Dermatology Basics
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
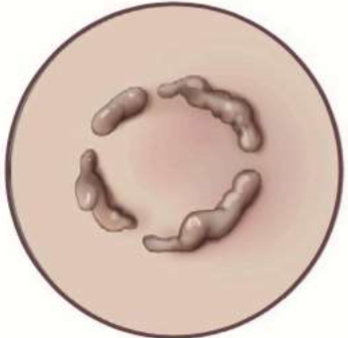
shape = circle
annular

single
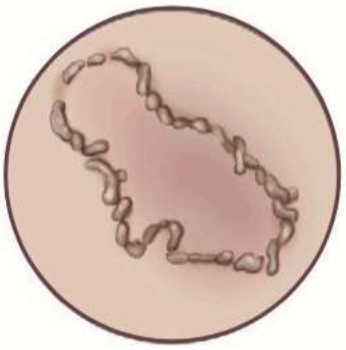
shape = wavy circle
polycyclic
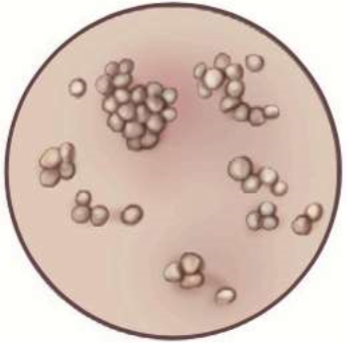
grouped
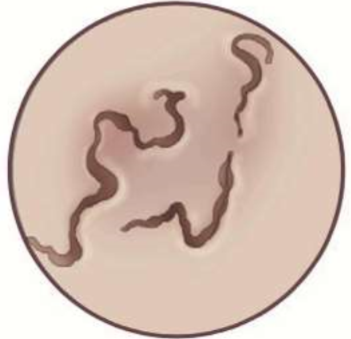
shape = snake-like
serpiginous
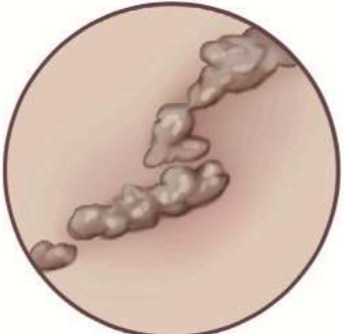
shape = line (roughly)
linear
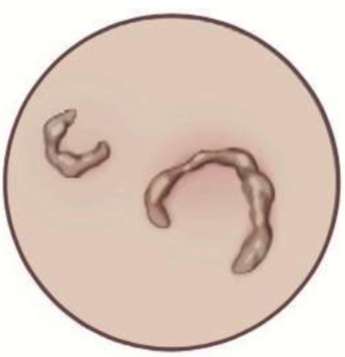
shape = half moon
arciform
shape = round
iris (central healing)
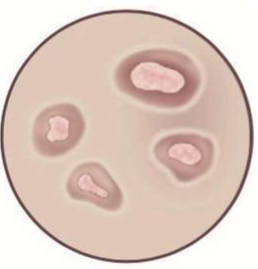
circumscribed color change
normal feel
primary
macule (under 1 cm), patch (over 1 cm)
darker, lighter, or red
macule → patch

partial or complete absence of hair
damage to hairs or hair follicles, abnormal hair growth
normal feel
primary or secondary
hypotrichosis → alopecia
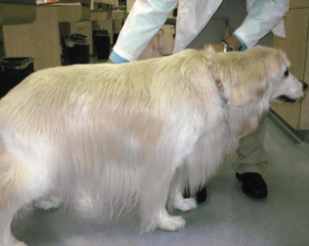
excessive hair growth
normal feel
primary or secondary
hypertrichosis
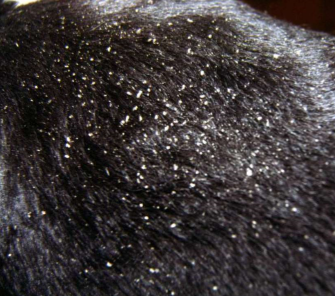
pieces of stratum corneum
imbalance in keratinization/desquamation homeostasis
normal feel
scale
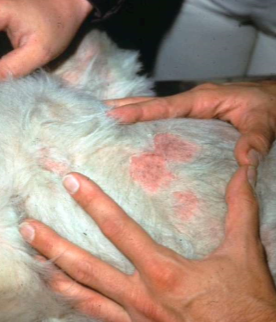
circular scale around abnormal skin
remains of roof of papule, pustule, hyperkeratosis, vesicle, bulla
