Amino acids and proteins - Chemistry study guide
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
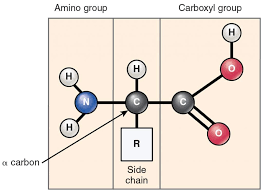
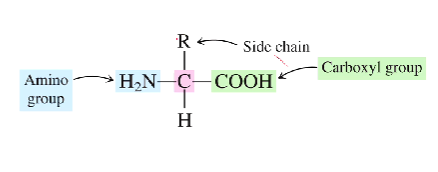
What is the generalized structure of an amino acid?
There will be an amino group attached to a chiral carbon on the left side, with a hydrogen beneath the carbon, an r-group above the carbon, and finally a carboxyl group to the right
What is the handedness of an amino acid?
The carbon in the amino acid will be an alpha-carbon that also has L-isomerism
What are proteins?
Naturally occurring, unbranched polymer in which the monomer units are amino acids
second most abundant substance in cells next to water
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Monomer units
Which protein acts as a catalyst in reactions?
Catalytic protein
Which protein recognizes and destroys foreign substances?
Defense protein
What kind of protein carries essential substances throughout the body
Transport proteins
What proteins transmit signals between tissues
Messenger proteins
What protein controls muscle movement?
Contractile proteins
What proteins provides structural components?
Structural proteins
Which proteins bind to small molecules to store for later use?
Storage proteins
What is an alpha-amino acid?
Amino group and carboxyl group are attached to the same (alpha) carbon
How many amino acids are found in proteins?
20 amino acids
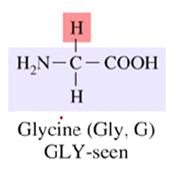
What is the only achiral amino acid?
Glycine
What are the four groups the amino acid side chains are classified into?
1.) Nonpolar amino acids
2.) Polar neutral amino acids
3.) Polar acidic amino acids
4.) Polar basic amino acids
Where are nonpolar amino acids found in proteins?
Found on the interior parts of proteins
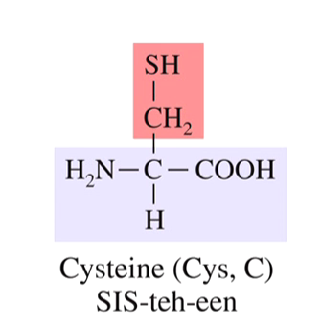
What is special about cysteine?
Only amino acid with sulfhydryl group
can create a disulfide bond with another cysteine
needs an oxidizing agent
What is a disulfide bond?
Where two sulfurs are involved in a bond the two cysteines bond together
How many carboxyl groups are found in polar acidic amino acids?
Both contain two carboxyl groups
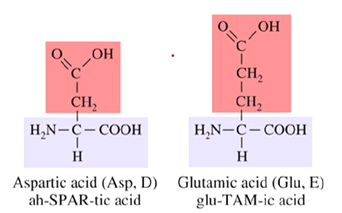
How many amino groups are found in polar basic amino acids?
Two amino groups
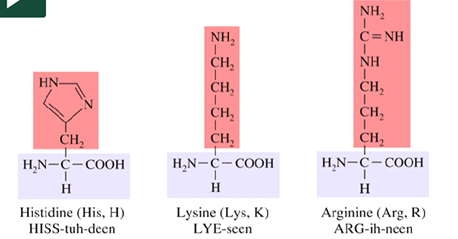
What are essential amino acids?
Standard amino acids needed for protein synthesis that must be obtained from a dietary source
List the essential amino acids.
What amino acid is essential for babies but not for adults?
Histidine
Isoleucine
leucine
lysine
methionine
phenylalanine
threonine
tryptophan
valine
Arginine is needed for babies because it is required for growth
What are complete dietary proteins?
Protein that contains all the essential amino acids in the same relative amount that is needed by the body
this is protein from animal sources: meat, egg, milk and fish
What are incomplete dietary proteins?
Protein that does not contain all the essential amino acids in the same relative is needed by the body
protein from plant sources: wheat, rice, oats, beans, peas and corn
What is the limiting amino acids?
