Session 7: Infections of the Reproductive System
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
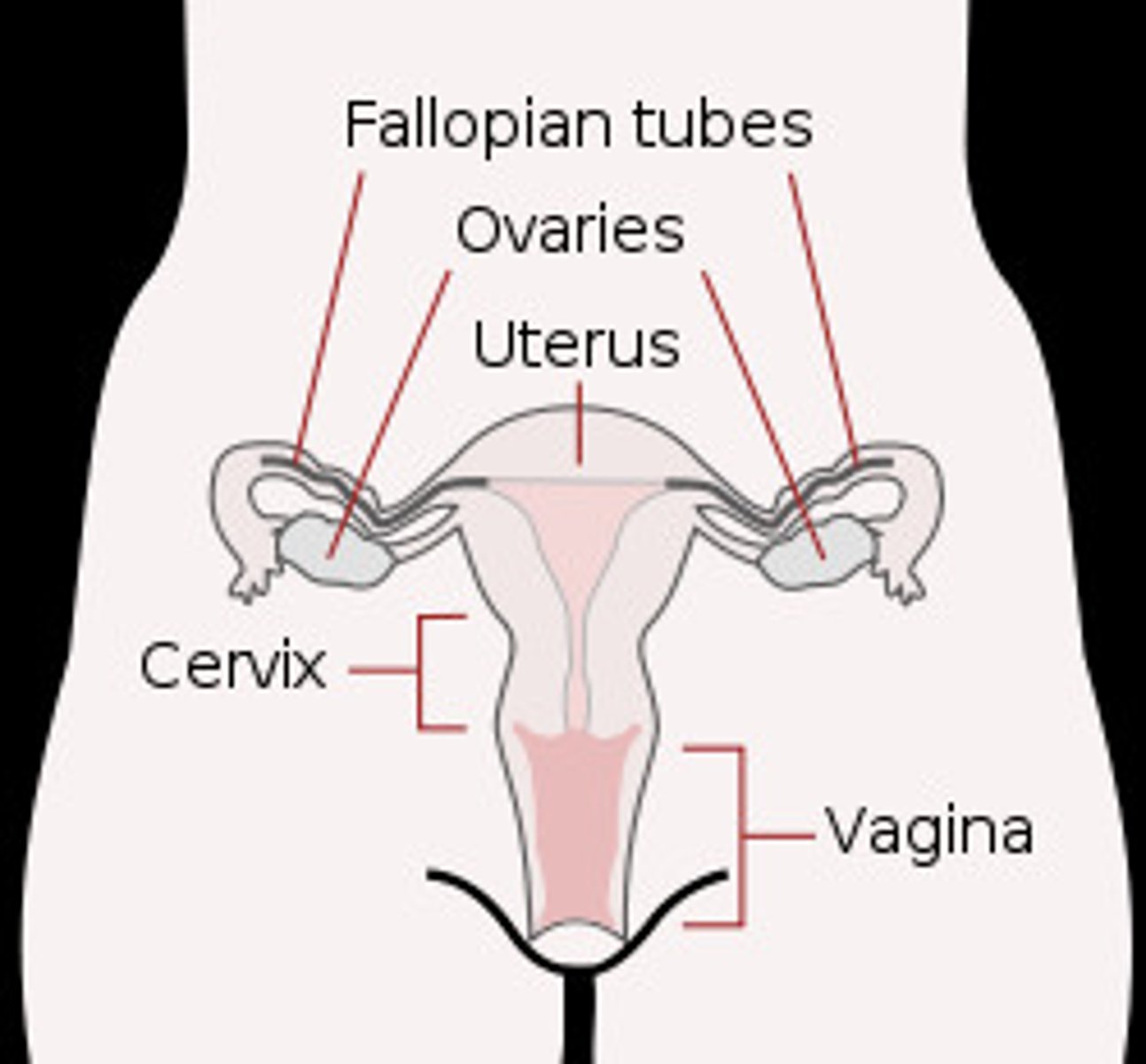
Structures in the female reproductive system
- Two ovaries
- Two fallopian tubes
- Vagina (lined with mucous membrane)
- External genitalia = clitoris, labia, opening of vagina
The vaginal commensal flora out-compete other pathogens and produce two substances which help to protect against infection.
What are these substances?
Lactic Acid
Hydrogen Peroxide
Innate immune system protective mechanisms of the vagina
- Low pH
- Physical barrier
- Hormonal regulation
Sometimes, infection can ascend into the vagina leading to two different potential conditions.
What are these conditions?
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Tubo-ovarian abscess
Potential complications of tubo-ovarian abscess
Scarring
Sepsis
Subfertility
Structures in the male reproductive system
- Two testes
- Scrotum
- Duct system (vas deferens)
- Prostate
- Urethra
- Penis (covered by foreskin)
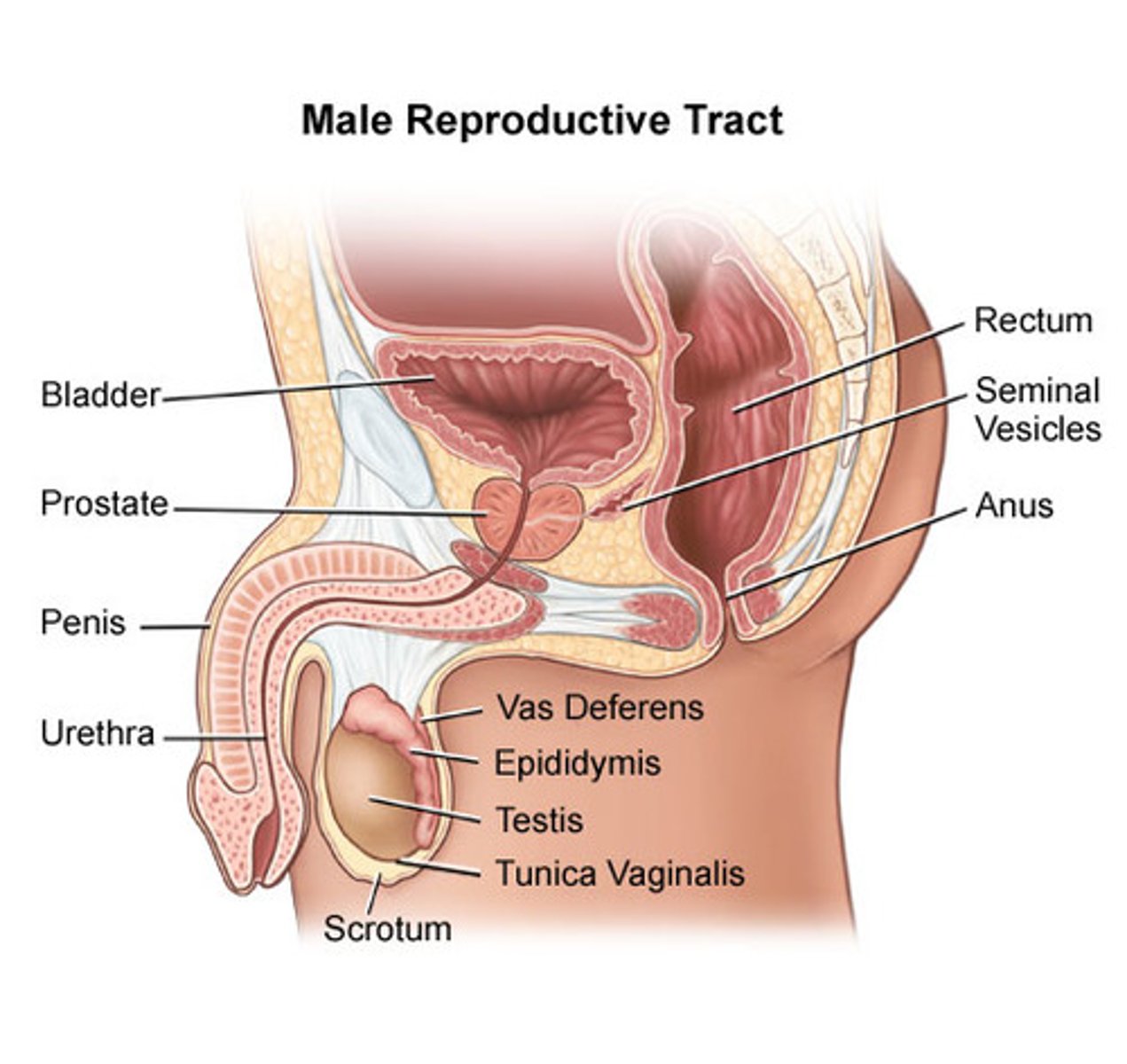
Where do micro-organisms commonly invade the male reproductive system?
