ECO 239 Managerial Economics Midterm
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Accounting profits
The total amount of money taken in from sales minus the dollar cost of producing goods or services.
Economic profits
the difference between the total revenue and the total opportunity cost of producing the firm’s goods or services.
Opportunity cost
the loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen
sum of explicit costs and implicit costs
Explicit cost
Accounting cost
Implicit cost
Best alternative
Consumer-Producer Rivalry
Consumers attempt to locate low prices, while producers attempt to charge high prices.
Consumer-Consumer Rivalry
Scarcity of goods reduces the negotiating power of consumers as they compete for the right to those goods.
Producer-Producer Rivalry
Scarcity of consumers causes producers to compete with one another for the right to service customers.
Present value
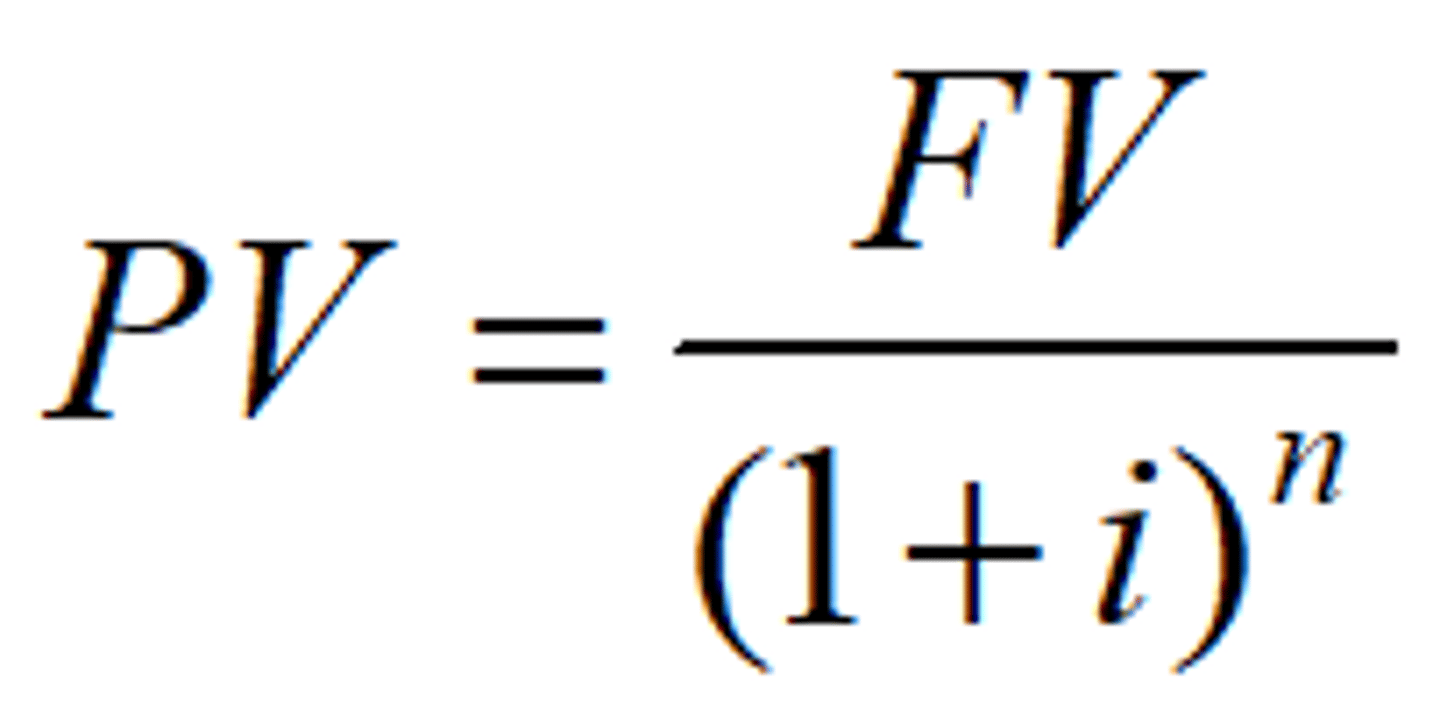
Present value of a stream
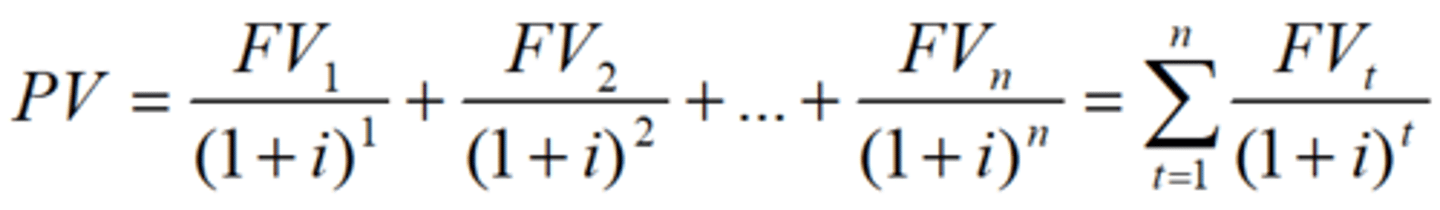
Net present value
If NPV is greater than or equal to zero, the manager should carry out the project.
If NPV is less than zero, the manager should NOT carry out the project.
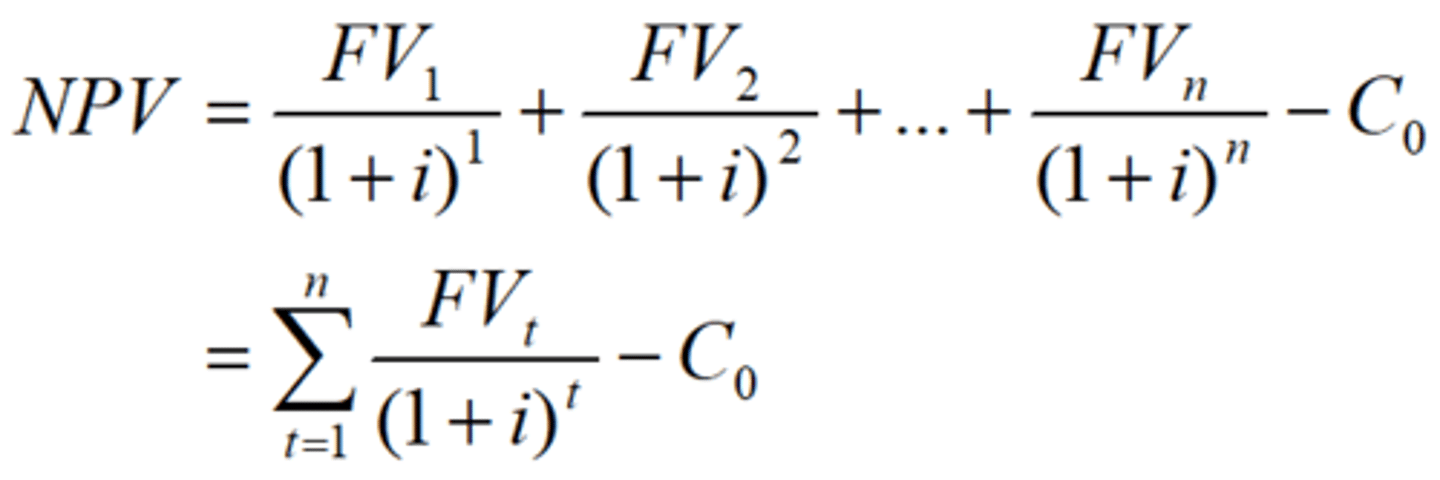
Managerial Control Variables
Output, Price, Product Quality, Advertising, R&D
Basic Managerial Question
How to choose the level of control variables to maximize profits?
Marginal Analysis
Marginal benefit (MB): The change in total benefits arising from a change in the managerial control variable.
Marginal cost (MC): The change in total costs arising from a change in the managerial control variable.
Net benefit is maximized when marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
Chapter 2
Law of Demand
Price and quantity demanded are inversely related, holding other factors constant
Normal goods
Increase (decrease) in income leads to an increase (decrease) in demand.
