Kinesiology Lecture Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:43 PM on 5/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards
What is the mediastinum
The center of the lungs where a bunch of structures come together including heart, trachea, and esophagus - there are 2 surfaces which face one another
2
New cards
What is the visceral pleura
The lining of the lungs
3
New cards
What is the parietal pleura
The lining of the thoracic cavity
4
New cards
Purpose of pleura in the thoracic cavity
Allow movement and sliding with breath, protection of thoracic and abdominal organs, resist negative pressures and allow recoil of lungs, provide attachment for muscles involved in inhalation, support weight of UE
5
New cards
What can occur with too much fluid in between the cavities of the lungs
Lung collapse - lung tap can prevent this
6
New cards
What is the fluid in between the cavities of the lungs called
Serous fluid
7
New cards
How many lobes in the L lung?
2
8
New cards
How many lobes in the R lung
3
9
New cards
Intrathoracic volume is ________ to intrathoracic pressure
Inversely proportional
10
New cards
Ribs move in 2 kinds of motion:
Bucket handle and pump handle
11
New cards
Origin of diaphragm
Lumbar vertebrae, sternum, costal cartalige
12
New cards
Insertion of diaphragm
Aponeurosis in the center
13
New cards
Innervation of diaphragm
Phrenic nerve
14
New cards
Movements of diaphragm
Dome-like when resting (exhale) and flattens engaged (inhale)
15
New cards
What is an incentive spirometer
A tool that has a bobber which goes up when a person sucks in - used after a person is on anesthesia
16
New cards
What does an incentive spirometer prevent
Infection of the lungs (pneumonia)
17
New cards
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Pinching of the brachial plexus between the ribs and clavicle which impairs UE function
18
New cards
Cardiac output
The volume of blood pumped thru the body per minute
19
New cards
What makes the lub sound?
Closure of tricuspid and mitral valves
20
New cards
What makes the dub sound?
Closure of aortic and pulmonary valves
21
New cards
Chordae tendonae
The chords that make up the “heart strings” of mitral and tricuspid valves
22
New cards
Pericardium
Membrane enclosing the heart
23
New cards
Which quadrant is the liver in
RUQ
24
New cards
Which quadrant is the appendix in
RLQ
25
New cards
Which quadrant is the spleen in
LUQ
26
New cards
Which quadrant is the tail of the pancreas in
RUQ
27
New cards
Which quadrant has the descending colon
LLQ
28
New cards
Parietal perineum
Covers the organs in the abdominal cavity
29
New cards
Mesentary
Anchors down and provides blood supply to the intestines
30
New cards
Omentum
Adipose on the organs in the abdominal cavity
31
New cards
Three parts of small intestines in order
Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
32
New cards
Compartments of the lower leg
Anterior, posterior, lateral
33
New cards
Anterior compartment LL movements
Dorsiflexion and extension of toes
34
New cards
Anterior compartment innervation
Common fibular nerve
35
New cards
Posterior compartment LL movements
Plantar flexion and toe flexion
36
New cards
Posterior compartment innervation
Tibial nerve
37
New cards
Lateral compartment movements
Eversion
38
New cards
Lateral compartment innervation
Common fibular
39
New cards
Interosseus membrane purpose
Hold together tibia and fibular and transfers 10% of weight to fibula
40
New cards
Open packed ankle position
Plantar flexion
41
New cards
Closed packed ankle position
Dorsiflexion
42
New cards
Hindfoot
The tarsals
43
New cards
Forefoot
Anything more distal than the tarsals
44
New cards
How many tarsals
7
45
New cards
How many metatarsals
5
46
New cards
How many phalanges
14
47
New cards
Names of the tarsal bones
Talus, Calcaneus, Navicular, Cuboid, Medial, Lateral, and intermediate cuneforms
48
New cards
TBW on the ankle joint in a unilateral stance
4x TBW
49
New cards
Dorsiflexion/plantarflexion plane and axis
Sagittal plane, frontal axis
50
New cards