Micro-organisms can invade the urethra or the skin of the penis (foreskin)
Sometimes, infection can ascend into the penis leading to what potential condition?
Epididymo-orchitis
Innate immune system protective mechanisms of the penis
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) initiate pathway to lead to inflammation to fight off the invading pathogens
If micro-organisms are to colonise the vagina and invade they must either...
- Have specific mechanisms for attachment to vaginal/cervical mucosa
- Take advantage of minute local injuries during coitus (genital warts/syphilis) or impaired defences (presence of tampons, oestrogen imbalance)
List some non-venereal infection examples
- Bacterial vaginosis (BV)
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis (thrush)
- Bartholin's cysts
- Toxic shock syndrome
List some examples of STIs (bacterial)
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Syphilis
- Mycoplasma genitalium
List some examples of STIs (viral)
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Human papilloma virus (HPV)
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- Hepatits B
List some examples of STIs (parasitic)
- Trichomoniasis
- Pubic lice
- Scabies
What is the dominant bacteria in a healthy vagina
Lactobacilli
What is the normal pH of a healthy vagina
pH is usually <4.5 in a healthy vagina
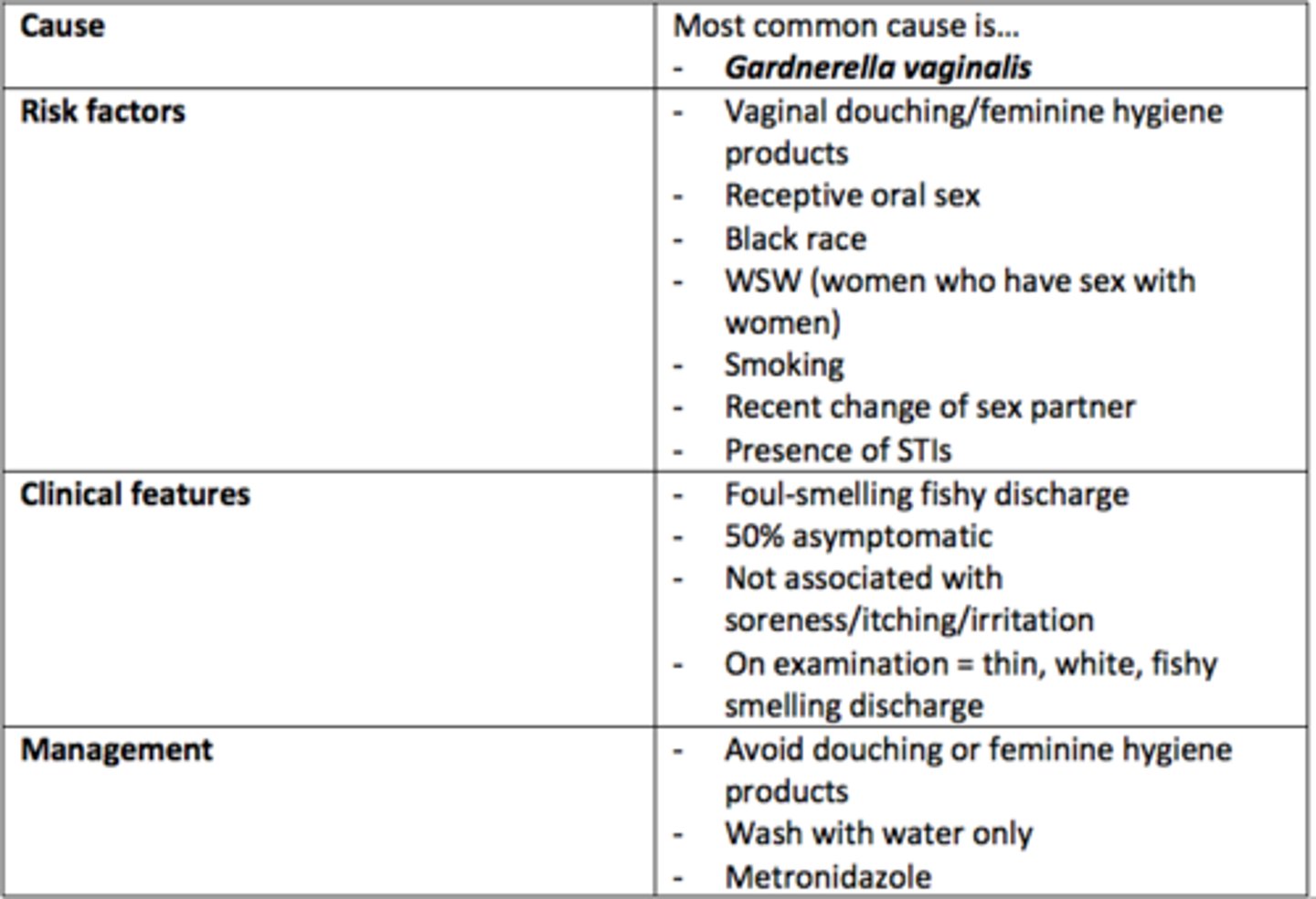
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
Cause
Gardnerella vaginalis
Risk Factors
- Vaginal douching
- Receptive oral sex
- Black race
- WSW
- Smoking
- Recent change of sexual partner
- Presence of STIs
Clinical Features
- Foul-smelling fishy discharge
- Thin, white, fishy-smelling discharge
- Can be asymptomatic (50%)
Management
- Avoid douching
- Wash with water only
- Metronidazole antibiotic
Describe the pathophysiology of Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
- Lactobacilli are dominant bacteria in healthy vagina.
- Healthy pH is <4.5. However, in BV, the pH becomes 4.5 - 6.0.
