Biology Lab - Lab 8: Special Senses: Vision, Equilibrium, and Hearing
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
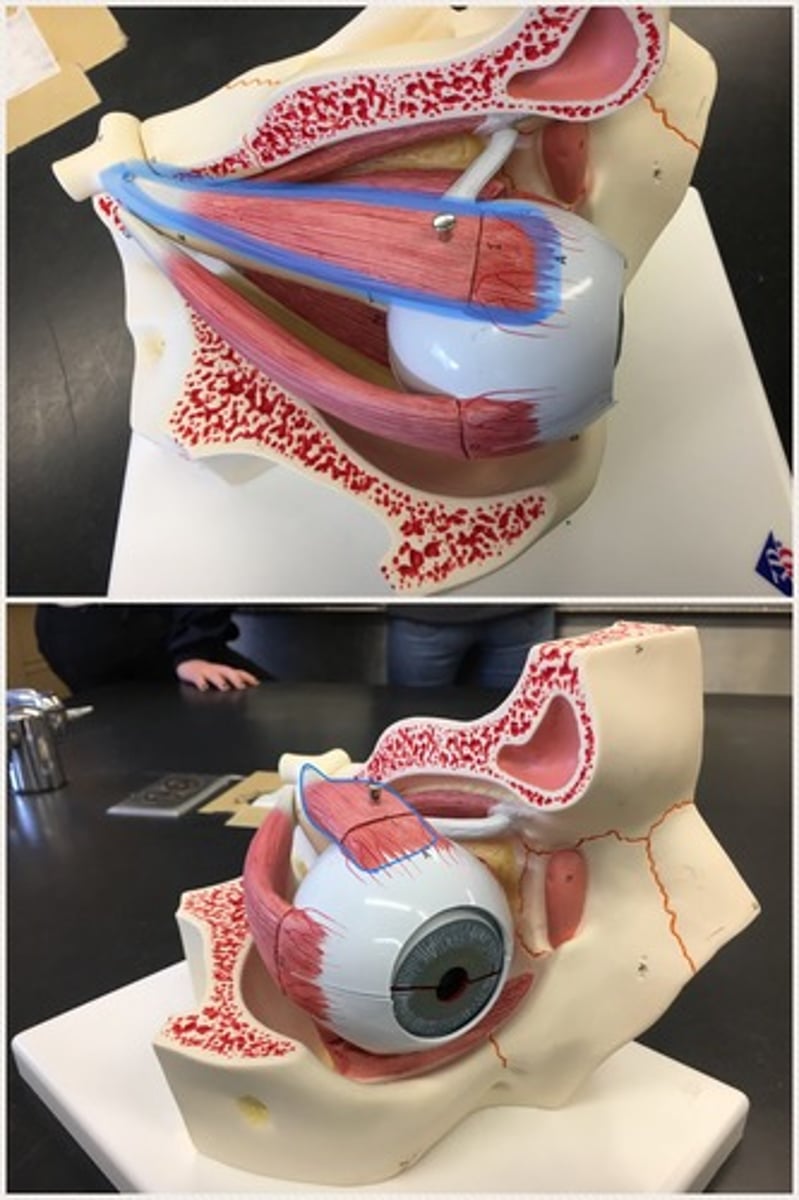
Superior rectus muscle
an eye muscle, controlling the eye as it moves up.; It is one of the extraocular muscles. It is innervated by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (Cranial Nerve III). Connects to the sclera muscle.
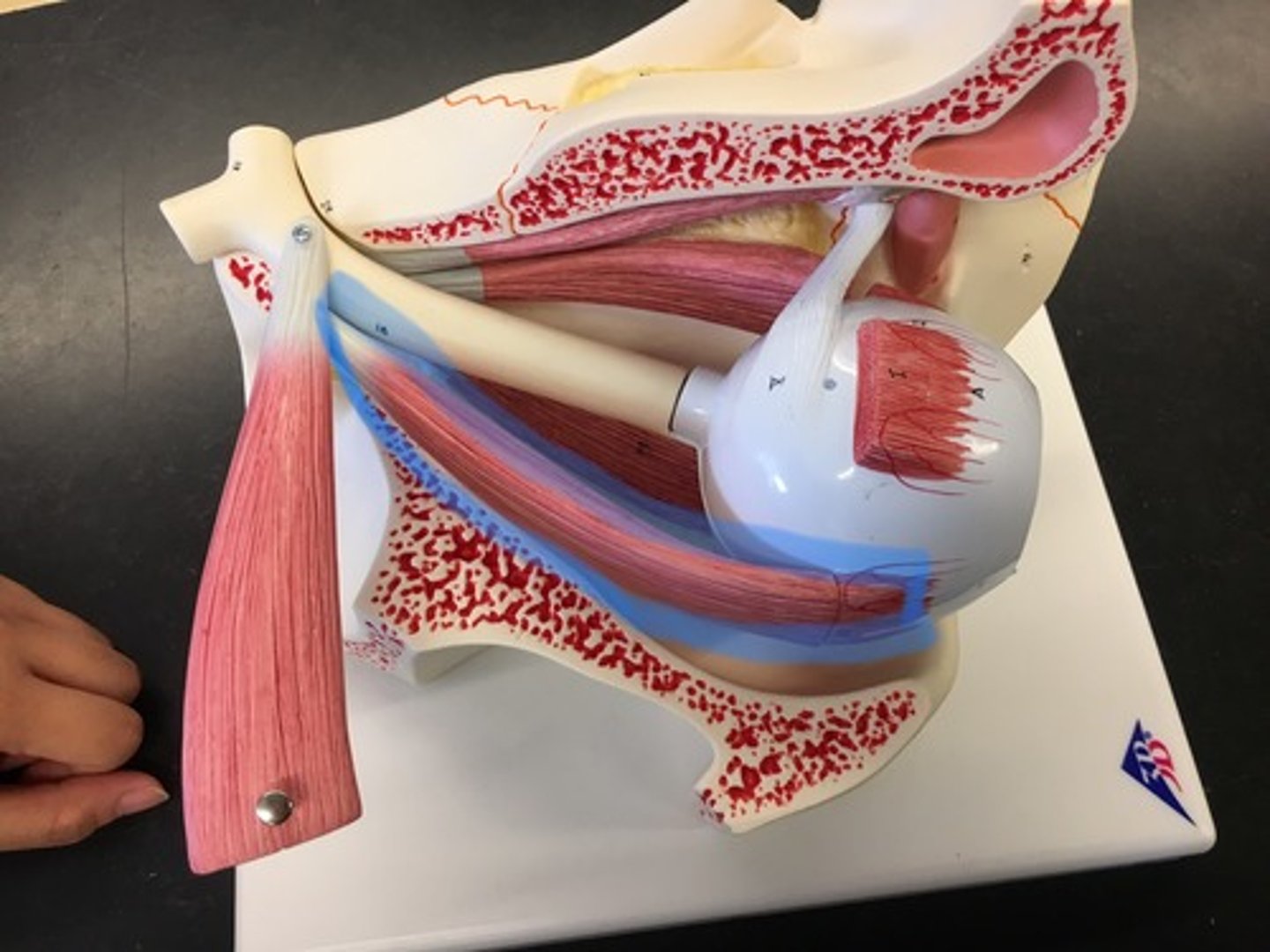
Inferior rectus muscle
the ocular muscle whose contraction turns the eyeball down and medially. On the bottom, also connects to the sclera muscle.

