Friedland Environmental Science for AP® Course, 4th Edition - Comprehensive Vocabulary for Unit 1
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Abiotic
Nonliving.
Accuracy
How close a measured value is to the actual or true value.
Biotic
Living.
Control group
In a scientific investigation, a group that experiences exactly the same conditions as the experimental group, except for the single variable under study.
Deductive reasoning
The process of applying a general statement to specific facts or situations.
Dependent variable
A variable that is dependent on other factors.
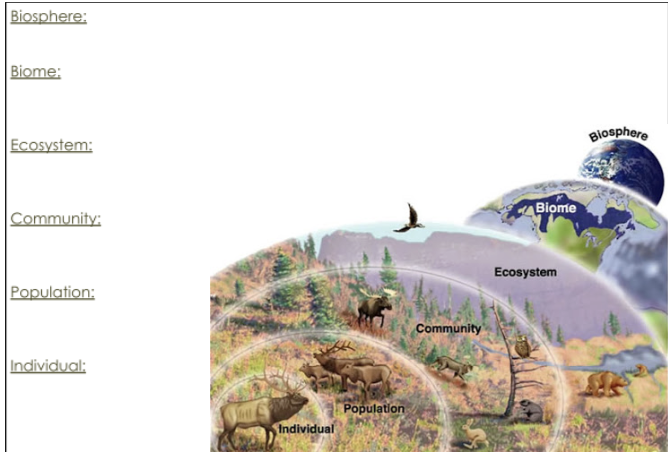

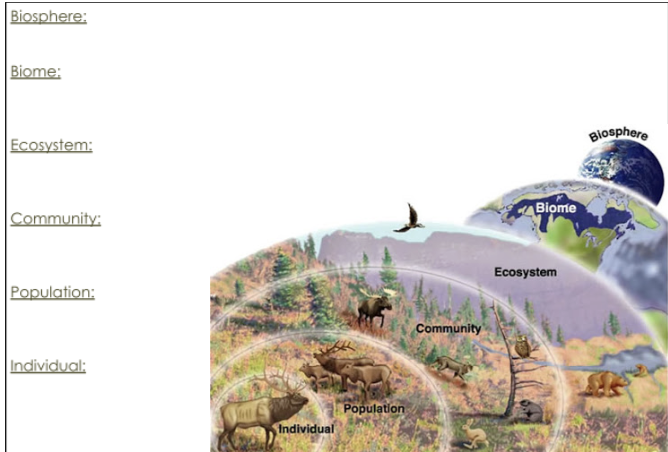
Ecosystem
A particular location on Earth with interacting biotic and abiotic components.

Environment
The sum of all the conditions surrounding us that influence life.
Environmental science
The field of study that looks at interactions among human systems and those found in nature.
Environmental studies
The field of study that includes environmental science and additional subjects such as environmental policy, economics, literature, and ethics.
Environmentalism
A social movement that seeks to protect the environment through lobbying, activism, and education.
First law of thermodynamics
A theory with no known exception that states that energy is neither created nor destroyed but it can change from one form to another.
Hypothesis
A testable conjecture about how something works.
Independent variable
A variable that is not dependent on other factors.
Inductive reasoning
The process of making general statements from specific facts or examples.
Natural experiment
A natural event that acts as an experimental treatment in an ecosystem.
Null hypothesis
A prediction that there is no difference between the groups or conditions that are being compared.
Precision
How close the repeated measurements of a sample are to one another.
Replication
The data collection procedure of taking repeated measurements.
Sample size (n)
The number of times a measurement is replicated in data collection.
Scientific method
An objective method to explore the natural world, draw inferences from it, and predict the outcome of certain events, processes, or changes.
Second law of thermodynamics
The physical law stating that when energy is transformed, the quantity of energy remains the same, but its ability to do work diminishes. In other words, energy is used as it dissipates and degrades
Sustainability
Living on Earth in a way that allows humans to use its resources without depriving future generations of those resources.
Theory
A hypothesis that has been repeatedly tested and confirmed by multiple groups of researchers and has reached wide acceptance.
