DNA /RNA, Honors Biology Unit 5 Test: DNA/ RNA, Protein Synthesis and Mutations T
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid,an organisms genetic information
Deoxyribose
the 5 carbon sugar that makes up the back bone of the dna molecule
Phosphate group
the 3 phosphates that make up the back bone of the dna molecule
Nucleotide
made up of 1 deoxyribose, 1 phosphate group and one of 4 nitrogen bases (a,t,c,g)
Adenine
a dna component, a chemical (purine) that is always combined with a thymine (pyrimidine)
Guanine
a dna component, a chemical (purine) that is always combined with a cytosine (pyrimidine)
Thymine
a dna component, a chemical (pyrimidine) that is always combined with an adenine (purine)
Cytosine
a dna component, a chemical (pyrimidine) that is always combined with an guanine (purine)
Base Pair Rule
the rule for nitrogen base pairing, A-T & G-C
Double Helix
the shape of the DNA molecule, like a twisted ladder
Hydrogen Bond
the weak bond that holds nitrogen bases (a,t,c,g) together
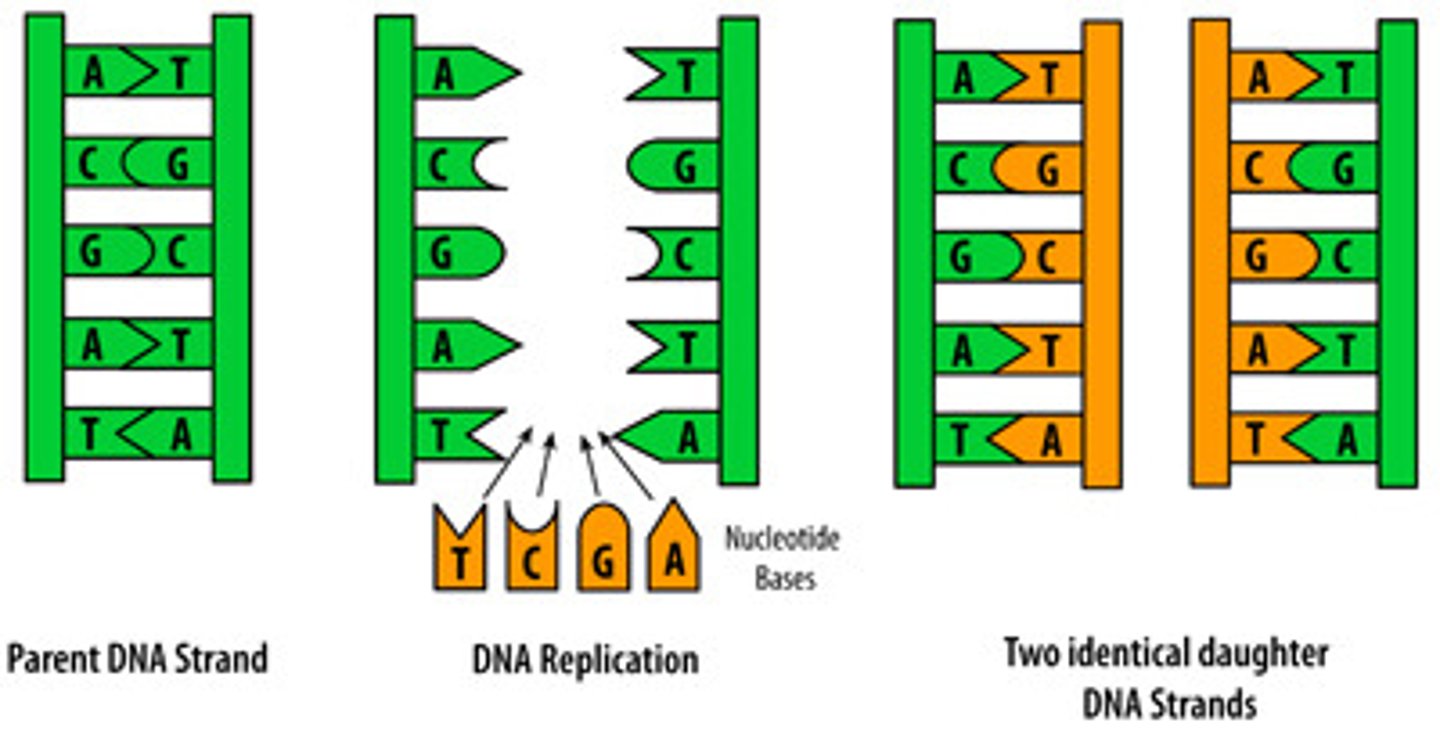
DNA replication
the process by which a cell copies a dna molecule prior to mitosis
Helicase
an enzyme that "unzips" the dna molecule in preparation for replication
DNA Polymerase
an enzyme that finds and places complimentary nucleotides in open areas of the original dna strand
Semi Conservative Model
the idea that dna replication saves half of the original dna strand when replicating
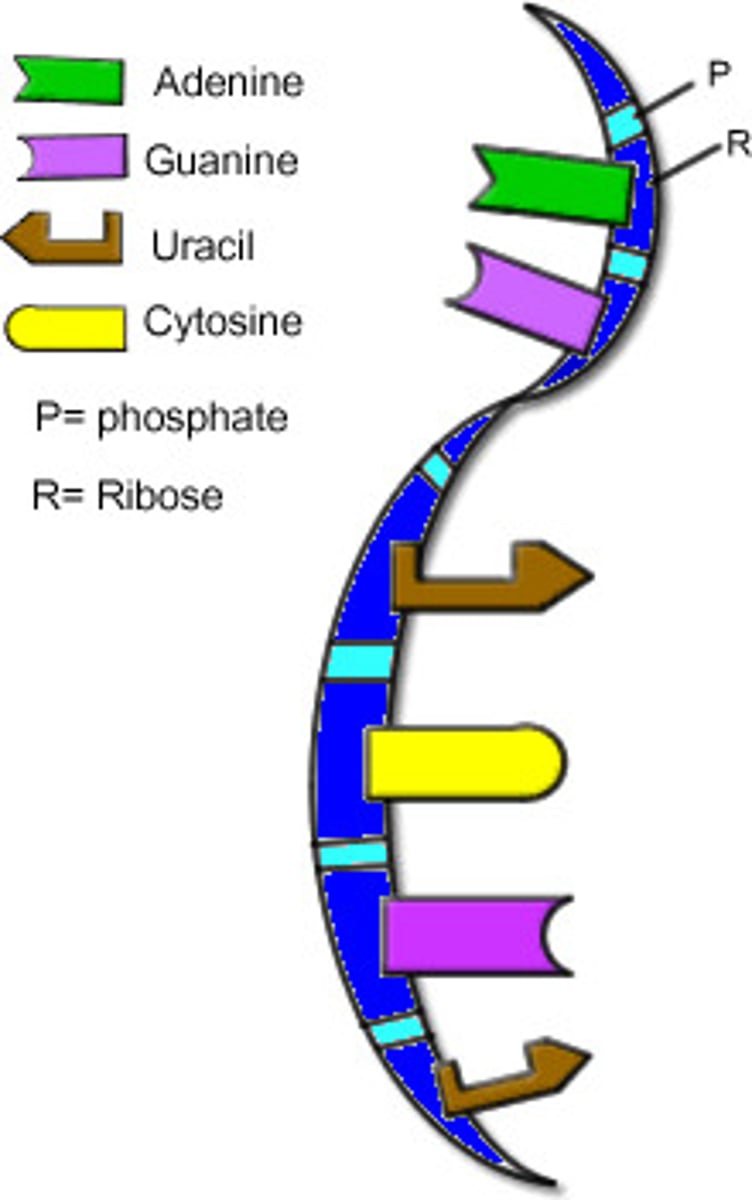
RNA
ribonucleic acid, a spiral helix strand that reads dna instructions to make proteins