Amino acids that are missing
Lysine - wheat, rice, oats and corn
Methionine - beans, peas
Tryptophan - beans, corn
What are complimentary dietary proteins?
Two or more incomplete dietary proteins that when mixed provide adequate amount
What is the basic group in an amino acid?
What is the acidic group?
The amine group is the basic group
The carboxyl group is the acidic group
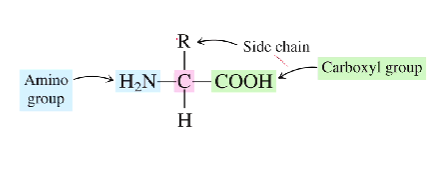
What charges are present in an amino acid at neutral pH? (pH = 7.0)
The carboxyl group loses a proton (hydrogen) so it will carry a negative charge
The amino group will gain a proton (hydrogen) so it will carry a positive charge
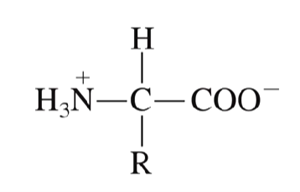
What is a zwitterion?
Molecule that carries both a positive and negative charge so that the net charge on the molecule is zero
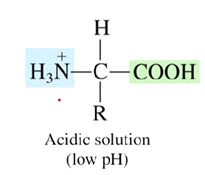
What is the charge of an amino acid at acidic pH values? (low pH)
A positive charge
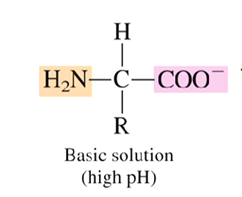
What is the charge of an amino acid at basic pH values? (high pH)
negatively charged
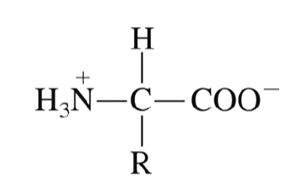
What is the charge of an amino acid at neutral pH values?
a net zero charge
What are peptides?
What are the prefixes associated with them?
Short, unbranched chains of amino acids
Di - two amino acids
Tri - three amino acids
Oligo - 10-20 amino acids
Poly - more than 20 amino acids
What is the N-terminus?
What is the C-terminus?
The N-terminus is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group located at the end of the polypeptide
C-terminus is the end with the free carboxyl group
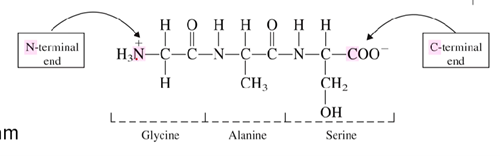
What is a peptide bond?
It is the bond that connects amino acids
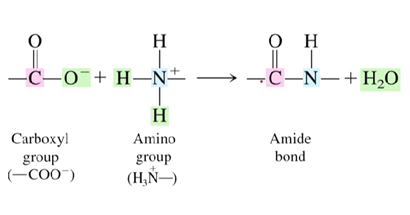
What type of bond is a peptide bond?
Amide bond
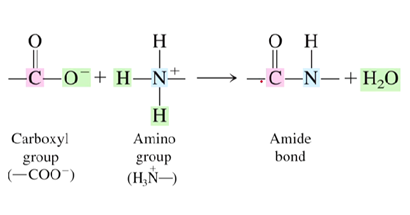
What reacts to form the amide bond?
The carboxyl group and amino group from the two different amino acids
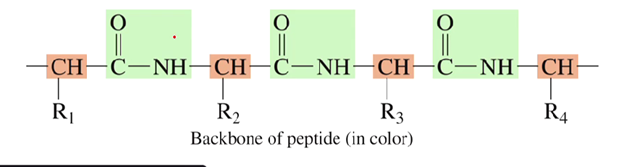
What is the peptide backbone?
Alternating sequence of peptide bonds and the -CH groups
What are some examples of small peptide horomones?