Inferior goods
Increase (decrease) in income leads to an decrease (increase) in demand
Complement
Increase in the price of one good leads to a decrease in the demand of other good
Substitutes
Increase in the price of one good leads to an increase in the demand for the other good
Demand Shifters
- Income
- Price of related goods
- Advertisements
- Population
- Consumer expectation
Demand function general form
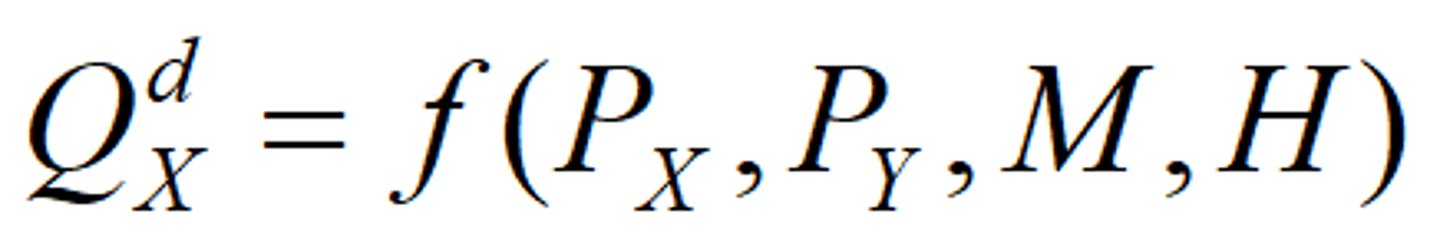
The linear demand function
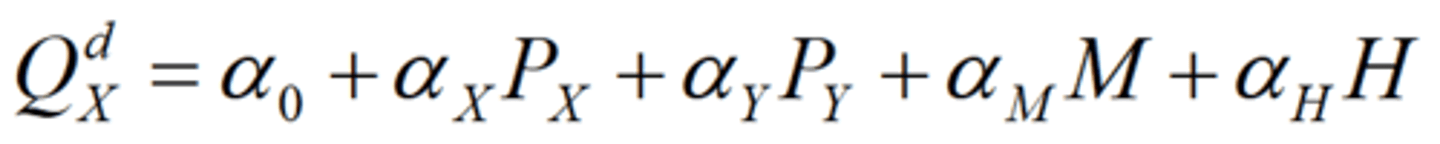
Consumer Surplus
The value consumers get from a good but do not have to pay for
Law of Supply
As the price of a good rises (falls) and other things remain constant, the quantity supplied of the good rises (falls)