Uncertainty
An estimate of how much a measured or calculated value differs from a true value.
Variable
Any categories, conditions, factors, or traits that differ in the natural world or in experimental situations.
Aerobic
An environment with abundant oxygen.
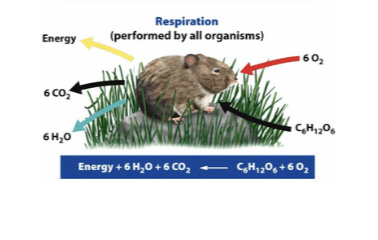
Aerobic respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
Algal bloom
A rapid increase in the algal population of a waterway.
Anaerobic
An environment that lacks oxygen.
Anaerobic respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose into energy in the absence of oxygen.
Aphotic zone
The deeper layer of ocean water that lacks sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis.
Aquatic biome
An aquatic region characterized by a particular combination of salinity, depth, and water flow.
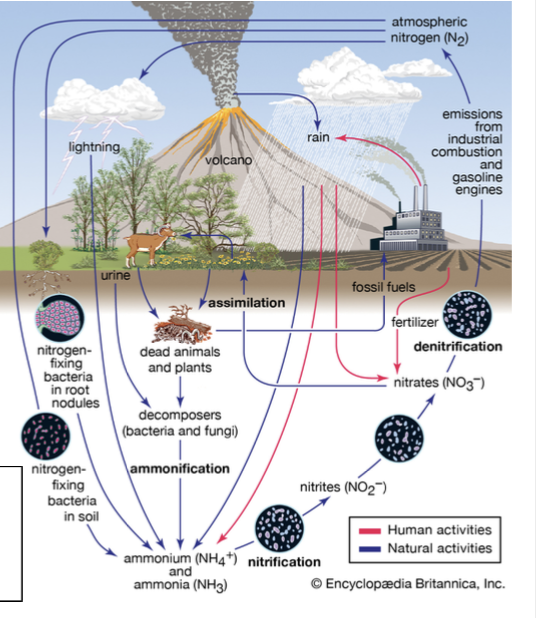
Assimilation
A process by which plants and algae incorporate nitrogen into their tissues.
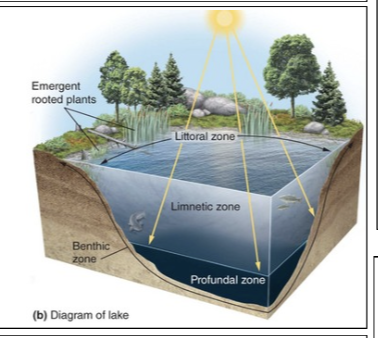
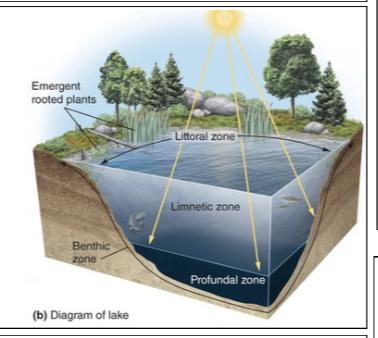
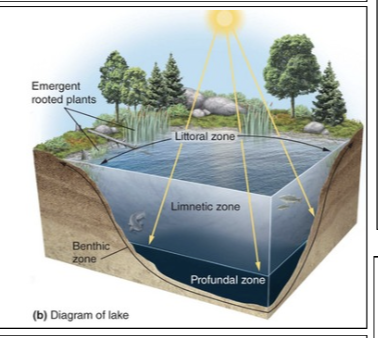
Benthic zone
The muddy bottom of a lake, pond, or ocean beneath the limnetic and profundal zones.
Biogeochemical cycle
The movements of matter within and between ecosystems involving cycles of biological, geological, and chemical processes.
Biomass
Biological material that has mass.