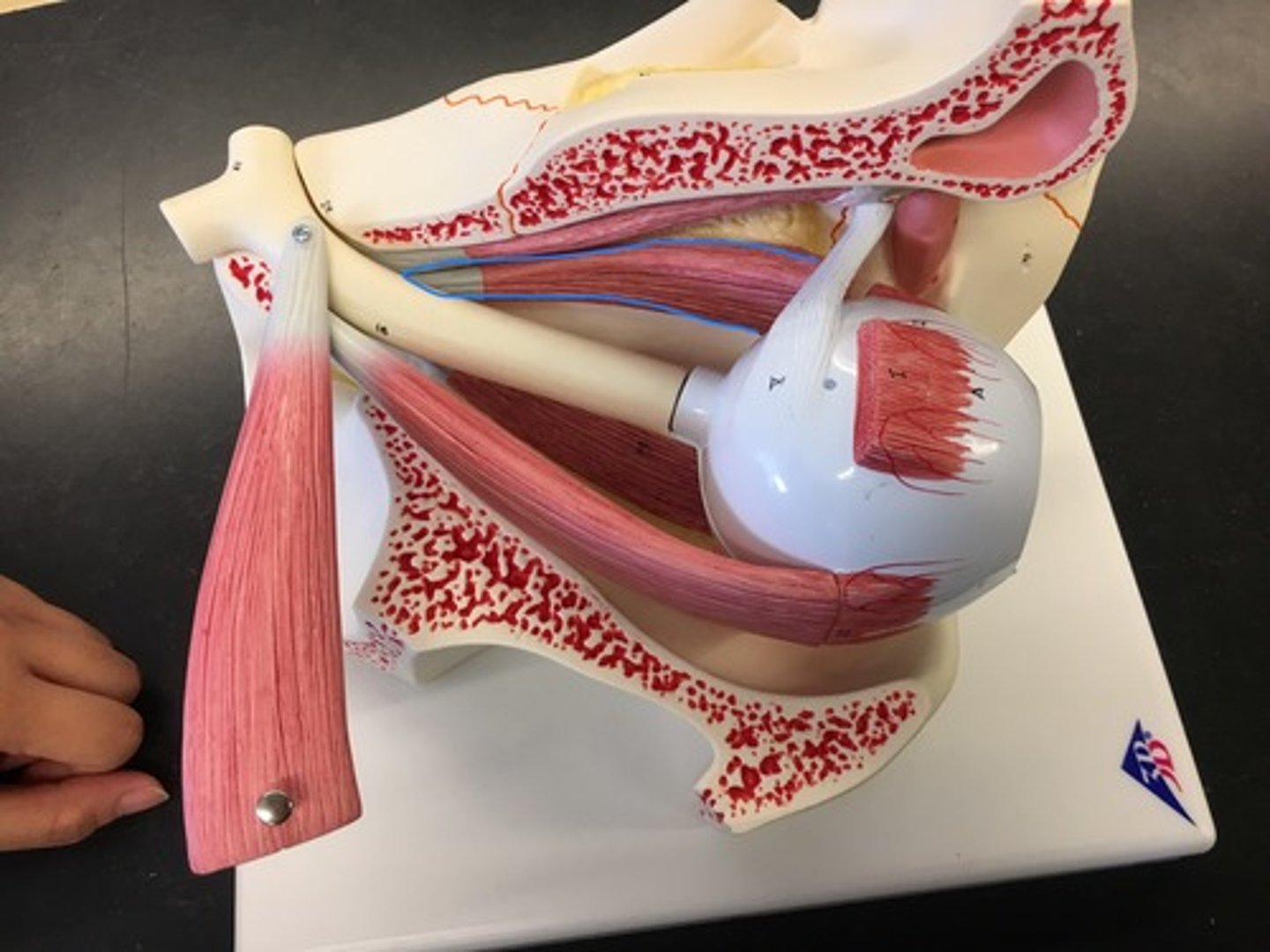
Lateral rectus muscle
responsible for lateral movement of the eyeball, specifically abduction; the only muscle that is innervated by the abducens nerve (CN VI). On the side, connects to the sclera muscle.
Medial rectus muscle
the largest of the eye's extraocular movement muscles; works to keep the pupil closer to the midline of the body. On the side, connects to the sclera muscle.
Superior oblique muscle
a fusiform (spindle-shaped) muscle belonging to the extraocular group of muscles; It originates near the nose. it performs the role of controlling eye movements. On the side of the eye, connects to the trochlea.
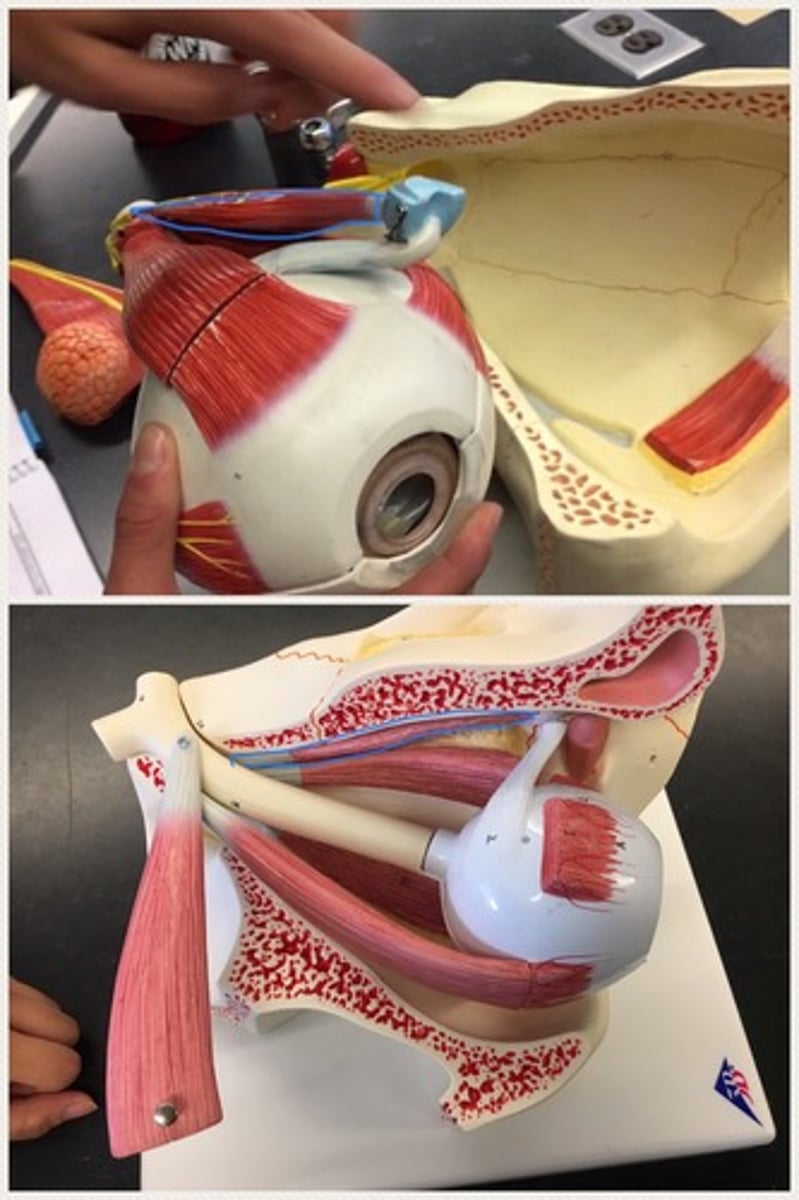
Trochlea of eye
a ring-like apparatus of cartilage through which passes the tendon of the superior oblique muscle; located in the superior nasal orbit
Inferior oblique muscle
responsible for elevating the eye, turning the top of it away from the nose, and moving it outward; is attached to the maxillary bone (origin) and the posterior, inferior, lateral surface of the eye (insertion). Underneath the lateral rectus muscle.
Levator palpebrae superioris
the muscle in the orbit that elevates the superior (upper) eyelid. Has the lacrimal gland. Above the superior rectus muscle
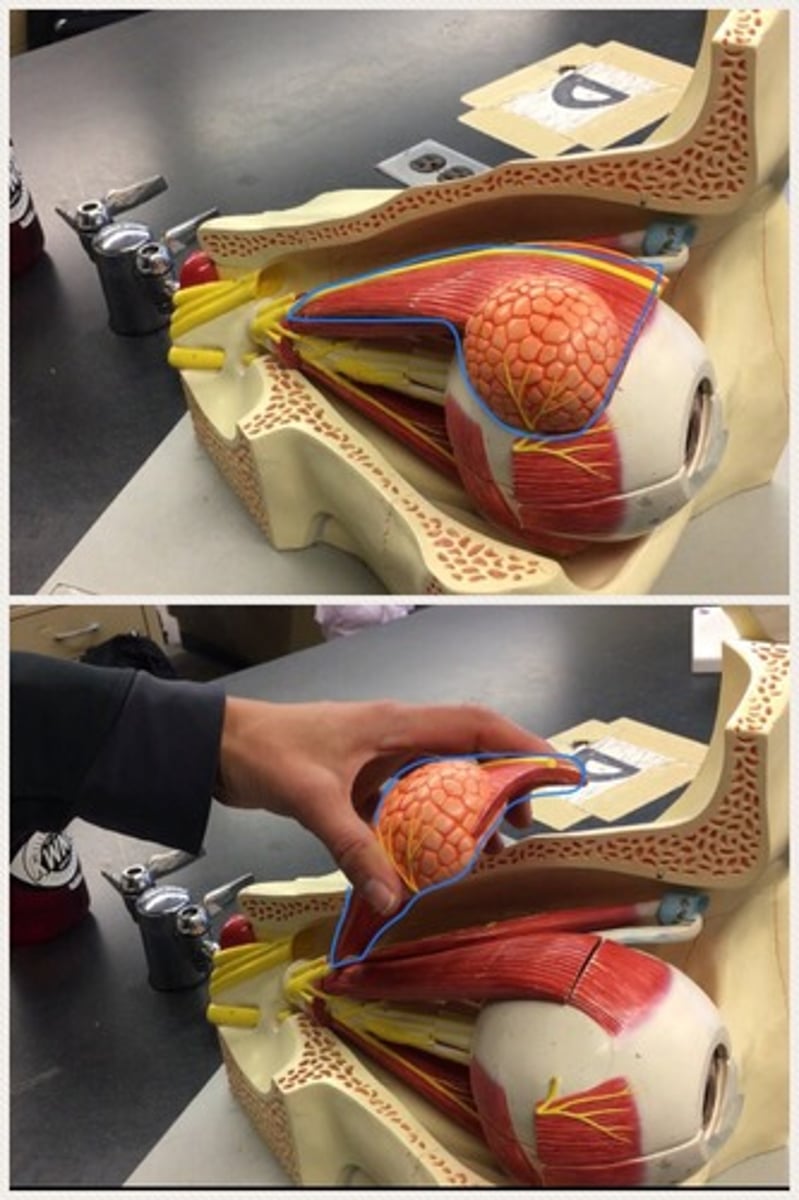
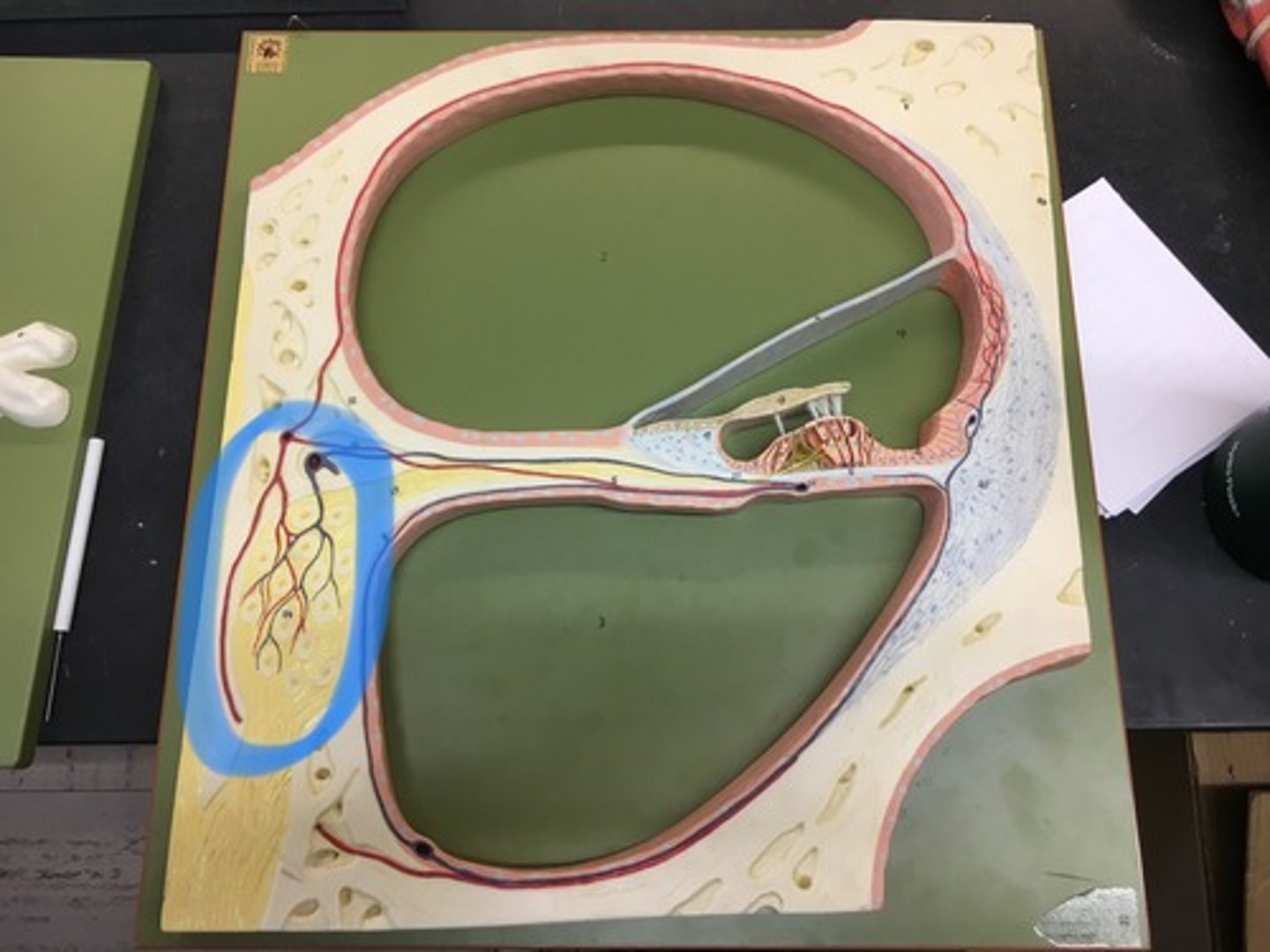
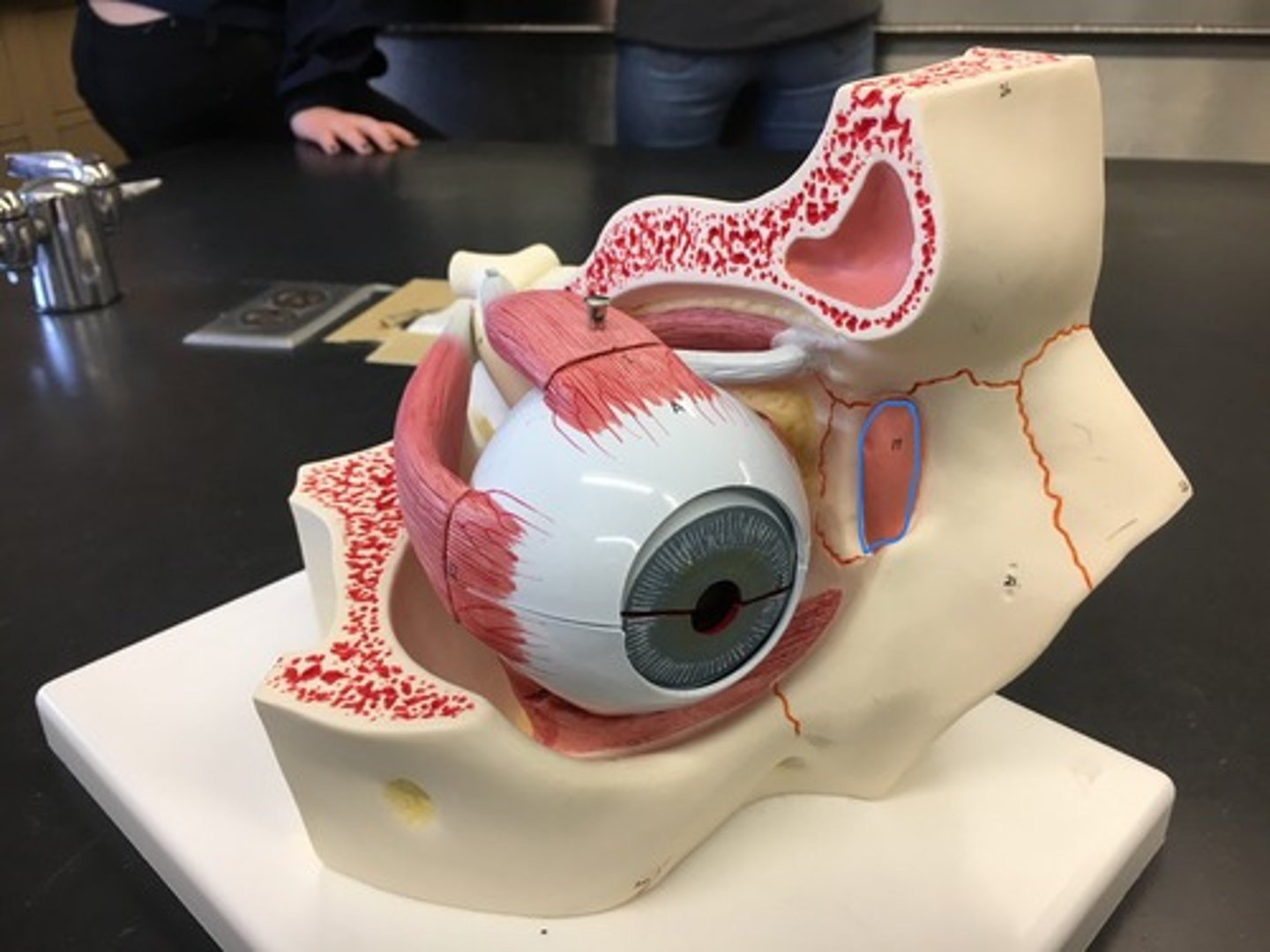
Lacrimal gland
Found in the upper lateral region of each orbit. In lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone.
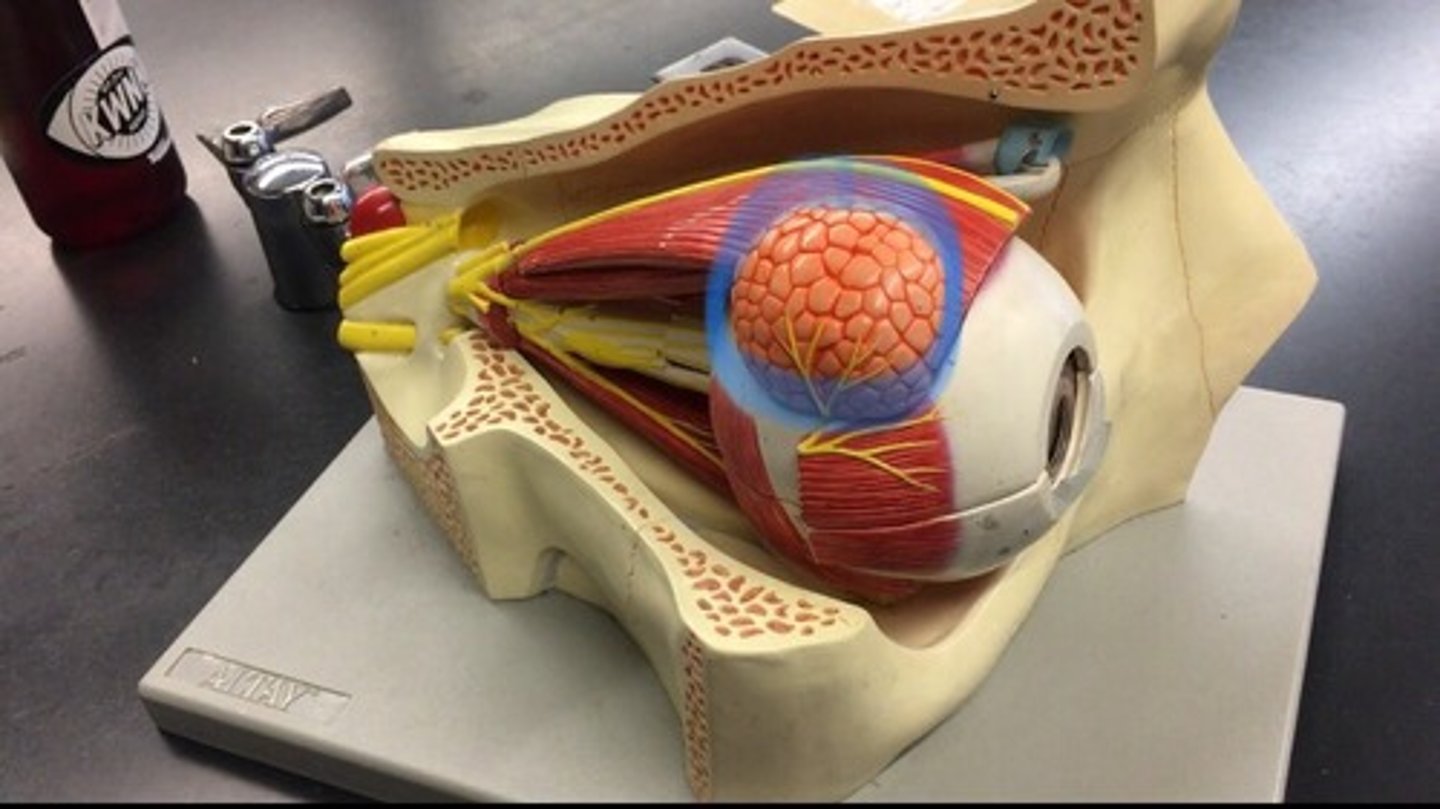
Lacrimal sac
usually stemming from obstruction of the flow of tears into the nose; Tears leave the eye through small openings called puncta in the inner corner of the eye and flow into the nasolacrimal canal.
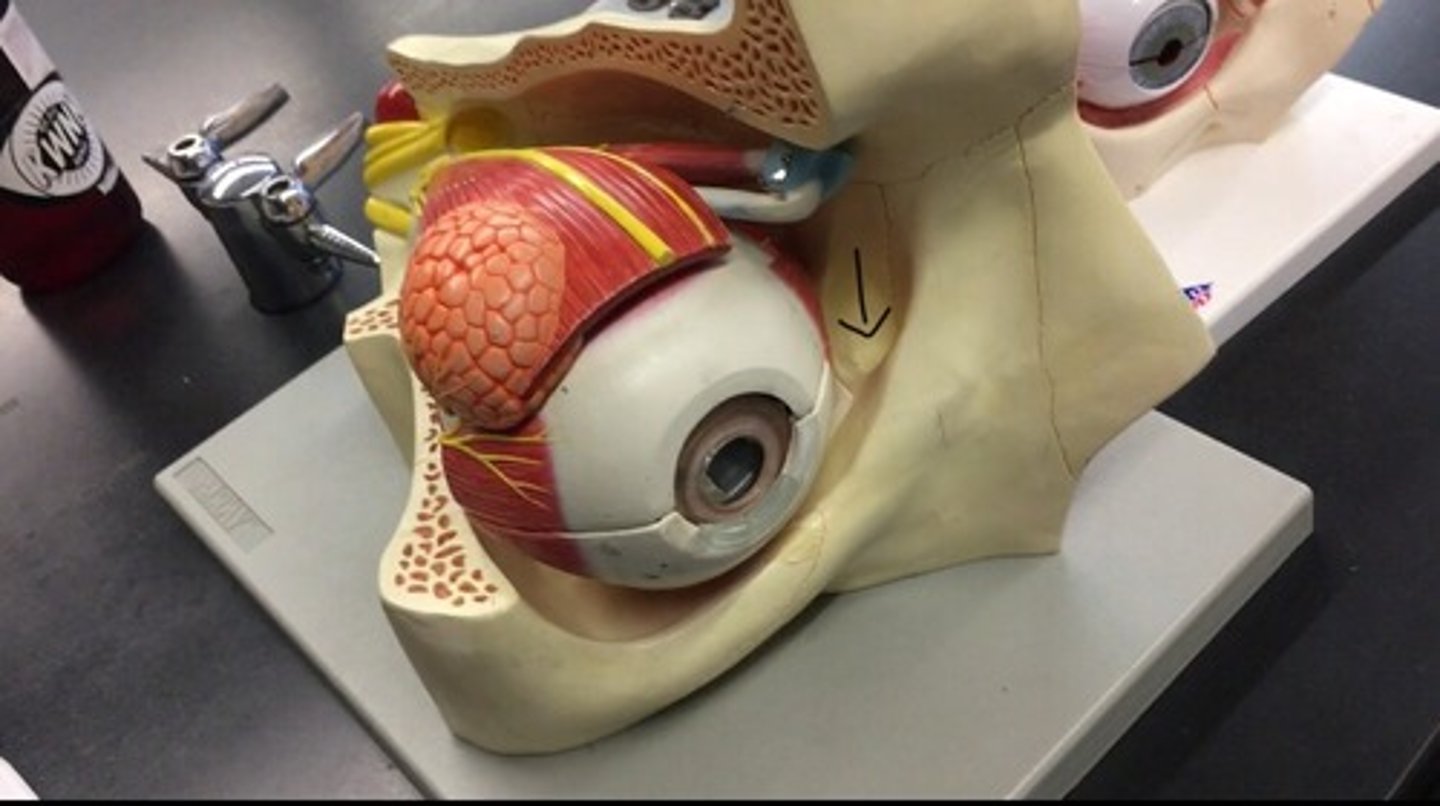
Nasolacrimal duct
(probably wont be tested on the model)
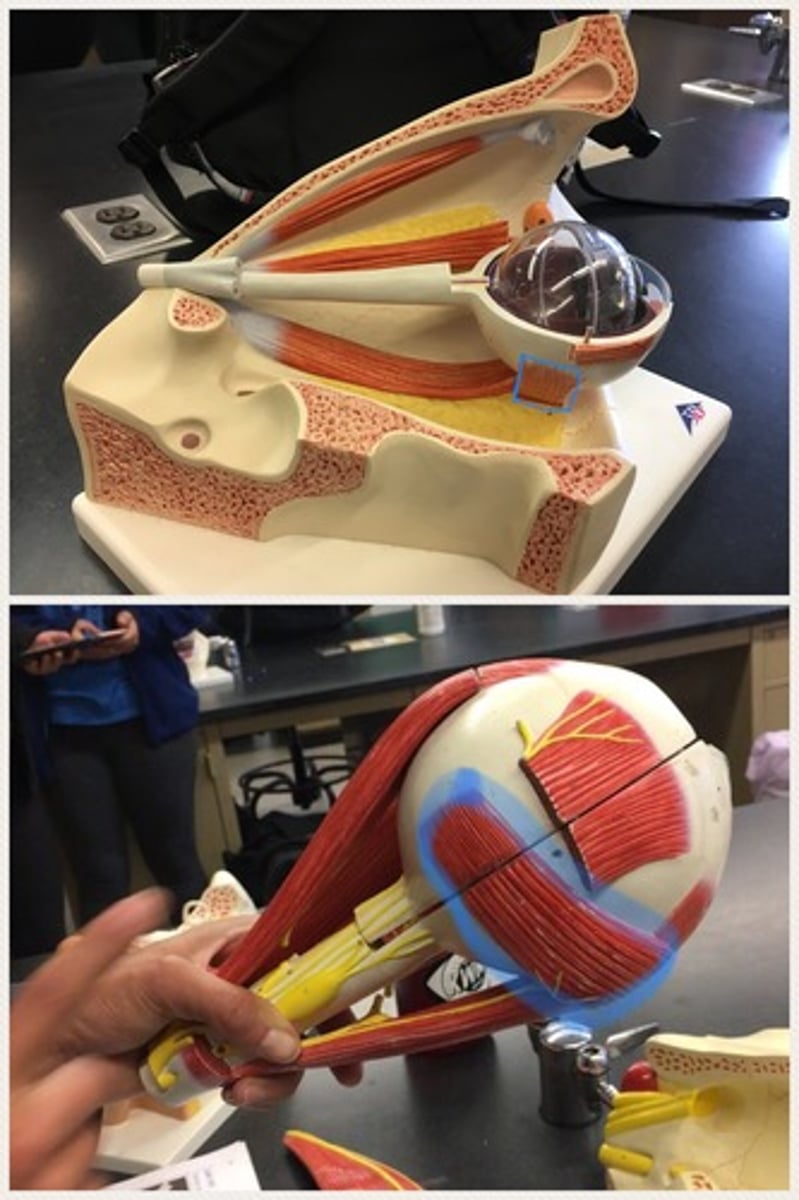
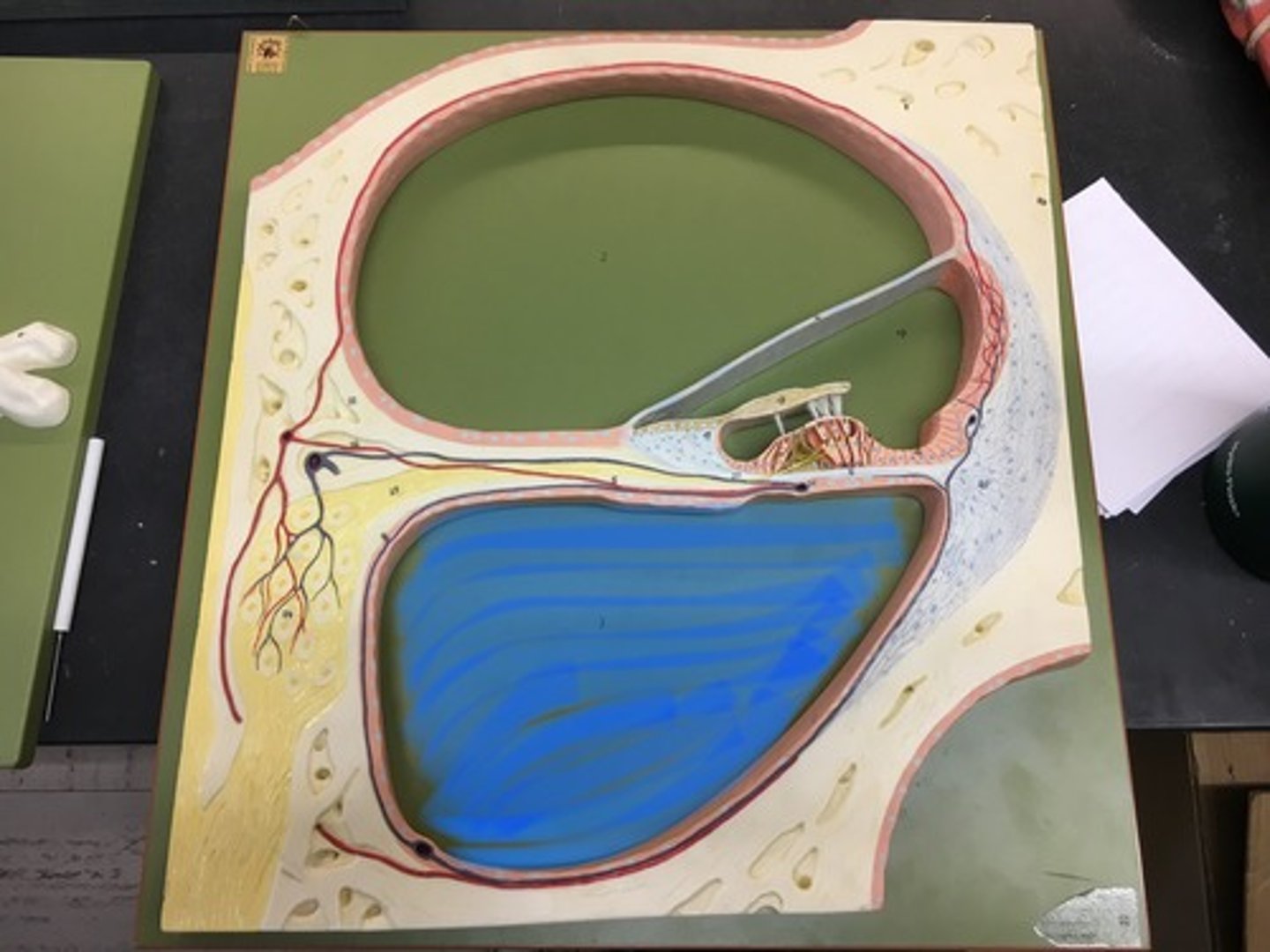
Vitreous chamber
largest of the three chambers and is located behind the lens and in front of the optic nerve. The actually space between the lens and the retina.
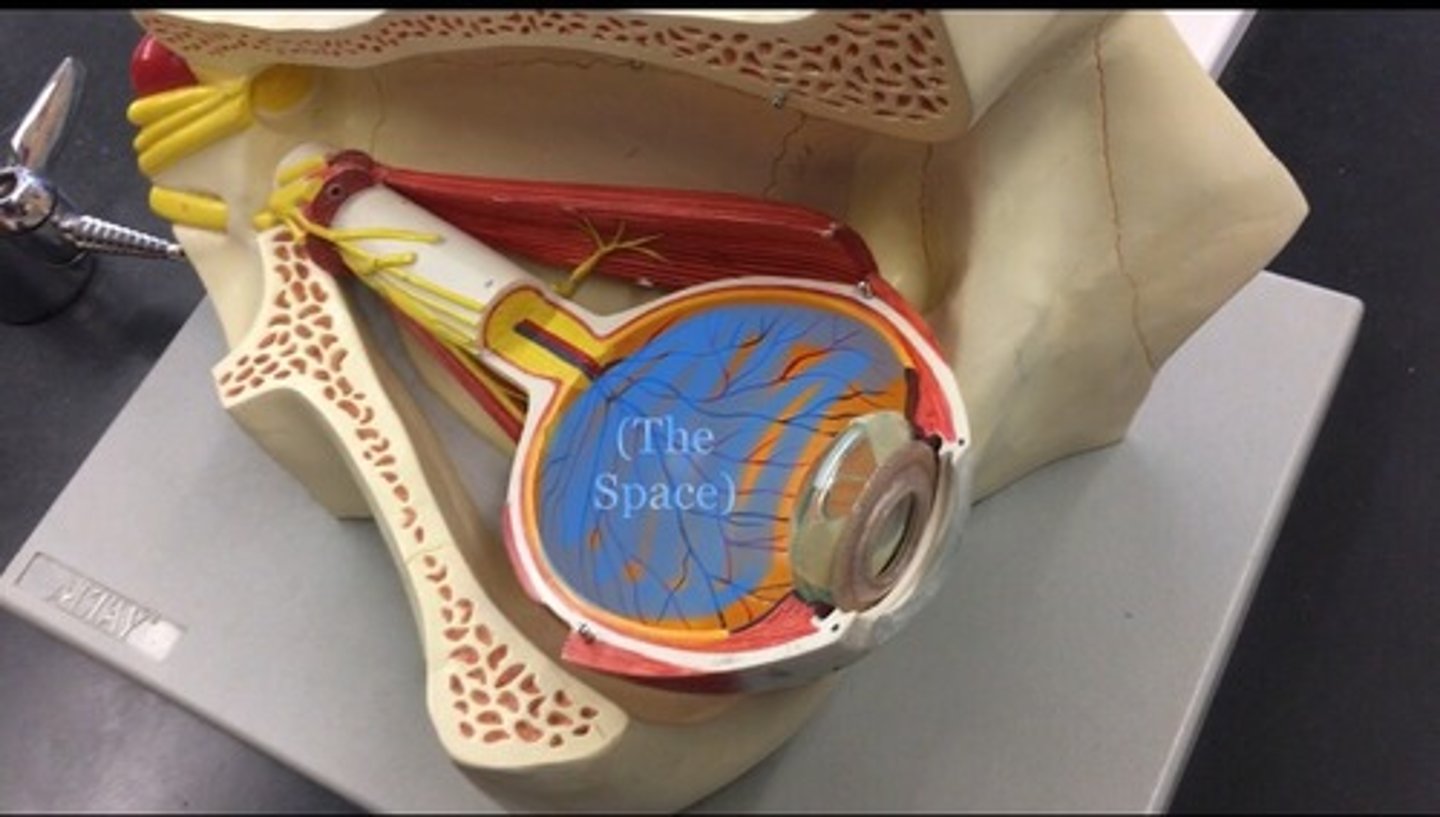
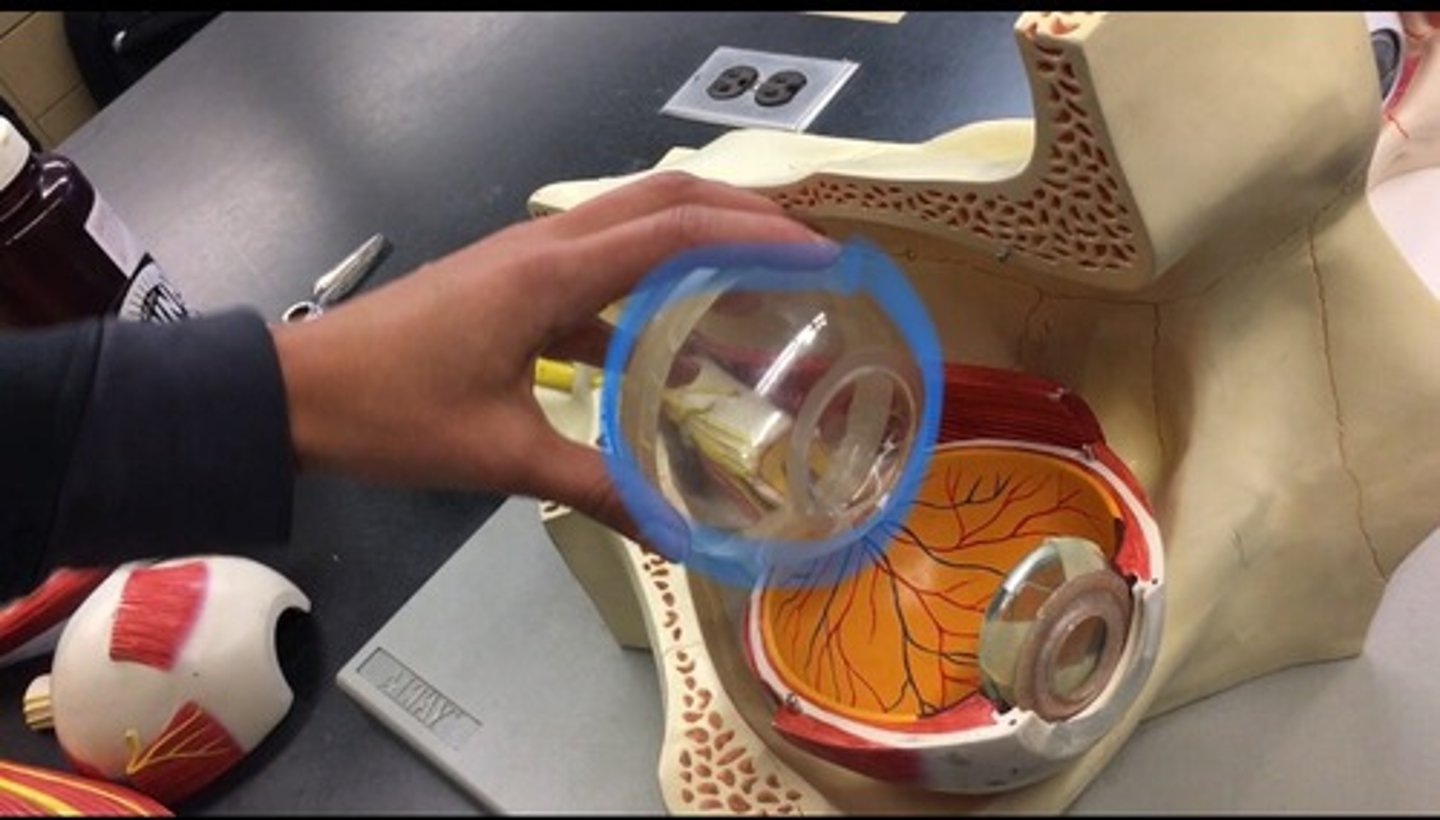
Vitreous body
clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball of humans and other vertebrates. All the goo found in cow eye, represented by the clear ball.