normal-ish feel
secondary
epidermal collarette
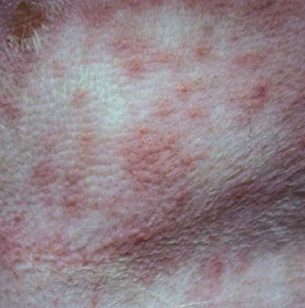
circumscribed solid elevation
infiltration of inflammatory cells, edema, or hyperplasia of epidermis
under 1 cm
raised
primary
papule
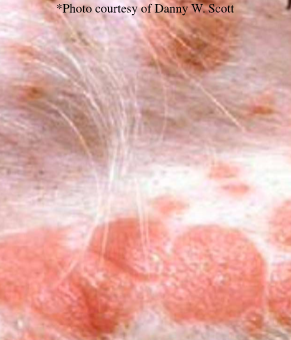
circumscribed flat topped elevation
extension or coalescence of papules
over 1 cm
raised
primary
plaque
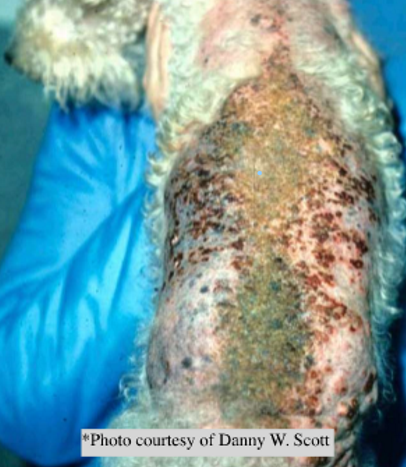
plaque with projecting elevations
heaped up crusts
over 1 cm
raised
primary
vegetation
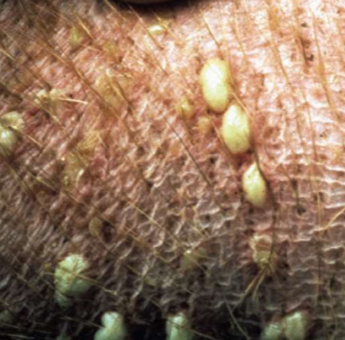
circumscribed elevation of skin with pus inside
infiltration of neutrophils, usually follicular, can be intraepidermal or subepidermal
any size
rounded feel
primary
pustule
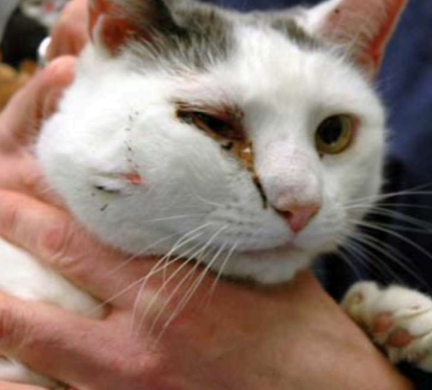
dermal or SQ accumulation of pus
larger and deeper than pustule
raised but pus not visible on skin surface until it drains
abscess
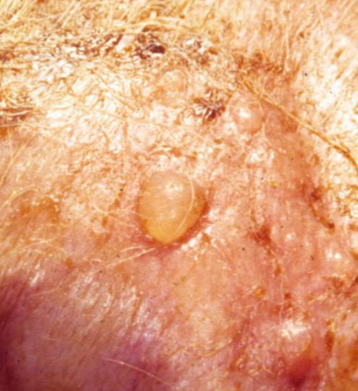
well circumscribed elevation of epidermis, can be intra-or sub-epidermal
accumulation of clear fluid, transient
vesicle (under 1 cm), bulla (over 1 cm)
raised
primary
vesicle → bullae
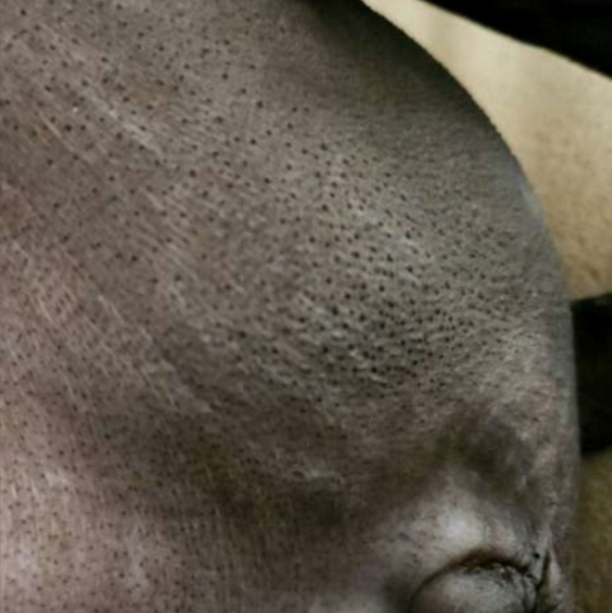
blackhead: open dilated hair follicle
hair follicle becomes full of keratin or other secretions
