Chemistry: Organic Chl
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What does phenol not react with?
Na2CO3
Reagent for amine to ammonium chloride salt
HCl(aq)
Reagent for ammonium chloride salt to amine
NaOH(aq)
R+C: amide (NO2) → amine (NH2)
1) Tin (Sn) and conc HCl, heat under reflux (forms ammonium salt)
2) Neutralise with NaOH(aq)
Formation of electrophile in nitration of benzene
HNO3+ H2SO4→ NO2++HSO4-+H2O
End point observation for titration with iodine
Starch indicator causes colour change from blue/black to colourless
R+C: Haloalkane → Amine
Excess ethanolic NH3
R+C: Haloalkane → Nitrile
Ethanolic NaCN/KCN
Acid anhydride + primary alcohol (inc. phenol) →
Ester + Carboxylic acid
Acid anhydride + COOH →
R+C: Carboxylic acid → Acyl chloride
SOCl2
R+C: Acyl chloride → Carboxylic acid
H2O
What happens when acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides react in hydrous conditions?
Forms carboxylic acids
R+C: Carboxylic acid → haloalkane
NaBr(aq)
Acyl chloride + (2NH3)/Amide →
Amide + ammonium salt (HCl+NH3→NH4Cl for 2NH3)
-OH directing effect
2,4- directing (electron donating group)
-NH2 directing effect
2,4- directing (electron donating group)
-NO2 directing effect
3- directing (electron withdrawing group)
What is the use of CDCl3?
Use as a solvent that won’t affect the spectrum to dissolve solids
What is the use of D2O?
Will remove -OH and -NH peaks as H is exchanged for deuterium
What is the use of tetramethylsilane, (CH3)4Si?
To provide a reference peak
How does gas chromatography work?
Stationary phase: liquid adsorbed on inert solid/ solid on solid support
Mobile phase: gas
Retention time depends on:
high boiling point (longer RT)
greater solubility in liquid phase (longer RT)
In summary the more affinity a substance has for the liquid or solid in the stationary phase, the longer the retention time and higher peak on mass spec.
Radical substitution mechanism to show Cl* catalysing breakdown of ozone
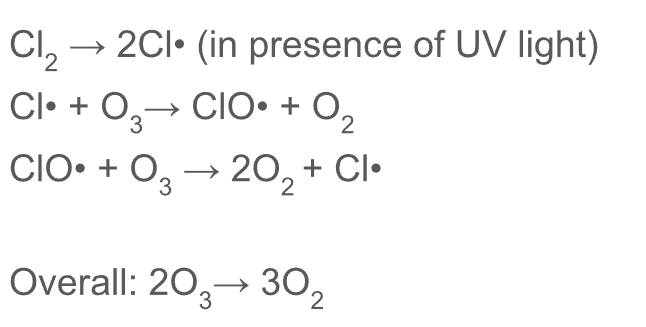
Radical substitution mechanism to show how nitrogen monoxide radicals catalyse breakdown of ozone
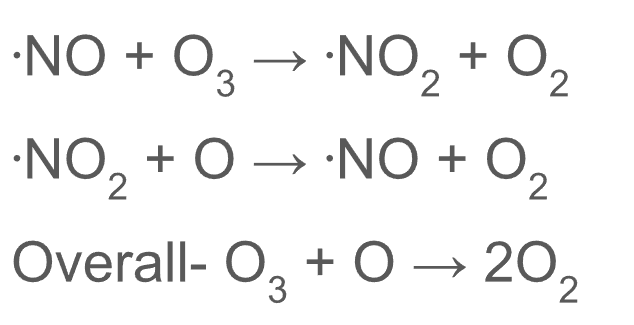
Trend in reactivity of haloalkanes
Bond enthalpy decreases down the table as carbon-halogen bond strength decreases. This means iodoalkanes are the most reactive (least energy needed to break bond)
Effect of infrared radiation on covalent bonds
Cause them to absorb energy and vibrate more
Why are alkanes unreactive?
They have a high bond enthalpy and low polarity of sigma bonds
R+C: Nitrobenzene → phenylamine
Sn, conc HCl, reflux
R+C+M: Aldehyde/Ketone → Hydroxynitrile
NaCN, H2SO4, nucleophilic addition
R+C: Benzene → nitrobenzene
Conc HNO3, conc H2SO4, heat 50-55 degrees C
R+C: Benzene → Alkylbenzene
Haloalkane, AlCl3 catalyst, reflux
Where do curly arrows go from?
Centre of covalent bond
Lone pair
Delocalised Pi system in benzene
Are balancing numbers included in atom economy?
YES
Limitations of radical substitution
waste products in termination
further substitution may occur
substitution can occur anywhere on the chain to form structural isomers
Dipoles in C-Halogen bond
Halogen has negative dipole as is more electronegative than carbon
Test to measure the rate of hydrolysis of haloalkane
Add AgNO3 to haloalkane
Time taken to form AgX precipitate
Rate is 1/time
Describe trend down group of rate of hydrolysis of haloalkane
Rate increases down the group (iodoalkanes hydrolysed faster than chloroalkanes)
C-I bond is weakest as difference in electronegativity is smallest
Initiation and propagation steps of CFCs breaking down ozone

Why is the breakdown of ozone by CFCs bad for humans?
O3 + O → 2O2 (catalysed by chlorine radicals)
This is irreversible so ozone cannot reform. Less ozone means more UV penetrates and causes skin cancer
Why is benzene less reactive than alkenes?