Oxytocin → synthesized in the pituitary gland → nonapeptide (has 9 amino acid residues
Vasopressin → same characteristics as oxytocin
Has the same general structure except on where the oxytocin and vasopressin are located on the 3 and atom
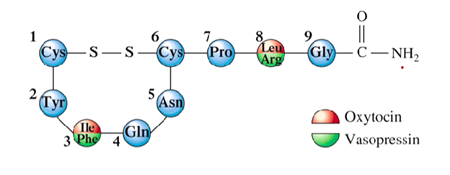
What is the function of oxytocin?
Regulates uterine contractions and lactation
What is the function of vasopressin?
regulates excretion of water by the kidneys; affects blood pressure
What are some examples of small peptide neurotransmitters?
Enkephalins → synthesized in brain → pentapeptide (5 amino acid residues)

What is the function of enkephalin?
binds to receptors in brain to reduce pain
What is an example of a small peptide antioxidant?
Glutathione → present in most cells → tripeptide
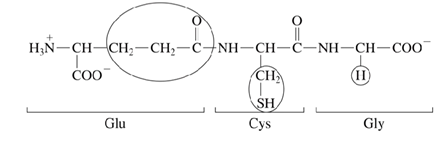
What is the function of glutathione?
regulates redox reactions within the cell
What are proteins?
What term is interchangeable with protein?
How many amino acids do larger and small proteins contain?
Peptide that contains at least 40 amino acid residues
Polypeptide is a term that is interchangeable with protein '
Larger proteins have 10K amino acid residues
Small proteins have between 40-100 amino acid residues
What are proteins called that contain more than one peptide chain?
multimeric proteins
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The order in which the amino acid residues are linked together
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
Special arrangement of the protein backbone
What are the two main types of secondary structure?
Alpha helix → secondary structure where a single peptide chain is shaped like a coil
Beta pleated sheet → secondary structure where fully extended segments of protein are held together by hydrogen
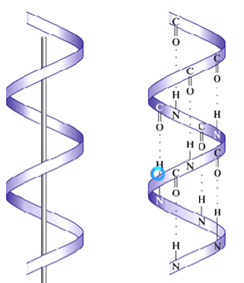
Which structure is this?
Alpha helix
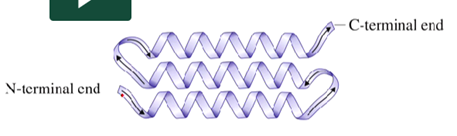
What structure is this?
beta pleated sheet
What are the general characteristics of an alpha helix?
Coil shape is maintained by hydrogen bonds
Coil twists in a clockwise direction
R-groups extend outward from the coil
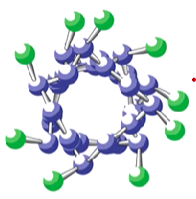
What are the general characteristics of a beta pleated sheet?
Can be two different subunits, or within the same protein chain
forms a zigzag also bonded together by hydrogen
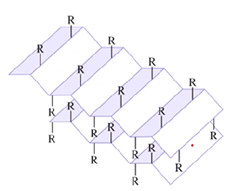
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
The overall 3D shape of the protein that results from the interactions between amino acid side chains
The shape can be compared to a phone chain
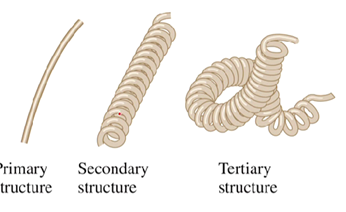
What causes the tertiary structure to occur?
results from the interactions between amino acid side chains
What types of interactions occur between the side chains of amino acid residues in a protein?
Covalent disulfide bonds
Electrostatic interactions
Hydrogen bonding'
Hydrophobic interactions
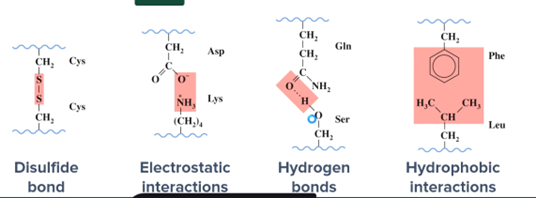
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
The organization of various protein subunits
found in only multimeric proteins
contains an even number of subunits
held together by electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic reactions
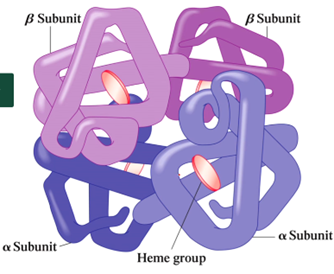
What types of proteins do not have quaternary structure?