Uracil
a chemical found in a rna molecule
Ribose
the sugar found in rna molecules
tRna
a molecule involve in protein synthesis that transports an amino acid and has an anticodon
mRna
a molecule that carries a message for making proteins
Rna Polyermase
an enzyme that make the polymer rna in transcription
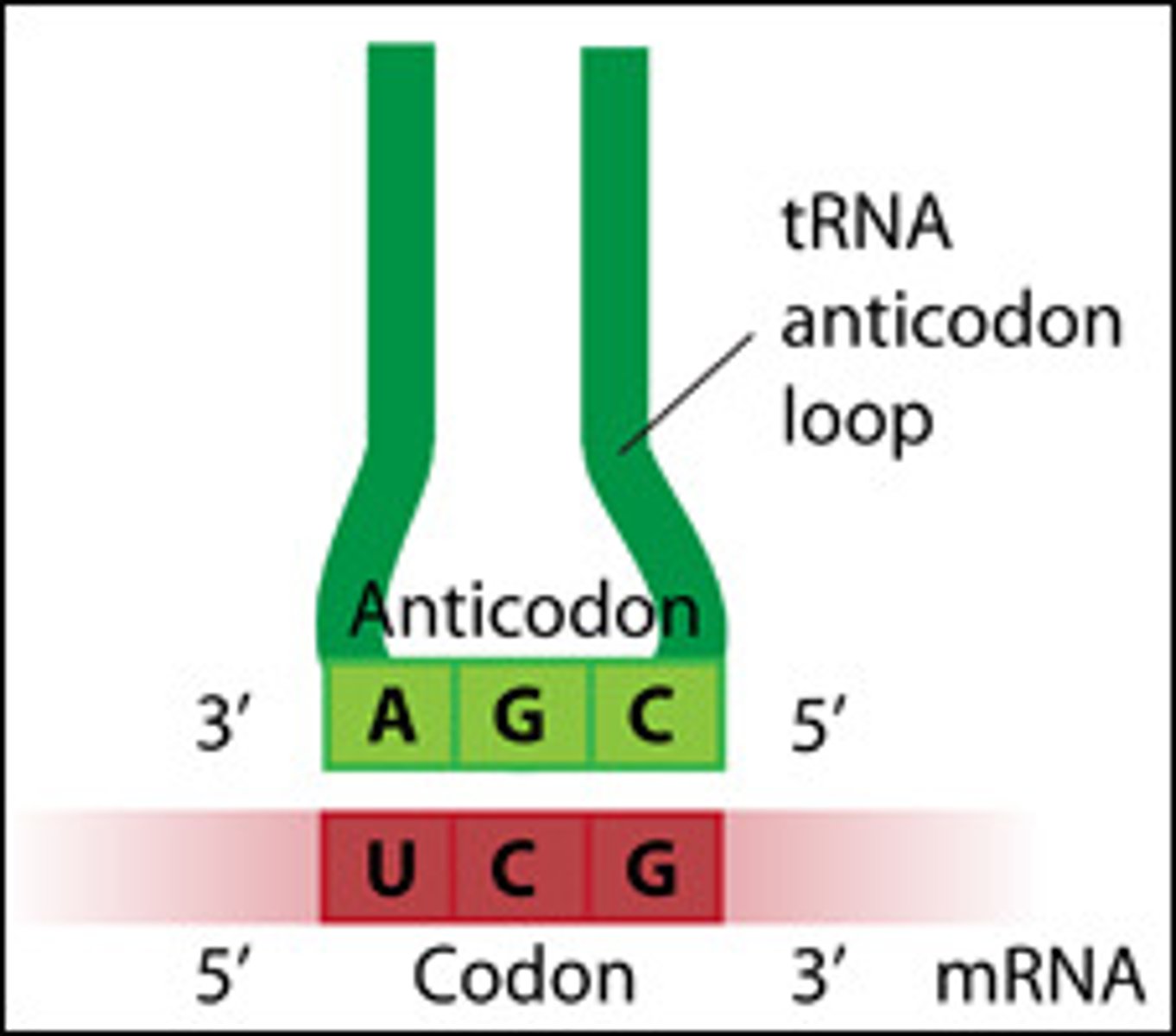
codon
a three letter base on a rna molecule
anti-codon
a three letter base on a tRna molecule
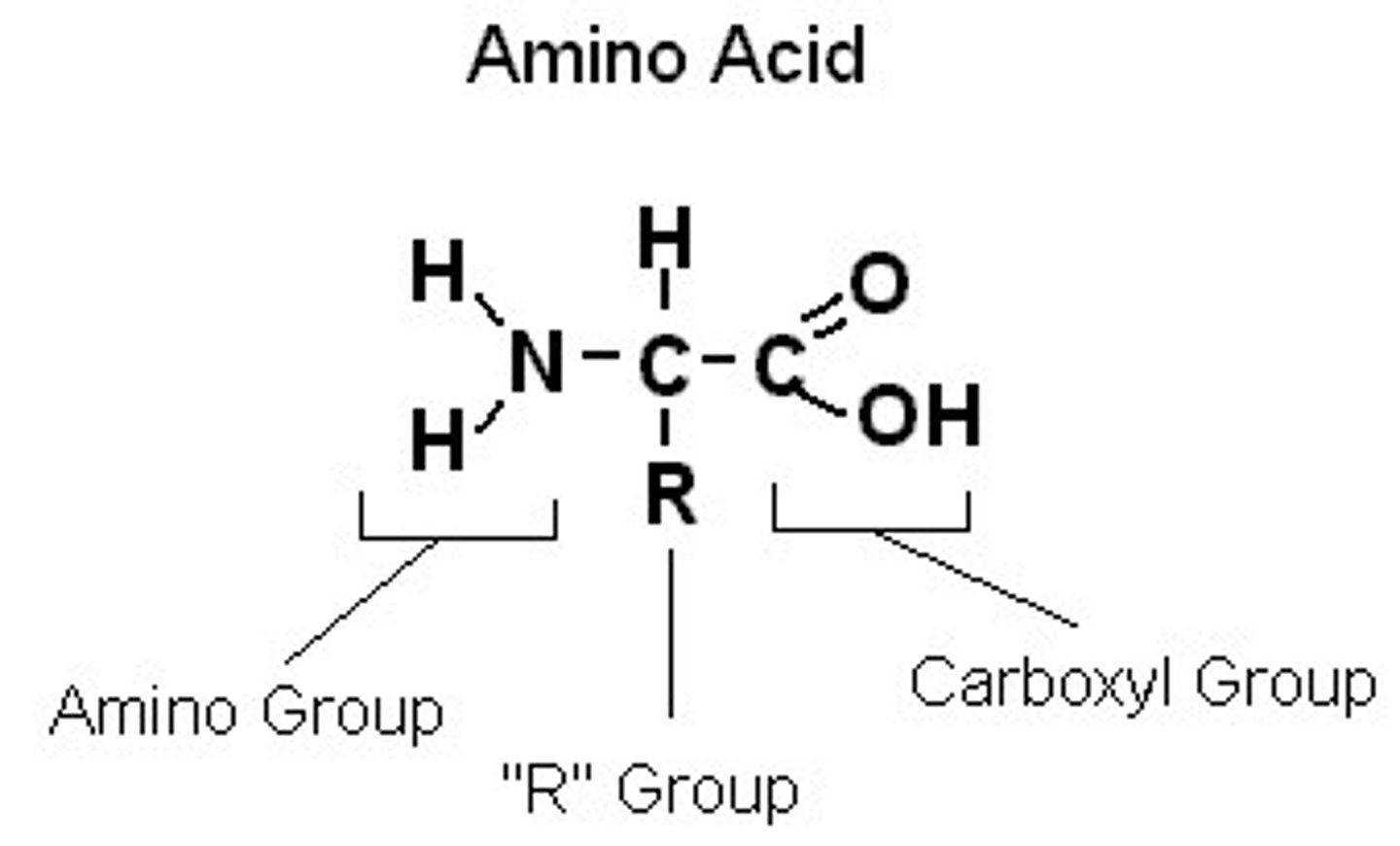
amino acid
a monomer that makes up the polymer protein
helix
the single strand molecule produced in transcription
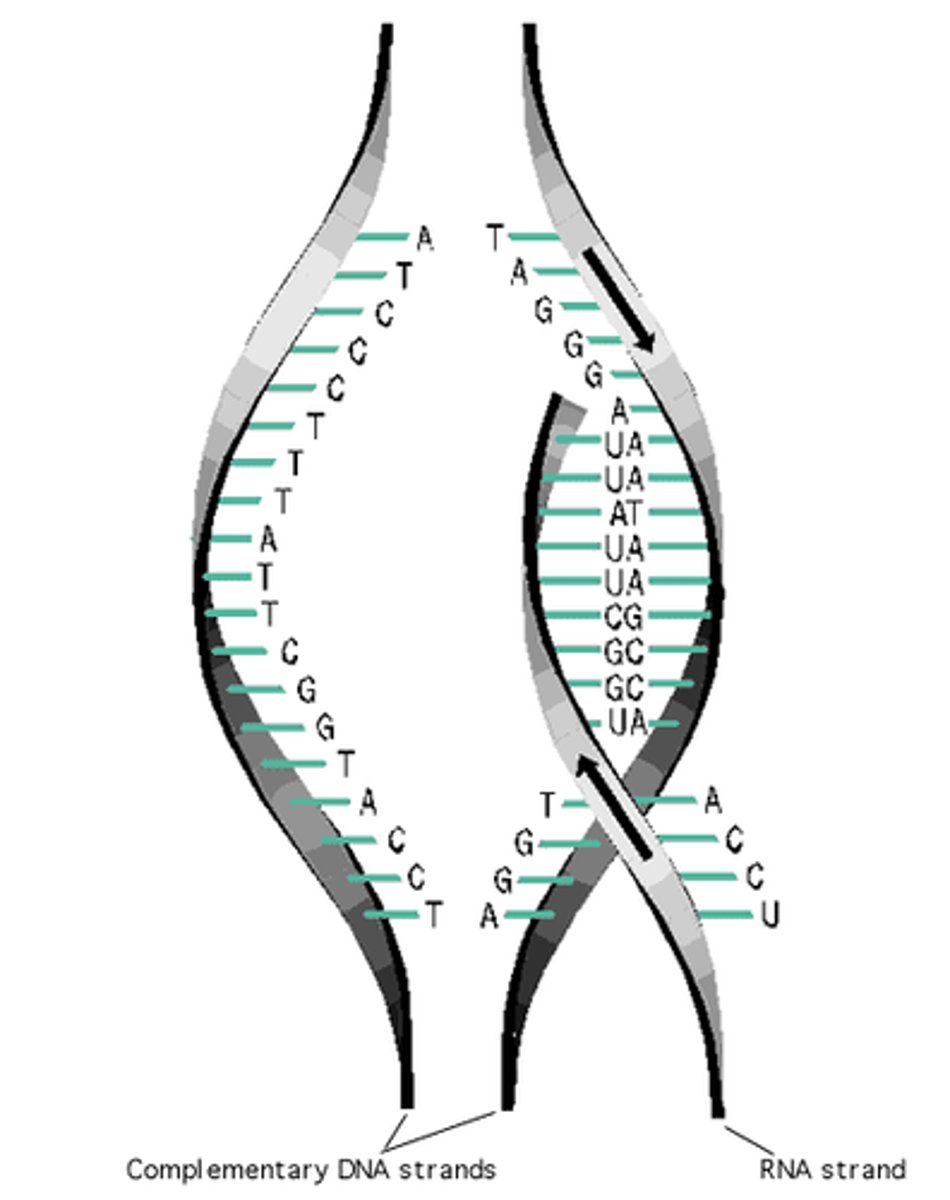
transcription
the process of making rna from a segment of dna called a gene
translation
the process where a tRna decodes a rna to make a protein