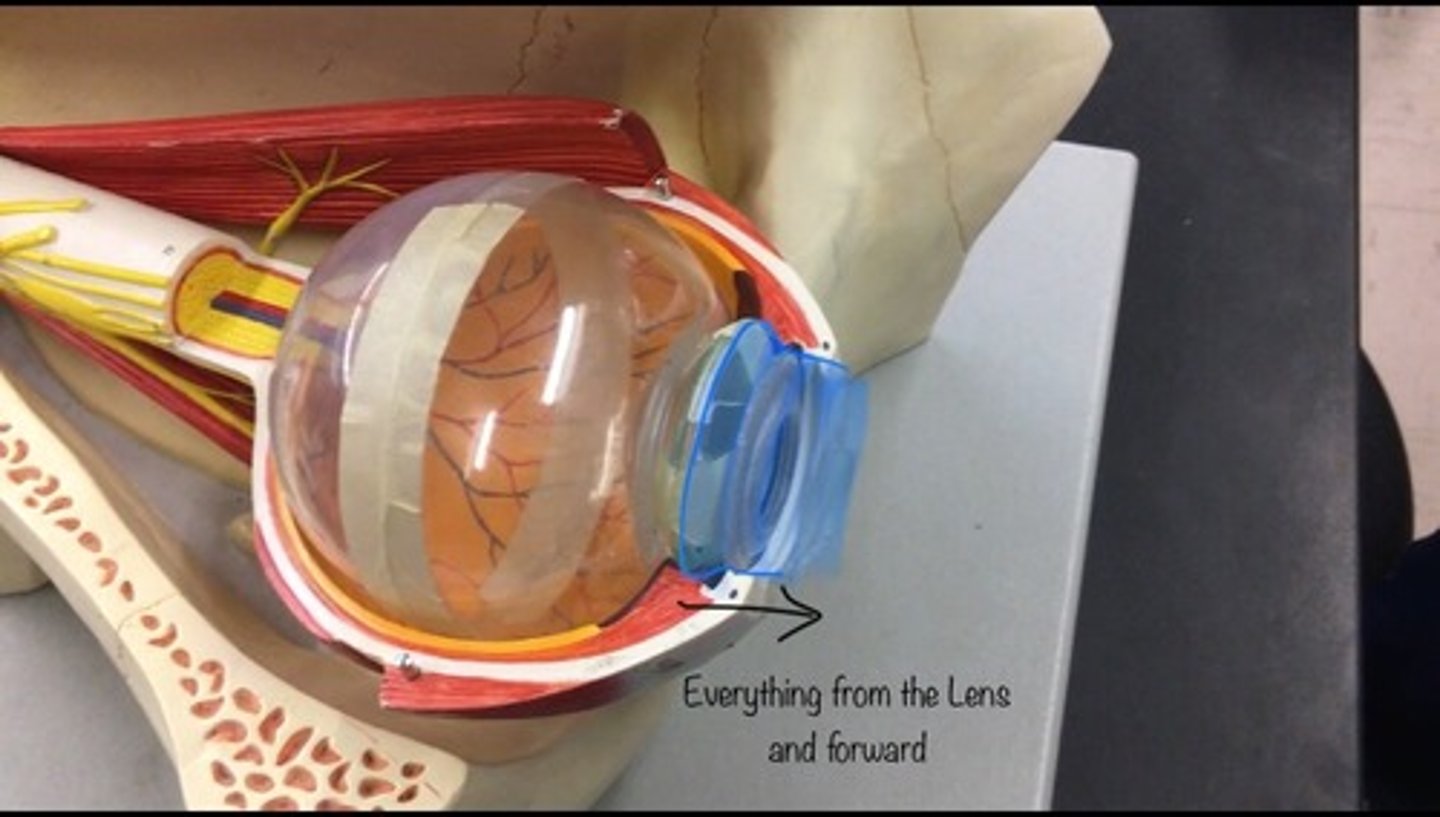
Anterior cavity
contains this water like fluid called aquaneous humor; includes the cornea, iris, ciliary body, and lens. Everything in front the lens.
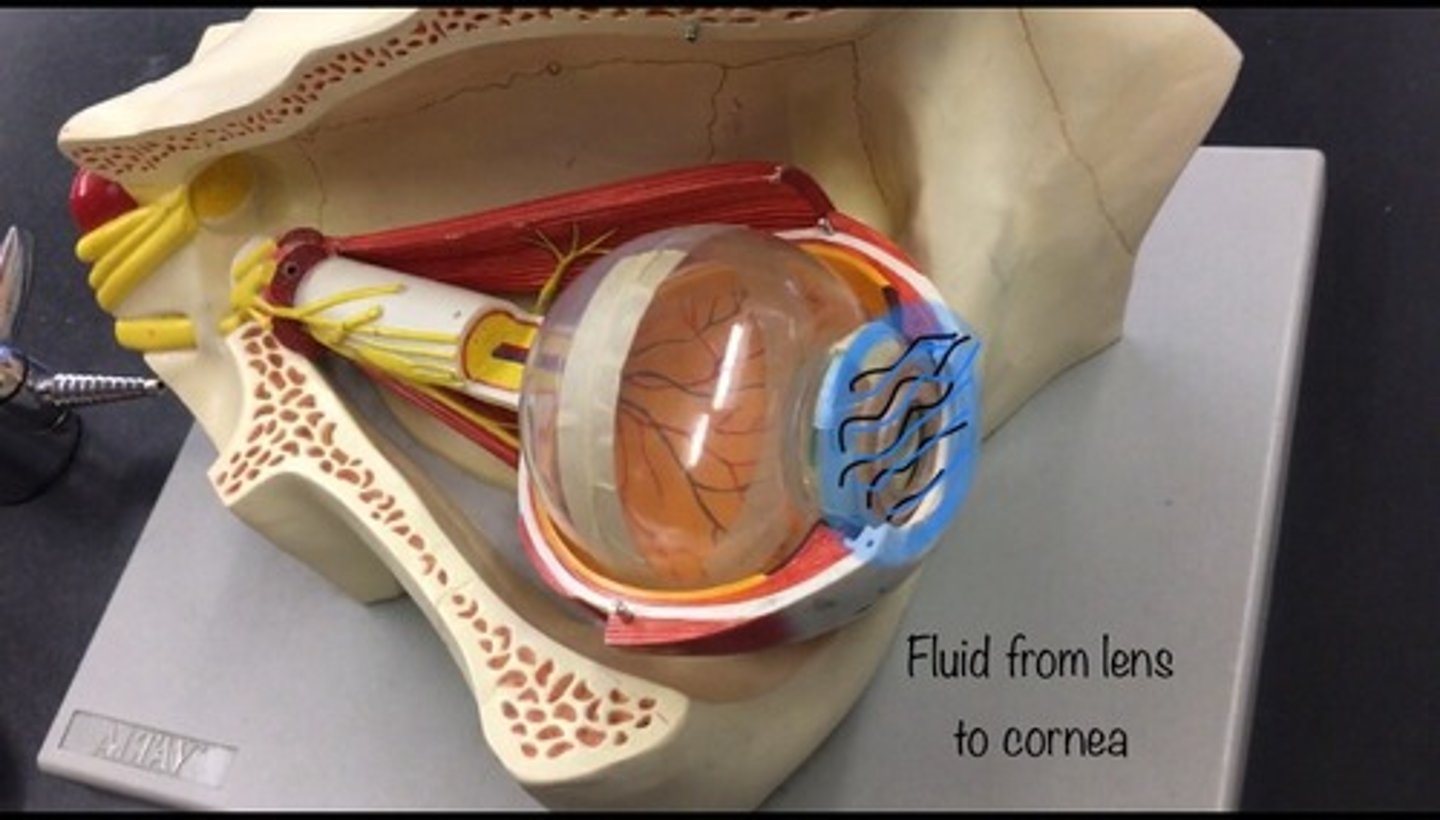
Aqueous humor
the clear fluid filling the space in the front of the eyeball between the lens and the cornea. The goo inside the anterior chamber, not represented in our models.
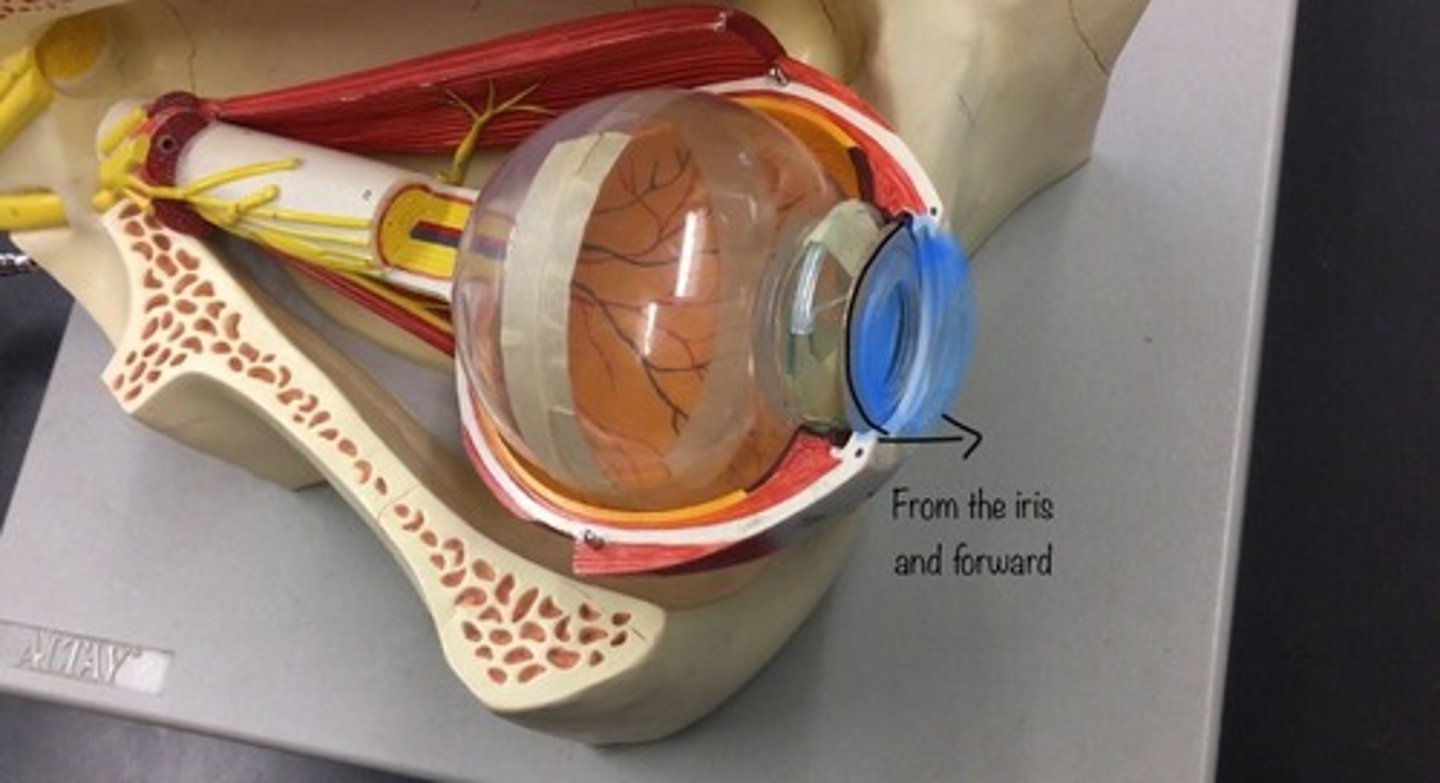
Anterior chamber
the fluid-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface; the aqueous humor is the clear fluid that fills it. Everything in front of the iris.
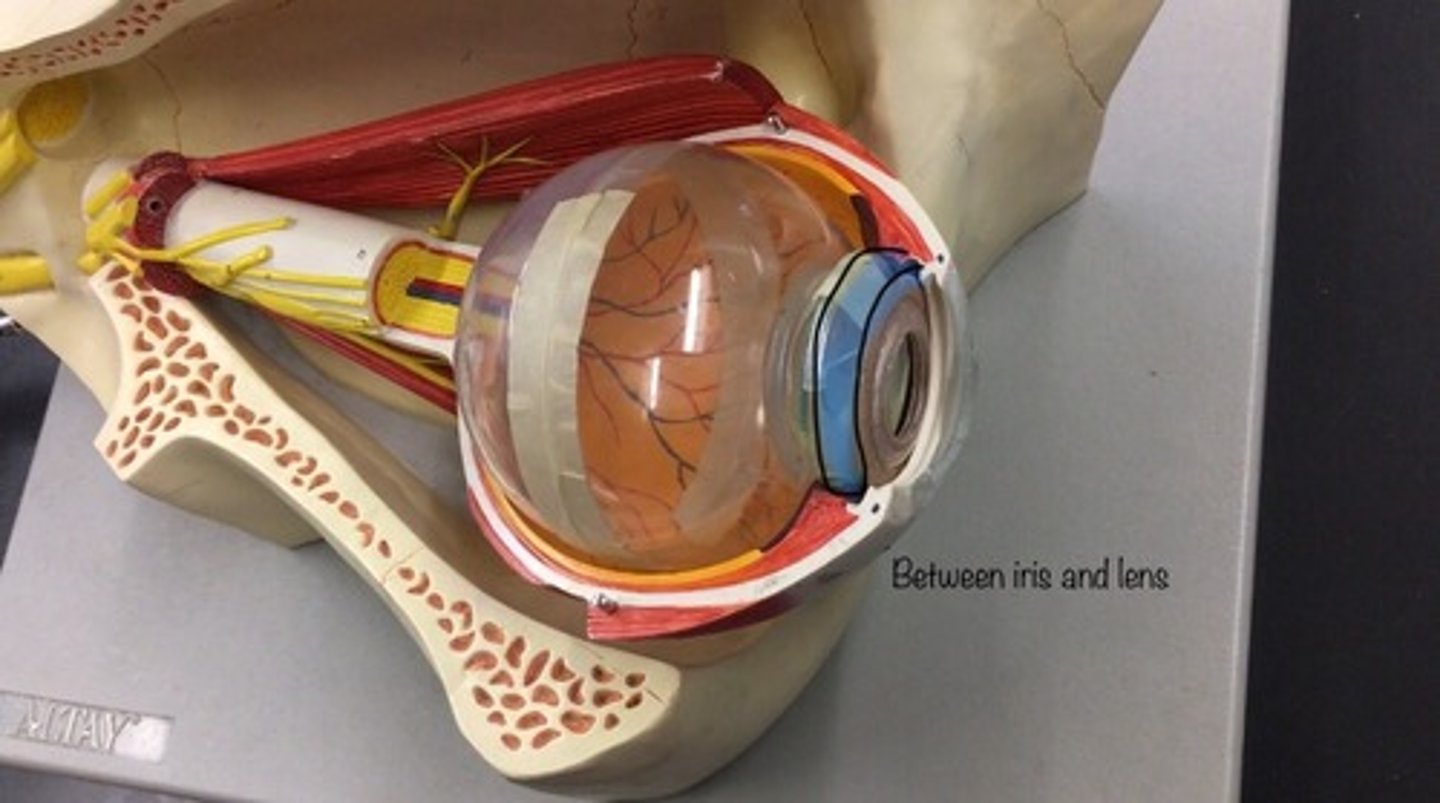
Posterior chamber
a narrow space behind the peripheral part of the iris, and in front of the suspensory ligament of the lens and the ciliary processes. The space between the iris and the lens.
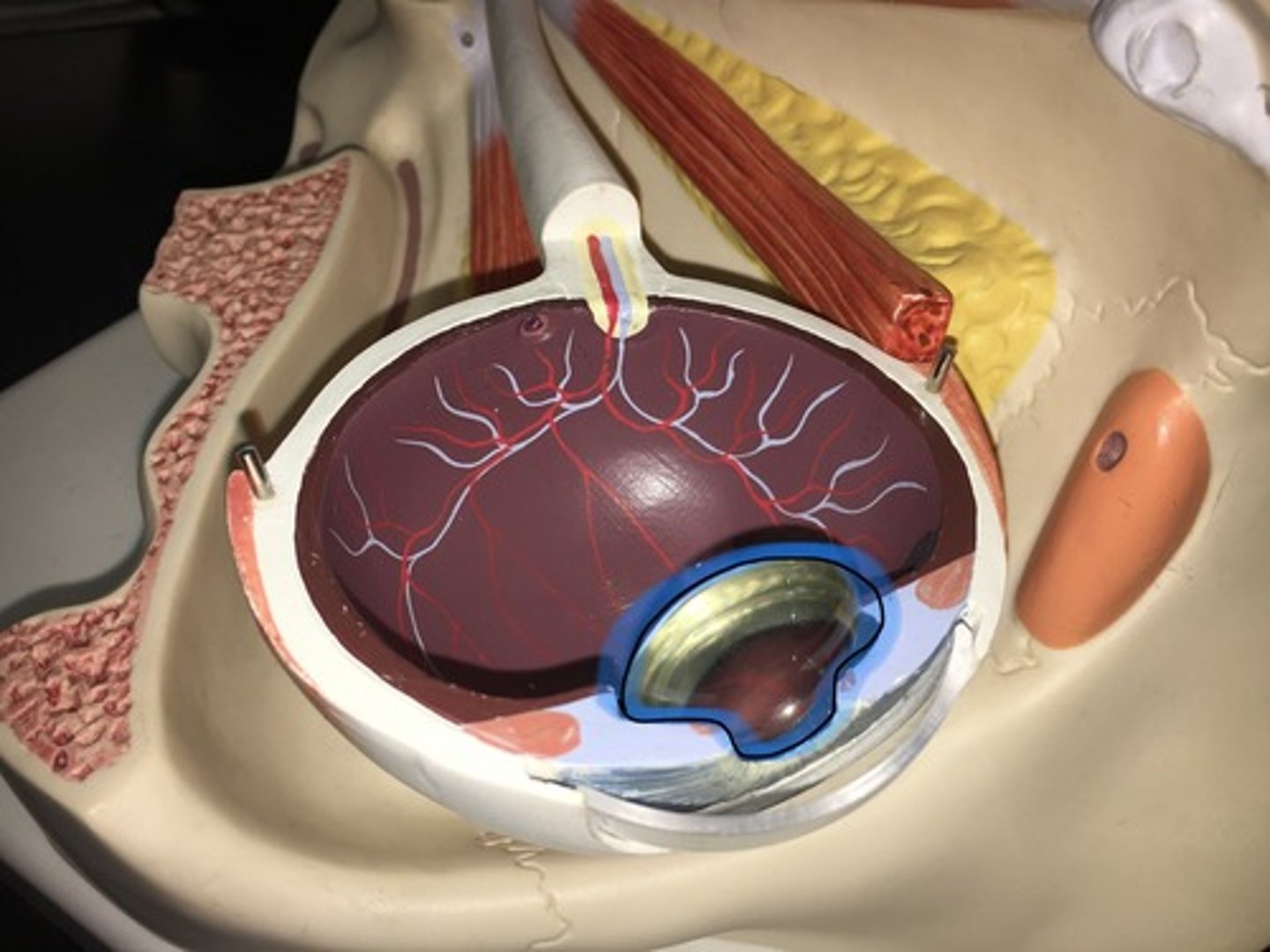
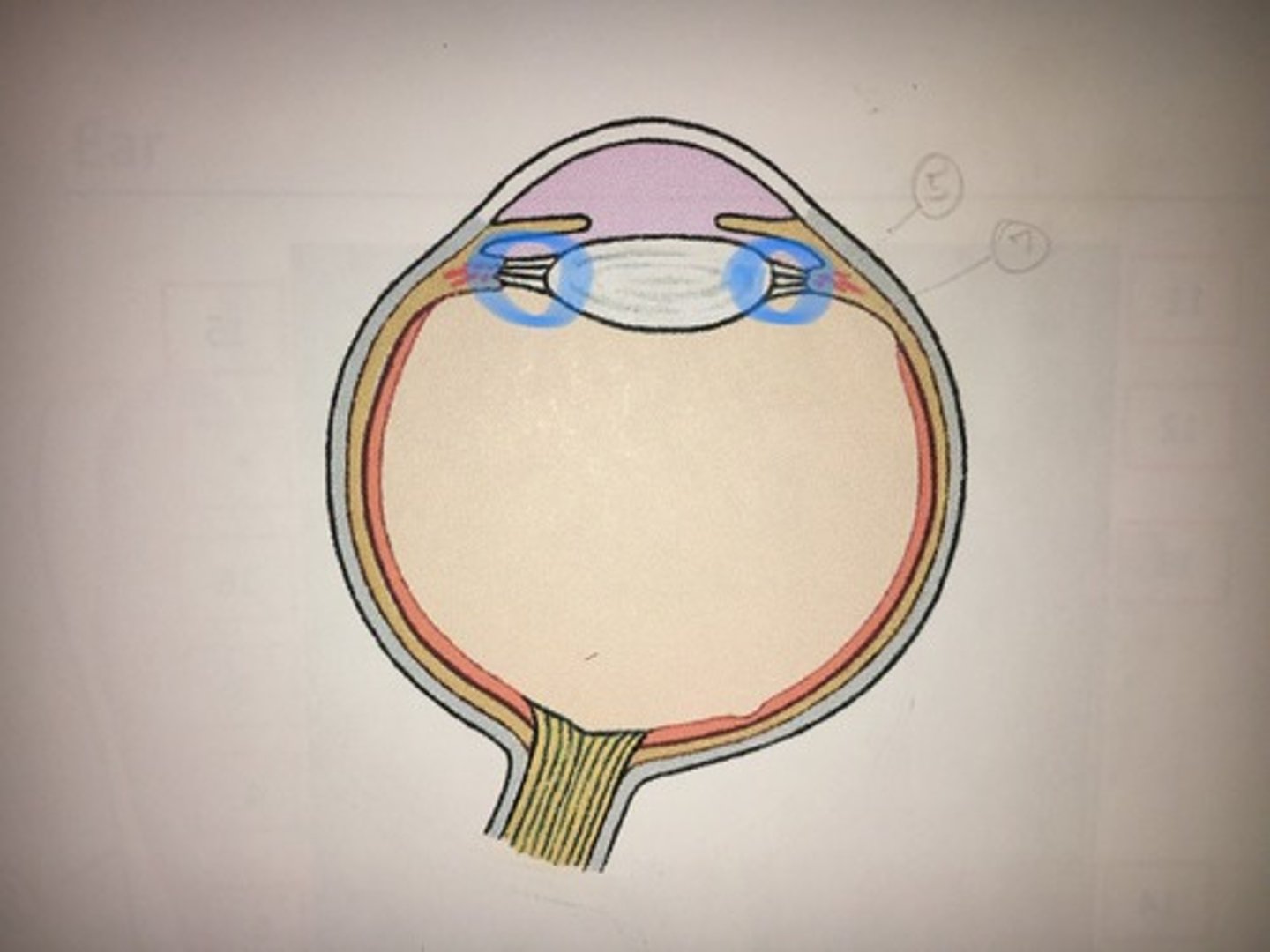
Lens
Located directly behind the iris and the pupil. It is the second part of your eye, after the cornea. Clear disk: can be removed on model. Helps you focus.
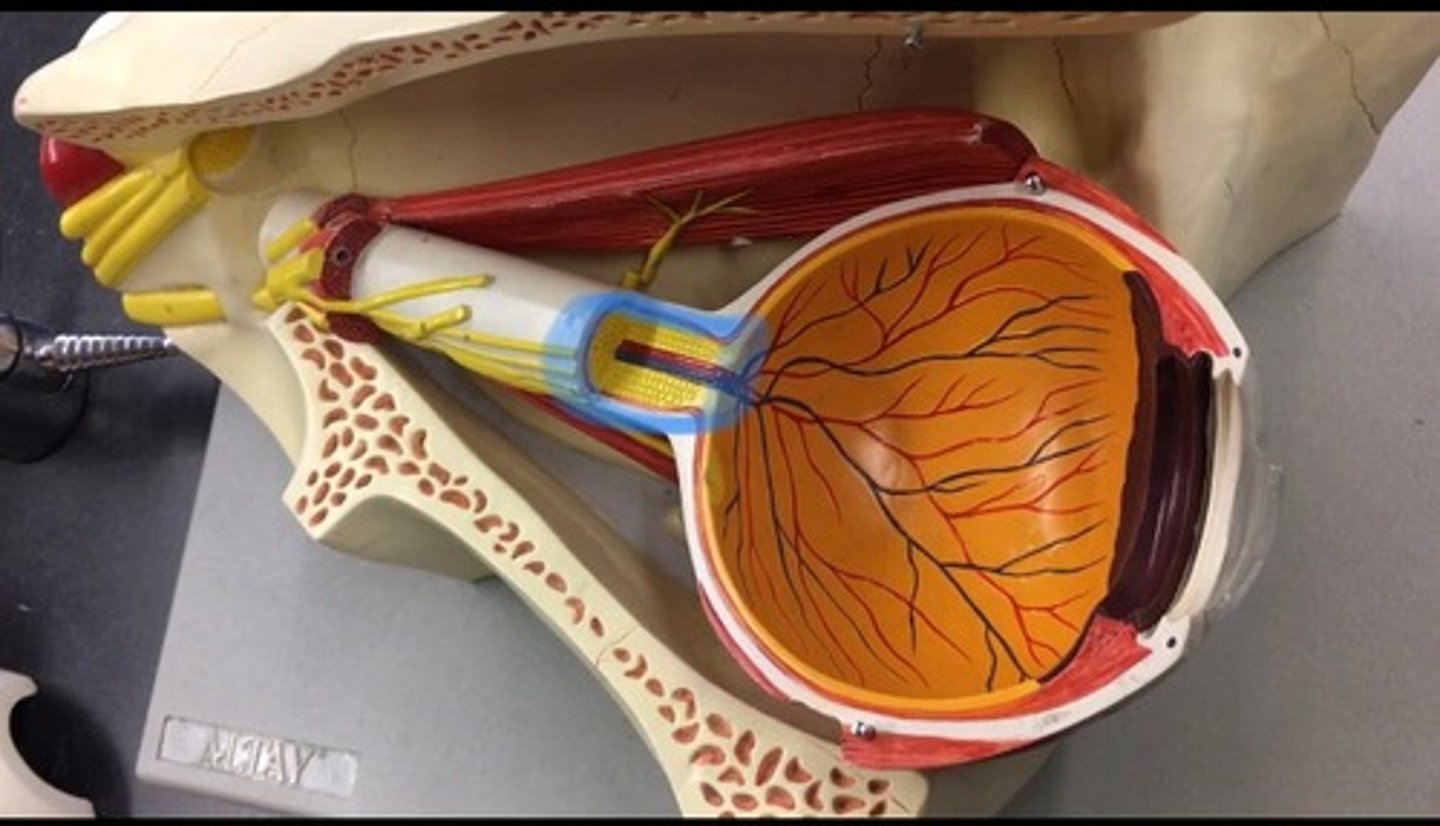
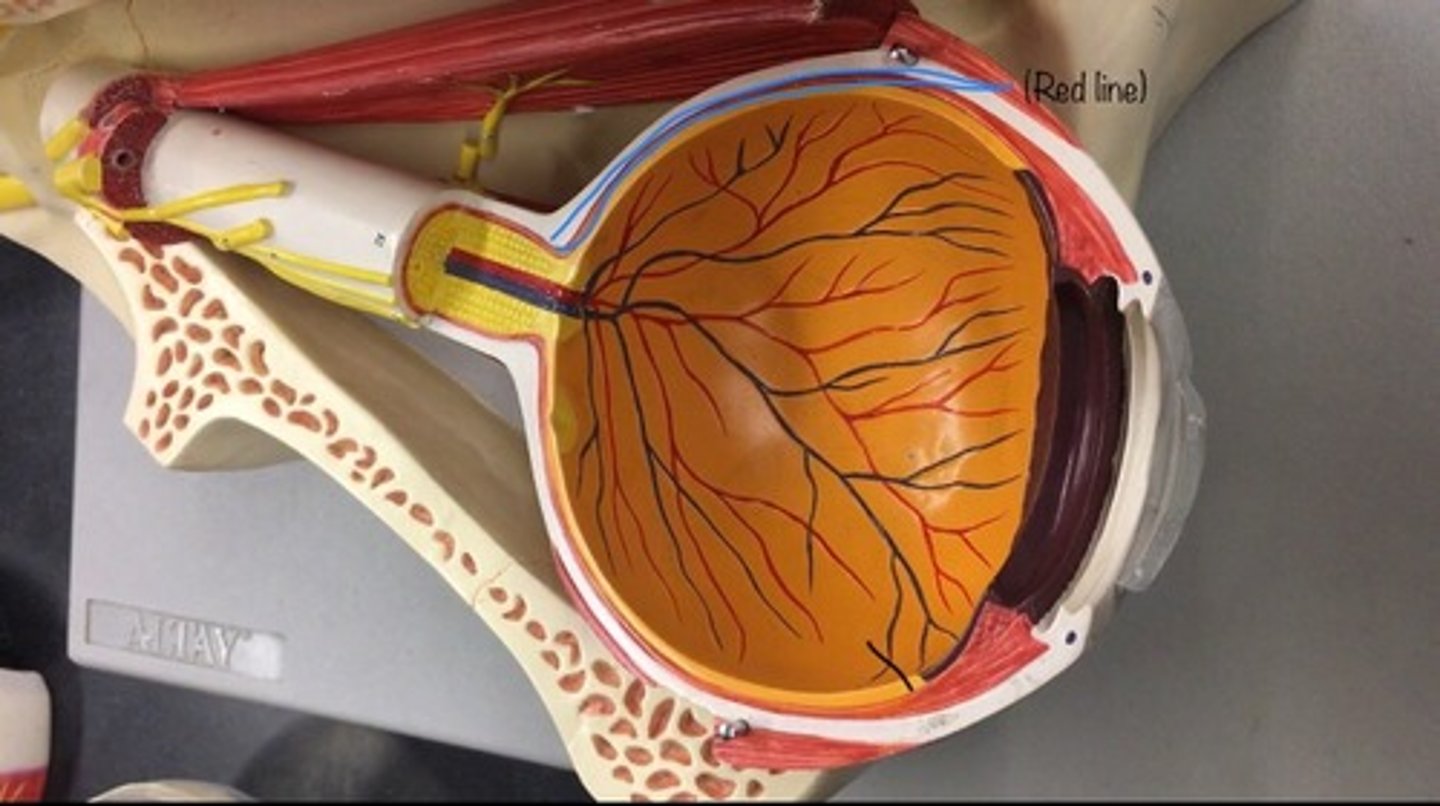
Optic nerve II
also known as cranial nerve II, is a paired nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In the back, looks like corn.
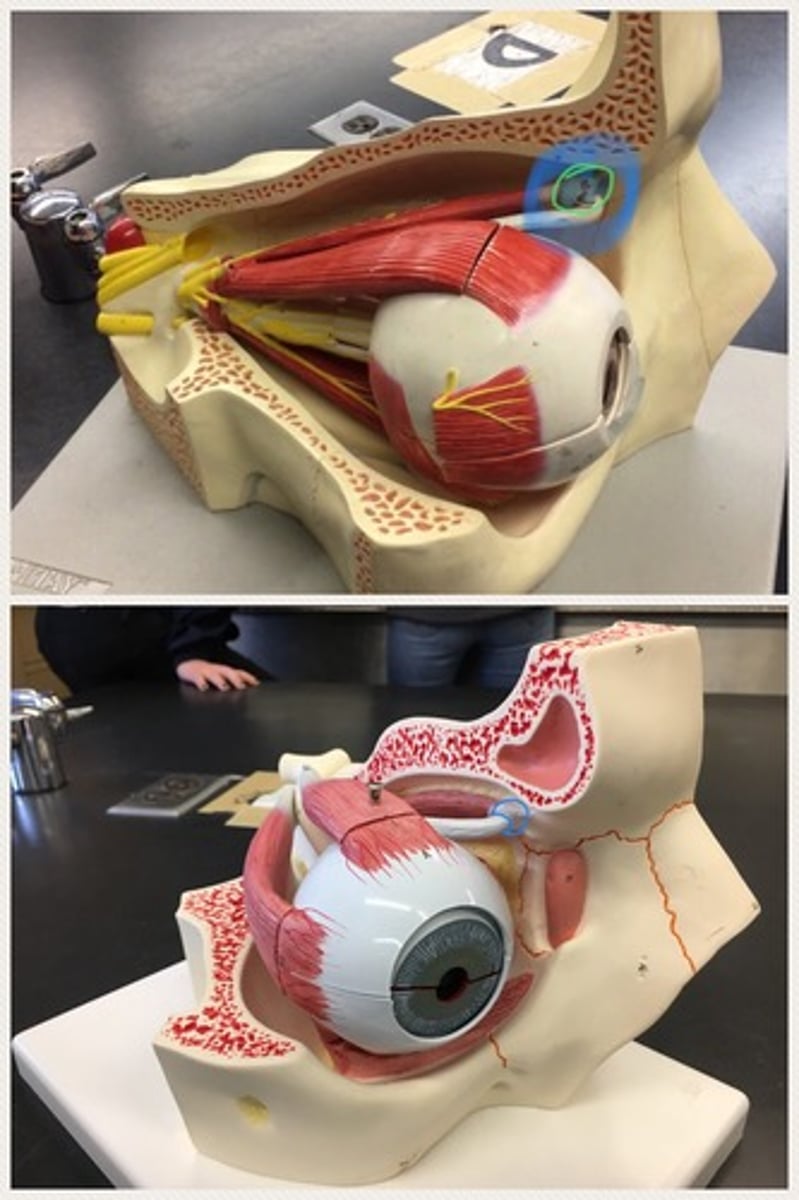
Fibrous tunic
the outermost layer of the eye, the white layer on the outside.
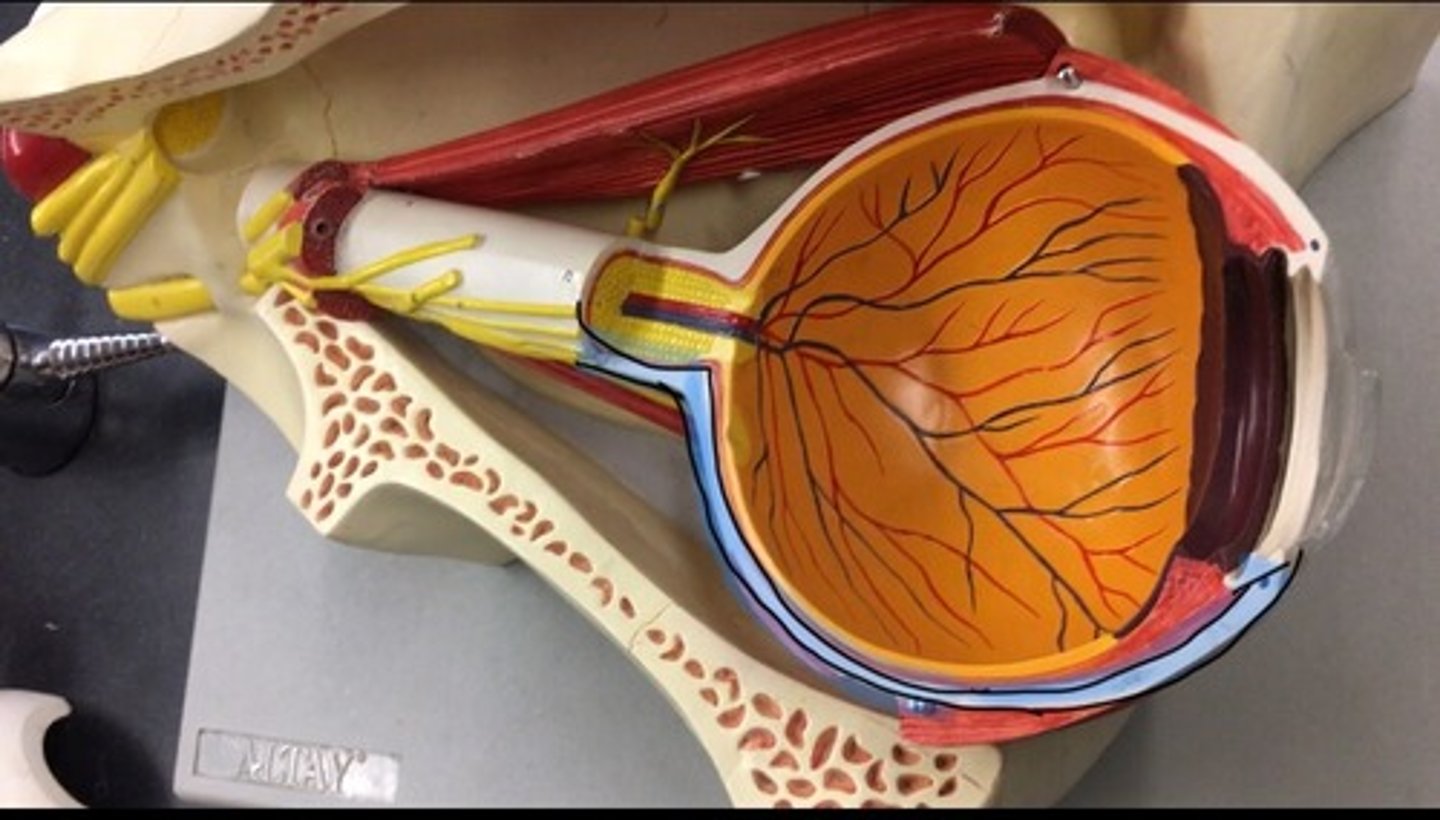
Vascular tunic (uvea)
the pigmented middle of the three concentric layers that make up an eye. The red layer
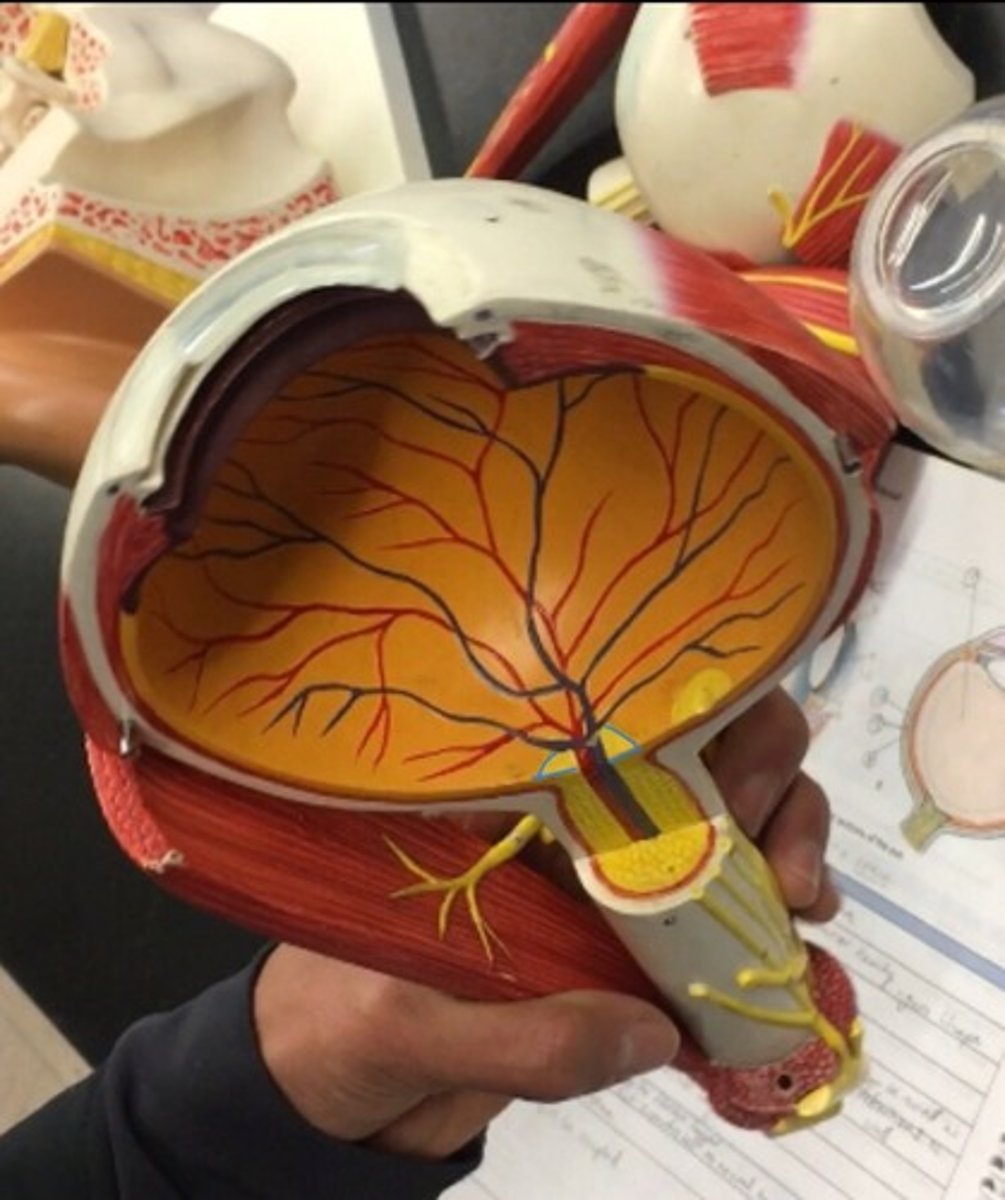
Retina
a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye on the inside. It is located near the optic nerve. Also called the neural tunic. All the orange

