Microbio lab practical
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Selective Media
Contains one or more ingredients that inhibit the growth of unwanted bacteria while encouraging the growth of desired ones
If a microorganism is resistant to an antibiotic like ampicillin or tetracycline, then it would be added to the medium to prevent other cells, which aren’t resistant, from growing
Example: 7% NaCl media is selective for gram-positive organisms
Media lacking histidine
MSA is selective for gram-positive, favoring cocci
Differential Media
Distinguishes one microorganism type from another growing on the same medium. Uses biochemical characteristics of a microorganism growing in the presence of specific nutrients/indicators added to the medium to visibly indicate the defining characteristics
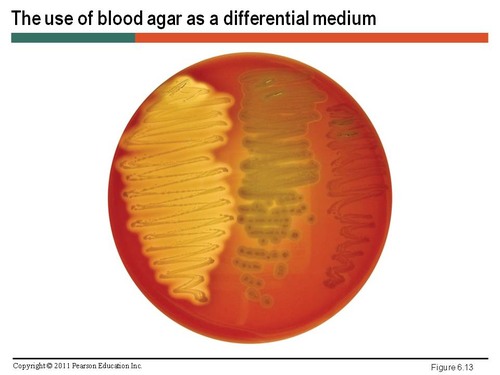
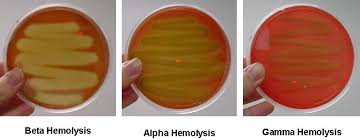
Examples: Blood agar plates (5% sheep blood)
Beta-hemolytic - Organisms that produce hemolysin and can completely digest RBCs