protein synthesis
the process involving transcription & translation whereby proteins are made
The 4 bases of RNA are:
adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
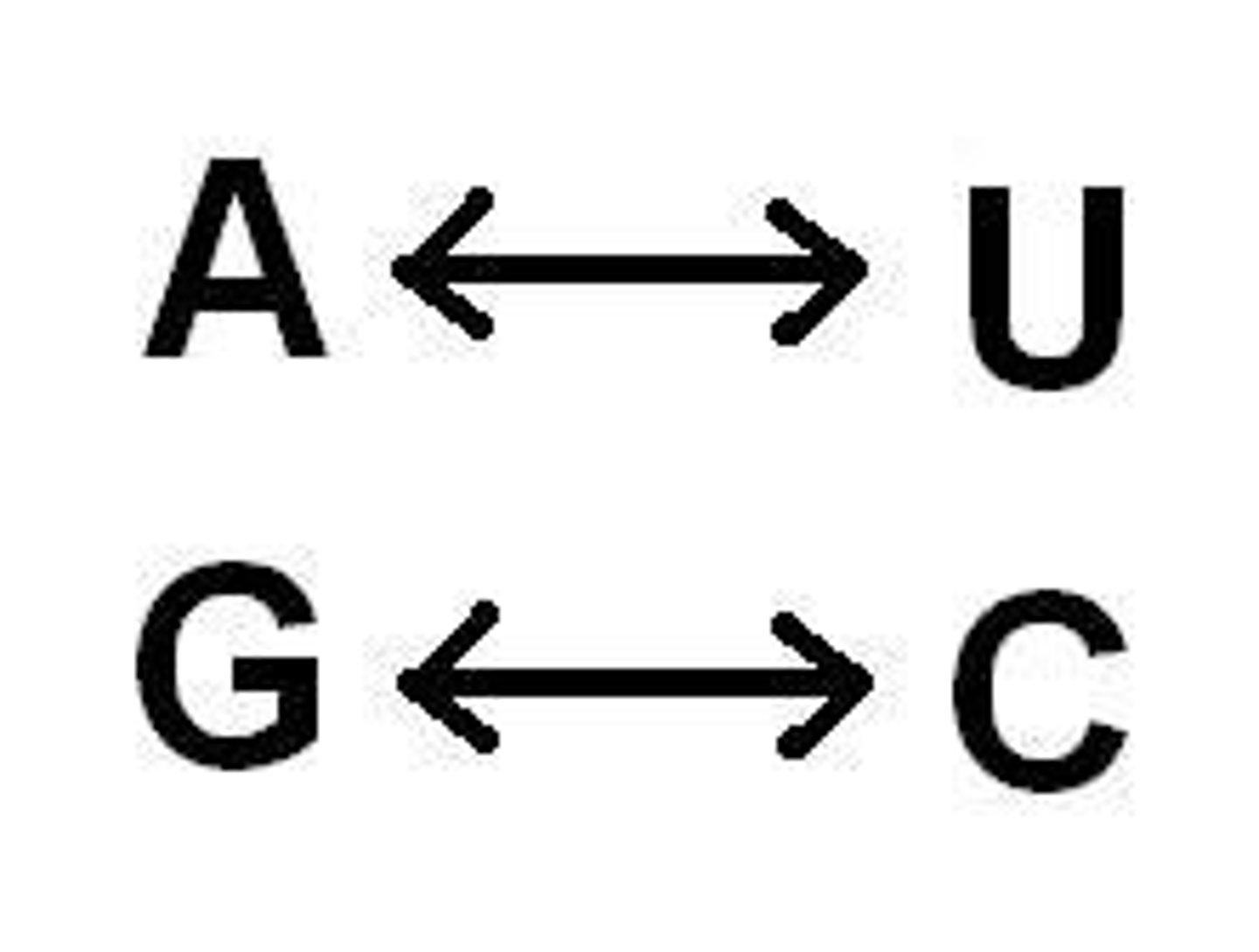
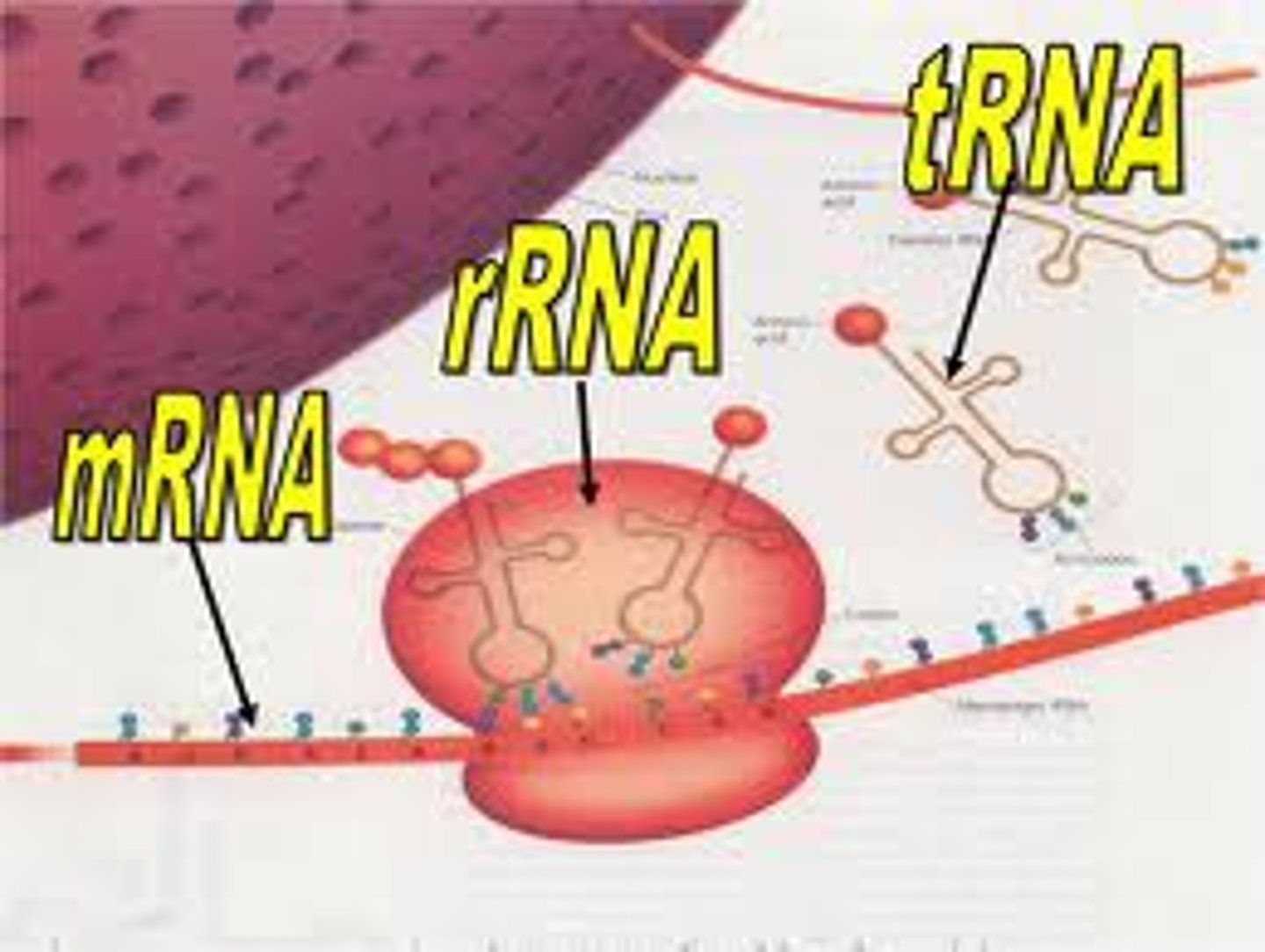
RNA types
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
In RNA, adenine matches up with
uracil
mRNA
messenger RNA
tRNA
transfer RNA
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA
Transcription
DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
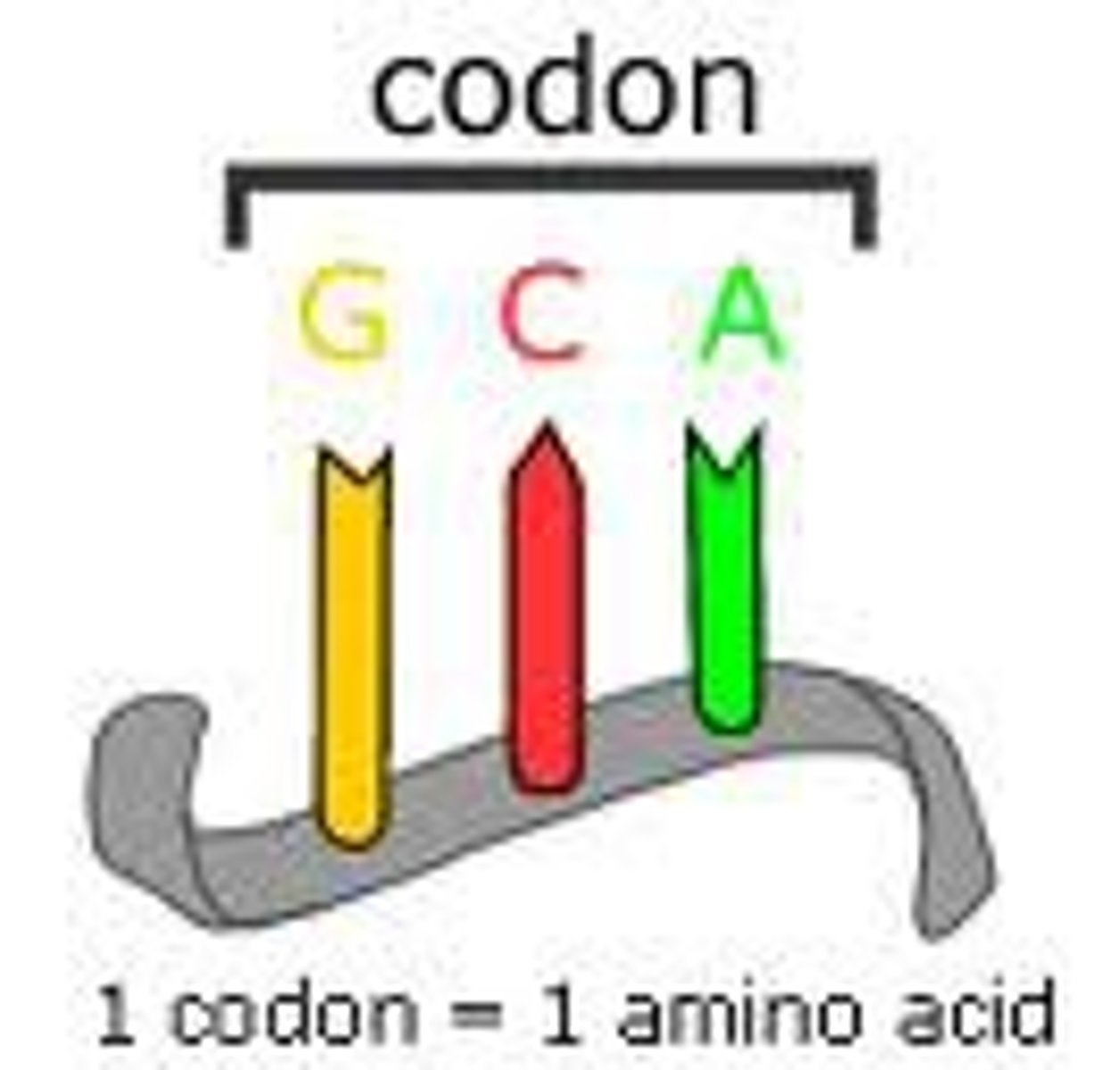
Codon
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid
Anticodon
A sequence of three bases of a tRNA molecule that pairs with the complementary three-nucleotide codon of an mRNA molecule during protein synthesis.