Sclera
The white outer part of the eye.
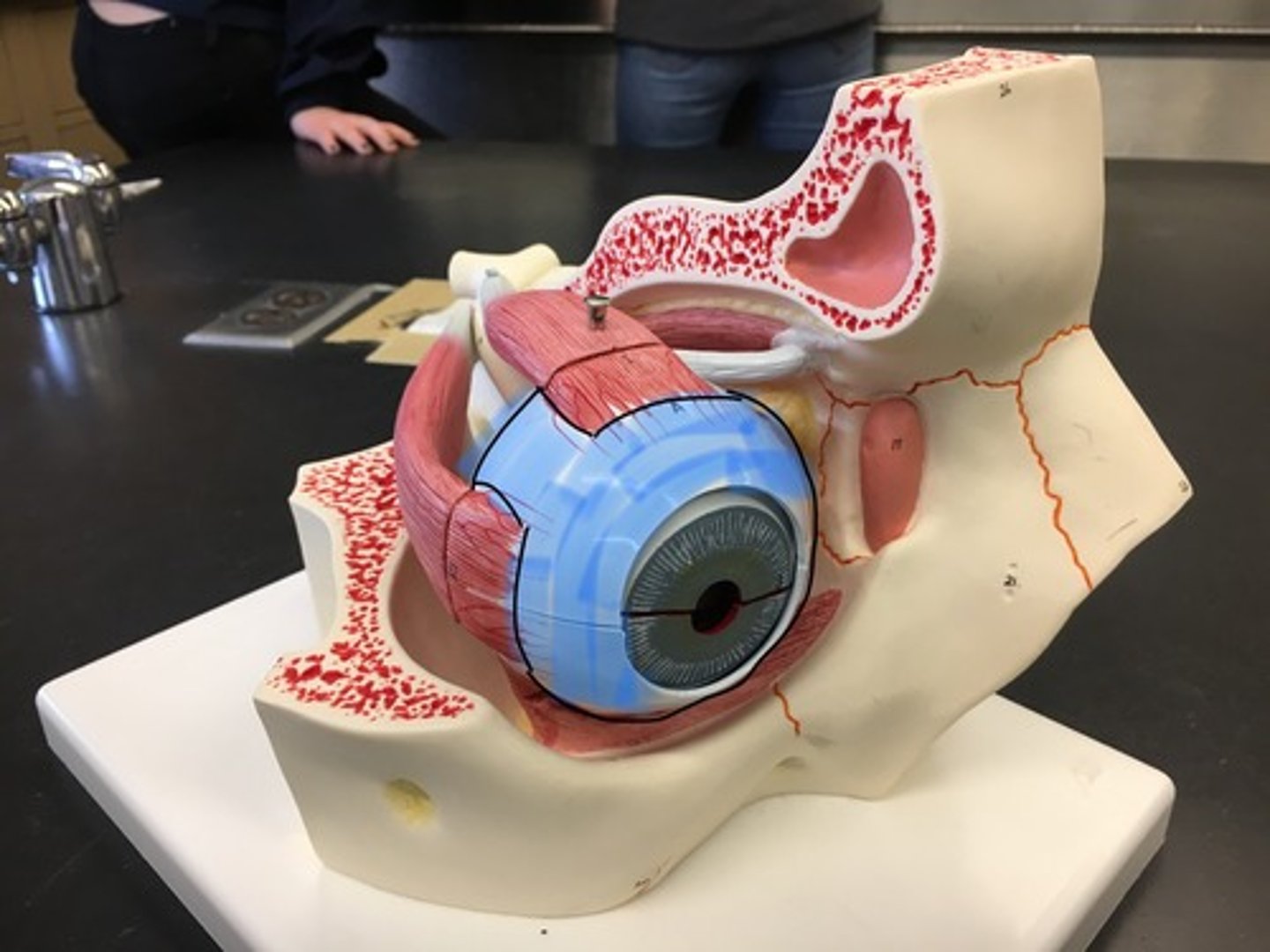
Cornea
The transparent part of the eye that covers the front portion of the eye.
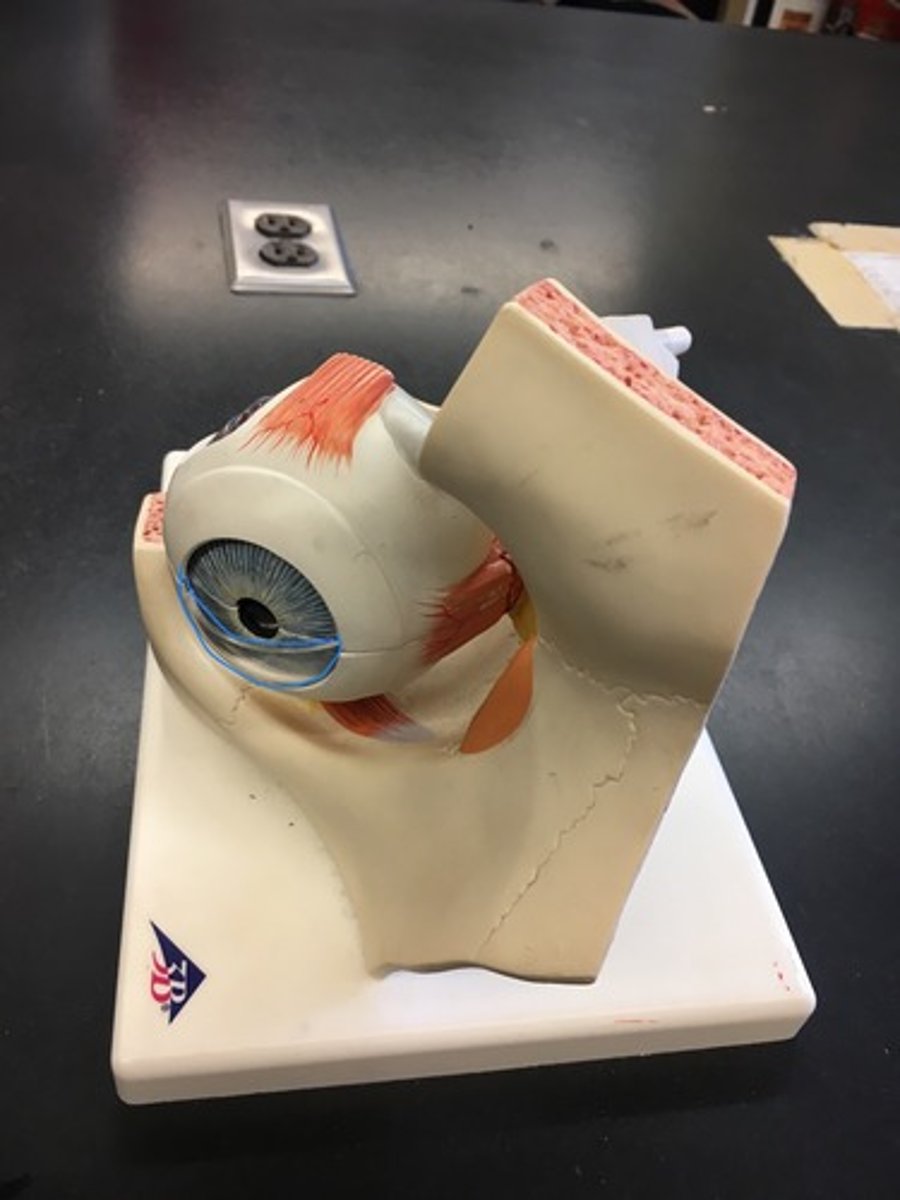