hair follicle sized
slightly raised
primary or secondary
comedone
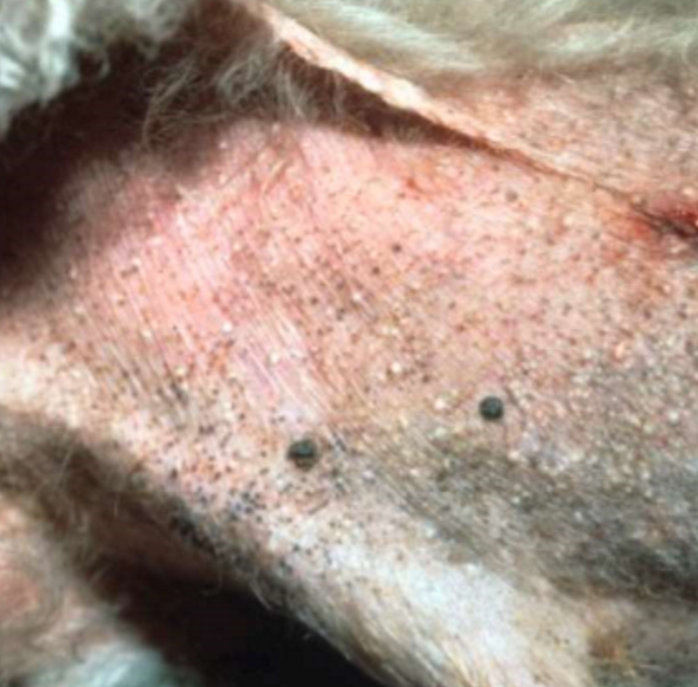
whitehead: closed dilated hair follicle
hair follicle filled with keratin
primary or secondary
milium
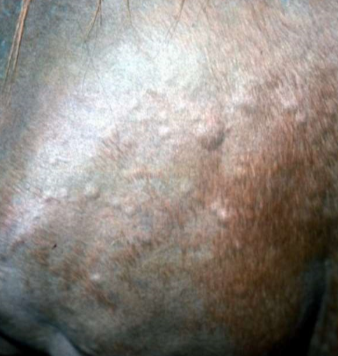
well circumscribed, annular, flat topped area of dermal edema that pits with pressure
edema, comes and goes within minutes
wheal (any), angioedema (many wheals in specific body region)
raised
primary
wheal (“hive”)
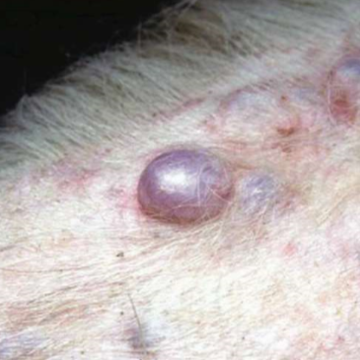
epithelial lined cavity with fluid or solid material inside
infiltration of cornified cellular debris or sebaceous or epitrichial secretions
any size
raised
primary
cyst
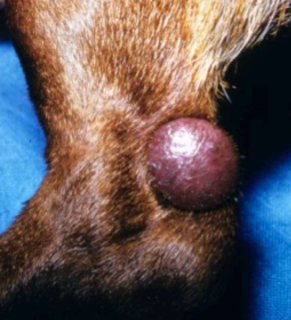
deep well circumscribed skin elevation
infiltration of inflammatory or neoplastic cells, fibrin, or crystalline material into DERMIS or SQ
nodule (1-3cm), tumor (over 3 cm)
raised
primary
nodule
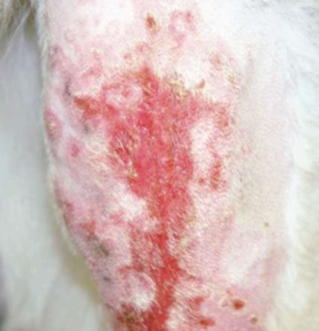
epidermal defect that heals without scar
self-trauma, ruptured papule, pustule, vesicle, bulla
does NOT breach basement membrane zone
negative
secondary
erosion
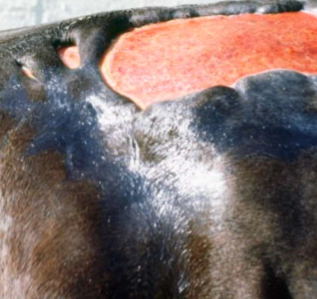
epidermal defect that heals WITH scar
deep pathological process