Determinants of Supply
- Input prices
- Technology or government regulations
- Number of firms
- Substitutes in production
- Taxes
- Producer expectations
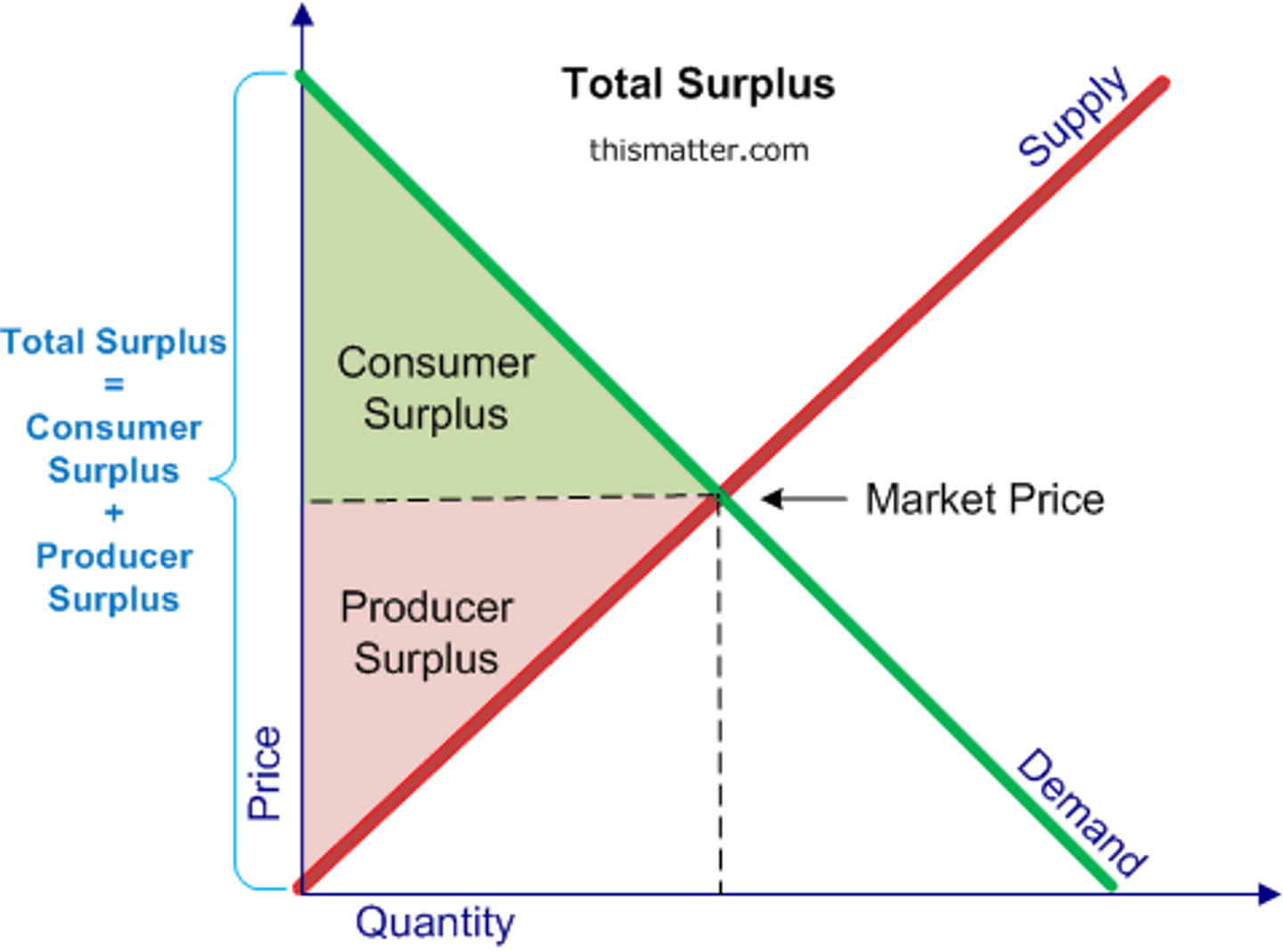
Producer Surplus
The amount producers receive in excess of the amount necessary to induce them to produce the good
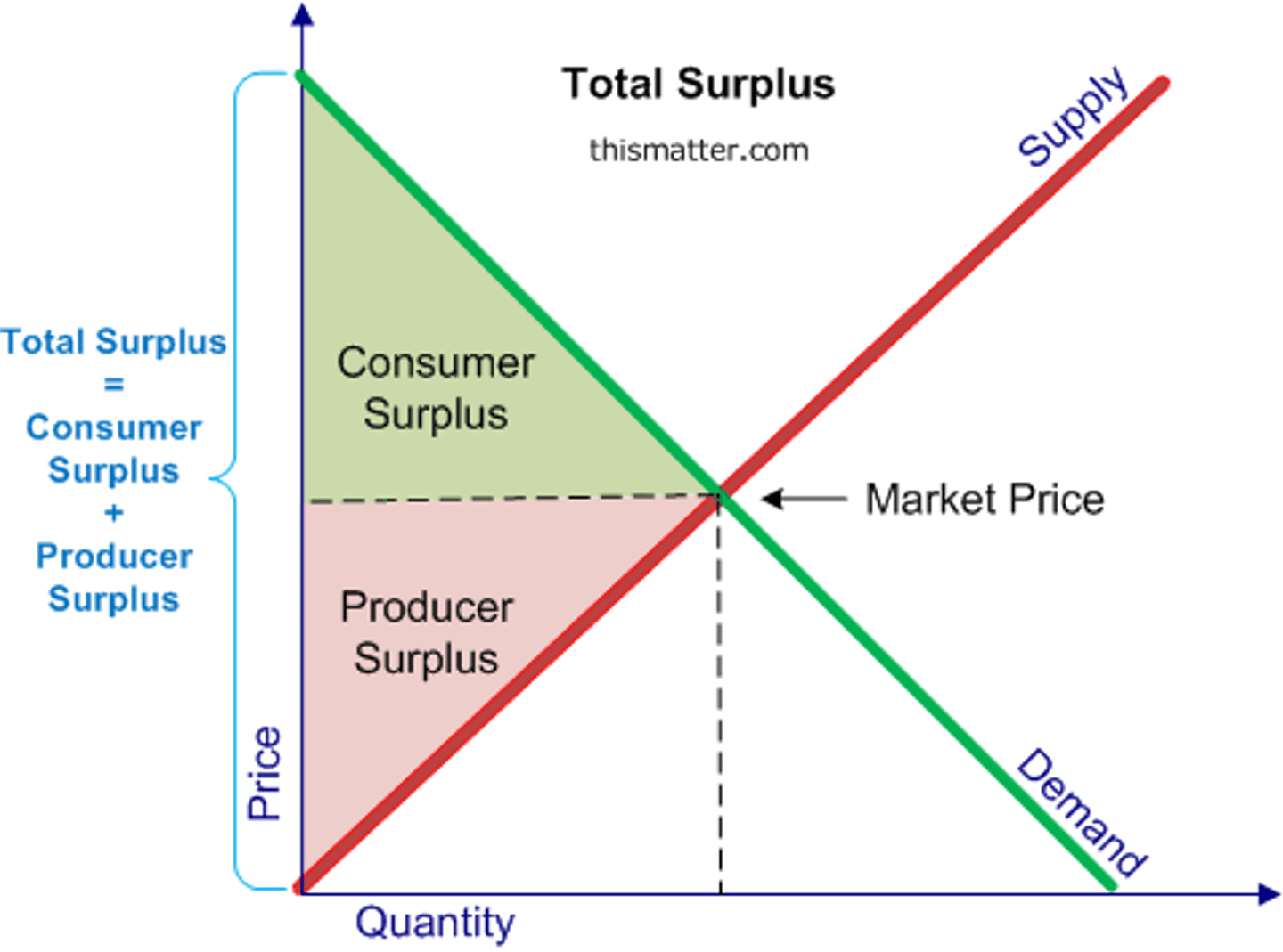
Market Equilibrium
demand = supply
Price Floor
The minimum legal price that can be charged
Ex. minimum wage, farming goods
Surplus
Price Ceiling
The maximum legal price that can be charged
Ex. Rent
Shortage
Chapter 3
Elasticity
- is a measure of how much buyers and sellers respond to changes in market conditions