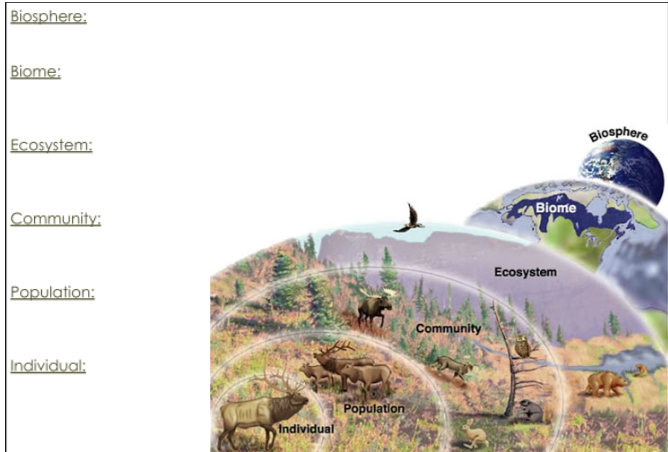

Biome
The plants and animals that are found in a particular region of the world. It is characterized by, at least for terrestrial biomes, the annual precipitation and temperature.
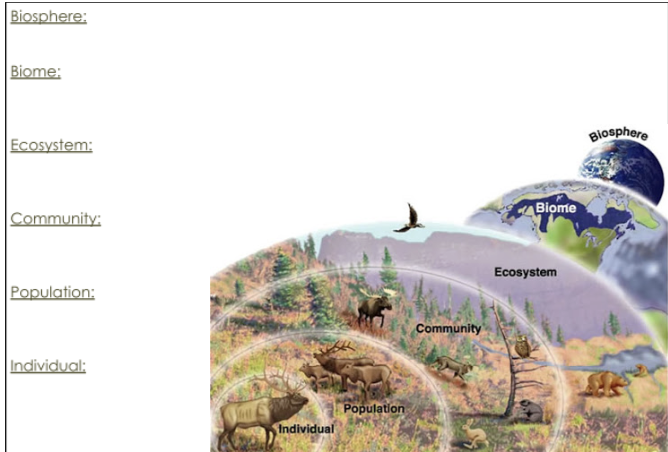

Biosphere
The region of our planet where life resides.
20killometer layer between deepest ocean bottom and highest mountain point
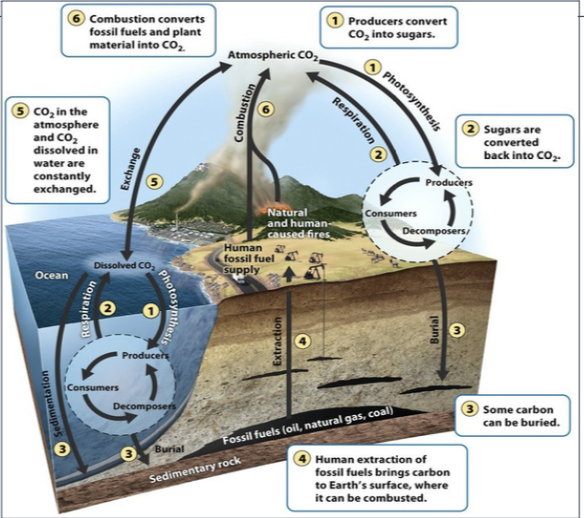
Carbon cycle
The movement of carbon around the biosphere among reservoir sources and sinks.
in depth overview:
Plants and algae use photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Organisms use their portion of carbon and release carbon dioxide through aerobic respiration and decomposition.
Another form of carbon movement is sedimentation, where carbon dioxide in the ocean is used to make calcium carbonate.
These movements allow for a steady state, where the inputs of carbon equal the outputs of carbon.
Human extraction and combustion of carbon locked in fossil fuels leads to a lack of steady state of carbon.
Carnivore
A consumer that eats other consumers.
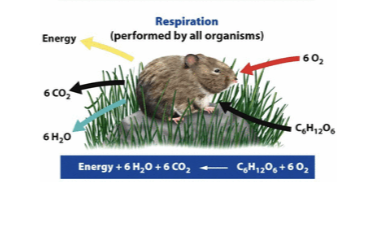
Cellular respiration
The process by which cells unlock the energy of chemical compounds.