In proteins that only have one subunit
What happens during protein hydrolysis?
The peptide bond breaks in the presence of a strong acid or base and heat which produces free amino acids
What is complete hydrolysis?
Where all amino acids are broken and become free amino acids
What is partial hydrolysis?
Some peptide bonds will be left intact
What is protein denaturation?
Partial or complete disorganization of a proteins tertiary structure due to disruptions in the protein’s primary, secondary, and quaternary structure
What causes protein denaturation?
Disruptions in the proteins structure
What is the relationship between the shape of protein and its function
The shape of the protein regulates its function
What are some characteristics of denaturation?
o Denaturation causes loss of biochemical ability
o Some proteins can be re-folded → renaturation
o renaturation is impossible for some proteins (like albumin in egg whites)
o Denaturation causes decrease water solubility à curdling of milk (casein)
o Cauterization – heat used to denature proteins à used to seal blood vessels
o Perms – combination of denaturing and renaturing the disulfide bonds within hair proteins
What are the three main types of proteins?
fibrous
globular
membrane
What are the characteristics of fibrous proteins?
It has an elongated shape with one dimension longer than the other
simple, regular linear structures
tend to aggregate
water insoluble
What are the characteristics of globular proteins?
has peptide chains that are folded into a spherical or globular shape
hydrophobic side chains on the interior of the structure
hydrophilic side chains on the exterior of a cell
water soluble
What are the characteristics of membrane proteins?
protein that is found associated with the membrane of the cell
most hydrophobic side chains are on the exterior of the molecule
water insoluble
fewer hydrophobic amino acid residues
What type of protein shape is alpha-keratin?
Fibrous protein that functions as a protective coating
What is the shape of alpha-keratin?
Coiled-coil shape
two alpha helix subunits that coil around each other
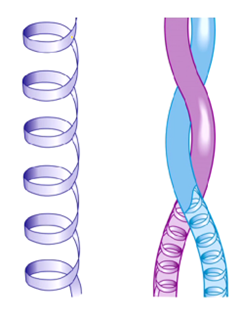
How does disulfide bonds affect the structure of the alpha-keratin?
It increases the rigidity of structure
the harder the structure the more disulfide bonds
What type of protein shape is collagen?
Triple helix made of glycine and proline
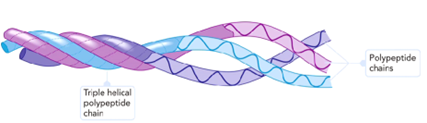
What increases the rigidity of the collagen?
The crosslinking of collagen fibrils
What type of protein shape are hemoglobin and myoglobin?
Globular proteins
What is the function of hemoglobin?
Transports oxygen from lungs to tissues
What is the function of myoglobin?
oxygen storage molecule in muscles
What is the shape of hemoglobin?
Tetramer → 4 subunits that contains a heme group
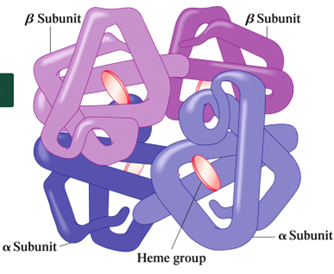
What is the shape of myoglobin?
Monomer → 1 subunit that contains only one heme group
True or false: Are proteins bonded together by ionic bonds?
False
What elements do all proteins contain?
Hydrogen
Carbon
Nitrogen
Oxygen
What are all proteins made up from?
Amino acids
What is the electron distribution of amino acids in proteins?
polar
nonpolar
neutral
Are any of the standard amino acids chiral?
No, none of them are
How do standard amino acids differ from one another?
In the identity of the R group (side chain)
How is the protein backbone represented?