DOES breach basement membrane zone
negative
secondary
ulcer
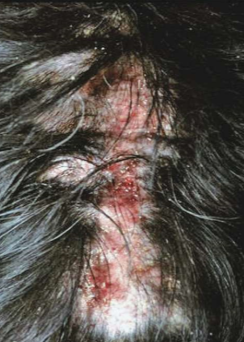
erosion or ulcer that is self-inflicted
scratching, licking, biting, rubbing
usually linear
negative
secondary
excoriation

linear split in skin
thick, dry, inelastic skin subjected to sudden swelling from inflammation or trauma
epidermal or dermal
negative
secondary
fissure
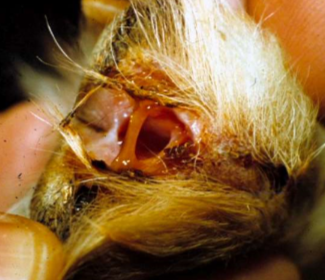
tract that connects focus of inflammation to skin surface
inflammation traveling path of least resistance
negative
secondary
draining tract
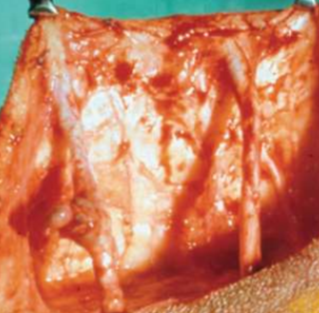
tract that connects 2 INTERNAL organs or one internal organ to skin surface
path of least resistance
secondary
fistula, sinus
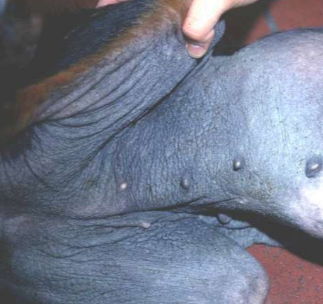
thickening and hardening of skin, exaggerated skin markings, hyperpigmentation
thick
secondary
lichenification
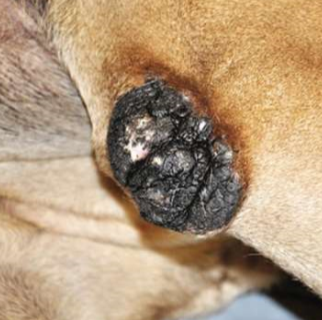
thick, rough, plaque-like area of skin
pressure, low-grade friction over bony prominence
thick
secondary
callus
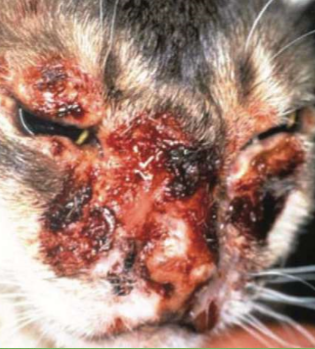
accumulation of dried exudate, serum, pus, blood, cells, scales, or medication
papule, pustule, vesicle, bulla ooze
rough
primary or secondary