Chemosynthesis
A process used by some bacteria to generate energy with methane and hydrogen sulfide.
Climate
The average weather that occurs in a given region over a long period of time.
Commensalism
An interaction between two species in which one species benefits and the other species is neither harmed nor helped.
Community ecology
The study of interactions among species.
Competition
The struggle of individuals, either within or between species, to obtain a shared limiting resource.
Competitive exclusion principle
The principle stating that two species competing for the same limiting resource cannot coexist.
Consumer (Heterotroph)
An organism that is incapable of photosynthesis and must therefore obtain its energy by consuming other organisms.
Coral bleaching
A phenomenon in which algae inside corals die, causing the corals to turn white.
Coral reef
Represents Earth’s most diverse marine biome, and are found in warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline in tropical regions. characterized by symbiotic coral species that are prone to coral bleaching
Dead zone
When oxygen concentrations become so low that it kills fish and other aquatic animals.
Decomposers
Fungi and bacteria that complete the breakdown process by converting organic matter into small elements and molecules that can be recycled back into the ecosystem.
Denitrification
The conversion of nitrate (NO3) in a series of steps into the gases nitrous oxide (N2O) and, eventually, nitrogen gas (N2O), which is emitted into the atmosphere.
Detritivore
An organism that specializes in breaking down dead tissues and waste products into smaller particles.
Ecological efficiency
The proportion of consumed energy that can be passed from one trophic level to another.
Estuary
An area along the coast where the fresh water of rivers mixes with salt water from the ocean.
can filter contaminants
Very productive areas
Eutrophic
Describes a lake with a high level of fertility.
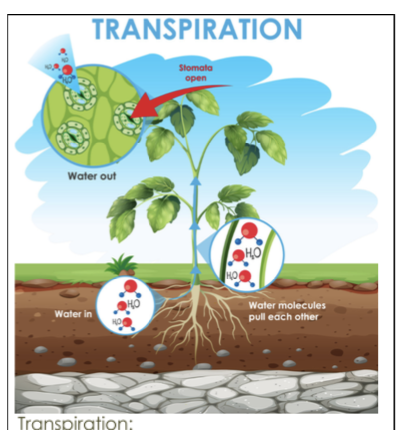
Evapotranspiration
The combined amount of evaporation and transpiration.
Exotic species (Alien species)
A species living outside its historical range.
Can have a negative impact on native species

Food chain
The sequence of consumption from producers through tertiary consumers.
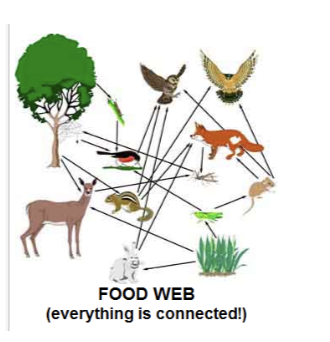
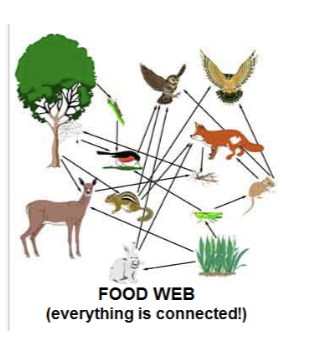
Food web
A model of how energy and matter move through two or more interconnected food chains.
Freshwater biomes
Categorized as streams and rivers, lakes and ponds, or freshwater wetlands.
they have low salinity
Freshwater wetland
An aquatic biome that is submerged or saturated by water for at least part of each year, but shallow enough to support emergent vegetation. Many birds depend on wetlands during migration and breeding seasons. much of these areas have been drained for agriculture and development
Global warming
The increase in global temperatures due to humans producing more greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gases
Gases in Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat near the surface.
