Session 8: Haemoglobinopathies NEW
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Normal hemoglobin structure
2 alpha-like globin chains
2 beta-like globin chains
4 heme molecules
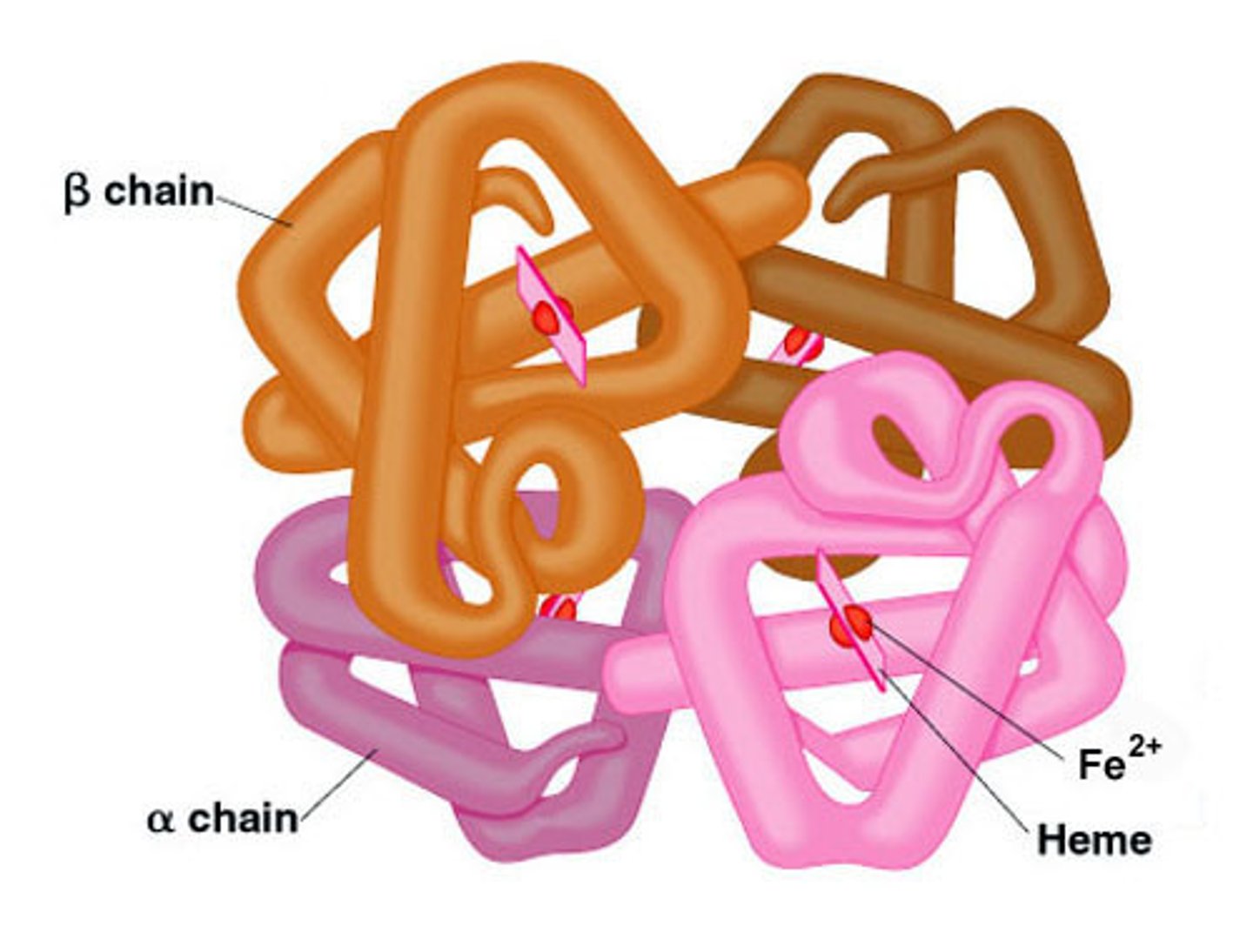
Each heme molecule ___ binds to ONE oxygen molecule
reversibly
Erythrocyte shape and the benefit of the structure/shape
Biconcave disc of RBC allows them to have large surface area and deform and bend to squeeze through capillaries
Function of RBC
Transport oxygen from the lungs to tissues
Lifespan of RBC
~120 days
Anemia
Decrease in hemoglobin level below the reference level for the age/sex of the individual
Male = 135 - 175 g/L
Female = 115 - 155 g/L
Classification of anemia
Classified by Mean Corpuscle Volume (MCV) as low, medium or high
The two NORMAL adult hemoglobin variants
HbA = a2b2 = 97%
HbA2 = a2δ2 = 2%

The one NORMAL fetal hemoglobin variant
HbF = a2γ2 = <1%

Too little or too much globin chain synthesis (quantitative) leads to...
Thalassemia
Synthesis of an abnormal gene product (qualitative) leading to abnormal structural variants of RBC leads to...
