PLTW PBS Principles of Biomedical Science WCHS Mrs. McCormick End of the Year WebXam
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Definition of standard operating procedure (SOP)
A detailed written set of instructions that outlines how to perform a specific task or process consistently and safely
Why are SOP’s important in schools, business, industry, etc.
SOP’s ensure that tasks are performed uniformly each time, leading to consistent and reliable results
Hazardous
Risky, dangerous
Environmental hazard
A substance or condition that has the potential to harm the natural environment
Physical hazard
Has potential to cause harm or injury
Health hazard
Has potential to cause harm or injury to someone’s health
Precaution
A measure taken to prevent something dangerous
Pictogram
A pictorial symbol for a word or phrase
What is an SDS (or sometimes known as an MSDS)?
A detailed document that provides information about the hazards of a chemical product and instructions for its safe handling, storage, and disposal
What is a flashpoint?
The minimum temperature at which a vapor can ignite when exposed to an external heat source
What is the role of the NFPA?
They prevent injury, death, a property damage from fire
How would you neutralize an acid?
By using a base
How would you neutralize a base?
By adding an acid
What does caustic mean?
Caustic refers to substances that are able to burn, wear away, or destroy living tissue
Why would you want to monitor and regulate the environmental conditions in a facility?
To keep yourself healthy and safe, and to ensure the quality of the product
Why is it important for employees to maintain and perform diagnostic testing on equipment?
To protect employees and allow the work environment to remain safe
Dermal sensitizer
Can cause an allergic reactions on the skin after exposed
Environmental toxicity
Can cause harm to the environment, specifically aquatic life
Carcinogen
Can cause cancer
Respiratory sensitizer
Can cause allergy, asthma symptoms, or breathing difficulties
Reproductive toxin
Can affect sexual function and fertility in males or females
Gases under pressure
Gases are contained in a container of 200 kPa or 29 psi
Oxidizer
Can cause or intensify fire; promotes combustion and increases burning
Emits flammable gas
Produces flammable gas when in contact with water
Acute toxicity
Harmful effects that can result from exposure to substance
Corrosives
Can cause irreversible damage to living tissue
Why is it important for employees to maintain equipment logs?
To keep employees safe and allow everything to run efficiently
Why is it important for employees to schedule preventative maintenance?
To allow equipment to be used longer and it improves safety and efficiency
Why is it important for employees to keep a well labeled chemical inventory?
So employees can know the hazards of chemicals and to allow them to be stored safely
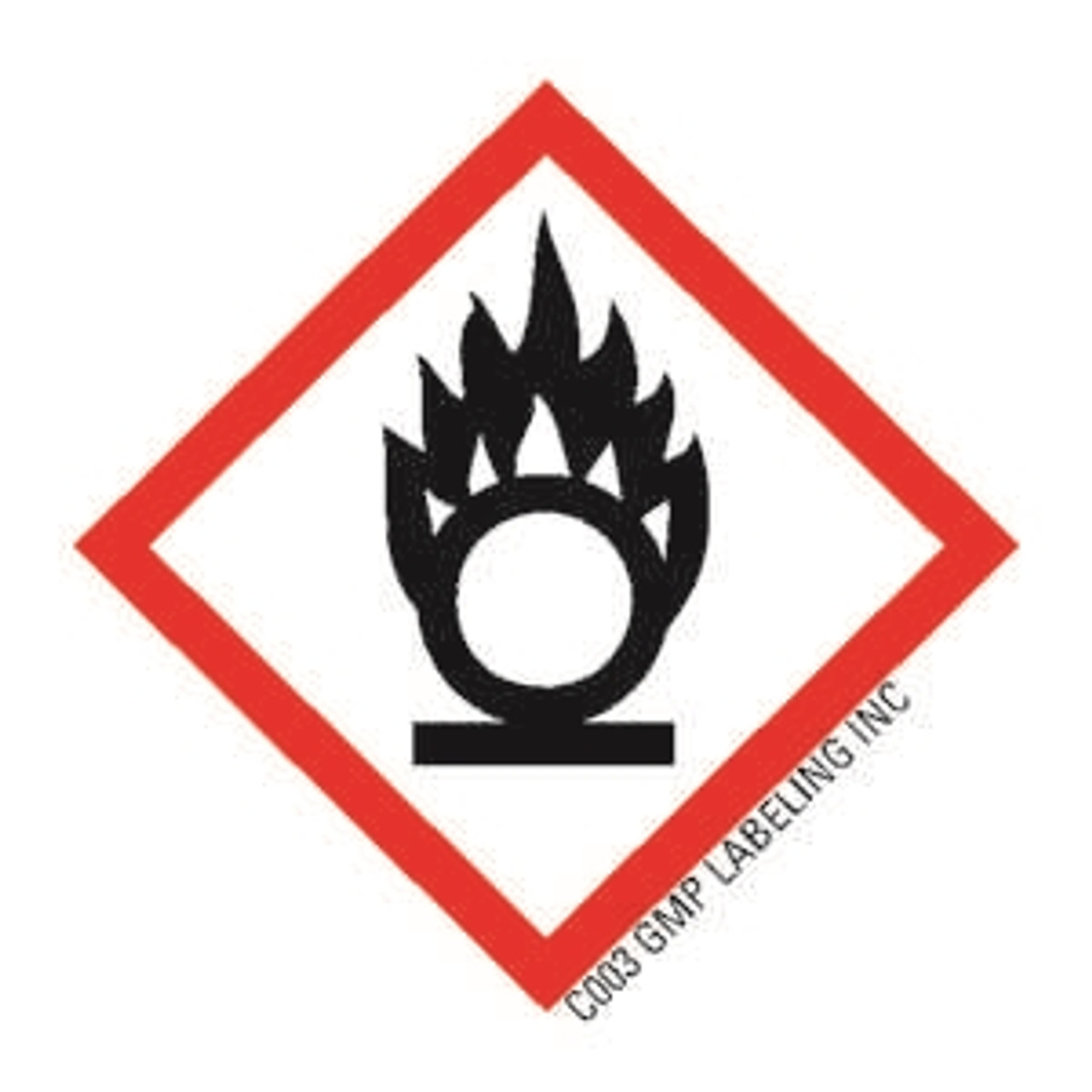

What GHS hazard class is this?
Oxidizer
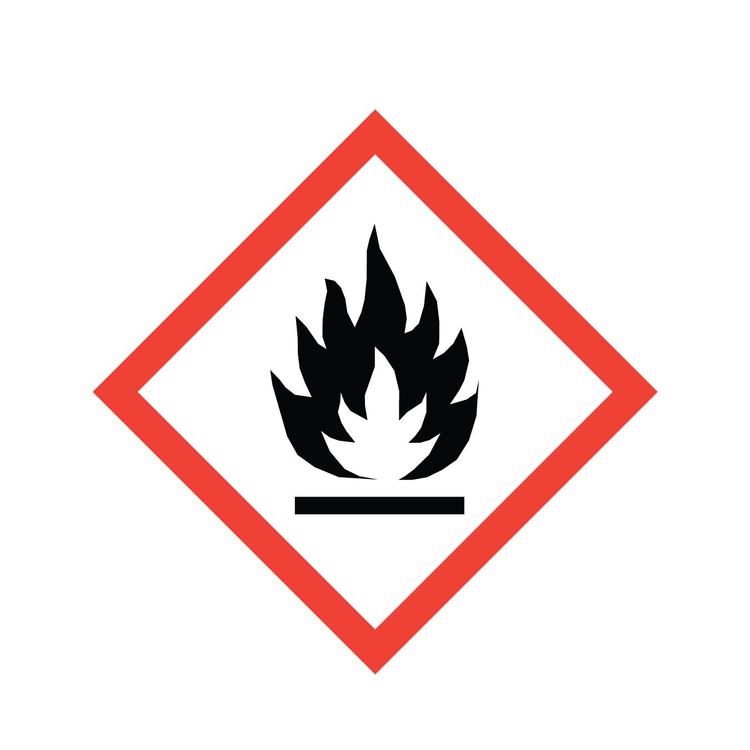

What GHS hazard class is this?