crust (aka. scab)
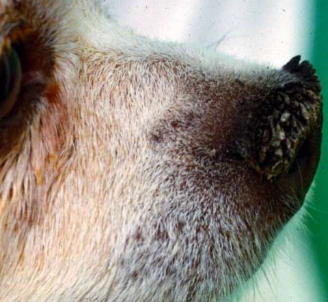
increased thickness of stratum corneum
rough
primary or secondary
hyperkeratosis
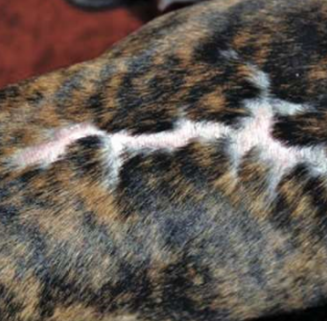
region of fibrous tissue that has replaced damaged dermis or SQ tissue
due to prior trauma, eg. ulcer, burn
thick
secondary
scar
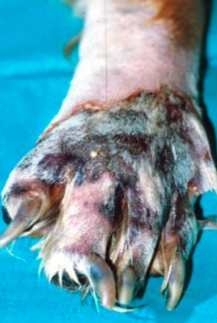
cell death → blue, purple, black, dry, firm tissue
loss of vascular supply to skin, extremities most common
primary or secondary
necrosis

accumulation of keratin and follicular debris that sticks to hair shaft
primary or secondary
follicular casting
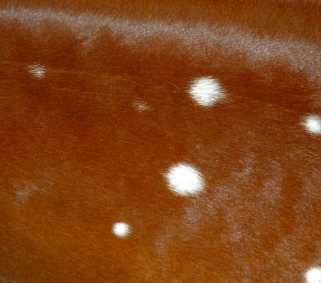
whitening of hairs
lack of pigment in hairs
leukotrichia
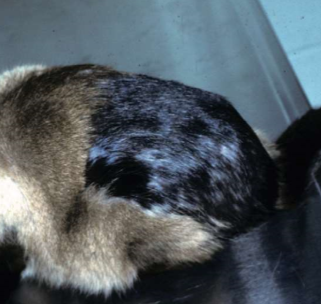
darkening of hairs
excess pigment in hairs
melanotrichia
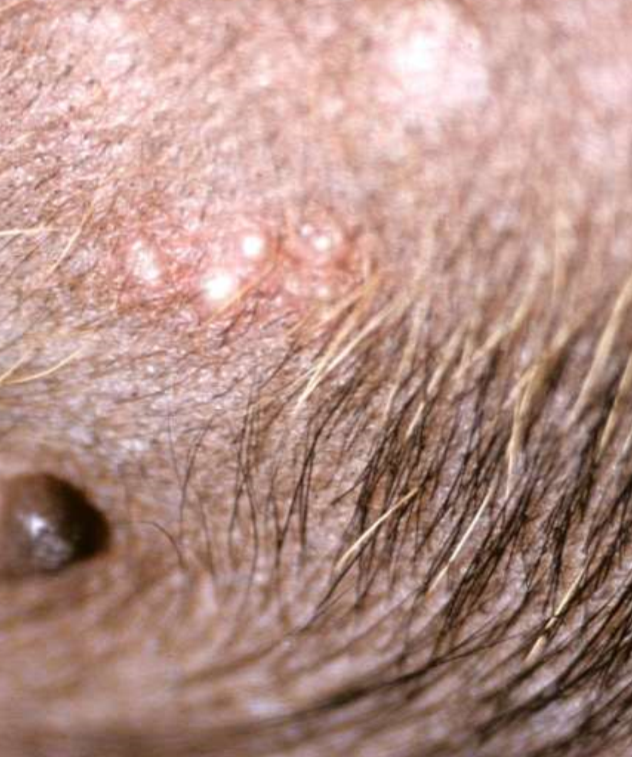
non-follicular bacterial pustular disease
impetigo
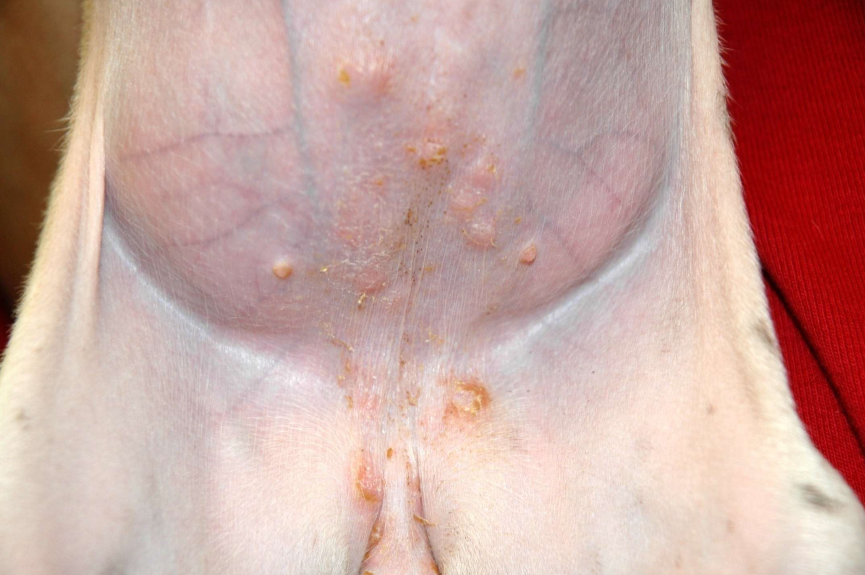
puppy impetigo
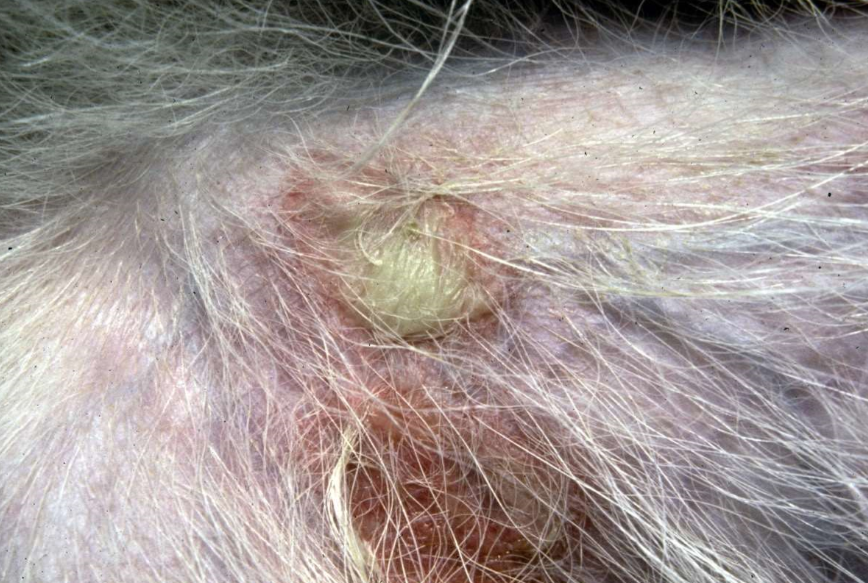
bullous impetigo
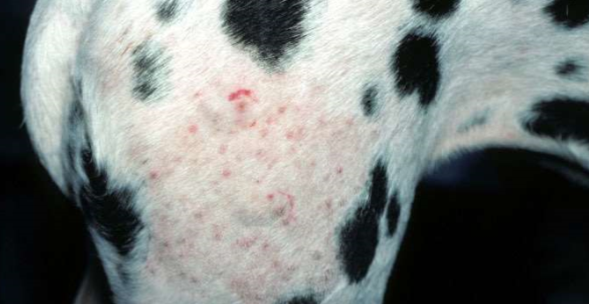
bacterial folliculitis
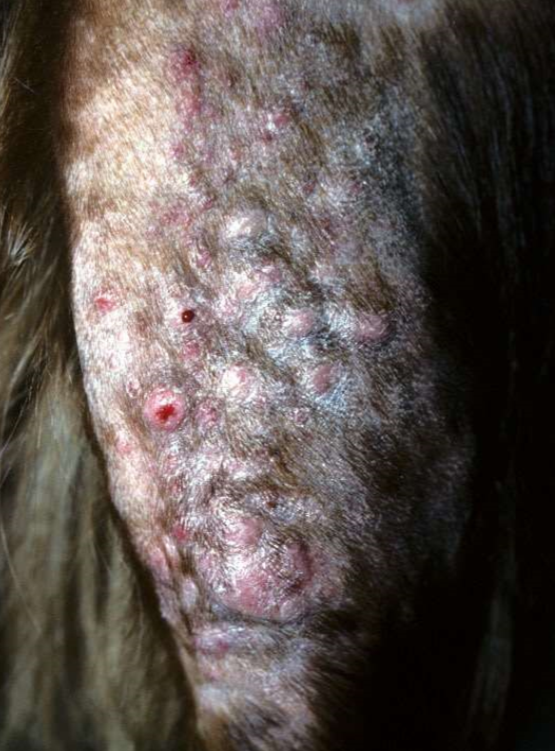
bacterial furcunculosis
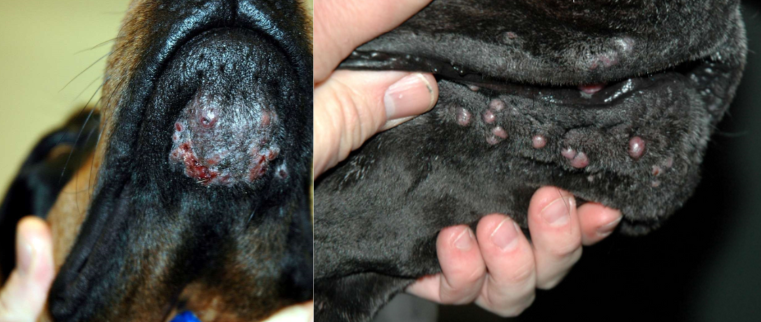
chin and muzzle furunculosis
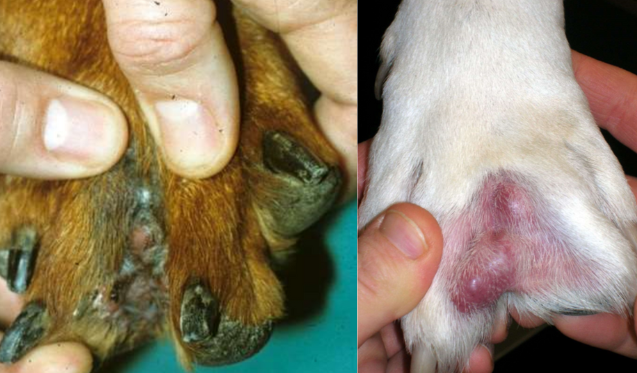
