CONTROL AND COORDINATION
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Summarize the general process that all sensory organs/structures use to sense
sensory cells translate stimuli into action potentials that are transferred and processed by the brain/NS
Summarize the pathway that electromagnetic waves take in order to get to our brains and allow us to see
Photoreceptors in our eyes convert light energy to electrical energy that then travel to the brain
list and describe each of the surrounding structures that protect and keep the eyeball healthy
Eyebrows - keep sweat and sun out of eyes
Eyelid and eyelashes - trigger reflective blinking to keep eyes moist
Lacrimal apparatus - consists of the lacrimal gland that makes and secretes tears and the ducts that drain the secretions
Distinguish between the three layers of the wall of the eyeball and their unique characteristics
Fibrous layer - outermost layer - anchors all eye muscles in place and lets light into eye
Vascular layer - middle layer - supplies layers with blood
inner layer - retina - absorbs light and creates pathway where light can be translated
Summarize the pathway and process that molecules take in order to get to our brain to allow us to process smells
Odor molecules hit olfactory epithelium, which is in the roof of the nasal cavity that has the olfactory sensory neuron then molecules bind to olfactory receptors - AP go down the olfactory nerve which connects to brain
Summarize the pathway and process that molecules take in order to get to our brain to allow us to process taste
Sensory receptor cells take in impulse - translated to AP - signaled to gustatory cortex - release of digestive enzymes to break down food = energy
sound wave pathway
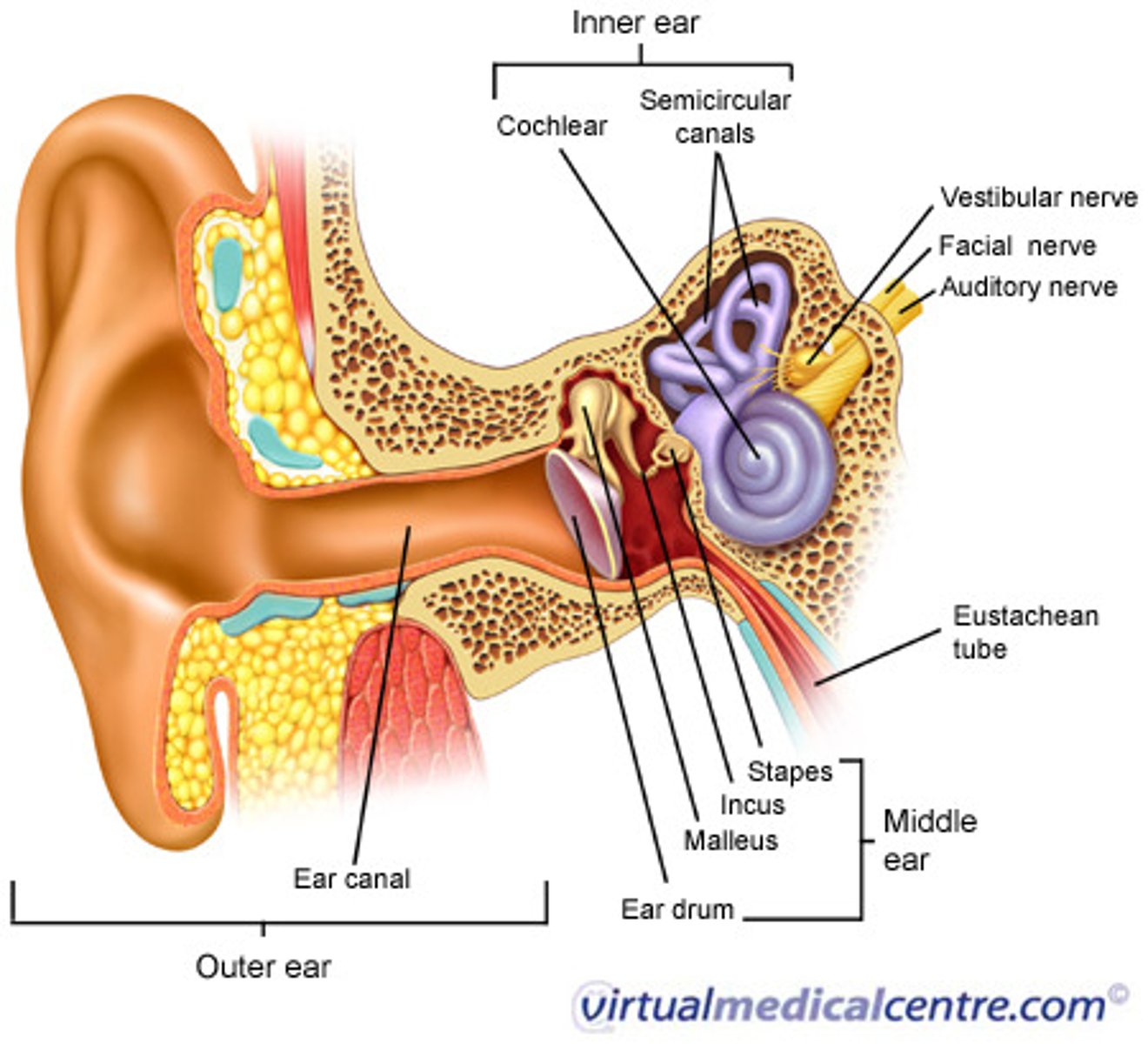
describe the function and components of the three parts of the ear
External (outer ear) - catch sound waves then pass them
Middle ear - tympanic cavity - relay station between the outer and inner ear
Inner portion = labyrinth - turn physical vibrations into electrical impulses that go to brain
Sensory Input
Receives stimuli via millions of sensory receptors throughout the body
Integration
Processes input stimuli and does decision-making
Motor Output
Activates effector organs to cause a response
Neuron Tissue
Densely packed with neurons and neuroglials
Neuroglial
Supportive cells that provide nutrition, insulation and help with signal transmission
Soma (Cell body)
Life support that contains the nucleus and most organelles
Ganglion