- allows us to analyze supply and demand with greater precision
Price Elasticity of Demand
- the percentage change in quantity demanded given a percent change in the price
- It is a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good
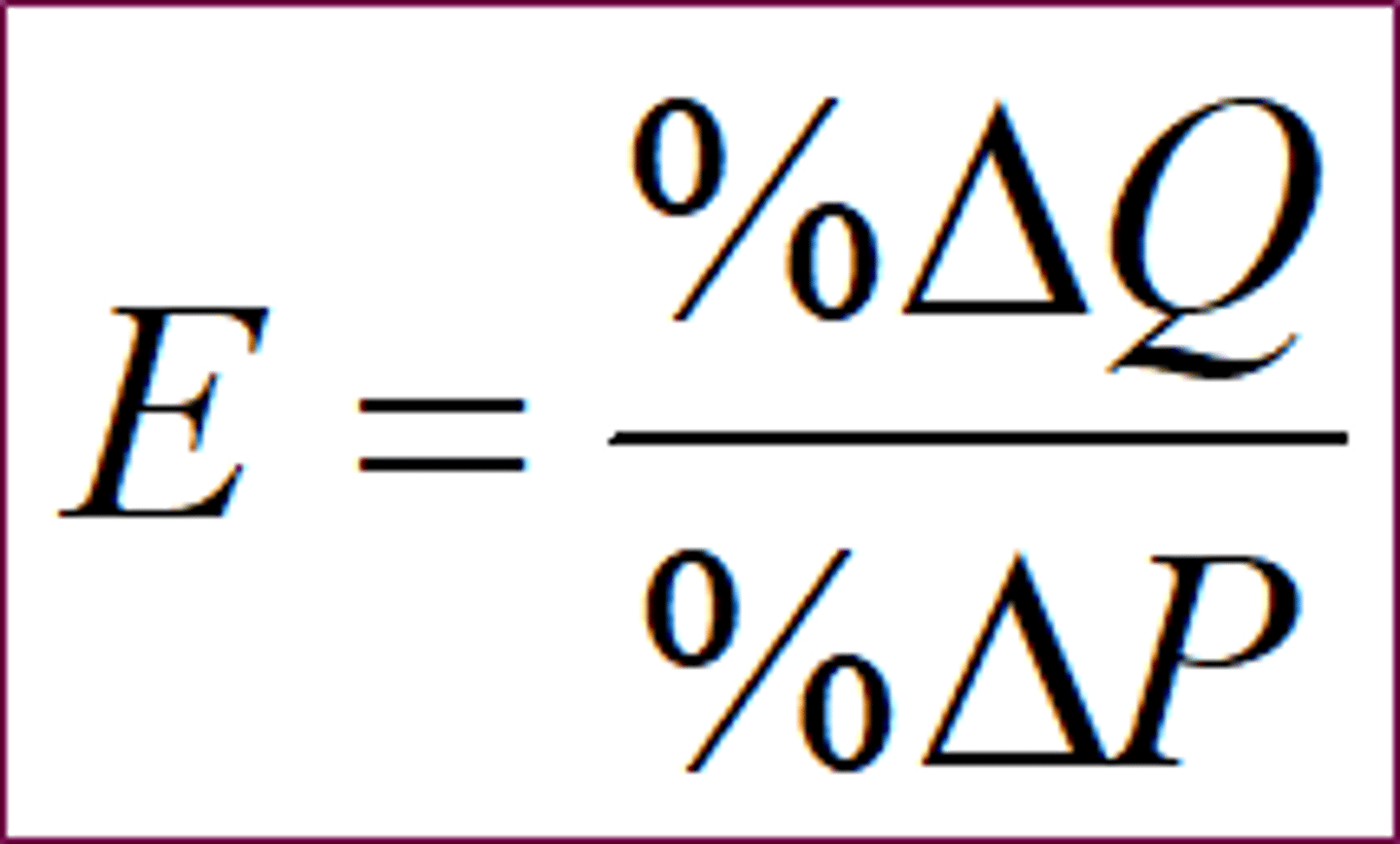
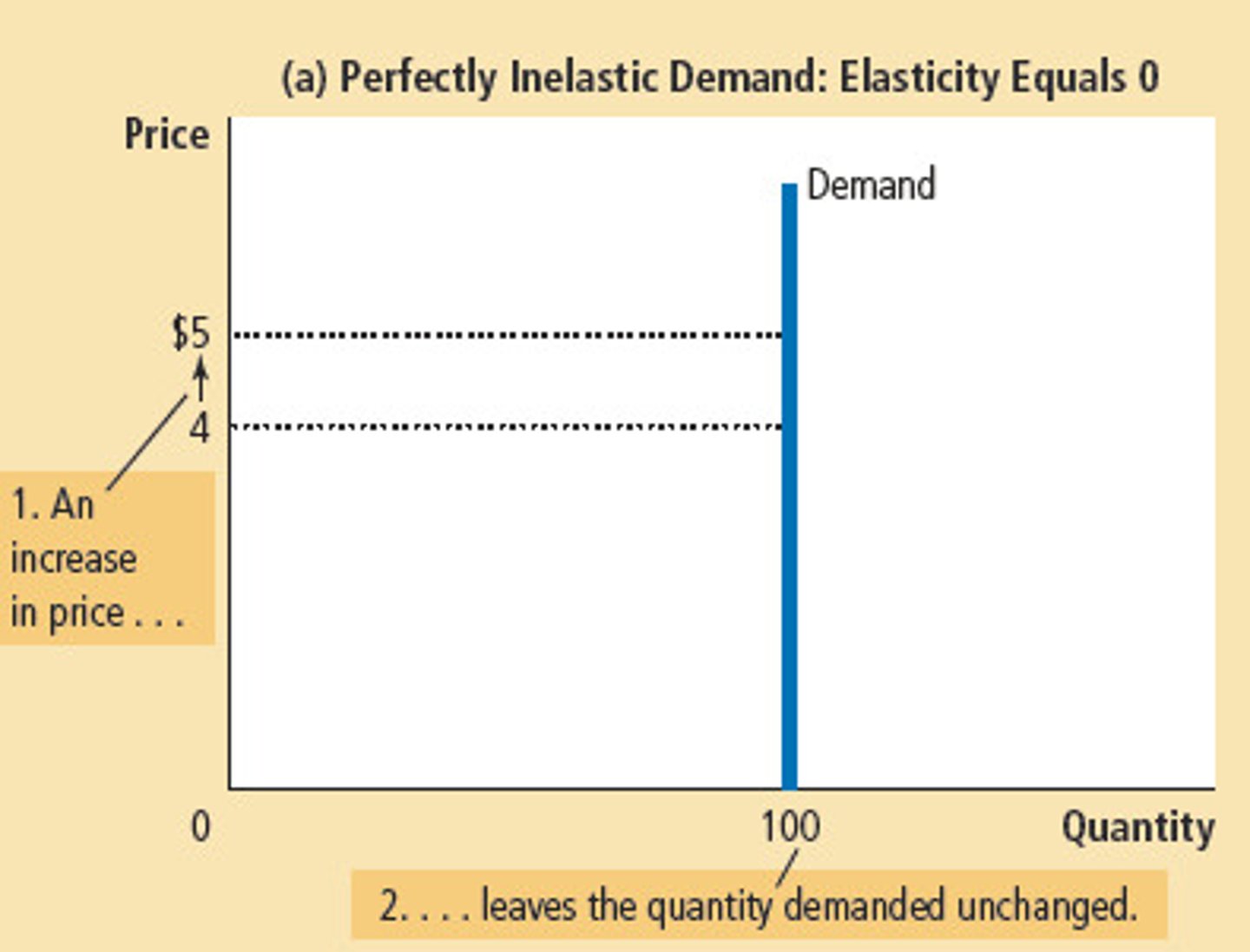
Perfectly Inelastic Demand
Elasticity equals 0
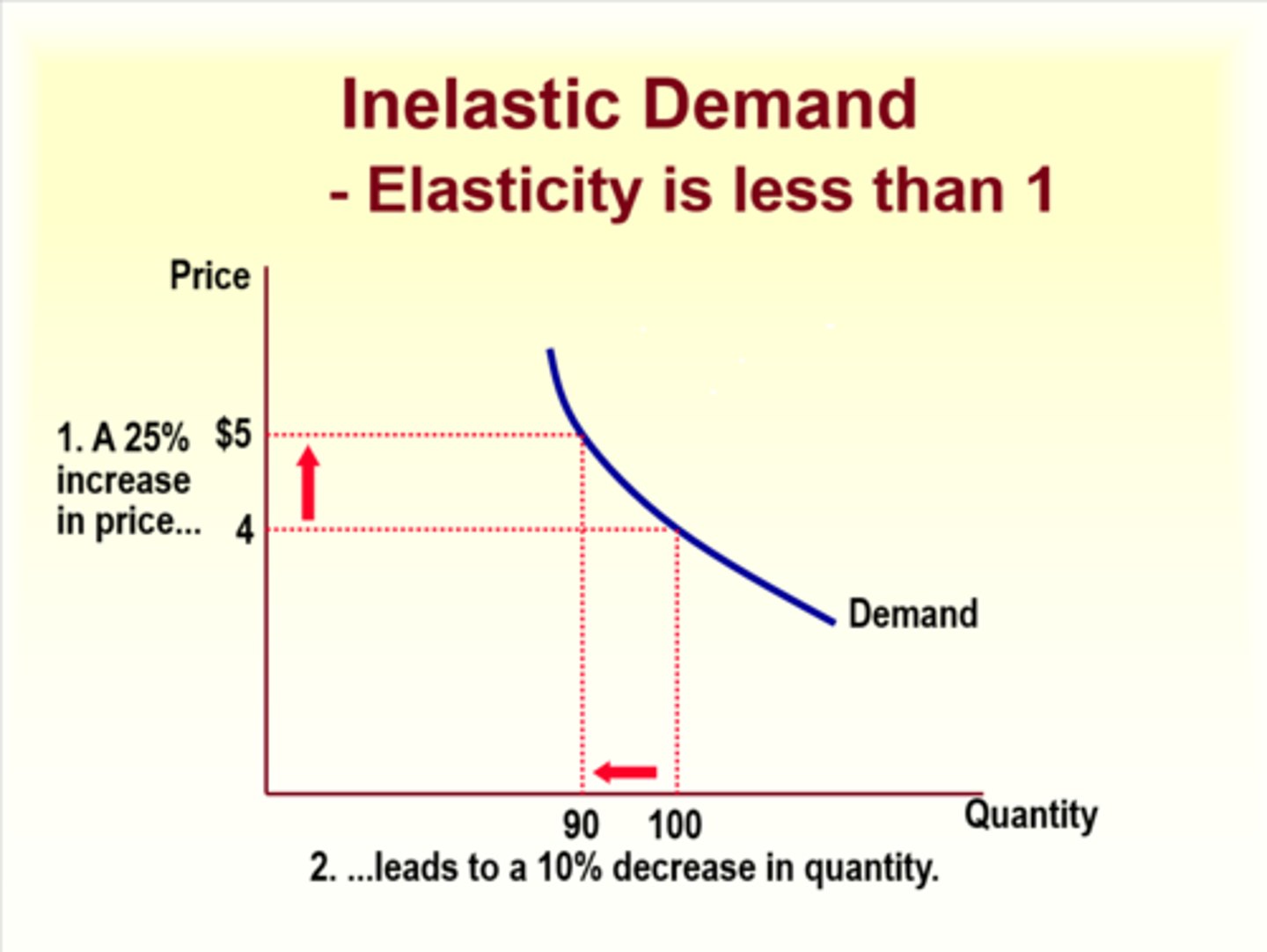
Inelastic Demand
Elasticity is less than 1
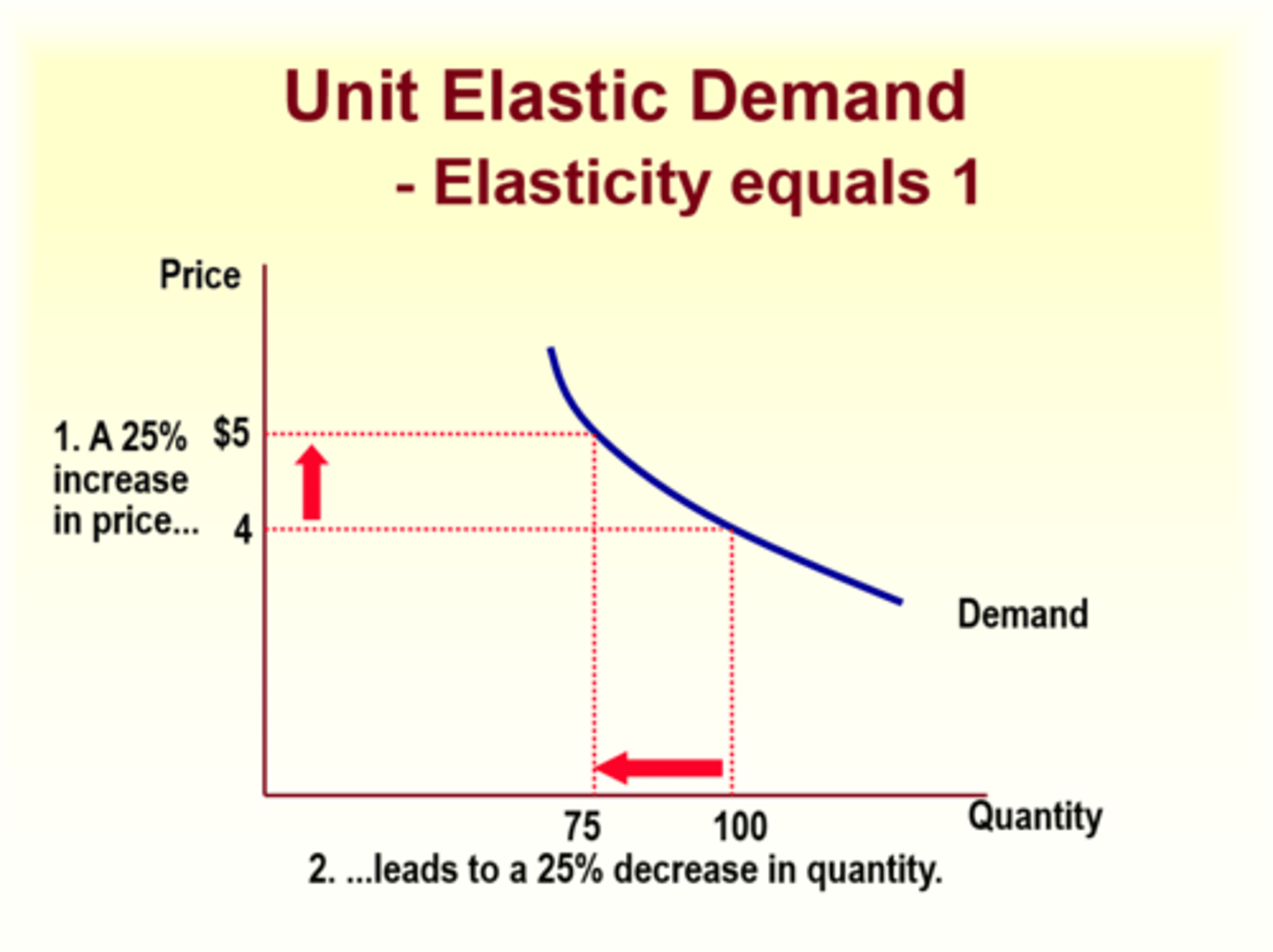
Unit Elastic Demand
Elasticity equals 1
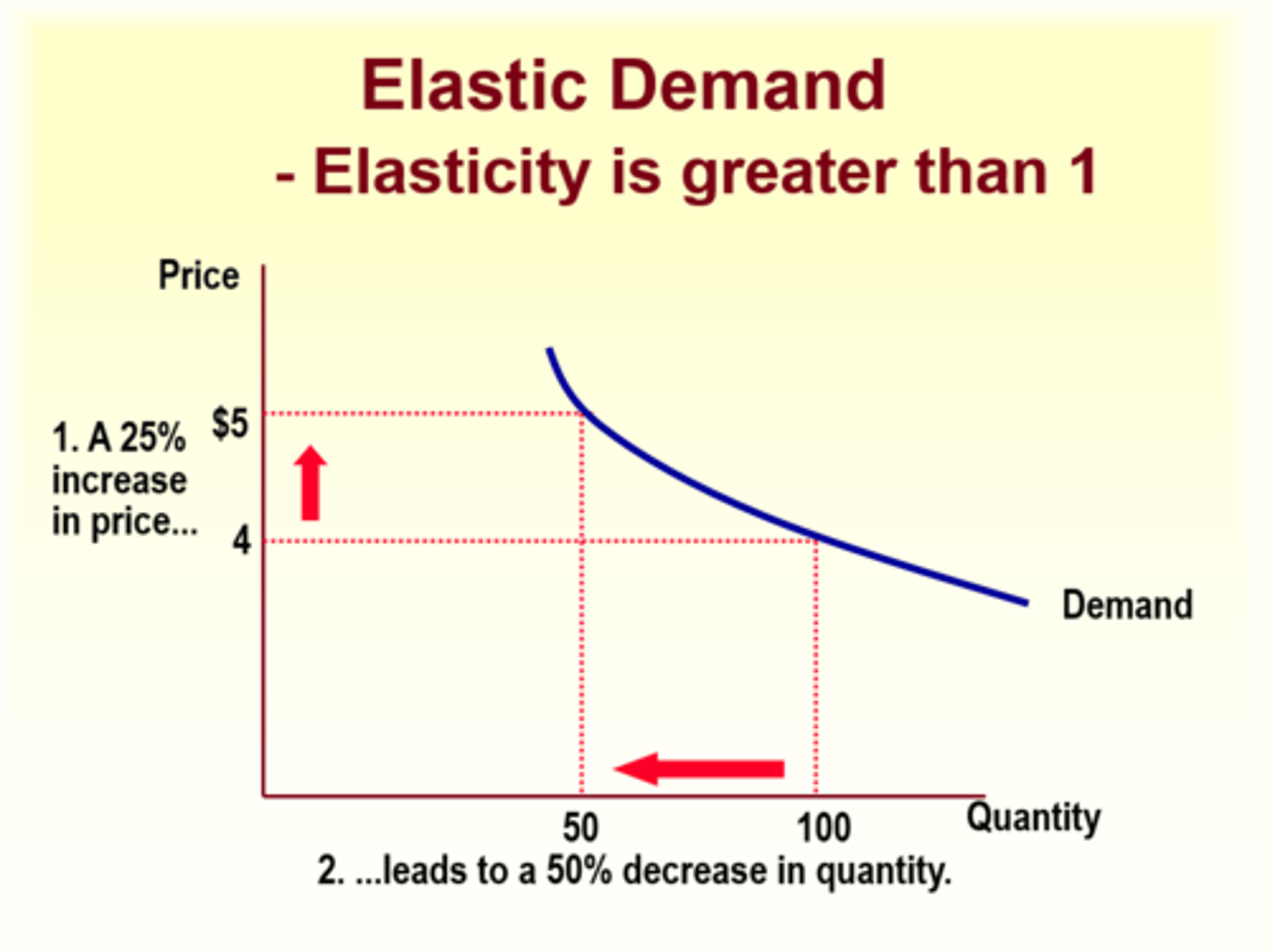
Elastic Demand
Elasticity is greater than 1
Perfectly Elastic Demand
Elasticity equals infinity
