Science in Action 9 - Unit E Vocabulary
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
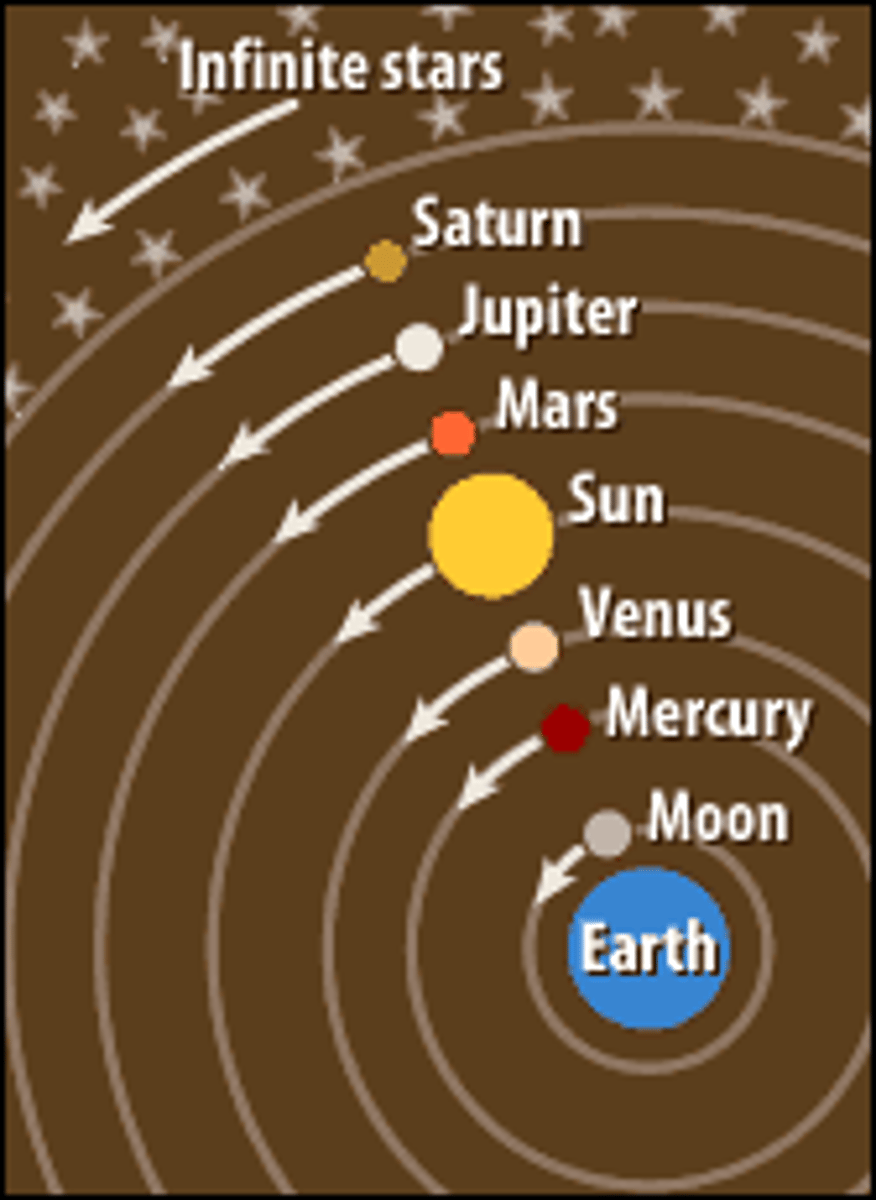
Heliocentric
The Sun-centred model of the solar system first proposed by Polish astronomer Nicholas Copernicus in 1530.
Ellipses
An oval formed around two foci (a circle is formed around one focus); the orbital paths of planets travelling around the Sun are ellipses.

Aristole
Greek philosopher that proposed a geocentric, Earth-centred, model to explain planetary motion.

Copernicus
Polish astronomer that proposed a different model to Aristotle, one that explained planetary motion much more simply than the geocentric model called the heliocentric model. He suggested that the Sun was at the centre, with Earth and other planets revolving around it in orbits.

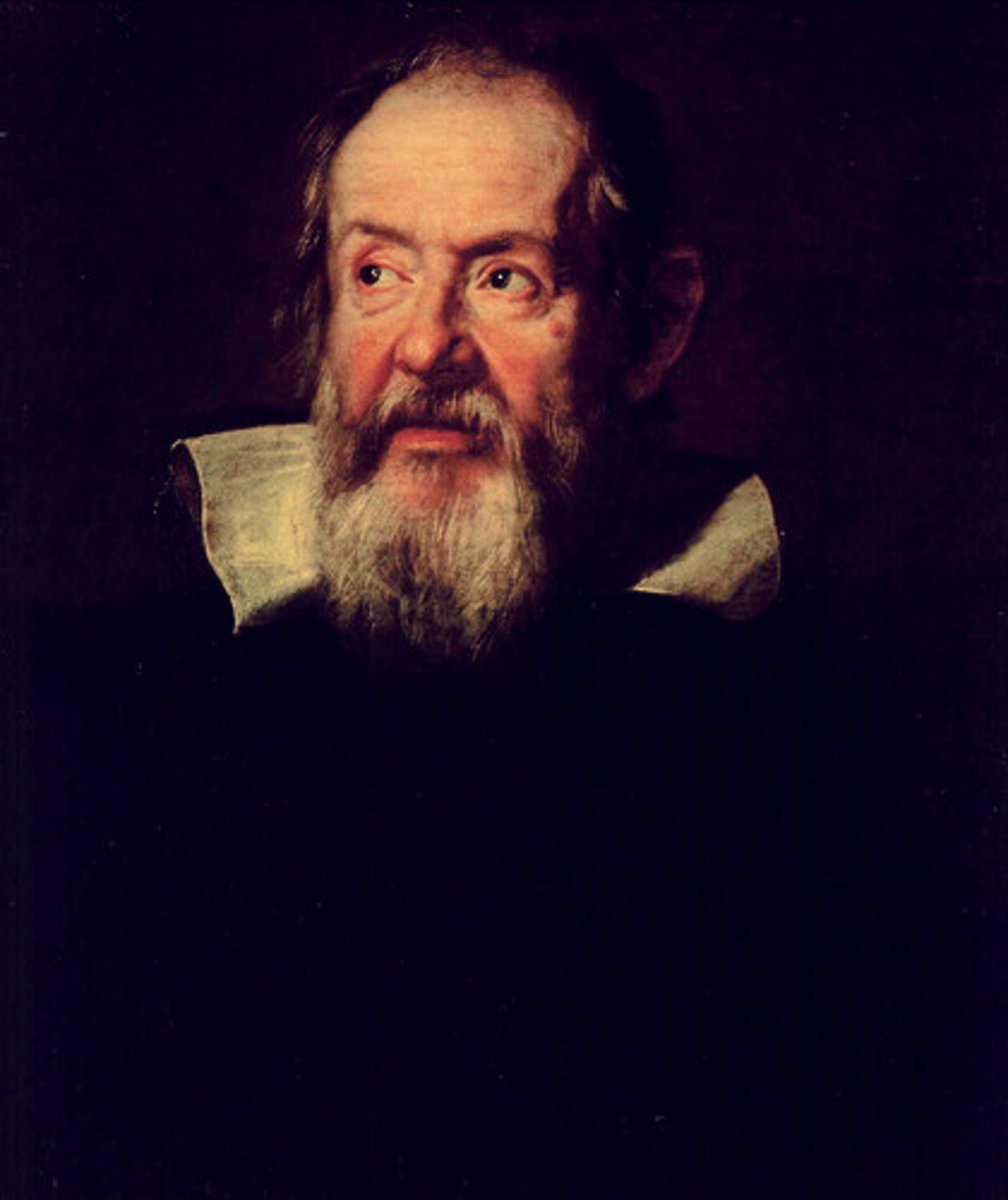
Galileo
Italian scientist who was the first person to view mountains on the Moon, a "bump" on either side of Saturn, spots on the Sun, moons orbiting Jupiter, and the distinct phases of Venus.

Quadrant
Invented in 2nd century A.D., it was a tool used to measure a star's height above the horizon.
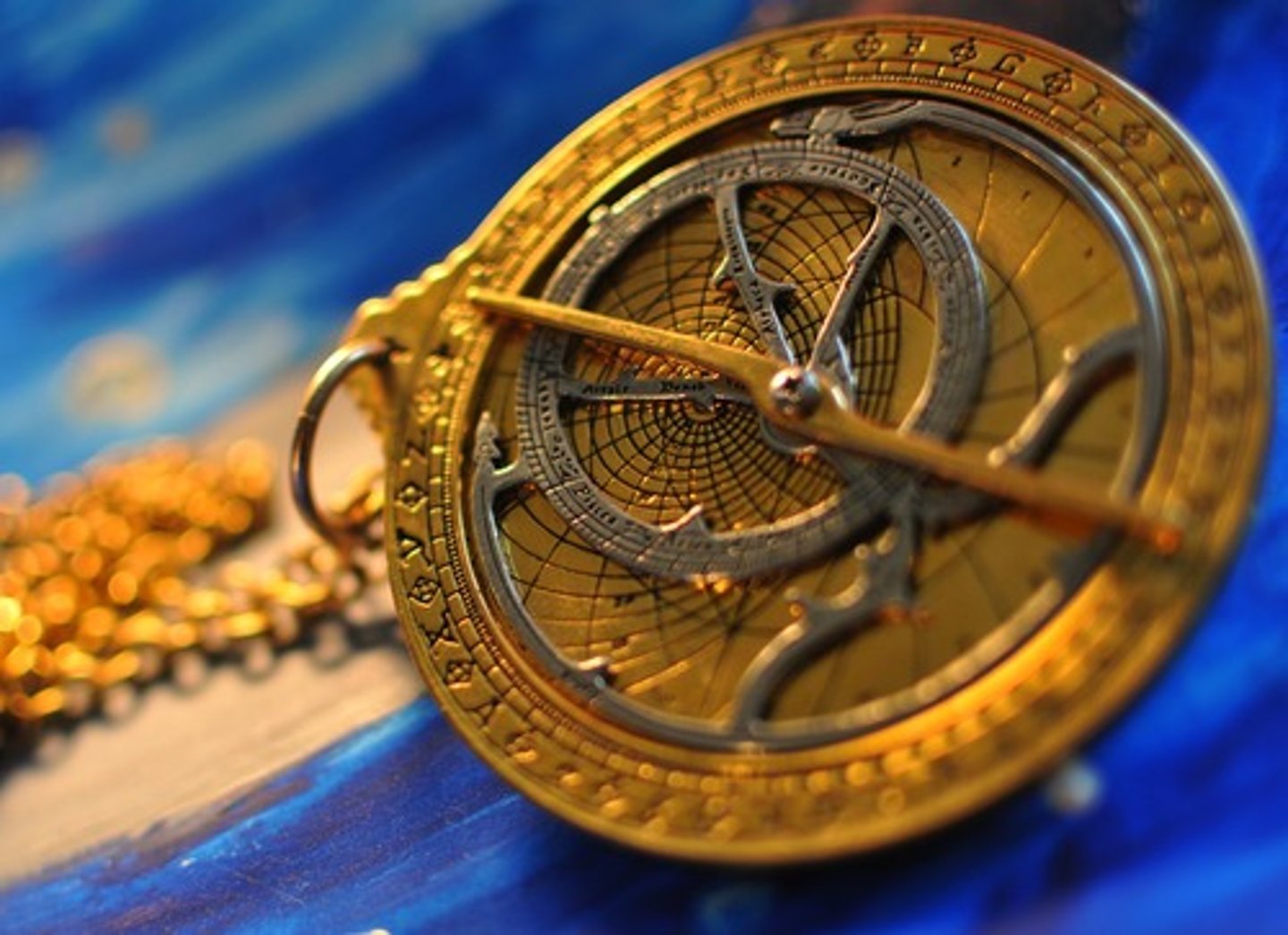
Astrolabe
Used to make accurate charts of star positions.

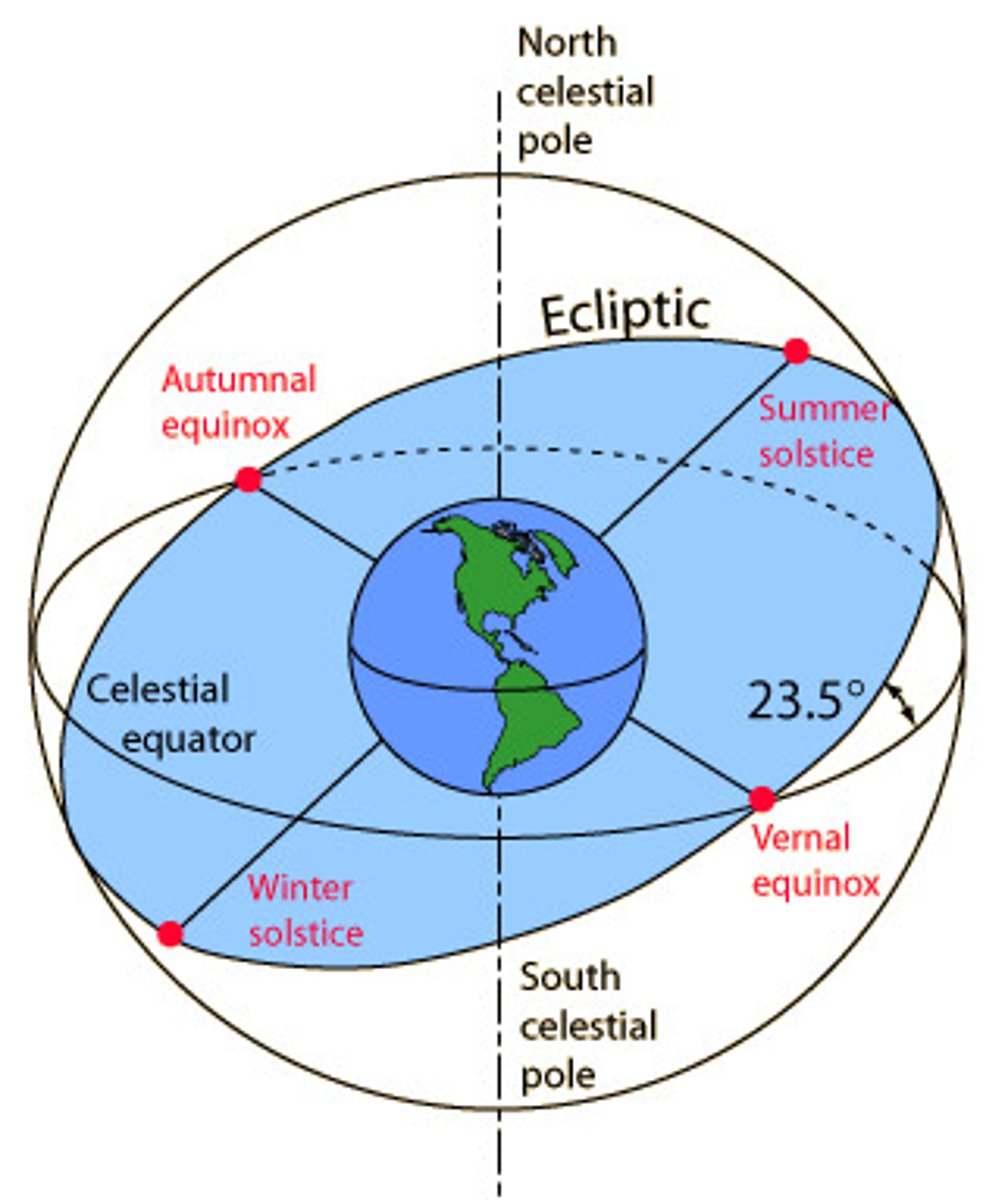
Solstice
Either of two times in the year when the Sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky at noon; in the northern hemisphere, the summer solstice occurs near June 21 (longest day of the year) and the winter solstice occurs near December 21 (shortest day).
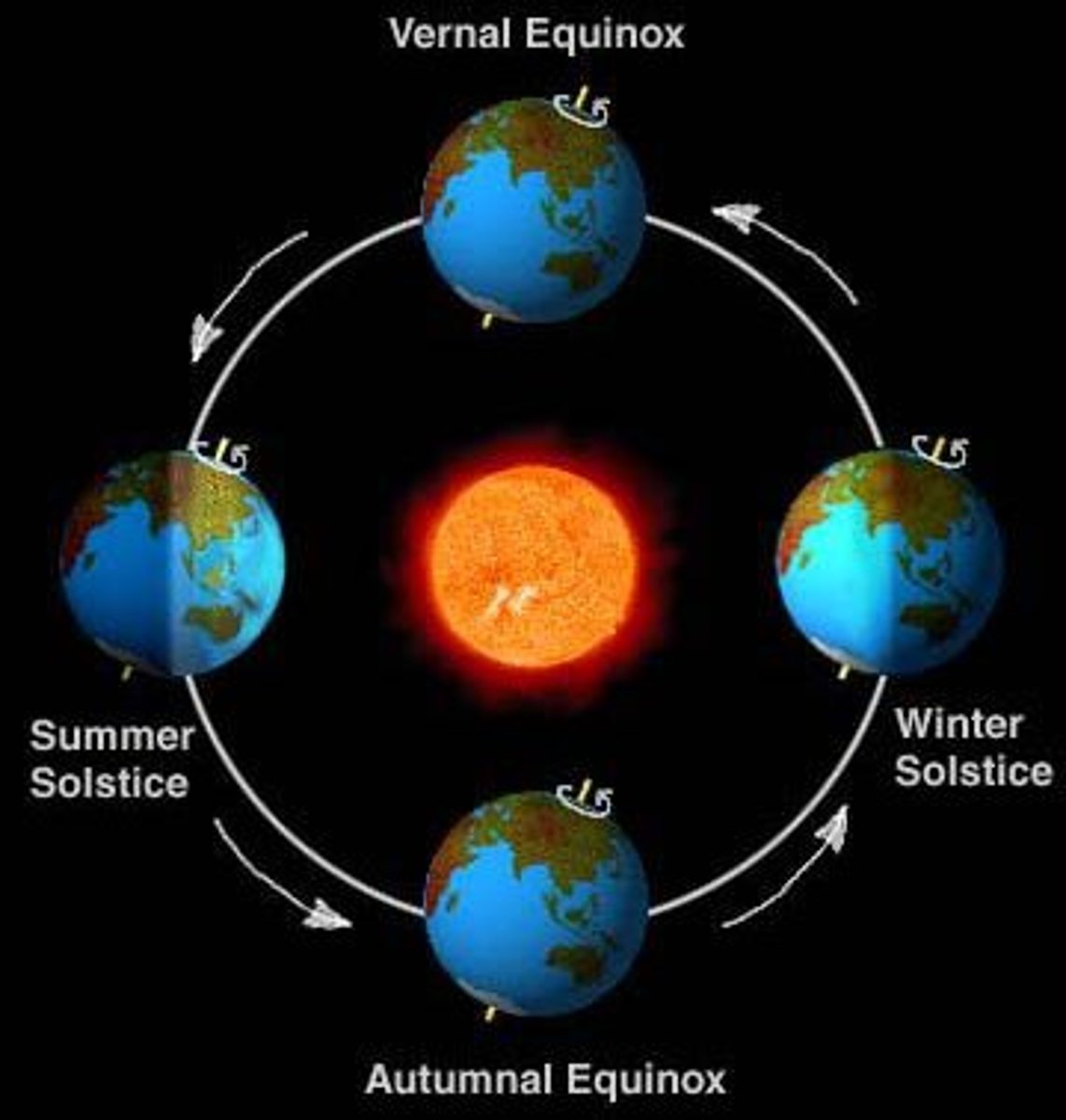
Equinox
Either of the two times a year (once in spring and once in autumn) when the Sun crosses the equator and day and night are of equal length; usually on or about March 21 and September 23.
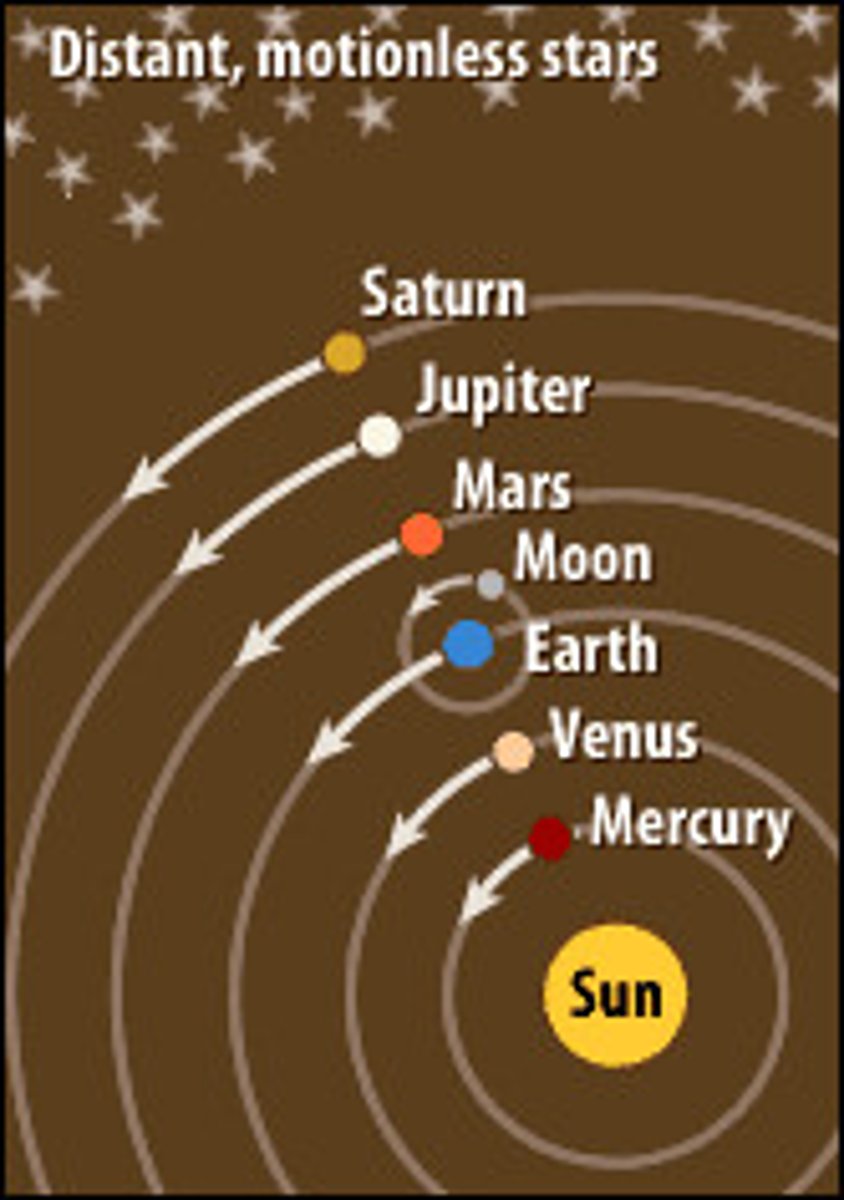
Geocentric Model
The Earth-centred model of the solar system originally proposed about 2000 years ago by the Greek philosopher Aristotle.
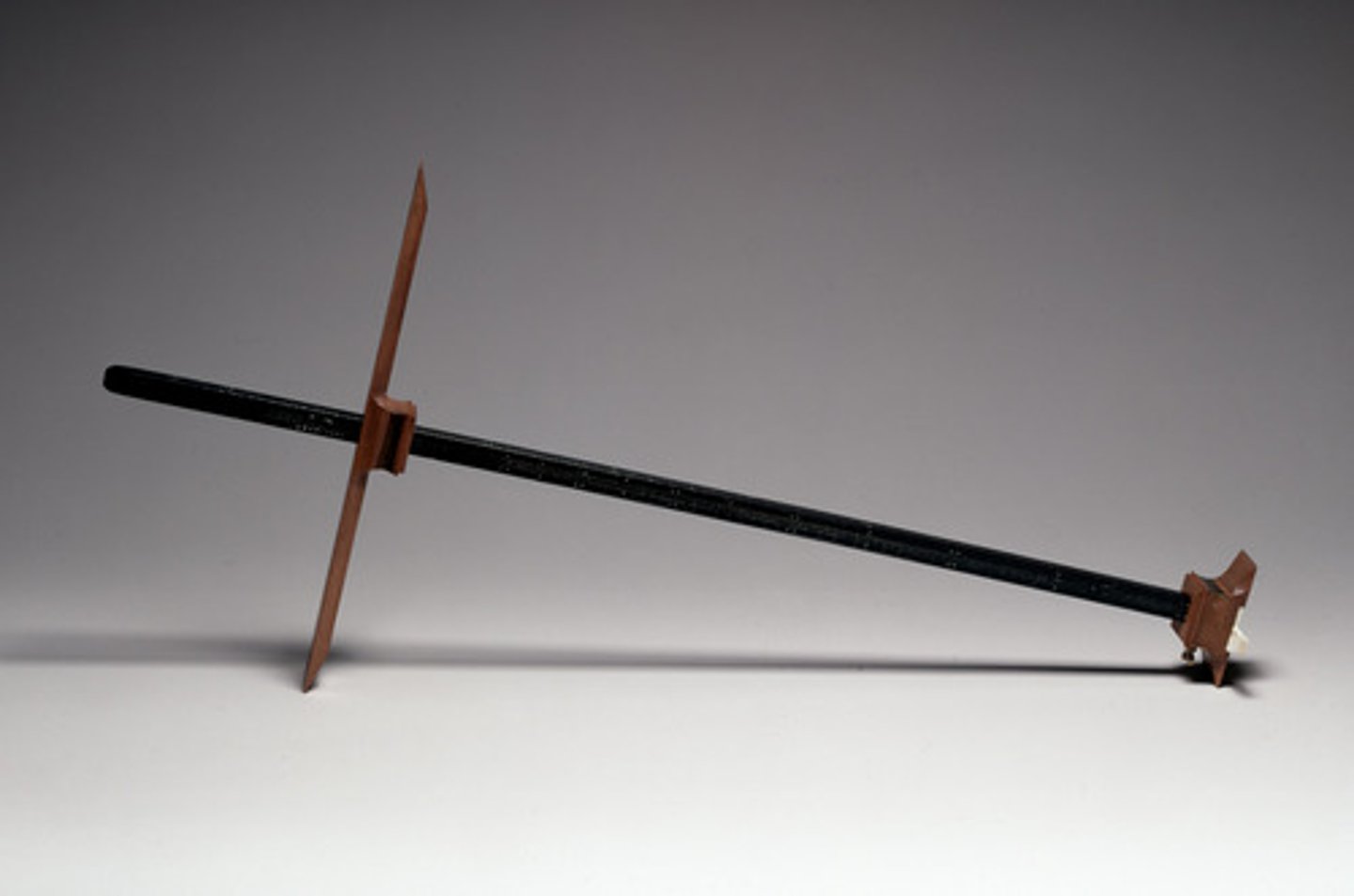
Cross Staff
Invented in the 14th century, it was a navigational tool to measure the angle between the Moon and any given star.