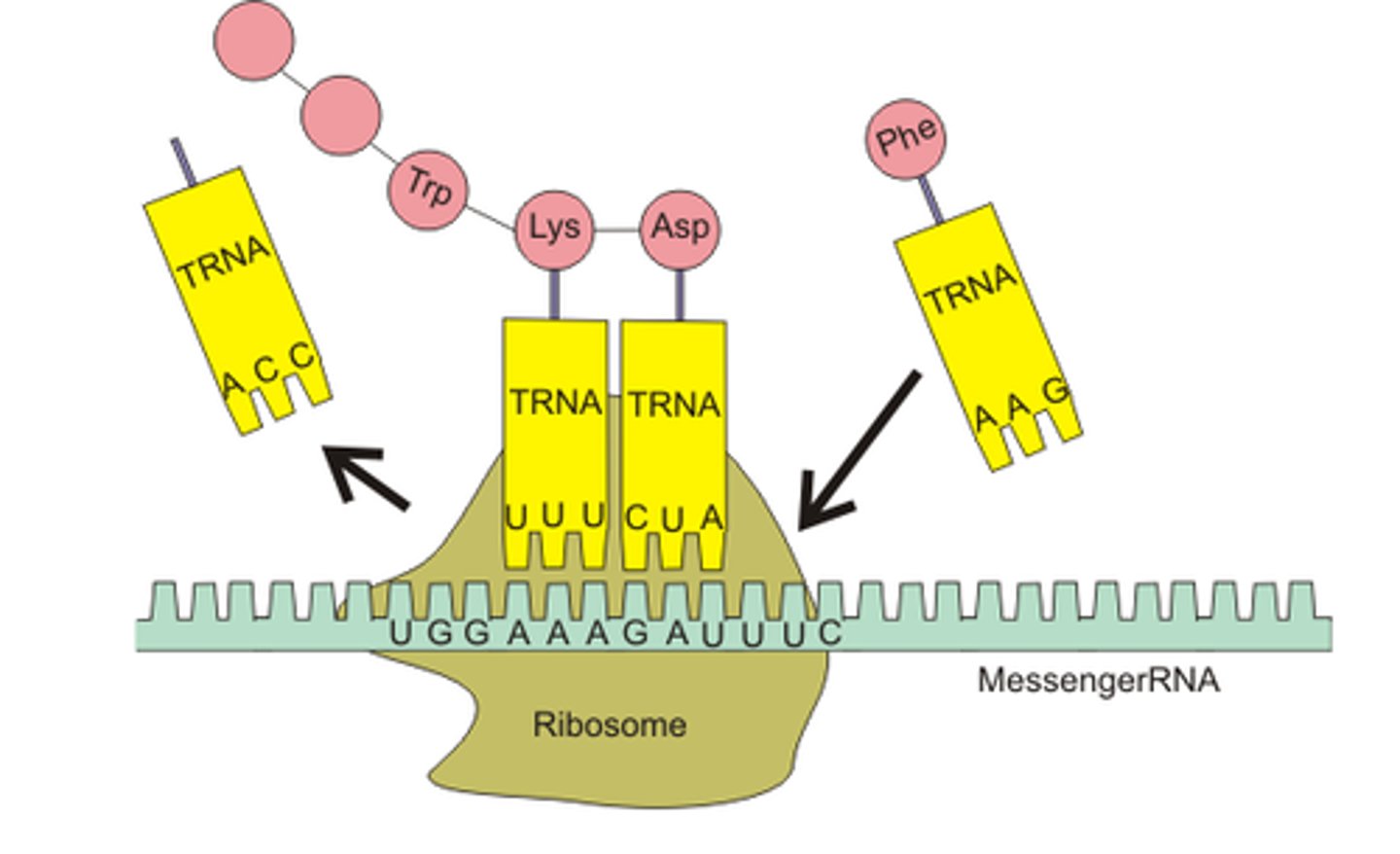
translation
Process by which a ribosome binds to mRNA
Can more than one codon code for the same amino acid?
YES!