Flammable & emits flammable gas

What GHS hazard class is this?
Self reacts
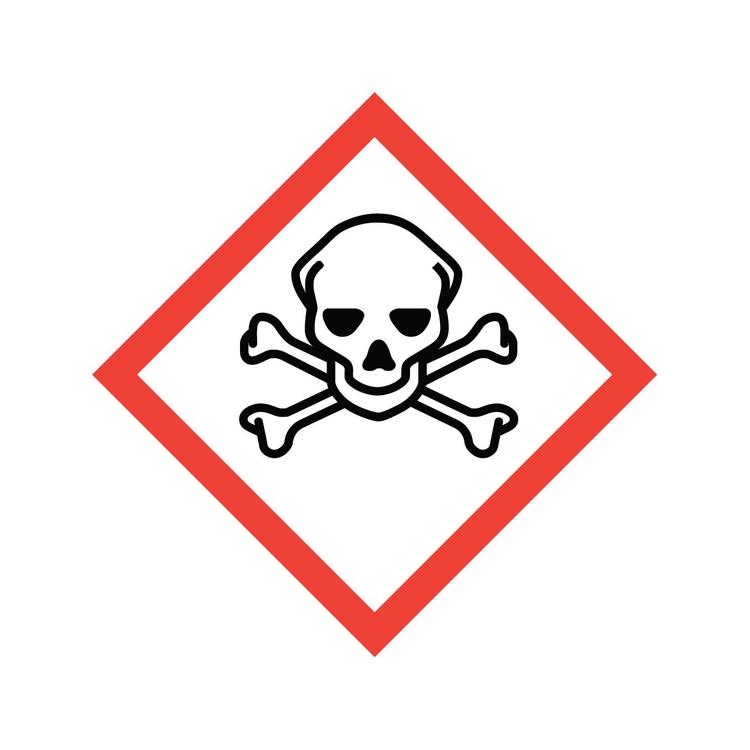

What GHS hazard class is this?
Acute toxicity
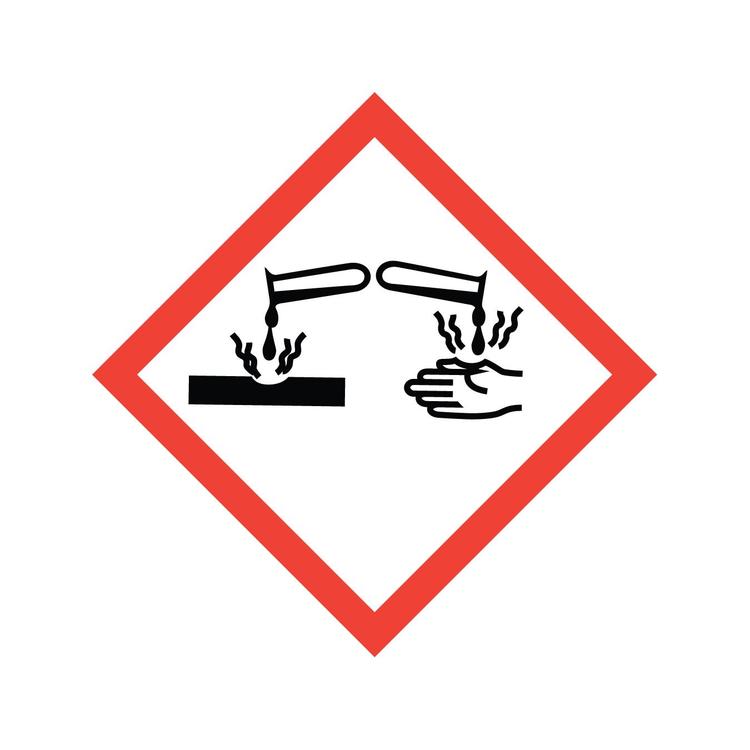
What GHS hazard class is this?