pedal furunculosis
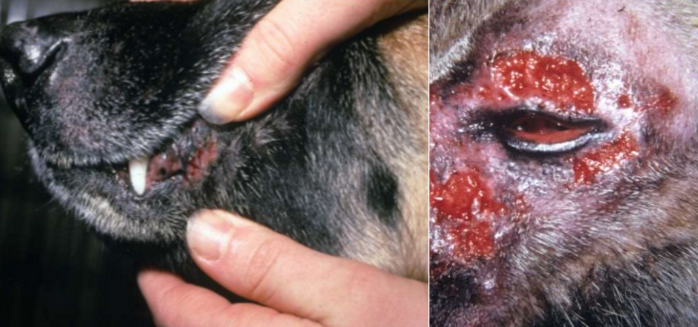
mucocutaneous pyoderma
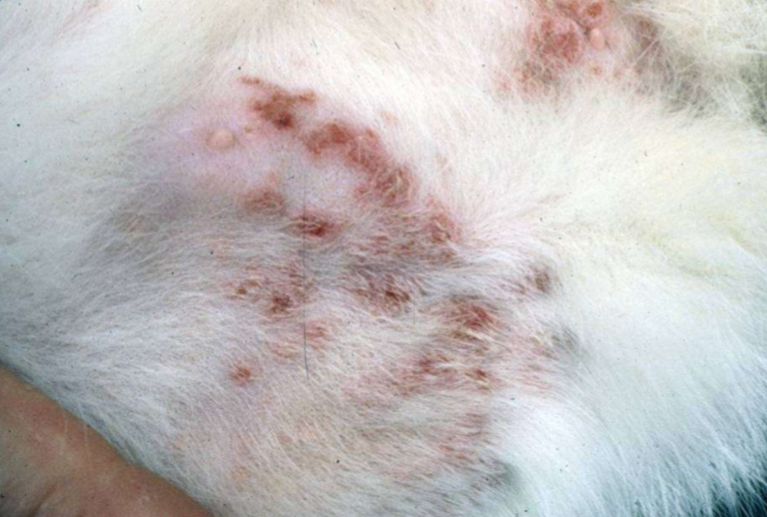
feline staphylococcal infection
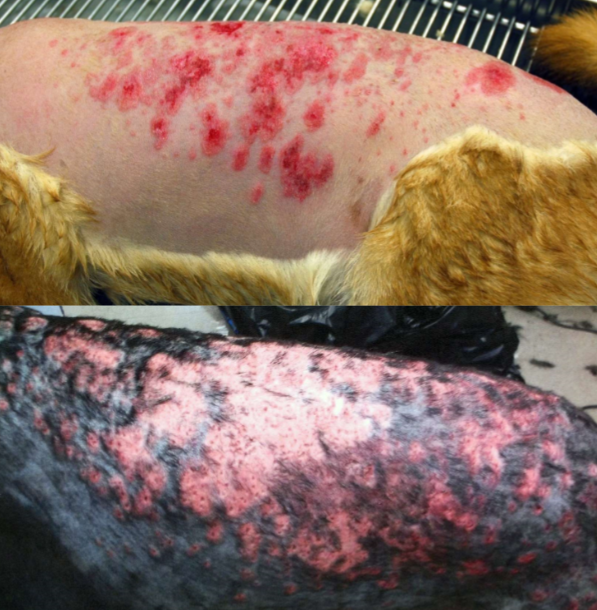
post-grooming folliculitis and furunculosis
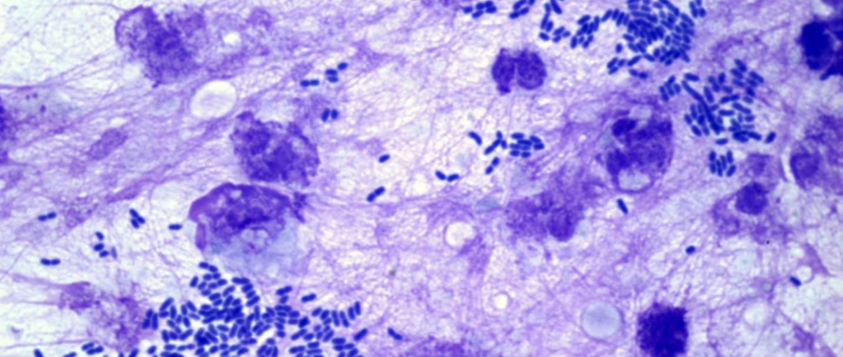
Pseudomonas folliculitis and furunculosis
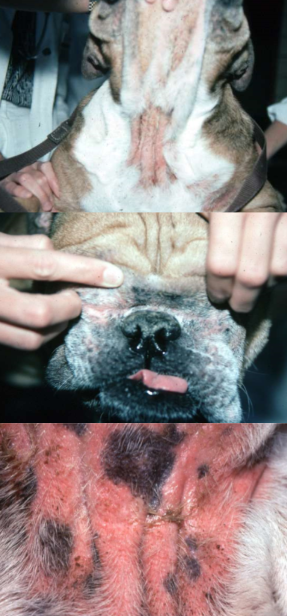
intertriginous dermatitis
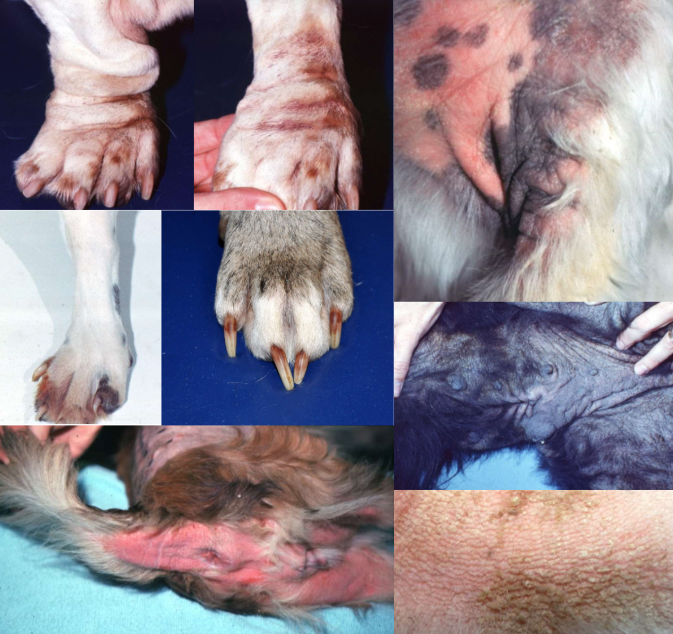
Malassezia dermatitis in dogs
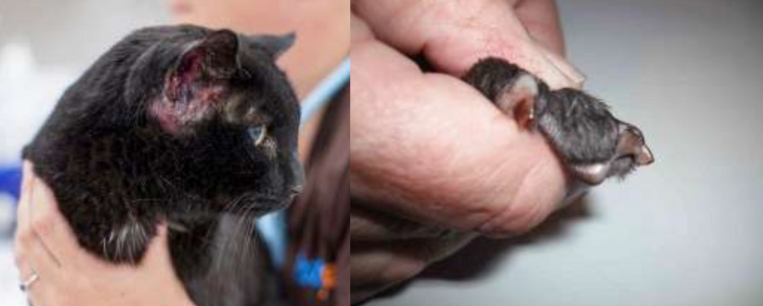
Malassezia dermatitis in cats
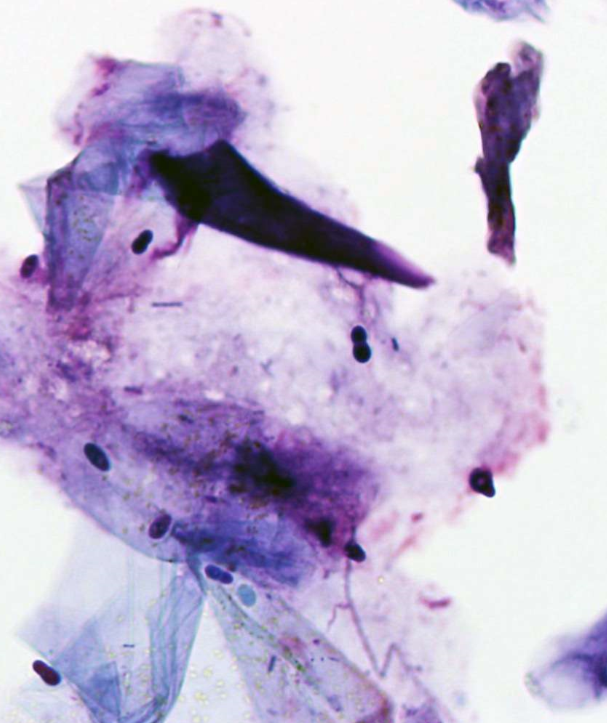
Malassezia
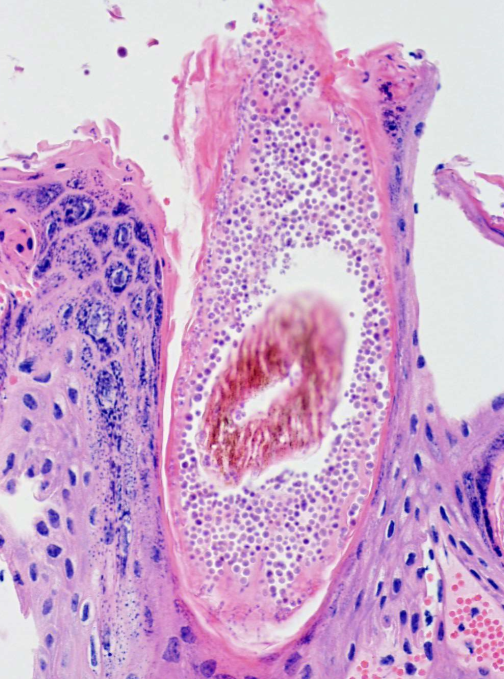
dermatophytosis
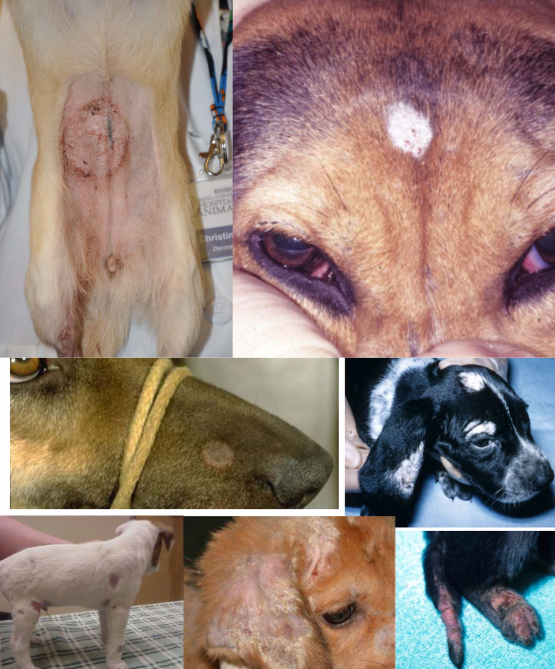
dermatophytosis in dogs
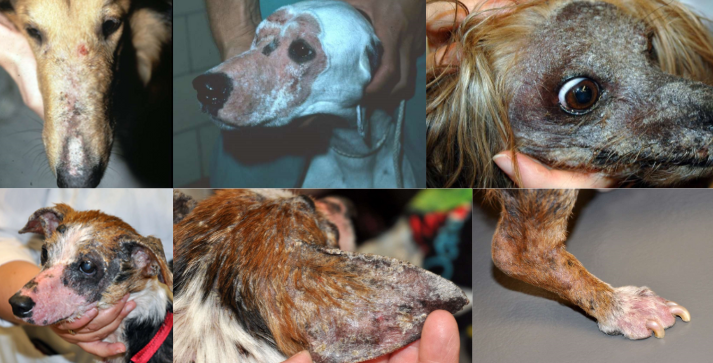
sylvatic ringworm
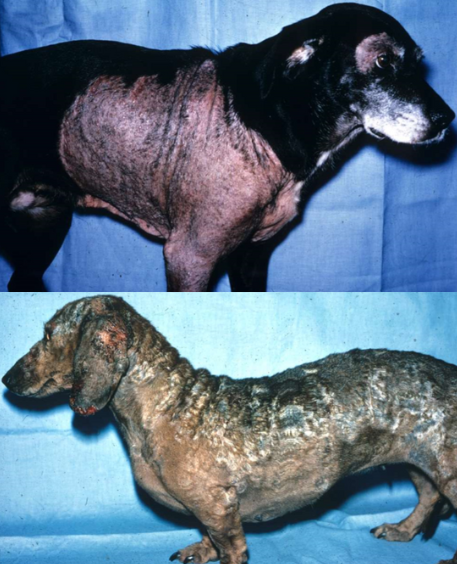
immune compromise
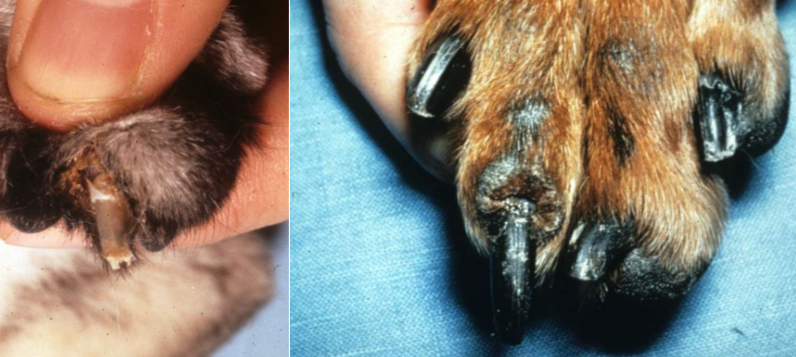
onychomycosis
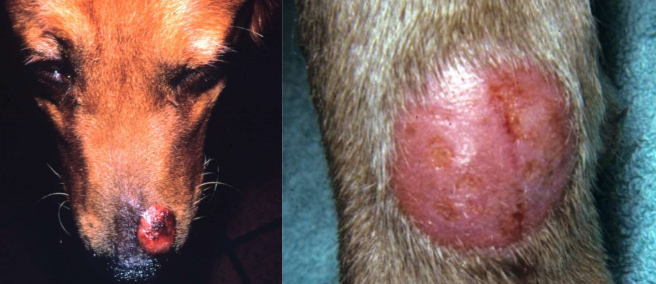
fungal kerion
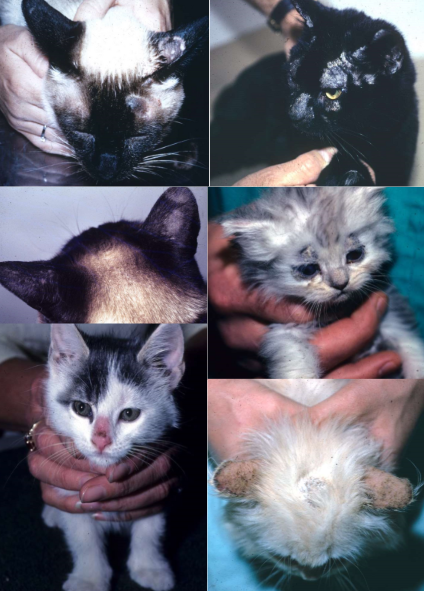
dermatophytosis in cats

Microsporum canis
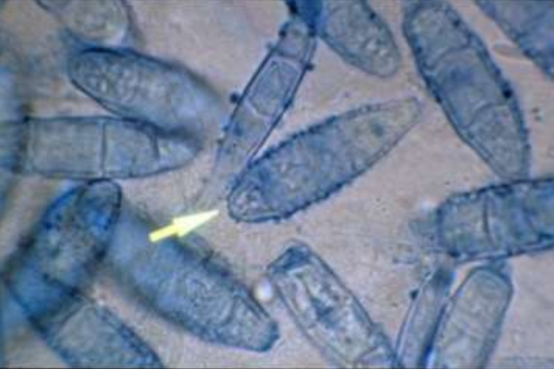
Microsporum gypseum
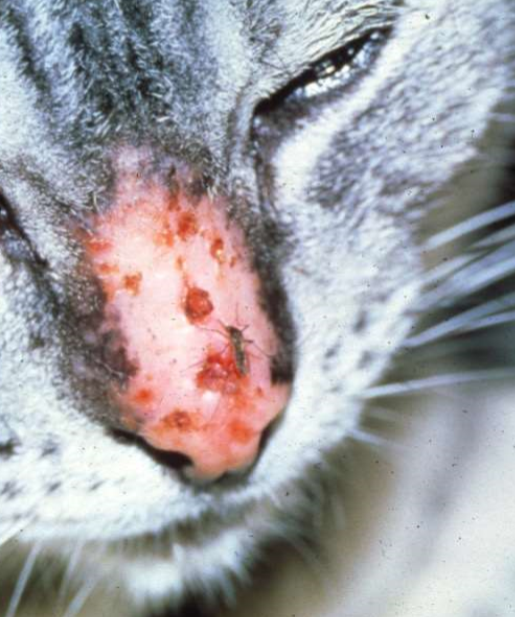
mosquito bite hypersensitivity (type I)
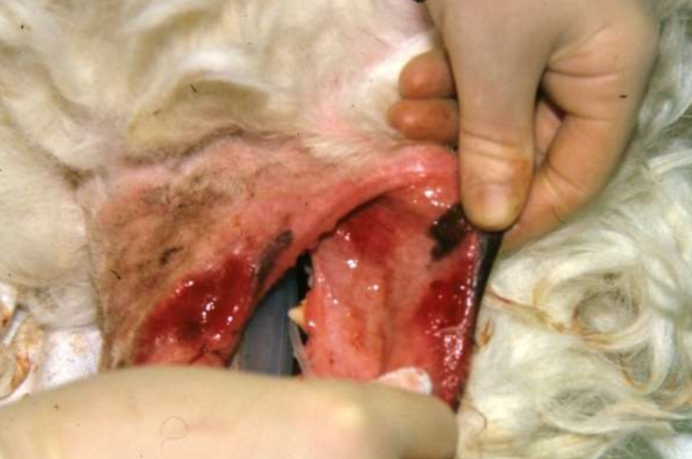