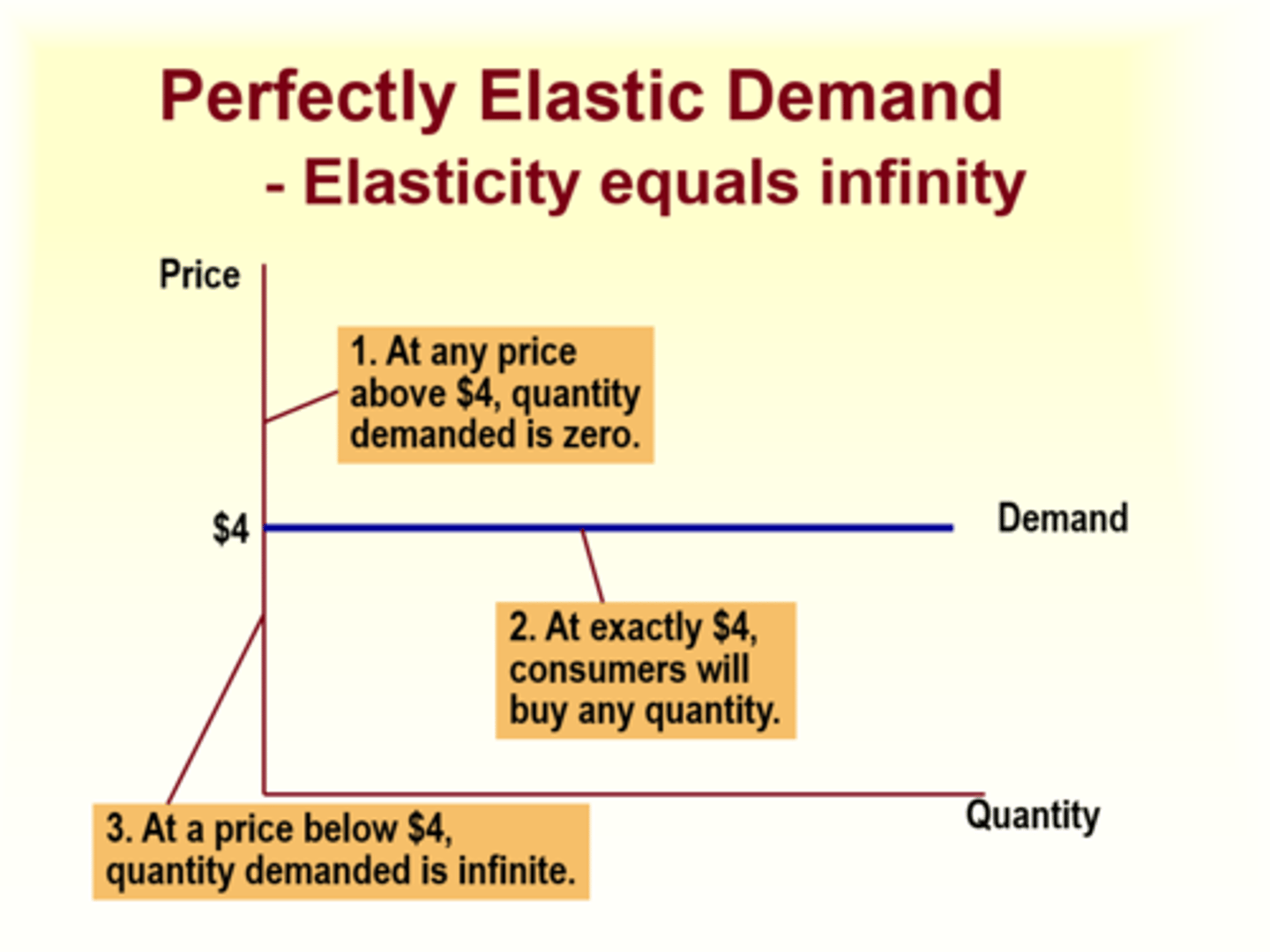
Available Substitutes
The greater the number of substitute products, the greater the elasticity
Time
Elasticity tend to be greater over the long run because consumers have more time to adjust their behavior to the price change
Expenditure Share
Products requiring a large proportion of the consumer's income tend to have greater elasticity
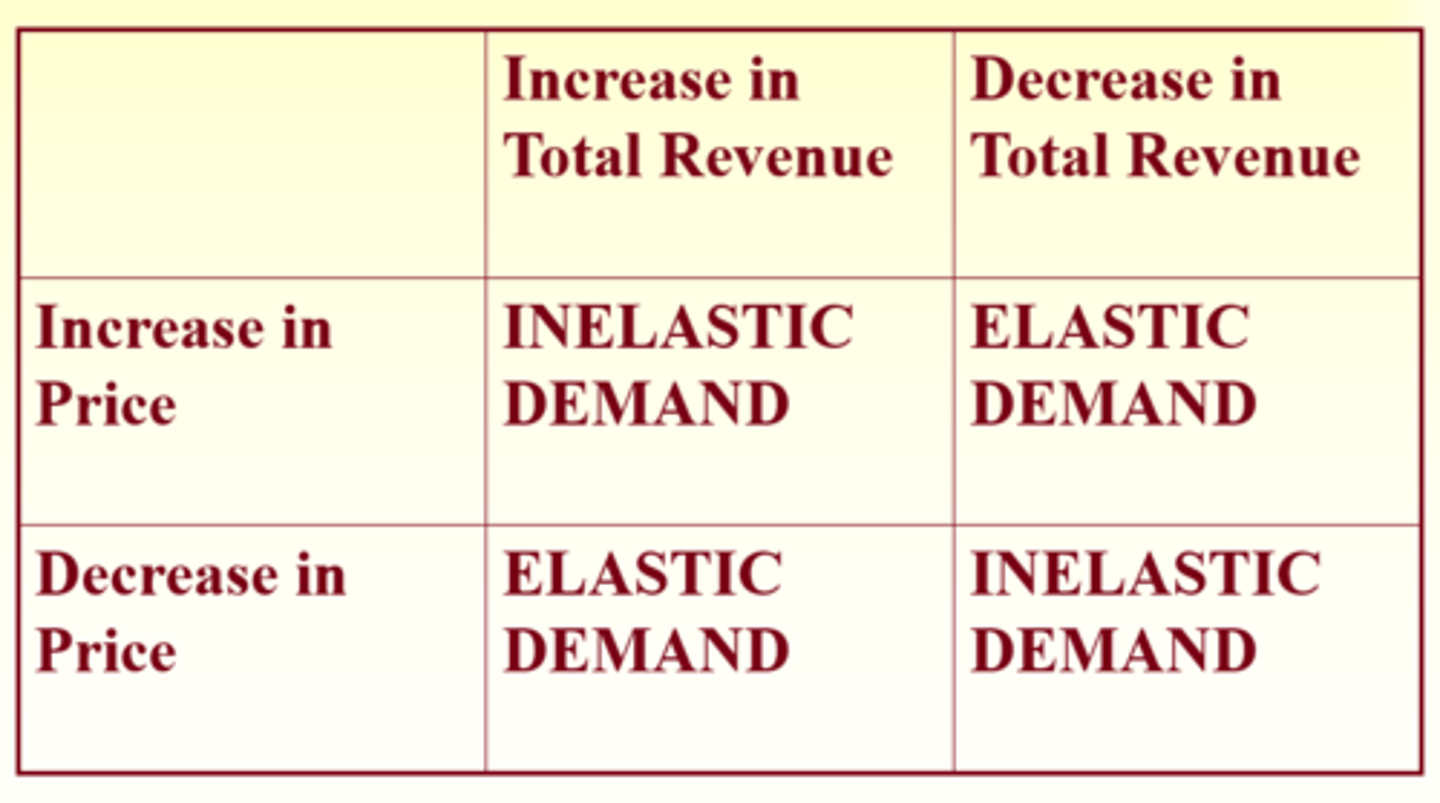
Elasticity and Total Revenue
Total revenue received for a supplier is the price charged times the quantity
Total revenue = total quantity sold * price of good
The Total Revenue Test for Elasticity
Cross Price Elasticity