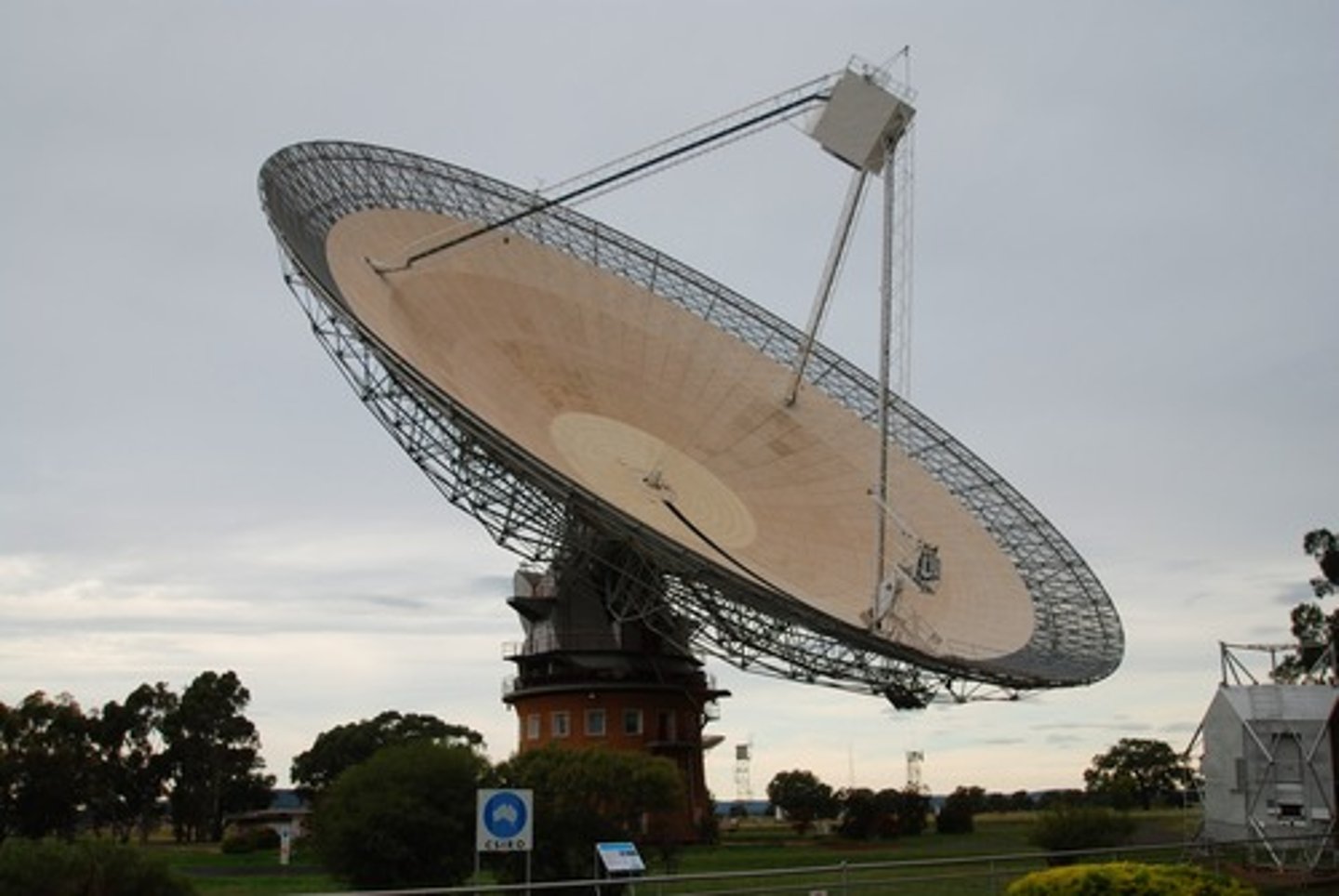
Telescope
Invented in the late 16th century, it revolutionized astronomy by allowing astronomers to see more in the night sky than they had ever possible. They revealed exciting details about nearby planetary neighbours, and of other neighbours in the solar system. As our viewing ability got better, the vast distance between objects in space became obvious. Today, powerful optical and radio telescopes, satellites and space-based telescopes have shown us the immensity of space and distance.

The Astronomical Unit (AU) is defined as
A measure of distance used to describe the position of planets relative to the Sun; 1 AU is equal to the average distance from the centre of Earth to the centre of the Sun (149 599 000 km).
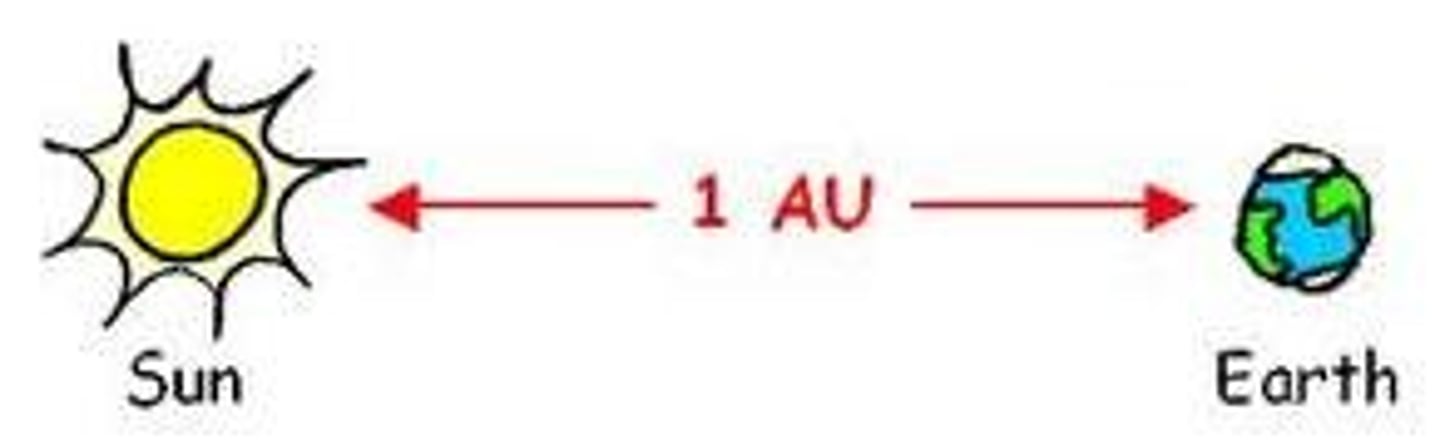
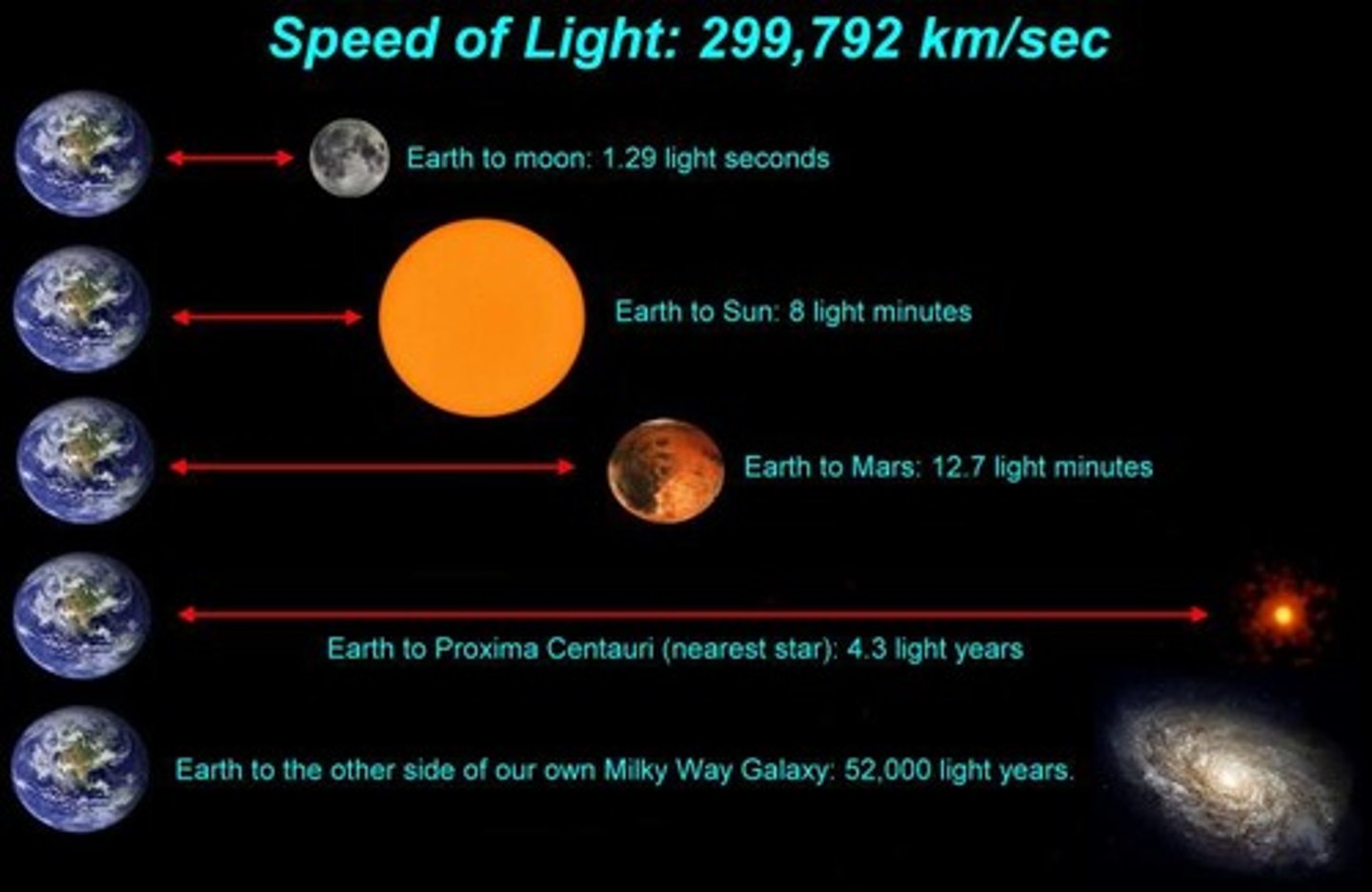
Light-year
The distance that light travels in 1 year (approximately 9.5 trillion km); used to measure distances between stars and galaxies.
Nebulae
Vast clouds of gas (mostly hydrogen) and dust in space, where stars form; nebula (singular).

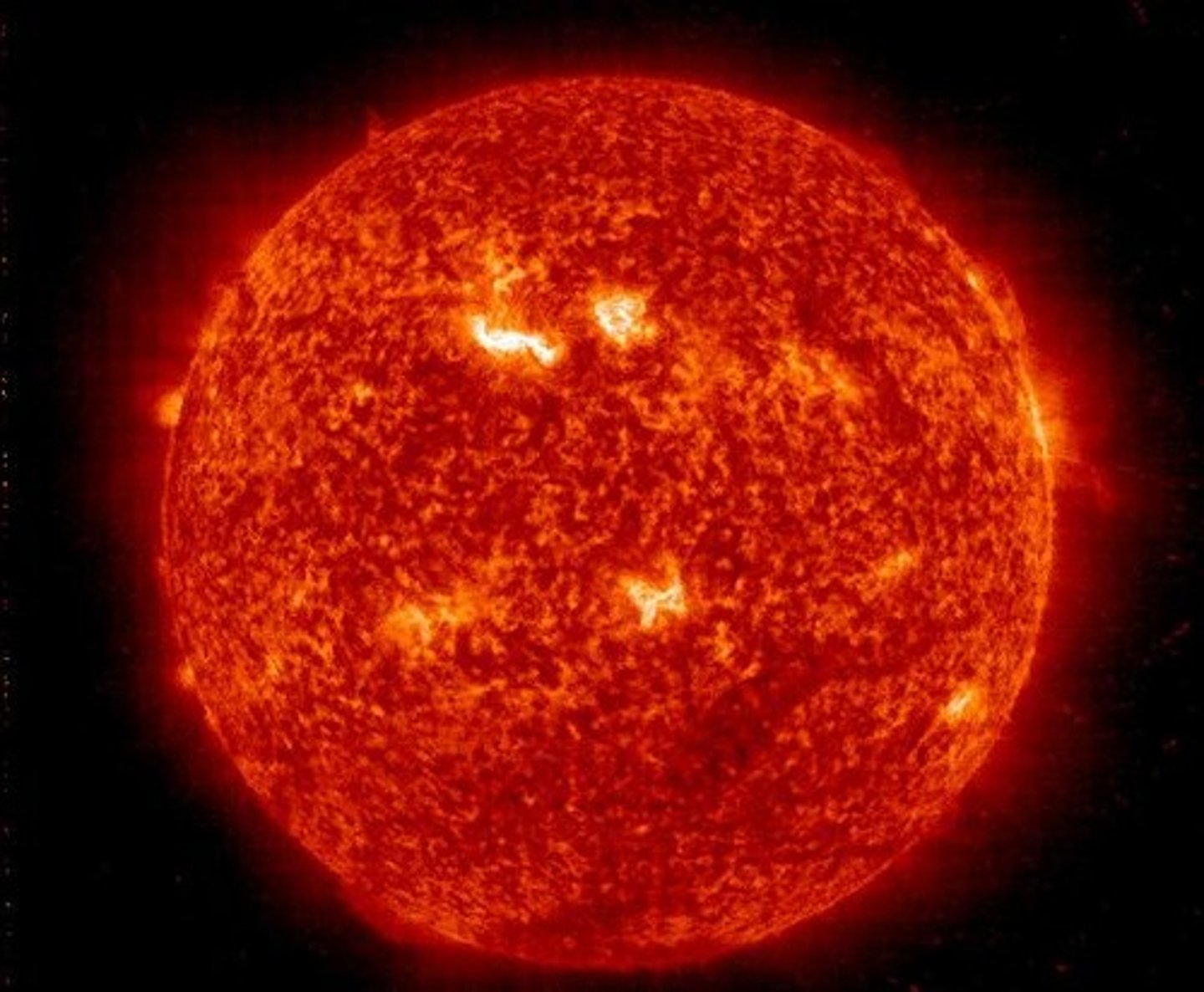
Red Giant
The stage in the life cycle of a Sun-like star during which the star increases in size and becomes very bright.

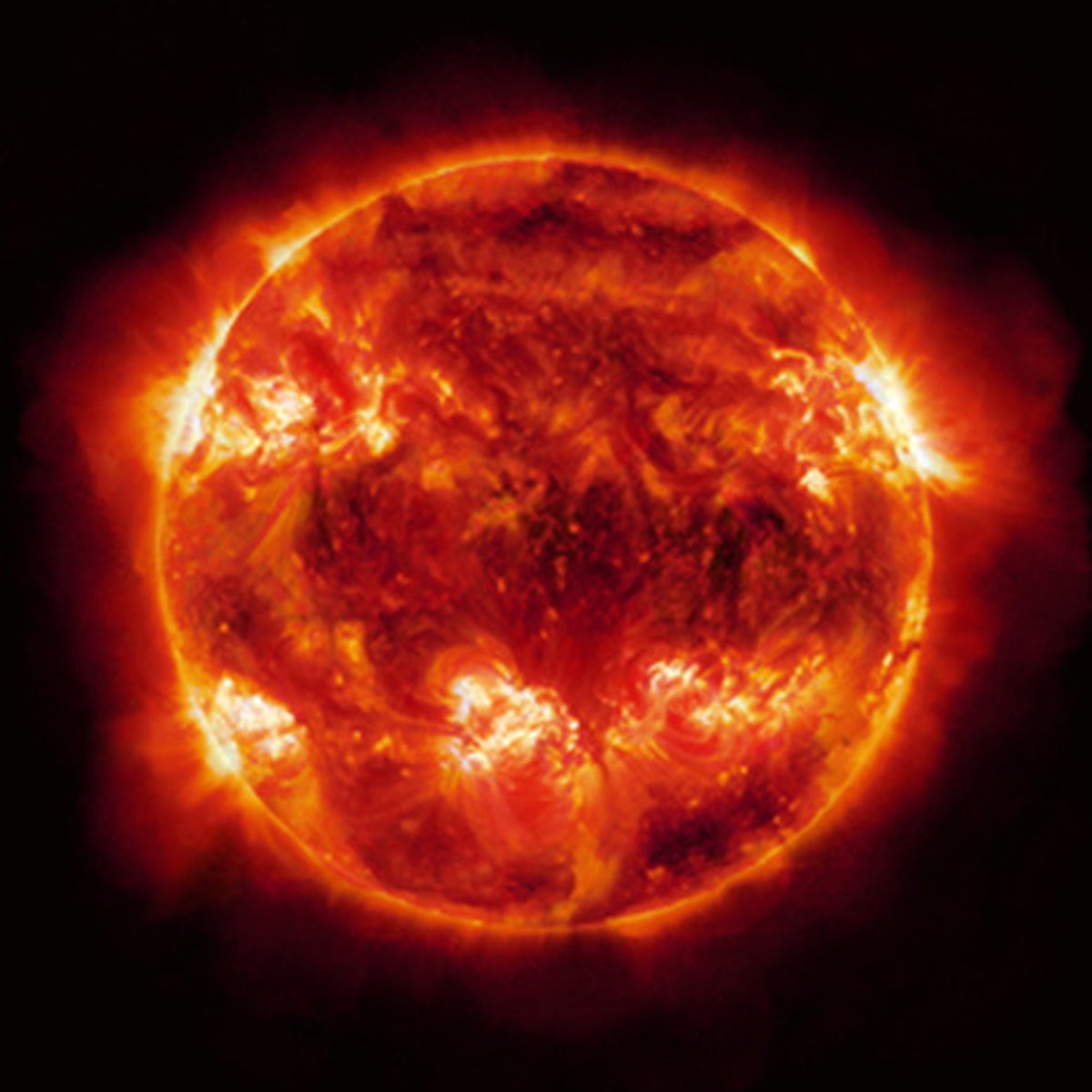
Red Supergiant
The stage in the life cycle of a massive star during which the star increases in size and becomes very bright.

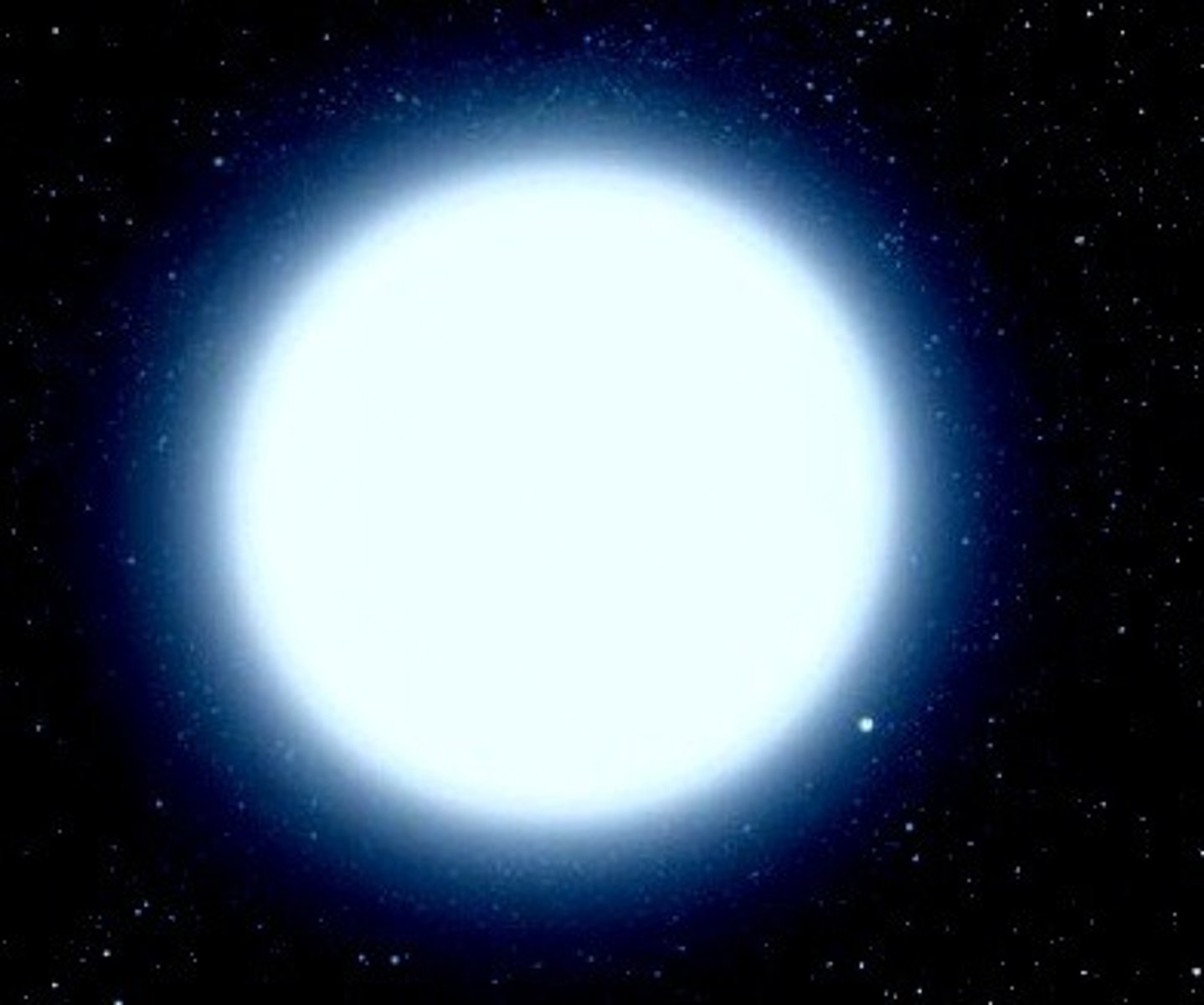
White Dwarf
One of the latter stages in the life cycle of a Sun-like star during which the star collapses; white dwarfs are hot but very faint.