pemphigus vulgaris (type II)
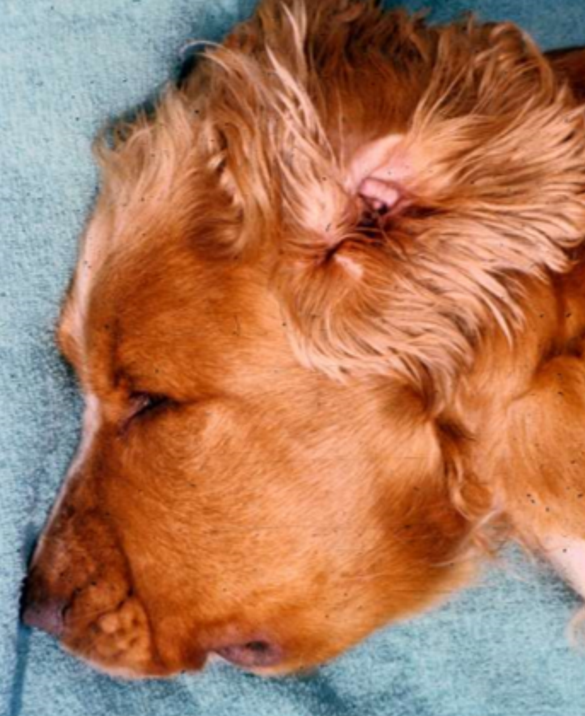

urticaria and angioedema
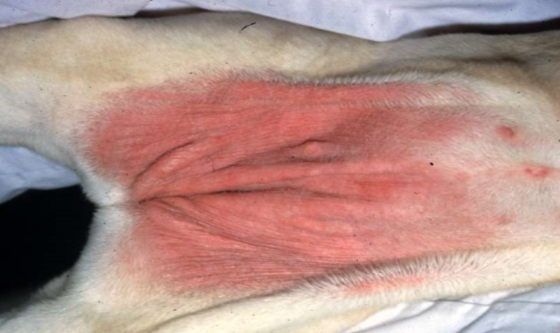
contact hypersensitivity
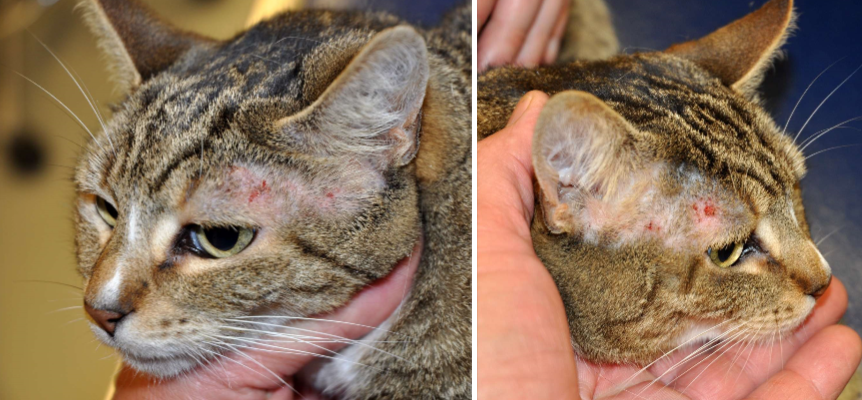
face, head and neck pruritus
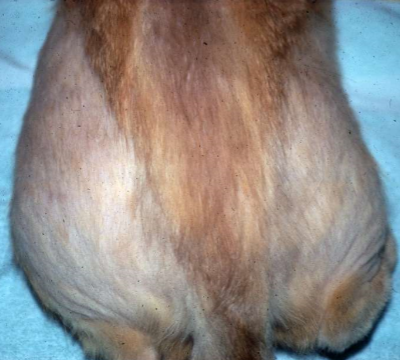
symmetrical self-induced hair loss (“fur mowing”)
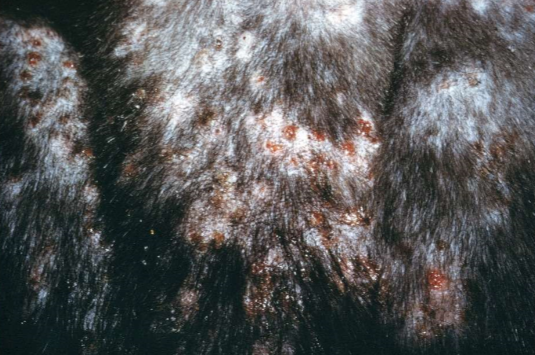
papulocrustous dermatitis (“miliary dermatitis”)
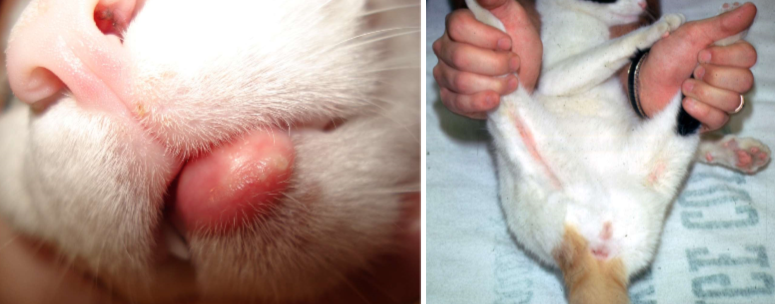
eosinophilic granuloma
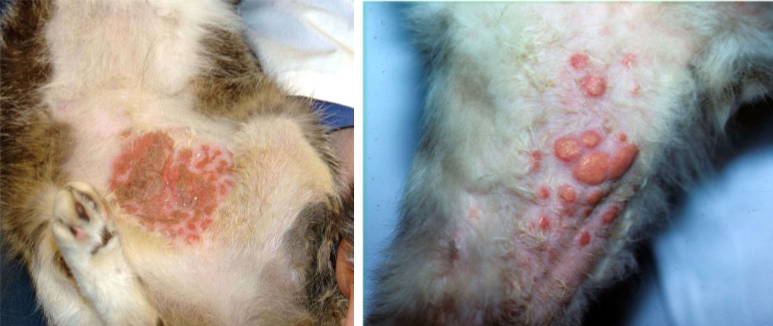
eosinophilic plaque
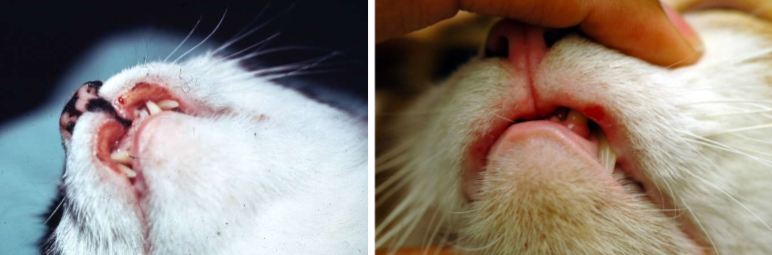
indolent ulcer (“rodent ulcer”)
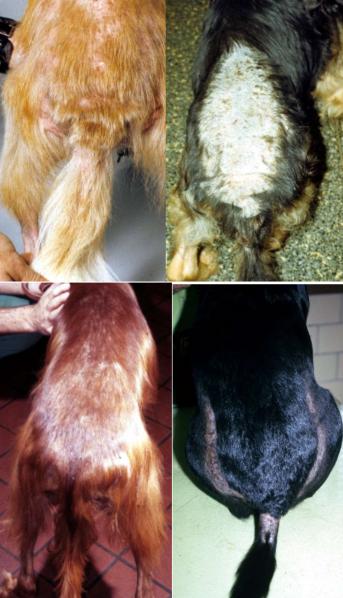
flea allergy dermatitis in dogs
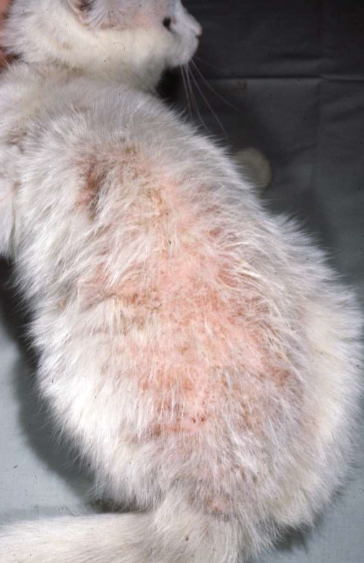
flea allergy dermatitis in cats
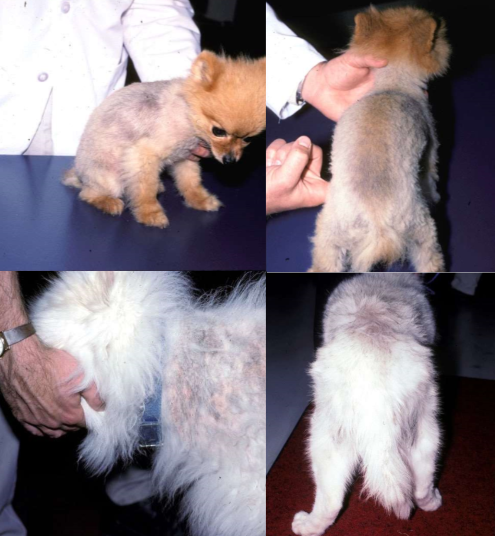
follicular arrest syndrome (aka. alopecia X)
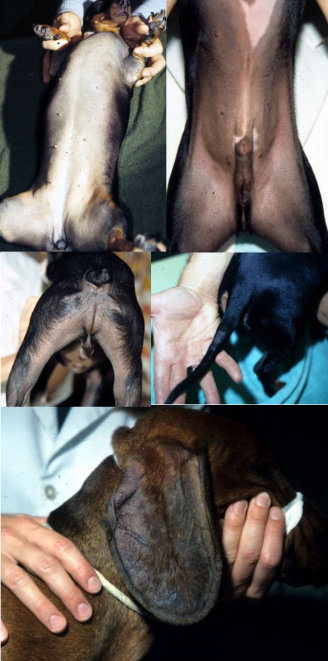
pattern baldness
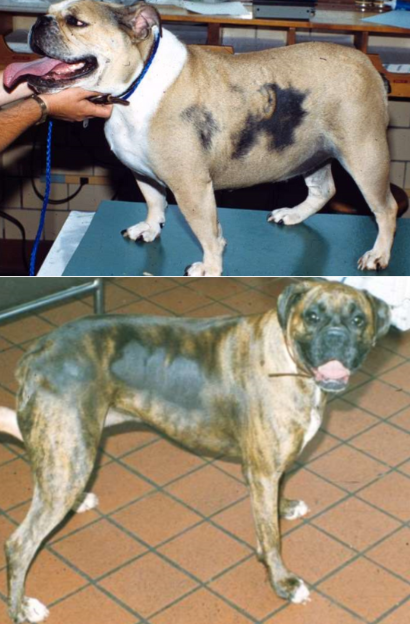
cyclical flank alopecia
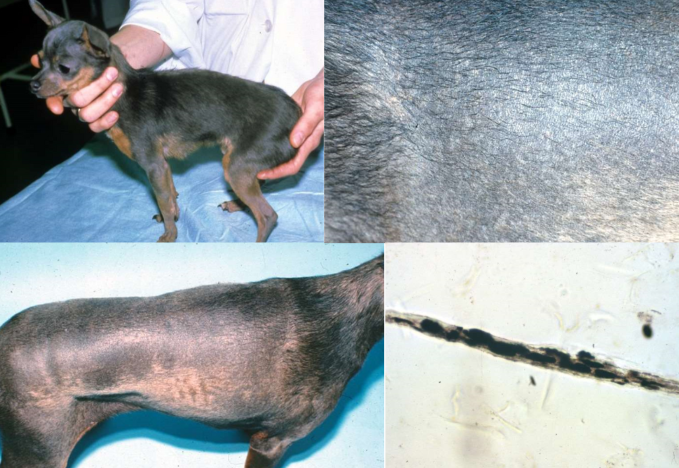
color dilution alopecia
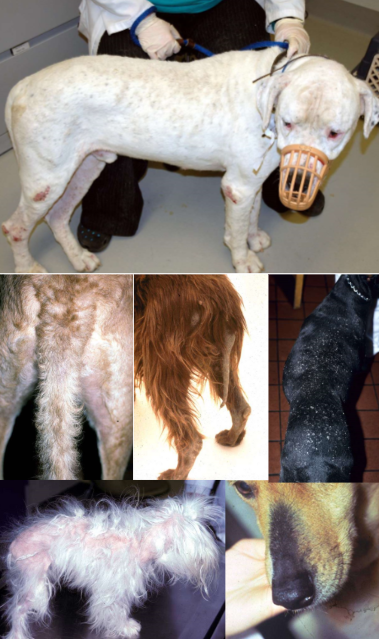
canine hypothyroidism
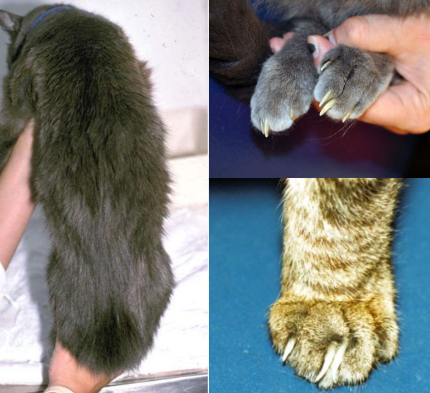
feline hyperthyroidism
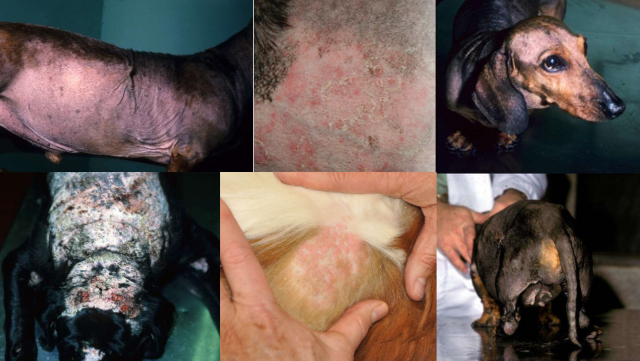
canine hyperadrenocorticism (aka. hypercortisolism, Cushing’s)