- Flora becomes dominated by anaerobic bacteria.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (thrush)
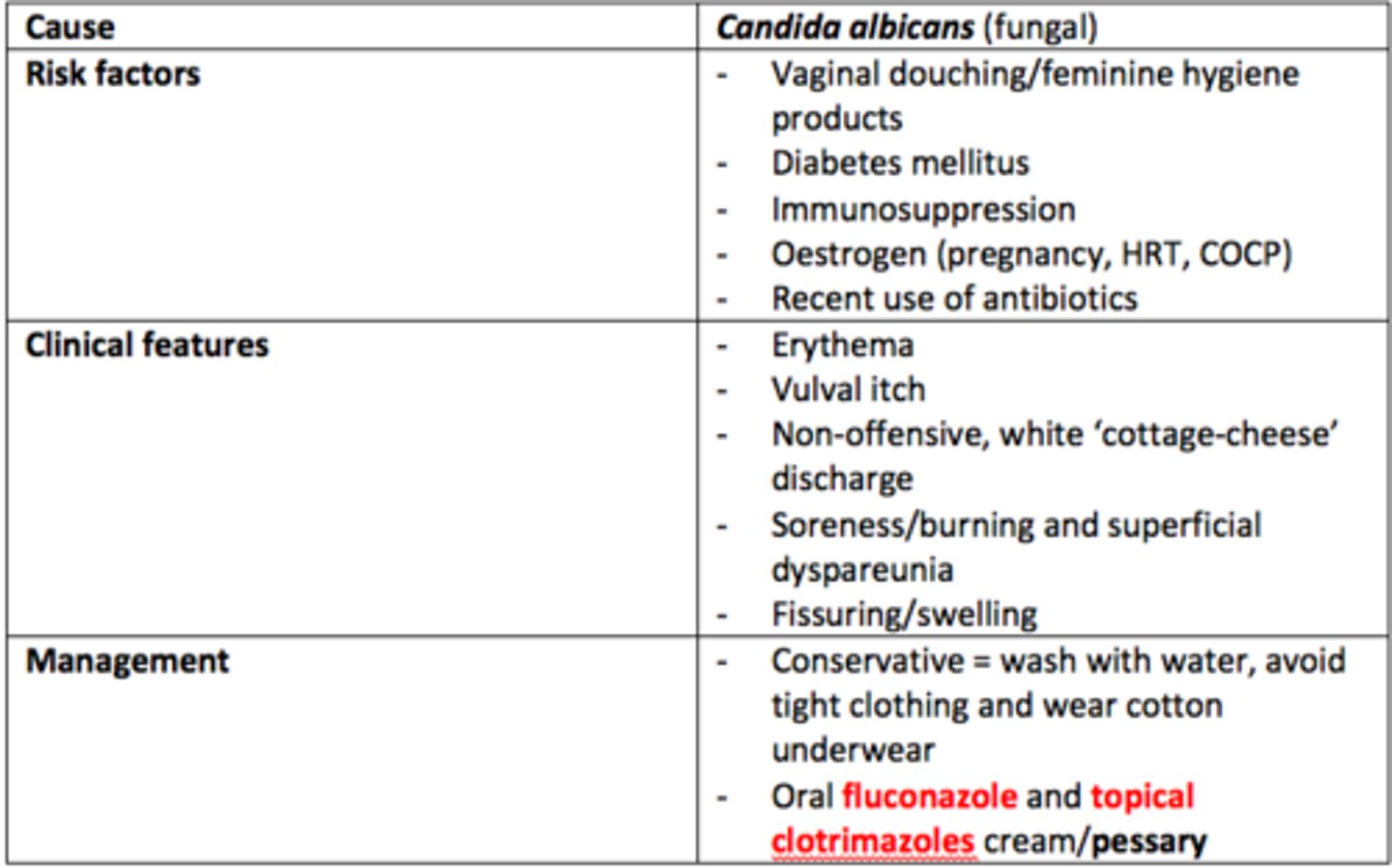
Decribe the pathophysiology of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (thrush)
- Caused by Candida albicans (fungal)
- C. albicans usually lives in competition with lactobacilli in the vagina.
- Change in vaginal pH to become more alkaline/changes in flora due to antibiotic use can lead to Candida multiplication
- Candida causes inflammation which results in vaginal itching and burning, especially during urination.
- Fungal burden & neutrophil infiltration
- Incubation period = 7-10 days
Bartholin's Glands Abscess
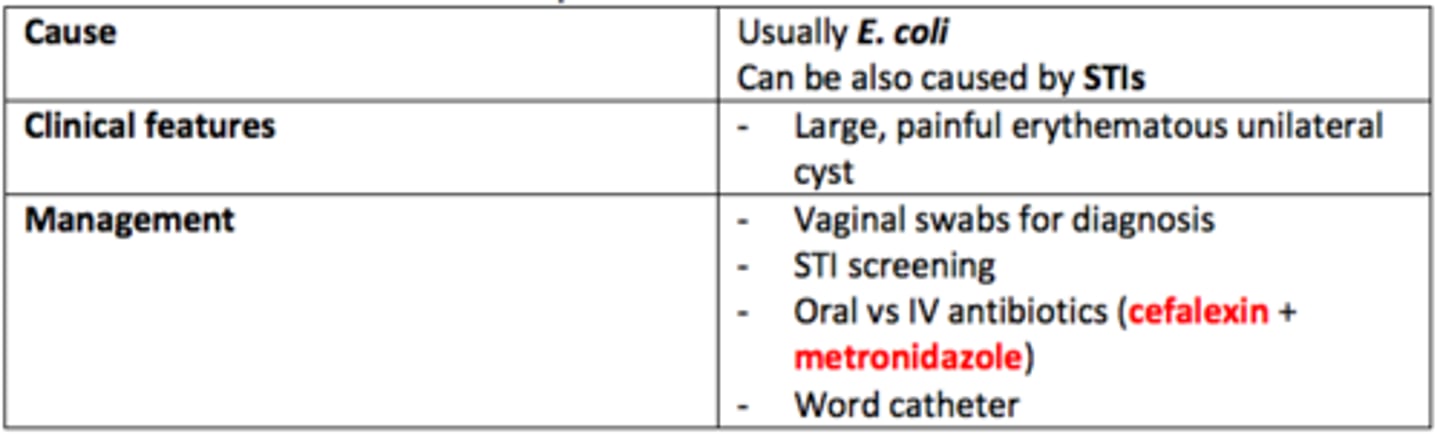
Describe the pathophysiology of Bartholin's Glands Abscess
- Bartholin's glands secrete vaginal lubricant. These ducts can become blocked/infected.
- This leads to cyst formation
- Usually caused by = E. coli. Can also be caused by STIs
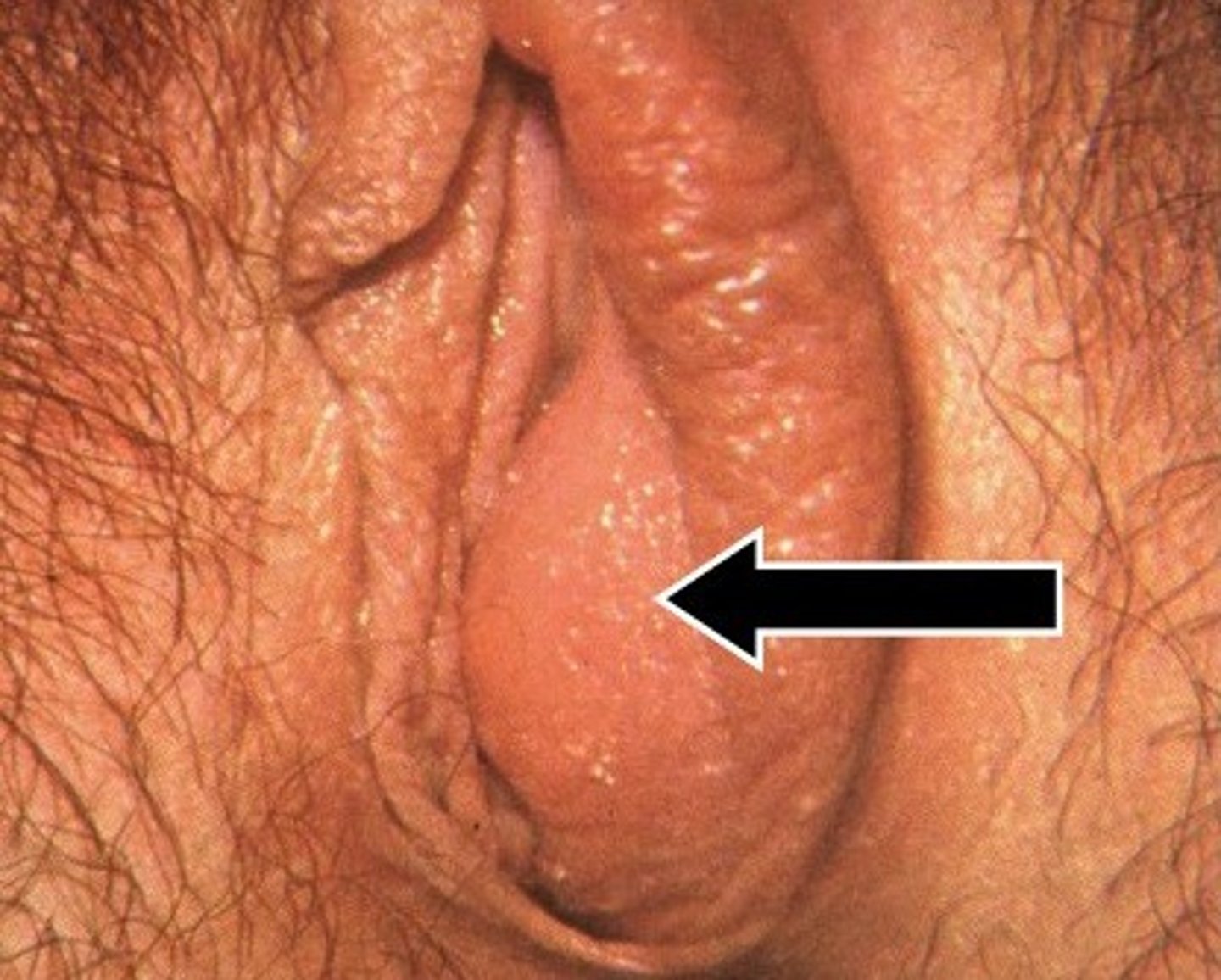
Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria life cycle
The bacteria enters the body via breaks in mucous membranes (e.g., micro-tears) and takes on two forms in its life cycle...
