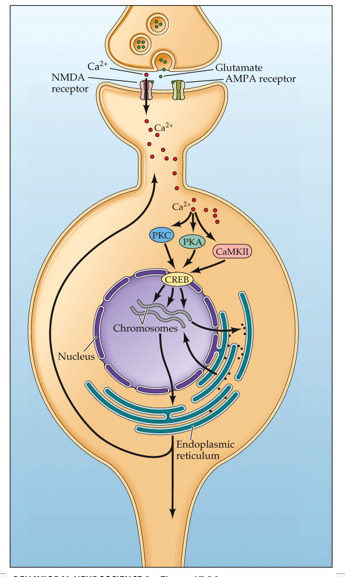
•Glutamate acts on two different types of receptors on the postsynaptic membrane
•AMPA (alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoa-zole-4-proprionic acid)
•NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate)
•NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate)
7
New cards
•Glutamate first activates
AMPA receptors.
•NMDA receptor blocked by Mg2+ ion
•NMDA receptors do not respond until enough AMPA receptors are stimulated, and the neuron is partially depolarized.
•Need Mg2+ to move
•NMDA receptor blocked by Mg2+ ion
•NMDA receptors do not respond until enough AMPA receptors are stimulated, and the neuron is partially depolarized.
•Need Mg2+ to move
8
New cards
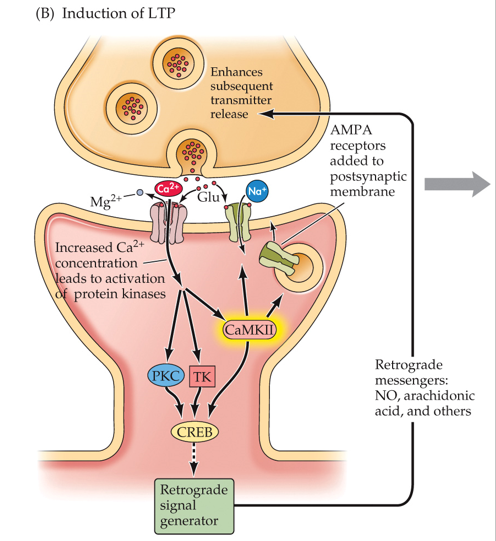
What happens after Mg2+ needs to move out?
•Mg2+ driven out, Ca2+ enter
•The large Ca2+ influx activates certain **protein kinases**
•One protein kinase, CaMKII (calcium-calmodulin kinase II), affects AMPA receptors
•AMPA receptors movement, production, insertion
•Increases conductance of Na+ and K+ ions
•The large Ca2+ influx activates certain **protein kinases**
•One protein kinase, CaMKII (calcium-calmodulin kinase II), affects AMPA receptors
•AMPA receptors movement, production, insertion
•Increases conductance of Na+ and K+ ions
9
New cards
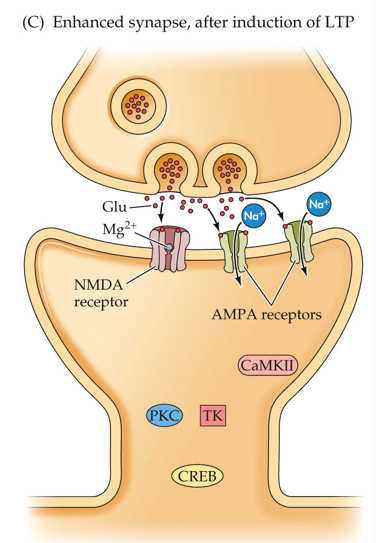
What do all these effects do?
•These effects all increase the synaptic sensitivity to glutamate
10
New cards
Steps in the Neurochemical cascade during the induction of LTP
•Kinases activate **CREB**—cAMP responsive element-binding protein.
•CREB binds to DNA promoter regions
•Strong stimulation of a postsynaptic cell causes release of a **retrograde messenger**
Travels across the synapse and alters function in the presynaptic neuron
•CREB binds to DNA promoter regions
•Strong stimulation of a postsynaptic cell causes release of a **retrograde messenger**
Travels across the synapse and alters function in the presynaptic neuron
11
New cards
•What neural processes underlie the persistent, long-term changes of learning?
•Ca2+ enters postsynaptic neuron and activates a second messenger
•cAMP alters gene expression in nucleus, which physically alters synapse
•cAMP alters gene expression in nucleus, which physically alters synapse
12
New cards
•Evidence indicates LTP may be one part of memory formation.
•Correlational observations
•Somatic intervention experiments
•Behavioral intervention experiments
•Somatic intervention experiments
•Behavioral intervention experiments
13
New cards
Long Term Depression (LTD)
•Another form of synaptic plasticity
•Neuron becomes less active in response to repeated stimulation
•Involves NMDA receptors
•Requires Ca2+ entry
•Neuron becomes less active in response to repeated stimulation
•Involves NMDA receptors
•Requires Ca2+ entry