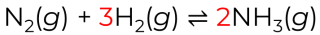Chemical Equilibrium (Module 3) - Mastery Reviewer with Answers
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Claude Berthollet, in Egypt, when he saw Na₂CO₃ forming at a lake edge (opposite of what he saw in the lab).
Who first observed that chemical reactions can be reversible, and where did he notice it?
→ Static equilibrium: no movement/change at all (e.g., a seesaw not moving).
→ Dynamic equilibrium: forward and reverse processes continue but at equal rates (e.g., melting and freezing of ice at 0 °C).
How is static equilibrium different from dynamic equilibrium?
When the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal, and concentrations remain constant.
When is a reaction considered to be at equilibrium?
Kc = [C]^c[D]^d / [A]^a[B]^b
How do you write a general equilibrium constant expression for a balanced chemical reaction?
Because their concentrations are constant and don’t affect the equilibrium ratio.
Why are pure solids and pure liquids excluded from equilibrium expressions?
Kc = [NH3]² / [N2][H2]³
Write the equilibrium expression for the Haber process:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ⇌ 2NH₃(g)
Only when the reaction has reached equilibrium.
When can equilibrium constants be calculated?
Temperature
What single factor affects the value of Kc?
The equilibrium favors products (forward reaction nearly complete).
What does a very large Kc (≫ 1) tell us about the reaction?
The equilibrium favors reactants (reverse reaction nearly complete).
What does a very small Kc (≪ 1) tell us?
Both reactants and products are present in significant amounts.
What does a moderate Kc (~1) mean?
Take the reciprocal (1/Kc).
What happens to Kc if we reverse the balanced chemical equation?
Raise Kc to the power of 2.
What happens to Kc if we multiply the coefficients of a reaction by 2?
Multiply their Kc values.
If two reactions are added together, how do you find the overall equilibrium constant?
Kc uses concentrations at equilibrium; Qc uses concentrations at any time.
What is the difference between Kc and Qc?
Too many products → shifts left (towards reactants).
What does it mean if Qc > Kc?
Too many reactants → shifts right (towards products).
What does it mean if Qc < Kc?
The system is at equilibrium.
What does it mean if Qc = Kc?
Solubility product constant → solubility of salts/precipitation.
What does Ksp represent?
Acid dissociation constant → strength of weak acids.
What does Ka represent?
Base dissociation constant → strength of weak bases.
What does Kb represent?
Ionization of water → [H+][OH−]
At 25 °C: 1.0 × 10⁻¹⁴.
What does Kw represent, and what is its value at 25 °C?
Formation constant → stability of metal-ligand complexes
What does Kf represent?
If a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it will shift to counteract the disturbance.
State Le Chatelier’s Principle in your own words.
Temperature
Which factor can actually change the value of the equilibrium constant?
Shifts right (toward products).
How does adding more reactant affect equilibrium?
Shifts right (toward fewer moles of gas).
How does decreasing the volume (increasing pressure) affect equilibrium if there are more moles of gas on the left?
Shifts left (toward reactants).
How does increasing temperature affect an exothermic reaction?
Shifts right (toward products).
How does increasing temperature affect an endothermic reaction?
No effect; it only speeds up reaching equilibrium.
What effect does a catalyst have on equilibrium position?
Fritz Haber (1868-1934)
Who developed the Haber Process ?