Iris
The colored part of the eye; separates posterior and anterior chamber
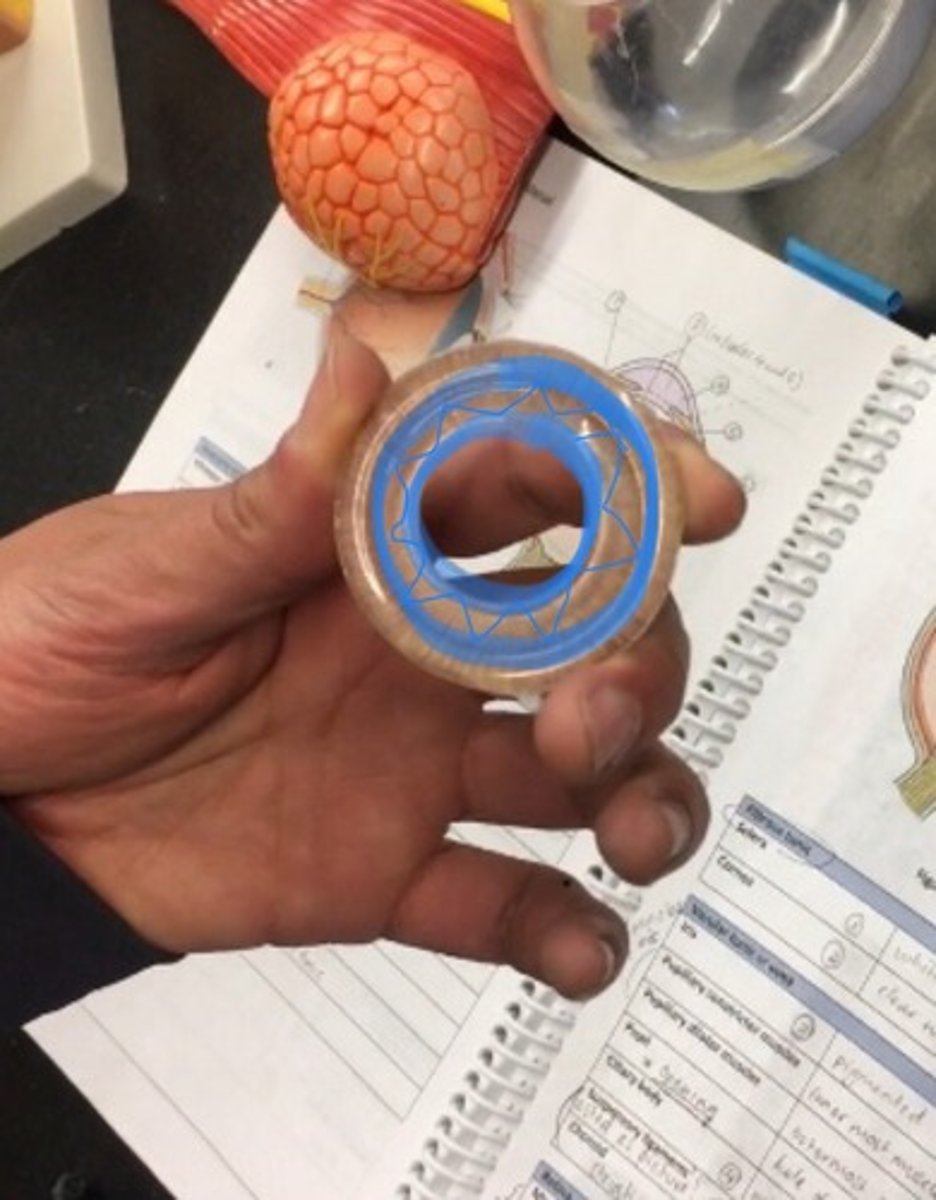
Pupillary constrictor muscles
inner ring of iris closes to pupil. The inside ring.
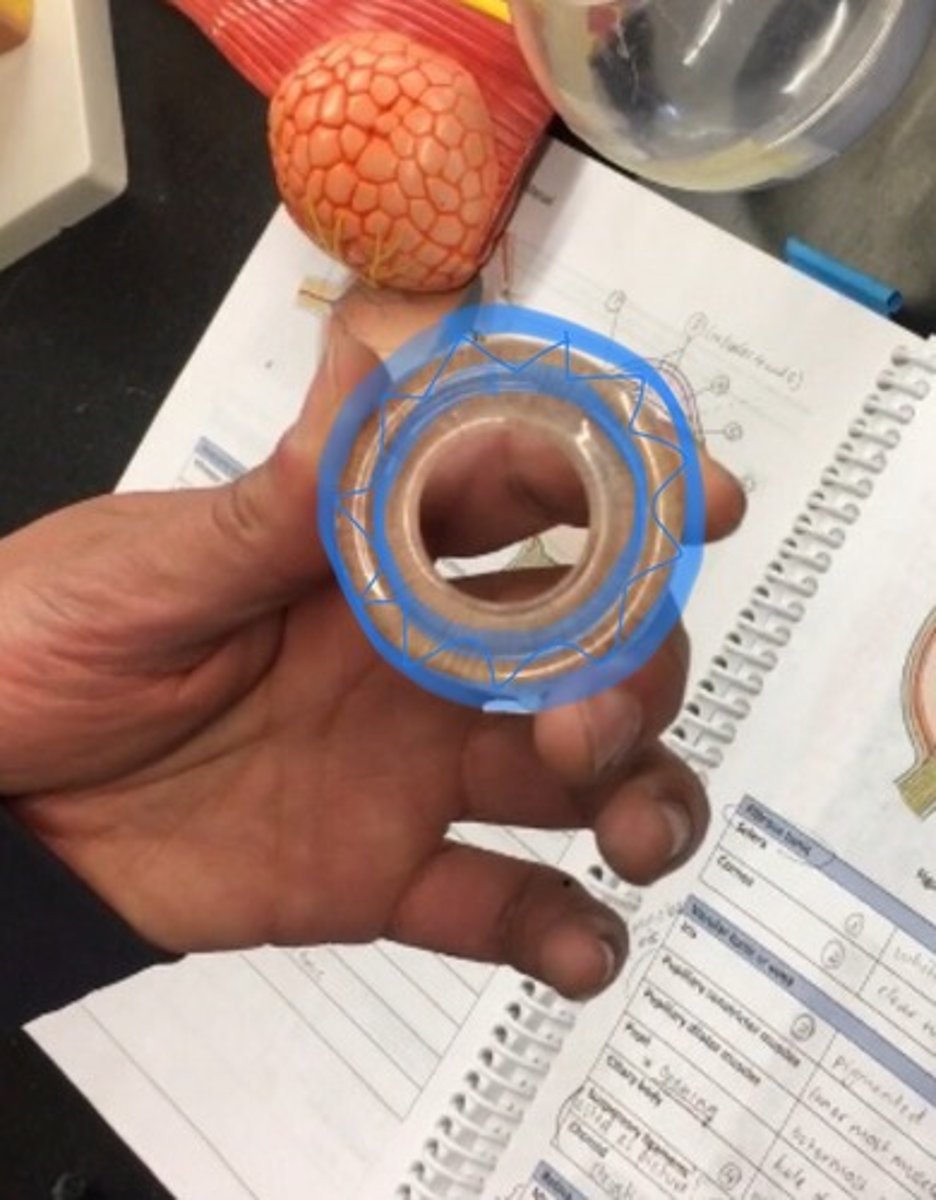
Pupillary dilator muscles
fan like striations on outside (still in iris) the outside ring.
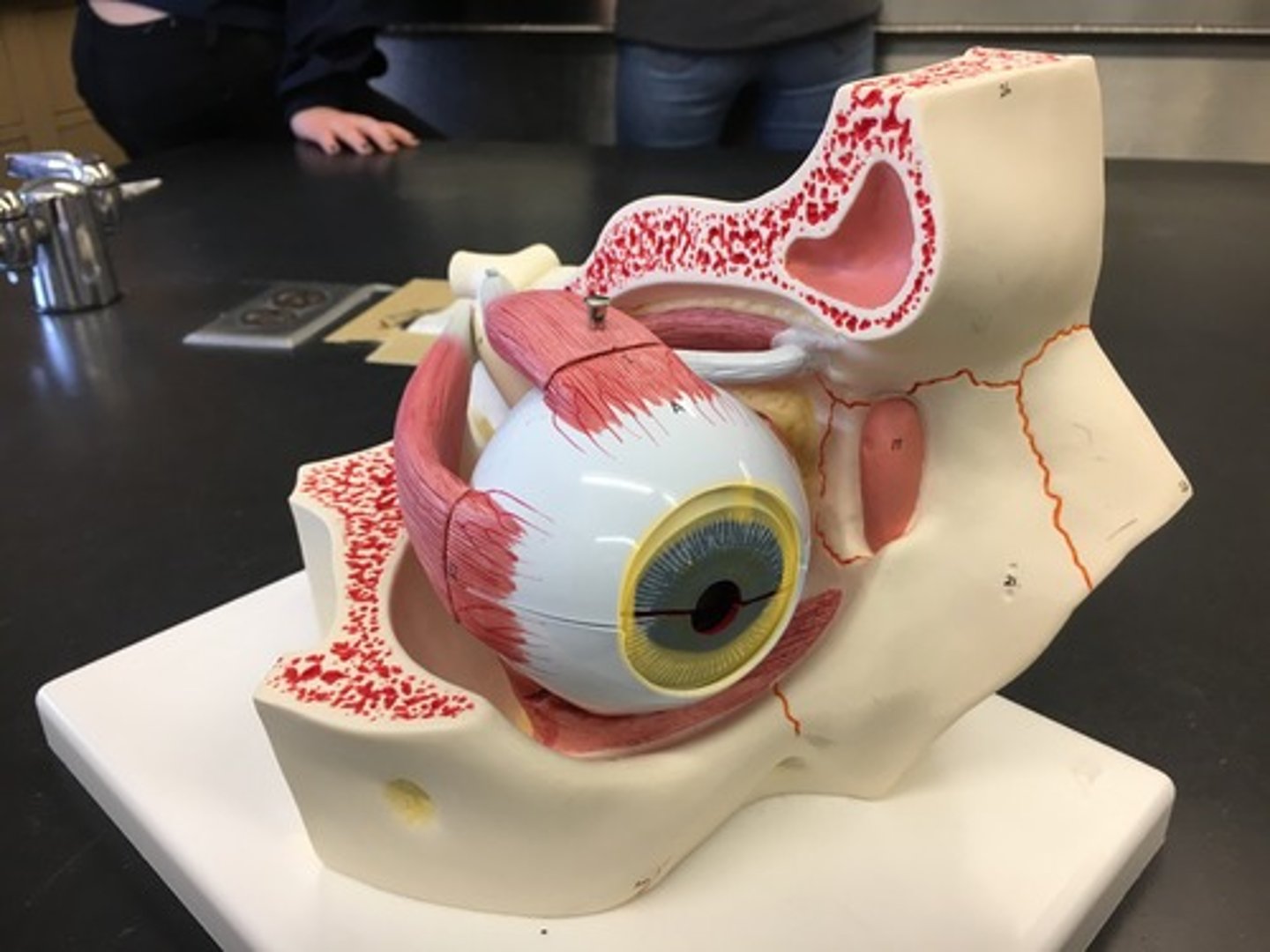
Pupil
a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.
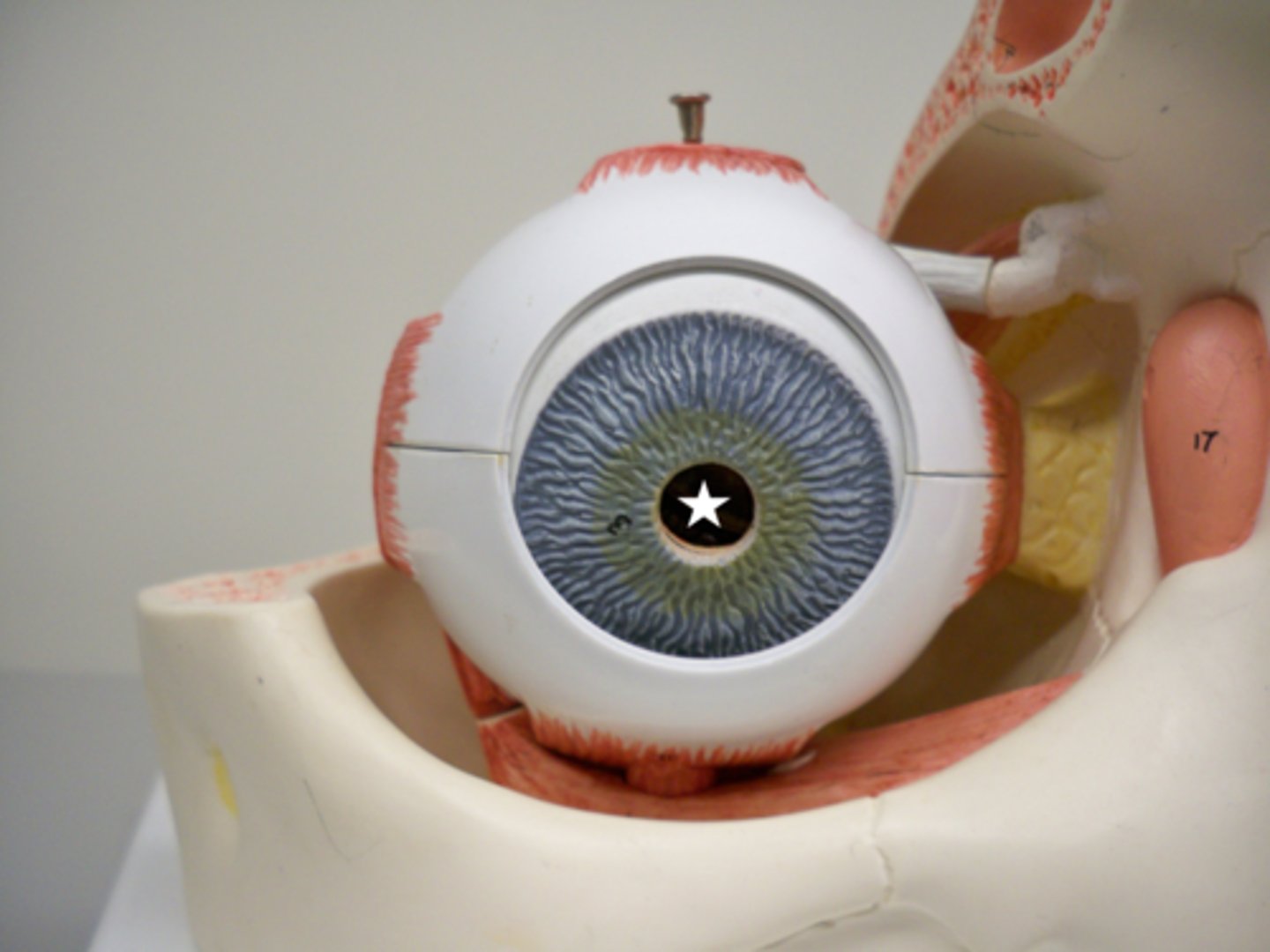
Ciliary body
a circular structure that is an extension of the iris; produces the fluid in the eye called aqueous humor; contains the ciliary muscle, which changes the shape of the lens when your eyes focus on a near object. Where the lens would sit, i little bit textured on the model.
Ciliary zonule (suspensory ligament)
holds the lens; NOT ON ANY MODELS. Will be tested as a picture not on model.
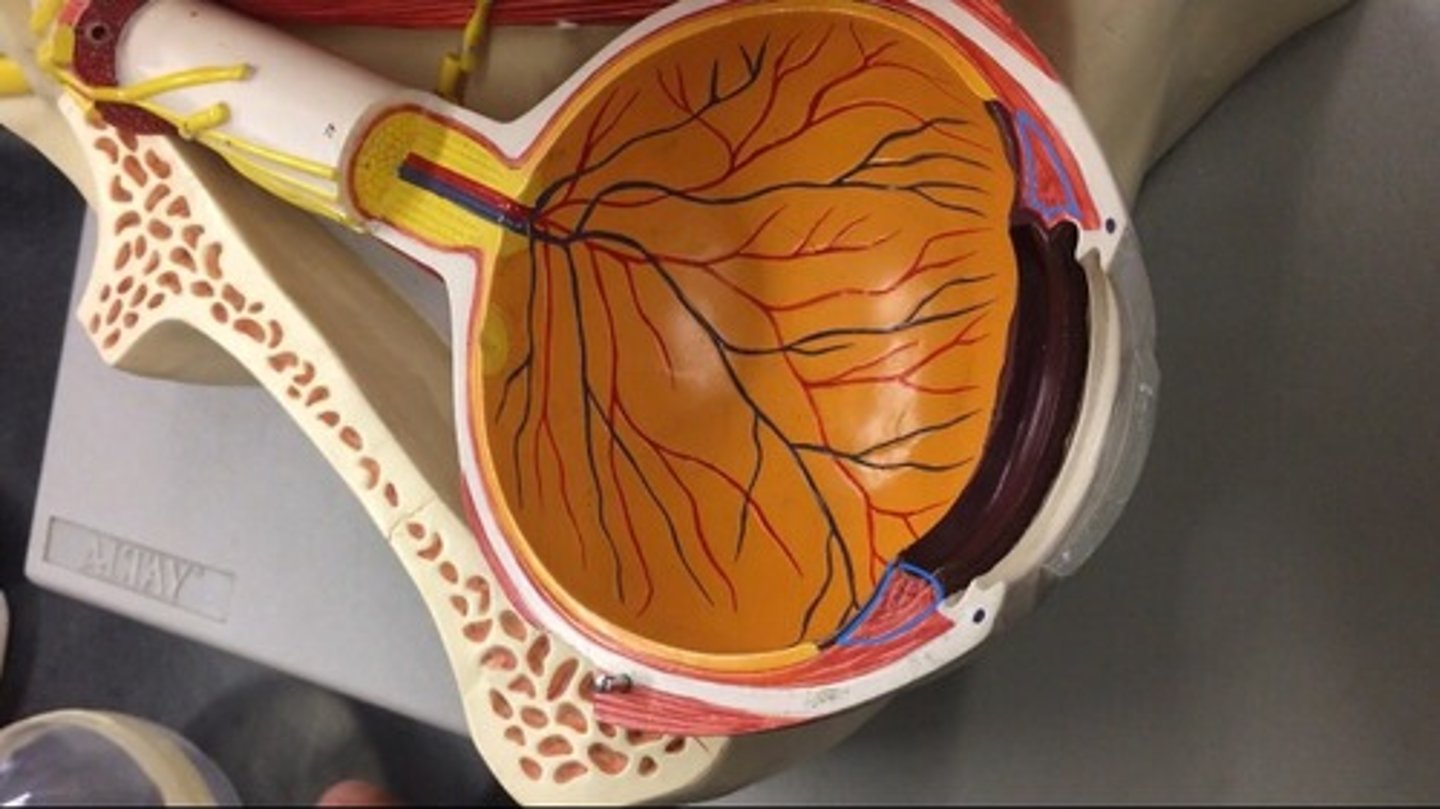
Choroid
the rest of the vascular tunic; the pigmented vascular layer of the eyeball between the retina and the sclera. Behind the ciliary body.
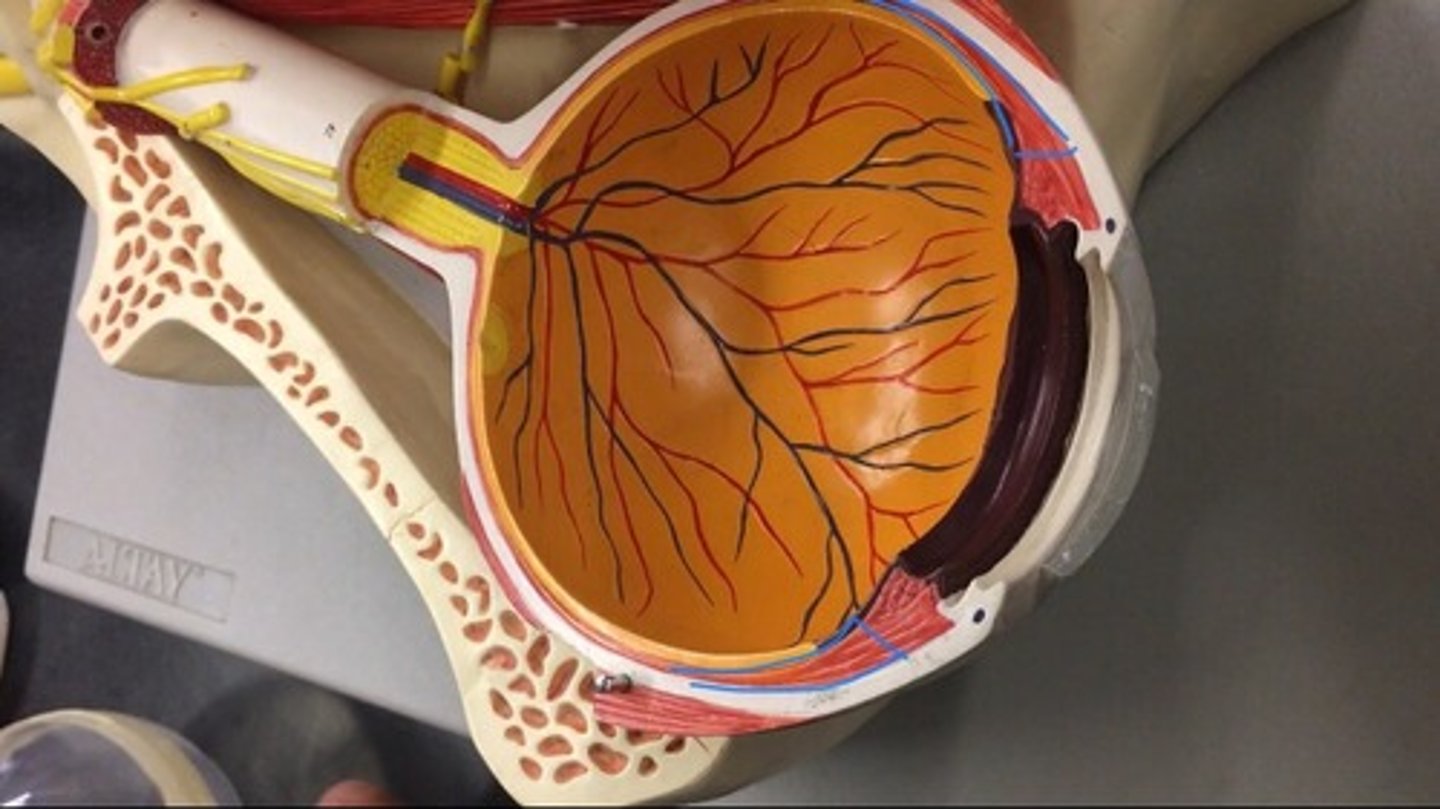
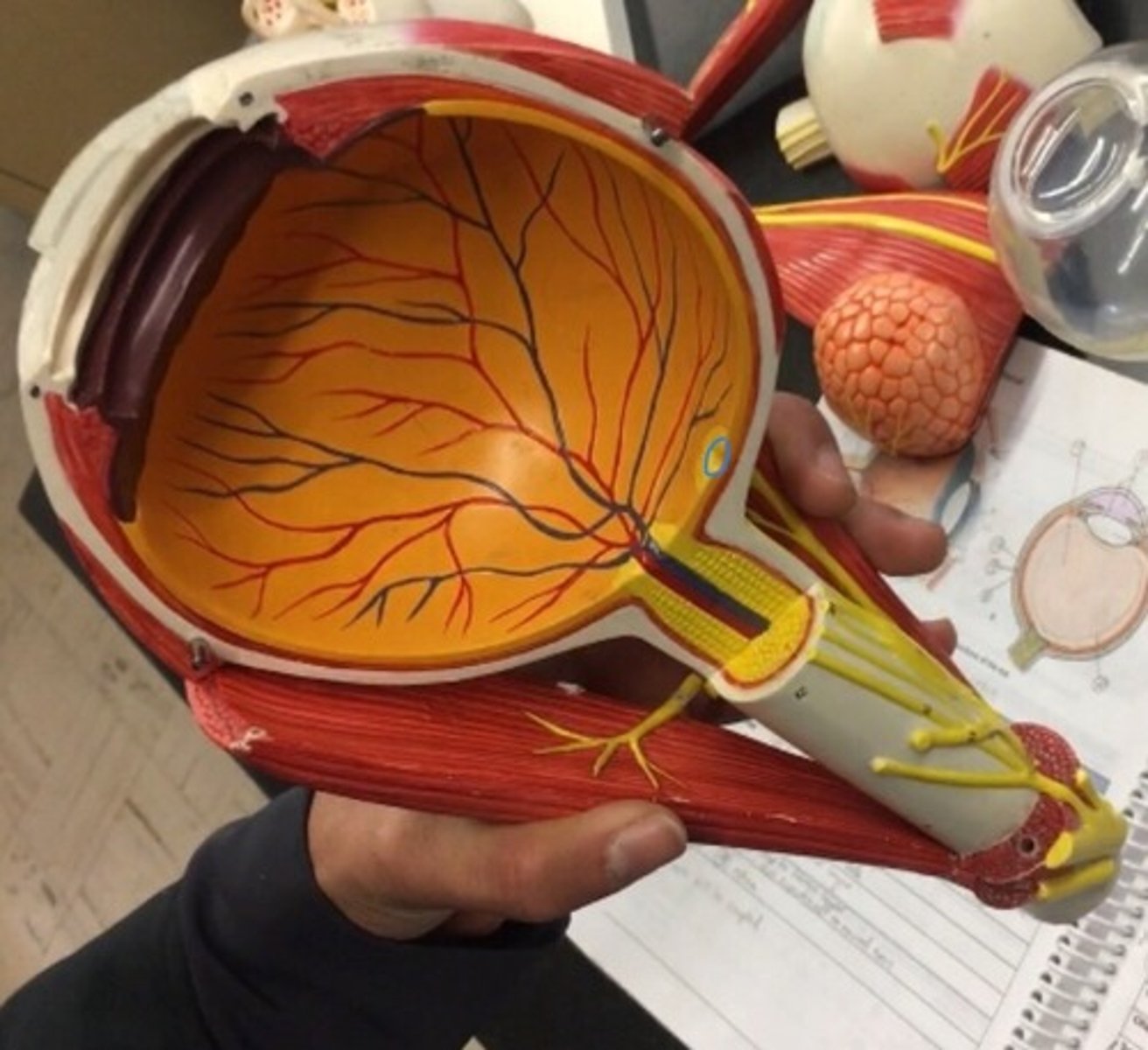
Macula lutea
the small yellowish area of the retina near the optic disk that provides central vision. The whole yellow spot on the model.
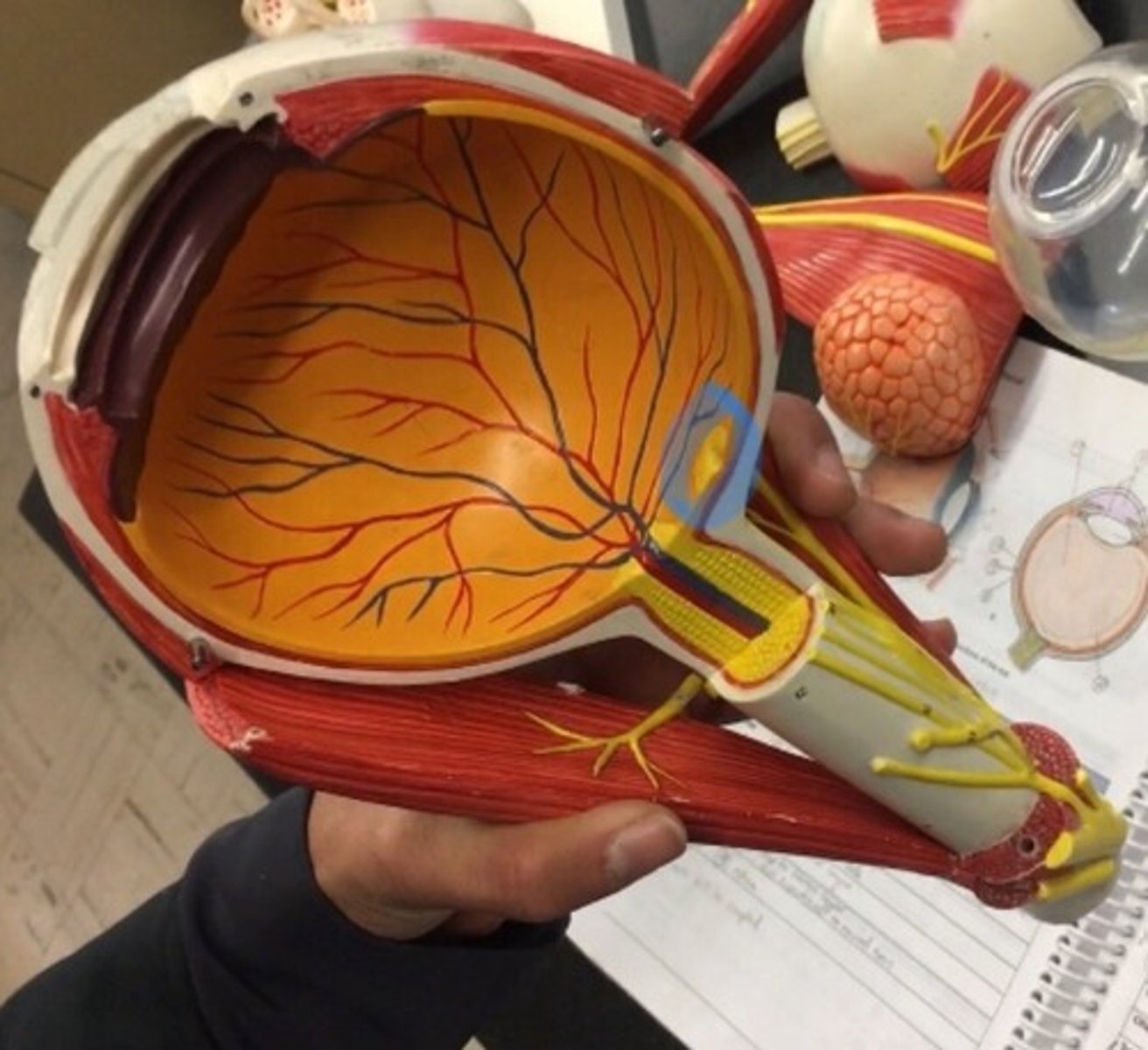
Fovea
a small depression in the retina of the eye where visual acuity is highest. The indent of the yellow dot on the model.
Optic disc
the raised disk on the retina at the point of entry of the optic nerve, lacking visual receptors and so creating a blind spot. The yellow dot surrounding the optic nerve is.
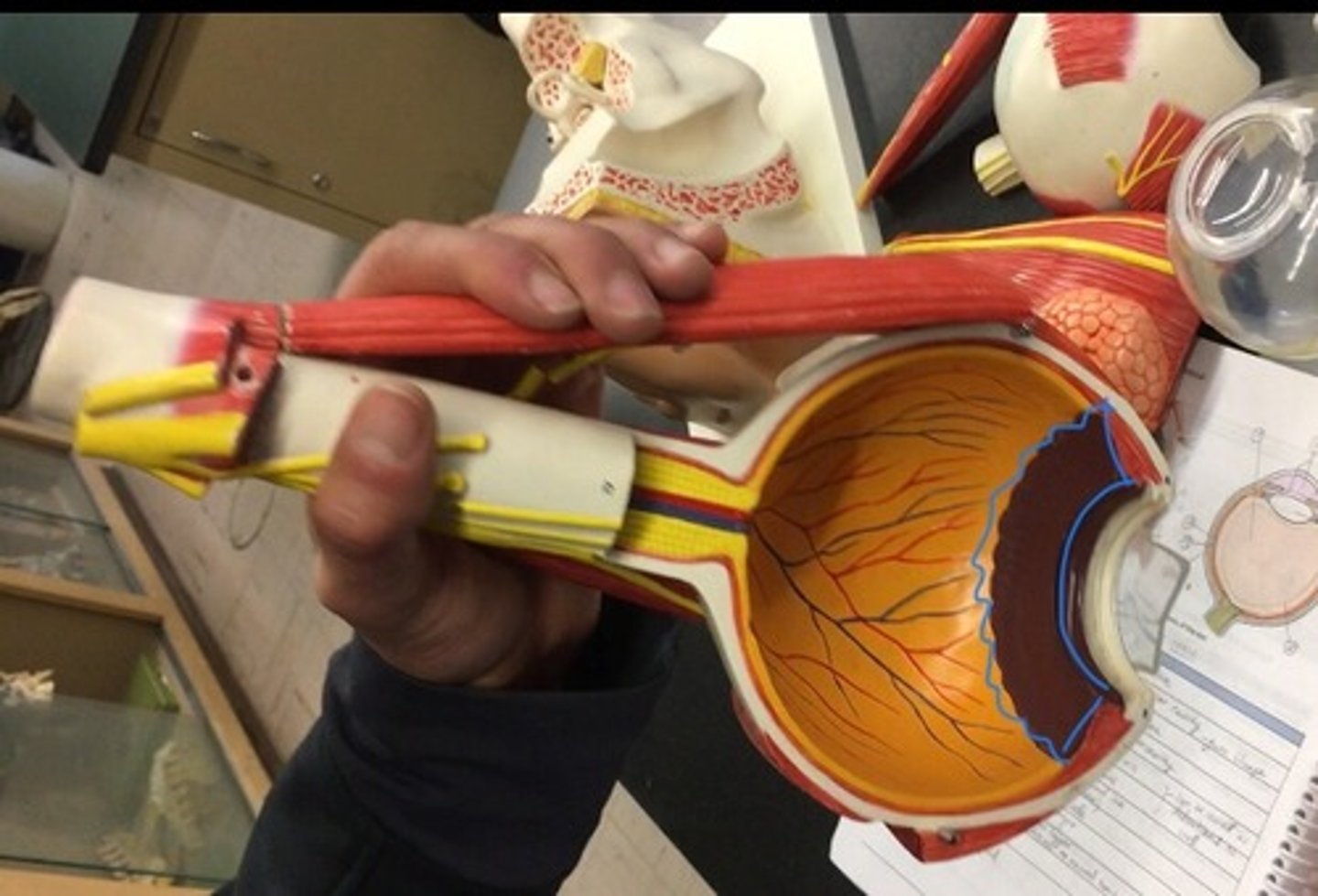
Ora serrata
the serrated junction between the retina and the ciliary body. The flower on the inside of the eye, surrounding the lens.
Pinna
The only visible part of the ear with its special helical shape.
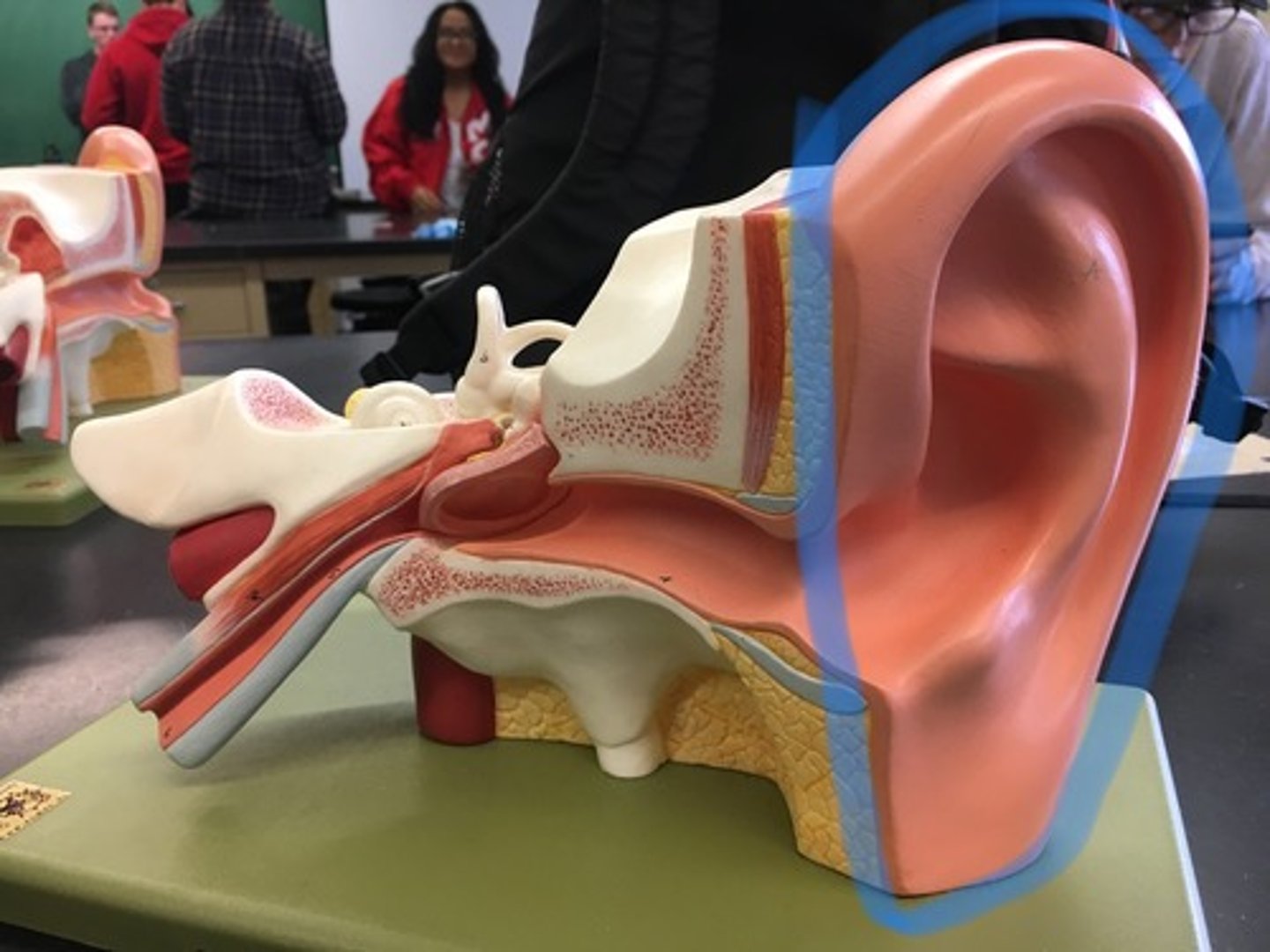
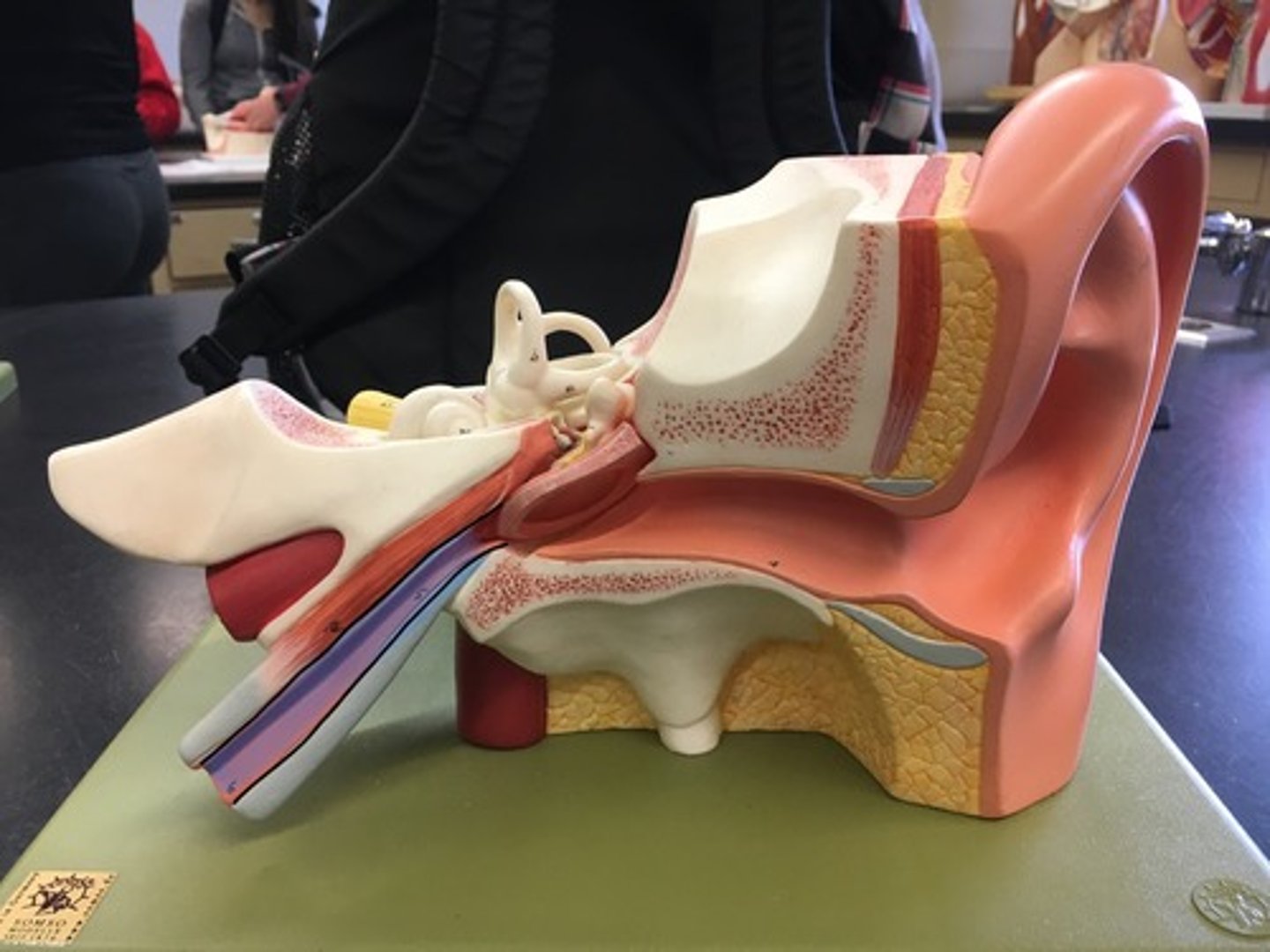
External acoustic meatus
A tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear. "Ear canal" It leads to the tympanic membrane.
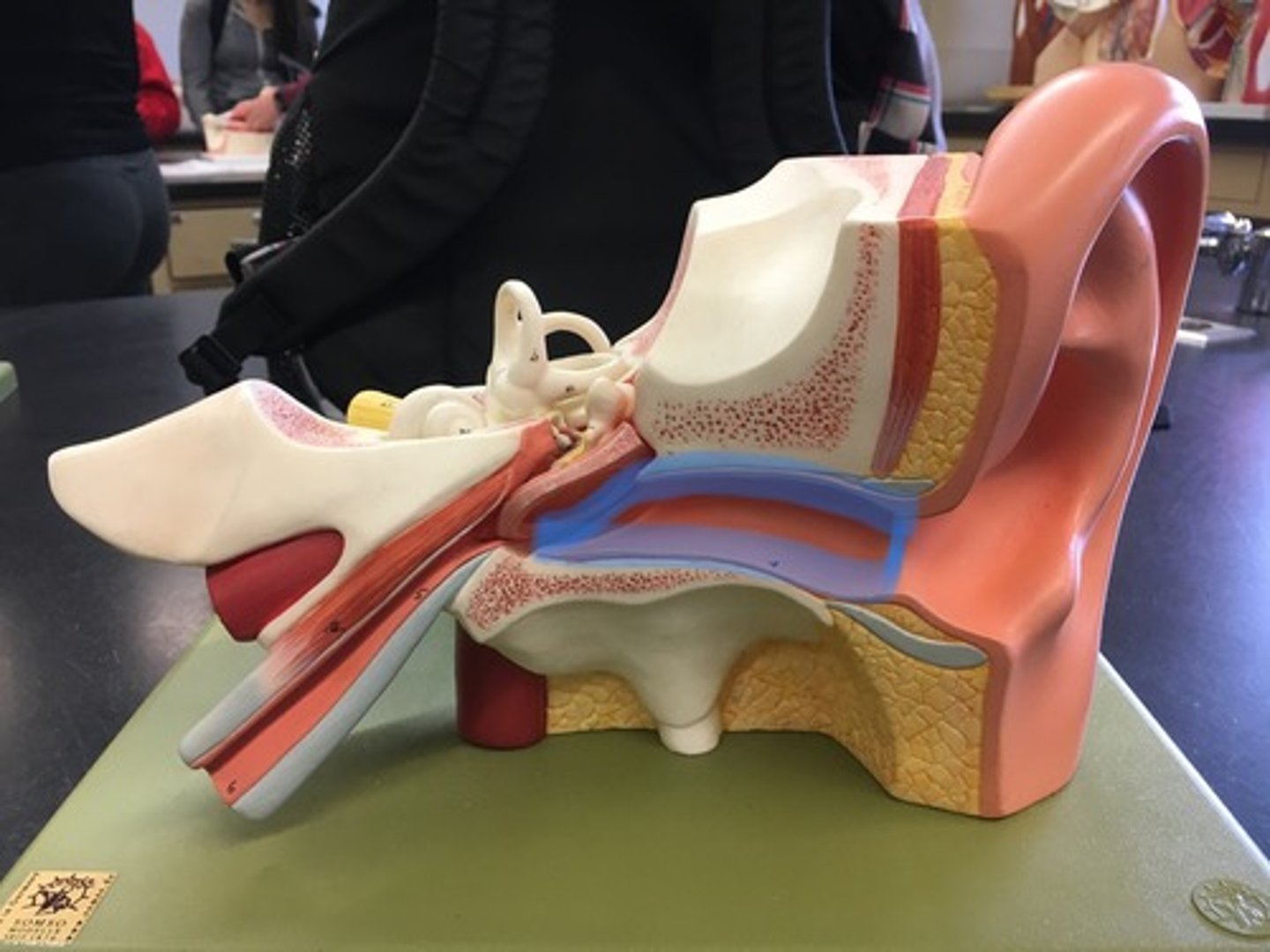
Tympanic membrane
Eardrum outer layer; thin cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. "Ear drum"
Auditory ossicles
three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body