Corrosive
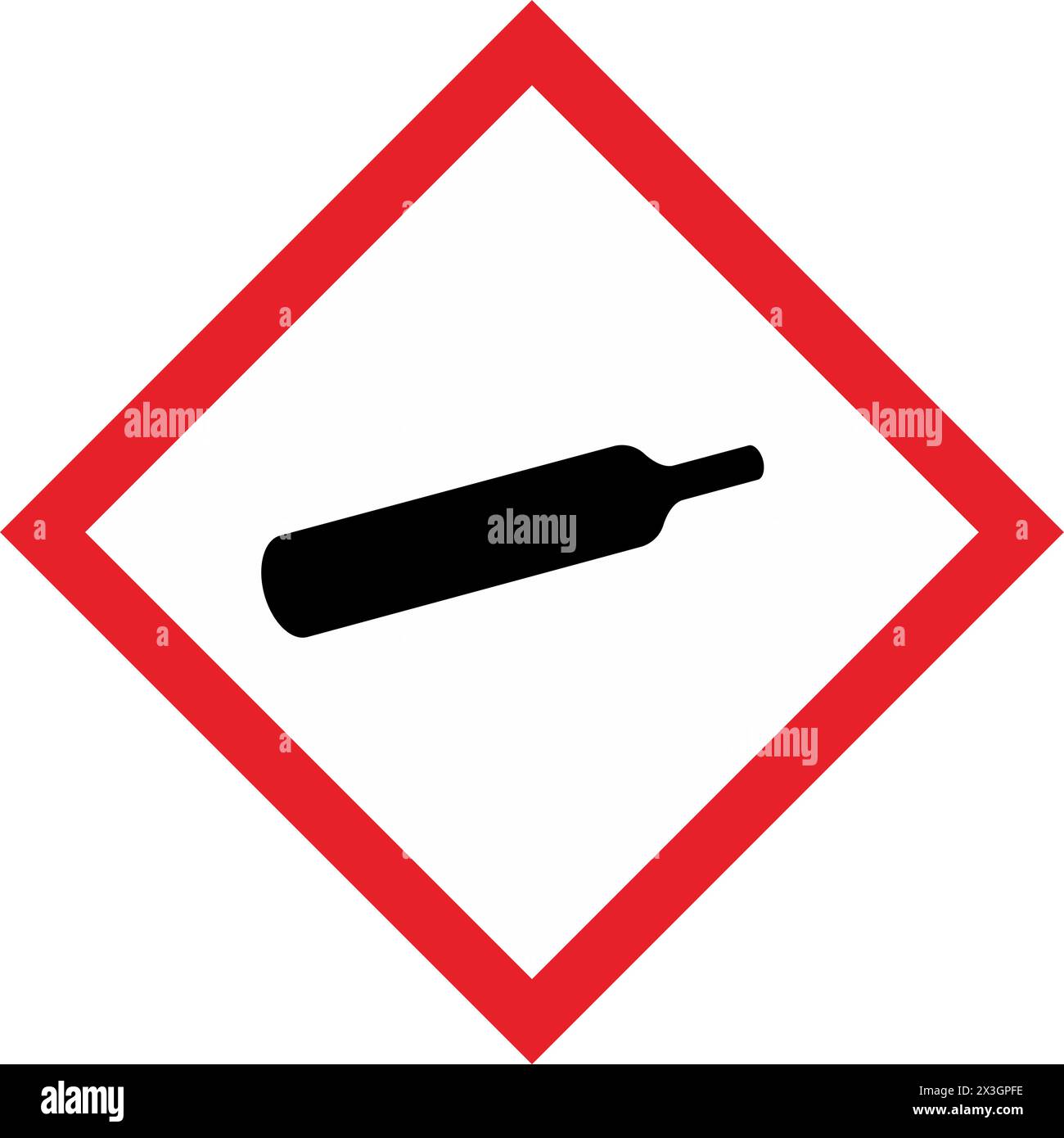

What GHS hazard class is this?