Alpha-hemolytic- Produce enzymes that partially digest RBCs, greenish colored growth
Both Differential and Selective Media
Glucose fermentation broth: Contains carbohydrates and an indicator, phenol red; if fermentation occurs, the media changes color
MacConkey media:
Bile salts - Inhibit the growth of gram-positive organisms and selects for gram-negative bacteria. [selective]
Lactose + neutral red dye - Colorless at pH 6.8, turns red at lower pH. If lactose fermentation occurs, colonies turn pink or red. [differential]
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA):
High salt concentration (7.5%) → Selective for gram-positive cocci like Staphylococcus
Mannitol + phenol red → fermentation turns the plate yellow, including pathogenic Staphylococcus species
Differentiates pathogenic from nonpathogenic strains
Eosin Methylene Blue:
Eosin Y + methylene blue dye - inhibits growth of gram-positive
Differentiates lactose fermenters from nonfermenters
Acid end products of lactose fermentation turns colonies black/dark purple (E.coli), less effective = pink/purple (Klebsiella, Enterobacter)
Biochemical Tests
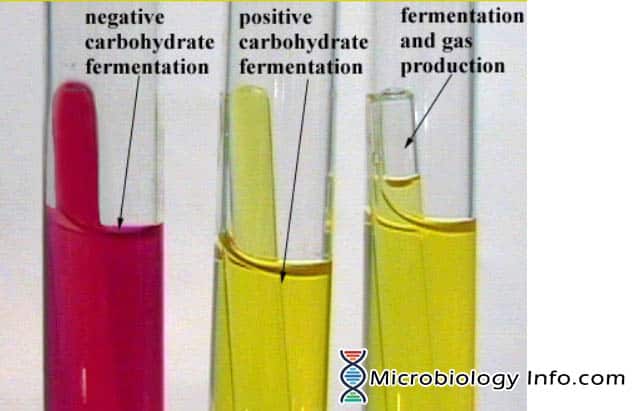
Fermentation of Carbohydrates
Anaerobic degradation of carbohydrates (glucose, lactose)
pH indicator - phenol red, red at pH 7, yellow when acidic
Production of acid indicates fermentation of carbohydrates
Deeper red = organism used protein (peptone) and made broth more alkaline
The Durham tube is used for collecting gas if produced

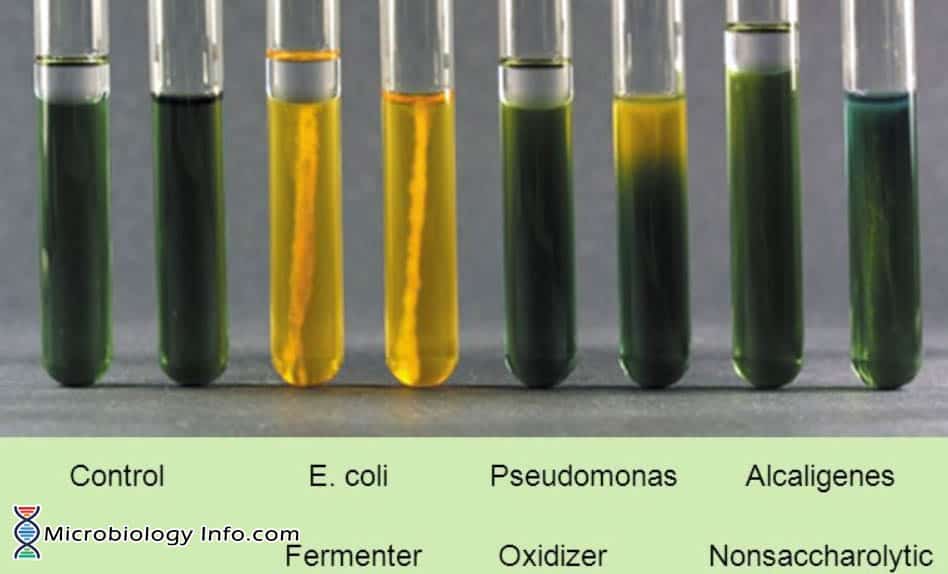
Oxidation-Fermentation Test (O-F test)
Detects acid byproducts of oxidative respiration (glucose breakdown via glycolysis and cellular respiration requiring oxygen as an ultimate electron acceptor)
Also indicates if sugar can be fermented (doesn’t require oxygen)
Bromothymol blue dye - green at pH 7.1, yellow at pH 6, blue at pH 7.6
IMViC Series
A series of tests that differentiate members of the Enterobacteriaceae family
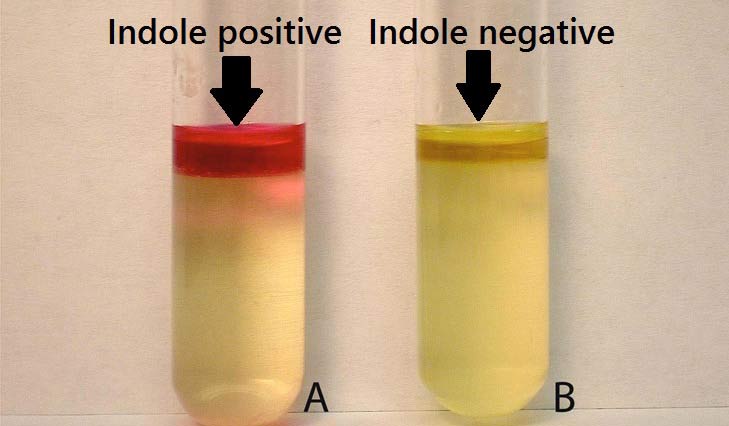
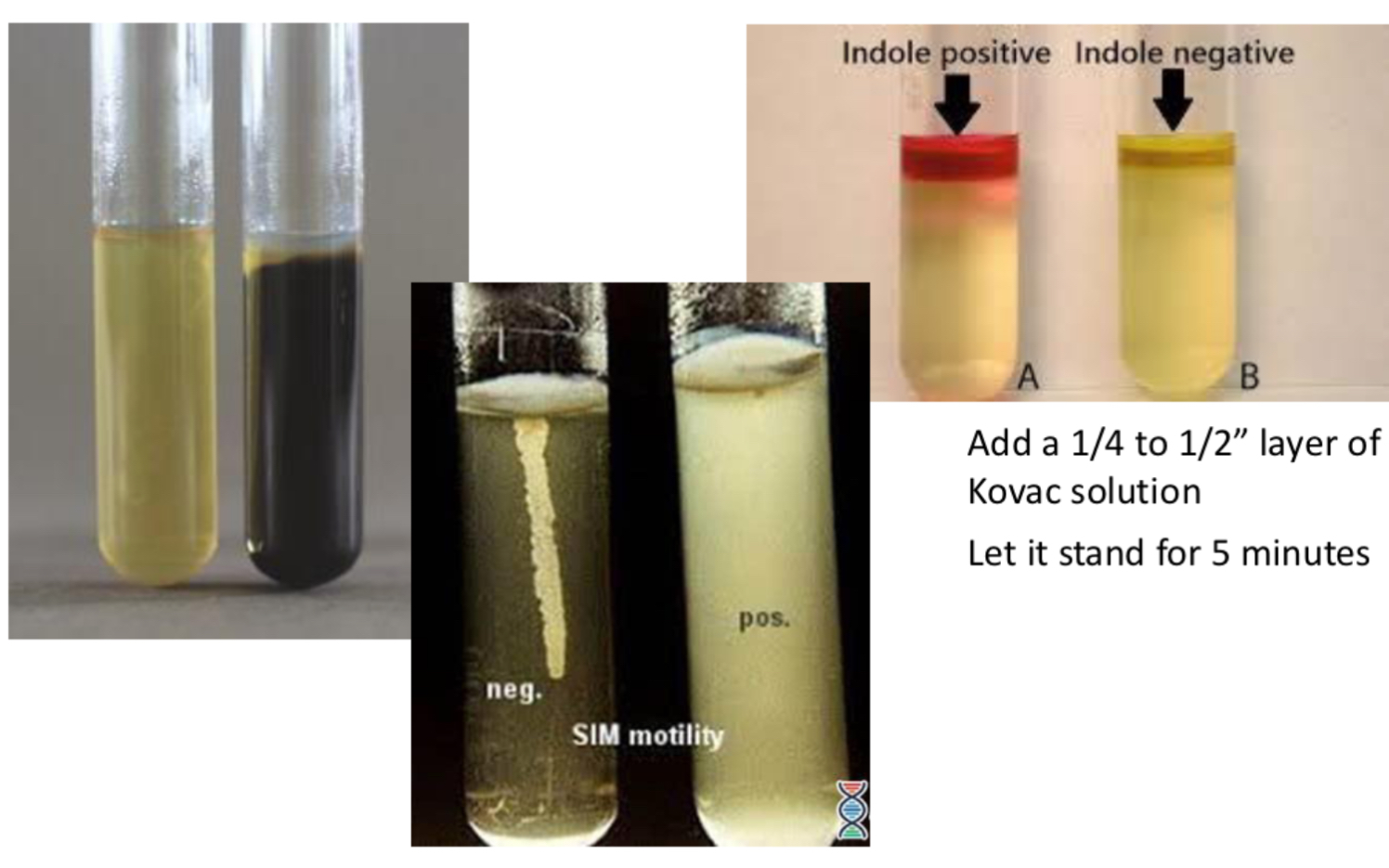
Indole test
MR/VP test
Citrate utilization test
Indole test