Sickle cell anemia
In sickle cell Hb (HbS) - a hydrophilic ___ on the surface of the protein is mutated to a hydrophobic ___
In sickle cell Hb (HbS) - a hydrophilic glutamate on the surface of the protein is mutated to a hydrophobic valine
In normal healthy hemoglobin, ___ alpha globin chain genes and 2 beta globin chain genes produce a balanced production of HbA (a2b2)
In normal healthy hemoglobin, four alpha globin chain genes and 2 beta globin chain genes produce a balanced production of HbA (a2b2)
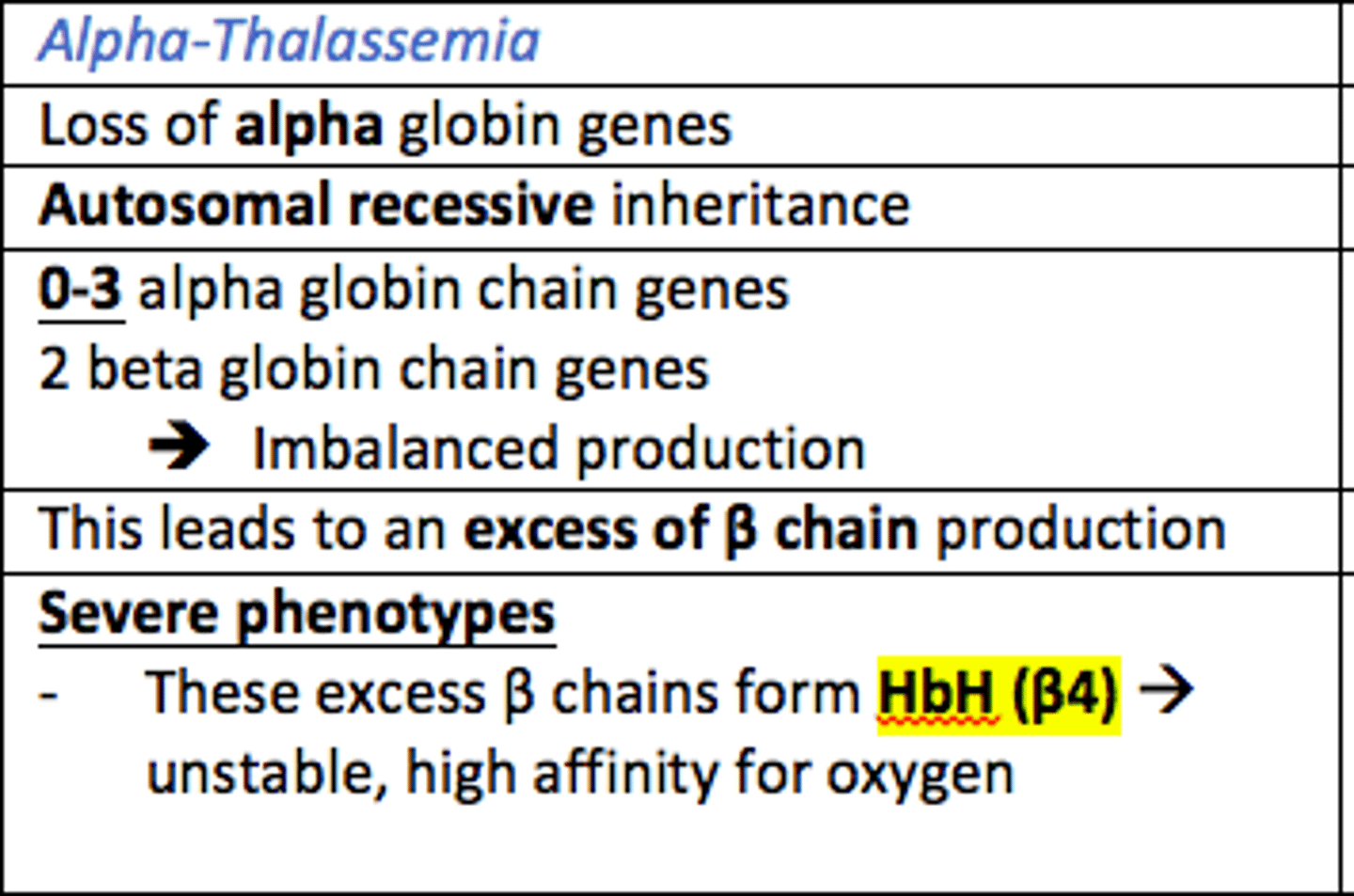
Alpha Thalassaemia inheritance pattern
Autosomal recessive
Alpha Thalassaemia leads to the loss of ___ globin genes which leads to the excess production of ___ globin chains
Alpha Thalassaemia leads to the loss of alpha globin genes which leads to the excess production of beta globin chains
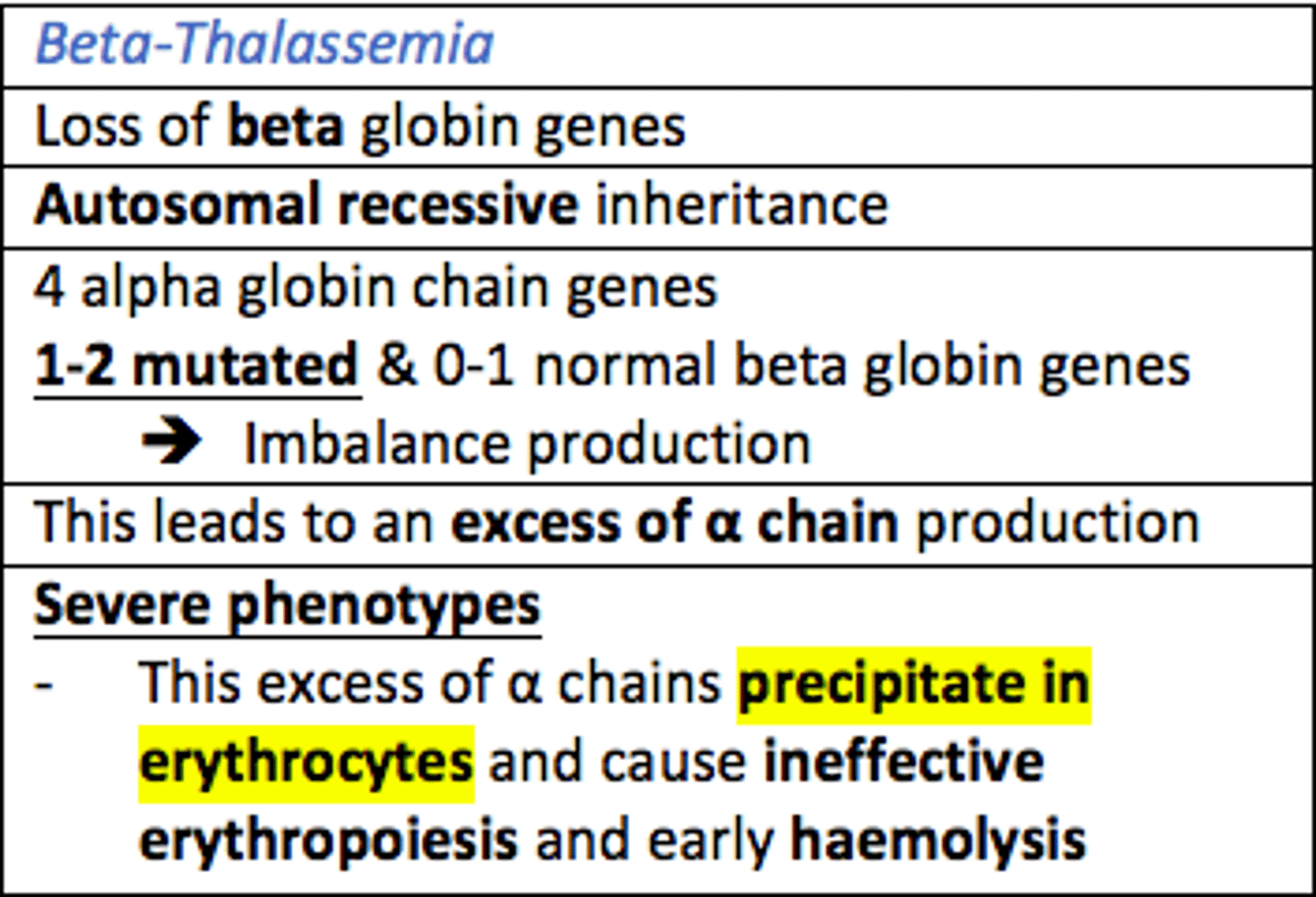
Beta Thalassaemia leads to the loss of ___ globin genes which leads to the excess production of ___ globin chains
Beta Thalassaemia leads to the loss of beta globin genes which leads to the excess production of alpha globin chains
Types of Alpha Thalassaemia
a,a/a,-
1 gene missing
- 'Silent' asymptomatic
- Low MCV
- Raised red cell count

Types of Alpha Thalassaemia
a,-/a,-
2 genes missing
- Trait
- Asymptomatic
- Low MCV
- Raised red cell count

Types of Alpha Thalassaemia
a,a/-,-
2 genes missing
- Trait (far east)
- Asymptomatic
- Low MCV
- Raised red cell count