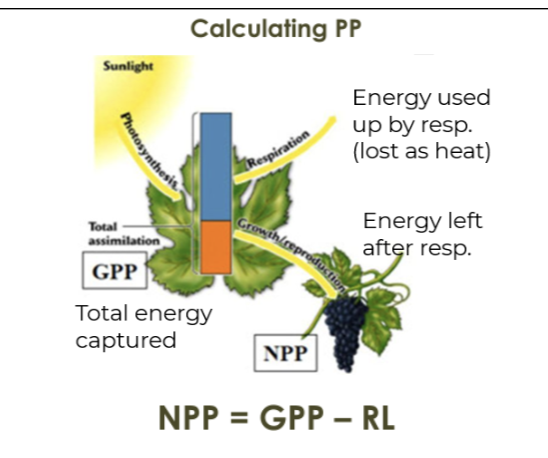
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time.
Habitat
An area where a particular species lives in nature.
Herbivore (Primary consumer)
A consumer that eats producers.
Herbivory
An interaction in which an animal consumes plants or algae.

Hot desert
A biome located at roughly 30° N and 30° S, and characterized by hot temperatures, extremely dry conditions, and sparse vegetation.
located near the equator
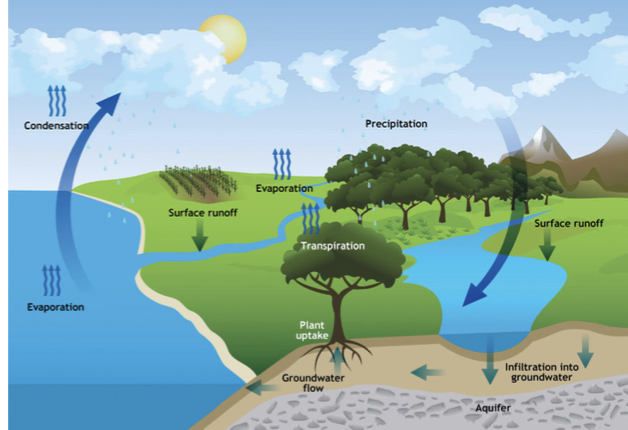
Hydrologic cycle
The movement of water around the biosphere among reservoir sources and sinks.
in depth review
Water is essential to life on this planet, especially for mammals, as over half of their body weight is made of water.
Water moves through reservoir sources and sinks called the hydrologic cycle.
During photosynthesis, water releases from leaves into the atmosphere. This is one of the first processes in the hydrologic cycle, called transpiration.
The combination of evaporation and the process of transpiration is evapotranspiration.
Other ways water moves are through precipitation forms and runoff into streams and rivers.
Hypoxic
Low in oxygen.
Intertidal zone
The narrow band of coastline that exists between the levels of high tide and low tide.
many species must adapt to extreme temperatures and desiccation
Invasive species
A species that spreads rapidly across large areas and causes harm.
Leaching
A process in which dissolved molecules are transported through the soil via groundwater.
Limiting nutrient
A nutrient required for the growth of an organism but available in a lower quantity than other nutrients.
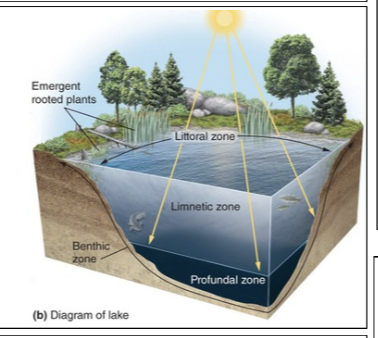
Limnetic zone
A zone of open water in lakes and ponds as deep as the sunlight can penetrate.
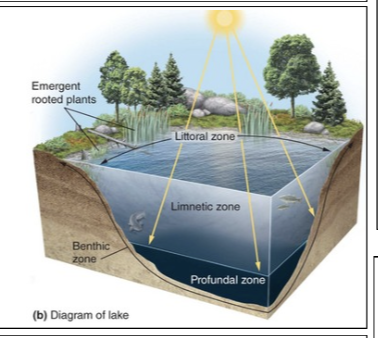
Littoral zone
The shallow zone of soil and water in lakes and ponds near the shore where most algae and emergent plants such as cattails grow.