Determines the ability to ferment the amino acid tryptophan into indole, ammonia, and pyruvic acid
After incubation, add Kovac solution, let stand for 5 minutes
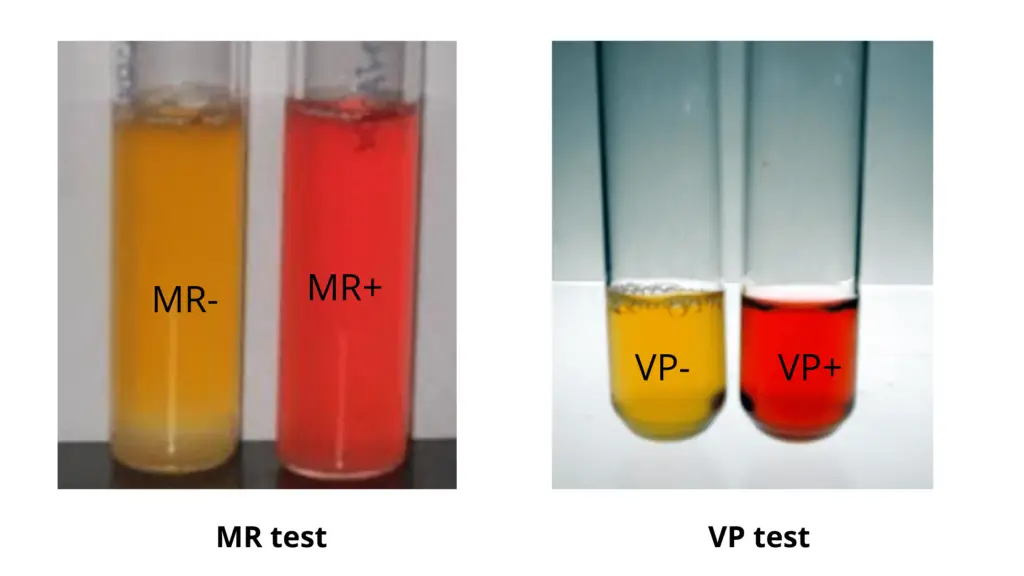
MR/VP Test
Methyl Red test and the Voges-Proskauer test → tests for end products of glucose metabolism
+ MR (Red) = Large production of acid from glucose metabolism
+ VP (Red) = Production of neutral substances like acetoin and alcohol from glucose metabolism
5 drops of methyl red,15 drops of VP reagent A, 5 drops of VP reagent B
1 hour wait
Citrate Utilization Test
Determines the ability of an organism to utilize citrate as a carbon source
Uses sodium citrate breaks down into → pyruvate
Also converts ammonium phosphate into → ammonia + ammonium hydroxide = increase in pH
Bromothymol blue dye becomes blue at higher pH (alkaline)

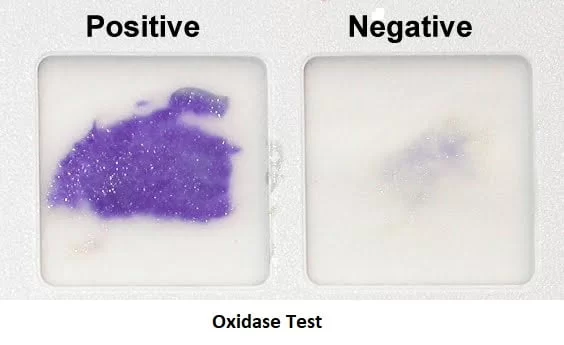
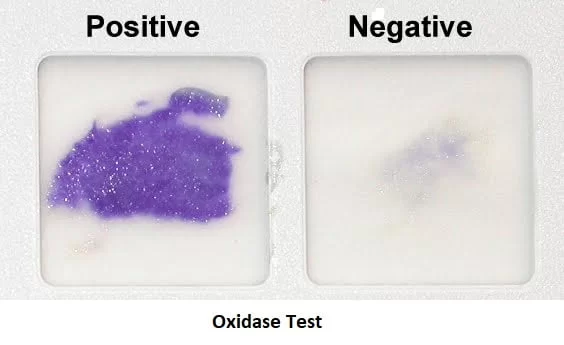
Oxidase Test
Tests for the presence of the oxidase enzyme, cytochrome C, an electron acceptor
Differentiates members of the Pseudomonadaceae and Enterobacteriaceae families
