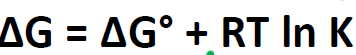Biochem exam
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the linkage in nucleic acids?
phosphodiester
What is the linkage in polysaccharides?
glycoside (ether)
What is the linkage in lipids?
Ester
Types of non-covalent interactions
charge-charge
charge-dipole
dipole-dipole
charge-induced dipole
dipole-induced dipole
dispersion / van der Waals
hydrogen bond
How many hydrogen bonds can a water make?
4
the physiological pH range
6.5-8.0
the acid dissociation constant
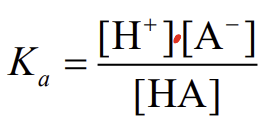
How is the strength of acids expressed?
pKa
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
a.k.a. buffer equation
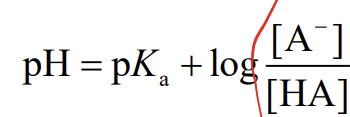
ampholyte
a molecule with both acidic and basic groups
many biologically relevant molecules
glycine
What is the role of reaction order in determining reaction velocity?
It determines the relation between reaction rate and initial reactant concentrations.
Major classes of enzymes
oxidoreductases
transferases
hydrolases
lyases
isomerases
ligases
Is the same enzyme in a different species exactly same or different?
A bit different
Why is the peptide bond planar and difficult to rotate?
the delocalisation of pi-electron orbitals over O-C-N
beta-sheet
interchain H-bonds
side chains alternate sides of sheet
strands parallel / antiparallel
What are charge-charge interactions in the tertiary structure of a protein called?
salt bridges
What type of bond does a sulfide bridge have?
covalent
open carbon chain molecule
aliphatic
pKa range of the carboxyl terminus
1.8-2.6
pKa range of amine terminus
9.1-10.8
cryo-electron microscopy
for molecules too large to be crystallised > 100 kDa
challenging if sample too flexible
What does ΔG = 0 mean?
The reaction is reversible, at equilibrium
Standard conditions
ΔG°
1 M of everything
including [H+] → pH 0
25*C
1 bar
How to calculate ΔG° from K?
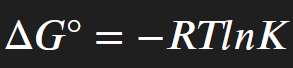
How to calculate ΔG from K?