Mangrove swamp
A swamp that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts, and contains salt-tolerant trees with roots submerged in water.
survives high salt content
Mesotrophic
Describes a lake with a moderate level of fertility.
Mineralization (Ammonification)
The process by which fungal and bacterial decomposers break down the organic matter found in dead bodies and waste products and convert it into inorganic compounds, such as inorganic ammonium (NH4+).
Mutualism
An interaction between two species that increases the chances of survival or reproduction for both species.
plants and pollinators are an example
Native species
A species that lives in its historical range, typically where it has lived for thousands or millions of years.
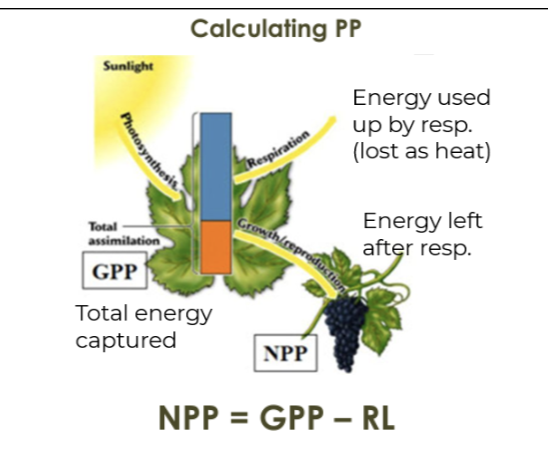
Net primary productivity (NPP)
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire.
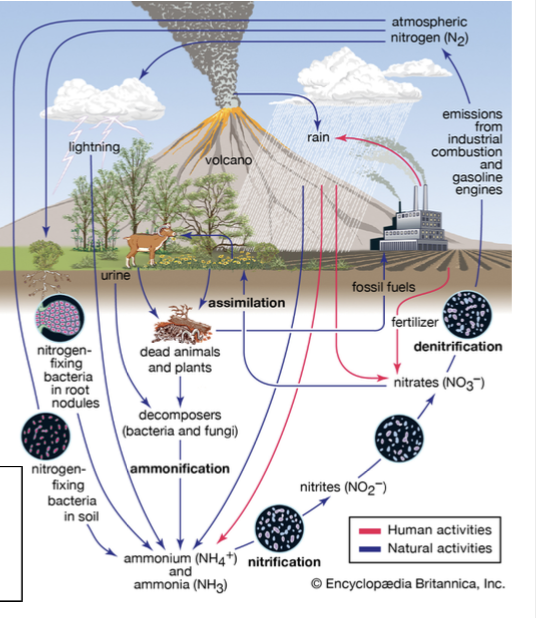
Nitrification
The conversion of ammonia (NH4+) into nitrite (NO2−) and then into nitrate (NO3−).
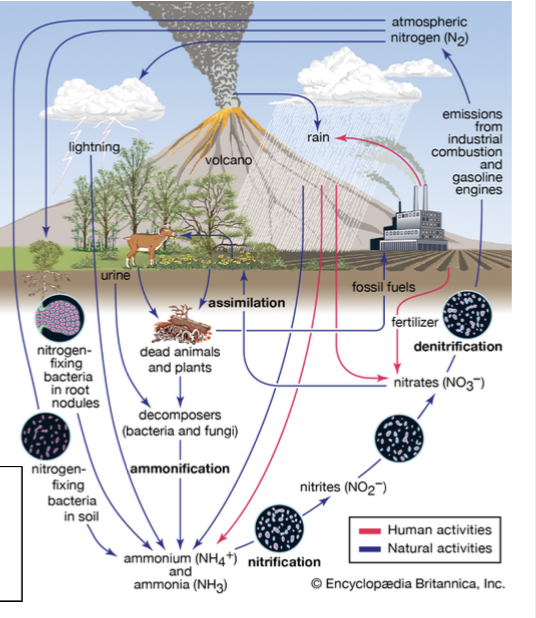
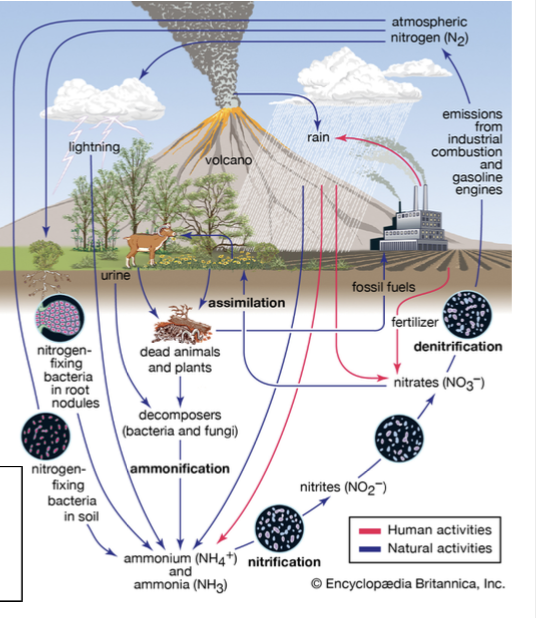
Nitrogen cycle
The movement of nitrogen around the biosphere among reservoir sources and sinks.