In benzene there are 6 delocalised electrons and there are 2 localised in alkenes
The alkene double bond is more electron dense than pi-system
Benzene is less able to polarise electrophiles so less susceptible to attack
Test for phenol
Br2 (aq) is decolourised (orange to colourless) and white precipitate is formed
Why does phenol not react with sodium carbonate?
Too weak of an acid to react with weak bases
R+C: Phenol → nitrophenol
Dilute HNO3, no catalyst required, RTP
How many moles of reducing agent [H] are needed to reduce aldehyde or ketone to alcohol?
2 [H] (no H2O)
How are short chain carboxylic acids more soluble in water?
Able to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
Acyl chloride + NH3 →
Primary amide + HCl
Acyl chloride + primary amine →
secondary amide + HCl
Acyl chloride + secondary amine →
tertiary amide + HCl
Acyl chlorides + phenol →
phenyl ester + HCl (g)
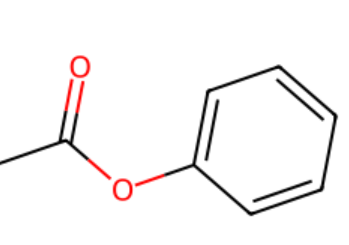
How do amines act as bases?
Can accept H+ ions using lone pair on N forming a dative covalent bond to form an ammonium salt
Equation for reduction of NO2 to NH2
NO2 + 6[H] → NH2 + 2H2O
Equation for reduction of nitriles to amines
CN + 2H2 → CH2NH2 (2 moles of H2 needed)
Which amino acid does not show optical isomerism?
Glycine (H for R-group)
Calculating the number of optical isomers in a molecule
2n where n is the number of chiral carbons
In which reactions are HCN or NaCN/KCN used?
NaCN and H2SO4 however HCN is made in situ is used in both carbonyls and haloalkanes (ethanolic) to nitriles
Products of acid hydrolysis of polyester
Carboxylic acid and alcohol
Products of acid hydrolysis of polyamide
Carboxylic acid and protonated amine
Products of alkaline hydrolysis of polyester
Carboxylate salt and alcohol
Products of alkaline hydrolysis of polyamide
Amine and carboxylate salt
Why are condensation polymers better for the environment than addition polymers?
Condensation polymers can be hydrolysed so are biodegradable, whereas addition polymers are not
Solutions to non-biodegradable addition polymers
developing photodegradable polymers
can be converted to monomers and used as chemical feedstock
can be combusted for energy use (not if chlorine present as HCl (g) is toxic)
How to obtain pure dry liquid from organic synthesis
If acid used then neutralise with Na2CO3 (aq) and release gas from tap of separating funnel
separate layers according to density
add drying agent e.g. MgSO4 to remove any aqueous
redistill and collect fraction at boiling point
Obtain a pure dry solid from organic synthesis
recrystallise by dissolving crystals in the minimum volume of hot solvent
allow to cool and crystals to form
filter under reduced pressure
wash and allow crystals to dry
If there is a liquid that needs testing for purity by chromatography, what method would be used and explain how it works
Gas chromatography is used and solubility is measured by relative solubility in mobile phase. The retention time is the time from injection to detection. Compare retention time to known value
What does the area under the peak for gas chromatography indictate?
Area is proportional to amount of components in the sample. Relative proportions are measured by dividing area under peak by total area under all peaks.
What charge do fragment ions have in mass spectroscopy
1+
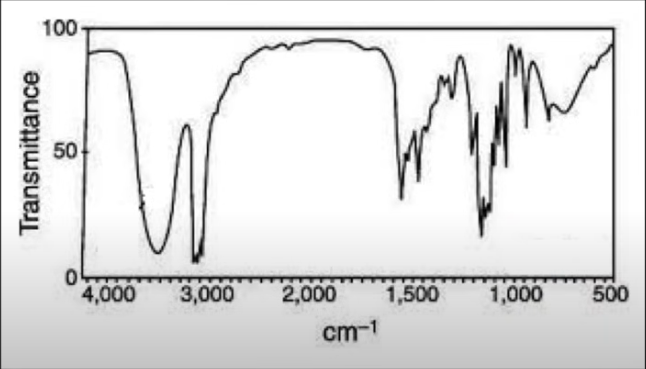
What molecule is this?
Carboxylic acid
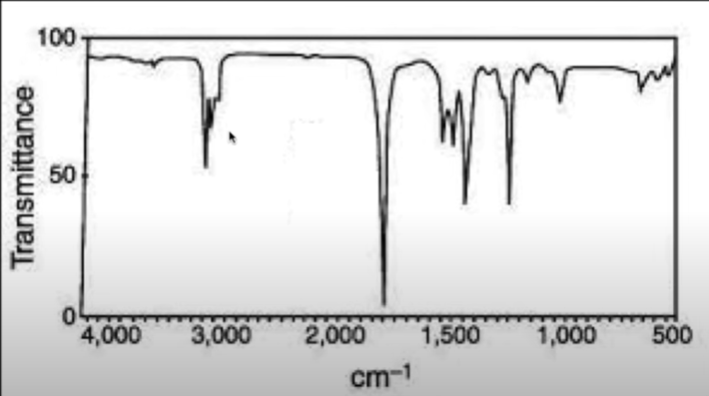
What molecule is this?
Alcohol
What molecule is this?
Aldehyde/ketone/ester
What does RPA 4 mean on aromatic peak on H-NMR spectroscopy
The benzene ring is disubstituted
R+C: Alkane → Haloalkane
Halogen , UV light, radical substitution
R+C: Alcohol → Haloalkane
NaOH, H2SO4, heat
R+C: Nitrile → carboxylic acid
HCl (aq), heat
R+C: Alkylation of benzene
CH3Cl, AlCl3