Dental acrylics 3 - Other room temperature cured acrylics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
what dental acrylics are used in materials
why don’t we go
Don’t use propyl - too reactive
Further than butyl - (you want dentures to be rigid, longer CH2 chains the material becomes more flexible - used for soft lining material, want dentures to be rigid to replace the lost dentition the stresses from chewing on the bone - keeps the bone stimulated so less bone loss due to the pressure as you need bone to for dentures)
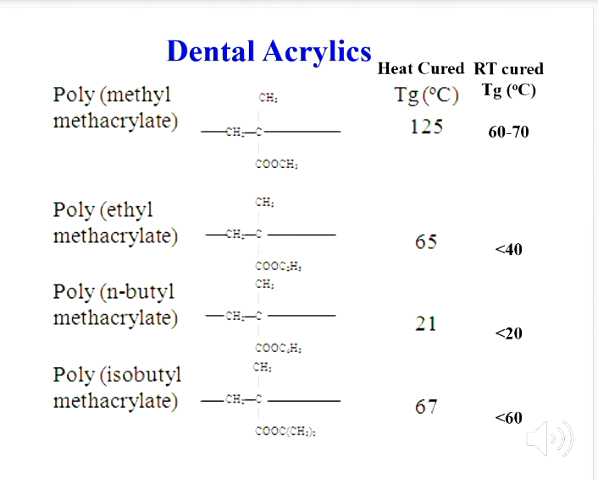
Methyl methacrylate is used because of its high Tg temperature
(Tg - going from rigid to soft material)
overall, RT have lower Tg than HC - need higher Tg than those enocuntered during use so it doesnt warm up adn flow
What are other cured acrylics? do we use PMMA/MMA?
These materials utilise another polymer powder in place of PMMA and a higher methacrylate monomer not MMA
What is the polymer powder that is used?
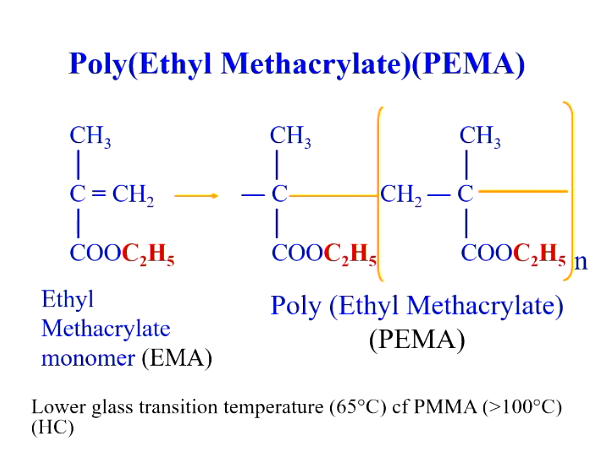
the polymer powder used is a higher methacrylate - poly(ethyl methacrylate) PEMA - next relative to PMMA in the homologous series
How is it mixed with a higher molecular weight monomer?
it is mixed using the dough technique
What is the role of PEMA?
PEMA, like PMMA is used to reduce the shrinkage and exotherm of the final set material
What is PEMA formed from and how, does it take part in the reaction?
it is a pre-polymerised ethyl methacrylate, - acts as a virtual filler - like PMMA and does not take part in the free radical polymerisation reaction - similarly to PMMA
What is important to note about the monomers that PMMA and PEMA can be mixed with?
PMMA cannot be mixed with any other monomer - it can only be mixed with MMA - because it forms an incoherent gel and a poorly formed product
PEMA cannot be used with MMA monomer - results in an incoherently mixed product
PEMA can be used with several higher molecular weight monomers in place of MMA
(won’t get a paste)
PEMA can be used without a monomer in what situation?
tissue conditioners
What are the impacts of an incoherently mixed product?
Detrimental effect on the physico-mechanical properties of the final product (appliance)
What is the Tg of PEMA compared to PMMA?