Types of Alpha Thalassaemia
a,-/-,-
3 genes missing
- Hemoglobin H disease (HbH disease)
- Anaemia
- Splenomegaly
- Not transfusion-dependent

Types of Alpha Thalassaemia
-,-/-,-
All 4 genes missing
- Hydrops fetalis
- Incompatible with life

Types of Beta Thalassaemia
β/β+ or β/β0 Beta thal minor
- Asymptomatic
- Low MCV
- Mild anemia

Types of Beta Thalassaemia
β+/β0 (mild variants) or β+/β+
- Splenomegaly
- Anaemia
- Non-transfusion dependent
- Bony deformity
- Gallstones
- Iron overload

Types of Beta Thalassaemia
β+/β0 (severe variants) or β0/β0
- Asymptomatic at birth
- Splenomegaly
- Severe anaemia
- Developmental delay
- Growth retardation
- Extramedullary erythropoiesis
- Marrow expansion (skull/long bones)
- Transfusion-dependent
- Iron overload

Signs and symptoms of thalassemia
Pallor
Weakness
Fatigue
Jaundice
Facial bone deformities
Abdominal swelling (splenomegaly)
Dark urine
Slow growth
Palpitations
Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
Thalassemia patients who are transfusion-dependent may develop issues such as ___ iron in the body. This is caused by regular blood transfusions which are required to treat their anaemia.
Thalassemia patients who are transfusion-dependent may develop issues such as excess iron in the body. This is caused by regular blood transfusions which are required to treat their anaemia.
Iron overload affects two organs particularly. Which organs are these?