1) Elementary body (small, rigid-walled, infectious particles that remain alive even after exiting host cell)
2) Reticulate body (larger, thin-walled, non-infectious particles that undergo cell division via binary fission)
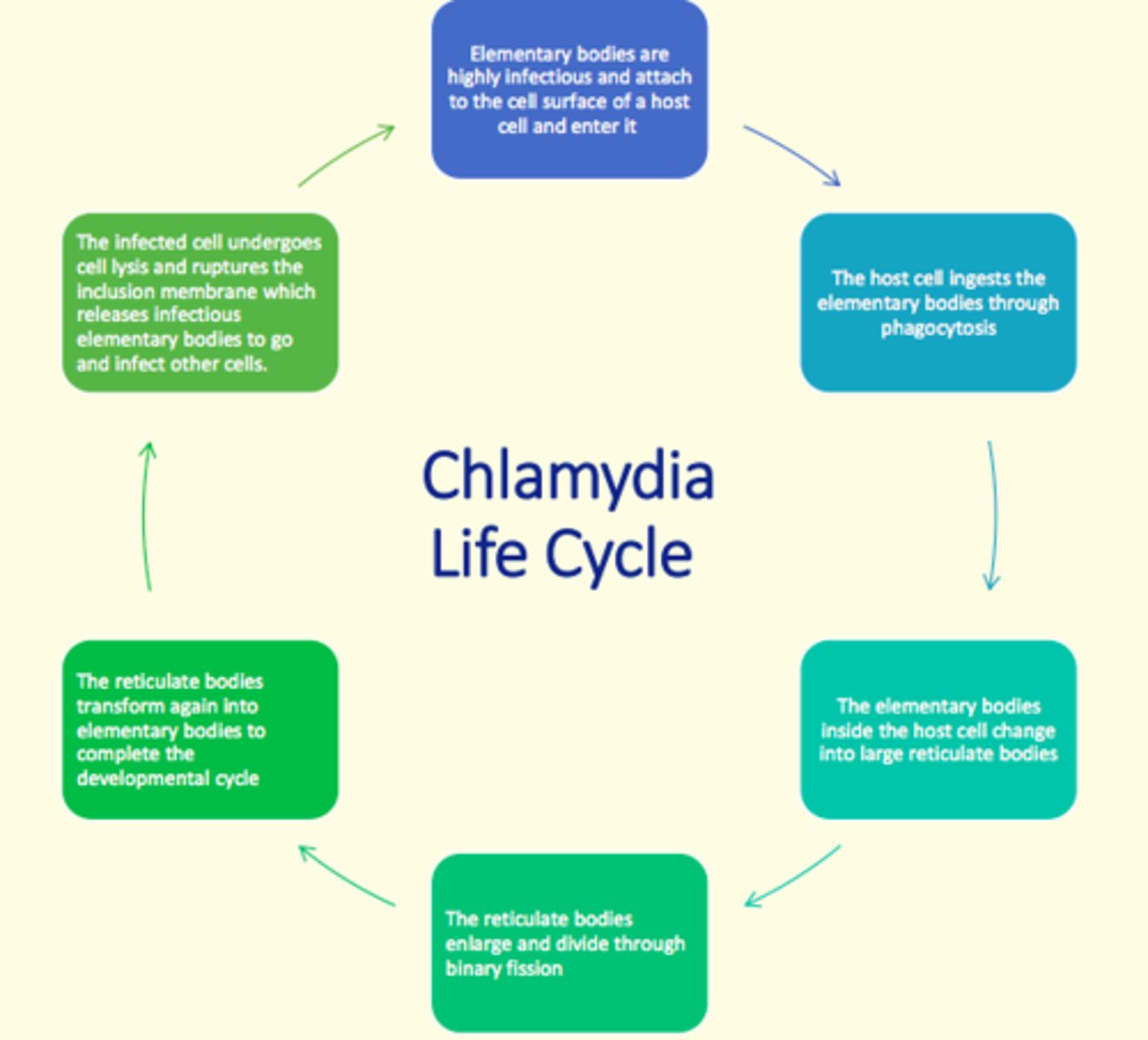
What are the clinical features of Chylamydia trachomatis in men and women?
Women
- Mainly asymptomatic
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Post-coital bleeding
- Intermenstrual bleeding
- Dysuria
- Pelvic pain
- Deep dyspareunia
Men
- Half are asymptomatic
- Urethral discharge
- Dysuria
What are the complications of Chlamydia trachomatis in men and women?
Women
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Tubal infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Peri-hepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome)
- Reactive arthritis
- Conjunctivitis - blindness
Men
- Epidymo-orchitis
- Reactive arthritis
- Conjunctivitis - blindness
- Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
How is Chlamydia trachomatis diagnosed?
NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test)
Self-tests also available...