Black Dwarf
The final phase in the life cycle of a Sun-like star.
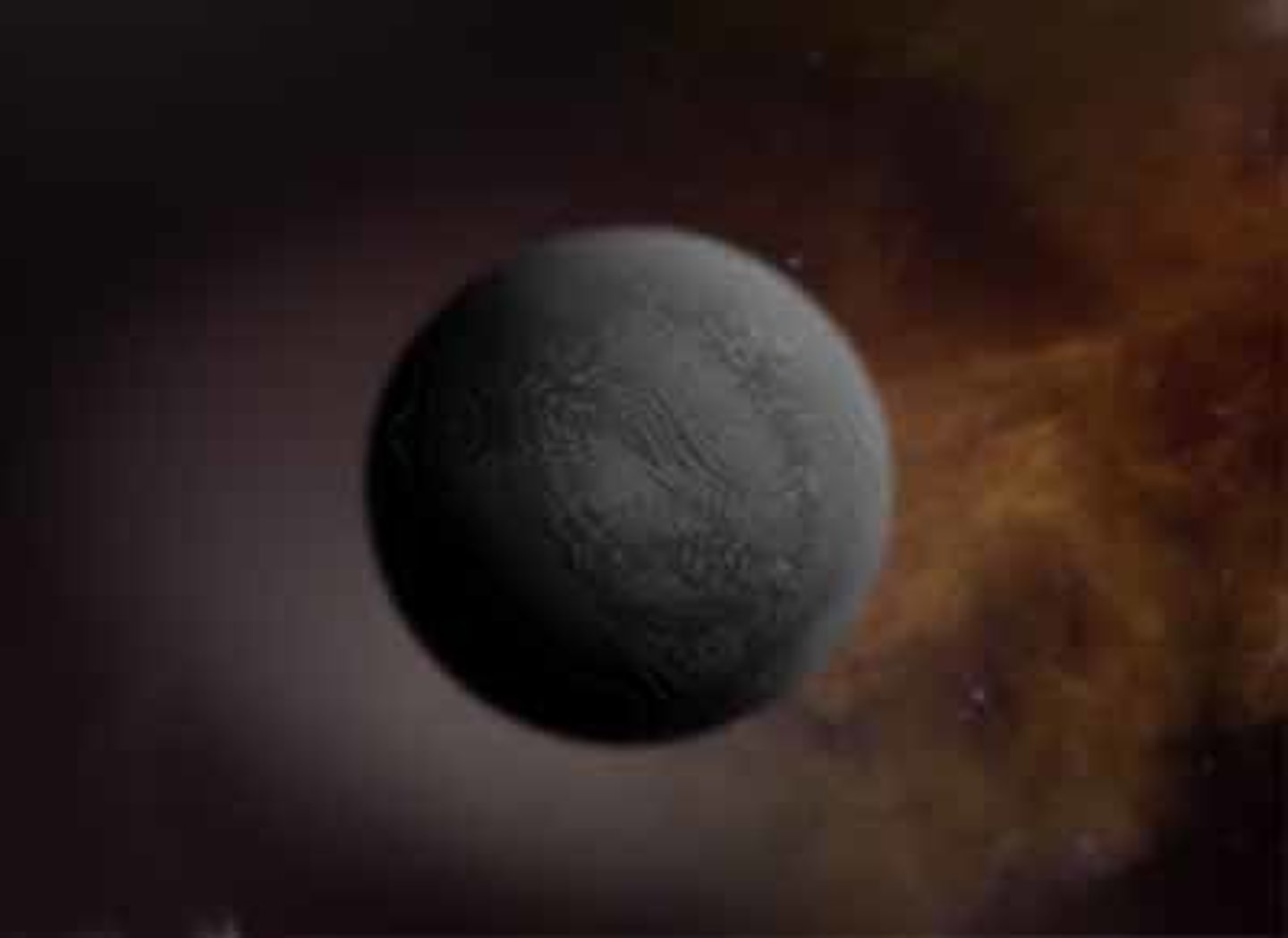

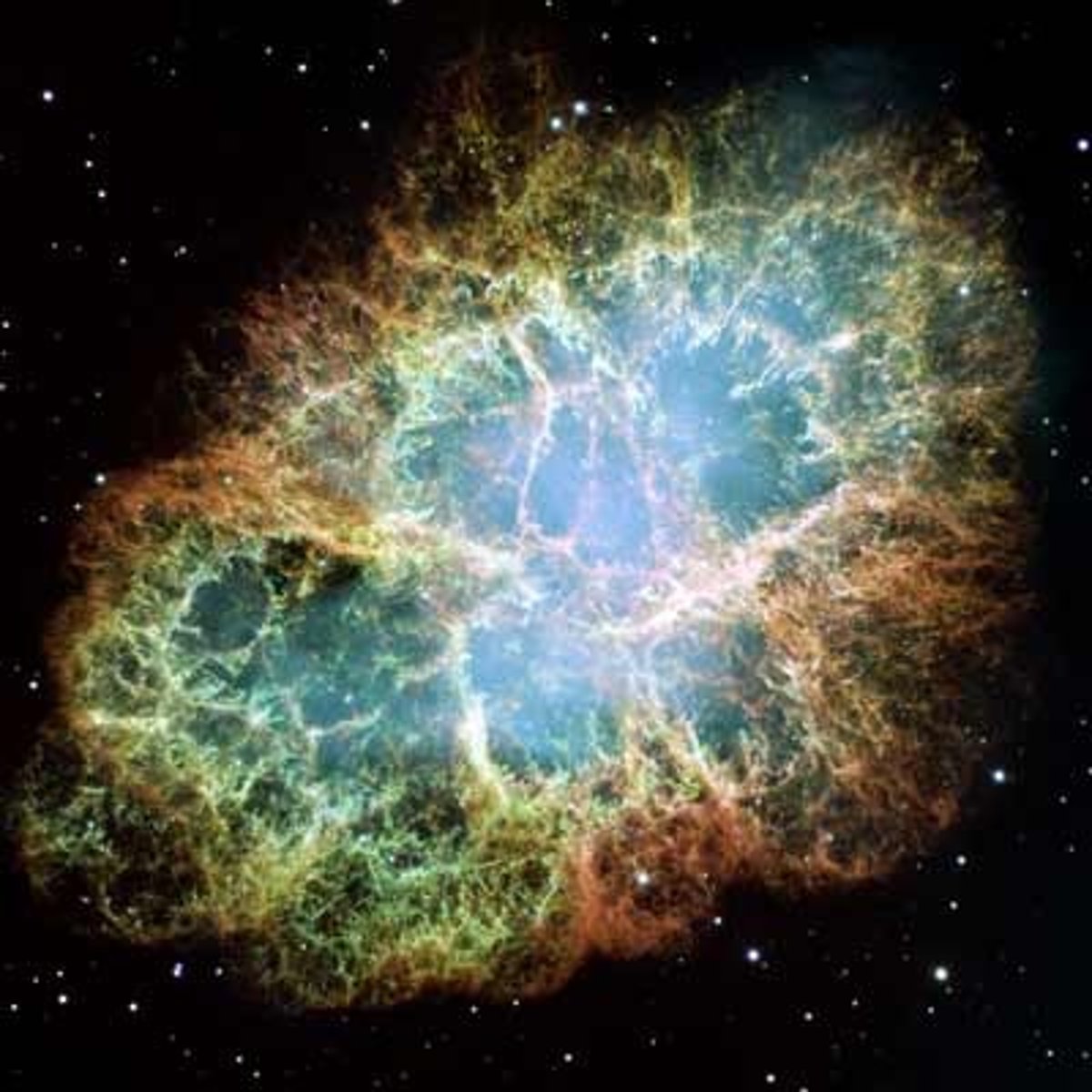
Supernova
An enormous explosion that marks the death of a massive star.

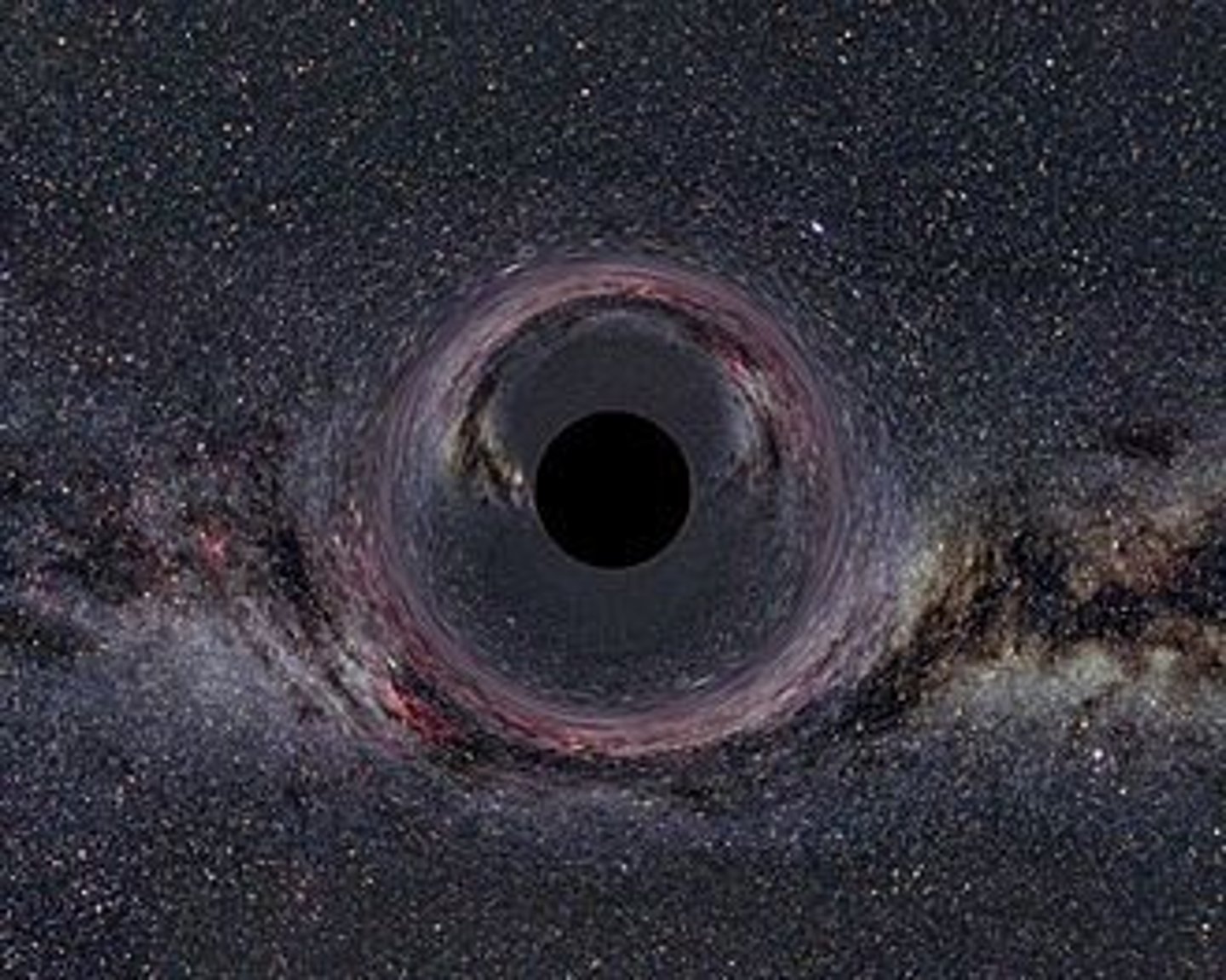
Black hole
A super-dense remnant of a supernova; an object around which gravity is so intense that even light cannot escape.

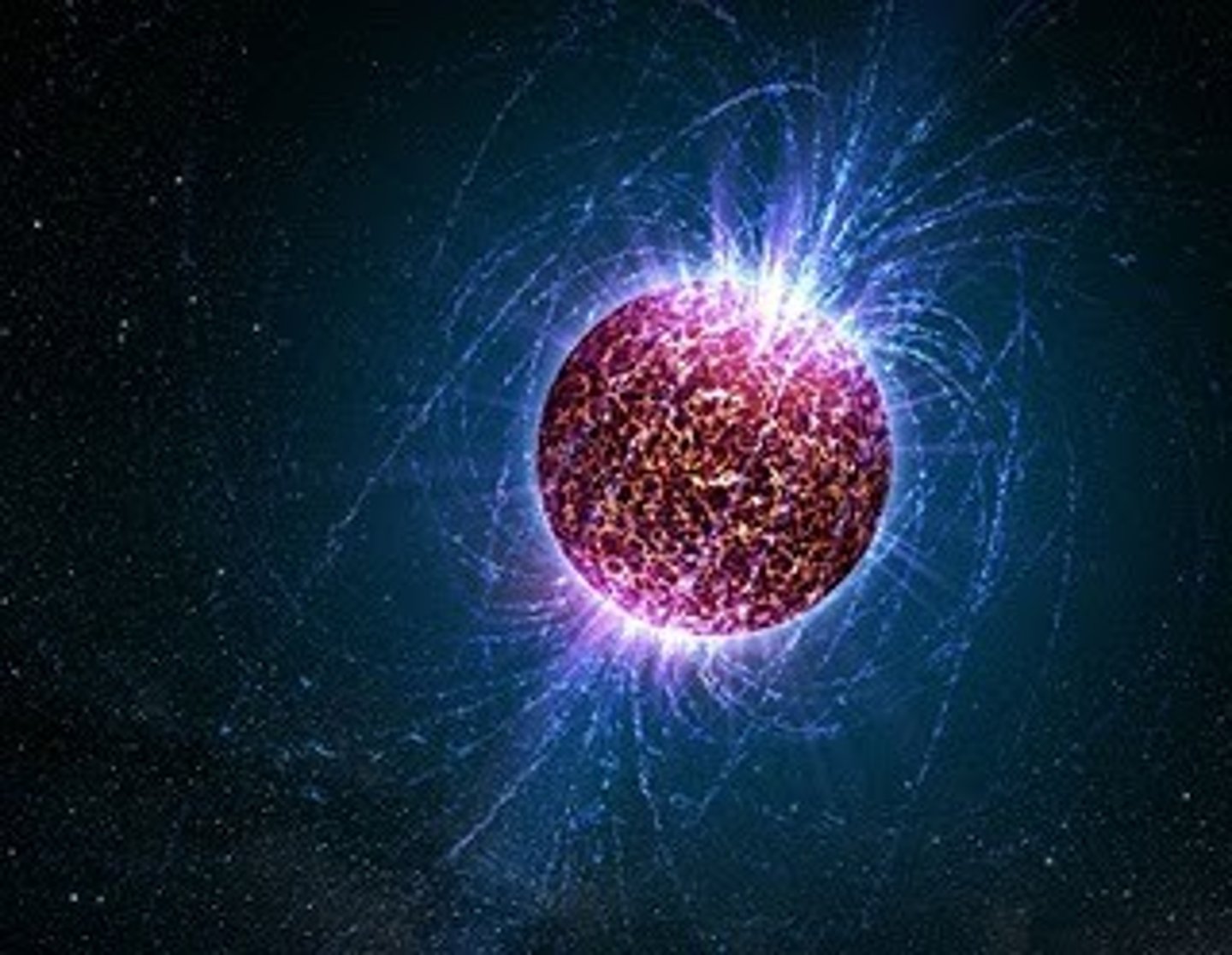
Neutron Star
A small, super-dense remnant of a supernova.

Gravity
The force of attraction between masses.
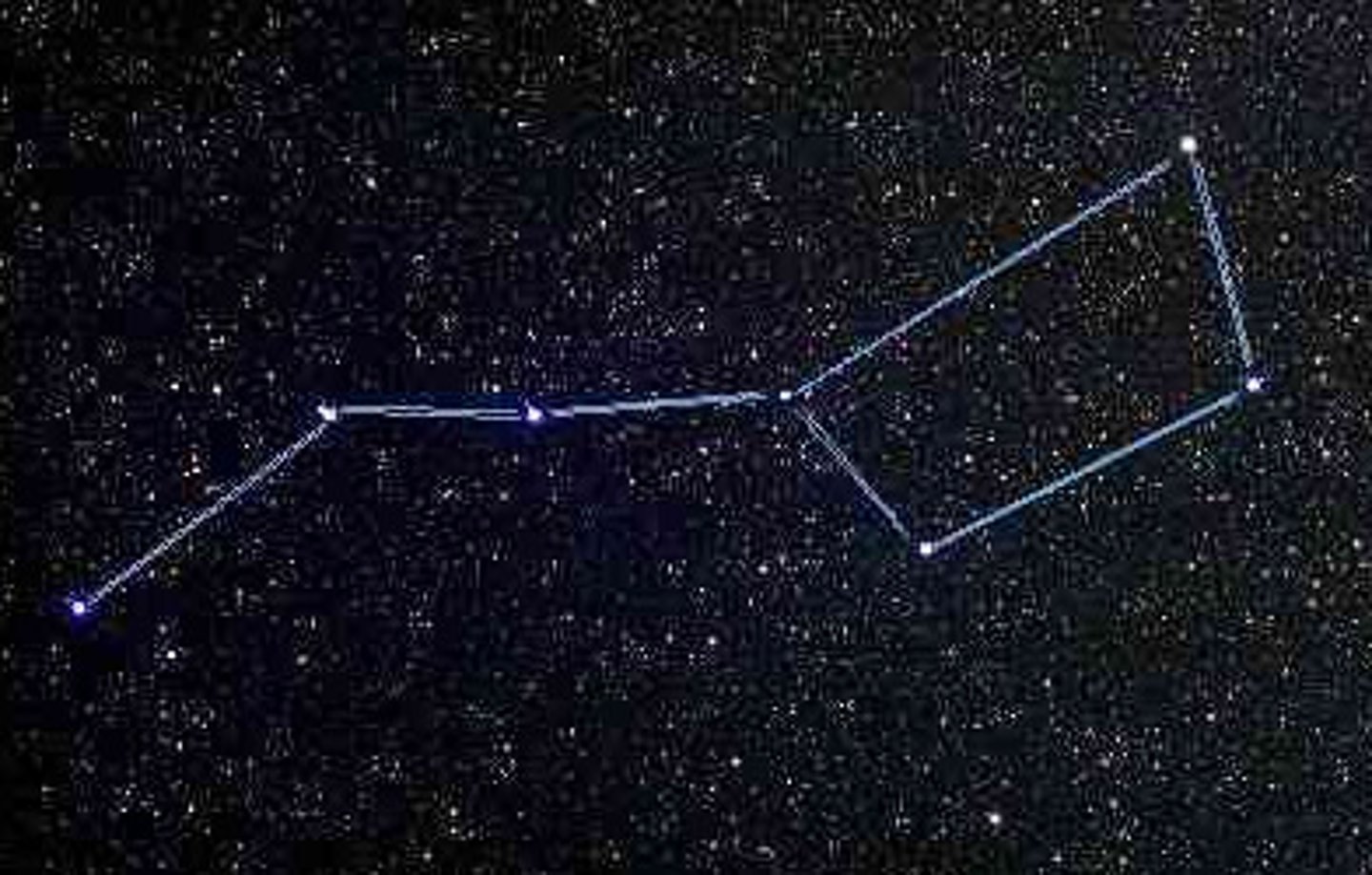
Constellation
Groups of stars that form patterns in the night sky (e.g., Ursa Major); officially there are 88 constellations.
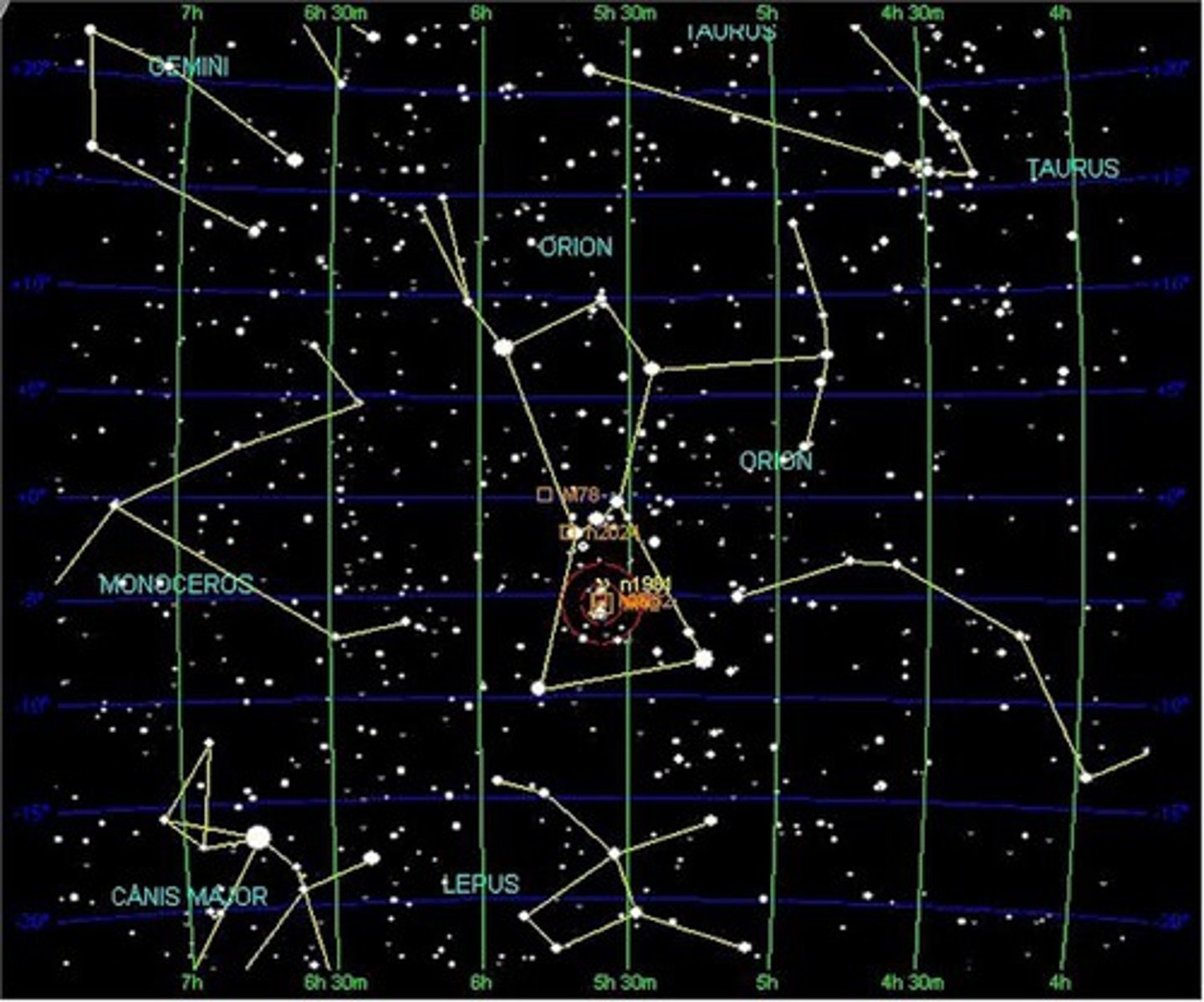
Asterisms
A distinctive star grouping that is not one of the 88 recognized constellations (e.g., the Big Dipper, which is part of the constellation Ursa Major).