Gases under pressure
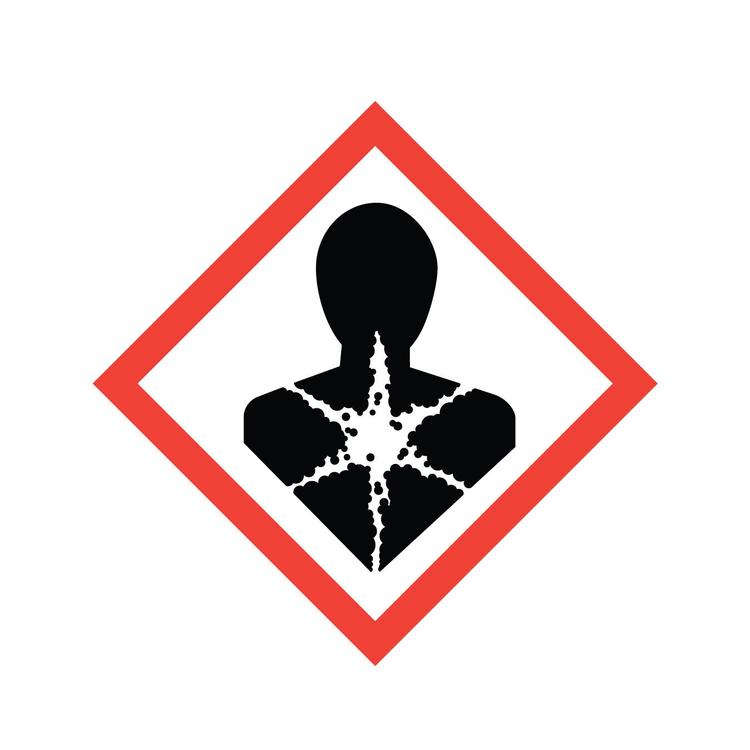

What GHS hazard class is this?
Carcinogen, respiratory sensitizer, & reproductive toxin
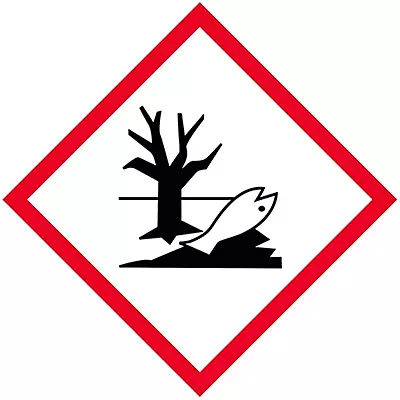

What GHS hazard class is this?