- Vulvo-vaginal swab
- Endocervical swab
- First-catch urine
- Urethral swab
Management of Chlamydia trachomatis
- Doxycycline (7 day course)
OR
- Azithromycin (single dose)
AND
- Avoid intercourse & oral sex until completed course
- Partner notification
- Contact tracing
Gonorrhea pathophysiology
1) Bacteria Neisseria gonorrhea (gram negative, diplococci) infects the columnar epithelium
2) Bacteria uses fimbriae and capsule to attach to host cells
3) Infection occurs in columnar epithelial cells of males and females (males = distal urethra; females = cervix)
4) Bacteria release protease enzyme which breaks down secretory IgA in mucous to protect themselves from host immune system
5) When bacteria are phagocytised, N. gonorrhoea have ability to survive and multiply inside neutrophils and travel through body = can lead to endocarditis or meningitis in some cases
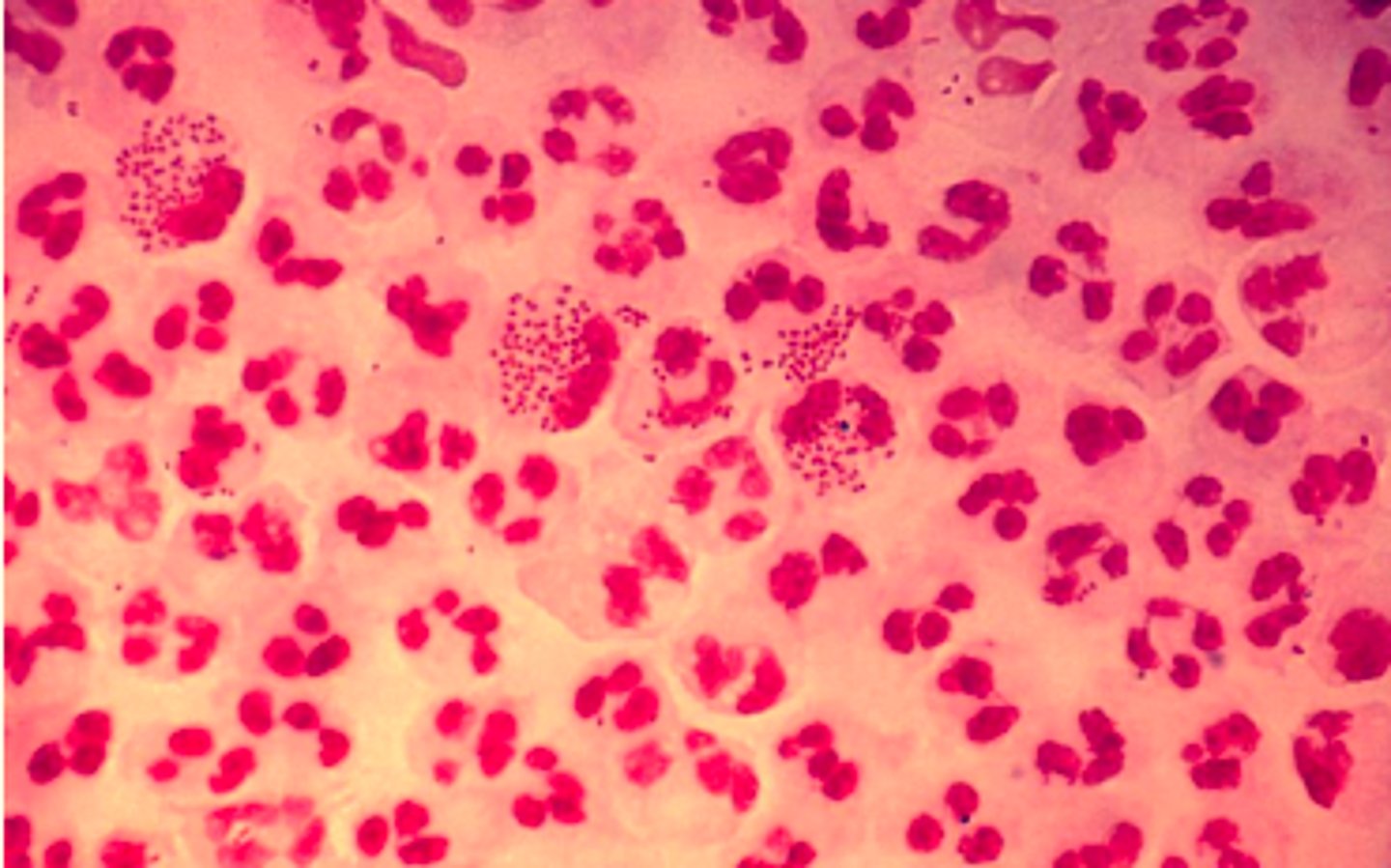
Pathogenic Neisseria gonorrhea are capable of changing the surface antigens via three highly efficient mechanisms. What are they?
1) Mutation of individual amino acids
2) Phase variation (switching genes on/off)
3) Horizontal exchange of DNA material
Clinical features of Gonorrhea in men and women
Women
- Often asymptomatic
- Increased/altered vaginal discharge
- Dysuria (without frequency)
- Pelvic pain
- Friable tissue around cervix
- IMB/PCB (rare)
- Sore throat
- Rectal discharge/discomfort
Men
- Symptoms in majority (90%)
- Occur 2-5 after exposure
- Urethral discharge
- Dysuria
- Testicular/epididymal pain/tender
- Sore throat
- Rectal discharge/discomfort
Complications of Gonorrhoea in men and women
Women
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Tubal infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Peri-hepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome)
- Reactive arthritis
- Conjunctivitis - blindness
- Multidrug resistance
- Disseminated gonoccocal infection
- Vertical transmission
Men
- Epidymo-orchitis
- Prostatitis
- Reactive arthritis
- Conjunctivitis - blindness
- Multidrug resistance
- Disseminated gonococcal infection
Diagnosis of Gonorrhea
- Microscopy/gram stain
- Culture
- NAAT = nucleic acid amplification test (more sensitive than culture)
Management of Gonorrhea
- Single dose Ciprofloxacin PO (if sensitivities known)
OR
- Ceftriaxone IM (if sensitivities unknown)
AND
- Partner notification
- Treat sexual partners of confimed cases
- Test of cure for all patients
Syphilis pathophysiology
Bacteria Treponema pallidum causes Syphilis
- Spirochete bacteria
- Spread via bodily fluids (sexual contact), bloodborne or vertical transmission
Clinical features of each stage of Syphilis
PRIMARY SYPHILIS
- Chancre found in genital area
- Chancres do not result in pain
SECONDARY SYPHILIS
- Skin rash = spots on palms of hands & bottom of feet
- Mucous membrane lesions throughout body (not itchy)
- Fever, sore throat, headache, swollen glands, weight loss, muscle ache, fatigue
TERTIARY SYPHILIS
- Blood vessels, cardiac, nerve system problems
- Damaged internal organs
- Death cases
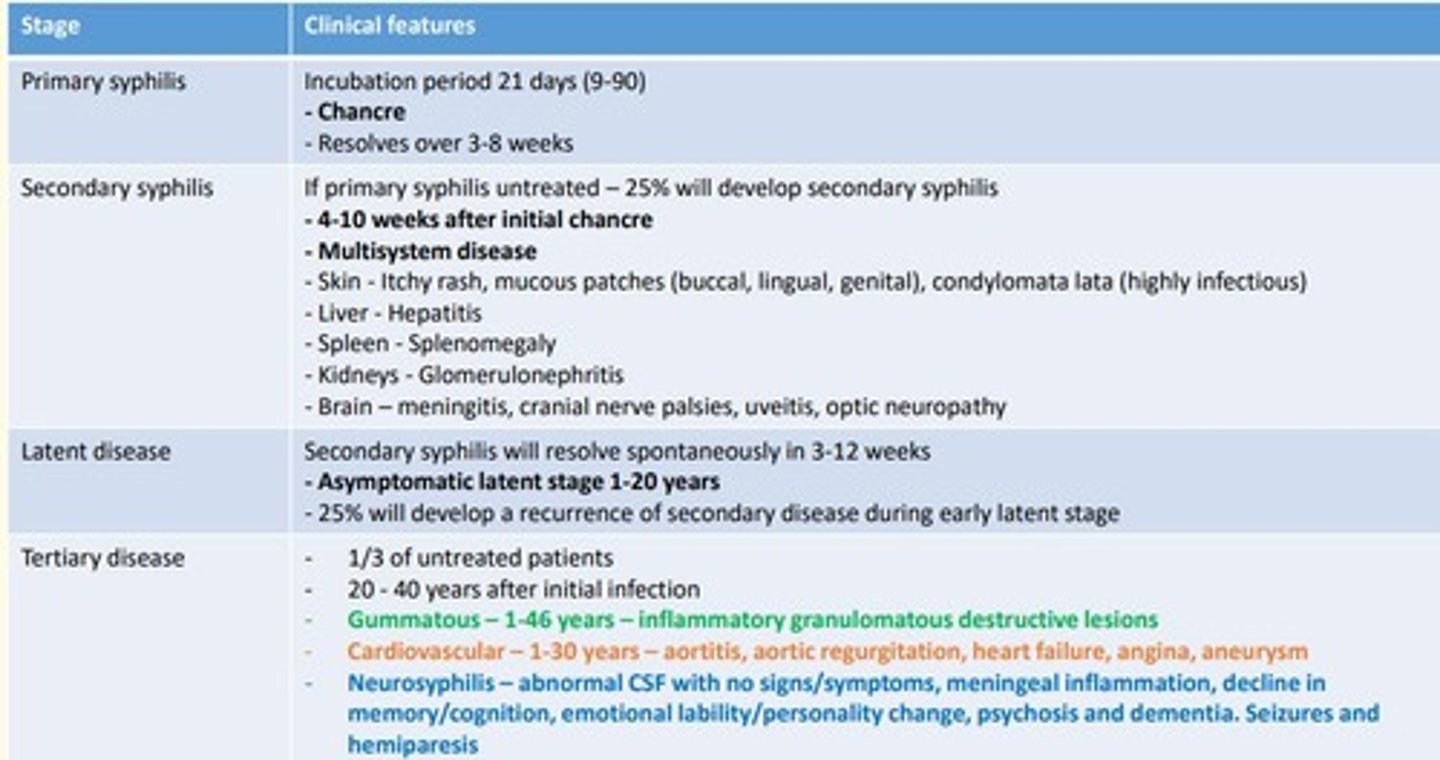
What is a chancre
Small, round, painless ulcerated sore.