Abduction/adduction of the ankle plane and axis
Transverse plane, vertical axis
51
New cards
Inversion/eversion plane and axis
Frontal plane, sagittal axis
52
New cards
Supination of the ankle in open chain
Plantar flexion, adduction, inversion
53
New cards
Pronation of the ankle in open chain
Dorsiflexion, abduction, eversion
54
New cards
Supination of the ankle in closed chain
Dorsiflexion, abduction, inversion
55
New cards
Pronation of the ankle in closed chain
Plantar flexion, adduction, eversion
56
New cards
How many types of joints are in the ankle
8
57
New cards
Superior tibiofibular joint
Synovial plane joint which allows gliding
58
New cards
Inferior tibiofibular joint
Contributes to the mortar joint of the ankle
59
New cards
Anterior and posterior joints of the tibiofibular joints
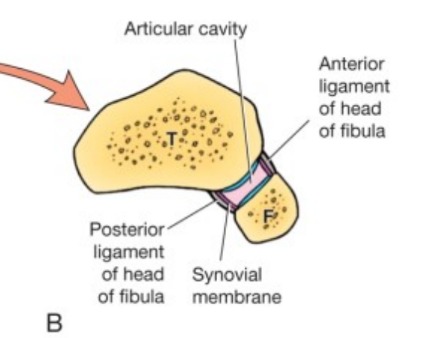
60
New cards
Inferior transverse ligament
61
New cards
Why is the open packed position of the ankle plantar flexion
Talus is narrower anteriorly, meaning less congruency with tibia/fibula
62
New cards
Only mortis joint in the whole body
Talocrural joint
63
New cards
Are there more ligaments medially or laterally on the ankle
Medially
64
New cards
Purpose of medial ligaments in the foot
Support the arch
65
New cards
Injuries are more common: medially or laterally
Medially
66
New cards
Why are trampolines dangerous for ankles
Changes ground reaction forces
67
New cards
Talus is convex or concave
Concave
68
New cards
Calcaneus is convex or concave
Convex
69
New cards
Motion of talocrural joint
Dorsi and plantar flexion
70
New cards
Motion of subtalar joint
Inversion/eversion
71
New cards
Open chain ankle is designed for
Mobility
72
New cards
Closed chain ankle is designed for
Stability
73
New cards
Dorsiflexion prime movers
Tibialis anterior
74
New cards
Plantar flexion prime movers
Gastrocnemius and soleus
75
New cards
Inversion prime movers
Tibialis posterior
76
New cards
Eversion prime movers
Fibularis brevis and fibularis longus
77
New cards
Muscles contributing to arch of foot
Tibialis posterior, flexor hallicus longus, flexor digitorum longus
78
New cards
Order of deep muscles in the calf (medially to laterally)
Flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior, flexor hallicus longus
79
New cards
FDL, tibialis posterior, and FHL passes by which structure
Medial malleus
80
New cards
Order of deep calf muscles past the medial malleus
Tibialis posterior, Flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallicus longus
81
New cards
Purpose of Tom, Dick and Harry (motion)
Inversion and plantar flexion
82
New cards
How do fibularis longus and brevis assist with the arch
Anchor the first digit to the ground
83
New cards
Bursae purpose
Allows for sliding and gliding
84
New cards
Extensor retinaculum purpose
Prevents bowstringing by holding tendons in place
85
New cards
If common fibular nerve was severed what motions couldn’t occur?
Eversion or dorsiflexion
86
New cards
Dorsal pedal pulse
Pulse in the ankle
87
New cards
Medial longitudinal arch of foot
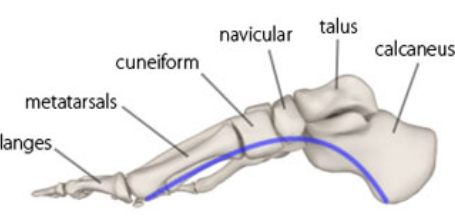
88
New cards
Lateral longitudinal arch of foot
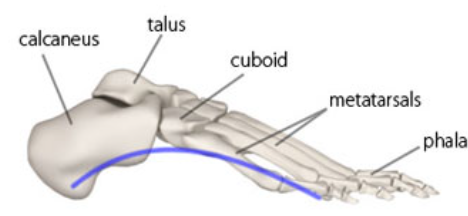
89
New cards
Transverse arch of foot
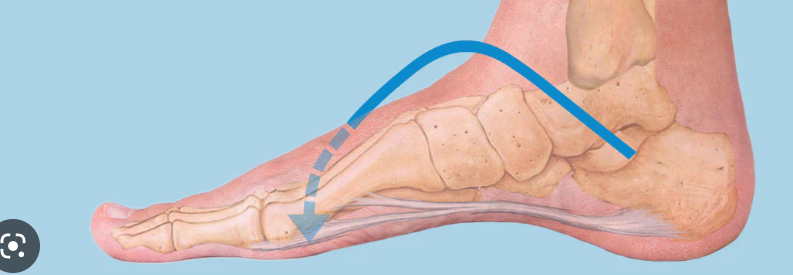
90
New cards
Purpose of arches of the foot
Disperse gravity throughout the foot and help with propulsion like an elastic
91
New cards
Windlass Mechanism
The spring system that the plantar fascia creates which assists with propulsion
92
New cards
When is tension the highest in the Windlass Mechanism
When the toes are extended - preswing
93
New cards
What class lever is the ankle joint
Second class lever (only one in the body)
94
New cards
Purpose of plantar flexors in heel off phase
Eccentric contraction
95
New cards
Pes Planus
Weak tibialis anterior causes low arch
96
New cards
Hallux valgus
Bunion
97
New cards
Pes Cavus
Overly high medial longitudinal arch
98
New cards
Spastic plantar flexors
Toe walk
99
New cards
Locomotion
Moving from one place to another
100
New cards
Ambulation
Type of locomotion used clinically