Heart
Liver
Management of thalassaemia
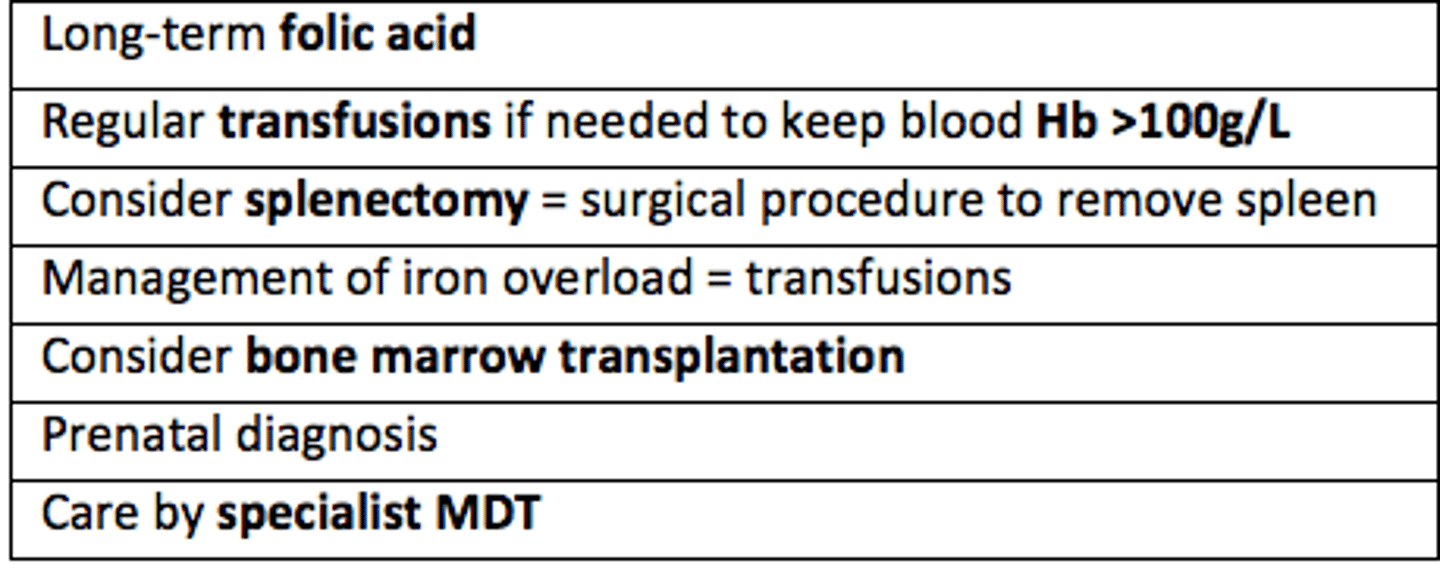
In thalassemia, regular transfusions may be needed to keep blood Hb >___g/L
Hb >100g/L
Sickle cell disease is caused by the homozygous sickle cell mutation (Hb SS).
This is due to a ___ of a single amino acid.
Hydrophilic glutamate is replaced which hydrophobic ___.
Sickle cell disease is caused by the homozygous sickle cell mutation (Hb SS).
This is due to a substitution of a single amino acid.
Hydrophilic glutamate is replaced which hydrophobic valine.
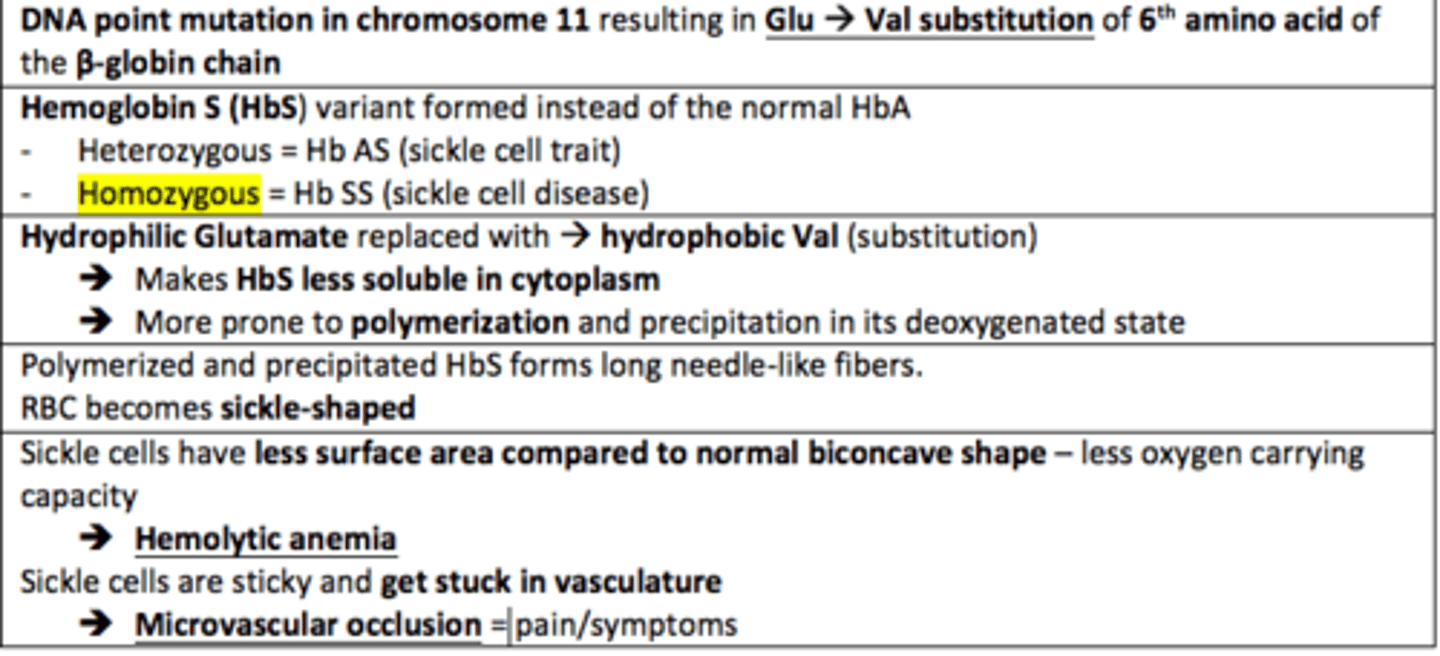