Mutations can be
neutral, beneficial, or harmful
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
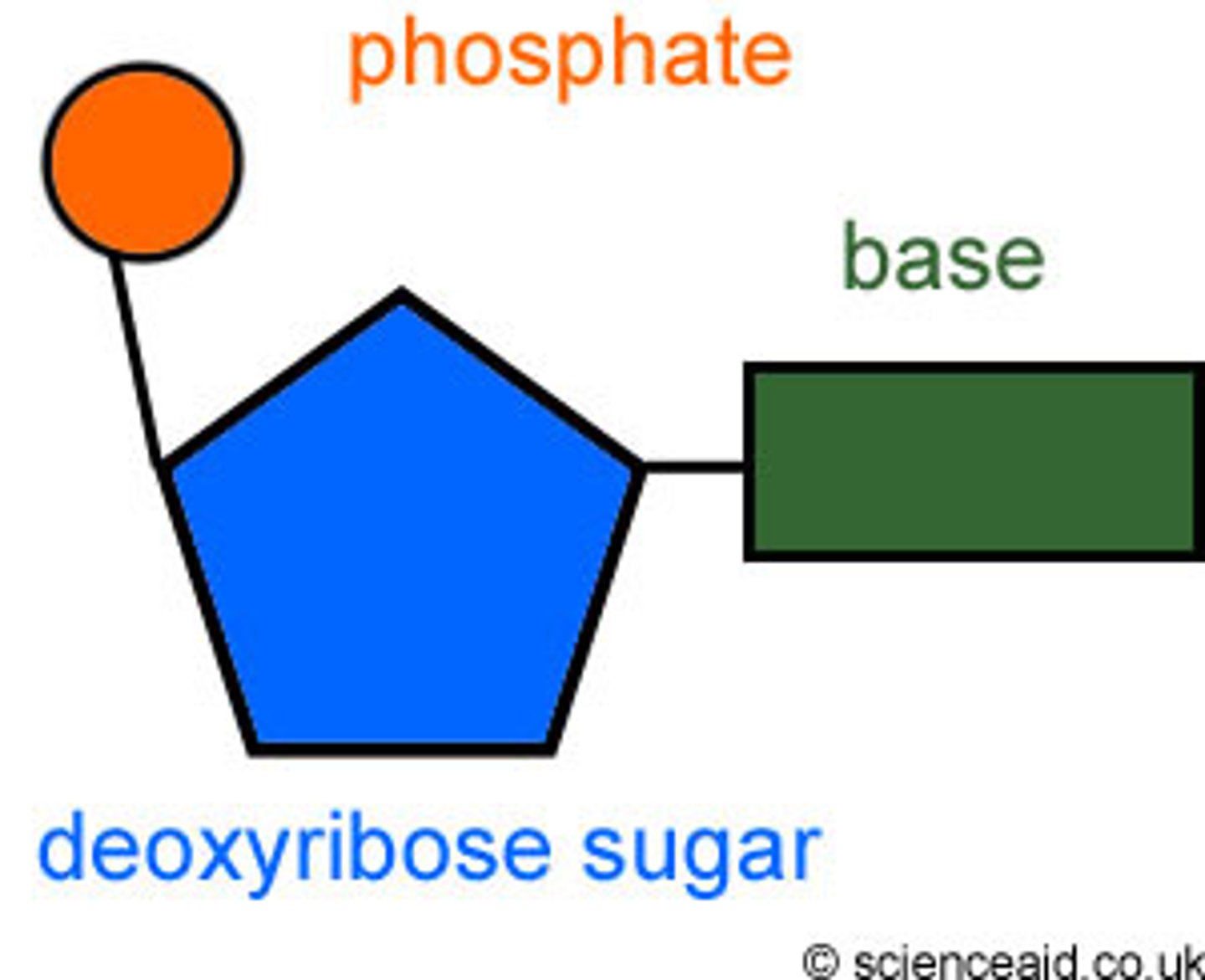
nucleotide of DNA
nitrogenous base, deoxyribose, phosphate
Uracil
a nitrogen-containing base found in RNA (but not in DNA)