The percentage change in the quantity demanded of one good that arises due to a given percentage change of the price of a related good.
- complements E<0 a consumption of a good goes down as the price of a related good goes up (-)
- substitutes E>0 a consumption of a good goes up as the price of a related good goes up (+)
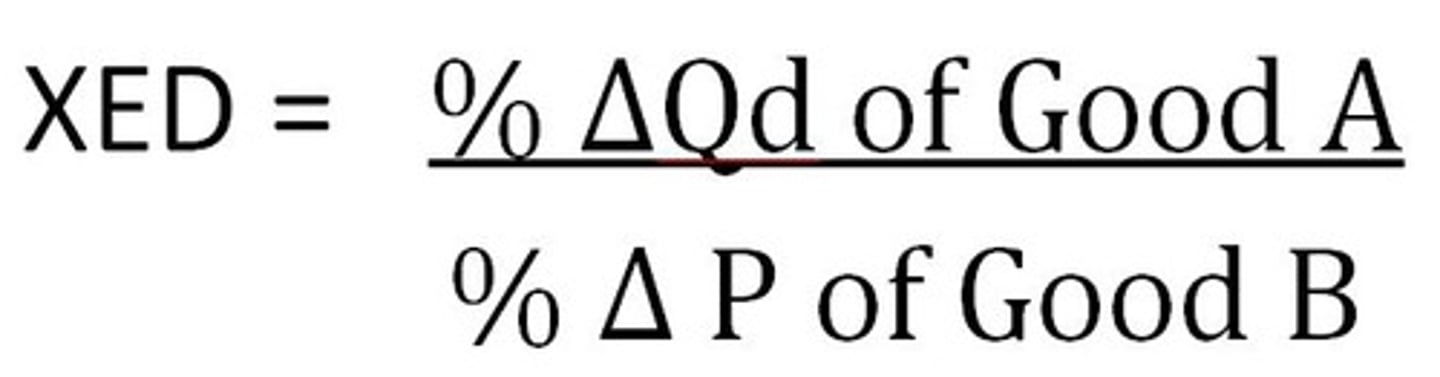
Income Elasticity
The percentage change in quantity demanded that arises due to a given percentage change in income
Inferior goods (E < 0) a consumption of a good goes down as income goes up
Normal goods (E > 0)
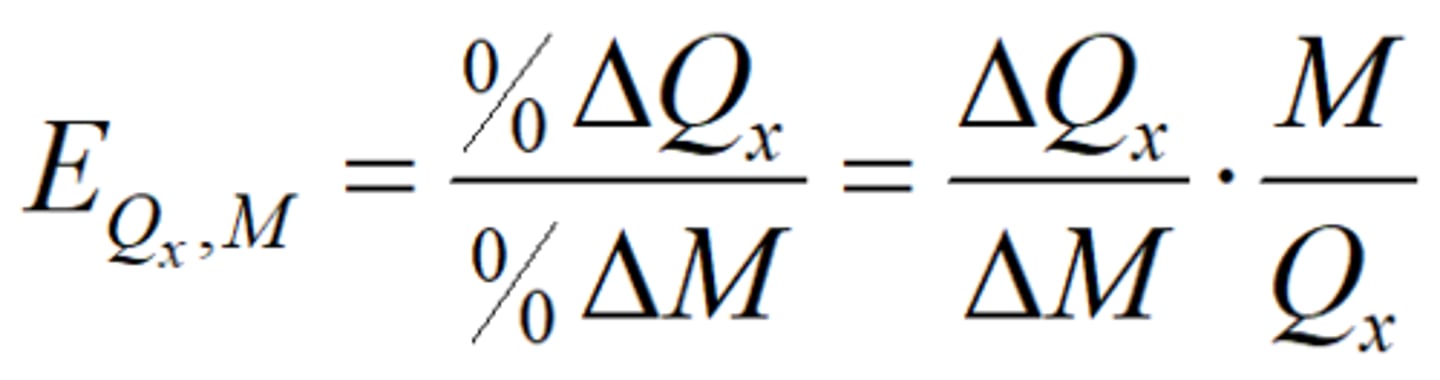
Chapter 5
Production Function
A function that defines the maximum amount of output that can be produced with a given set of inputs.