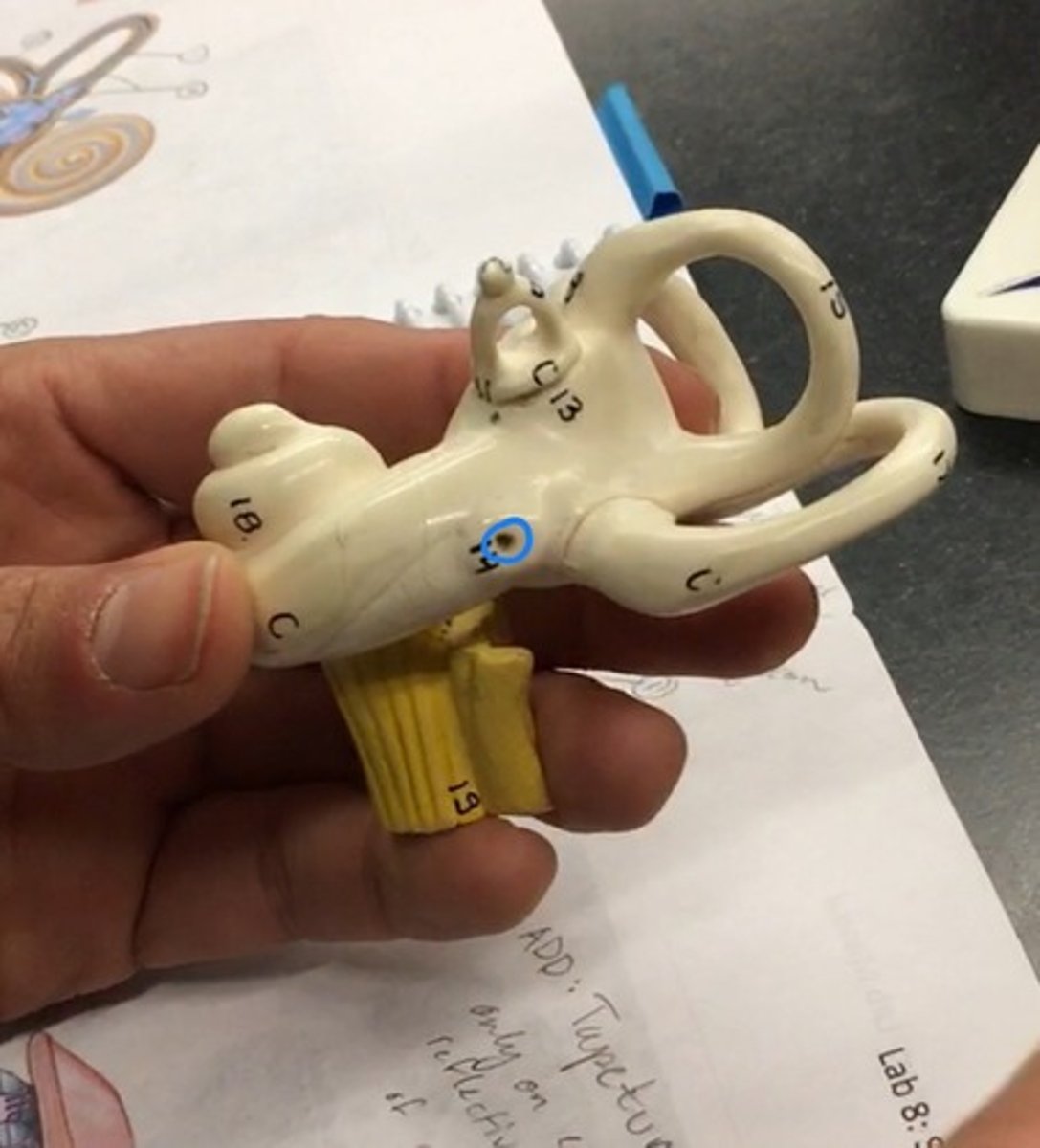
Malleus
a small bone in the middle ear that transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus. Connects to the tympanic membrane
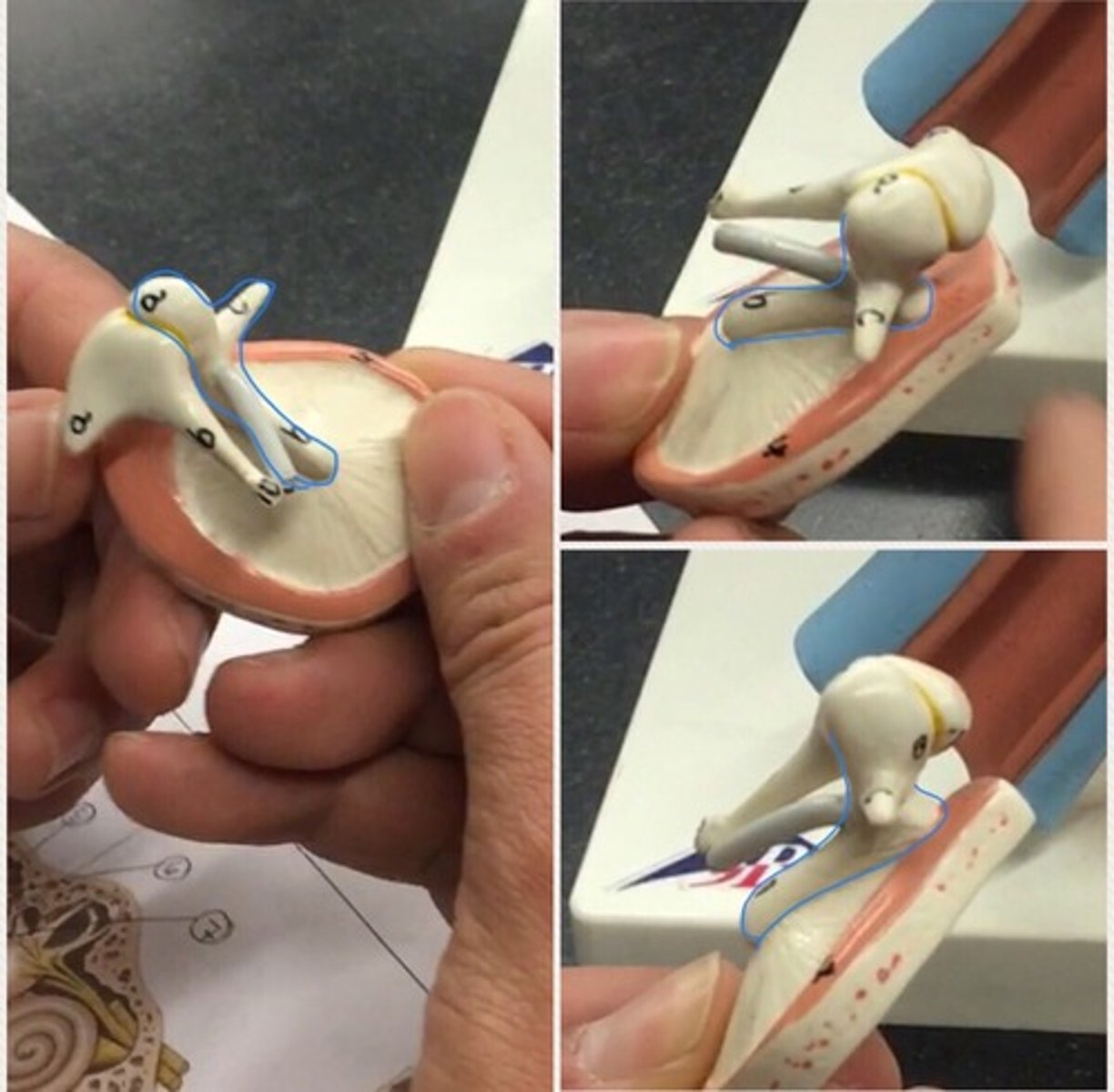
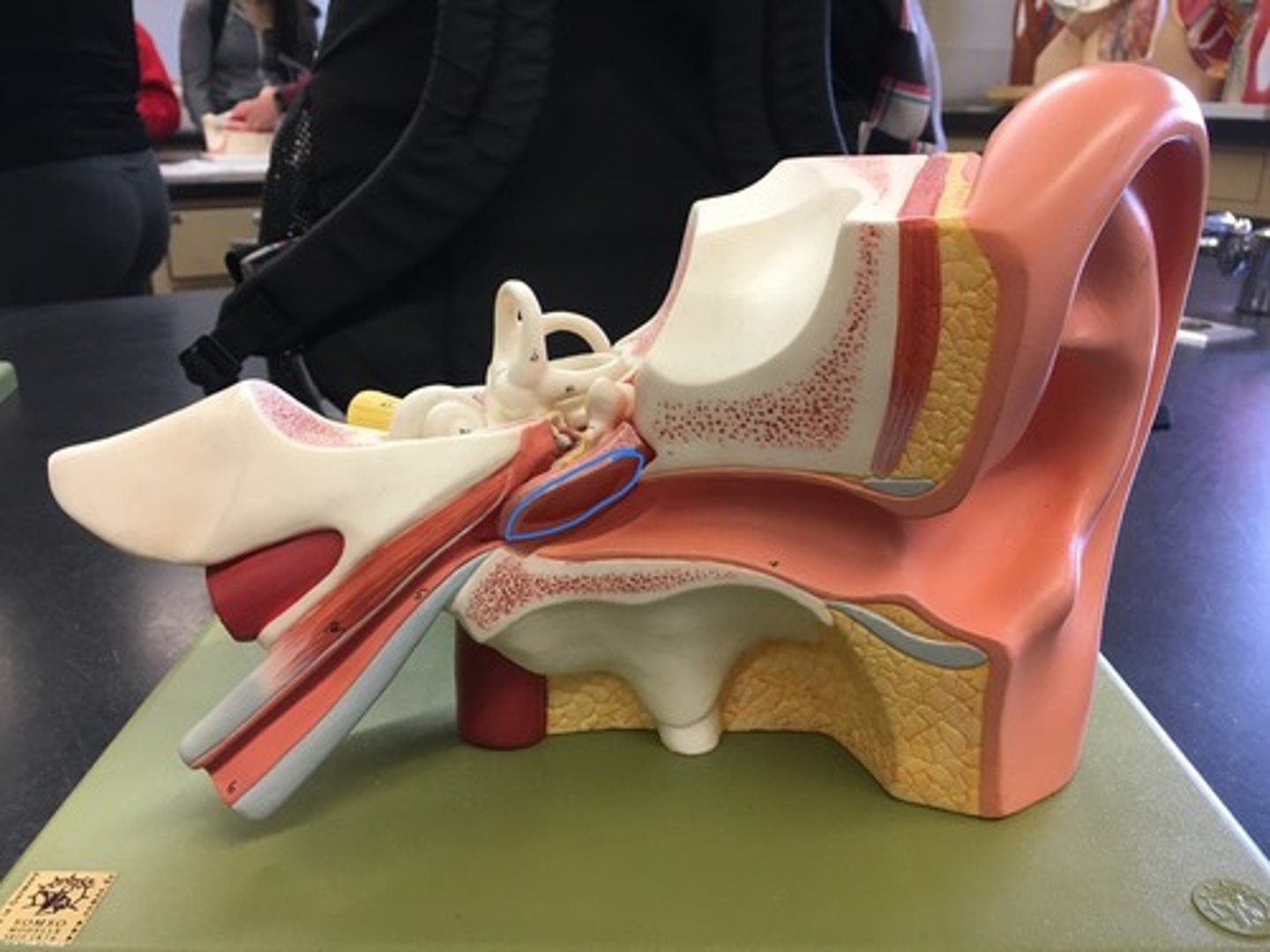
Incus
a small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations between the malleus and stapes. Behind malleus, looks like a tooth.
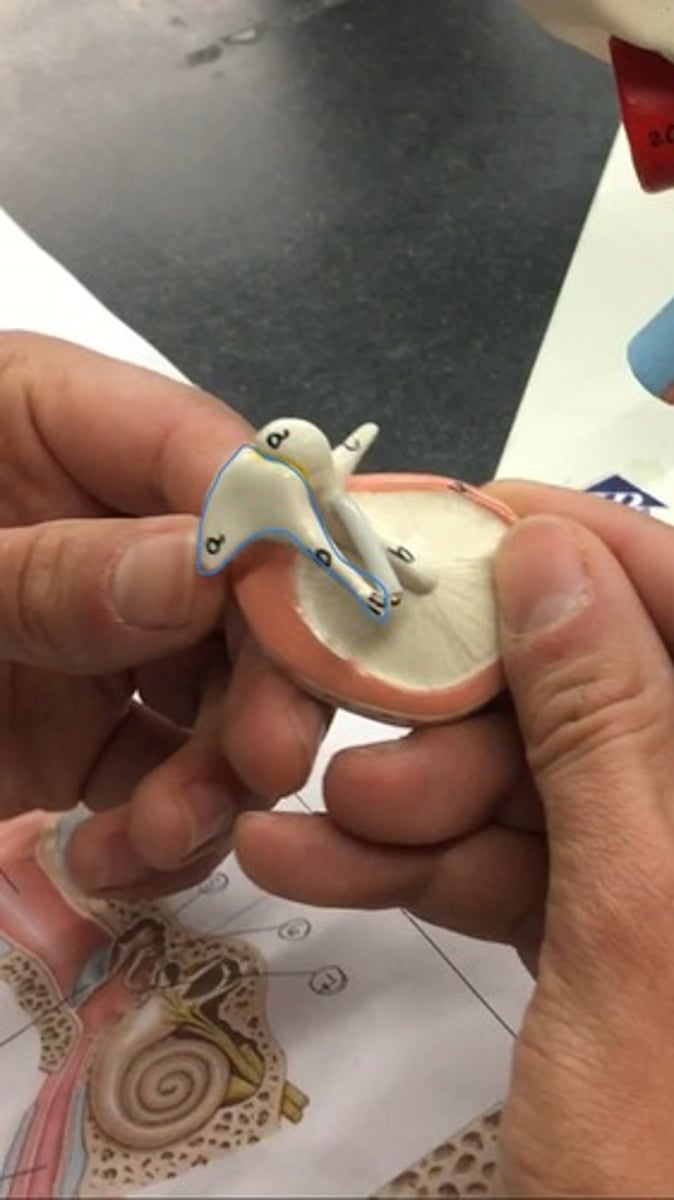
Stapes
the innermost, stirrup-shaped bone of a chain of three small bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear

Auditory tube
A tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear. It is a part of the middle ear. The canal right after the tympanic membrane.
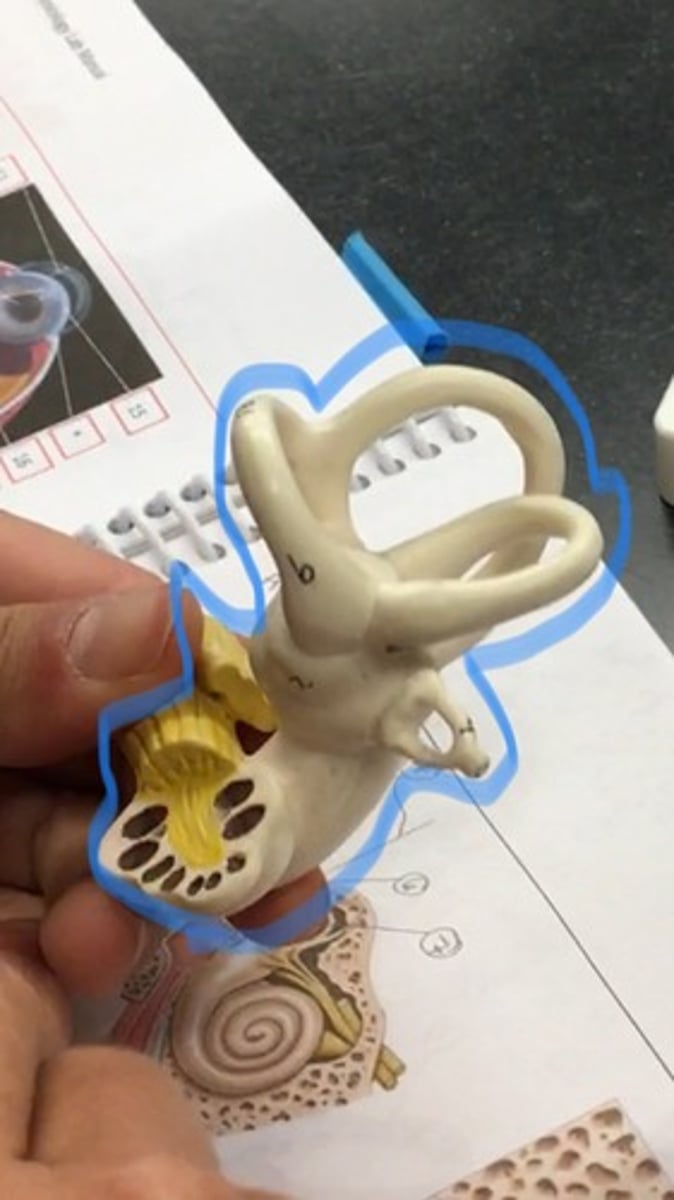
Bony labyrinth
rigid, bony outer wall of the inner ear in the temporal bone. It consists of three parts: the vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea.
Vestibulocochlear nerve VIII
known as the eighth cranial nerve, transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain
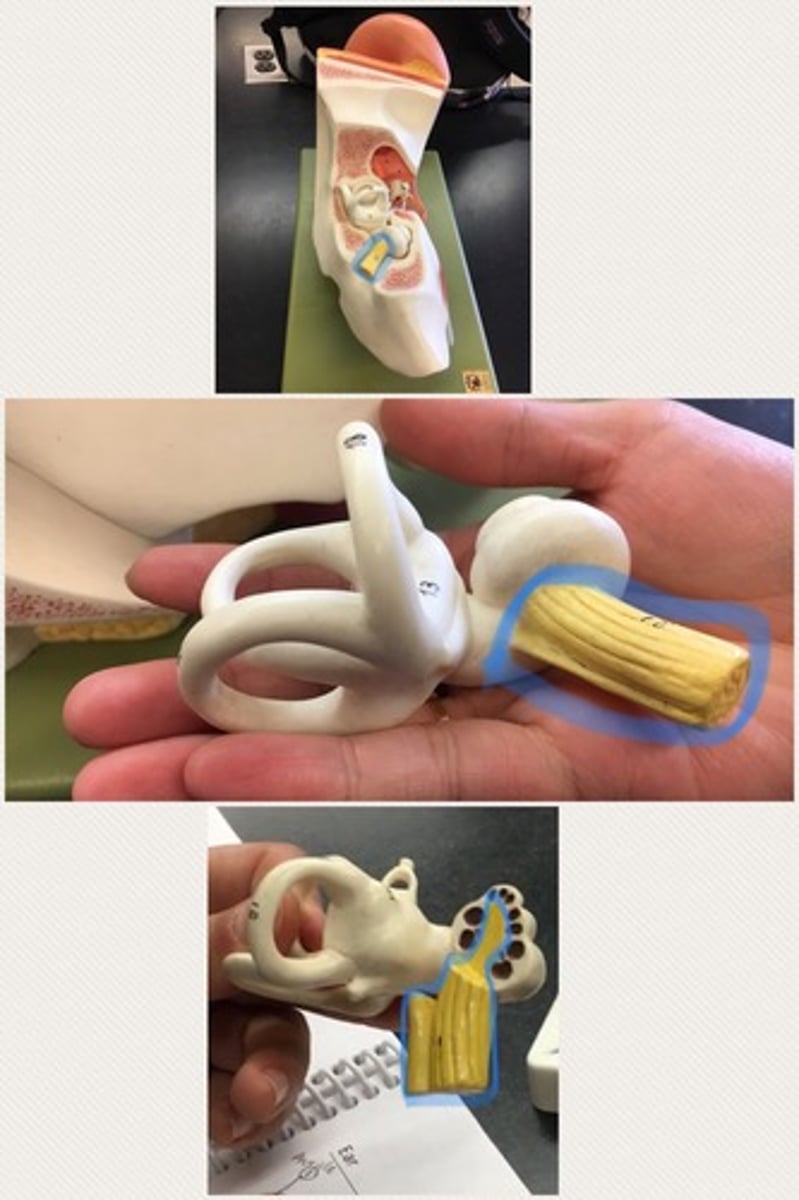
Vestibular complex
contains three semicircular canals in each labyrinth. "toilet"

Vestibule
the central part of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear, and is situated medial to the eardrum (tympanic cavity), behind the cochlea, and in front of the three semicircular canals. The trunk that is surrounded by the semicircular canals.

Anterior semicircular canal
"lid" of the toilet
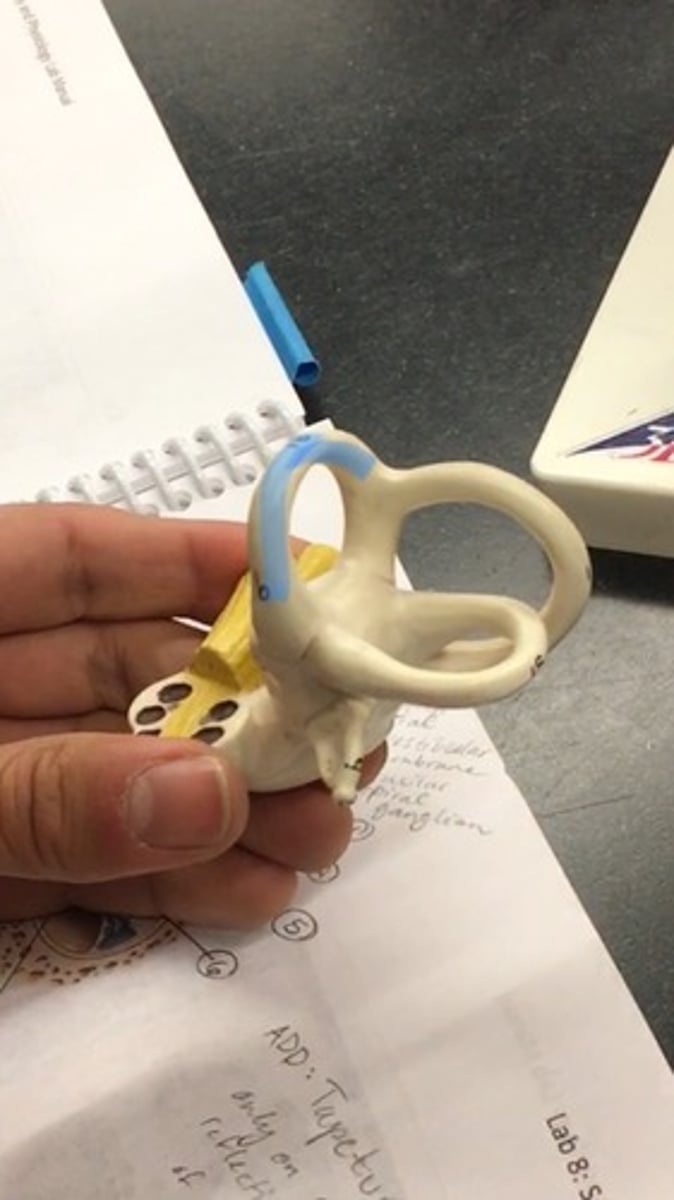
Posterior semicircular canal
"rail" of the toilet

Lateral semicircular canal
"seat" of the toilet
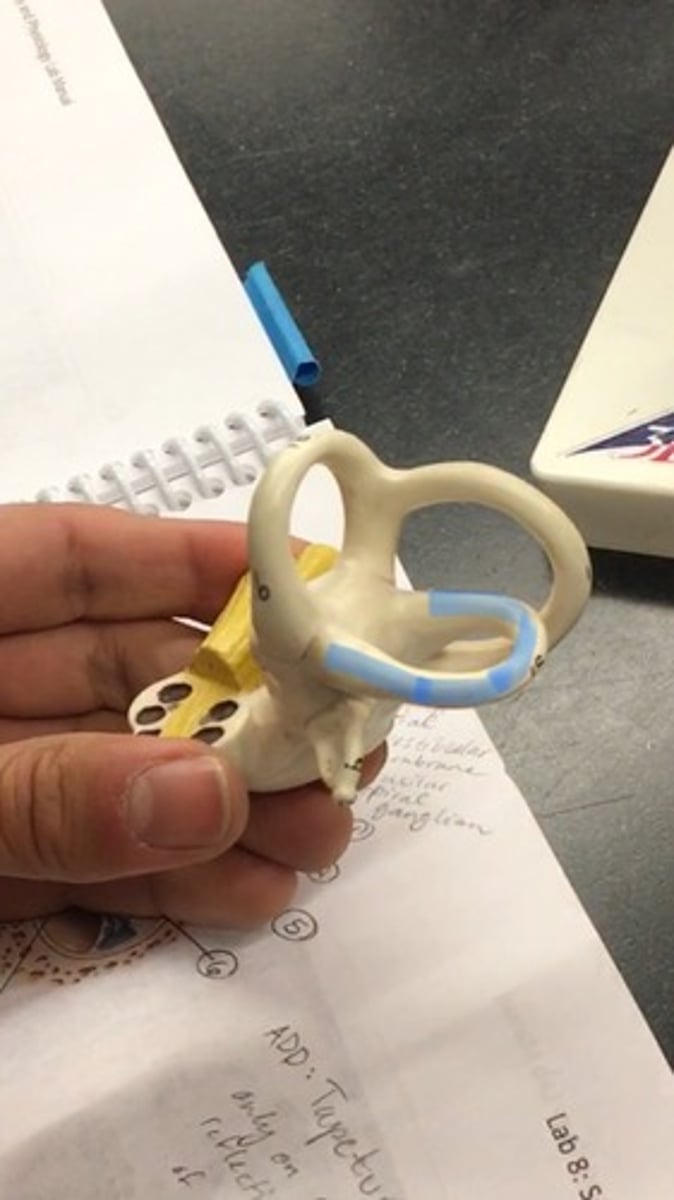
Ampulla
a sac-like enlargement of a canal or duct
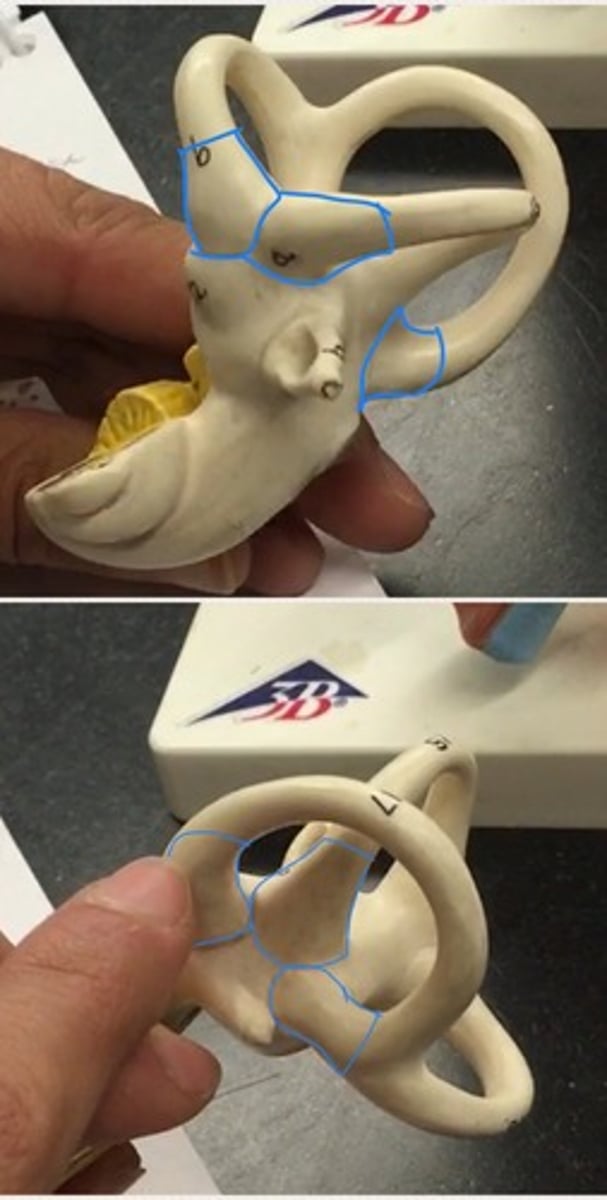
Cochlea
A portion of the inner ear that looks like a snail shell.
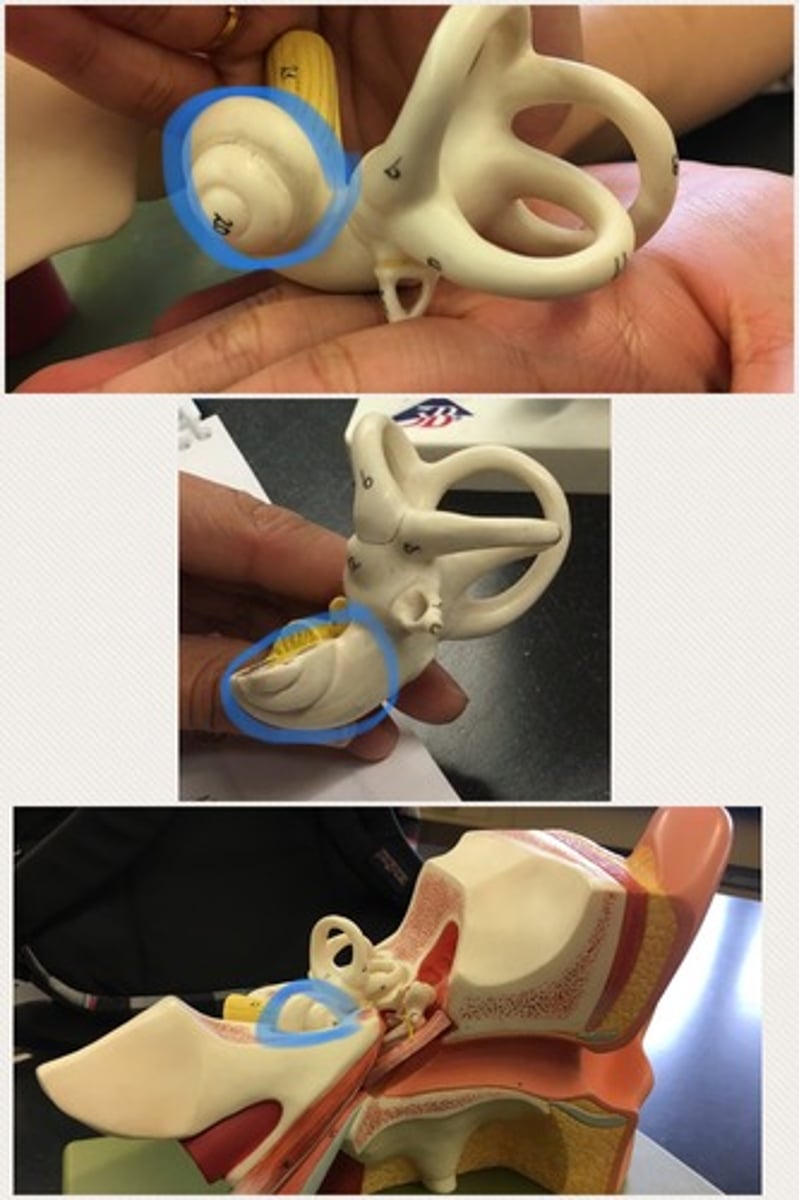
Oval window
a membrane-covered opening that leads from the middle ear to the vestibule of the inner ear.; goes IN, covered by stapes.
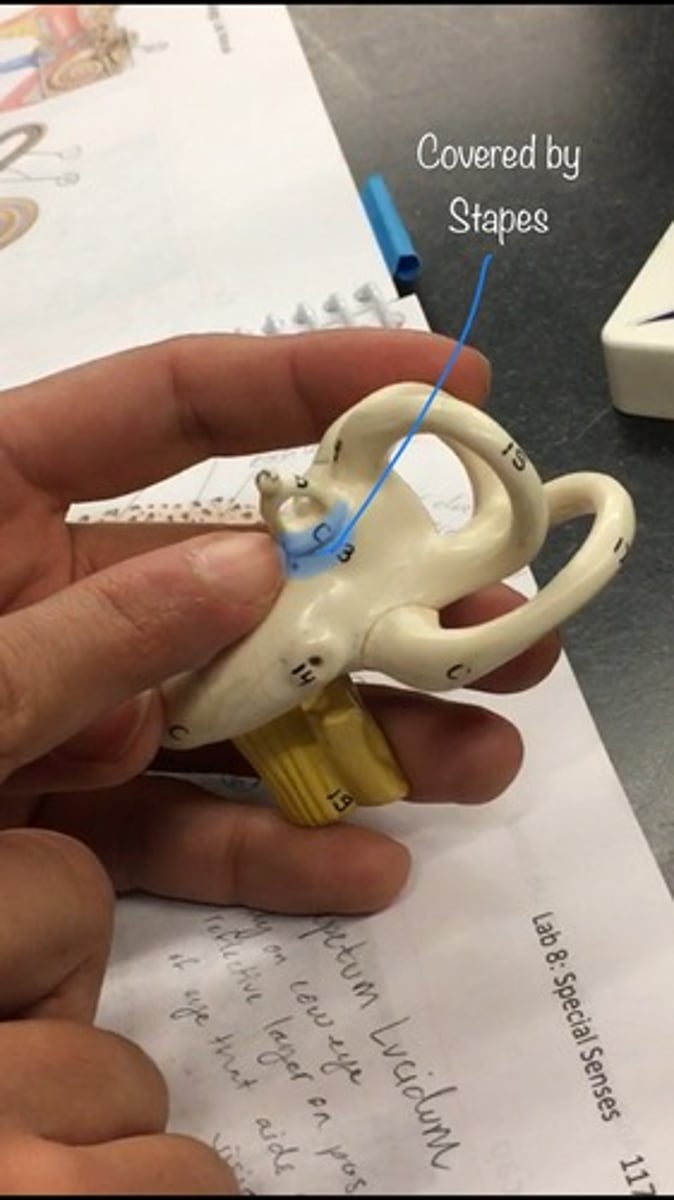
Round window
An opening on the medial wall of the middle ear that leads into the cochlea and is covered by the secondary tympanic membrane. On the bottom, like a pinhole.
Cochlear branch
also known as the acoustic nerve, is the sensory nerve that transfers auditory information from the cochlea (auditory area of the inner ear) to the brain