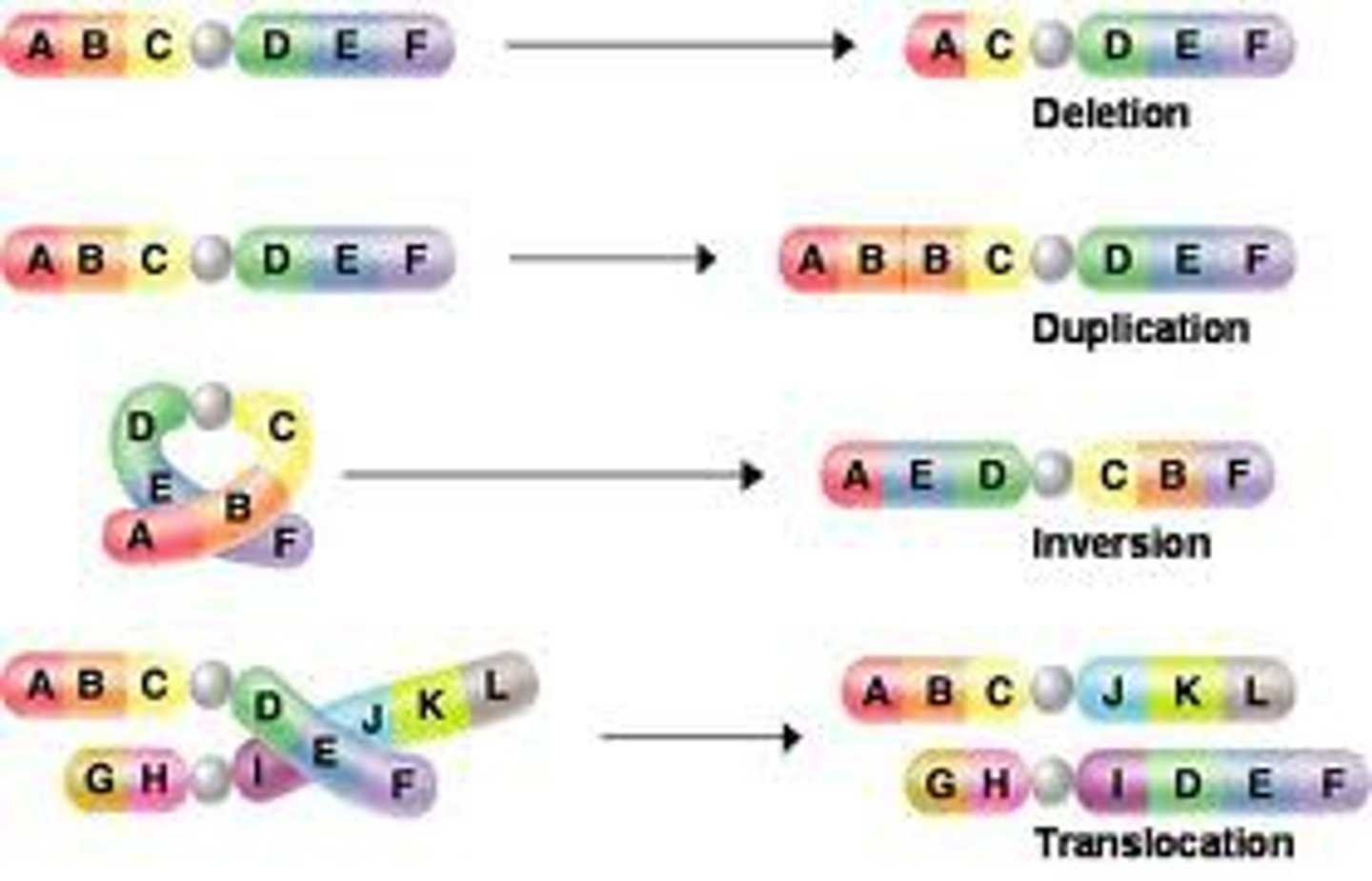
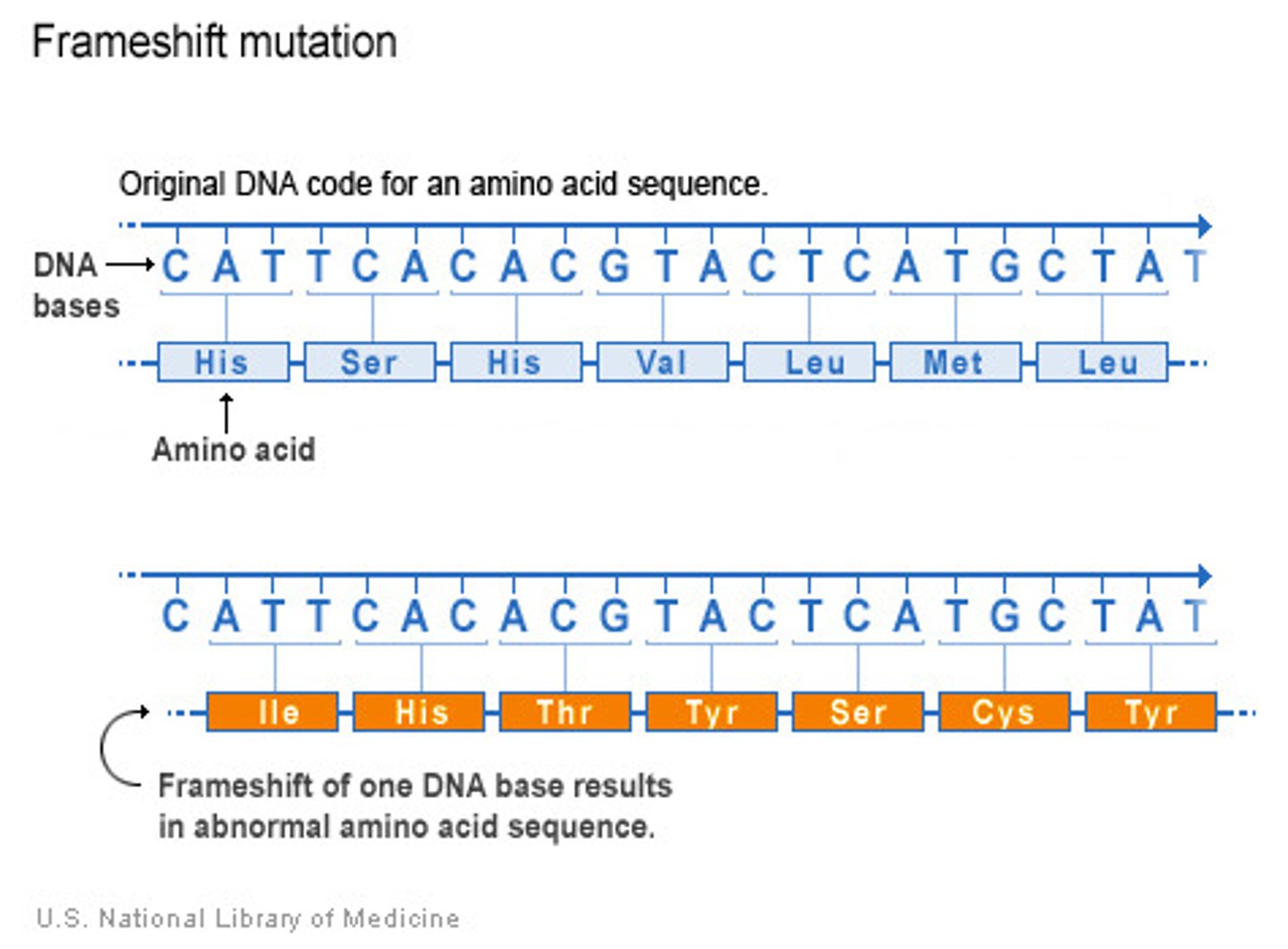
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
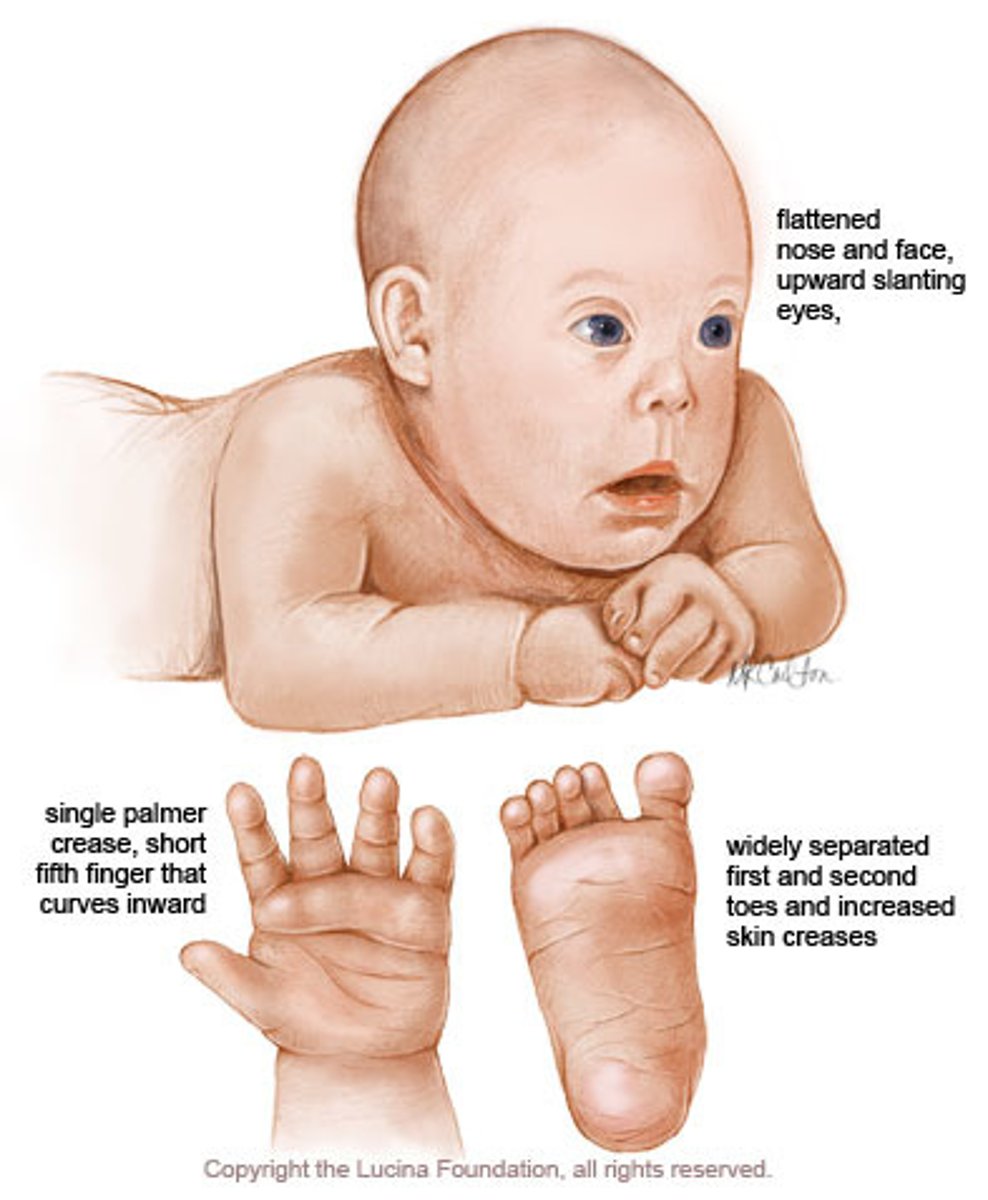
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
A genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21.
