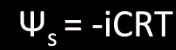2.7 Tonicity and Osmoregulation
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Tonicity
the ability of an extracellular solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
depends on the concentration of solutes that cannot pass through the cell membrane
cells can be in 3 types of solutions:
isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic
Osmoregulation
cells must be able to regulate their solute concentrations and maintain water balance
animal cells will react differently than cells with cell walls, like plants, fungi, and some protists
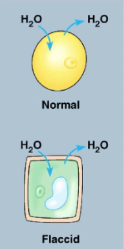
Isotonic solutions
the concentration of solutes inside the cell is equal to that outside the cell
no net movement of water
water diffuses into the cell at the same rate water moves out of the cell
makes plant cells flaccid(turgor pressure decreases)
ideal for animal cells
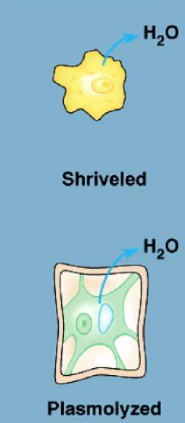
Hypertonic solutions
the concentration of solutes is higher outside of the cell
water will move to the extracellular fluid/outside
animal cells will shrivel and die
plant cells experience plasmolysis(vacuole shrinks and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall)
ex. 0.15 M inside cell 0.3 M outside cell, water moves out
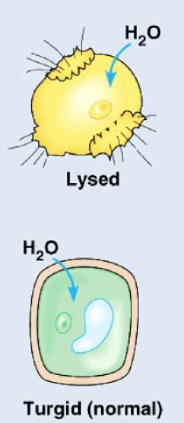
Hypotonic solutions
the concentration of solutes is lower outside of the cell
the cell will gain water/moves inside
animal cells will swell and lyse(break),cytolysis
plant cells work optimally(maintains turgor pressure,turgid)
ex. 0.3 M inside cell, 0.15 M outside cell, water moves in
Water potential
a physical property that predicts the direction water will flow
measured in megapascals(MPas) or bars
includes the effects of solute concentration and physical pressure
water will flow from areas of:
high water potential→low water potential
low solute concentration→high solute concentration
high pressure→low pressure
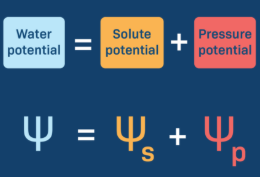
Water potential formula
water potential= solute potential + pressure potential
Pressure potential
the physical pressure on a solution
can be positive or negative relative to atmospheric pressure
open air means the pressure potential is 0 (usually is 0 in problems)
Solute potential
an increase in solutes causes binding to more free water
this reduces water potential
expressed as a negative number
pure/distilled water is 0 MPa(no solute potential)
Solute potential formula
solute potential = -iCRT
i= ionization constant, number of particles formed, if no ions are formed the ionization constant is 1
usually only case where it is not 1 is sodium chloride (NaCl)
C= molar concentration (given in problem)
R= pressure constant, always 0.0831
T= temperature in Kelvin's, degrees Celsius + 273
all formulas are given on tests so no need to memorize