Chromogenic reducing agent, TMPD, when oxidized to cytochrome C, it turns blue
No cytochrome C = stays colorless
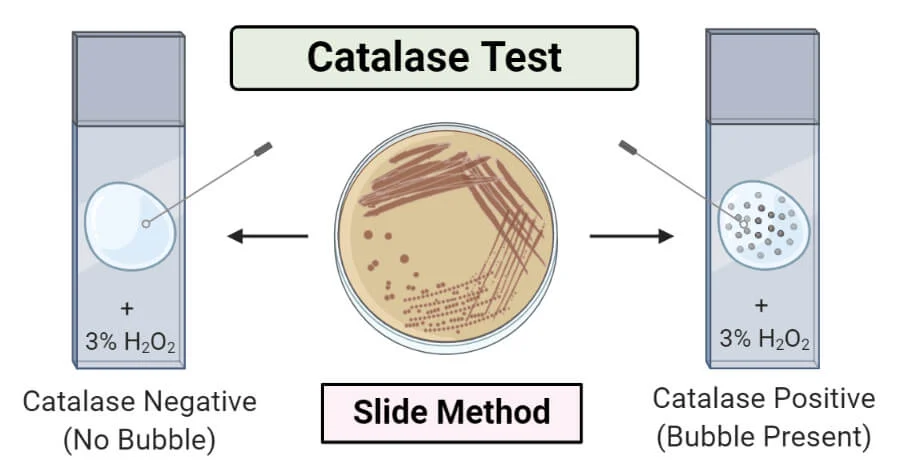
Catalase Test
Tests for the presence of catalase, an enzyme present in cytochrome-containing aerobic and facultative anaerobes
Using oxygen as an ultimate electron acceptor will result in toxic oxygen reactive species that need to be neutralized
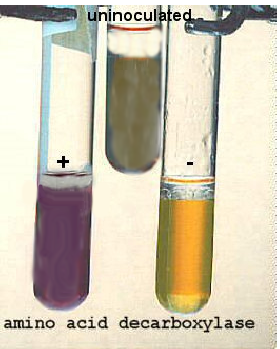
Decarboxylation test
Tests for the ability to decarboxylate amino acids, lysine, or ornithine
Differentiates members of Enterobacteriaceae
Bromocresol purple → purple in alkaline conditions, becomes yellow/clear due to acid production = negative decarboxylation test
Mineral oil
Decarboxylated media becomes more alkaline = stays purple/darker purple
Lysine decarboxylase that reduces/removes a carboxyl group from lysine
Ornithine decarboxylase converts ornithine to putrescine
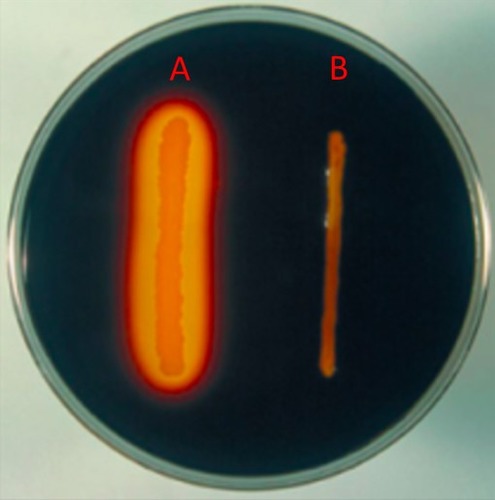
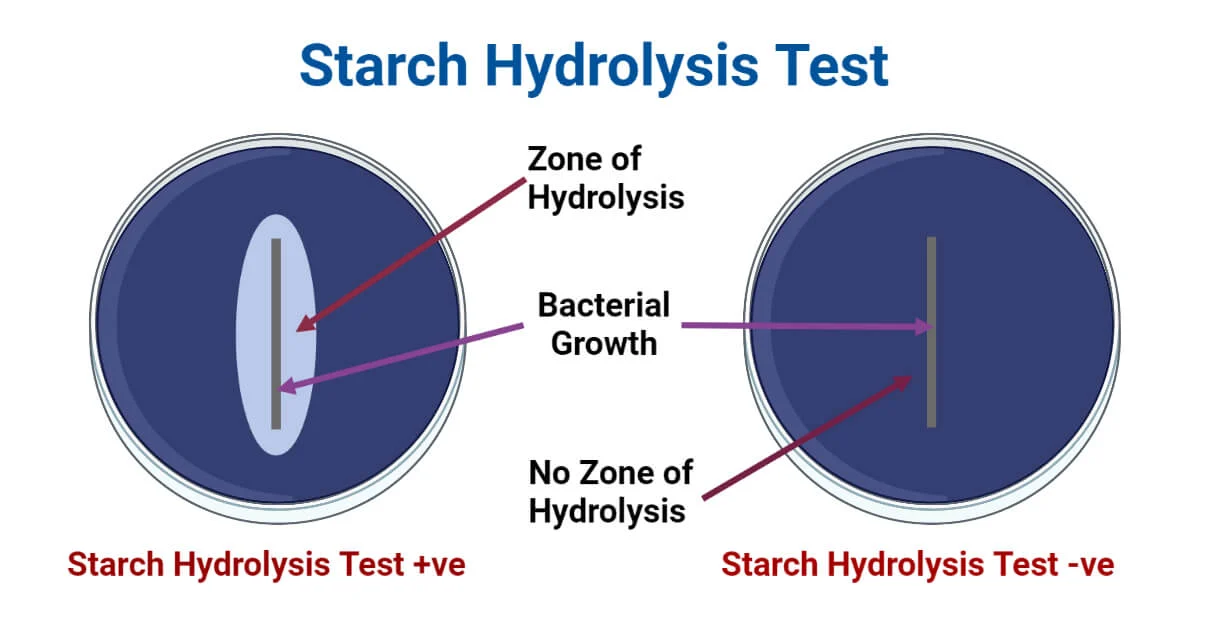
Starch Hydrolysis test
Detects the production of the exoenzyme amylase