in depth explanation:
Nitrogen is a building block of proteins and nucleic acids, making it one of the limiting nutrients.
The nitrogen cycle allows for the movement of nitrogen around the biosphere among reservoir sources and sinks.
The atmosphere is 78% nitrogen, but is in the biologically unusable form N2.
Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting nitrogen gas into forms that plants and algae can use.
Once plants and algae convert it into ions such as ammonia (NH4+), nitrite (NO2−), and then into nitrate (NO3−), they have completed the process of nitrification.
Once nitrogen is turned into usable ions, it is then assimilated into animal tissues and when herbivores feed on plants. The herbivores then release any nitrogen not assimilated as waste products.
Eventually, organisms die and fungal and bacterial organisms break down the organic matter to convert it back into ammonium, known as ammonification or mineralization.
The final step is to return nitrogen gas into the atmosphere through multiple steps: through anaerobic conditions by bacteria through the process of denitrification.
Human impacts to the nitrogen cycle:
Being a limiting factor, humans have developed ways to create synthetic nitrogen and add it to fertilizers.
This leads to leaching – dissolved molecules transported to groundwater through the soil.
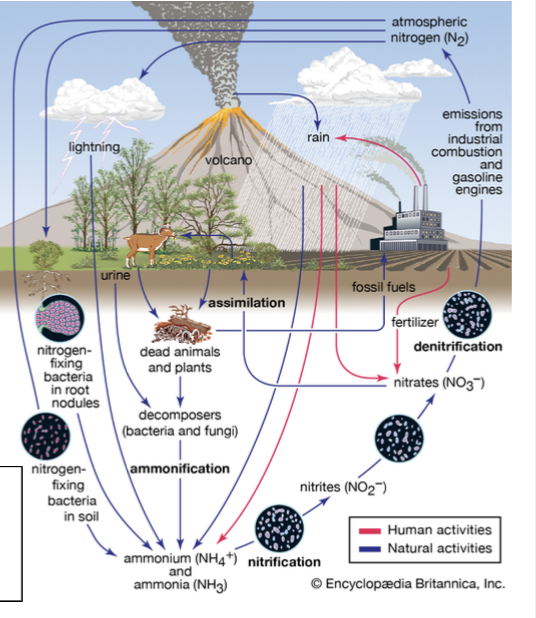
Nitrogen fixation
The process that converts nitrogen gas in the atmosphere (N2) into forms of nitrogen that plants and algae can use.
Oligotrophic
Describes a lake with a low level of phytoplankton due to low amounts of nutrients in the water.
Open ocean
Deep-ocean water, located away from the shoreline where sunlight can no longer reach the ocean bottom.
Parasitism
An interaction in which one organism lives on or in another organism, referred to as the host.
Parasitoid
A specialized type of predator that lays eggs inside other organisms—referred to as its host.