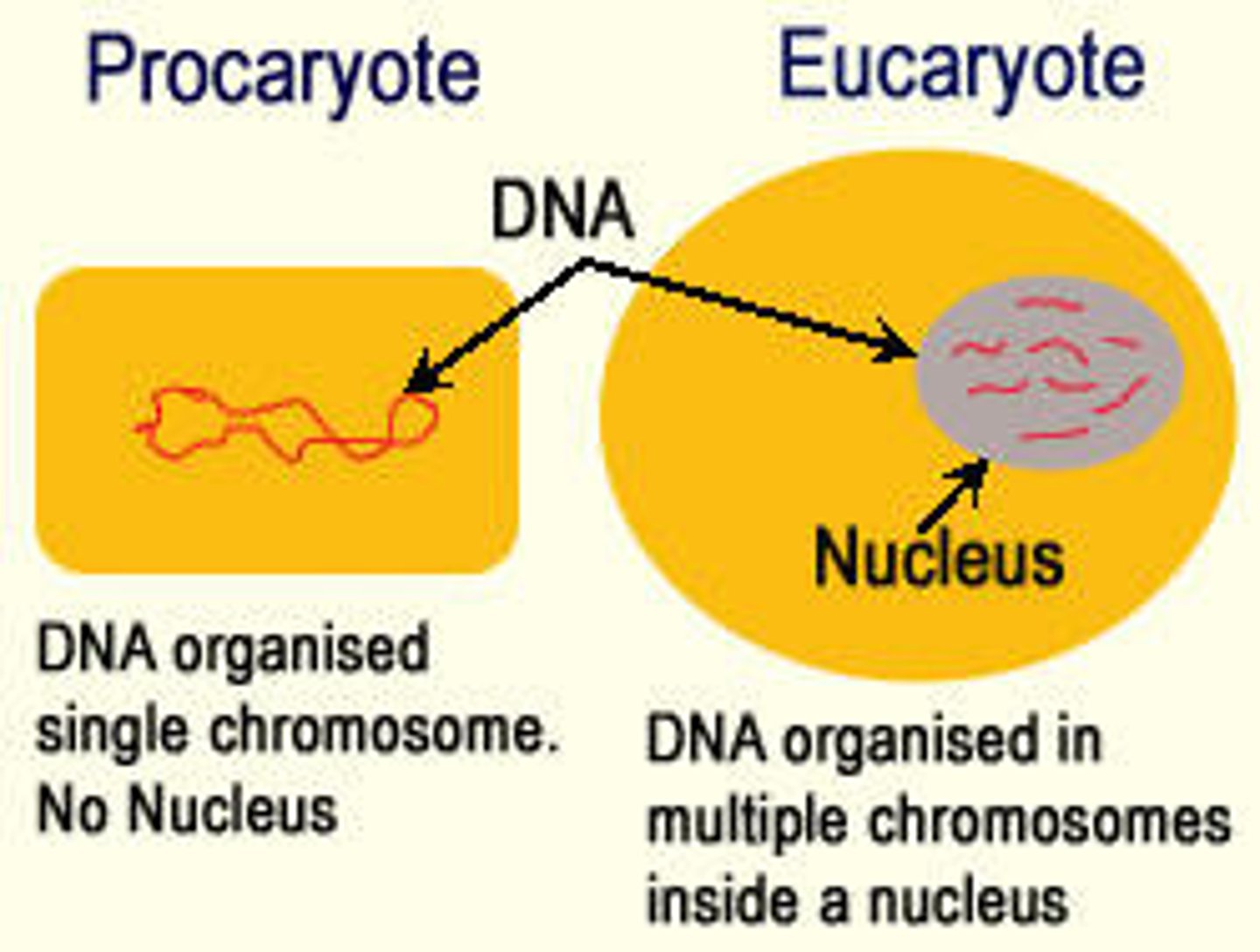
DNA is located in the _____ of the cell of eukaryotes.
nucleus
What sugar is in RNA?
ribose
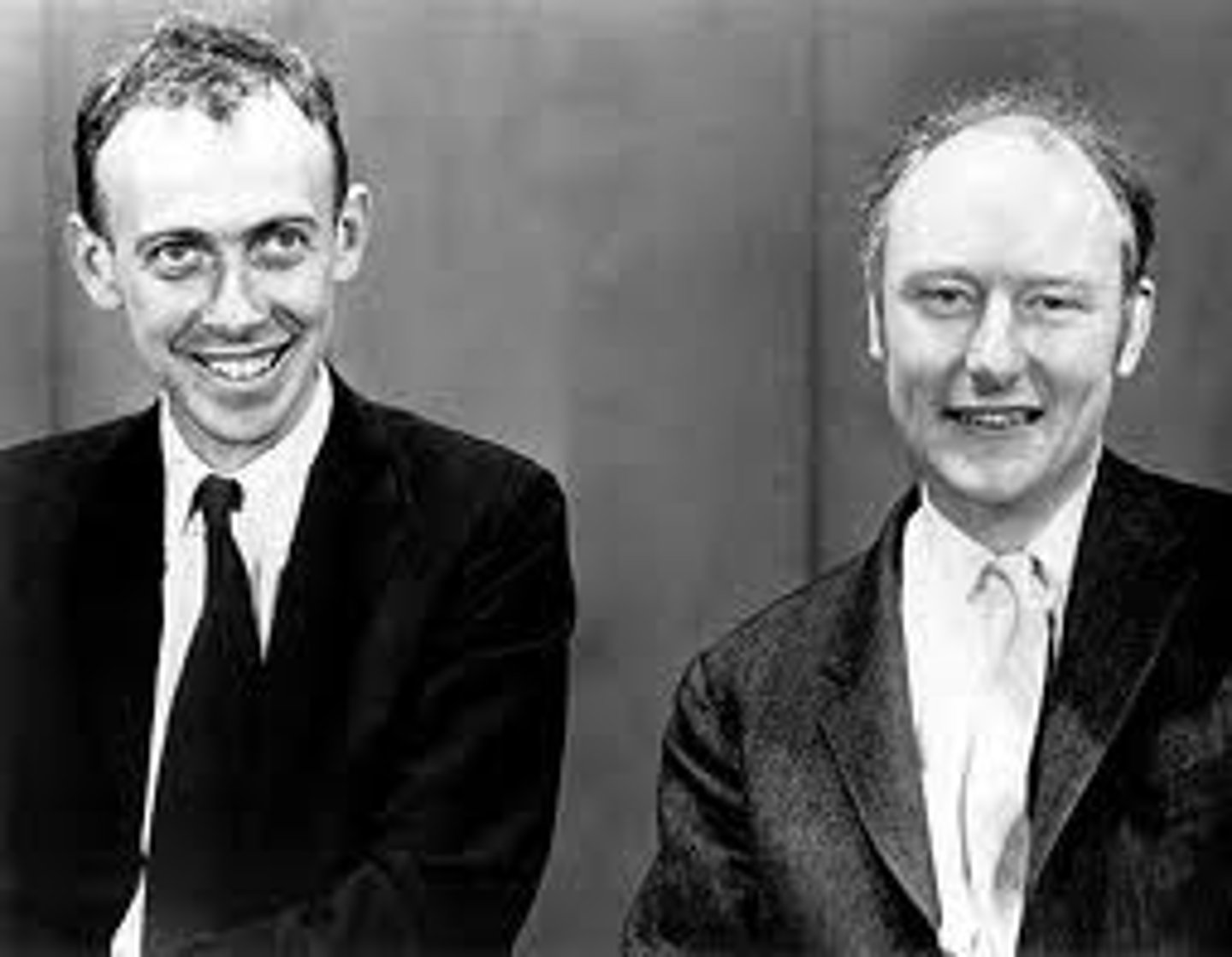
The scientists credited with establishing the structure of DNA are
Watson and Crick

Genes contain instructions for assembling
proteins
DNA polymerases
Enzymes responsible for adding nucleotides to the exposed DNA template bases
DNA replication results in
2 DNA MOLECULES EACH WITH ONE NEW STRAND AND ONE ORIGINAL STRAND
Gene regulation in eukaryotes
allows for cell specialization
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
substitution mutation
point mutation in which one nitrogeneous base (nucleotide) is changed to another
frameshift mutations
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide. KNOW THE EFFECTS.
substitution mutations
Mutation in which a single base is replaced, potentially altering the gene product. KNOW THE EFFECTS.
effects of mutations
may switch some genes on or off, which may affect how genes are expressed, may change the shape of an enzyme or weaken a structural protein
During translation, the amino acid detaches from the tRNA molecule and attaches to the end of a growing protein chain when=
tRNA anticodon is paired up with the mRNA codon
Mutation
A change in a gene or chromosome due to incorrect copying.