Not used for making a denture - low Tg, only used in temporary appliances and not for making a full denture
What are some uses of PEMA? (7)
Soft liners
Tissue conditioners (RT)
Temporary crown and bridge materials
Extension of impression trays and dentures
Hard reline material
Denture lining (for allowing traumatised oral tissues to recover)
Functional impression material
Maxillofacial prothesis - obturator e.g

What are tissue conditioners?
temporary denture lining materials
what type of gel are tissue conditioners? what 2 properties do they have (hint in name)
Viscoelastic gels - exhibit both elastic and viscous behaviour on the application of stress
What are the 3 components in a tissue conditioner?
PEMA powder (PMMA powder) + alcohol + plasticiser - no monomers
Tissue conditioners form a gel via what process?
Polymer chain entanglement and do not polymerise - remember no monomer is present
What is the main difference between a tissue conditioner and soft lining material ?
Soft liners contain a monomer while tissue conditioners don’t
Why is a soft lining material used?
a soft lining material is used to make the denture more comfortable for the patient
Dentures can cause patients persistence pain and discomfort, this is more common in which arch?
lower arch
Why ? (2)
The lower denture has a smaller surface area to distribute the load
also the patient could have sharp, thin or heavily resorbed alveolar ridges
What technique is used in soft lining material construction?
Dough technique to reduce overall shrinkage and exotherm of the material
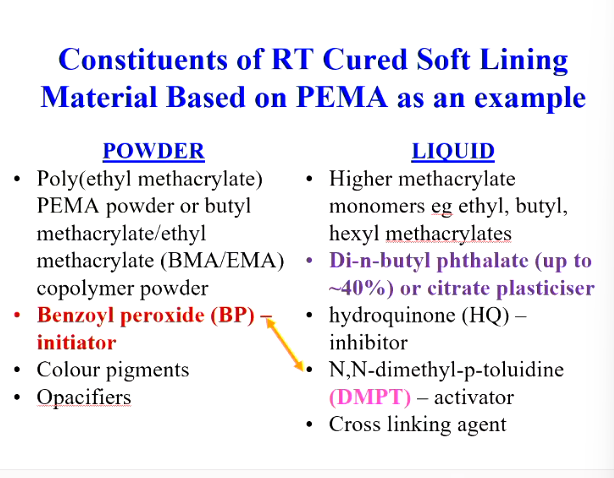
What is the powder (4) and liquid (5) composition of RT cured soft lining materials based on PEMA?
Powder:
PEMA powder (or butyl methacrylate/ethyl methacrylate - BMA/EMA)
Benzoyl peroxide - initiator
colour pigments
opacifiers
liquid:
Higher methacrylate monomers e.g ethyl, butyl, hexyl methacrylates
phthalate or citrate plasticiser
HQ - inhibitor
DMPT - activator
cross linking agent
Advantages of RT cured soft lining materials
what type of material are soft liner
its adhesion to acrylic denture base?
what do plasticisers do?
(name 2 types of plasticiser)
how do they work?
Soft lining material is soft, rubbery acrylic material
it adheres well to the acrylic denture base since it contains acrylic groups
Plasticisers reduce the glass transition temperature of the acrylic
aromatic ester or phthalate
plasticisers are an organic liquid that act as a lubricant, which seeps/flows between polymer chains and thus lowering/weakening the intermolecular forces between them - doesn’t take part in the free radical polymerisation reaction

Disadvantages of RT cured soft lining materials:
How much plasticiser should a soft lining material contain?
how does this impact the effectiveness of the soft lining material?
What is a disadvantage of a type of plasticier and is being replaced by another type?
a soft lining material should contain as little plasticiser as it tends to leach out in the oral fluids
with time, the material hardens
little amount - limits the life of the soft lining material
biocompatibility of phthalate based plasticisers
many products now contain citrate-based plasticisers instead
What are temporary crowns and why are they used?
where are they made?