The replacement of hydrophilic glutamate with hydrophobic valine in Sickle Cell Disease makes HbS ___ soluble and more prone to ___ in its deoxygenated state
The replacement of hydrophilic glutamate with hydrophobic valine in Sickle Cell Disease makes HbS less soluble and more prone to polymerisation in its deoxygenated state
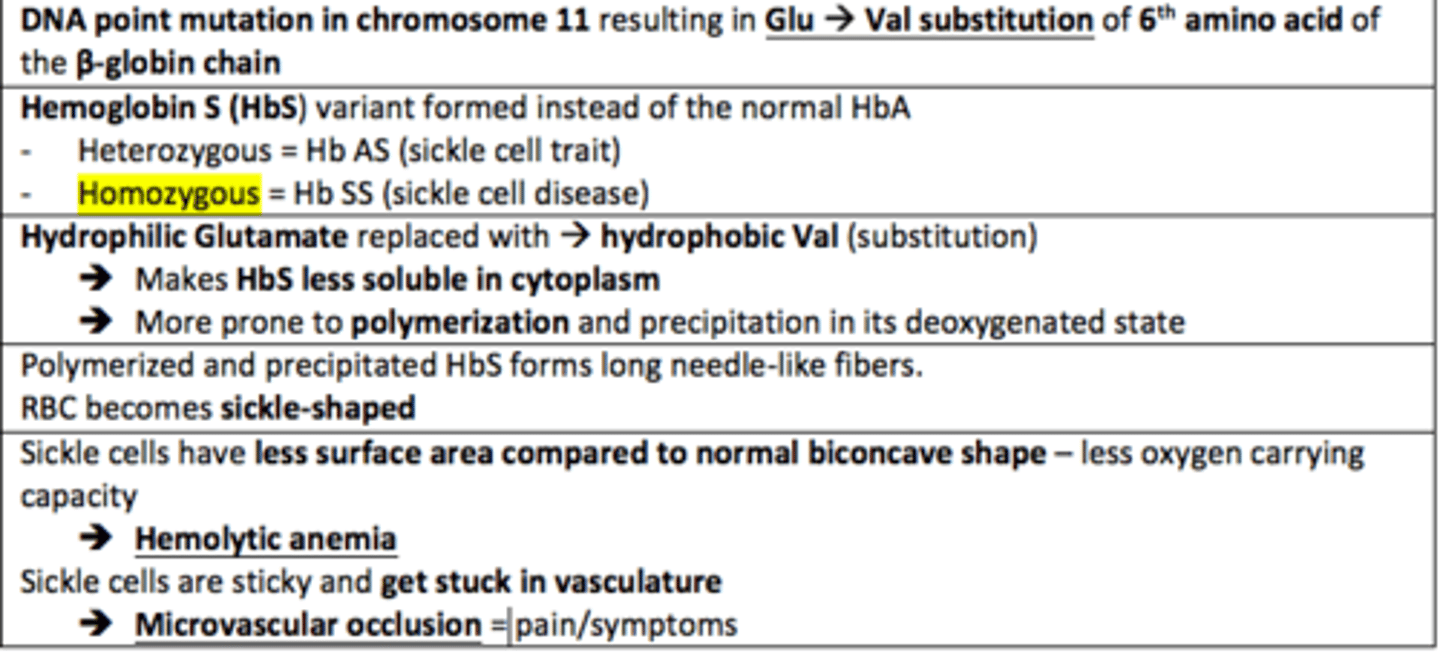
Sickled RBC (SCD) have less ___ ___ compared to the normal bioconcave shape of RBCs. This leads to less oxygen carrying capacity
Surface area
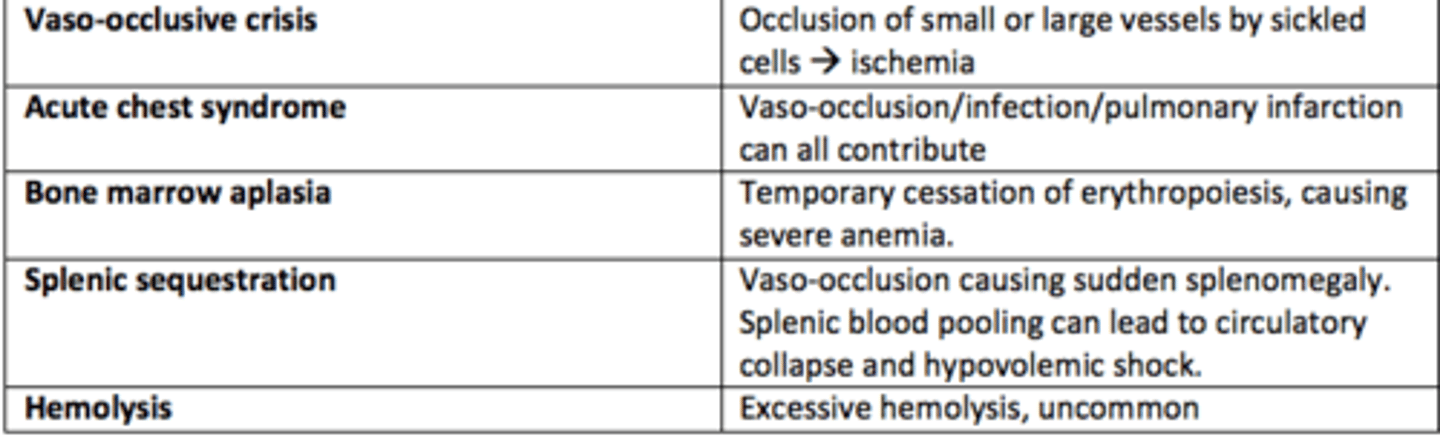
What are the five types of sickle cell crises?