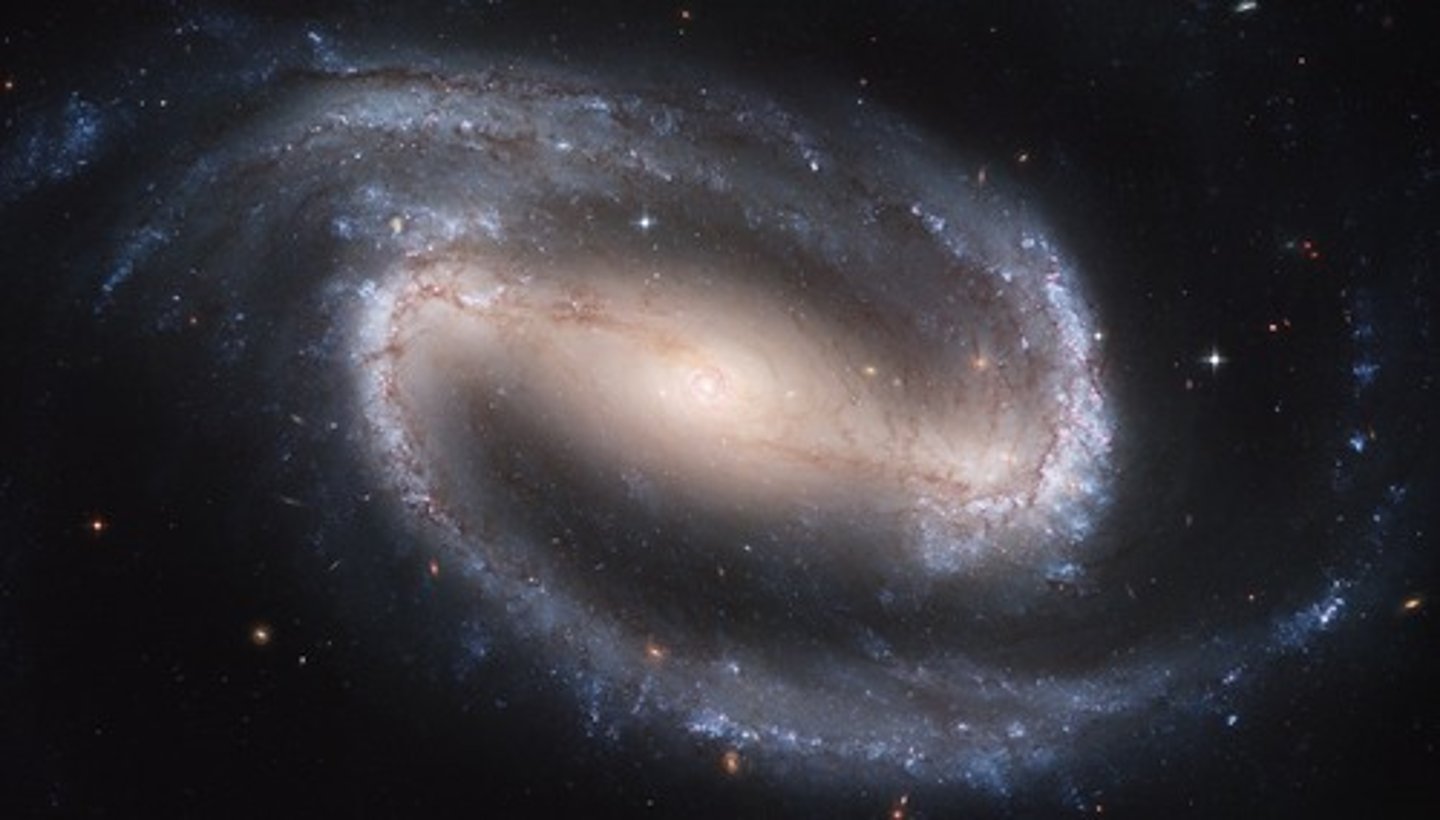
Galaxy
A groupings of millions or billions of stars, gas, and dust, held together by gravity.

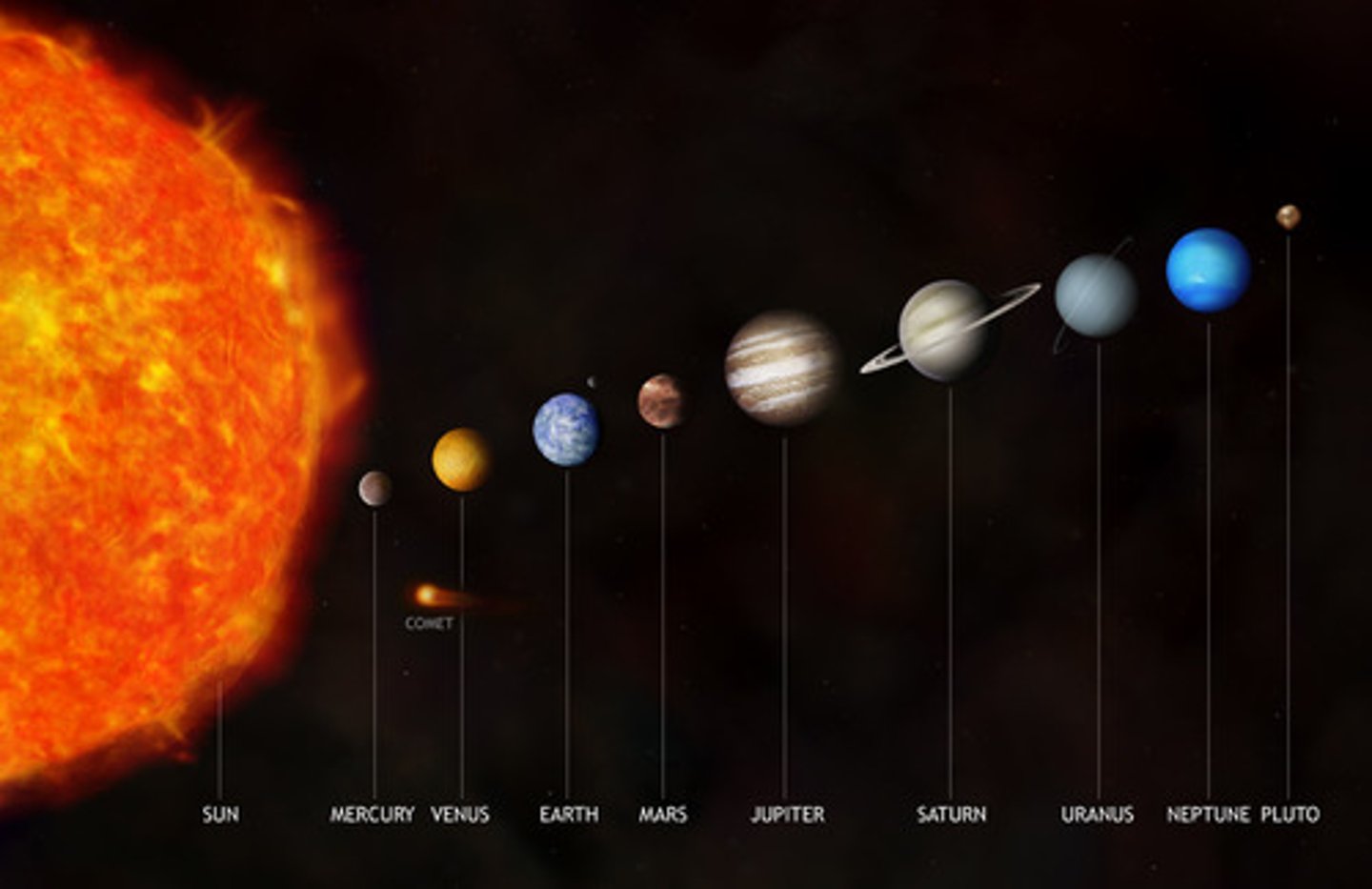
Solar System
Includes the Sun, planets, and all the other objects that revolve around the sun.

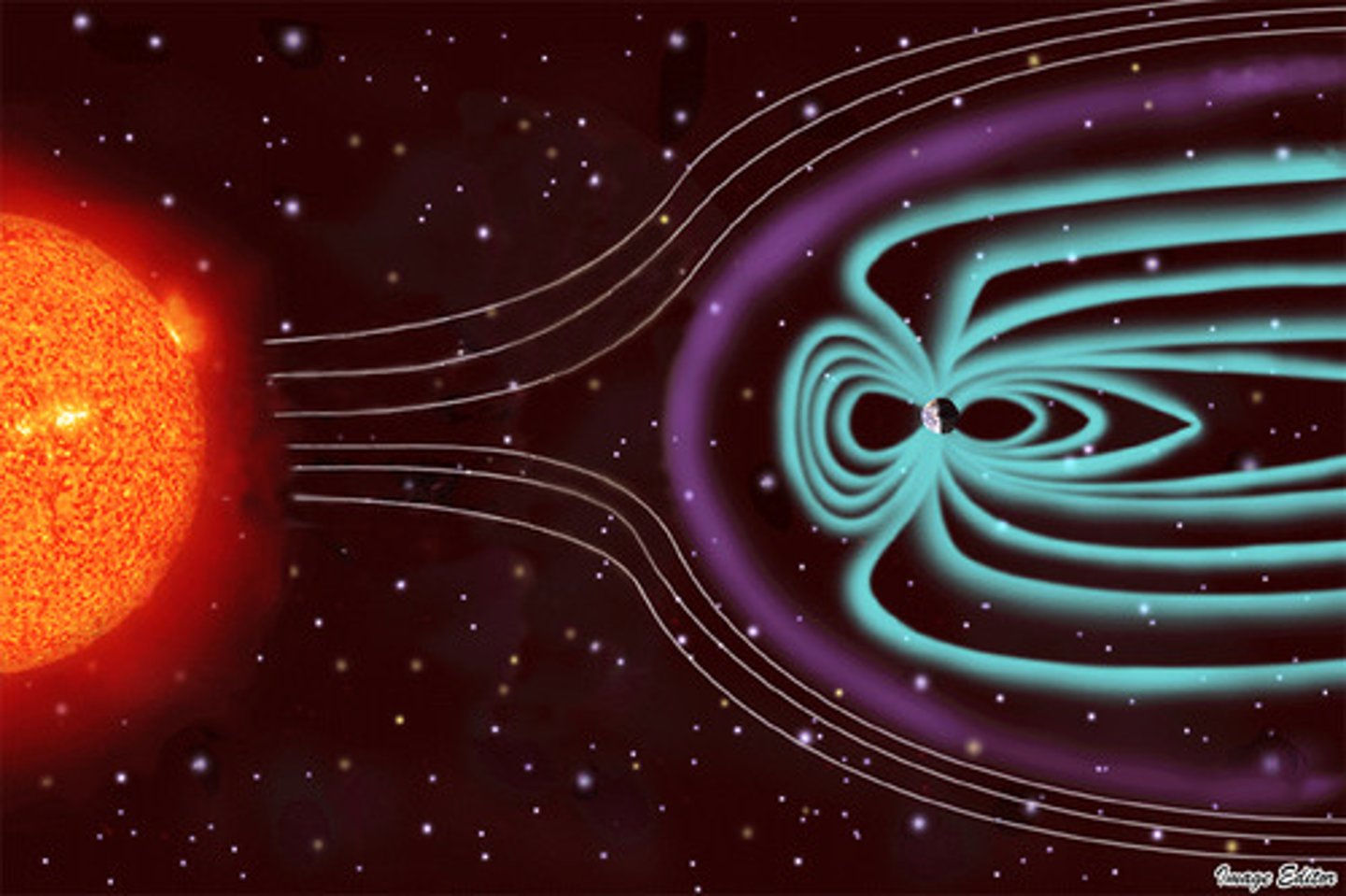
Solar Wind
Streams of electrically charged particles discharged by the Sun in every direction; solar wind passes Earth at nearly 400 km/s.

Planet
A celestial body moving in an elliptical orbit around a star.
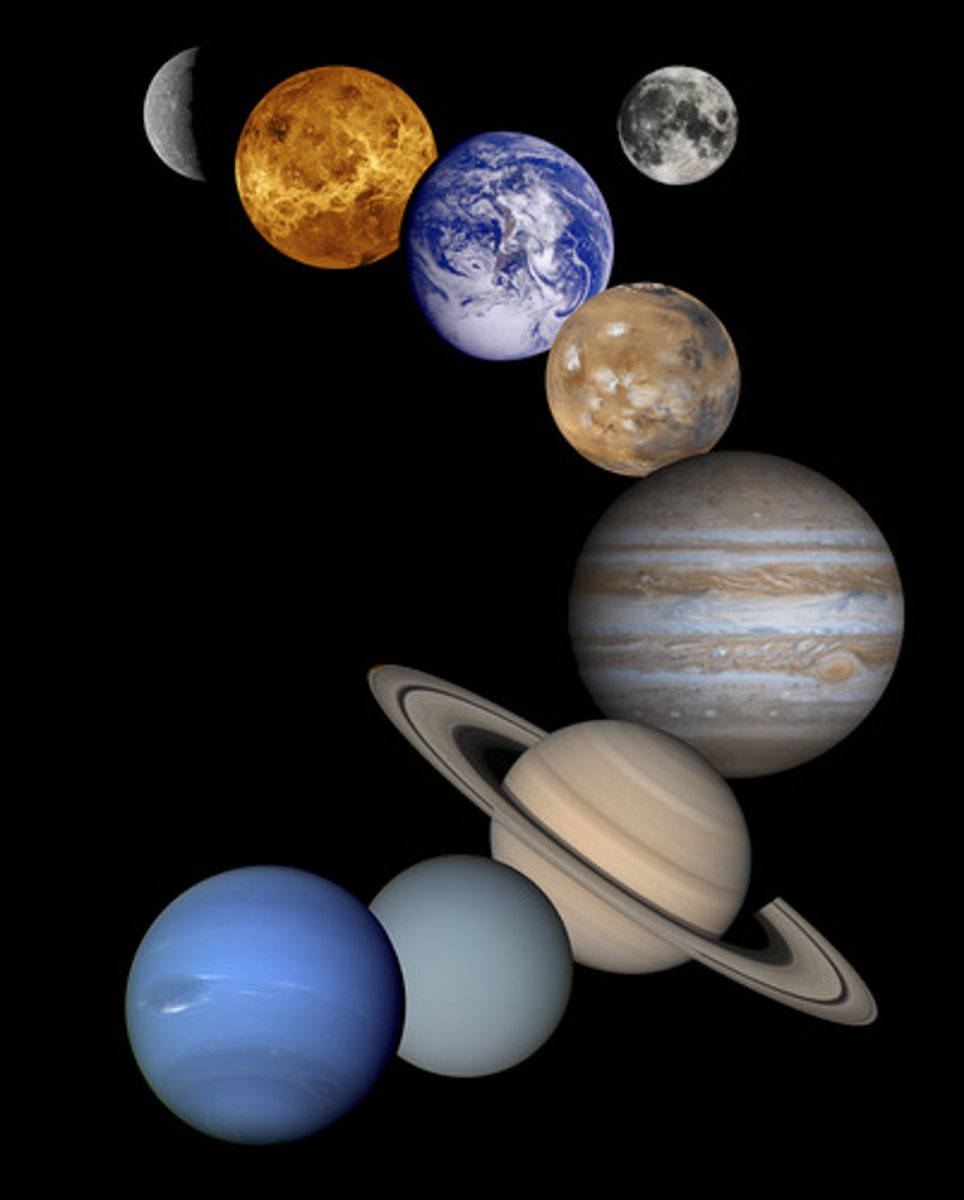

Asteroids
Small, rocky bodies orbiting the Sun and lying mainly in a narrow belt between Mars and Jupiter.
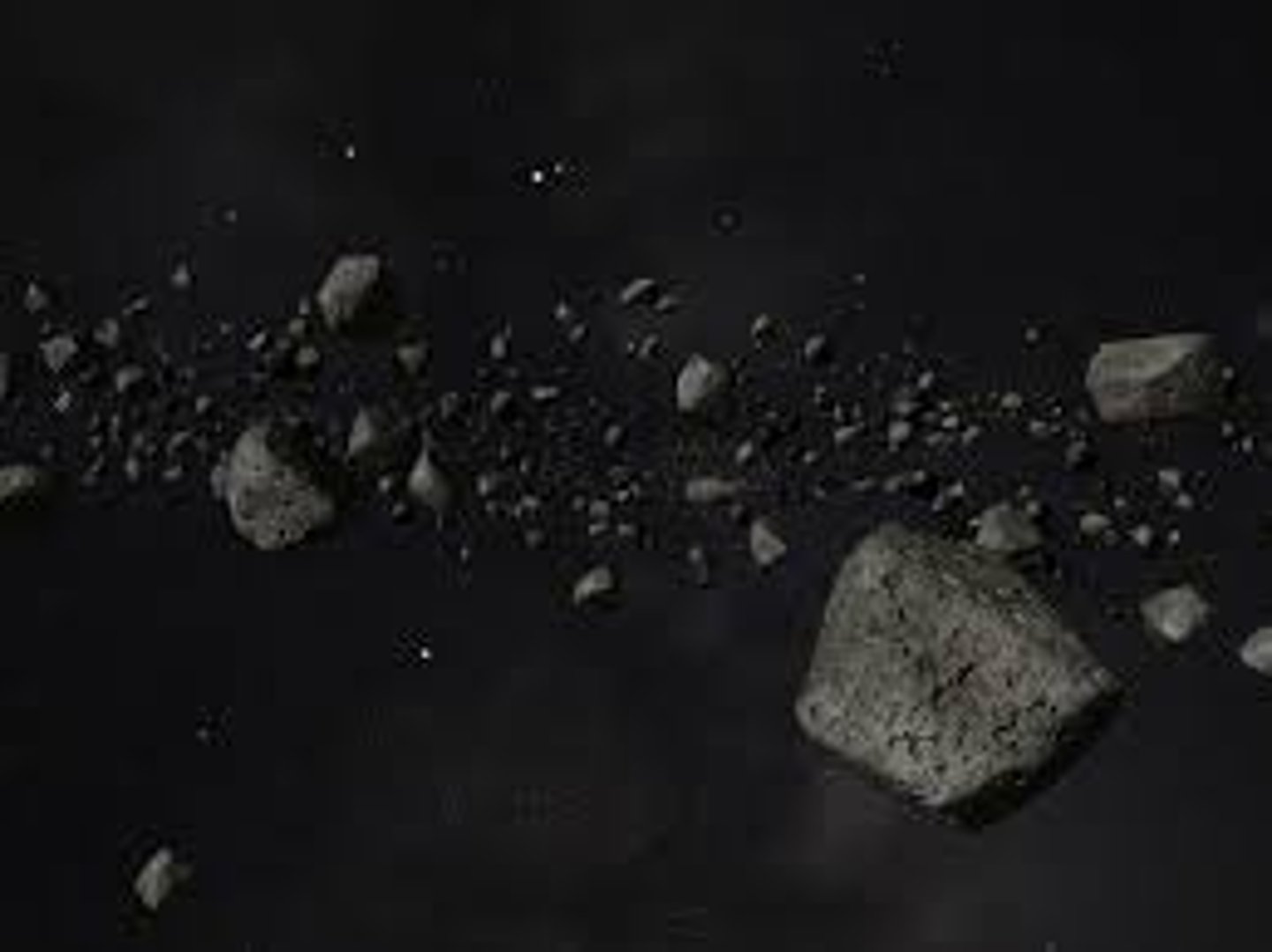

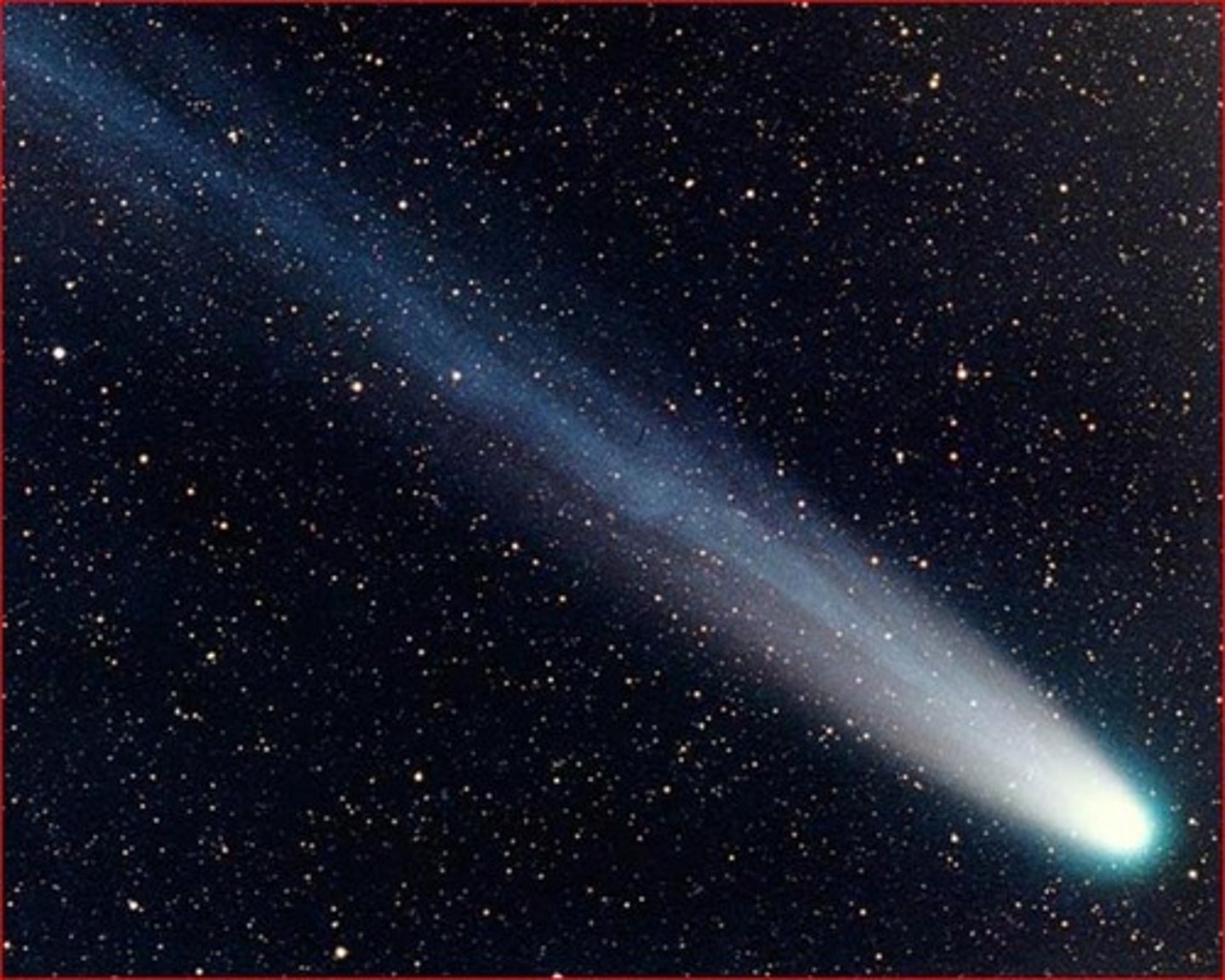
Comet
A celestial body composed of dust and ice that orbits the Sun; it has a bright centre and long, faint tail that always points away from the Sun.