This enzyme degrades starch (a polysaccharide)
Flood plate w/ iodine after inoculation
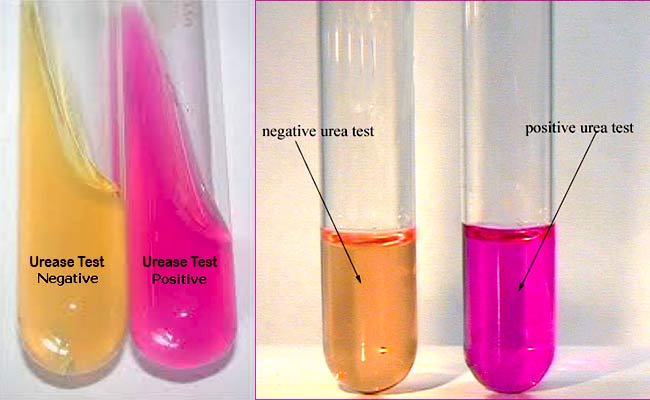
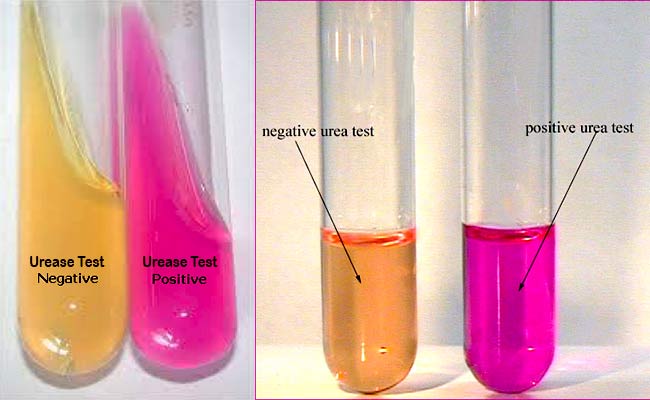
Urease test
Determines the ability of an organism to use urea as a source of nitrogen using the enzyme urease
Differentiates Proteus species from other organisms, identifies Heliobacter pylori
Alkaline byproducts of urease breakdown and turns the media from yellow to → pink/red (phenol red indicator)

SIM Deep
Semi-solid media, tests for 3 bacterial activities
1.) Reduce sulfur → forms black precipitate
Breaks down cysteine (contains sulfur), into hydrogen sulfide or has an enzyme, thiosulfate reductase, which catalyzes reduction of sulfur
2.) Contains the amino acid tryptophan - can be broken down w/ the presence of the enzyme tryptophanase into indole, ammonia, and pyruvic acid
Add kovac solution later on for indole
3.) A semi-solid media - if the bacteria is motile, agar will become hazy away from point of inoculation

Enzymes (What do they do and how do we test for them?)