1) Vaso-occlusive crises
2) Acute chest syndrome
3) Bone marrow aplasia
4) Splenic sequestration
5) Hemolysis
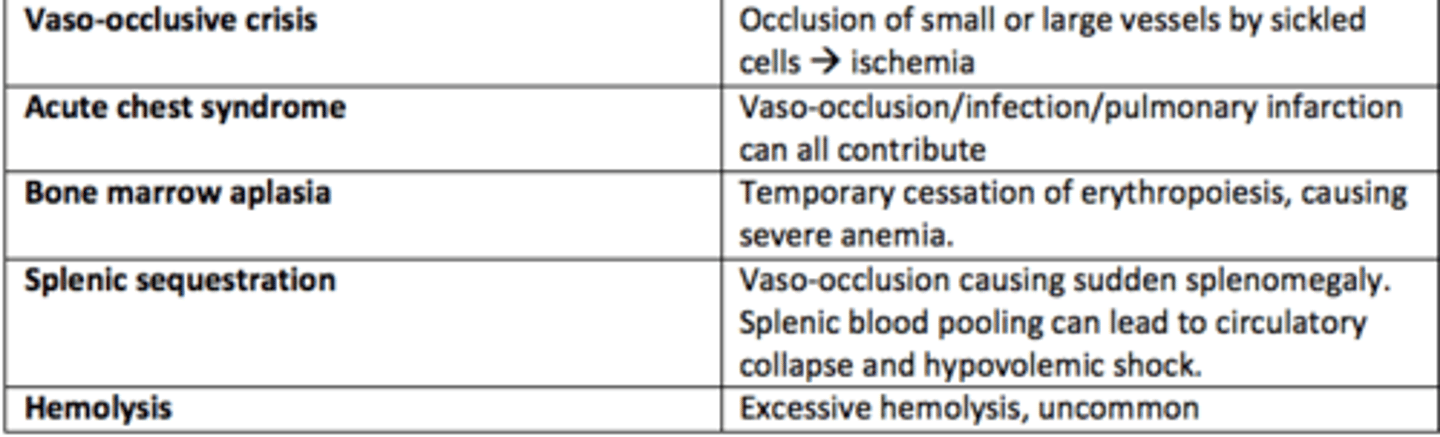
Vaso-occlusive crises in SCD
Occlusion of small or large vessels by sickled cells leading to ischemia
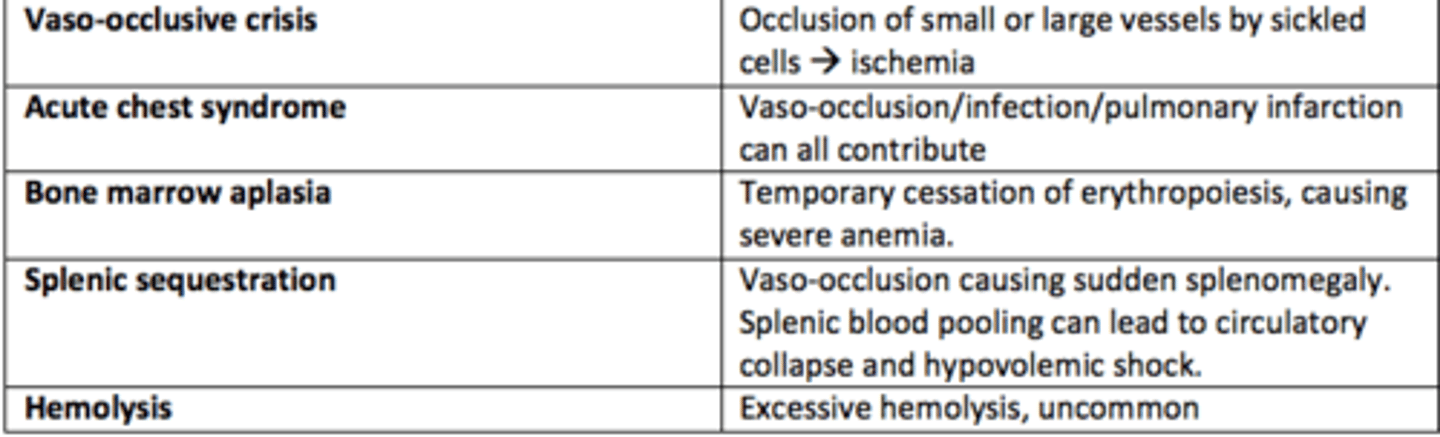
Acute chest syndrome crises in SCD
Vaso-occlusion within the pulmonary vasculature of patients with sickle cell disease.