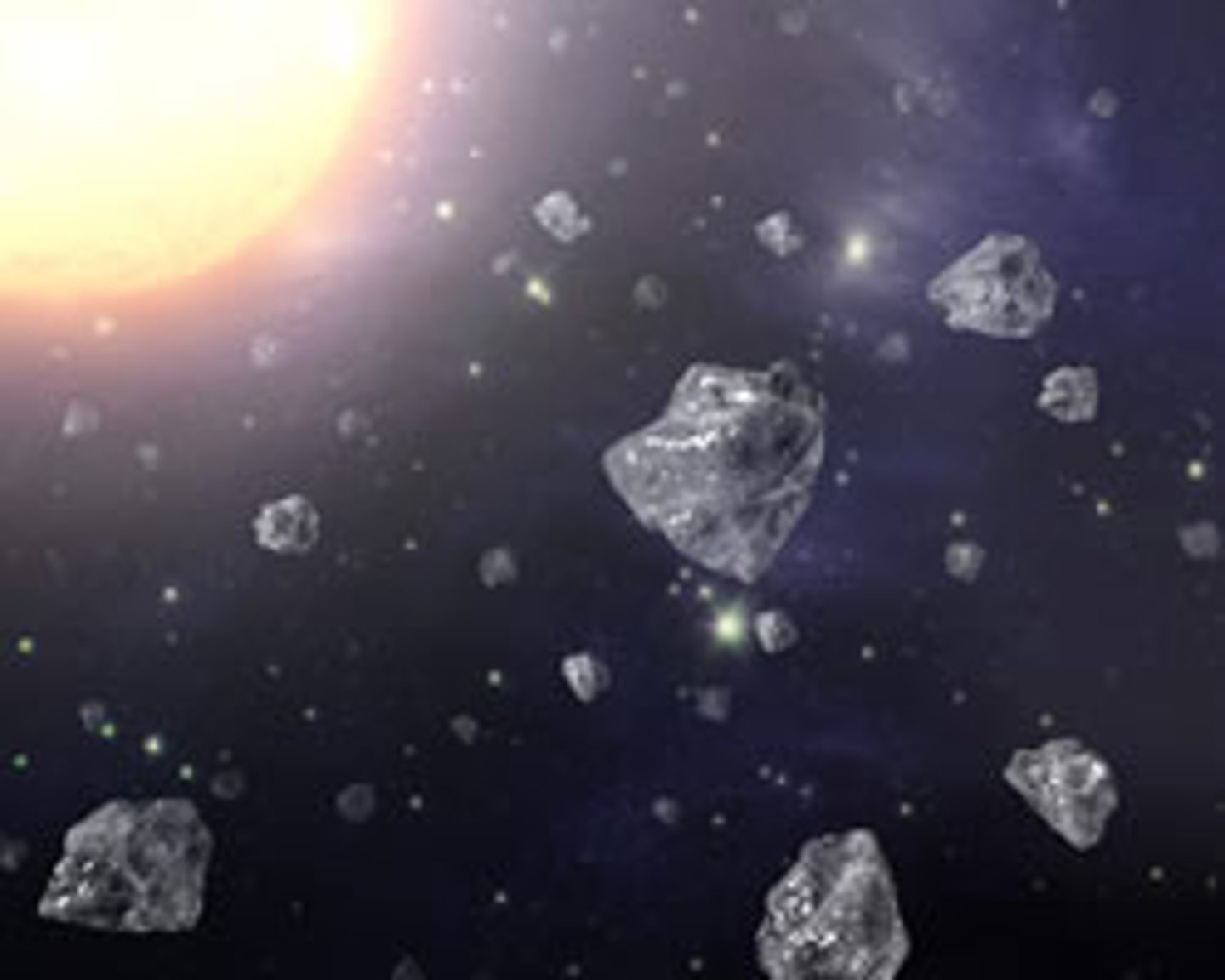
Meteoroid
A solid body, usually a fragment of rock or metal, travelling in space with no particular path.

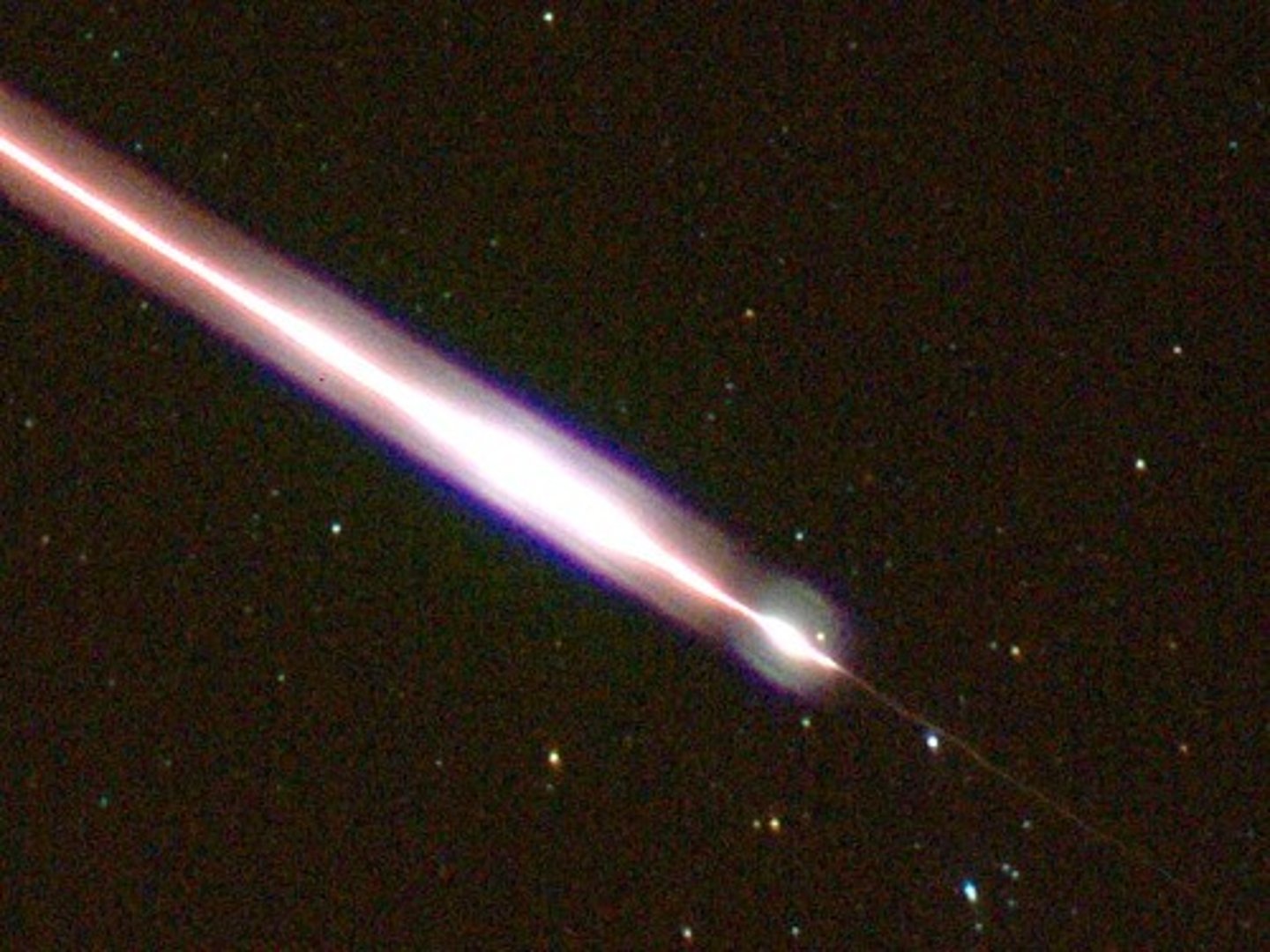
Meteor
A meteoroid that enters Earth's atmosphere, where the heat of friction causes it to glow brightly.

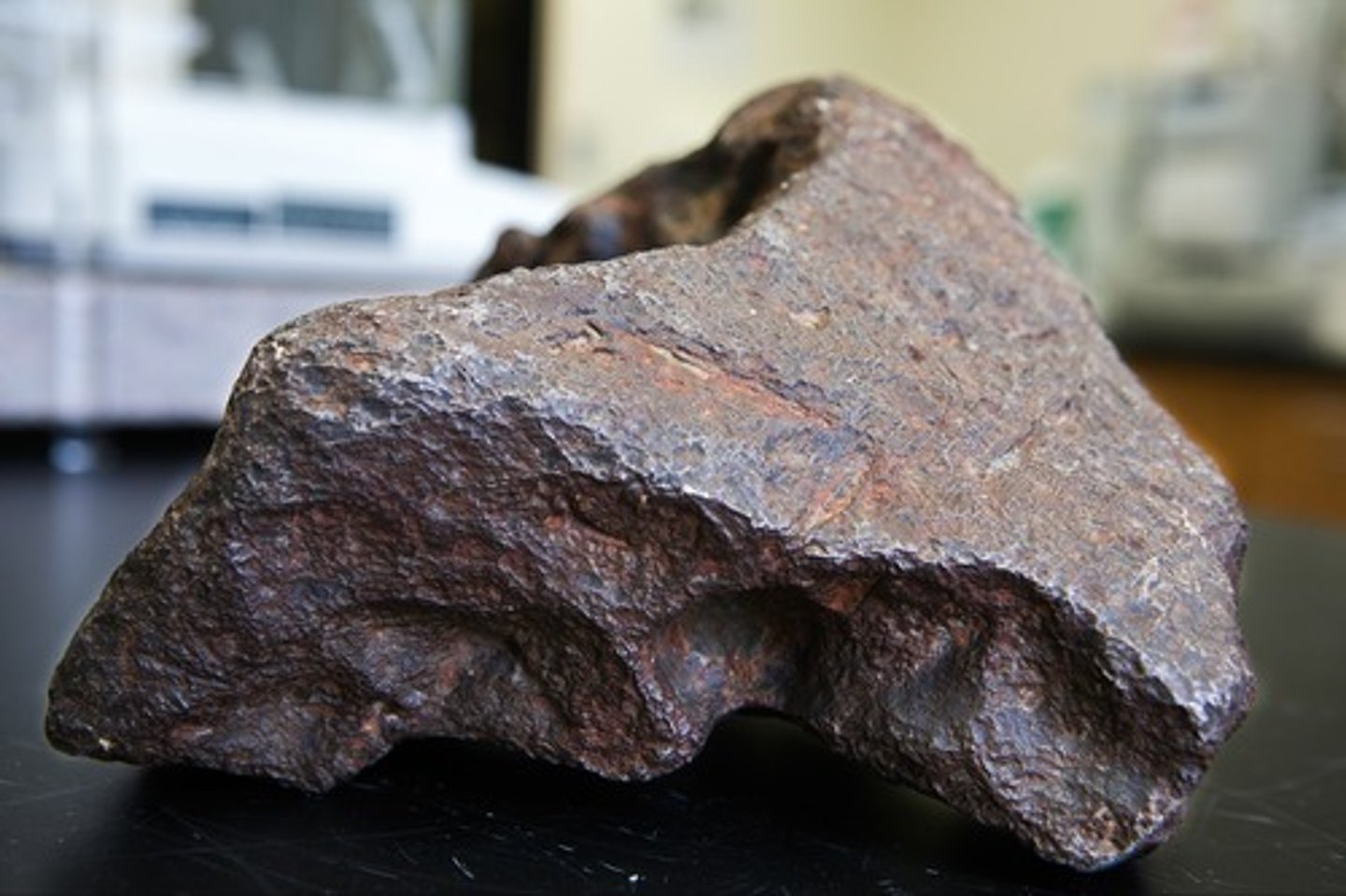
Meterorite
The remains of a meteor that do not burn up completely and so last long enough to hit Earth's surface.

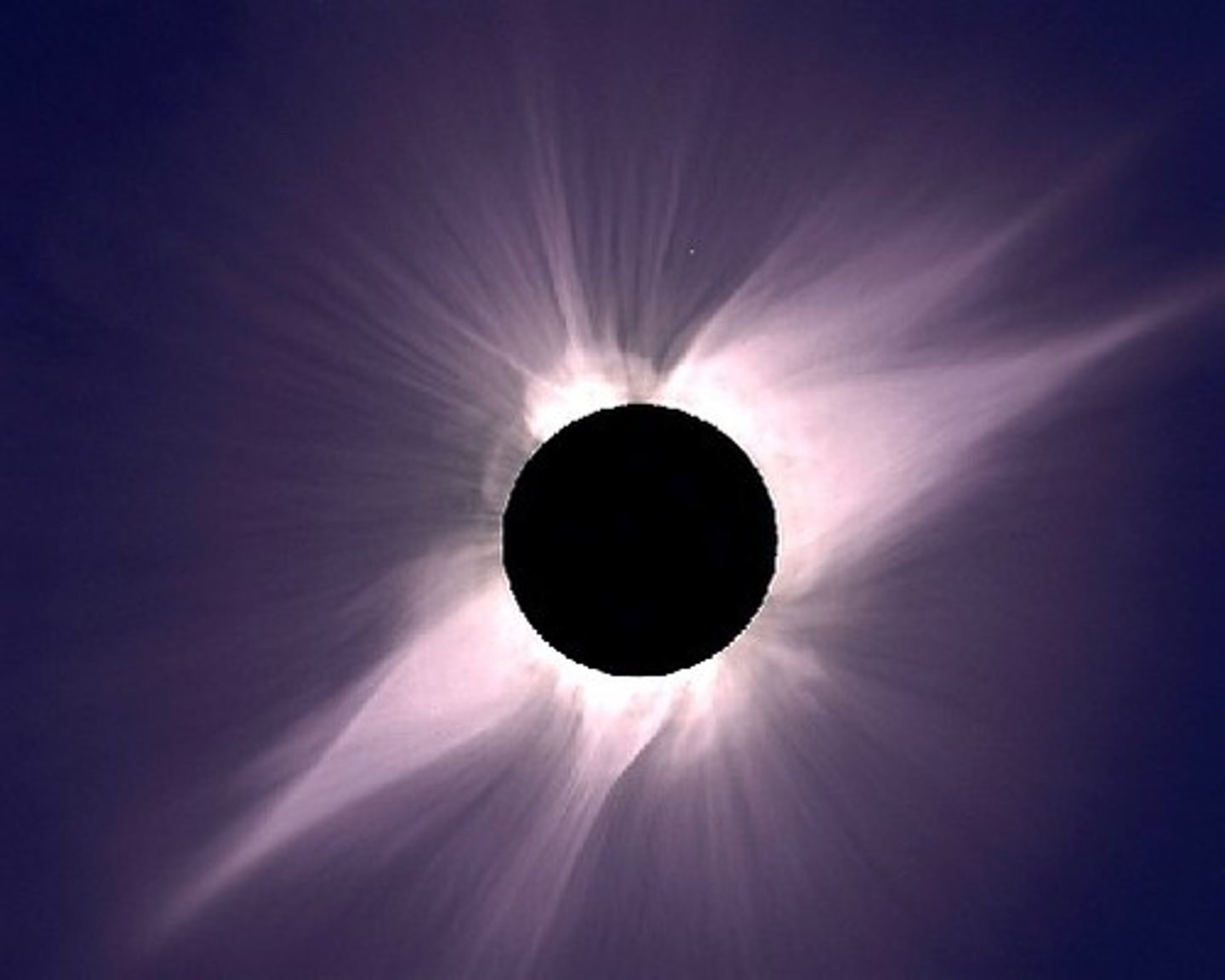
Eclipse
An obscuring of the light from one celestial body by the passage of another between it and the observer or between it and its source of illumination. A solar eclipse is when the Moon casts a shadow on Earth. A lunar eclipse is when Earth casts its shadow over the Moon.

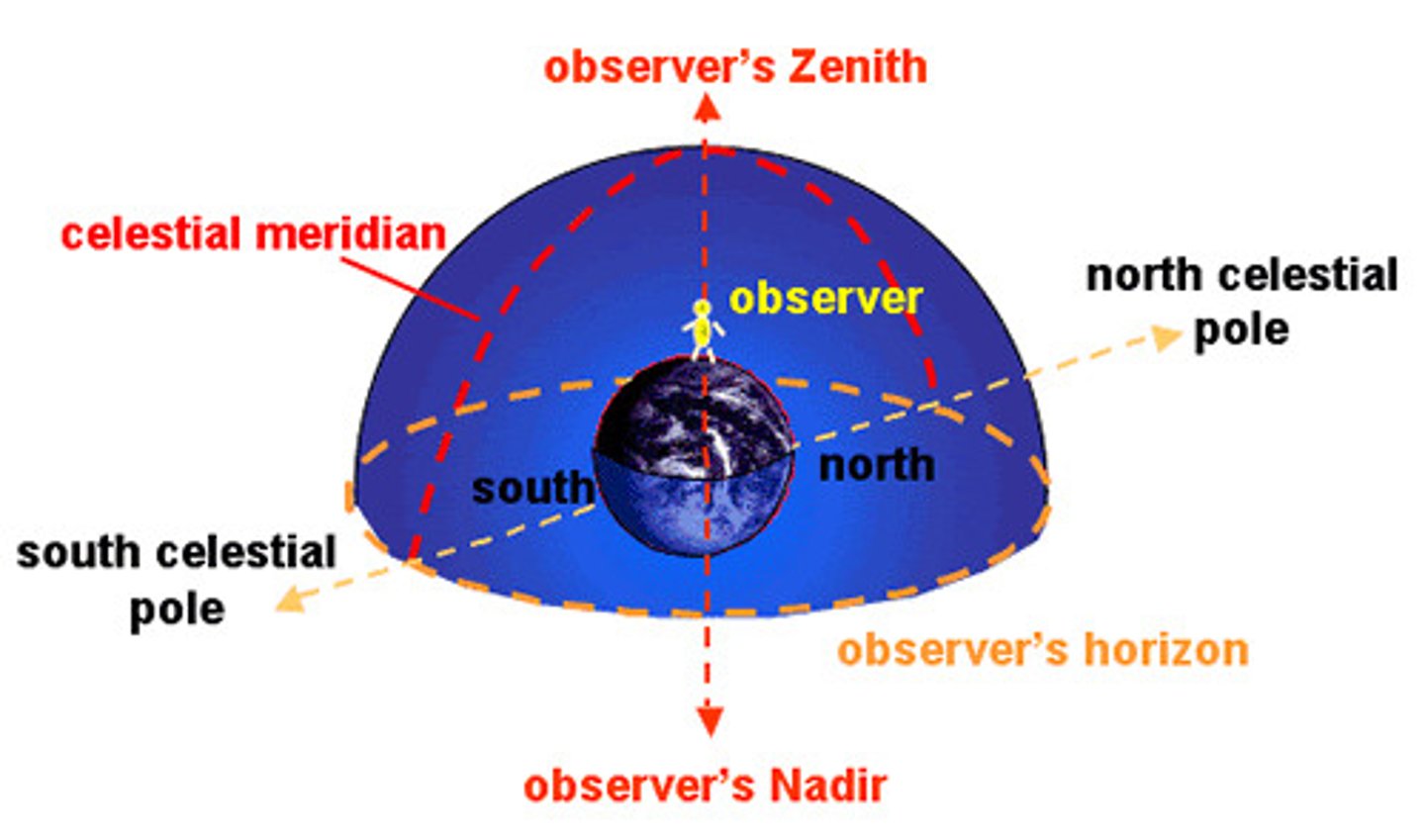
Azimuth
The angle between the most northerly point of the horizon and the point directly below a celestial body; also the horizontal angle or direction of a compass bearing.
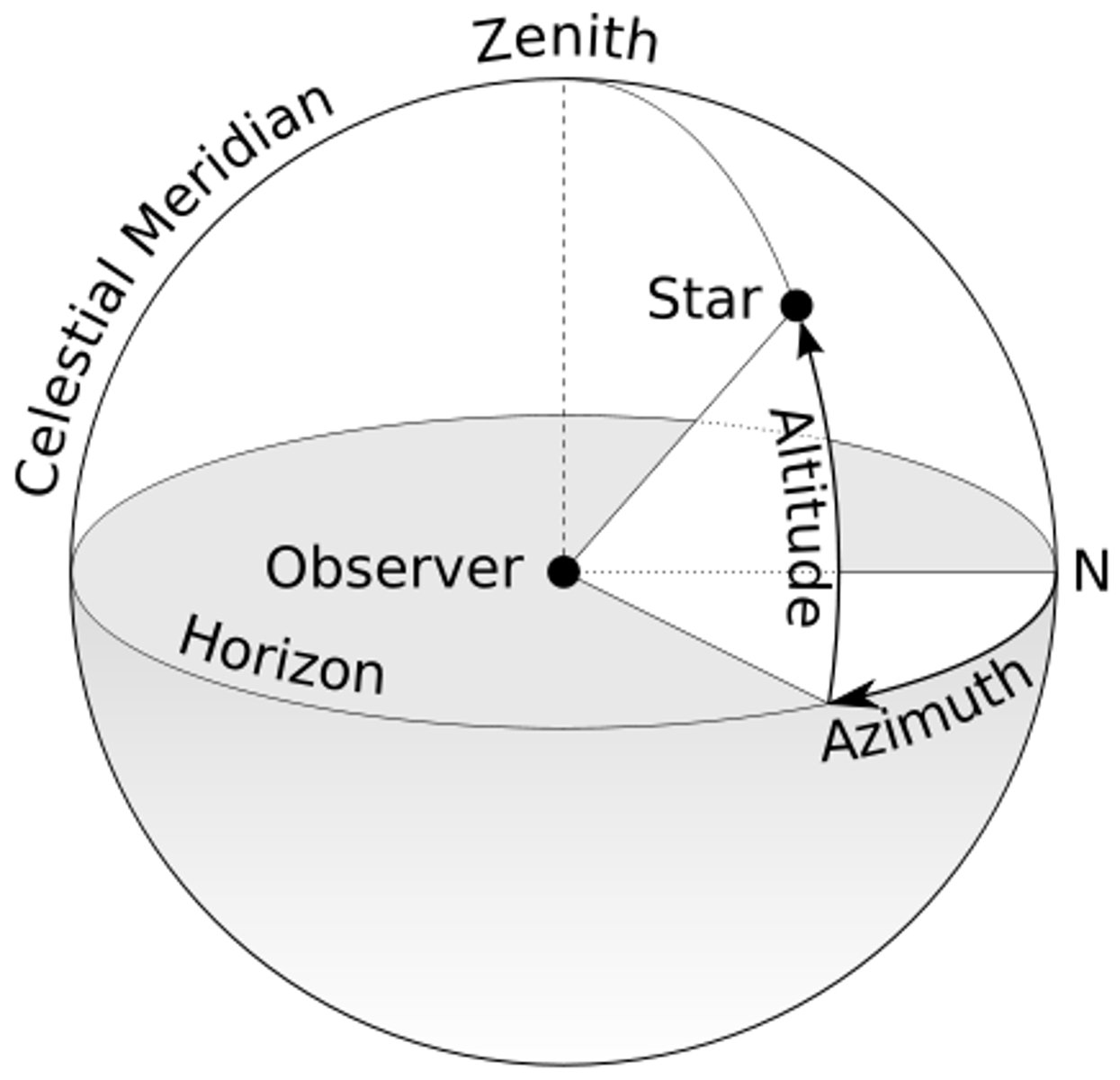
Altitude
The height of a celestial body above the horizon, ranging from 0 at sea level to 90° straight up.