The production function summarizes the available technology.
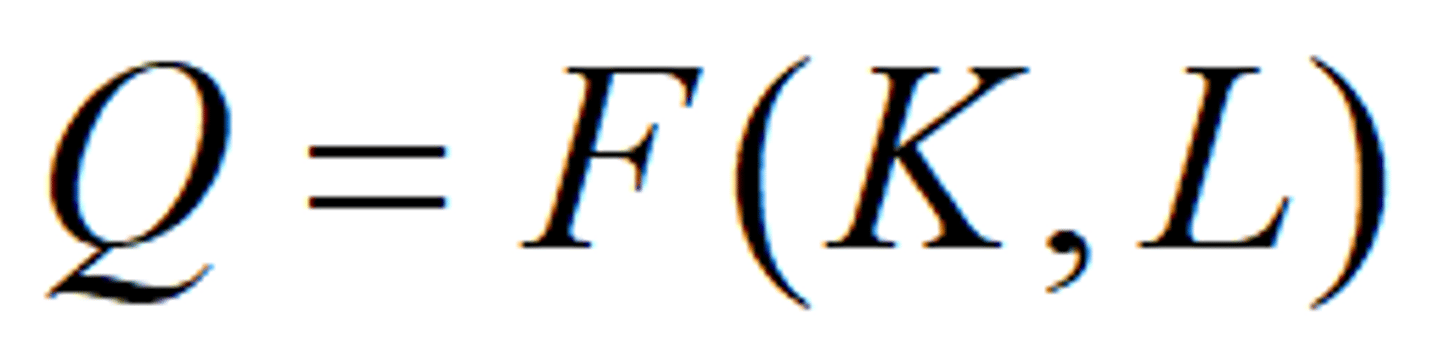
Short-Run vs. Long-Run Decisions.
Depending on the decision horizon, factors can be divided into fixed and variable factors.
Production Process
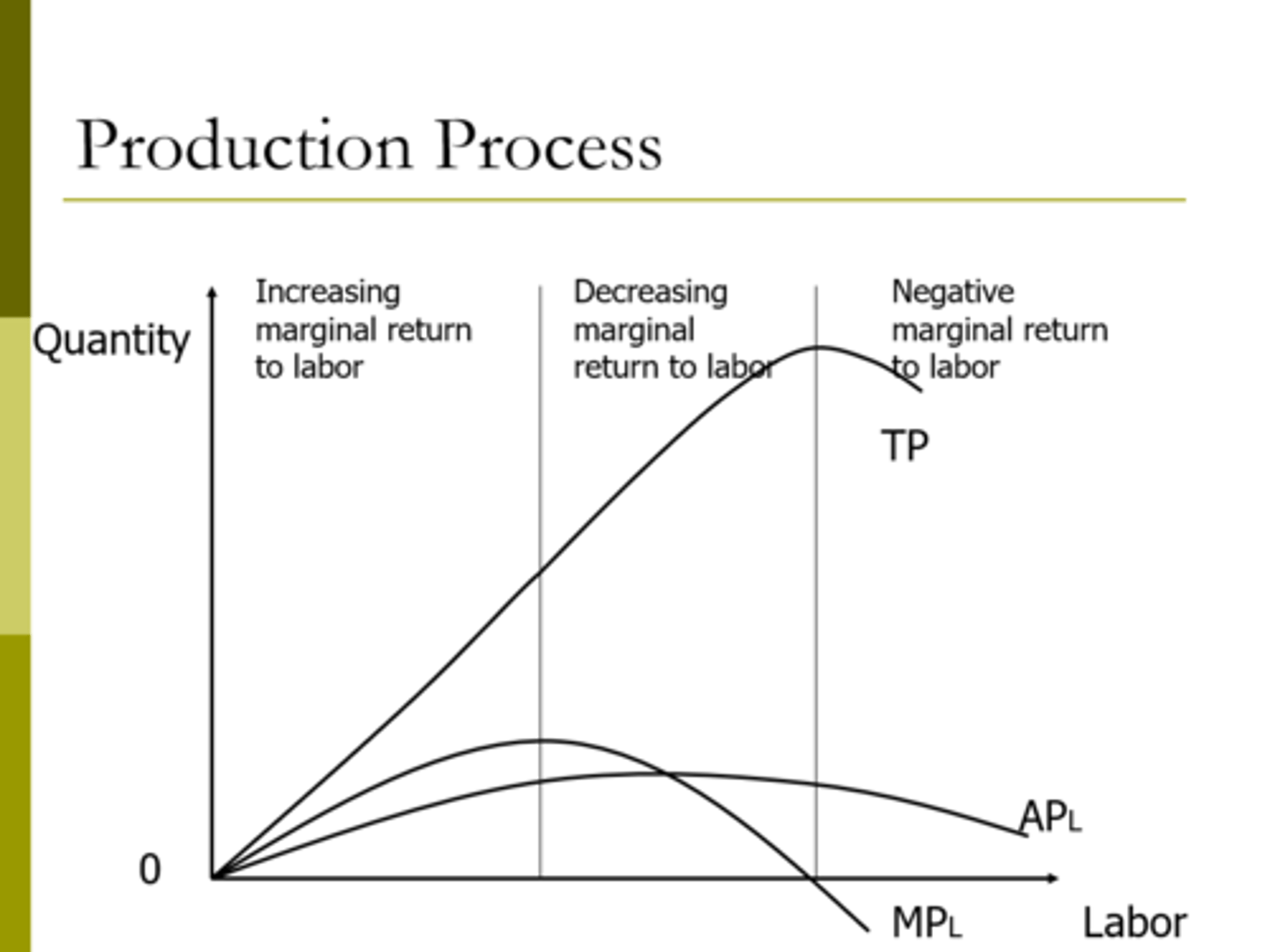
Use the Right Level of Inputs
Value marginal product (VMP):
The (monetary) value of the output produced by the last unit of input.