Temporary crowns are used to protect the tooth after being prepared for a permanent crown
they perform the functions of a natural tooth
it can take several weeks before permanent crowns are put in place
they are made at the chair side and placed on the prepared tooth while the permanent crown is made by a technician in the lab
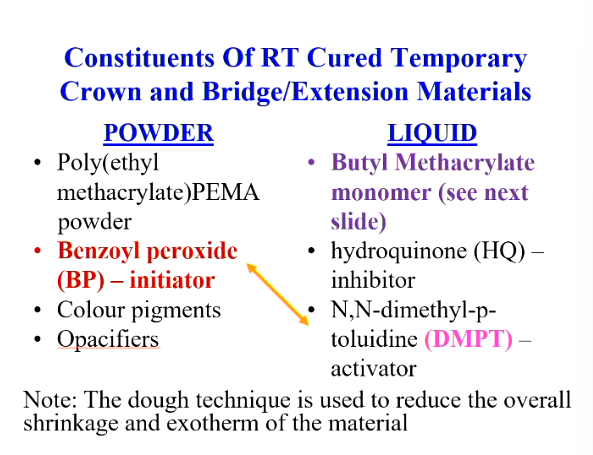
What is the powder and liquid composition of RT cured temporary crown and bridge/extension materials
Powder:
PEMA
BP - initiator
colour pigments
opacifiers
Liquid:
Butyl methacrylate
HQ - inhibitor
DMPT - activator
(no plasticisers or cross linking agent)
dough technique is still used
Not heat cured so temporary - so has to be replaced by a permanent crown
The butyl methacrylate can be 2 forms?
n-butyl methacrylate - straight chain
Iso-butyl methacrylate - higher Tg
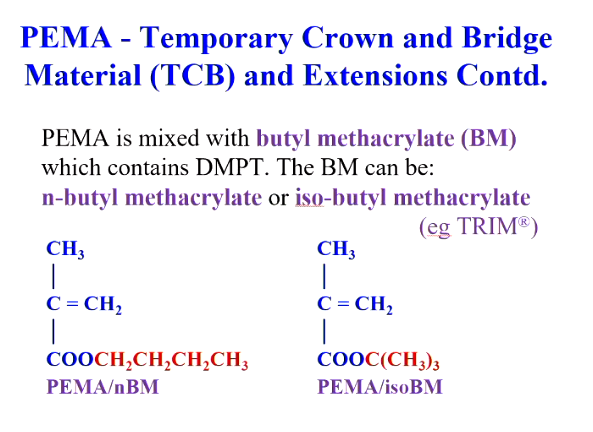
What are the monomers in TCBs for PEMA and PMMA?
PEMA - mixed with BM
PMMA - mixed with MMA
Advantages of PEMA/BM compared to PMMA/MMA TCBs? (5)
lower exotherm than PMMA/MMA : less heat - more comfortable for patient when setting in their mouth
Much less pulpal and soft tissue irritancy from residual monomer
Good handling properties
Not brittle, a ductile material - PMMA/MMA is a brittle material
BM a non-volatile monomer, MMA is a volatile monomer
volatile - you could tell from the smell far away
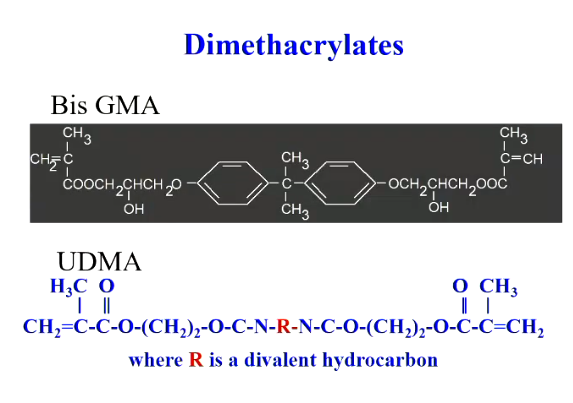
What are especial acrylic resins - how are they cured and what do they contain?
dimethacrylates
light cured or room temperature cured resins (remember - 2mm curing depth)
What are 3 uses of these special acrylic resins?
composite filling material
temporary crown and bridge material
fissure sealant
What are 2 examples of dimethacrylates that can be used?
2 other things that may be included in the formulation of special acrylic resins?
Bis GMA or urethan dimethacrylate
Pigments
Agents for light cure/RT (CQ)
What are some properties of special acrylic resins? (30
high modulus
low exotherm
adequate polymerisation shrinkage
how are the light or RT cured dimethacrylates for TCBs dispensed and what are the 3 main components?
Delivery gun not powder and liquid, cartridge and mixing tip - One paste
Dimethacrylate
filler - amorphous silica that is silane treated with
(similar to composite formulation)

What are the constituents of special acrylic resins (6)
bis GMA/urethan dimethacrylate
diluents (viscosity of materail)
fillers - silane coated
pigments
camphorquinone - light activated
DMPT
-one paste-
What are dimethacrylates?