Zenith
The highest point in the sky directly overhead.
Ecliptic
The apparent path of the Sun and planets through the stars during the year, as viewed from Earth.
Rocketeer
A person who works with space rockets; a rocket enthusiast.

Archytas
Greek mathematician that in around 400 B.C. used escaping steam to propel a model pigeon along wires.

Sputnik
A Soviet artificial satellite launched on October 4, 1957. It is the Russian word for satellite. With the size of a basketball, it marked the beginning of the satellite age.

Alouette 1
A satellite launched by Canada on September 29, 1962, the 3rd nation in the world to do this.

Payload
Refers to the materials needed for the flight, including crew cabins, food, water, air and people.
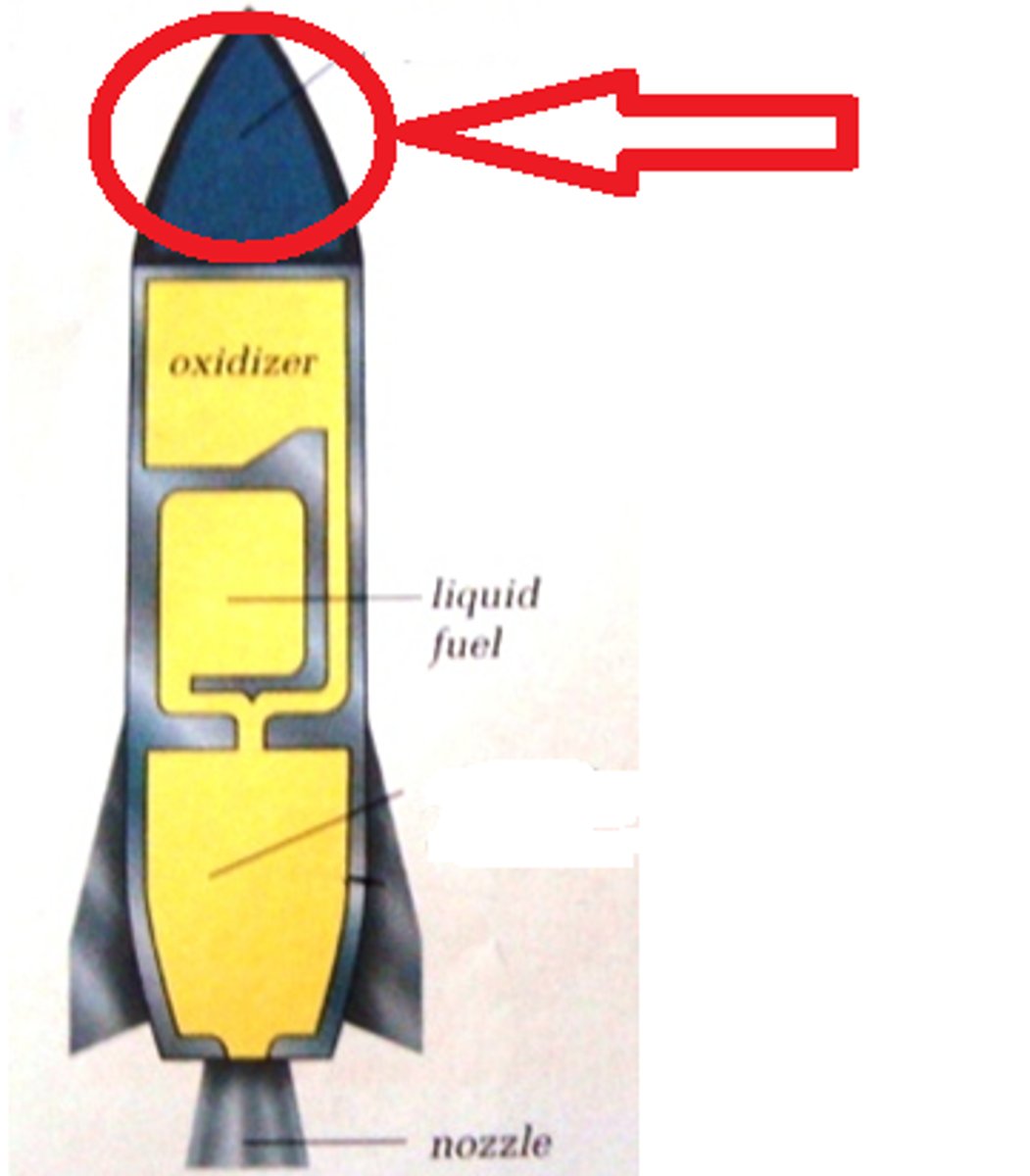
Combustion Chamber
An enclosed container in which fuel and air are ignited, causing the gases to expand and leave as an exhaust.
Nozzle
In a rocket, it is used to accelerate hot exhaust to produce thrust. Generally, nozzles direct or modify the flow of a fluid (a liquid or gas).
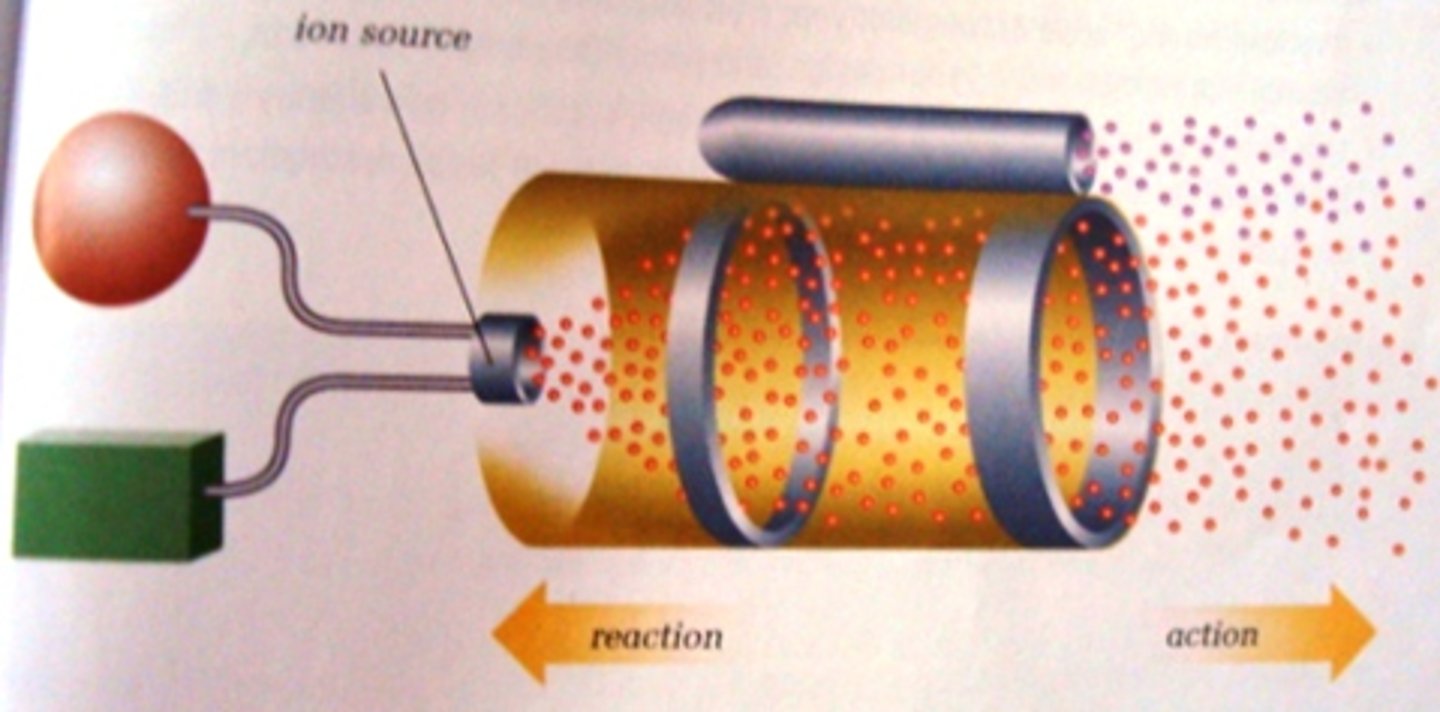
Ion Drive
Engines that use xenon gas instead of chemical fuels. The xenon is electrically charged, accelerated, and then emitted as exhaust. This pushes the spacecraft in the direction opposite to the emission. Trust is 10 000 times weaker than chemical fueled rockets. However, the thrust lasts an extremely long time.
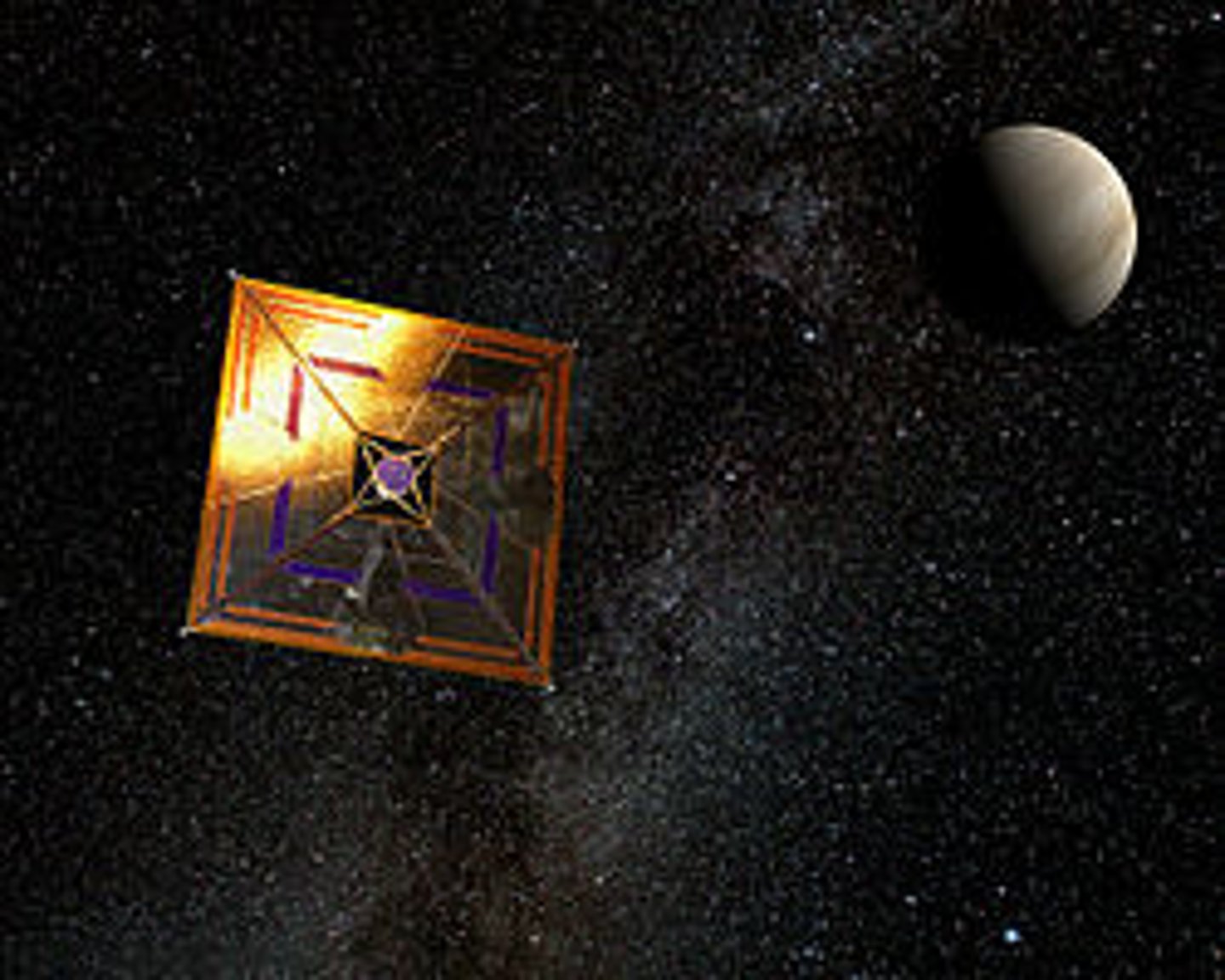
Solar Sail
Similar to propelling boats with wind sails. Solar sails use the Sun's light instead of air currents for energy. The Sun emits electromagnetic energy in the form of photons. WHen these photons hit the sail, the energy transmitted causes it to move.

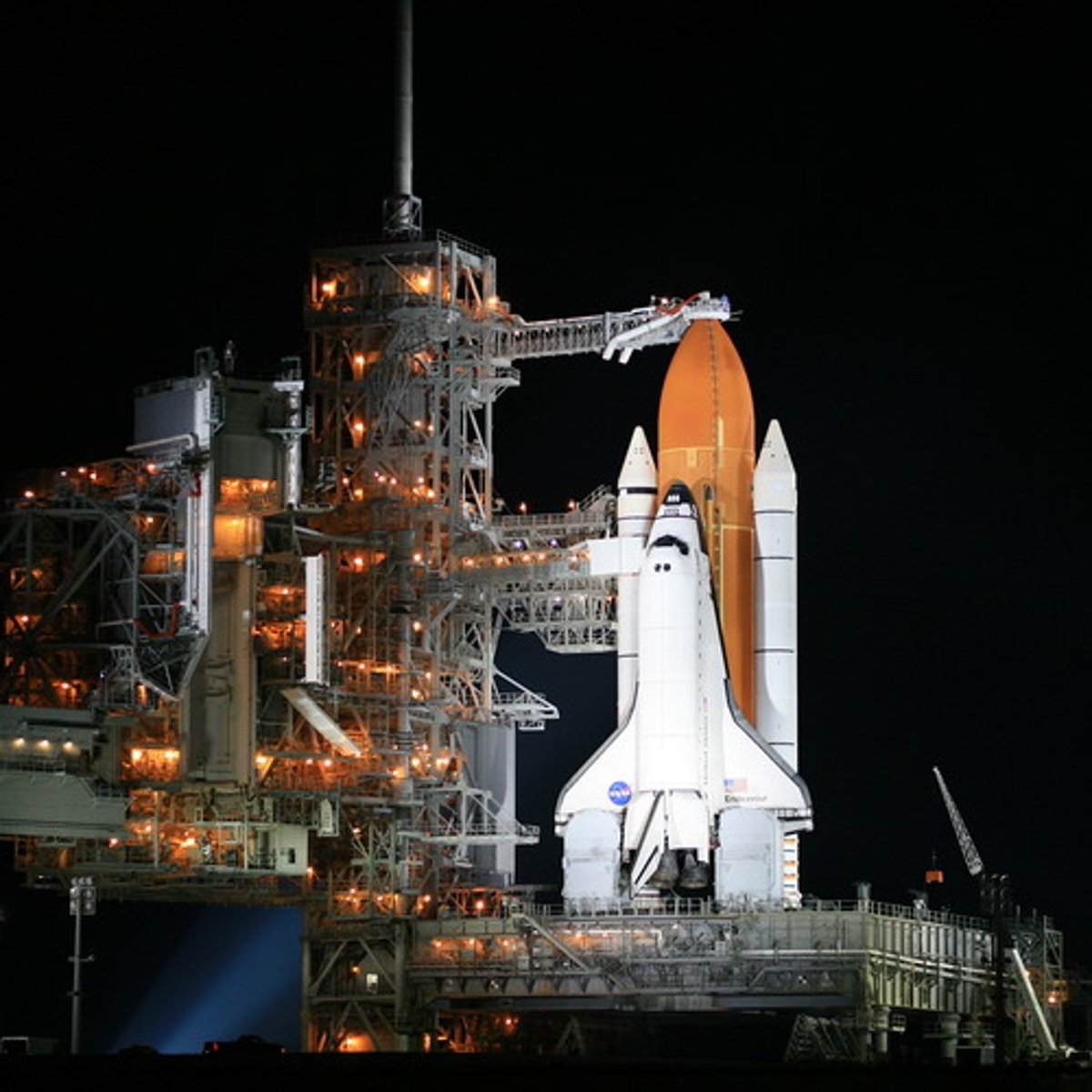
Shuttle
Transport personnel and equipment to orbiting spacecraft.

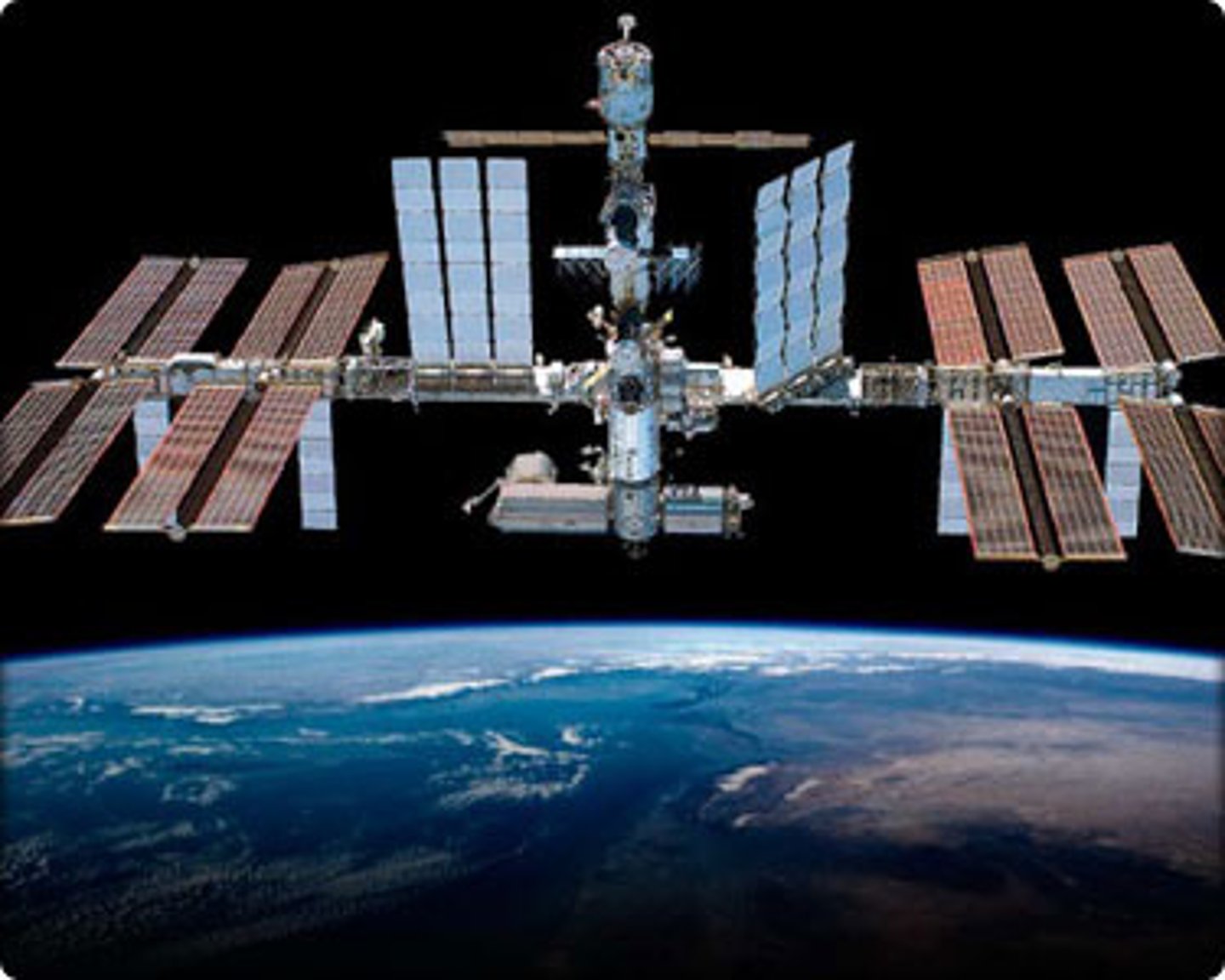
Space Station
Orbiting spacecraft that have living quarters, work areas, and all the support systems needed to allow people to live and work in space for extended periods of time.

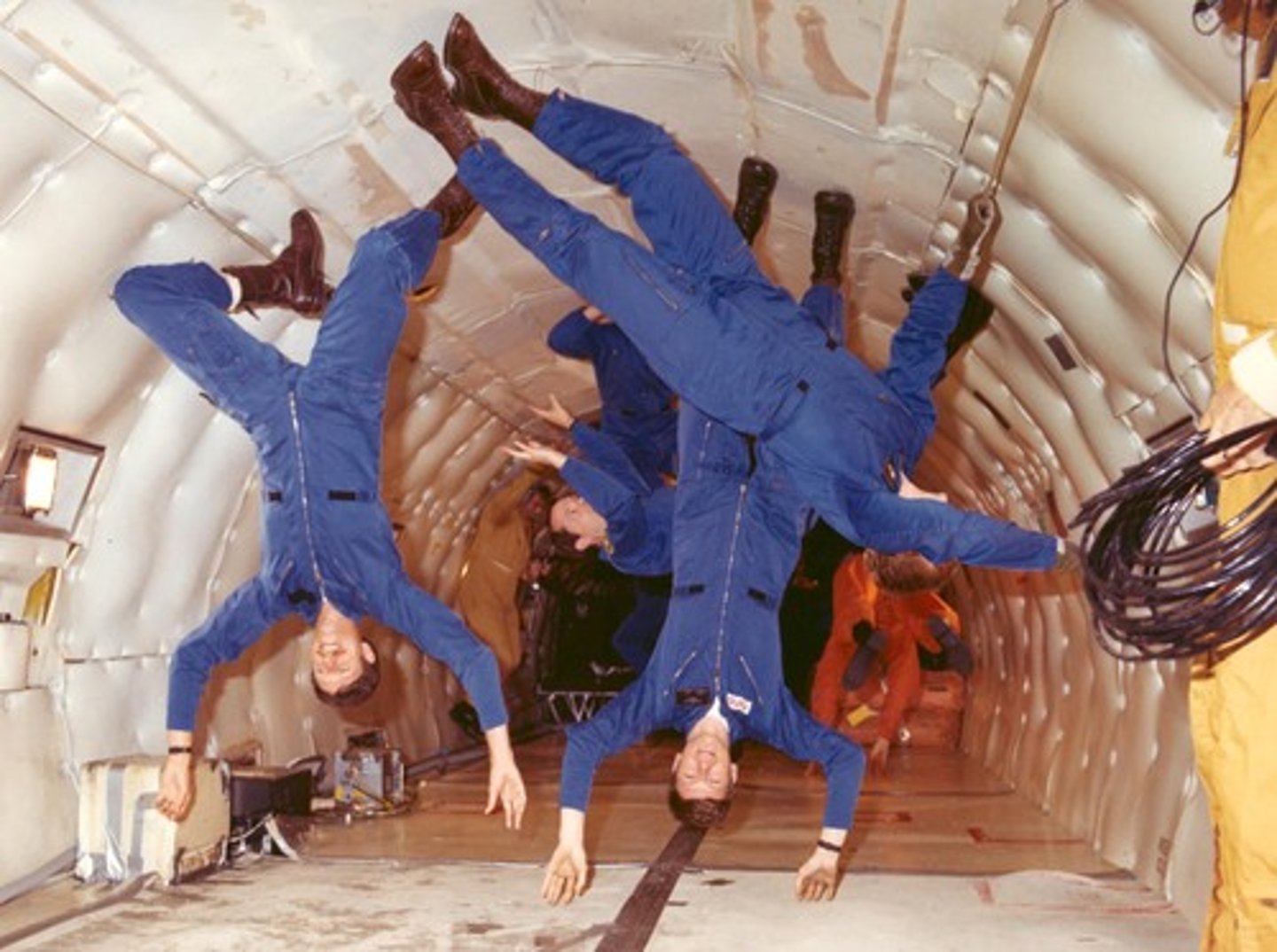
Microgravity
The condition in which the gravitational forces that act on a mass are greatly reduced.