Bone marrow aplasia crises in SCD
Temporary cessation of erythropoiesis causing severe anaemia
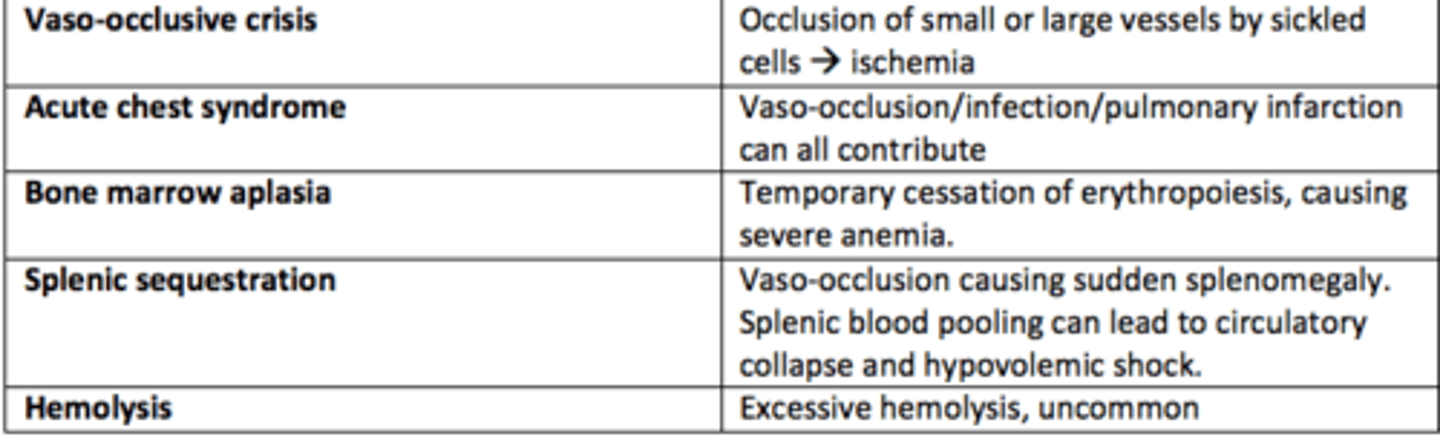
Hemolysis crises in SCD
Excessive hemolysis - uncommon
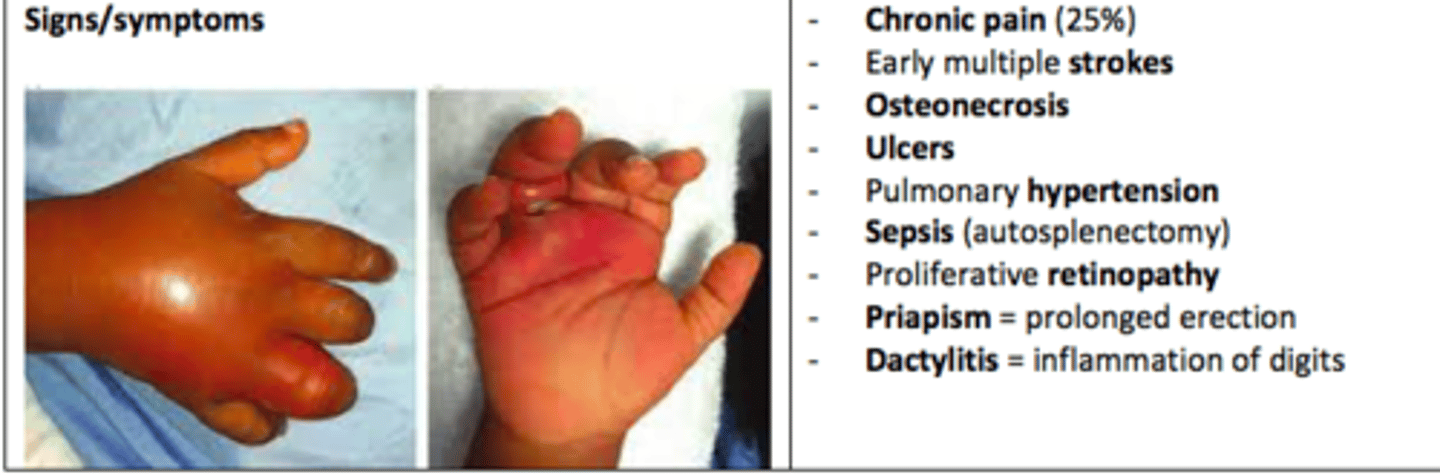
Sickle Cell Anemia presentation
Chronic pain (25%)
Early multiple strokes
Osteonecrosis
Ulcers
Pulmonary hypertension
Sepsis (autosplenectomy)
Proliferative retinopathy
Priapism
Dactylitis
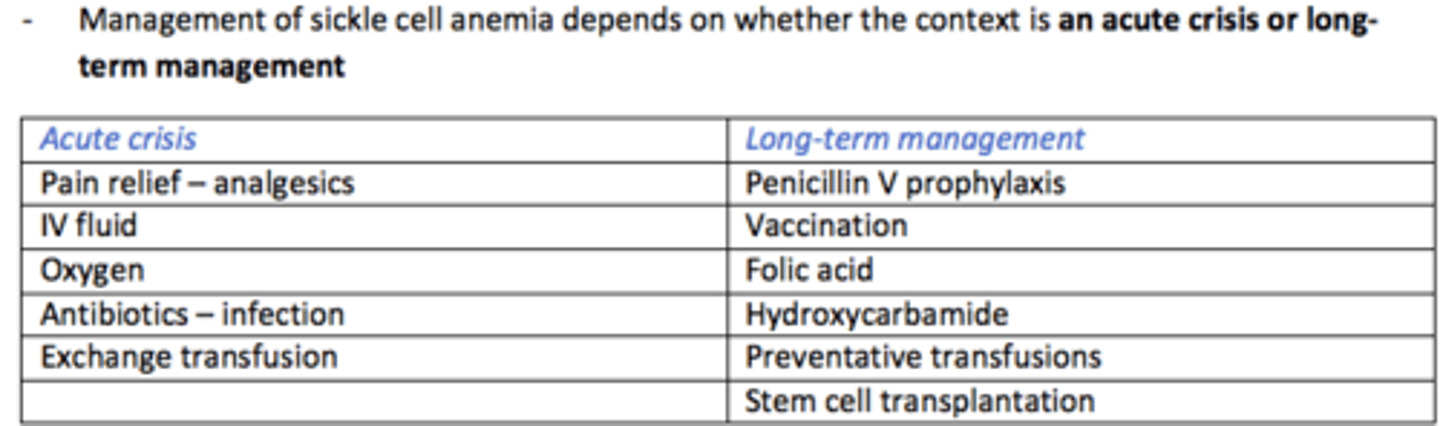
Management of Sickle Cell Anaemia during ACUTE CRISIS
Pain relief (analgesia)
IV fluids
Oxygen
Antibiotics for infections
Exchange transfusion
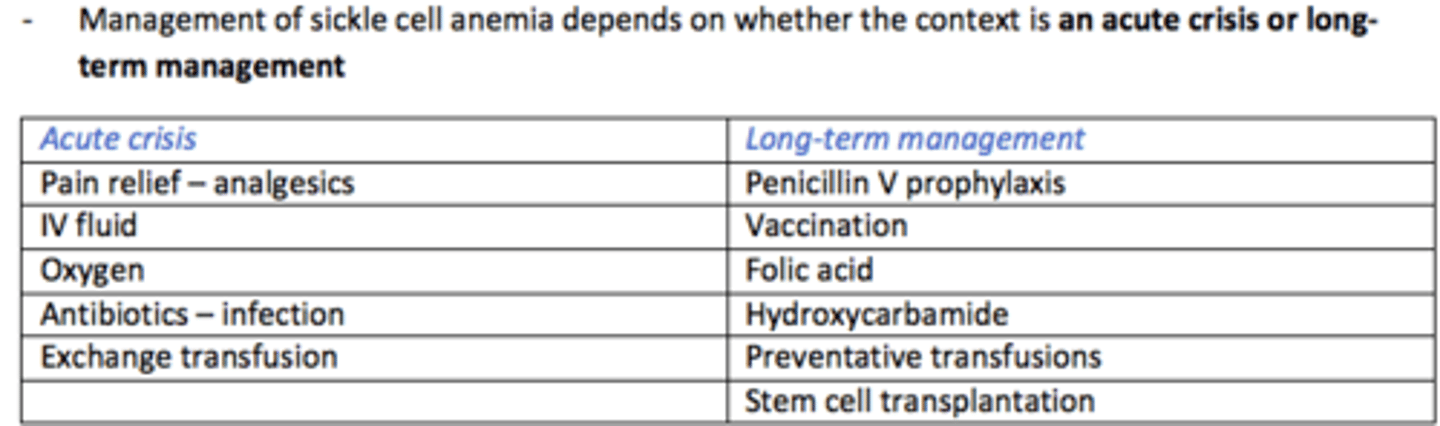
Management of Sickle Cell Anaemia LONG-TERM
Penicillin V prophylaxis
Vaccination
Folic acid
Hydroxycarbamide
Preventative transfusions
Stem cell transplantation
Name a drug which is used in the long-term management of Sickle Cell Anaemia which REDUCES the sickling of RBCs
Hydroxycarbamide
Sickle cell trait
Symptoms shown by those possessing a heterozygous genotype for sickle cell anemia
2 alpha chains
1 mutated B chain
1 normal B chain
4 heme

Sickle cell trait confers a resistance to what disease in 30-40% of sub-Saharan Africa?
Malaria
Patients with haemoglobinopathies are particularly vulnerable to iron overload. Why is this?
Regular transfusions
Excess iron from transfusions and body has no mechanism for excreting excess iron loads
Iron overload can be fatal for = heart, liver and endocrine glands
Managing iron overload - name three iron chelator oral and subcutaneous medications that can be given to patients with iron overload
- Deferoxamine
- Deferiprone
- Deferasirox
Caution of prescribing iron chelating drugs to patient with iron overload
1) Require long-term compliance to be effective
2) Have their own toxicities/risks
Pre-natal screening program in the UK for haemoglobinopathies
Family Origin Questionnaire (FOQ)
Screens women at risk and offers pre-natal diagnosis of the fetus
Screening for haemoglobinopathies in newborns
Newborn blood spot test
- 10 days post-birth
- Diagnosing many conditions such as sickle cell, CF, PKU