Collections of nerves in cell bodies located in the body with the exception of the spinal cord and brain
Processes
Extensions from the cell body
Dendrite
Main receptor of signals (Input region)
Axons
Generates/transmits nerve impulses (The conducting region)
Nerves
Bundles of axons that extend from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body
Axon Terminals
The end of the axon, releases neurotransmitters at a synapse when a nerve impulse is received
Myelin Sheath
Covers long axons (Nerve fibers) to protect and electrically insulate them to increase the speed of nerve impulse transmission
Multipolar
More than 3 cell processes
Bipolar
2 processes, one axon and one dendrite on opposite ends of the cell (Rare)
Unipolar
1 Cell process, divides like a T
Sensory Neurons
Transmits info from sensory receptors (Unipolar)
Motor Neuron
Transports info from CNS to most of the body
Interneurons
Housed in the CNS and transports info between sensory and motor neurons
CNS
Protected by the skull and surrounded by tissues and cerbospinal fluids that cushion the brain from injury
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain, divided into 4 lobes
Brainstem
Base of the cerebrum, relays info for the brain + spinal cord
Thalamus
Main relay station for sensory/motor information
Spinal Cord
Carries nerve signals between the brain and the body
Pituitary Gland
Keeps internal body stable and processes growth, metabolism, and blood pressure
Pineal Gland
Controls the body’s sleep/wake cycles
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary movement unconsciously
Heart rate, breathing, digestion
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary movement, processes sensory information
Touch, pain temperature
Reflex Arc
Neural pathway
Receptor
Sensory neuron
Integration center (processes it)
Motor neuron (transmits response)
Effector
Protein Channel
Crucial for nerve impulses, controls rapid ion flow through neuron membranes and creating electrical signals
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that increase the likelihood of a receiving neuron
Inhibitory Neutrotransmitter
Decreases a neuron’s likelihood of firing, calming neural activity
How protein channels can be gated
Voltage
Chemical messengers
Physical stretching
General senses
Basic awareness
Special senses
Complex receptors in the eye for seeing and hearing
Cornea
Eye’s front-domed surface, acts like a window that lets light in
Retina
Light sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye
the general process that all sensory organs structures use to sense