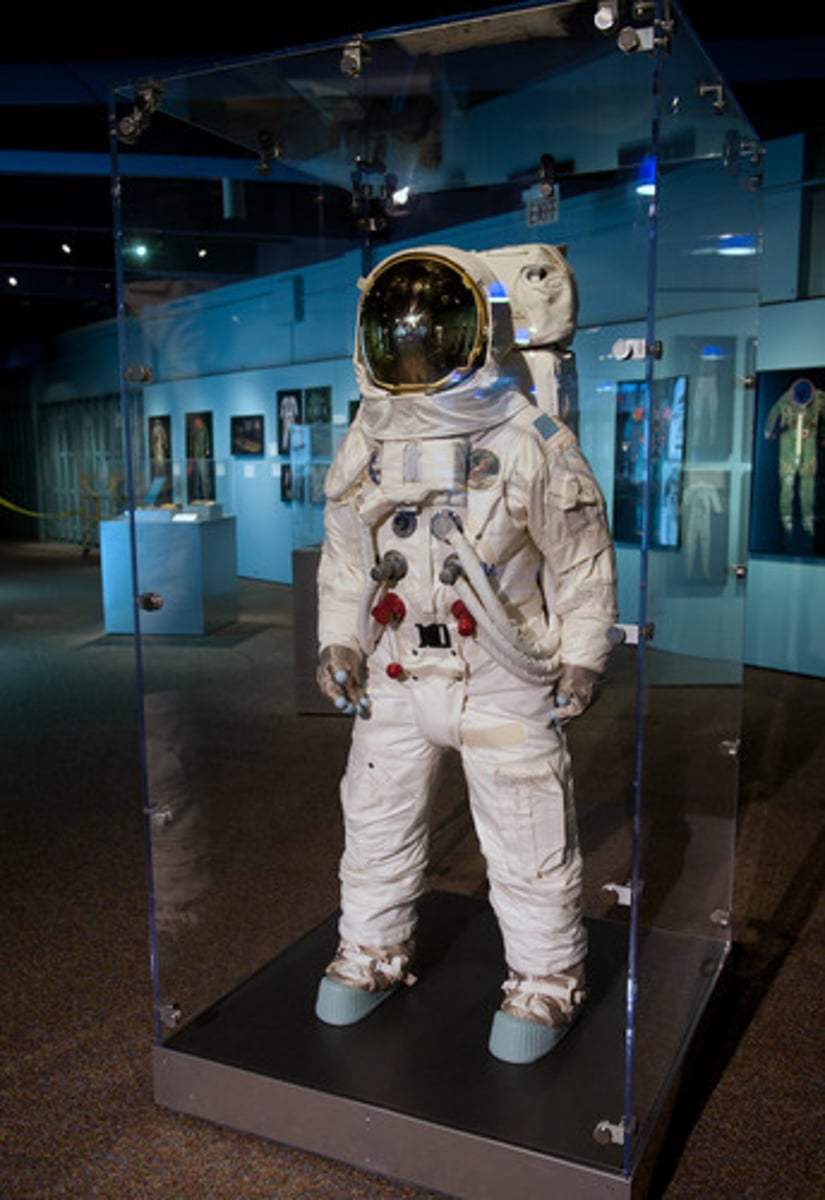
Spacesuit
A mini-Earth system that allows the wearer to work freely outside the spacecraft. The suit is flexible to allow the astronaut to graspo a wrench or twist a bolt. Modern spacesuits are completely self-contained, enabling them to work outside their crafts for up to 9 hours at a time.

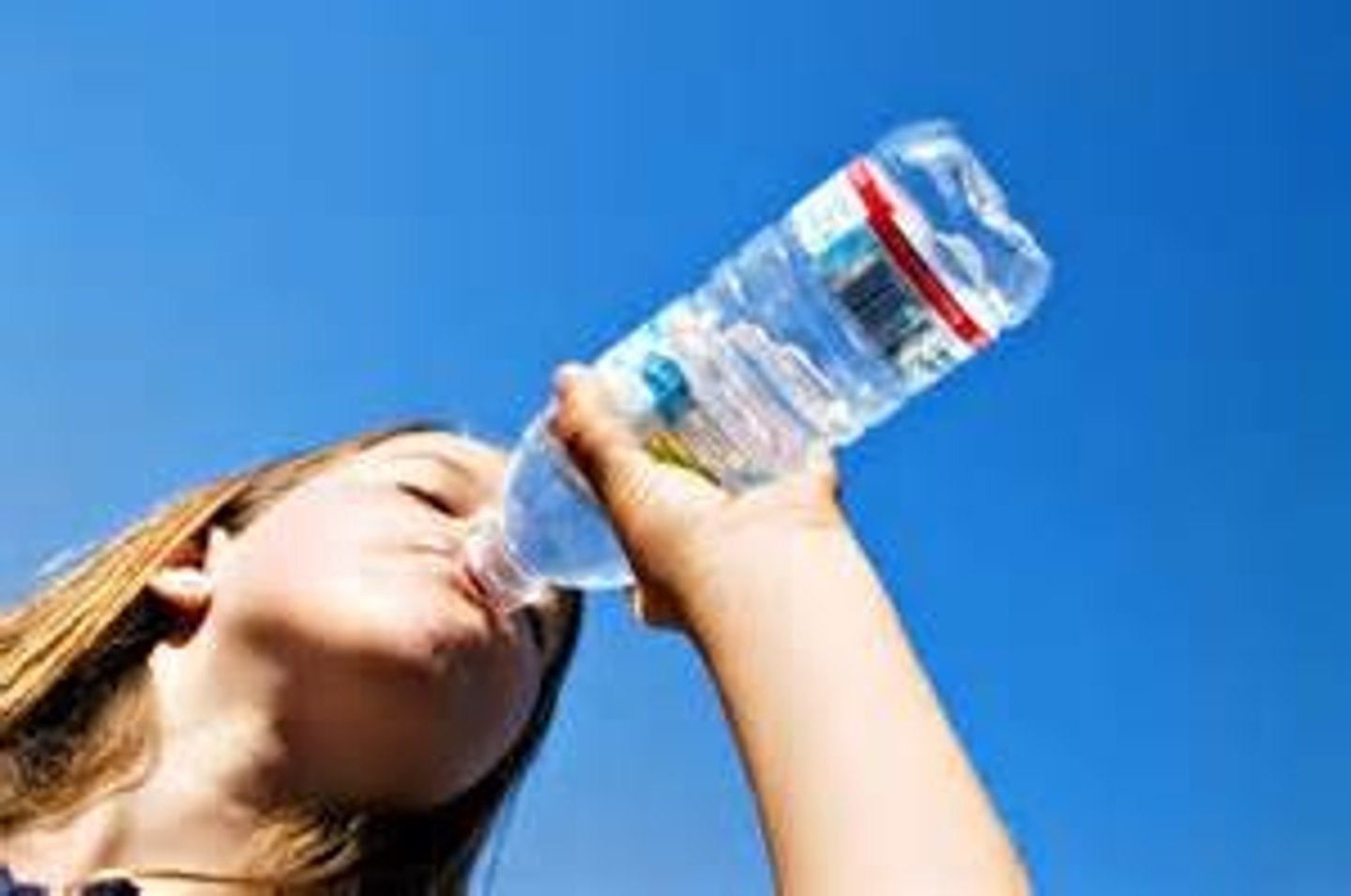
Potable Water
Drinking water; water that is safe to drink or use for food preparation.

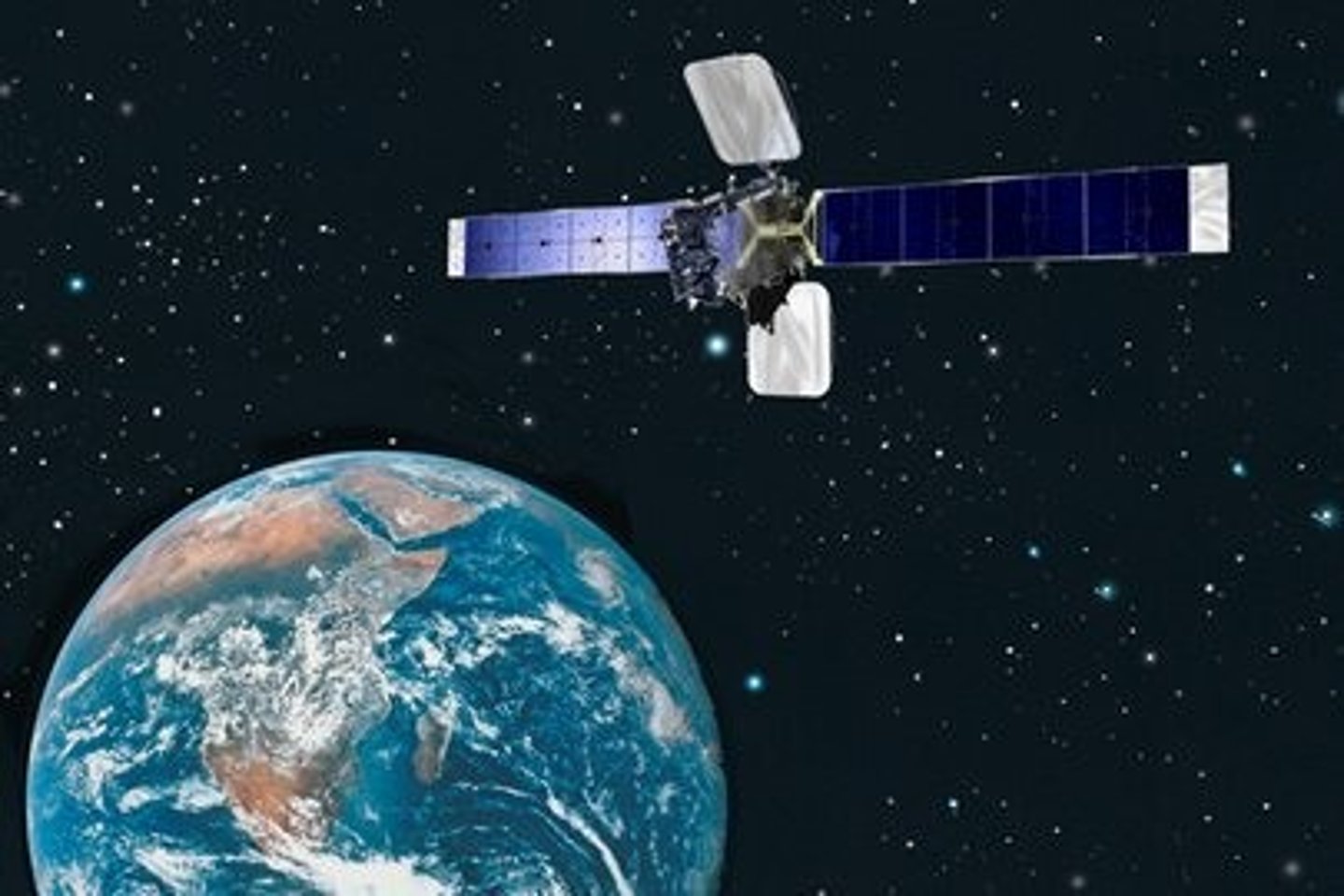
Satellite
A small body that orbits a larger one; satellites may be natural, such as a moon orbiting a planet, or artificial, such as a spacecraft put into orbit around Earth by humans for research or communication purposes.

Global Positioning System (GPS)
Technology designed to give people, wherever they are, their location on the ground at any time. Radio signals from GPS satellites are picked up by a hand-held receiver. The signals are translated by a computer in the receiver, which shows on a digital display the operator's position in correlation to the satellites.

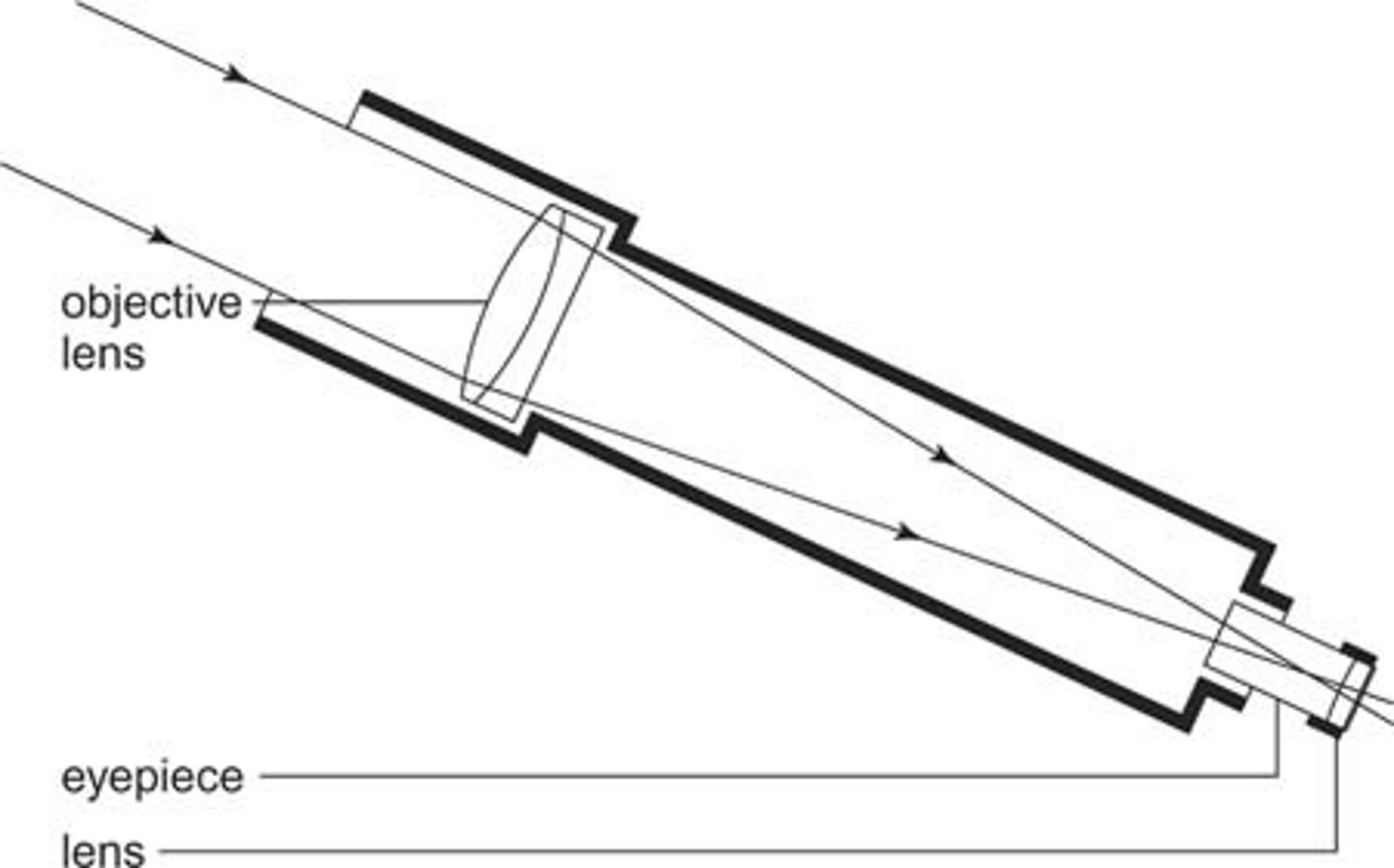
Refracting Telescope
A type of optical telescope that uses two lenses to gather and focus light.
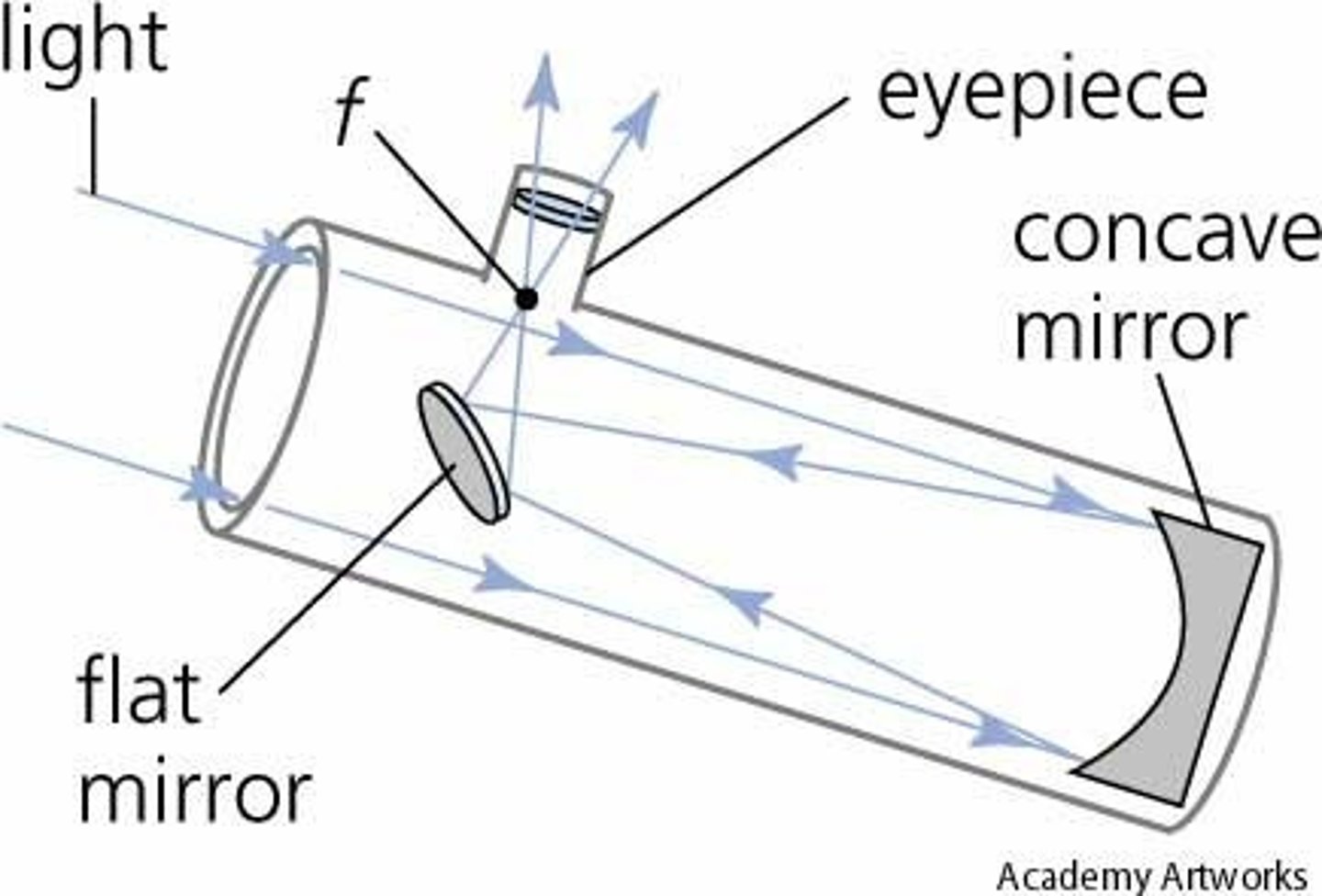
Reflecting Telescope
A type of optical telescope that uses mirrors instead of lenses to gather and focus light.
Interferometry
A technique of combining the observations of two or more telescopes to produce images that have better resolution than what one telescope alone could produce.

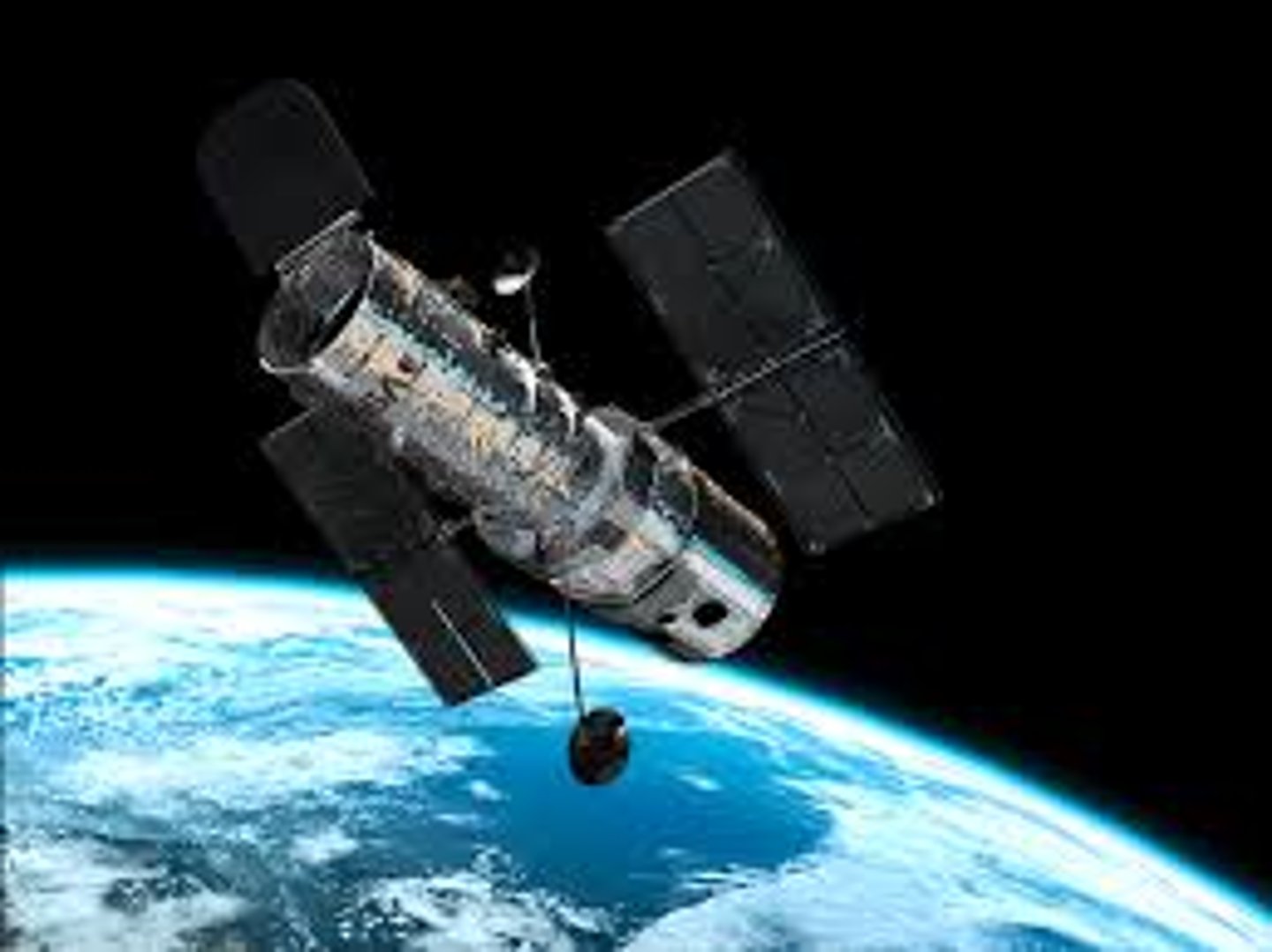
Hubble Space Telescope
One of the largest, most complex satellites ever built; launched in 1990 from the space shuttle Discovery, the HST (named for american astronomer Edwin P. Hubble) uses a series of mirrors to focus light from extremely distant objects.