They have 2 methacrylate groups - hydrophobic
What type of liquid is HEMA?
bifunctional (hydrophobic and hydrophilic end) and has low viscosity liquid
hydroxyethyl methacrylate
(dissolved in a solvent and used in primer to adhere composite to dentine)
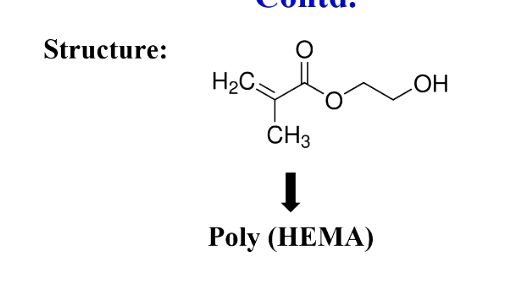
When it polymerises what does it form in the dry state?
hard resin in the dry state
In water?
it becomes a soft and rubbery hydrogel
it absorbs 10-100% of water
What are its (HEMA) uses? (2, unsuccessful in?)
unsuccessful as a soft liner material
RMGIC’s and dentine bonding agents
What are cyanoacrylates?
how fast do they polymerise and why?
how was it used? (2)
Uses in dentistry? (2)
general adhesive
polymerises very quickly at body temperature - absence of inhibitor
non-suture wound repair material, pre-fabricated surgical implants or prostheses
Perio surgery
adhesive for dentine - bonds to collagen, endodontic cements
What happens to the cyanoacrylate monomer for polymerisation reaction?
In presence of moisture (blood), the monomer polymerises to form a poly(cyanoacrylate)
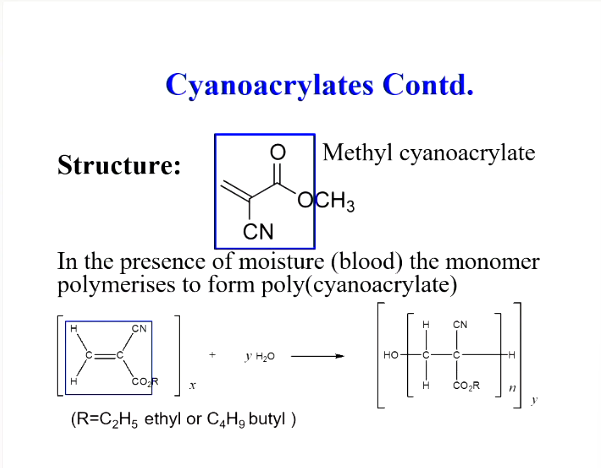
Medical grades of cyanoacrylates include 2 ?
butyl and octyl cyanoacrylates
what are some adv for tissue adhesion used for wound closure of cyanoacrylates? (3)
stop bleeding
waterproof
prevents bacteria from entering wound
when is full strength achieved?
within 24 hours,
What 2 thing fasten the cure?
the higher the humidity
thinner the bond-line
Different acrylates in dentistry?
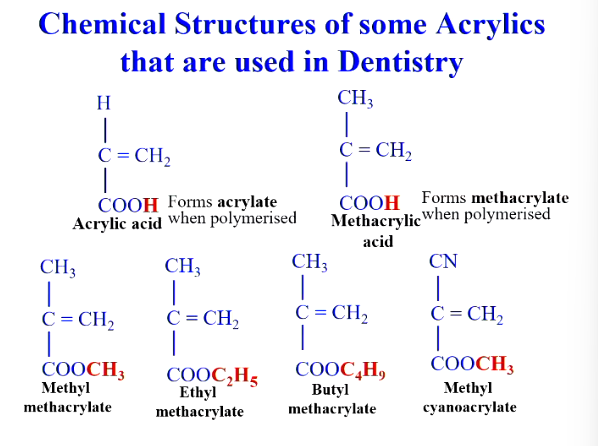
which has much more improved physico-mechanical properties? (HC/RT/LT)
HC will have more improved physico-mechanical properties
the amount of monomer released depends on what?
depends on the method of curing - LC and RT result in more residuals
remember:
be specific