Usually of the genital area, but can also be found on the mouth or anus.
Associated with primary syphilis infection.
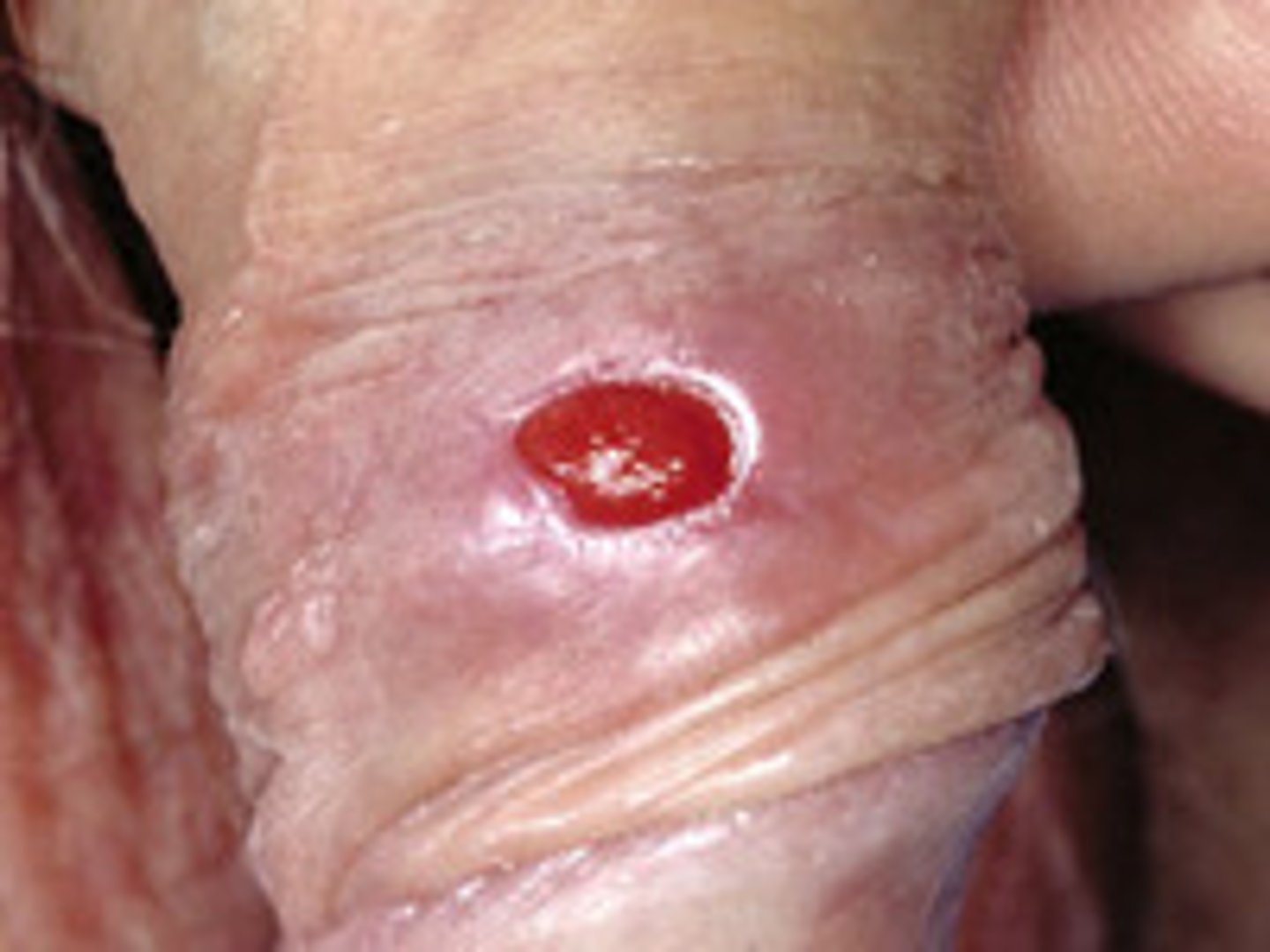
Condylomata lata
Wart-like lesions on the arms and genitals
Associated with secondary syphilis infection.
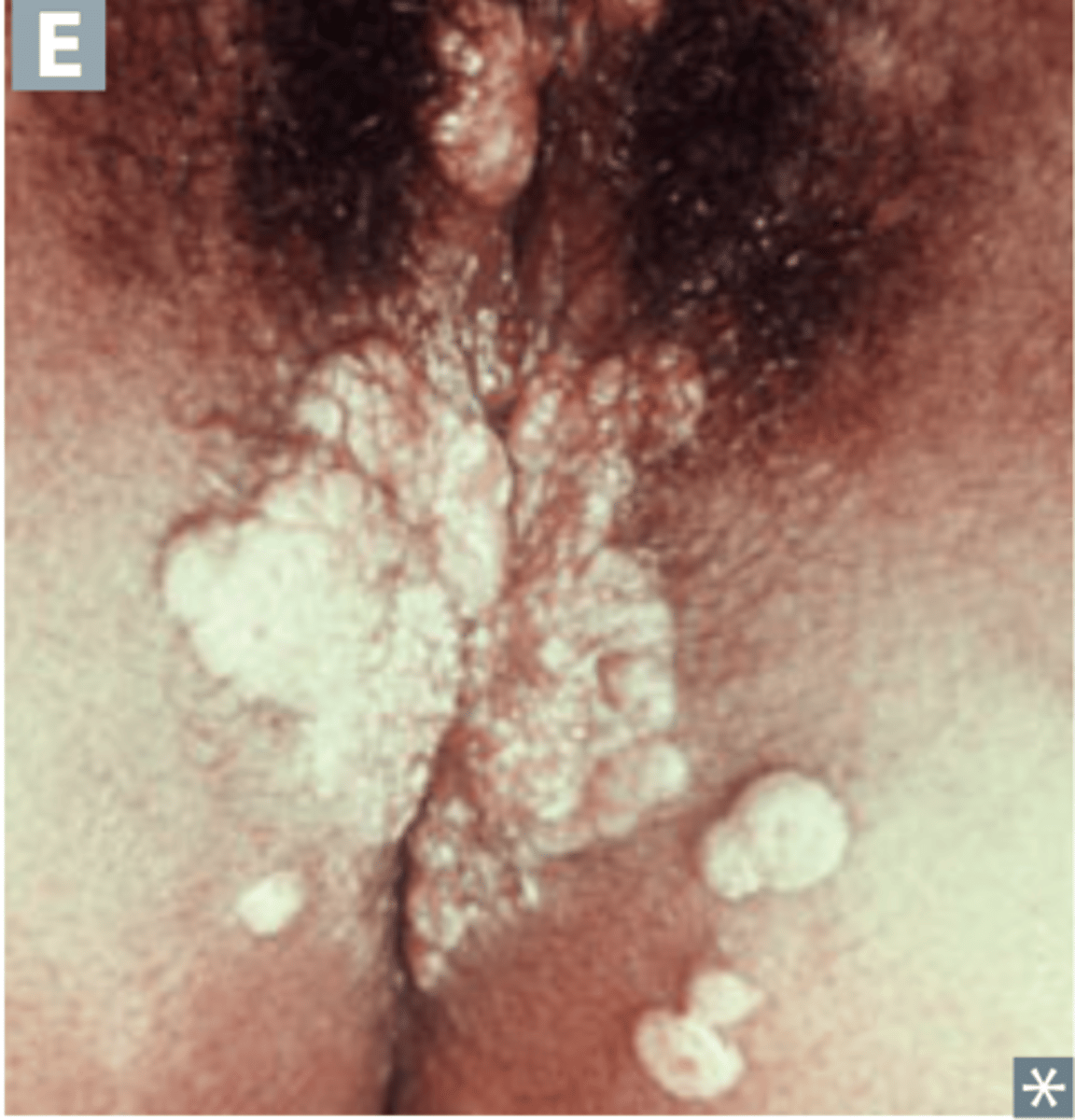
Gummatous syphilis
Gummatous lesions (inflammatory granulomas) - mass of necrotic and inflamed tissue.