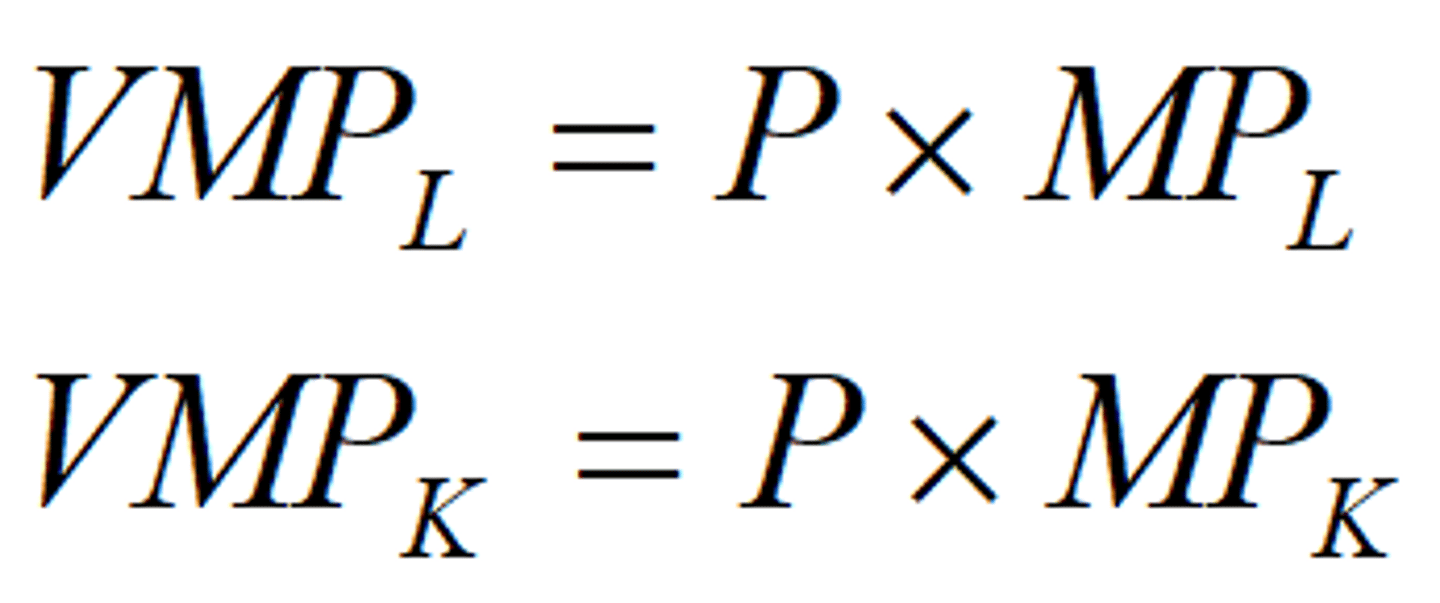
Linear Production Function
Form:

Linear Production Function
Marginal Products:
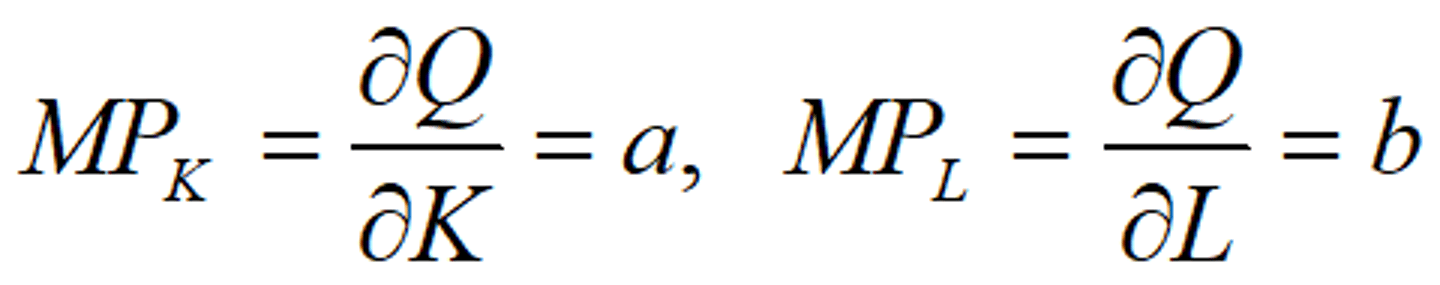
Cost Function
Cost function relates the output levels to the total cost (the minimum cost).
-Fixed cost (FC): cost of fixed inputs.
- Variable cost (VC): cost of variable inputs.
- Total cost: C(Q) = FC + VC.
Algebraic form of cost function C(Q).
Average and Marginal Costs
Average Fixed Cost: AFC = FC/Q
Average Variable Cost: AVC = VC/Q
Average Total Cost: ATC = C(Q)/Q
Marginal Cost: MC = ∂ C/ ∂ Q
Relationships Among Costs
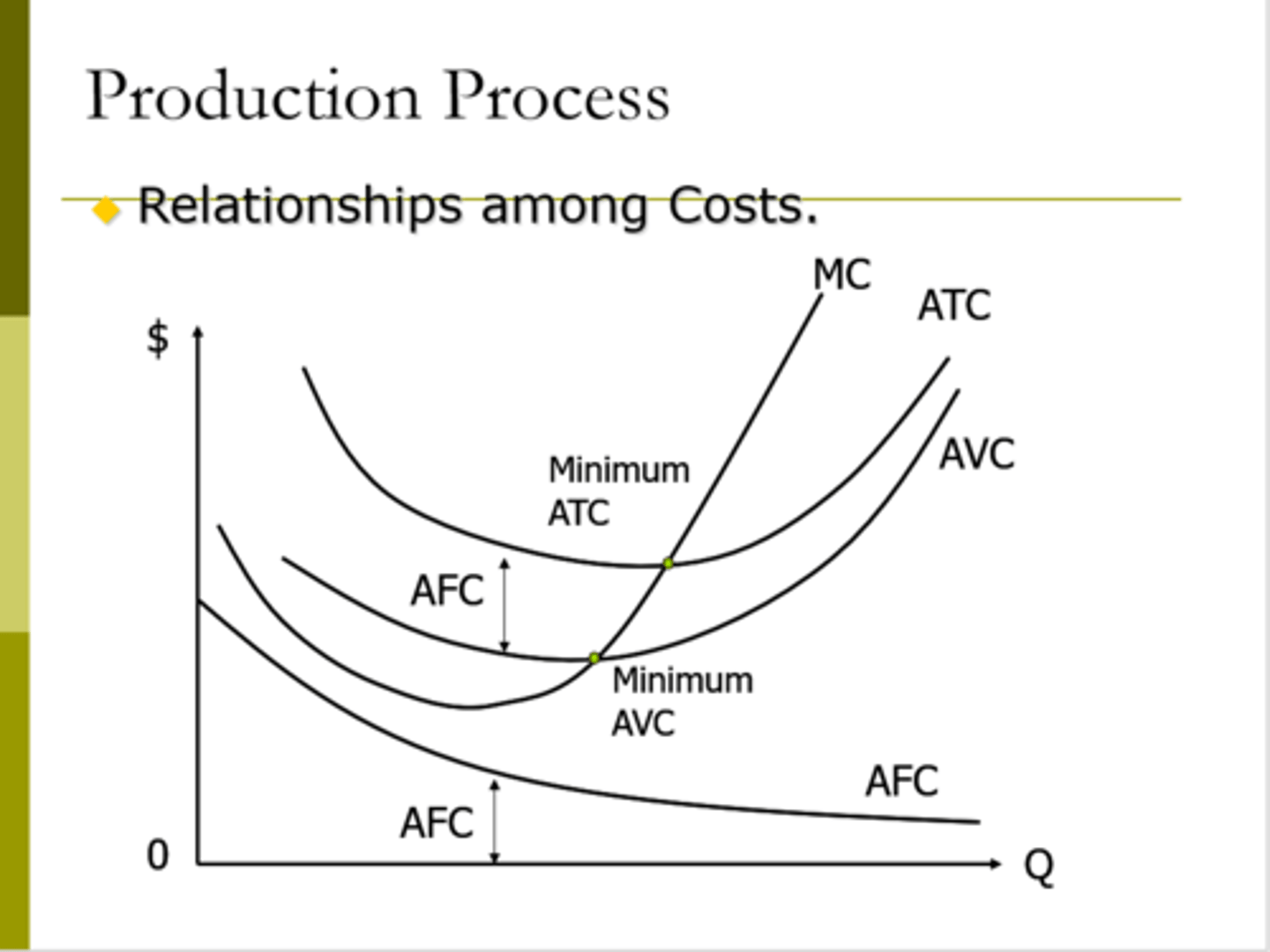
Chapter 8
Perfect Competition
- Many buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous product
- Perfect information
- No transaction cost
- Free entry and exit

Monopoly
- Single firm serves the "relevant market"
- Most monopolies are "local" monopolies
- The demand for the firm's product is the market demand curve
- The firm has control over the price
- But the price charged affects the quantity demanded of the monopolist's product
Monopolistic Competition
- Numerous buyers and sellers
- Implication: each firm has relatively small market share; each firm must be sensitive to average market price of its product (substitutes of each other’s product); collusion is impossible due to the large number of firms
- Differentiated products
- Implication: Since products are differentiated, each firm faces a downward sloping demand curve. Firms have limited market power.
- Product differentiation
- Free entry and exit
- Implication: Firms will earn zero profits in the long run.
Still learning (2)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!