Environmental toxicity
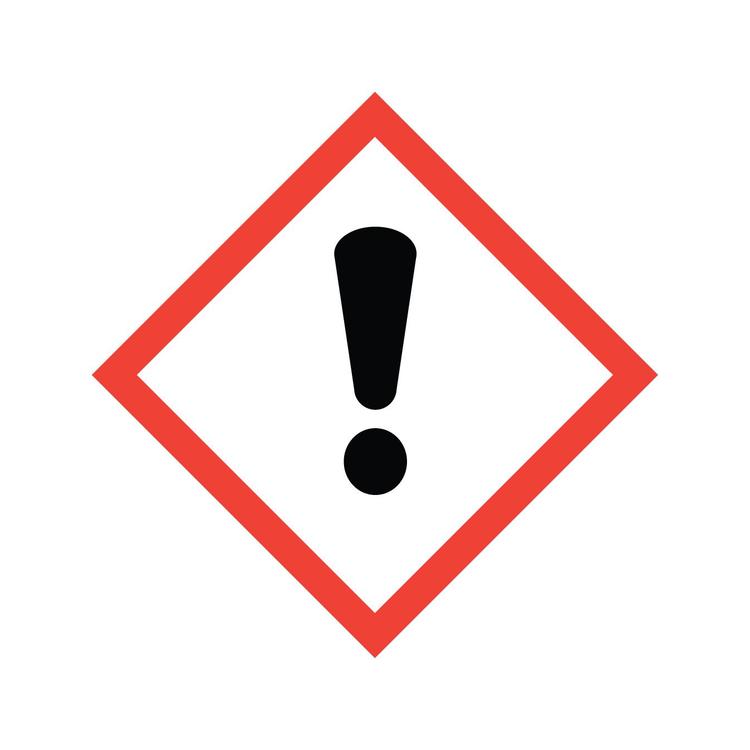

What GHS hazard class is this?
Dermal sensitizer & irritant
If caring for animals or specimen, why would it be necessary to isolate them?
To prevent the spread of diseases
If caring for animals or specimen, why would it be necessary to quarantine them?
To preventing diseases from entering the operation
If caring for animals or specimen, why would it be necessary to release them?
To allow them to thrive in their natural habitats
What is animal husbandry?
Controlled cultivation, management, and production of domestic animals, including improvement of the qualities considered desirable by humans by means of breeding
Why is aseptic technique important in labs and food processing?
To ensure that nothing gets contaminated, accurate research results, and to prevent foodborne illnesses
Pre-inoculation
Preparing tools and the environment and ensuring that they are sterile
Inoculation
Culture is introduced to the environment
Post-inoculation
Sterilize loop, seal culture container, and dispose of used materials
How is a Bunsen burner used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
Creates an upflow of air to minimize contamination
How is a wire loop used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
It is sterilized before and after each use
How is a cotton swab used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
Can clean or disinfect
How is an agar plate used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
Provides a sterile environment
How is an alcohol/disinfectant used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
Kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms
How is a biohazard bag used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
Contains hazardous materials so they stay there and don’t contaminate other areas
How is an autoclave used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
Sterilizes equipment and materials
How is PPE used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
Prevents the spread of microorganisms/ contamination
How is are culture tubes used to ensure aseptic technique and/or sterility?
Provides a contained and controlled environment
Scientific method
Systematic, logical process to test ideas
Lab objectives
What you are supposed to accomplish in the experiment
Trial group size
To study conditions and compare results
Validity
How accurate a method measures vs what it’s intended to
Sumarization of the 8 best laboratory notebook practices
Enter work in chronological order
Entries are legible and in permanent black or blue ink
Sign and date the bottom of the page as soon as its completed
Cross out errors using a single line and record correction with your initials
When referencing previous pages say “see page” or “go to”
Don’t abbreviate but create a key if used
Be precise and someone of the same skill should also be able to complete
Include discussion of sources of error
Best laboratory notebook practices NOTE
Don’t erase, write over, or white out any mistakes. They must remain legible
Laboratory notebook labels
Add meaningful title, numbered pages, all original pages intact, label figures and calculations, have a witness sign and date, add names of lab partners, if needed add a continued on, label and annotate sketches, and attach external items and describe them
Whenever you work with microorganisms, such as ________, you must use aseptic technique.
Bacteria
Aseptic technique ensures that you don’t introduce _____________ into a specimen and that you don't ______ infectious agents to _________ or _________ surfaces.
Contaminants, spread, yourself, laboratory
Standard guidelines summary
Wear PPE at all times, don’t bring food or drink, tie hair back, disinfect work surfaces before and after labs, wash hands before and after, never place a nonsterile loop in sample, and always hold caps of tubes on top of dishes during labs
Scientific method
Question or problem→ research→ hypothesis→ conduct an experiment→analyze your data→ report your results