Associated with tertiary syphilis infection.
How is syphilis diagnosed?
Symptomatic testing/antenatal screening/sexual health screening
SEROLOGY
1) TPPA = antibodies against T. pallidum in blood
2) RPR & VDRL = looks for anticardiolipin antibodies against chemicals that syphilis-infected or damaged cells release
How is syphilis treated?
Benzathine penicillin G
Monitor treatment = 4-fold decrease in RPR (serology) = then treatment is considered successful.
HPV (human papilloma virus) - Anogenital warts
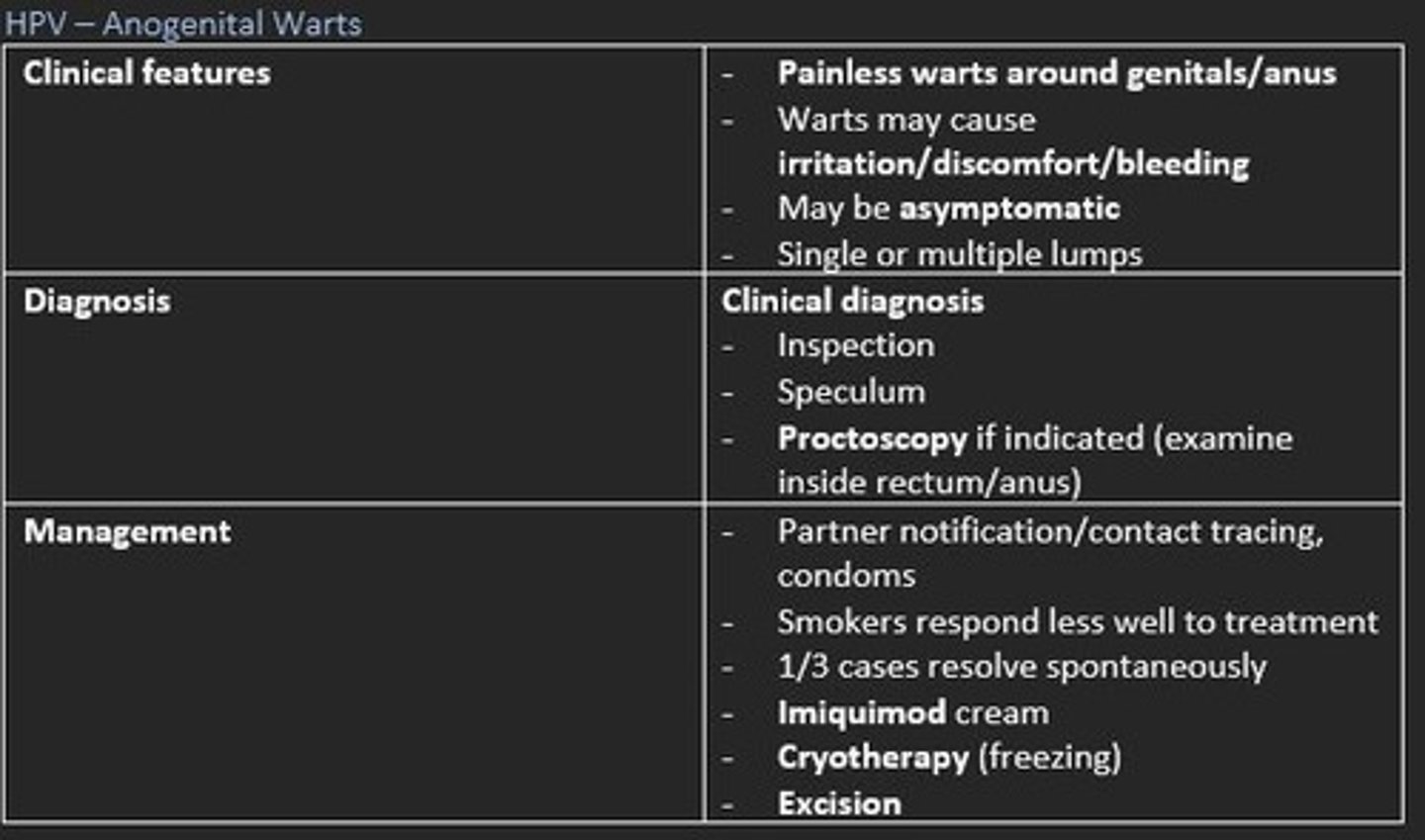
Herpes (HSV)
First episode of anogenital HSV is caused by sexual transmission (oral-labial/oral-penile/genital transmission).
Usually the first episode is the most symptomatic.
Following primary infection, the virus becomes latent in the sensory ganglia, periodically reactivating to cause symptomatic lesions or asymptomatic viral shedding.

Currently, the infectious diseases in pregnancy screening (IDPS) programme screens for what diseases?