Vestibular branch
The superior division of the vestibular nerve carries sensory fibres from the hair cells of the anterior and lateral semicircular canals and utricle

Vestibular duct
a perilymph-filled cavity inside the cochlea of the inner ear that conducts sound vibrations to the cochlear duct
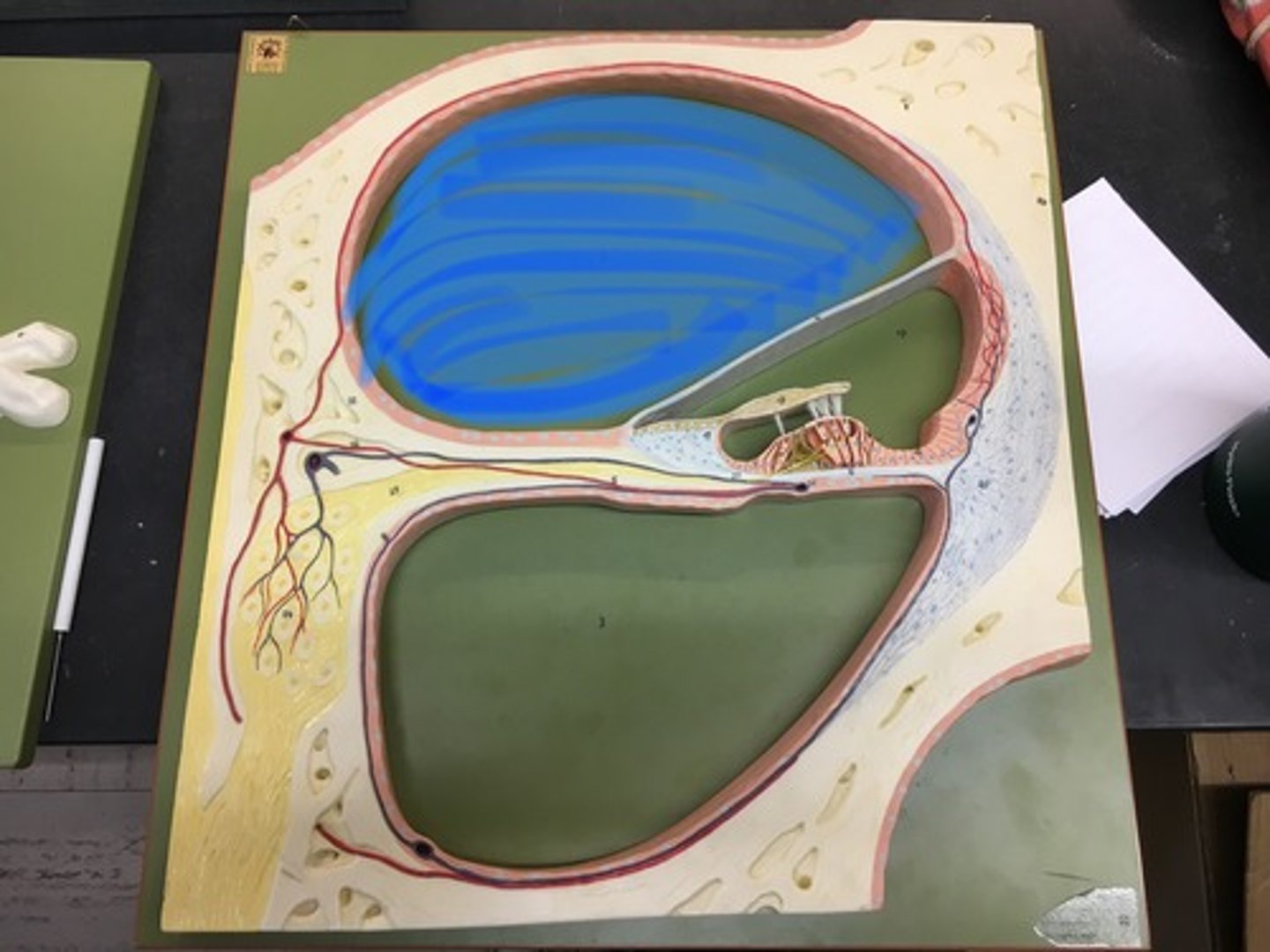

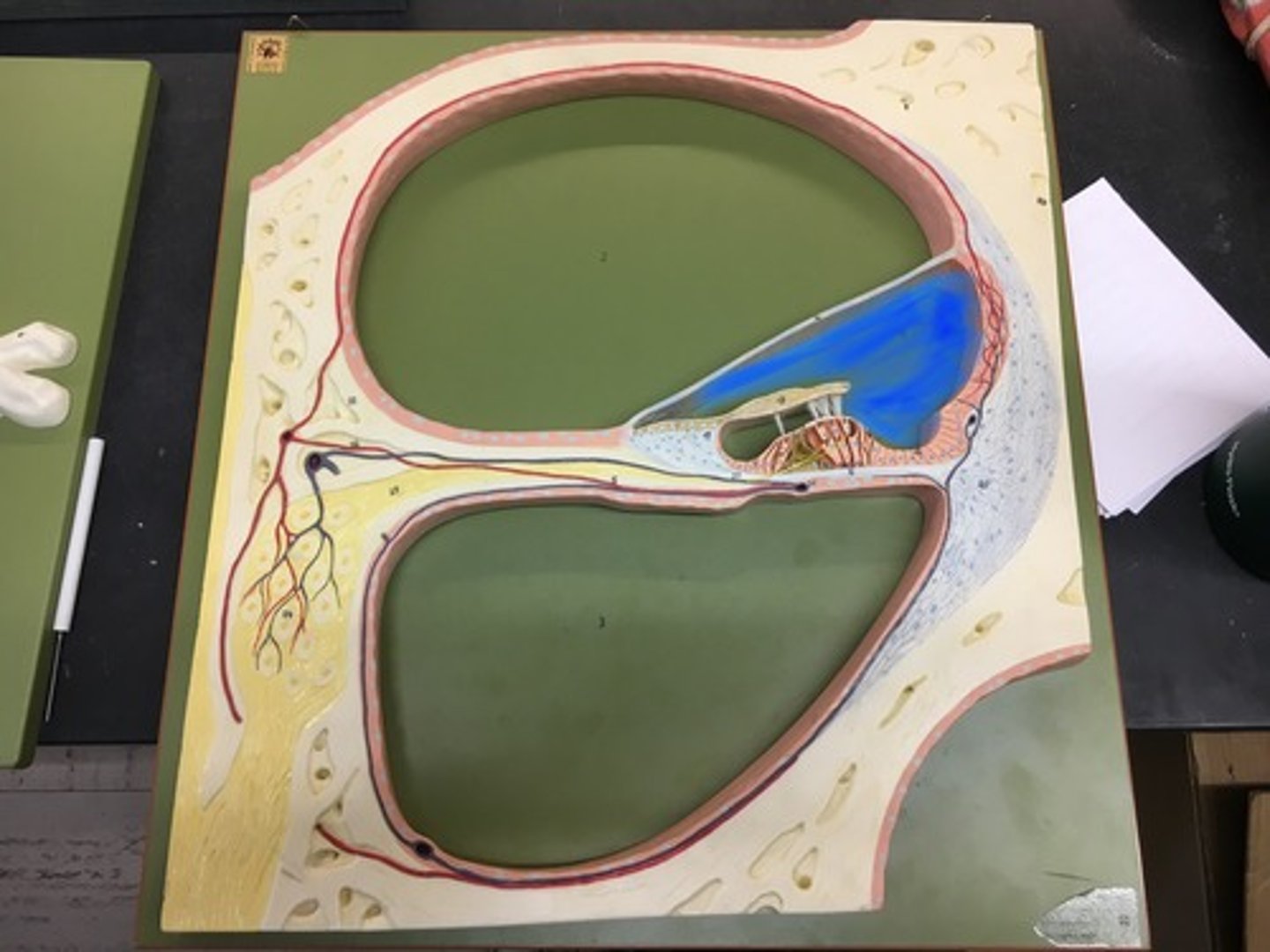
Cochlear duct
endolymph filled cavity inside the cochlea, located in between the tympanic duct and the vestibular duct, separated by the basilar membrane

Spiral organ (organ of Corti)
the receptor organ for hearing and is located in the mammalian cochlea.
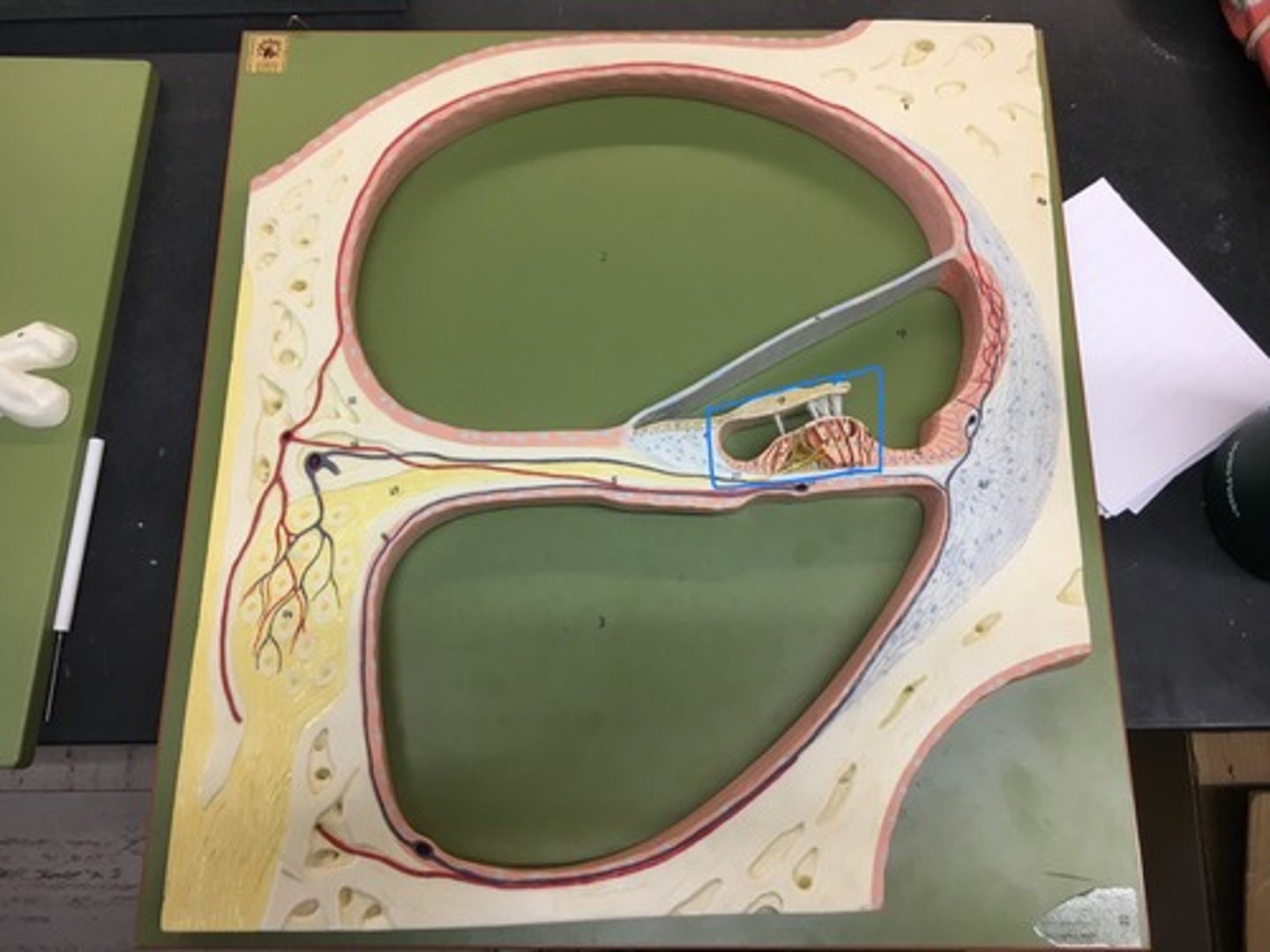

Hair cells
detect movement in their environment.
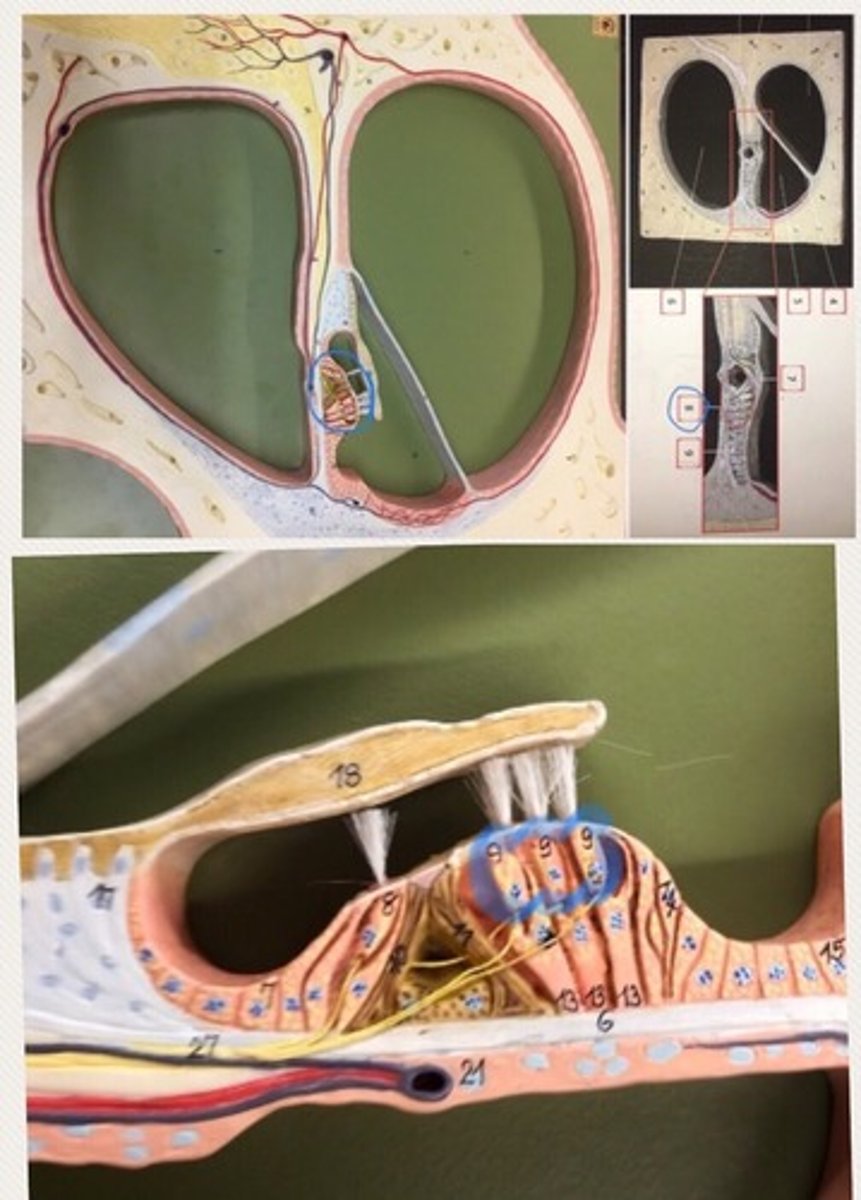
Tympanic duct
one of the perilymph-filled cavities in the inner ear of the human. It is separated from the cochlear duct by the basilar membrane
Vestibular membrane
a membrane inside the cochlea of the inner ear. It separates the cochlear duct from the vestibular duct.

Basilar membrane
a membrane in the cochlea that bears the organ of Corti.
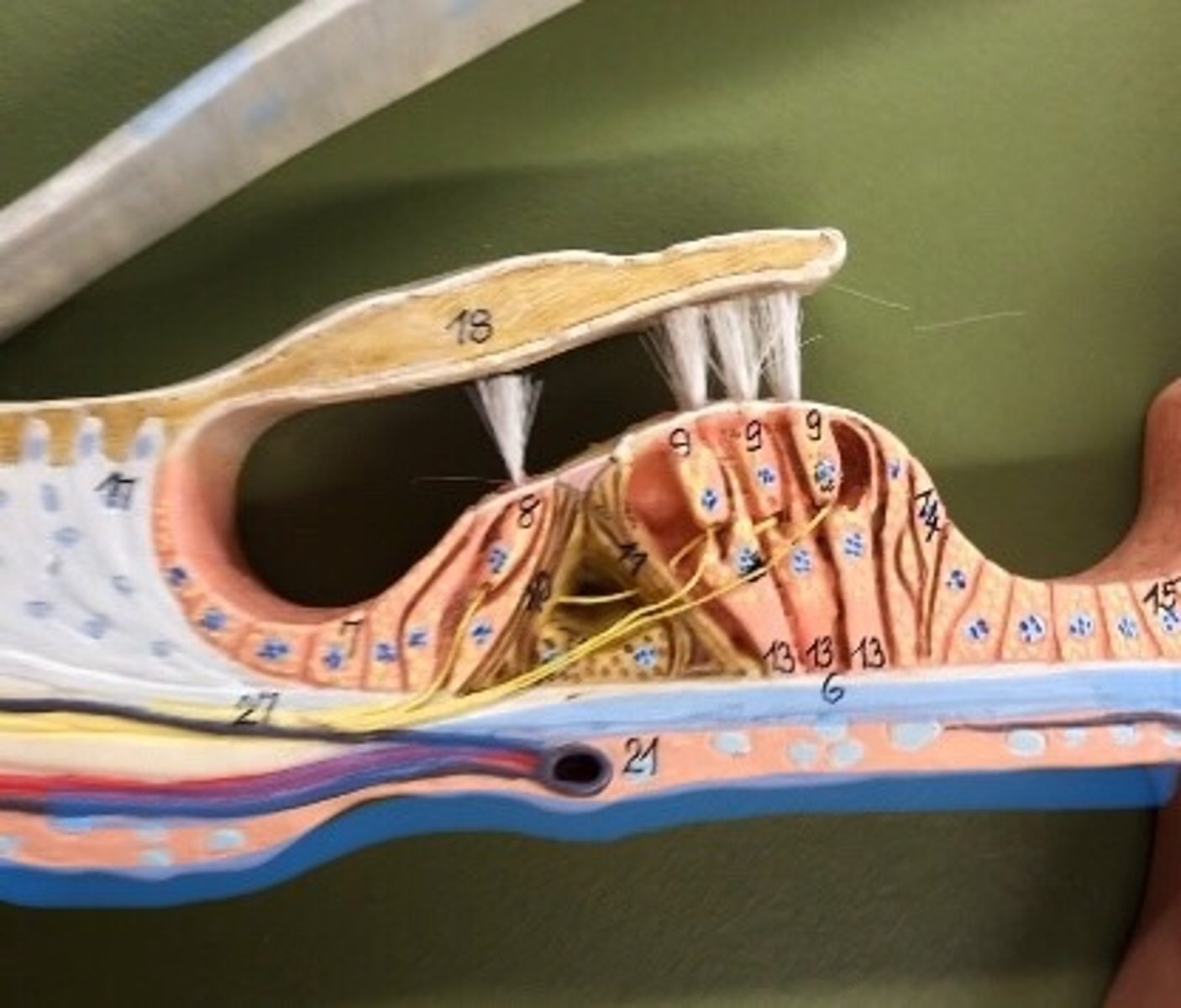
Tectorial membrane
one of two acellular membranes in the cochlea of the inner ear, the other being the basilar membrane
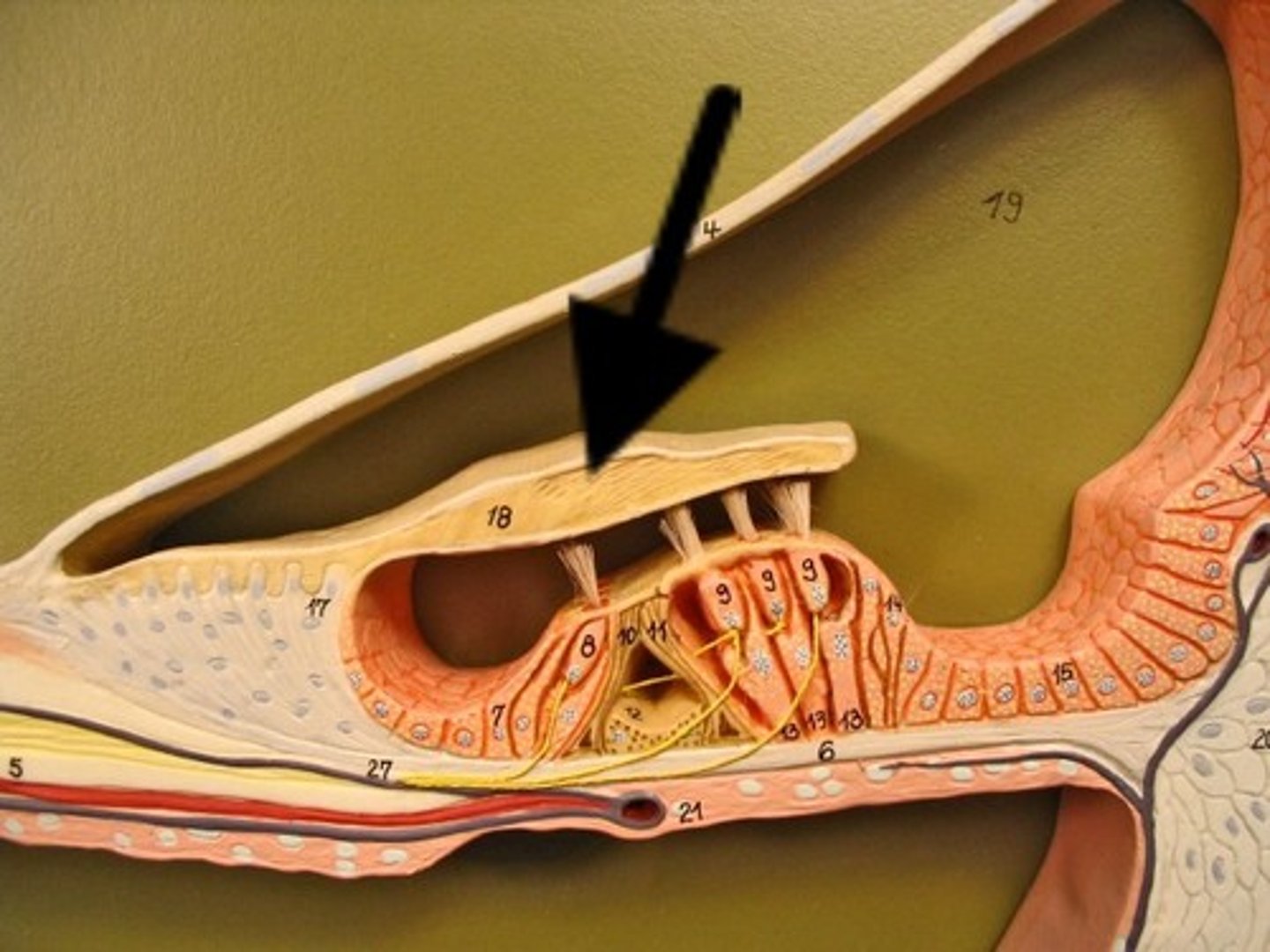
Spiral ganglion
the group of nerve cells that serve the sense of hearing by sending a representation of sound from the cochlea to the brain.