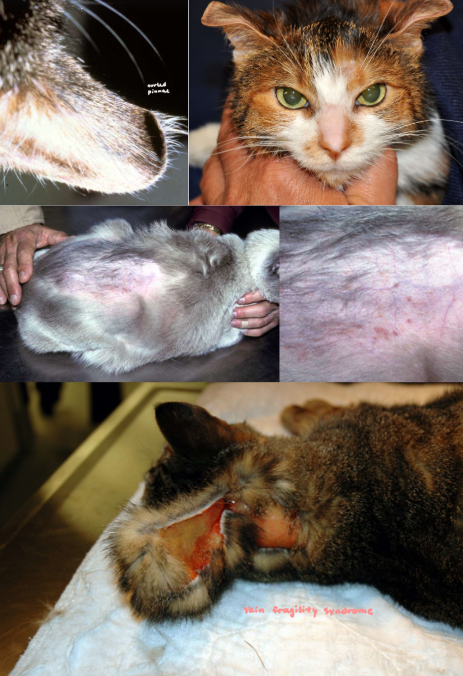
feline hyperadrenocorticism
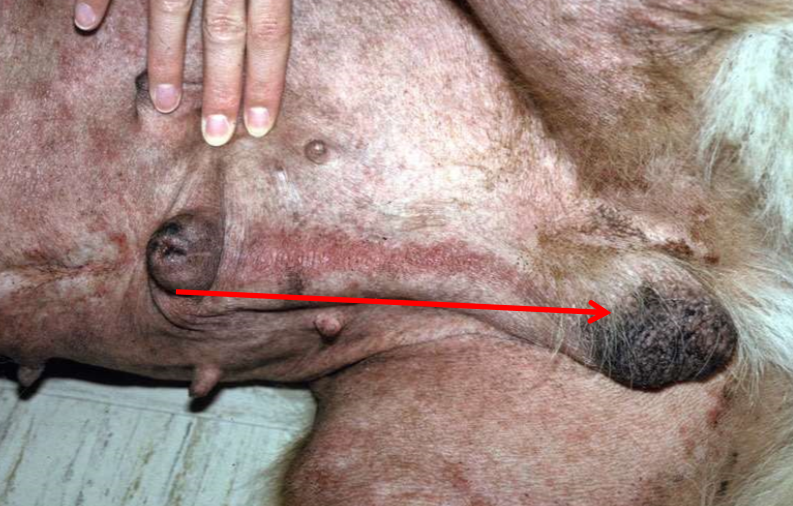
Sertoli cell tumor
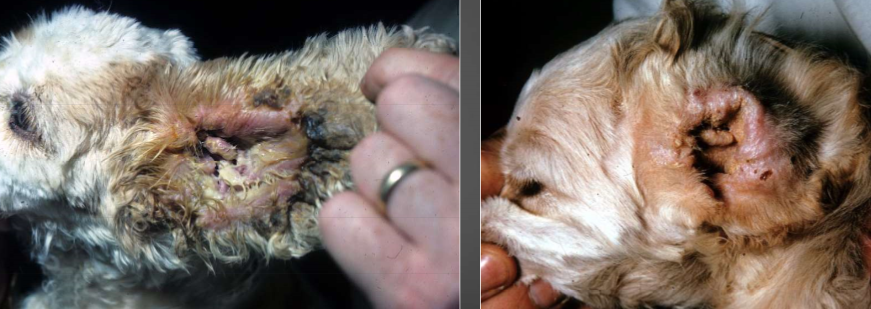
left:
right:
bacterial, yeast
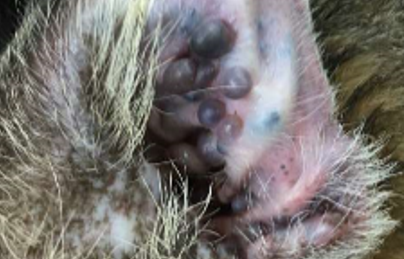
ceruminous cystomatotis
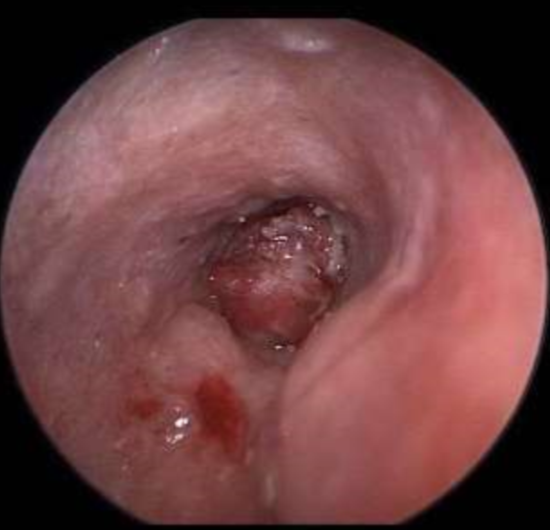
SCC or ceruminous gland tumor
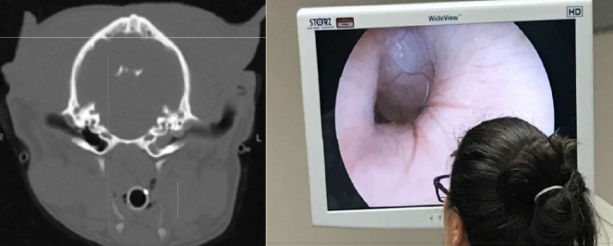
primary secretory otitis media (PSOM)
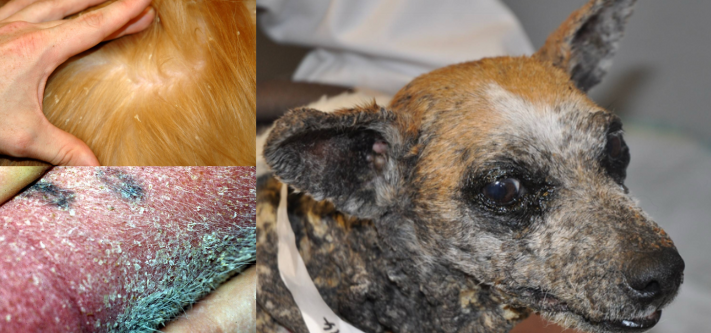
ichthyosis
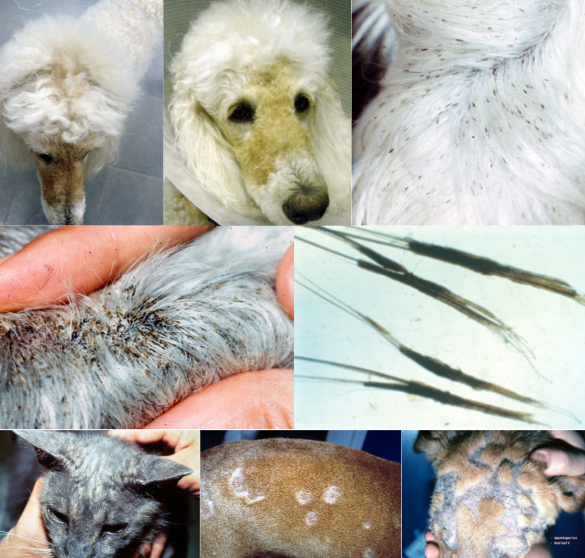
sebaceous adenitis
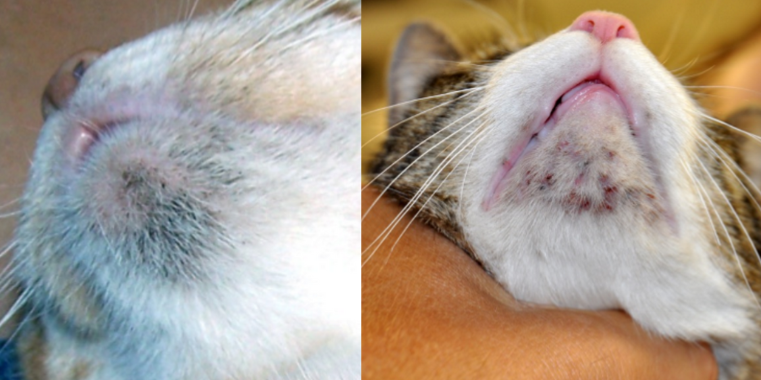
feline acne
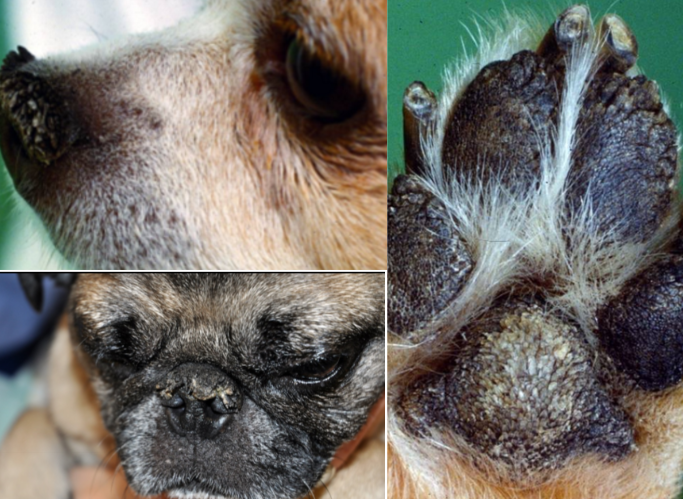
nasal and digital hyperkeratosis
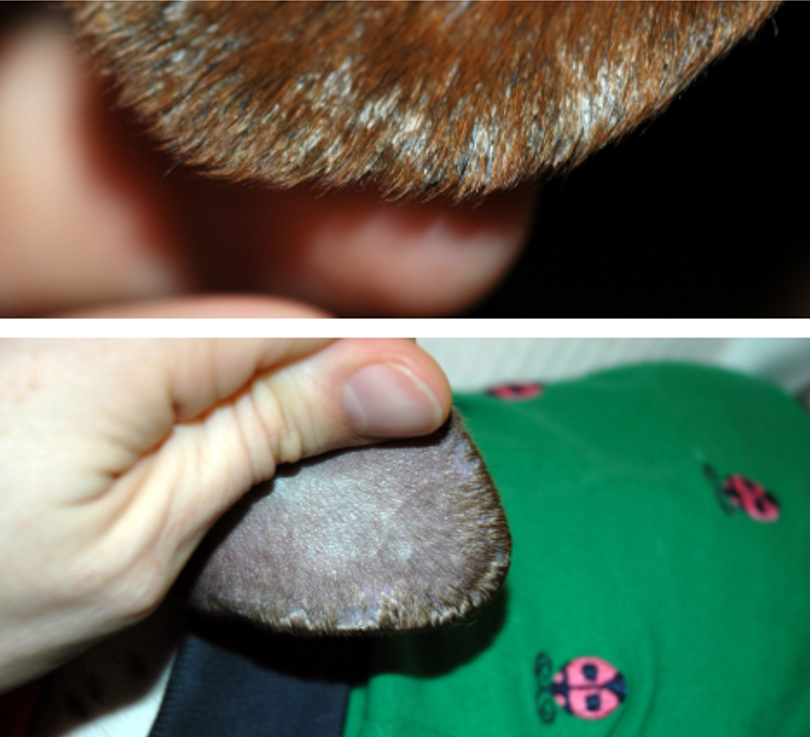
ear margin dermatosis (seborrhea)
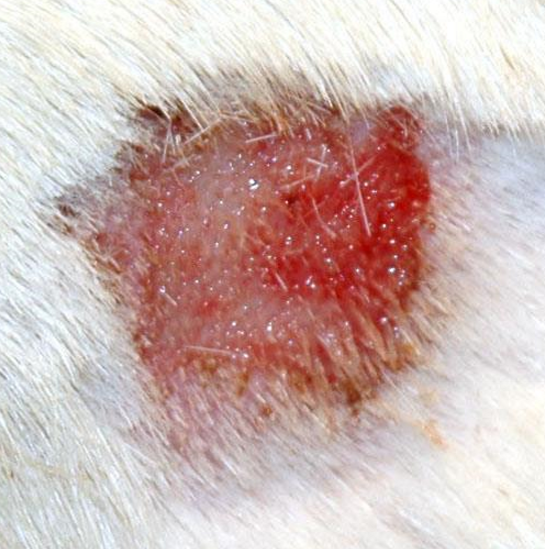
acute moist dermatitis (aka. “hot spot”)
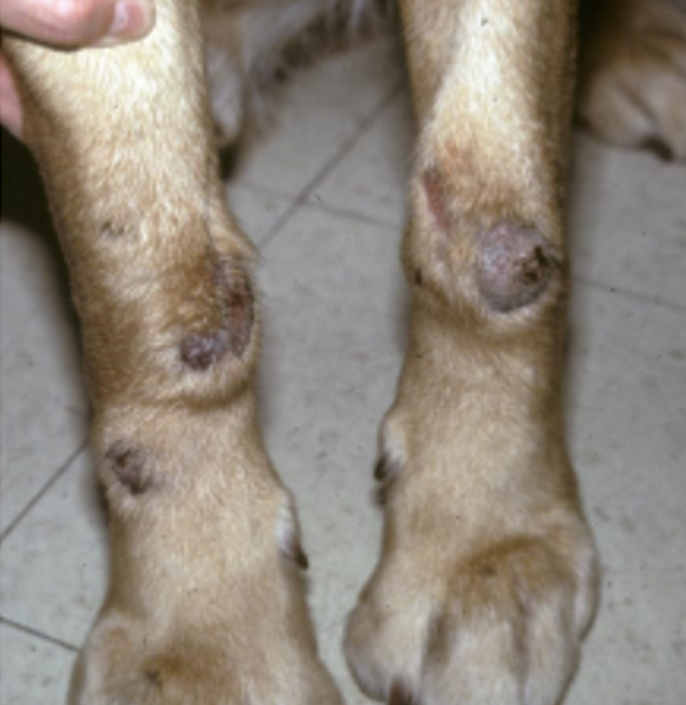
acral lick dermatitis (aka. lick “granuloma”)
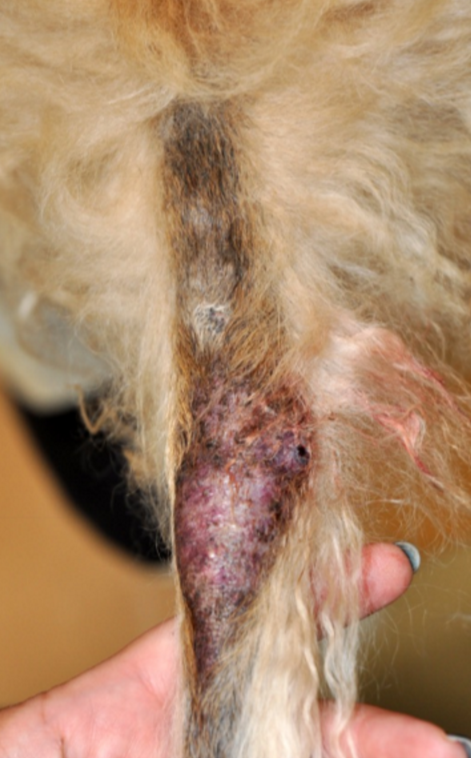
tail gland hyperplasia
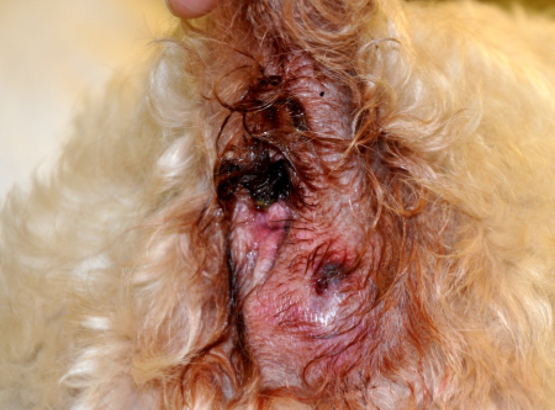
anal sacculitis
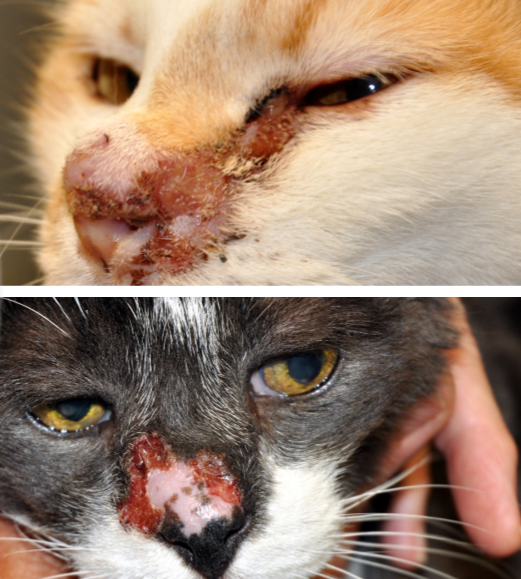
herpesvirus dermatitis
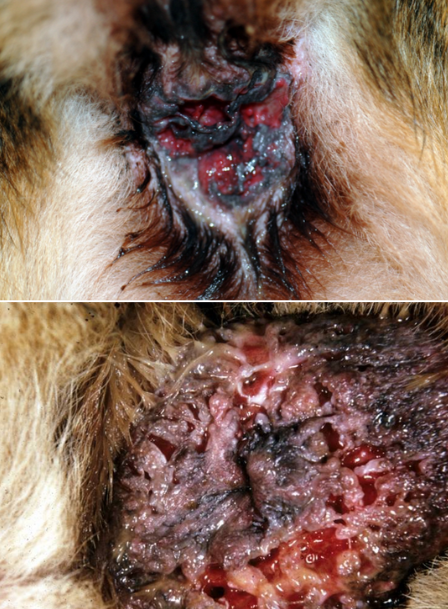
perianal fistulas
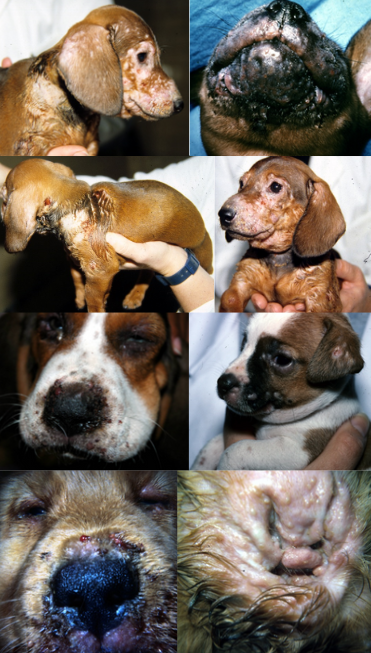
juvenile cellulitis