Amylase
An enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates, like starch, into simple sugars
Test: Starch hydrolysis test (starch plate)
Hemolysin
A toxin produced by some bacteria that causes the lysis of red blood cells, hemolysis
Test: Blood agar (Containing 5% sheep blood)
Urease
An enzyme produced by some bacteria that hydrolyzes urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide
Test: Urease test, a rise in pH causes a color change in the media due to ammonia production

Catalase
An enzyme that some bacteria produce to neutralize the bactericidal effects of hydrogen peroxide
Test: Catalase test - indicates if the bacteria produces an enzyme that can break down hydrogen peroxide into water and carbon dioxide
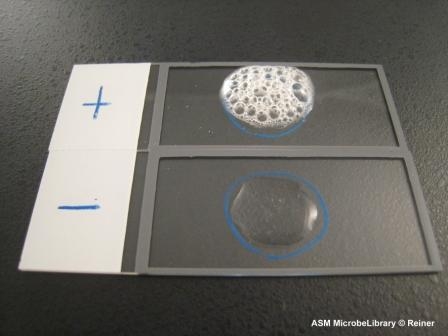
Oxidase
Cytochrome C oxidase, important component of the electron transport chain in aerobic bacteria
Test: Oxidase test (card) dark purple within 10-30 seconds indicates the presence of cytochrome C oxidase, reagent TMPD used and turns dark purple
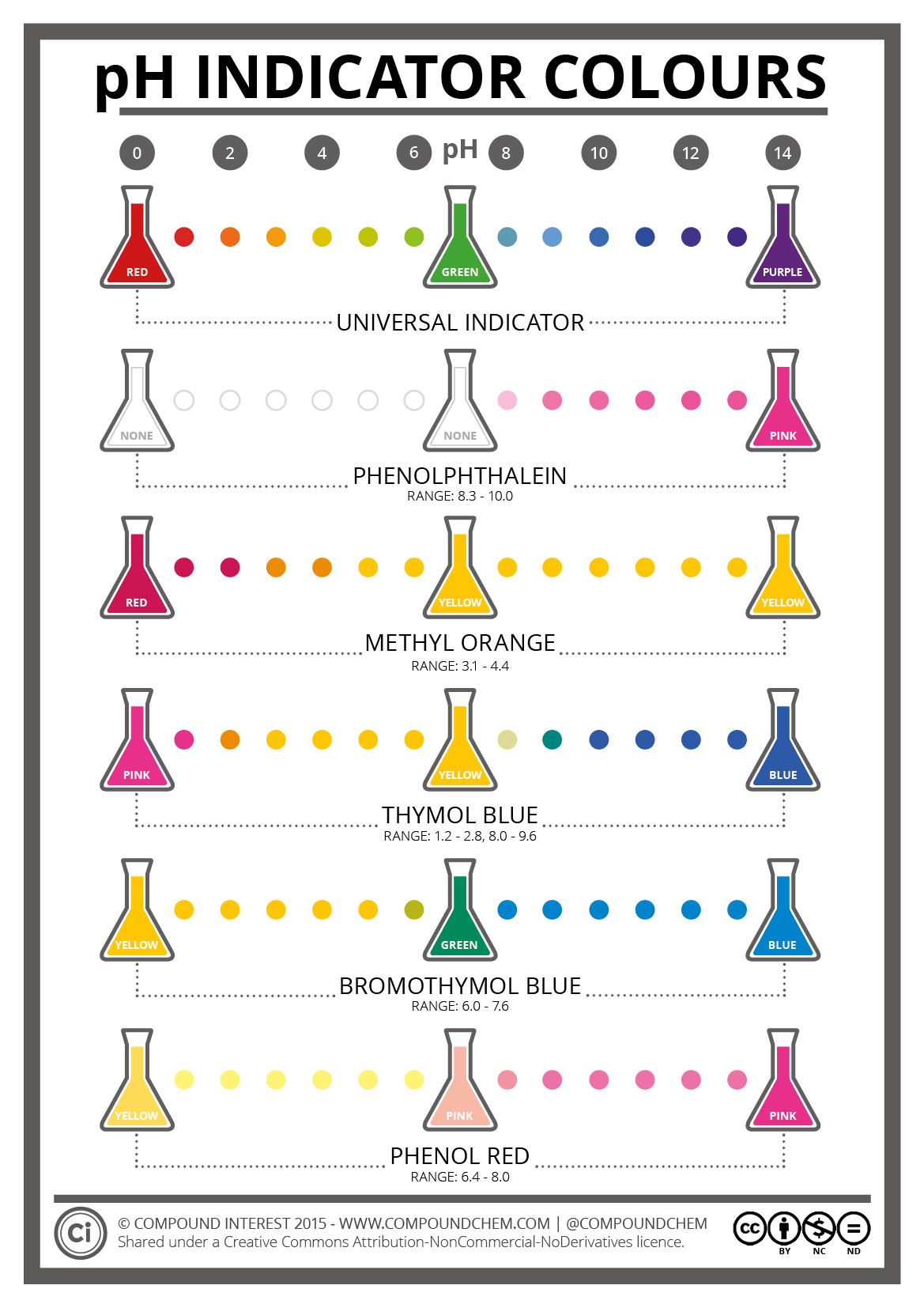
PH indicators
Phenol red → Acidic = yellow, Alkaline = red/pink
Methyl red → Neutral = Orange, Acidic = red, Alkaline = yellow
Bromocresol purple → purple in alkaline conditions, becomes yellow/clear due to acid production
Bromothymol blue → Acidic = yellow, Alkaline = blue, neutral = green
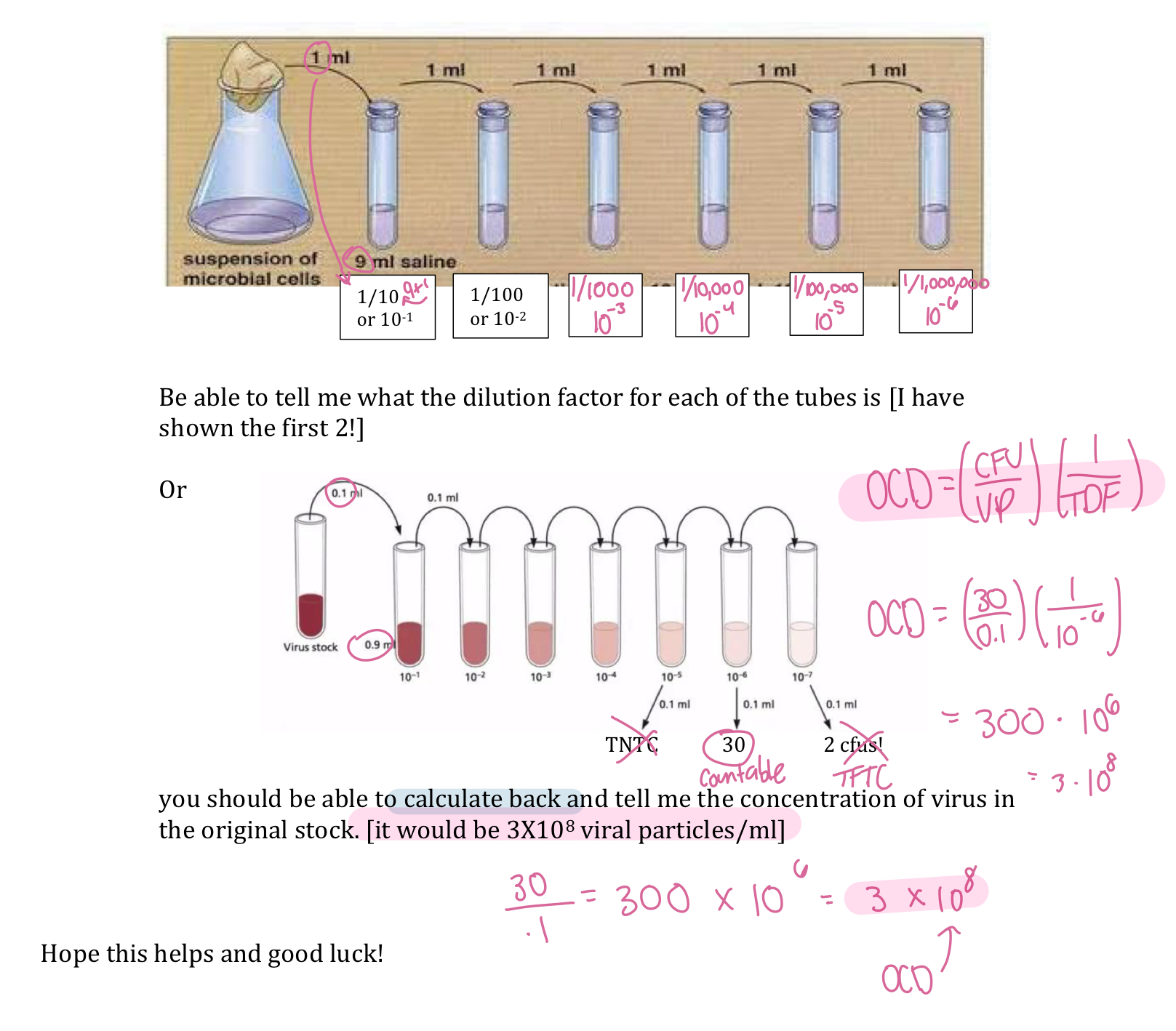
Basic Dilution Series
Original Concentration = CFU/volume plated times dilution factor