An example is parasetic wasps laying eggs inside of aphids
Pathogen
A parasite that causes disease in its host.
Some examples are viruses, bacteria, fungi, protists, and helminths
Permafrost
An impermeable, permanently frozen layer of soil.
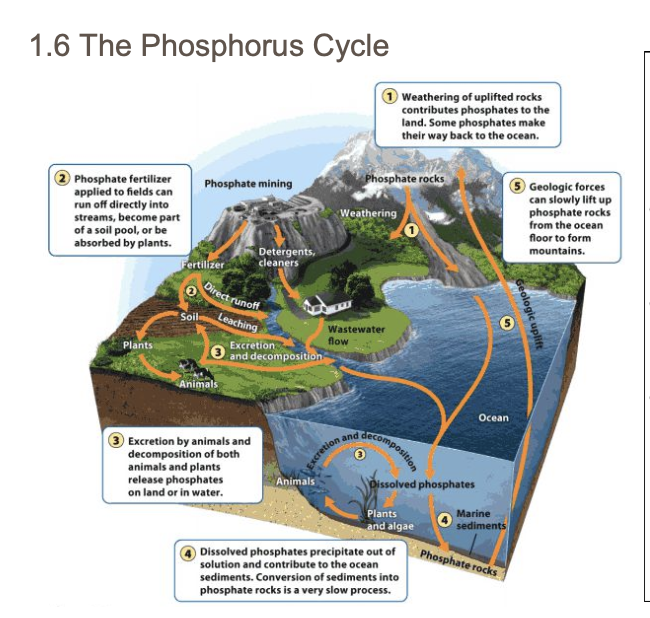
Phosphorus cycle
The movement of phosphorus around the biosphere among reservoir sources and sinks. does not have an atmospheric phase
in depth review
Phosphorus travels through assimilation and mineralization.
Its typical form is phosphate (PO43- ).
The abiotic processes that move phosphorus include sedimentation, geologic uplift, and weathering.
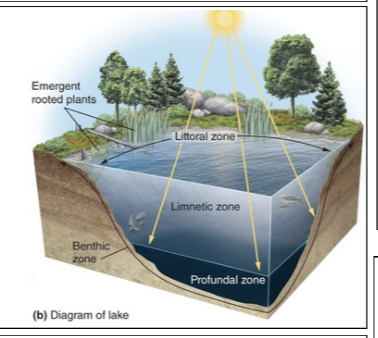
Photic zone
The upper layer of ocean water in the ocean that receives enough sunlight for photosynthesis.
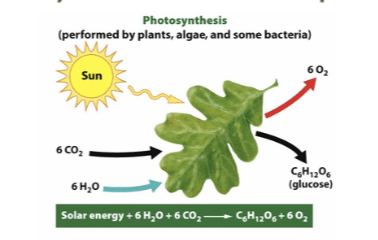
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants and algae use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) into glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
The formala, though not needed to memorize, is: 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(I) = C6H12O2 (s) + 6O2(g)
Phytoplankton
Floating algae.
Predation
An interaction in which one animal typically kills and consumes another animal.
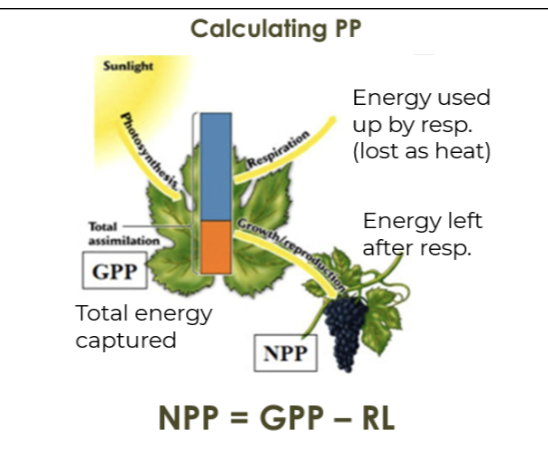
Primary productivity
The rate of converting solar energy into organic compounds over a period of time.