1) HIV
2) Hepatitis B
3) Syphilis
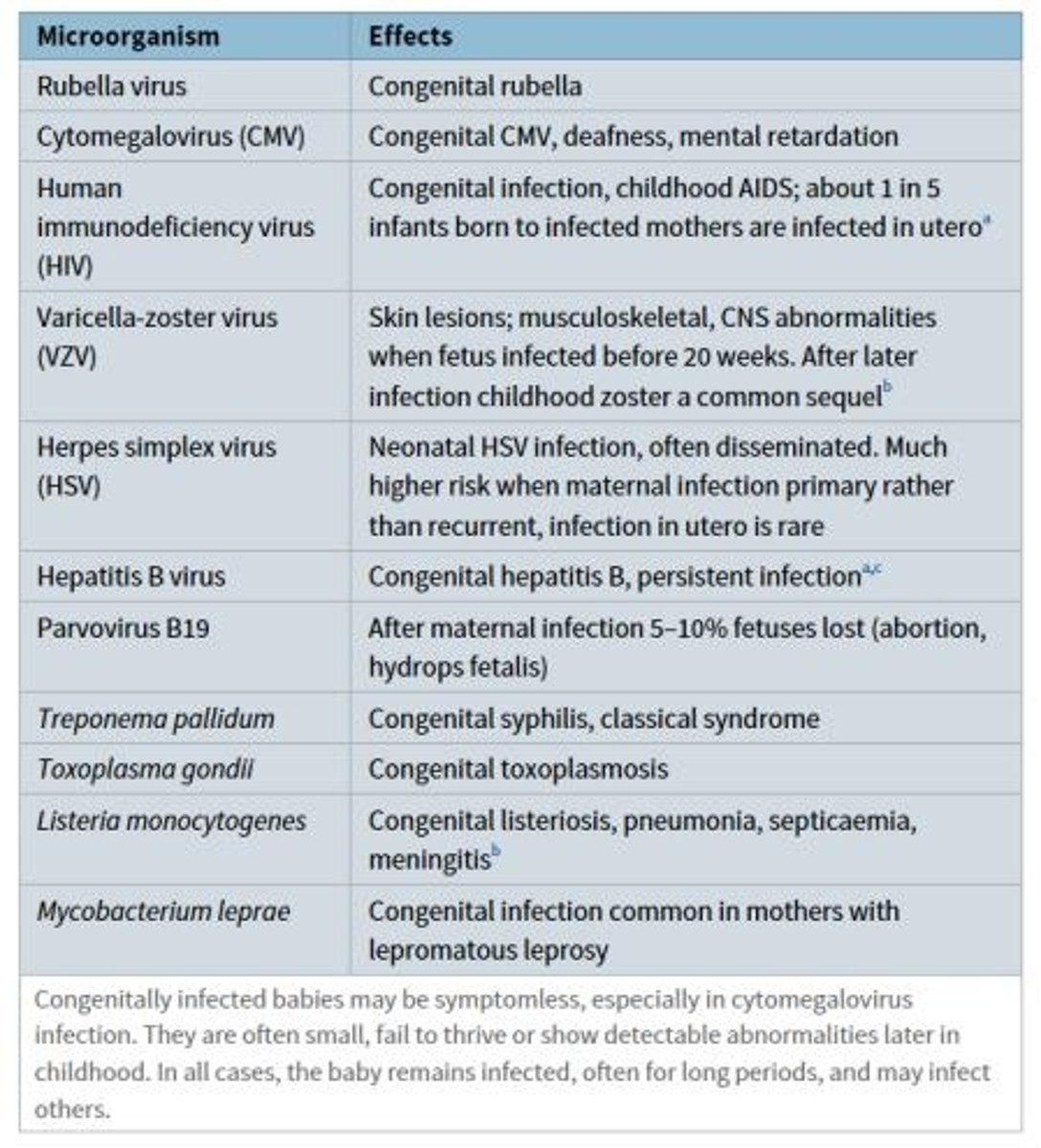
There are a number of infections that are not screened for by the IDPS programme, that may cause congenital defects or miscarriage.
Give two examples of infections that are NOT screened for and cause congenital defects in the fetus.
1) Rubella infection during pregnancy = causes congenital rubella syndrome (deafness, cardiac abnormalities, cataracts and other eye defects)
2) Varicella infection during pregnancy = causes limb hypoplasia, microcephaly, cataracts, growth retardation and skin scarring.
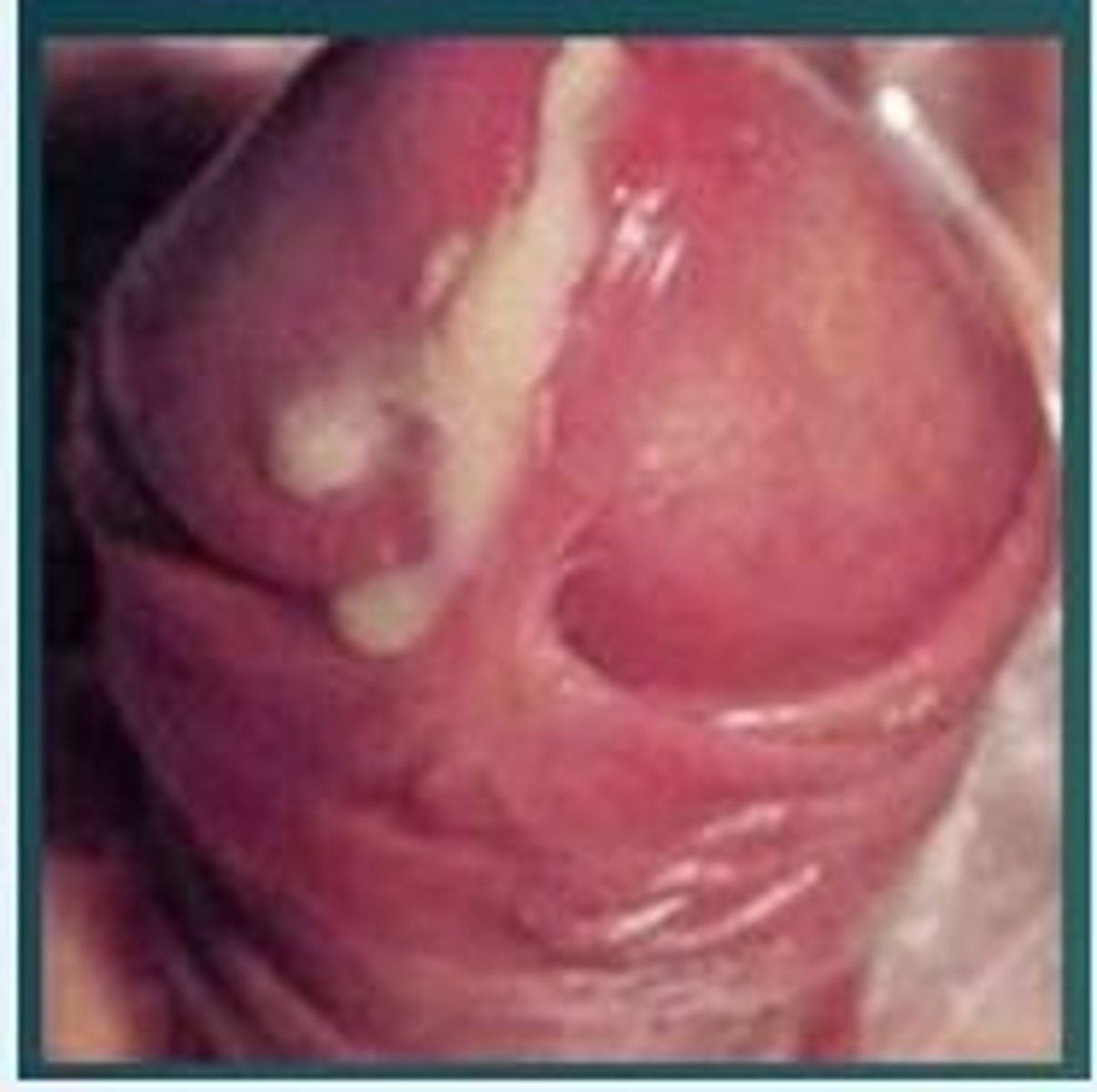
A man complains of pain on passing urine and a discharge from the end of his penis. Looking at the below picture, which is the most likely diagnosis?
a) Chancroid
b) Chlamydia
c) Gonorrhea
d) Lymphogranuloma venereum
e) Syphilis
c) Gonorrhea
What would be the preferred antibiotic to treat Chlamydia infection?
a) Amoxicillin
b) Nitrofurantoin
c) Penicillin
d) Doxycycline
e) Sulfamethoxazole
d) Doxycycline
Which microorganism metabolises glycogen in the vaginal epithelium to produce lactic acid?
a) Gardnerella vaginalis
b) Mycoplasma hominis
c) Candida albicans
d) Lactobacilli
e) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
d) Lactobacilli
Which bacteria can cause pelvic inflammatory disease when ascending from the cervix and vagina to the upper genital tract?
a) Gardnerella vaginalis
b) Mycoplasma hominis
c) Candida albicans
d) Lactobacilli
e) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
e) Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Which infection is characterized by a homogenous white vaginal discharge with a "fishy" odour?
a) Bacterial vaginosis
b) Vaginal candidiasis
c) Gonorrhea
d) Syphilis
e) Chlamydia
a) Bacterial vaginosis