Electromagnetic Energy
Forms of radiated energy that travel at the speed of light (300 000 km/s), although they have different wavelengths and frequencies than light.
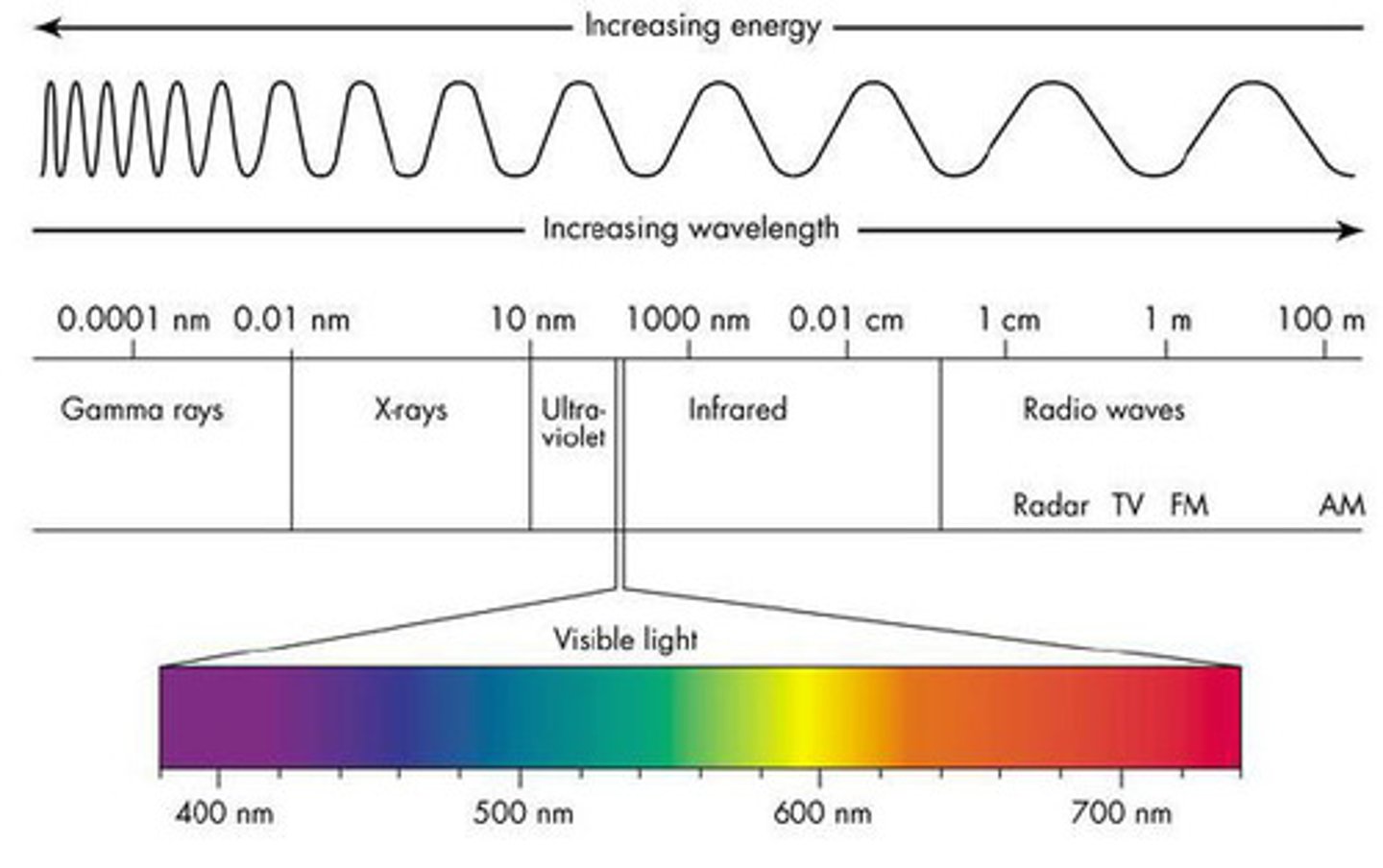
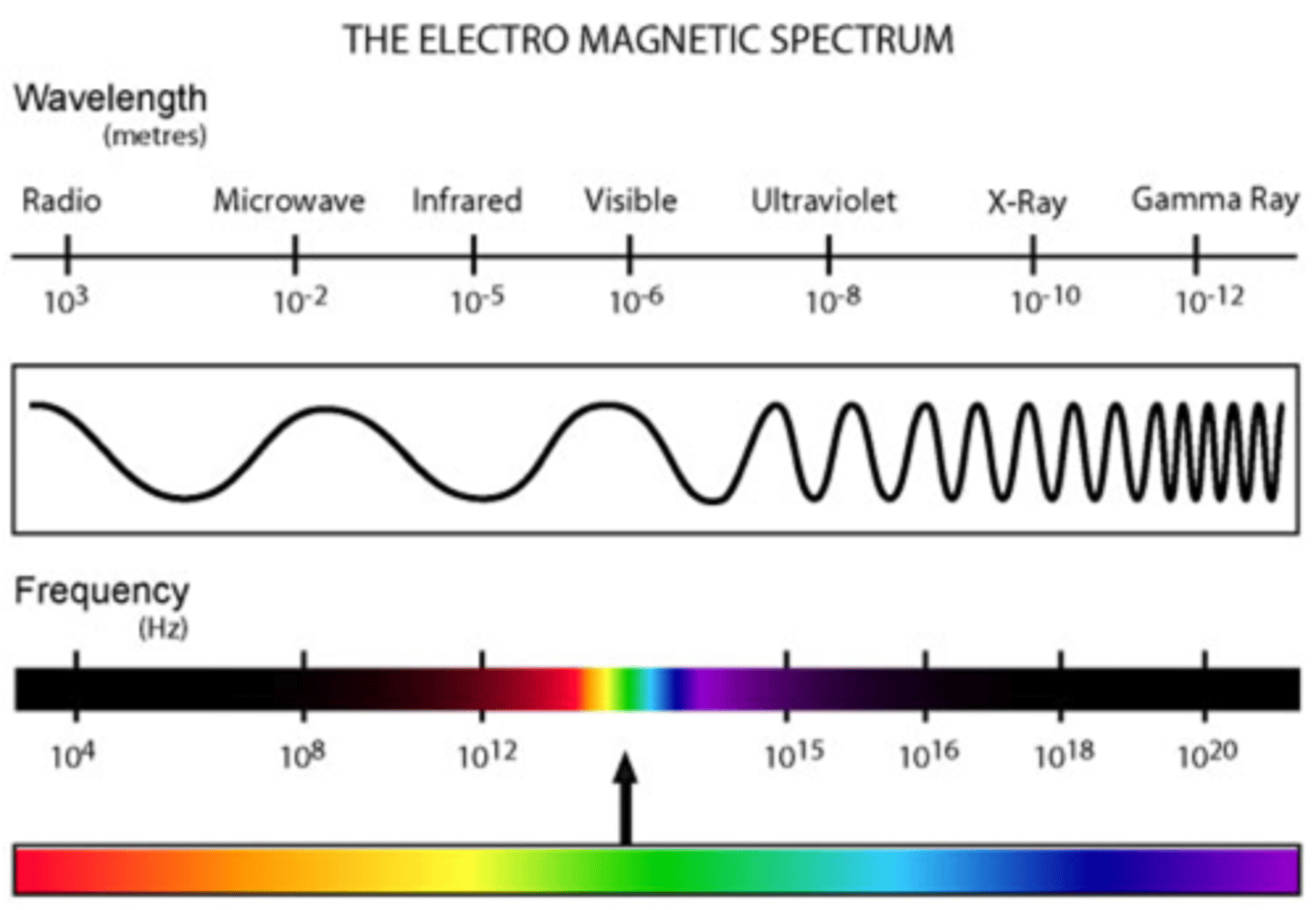
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The complete range of wavelengths over which electromagnetic energy extends; includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared radiation, microwaves, and radio and television signals.
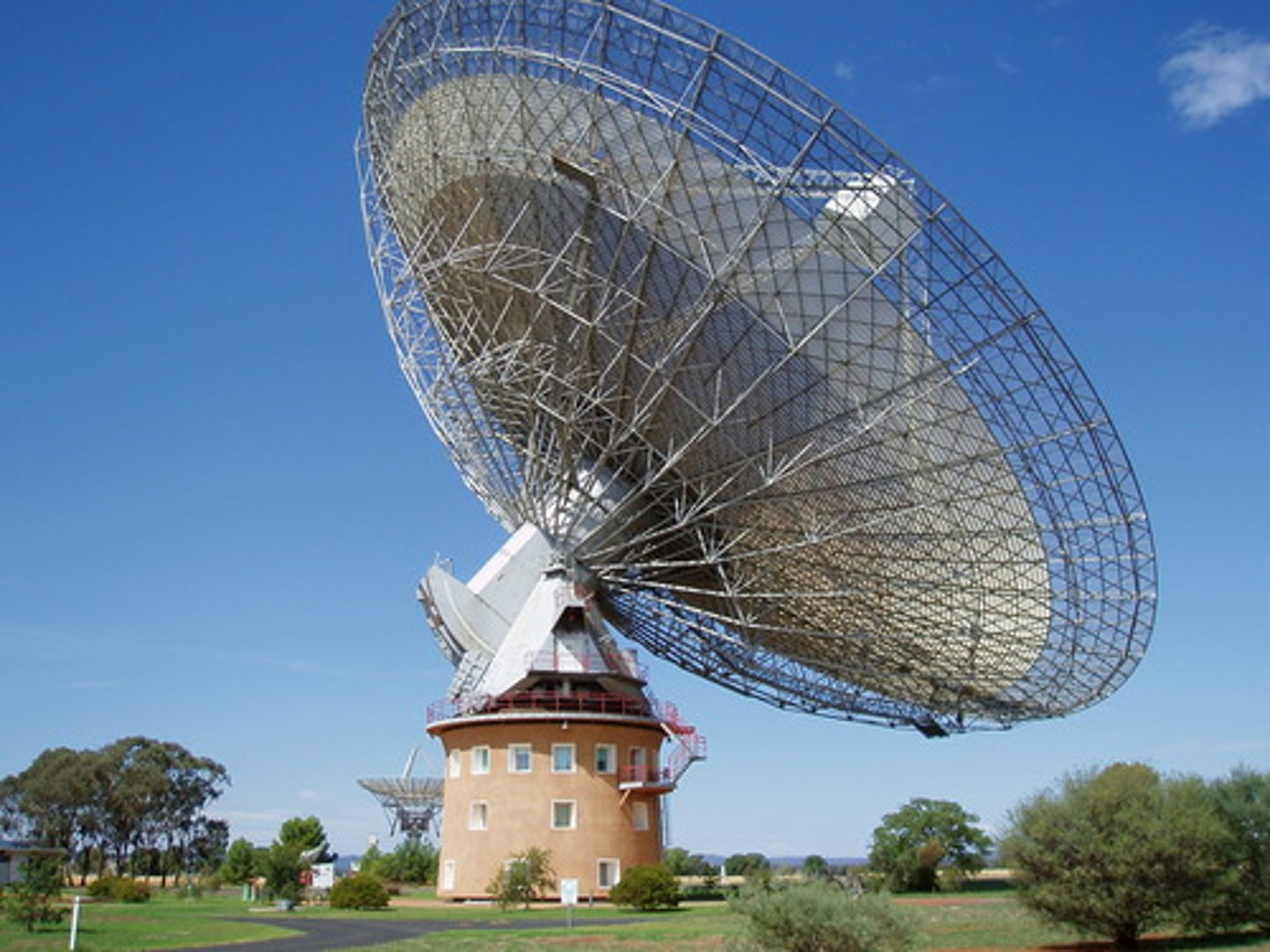
Radio Telescope
A telescope that collects and analyzes radiation in the radio frequency range from stars and other bodies in space.

X-Rays
An electromagnetic wave of high energy and very short wavelength.
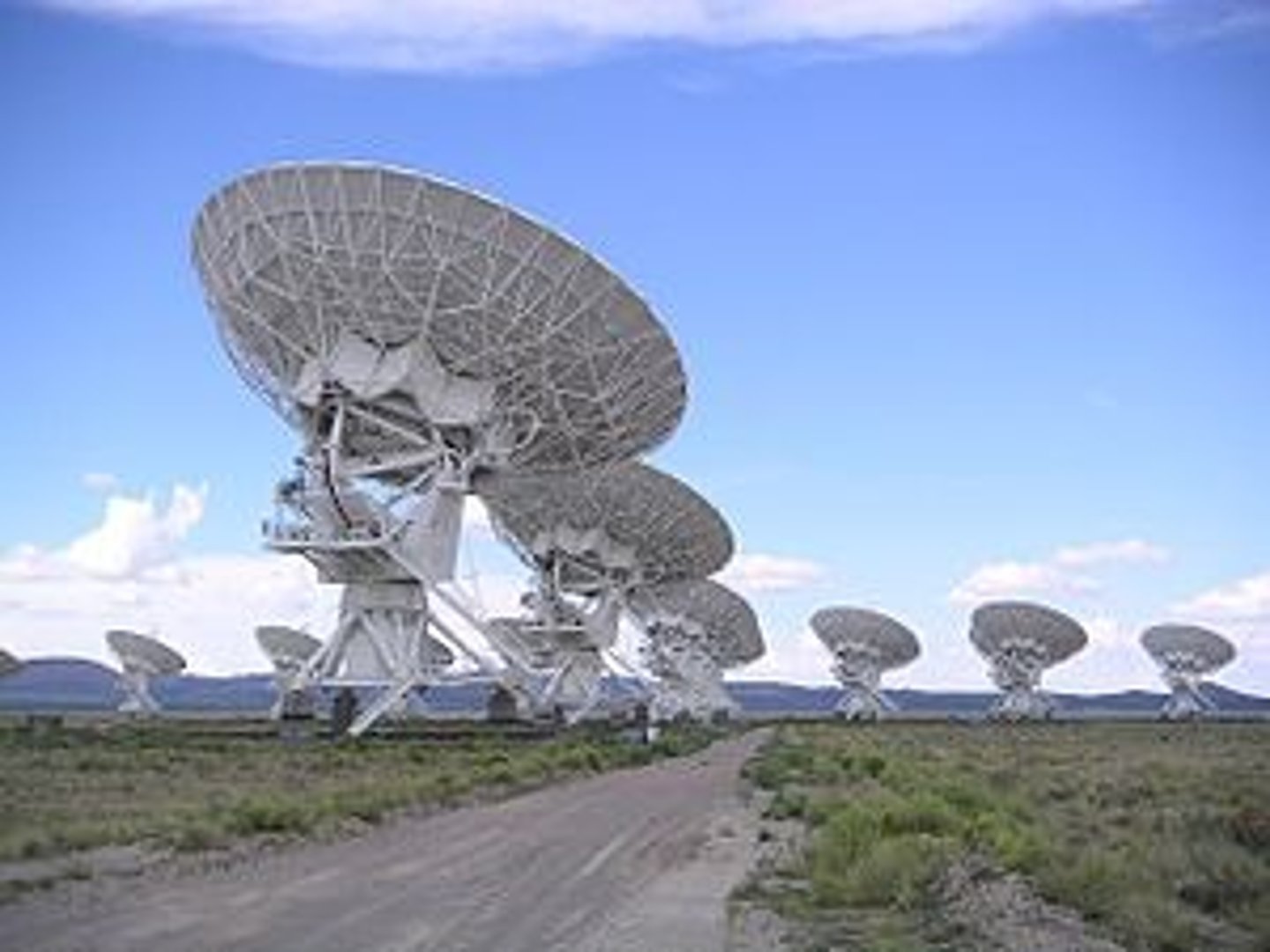
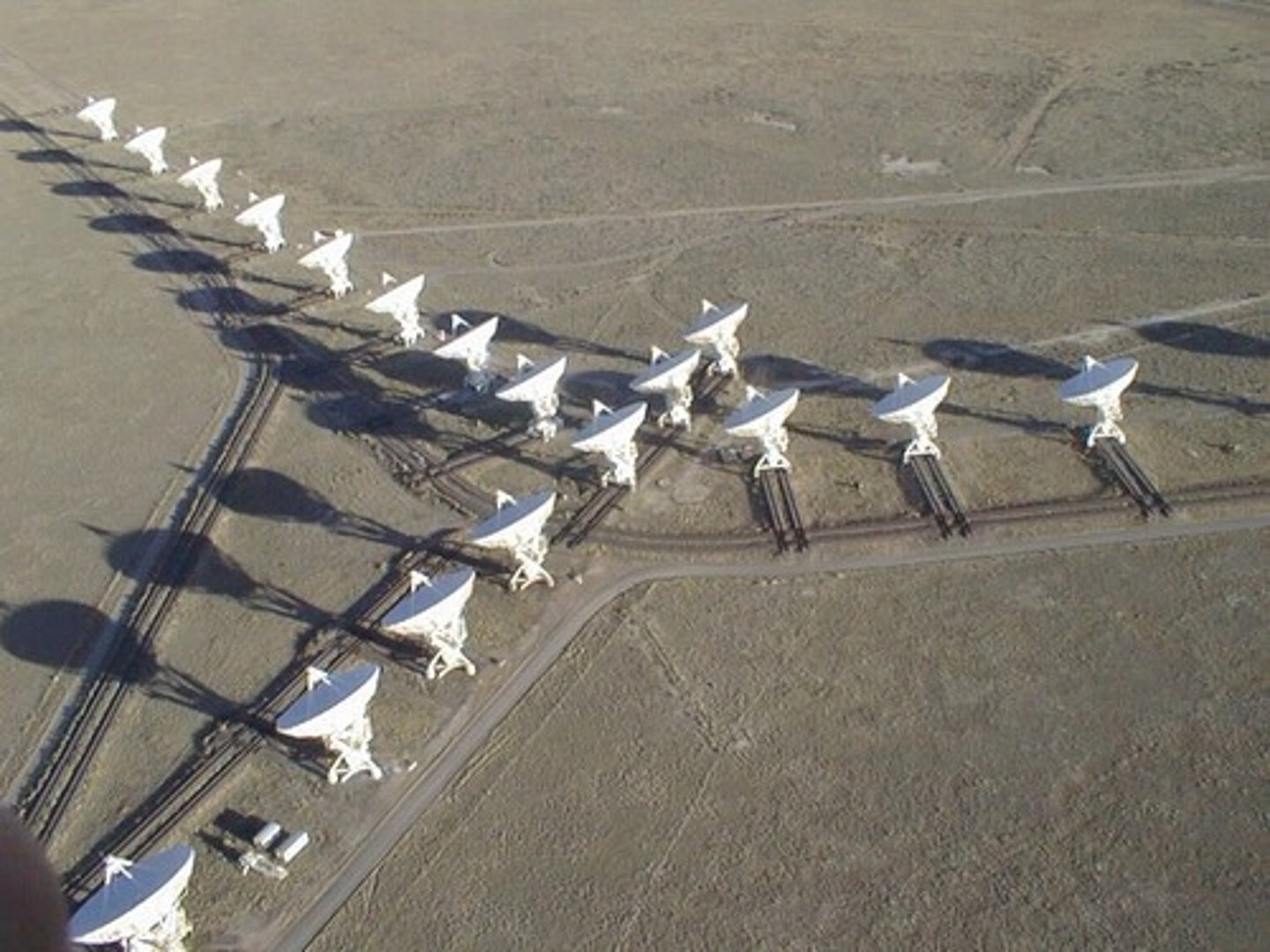
The Very Large Array
An observatory in Socorro, New Mexico, that uses 27 25-m radio telescopes arranged in a Y pattern. The arms of the Y cover a distance of 61 km.

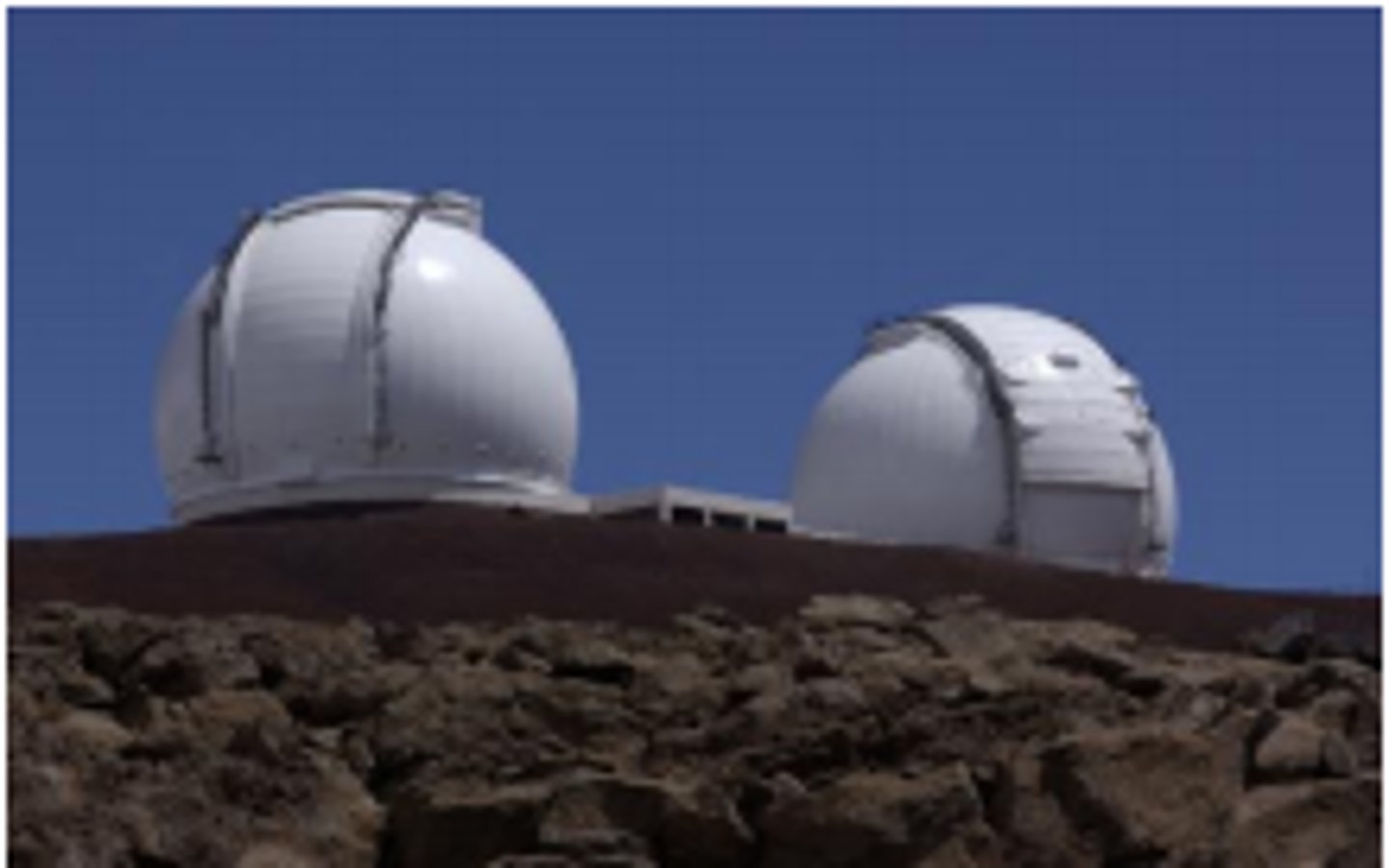
Keck Observatory
A two-telescope observatory in Hawaii equipped to make observations in infrared. It can view planets that are practically invisible, as the infrared spectrum reducing the brightness of stars and allows the planet's brightness to peak.

Space Probes
Unmanned satellites or remote-controlled "landers" used to explore areas or objects in space that are too difficult or dangerous to send humans to.

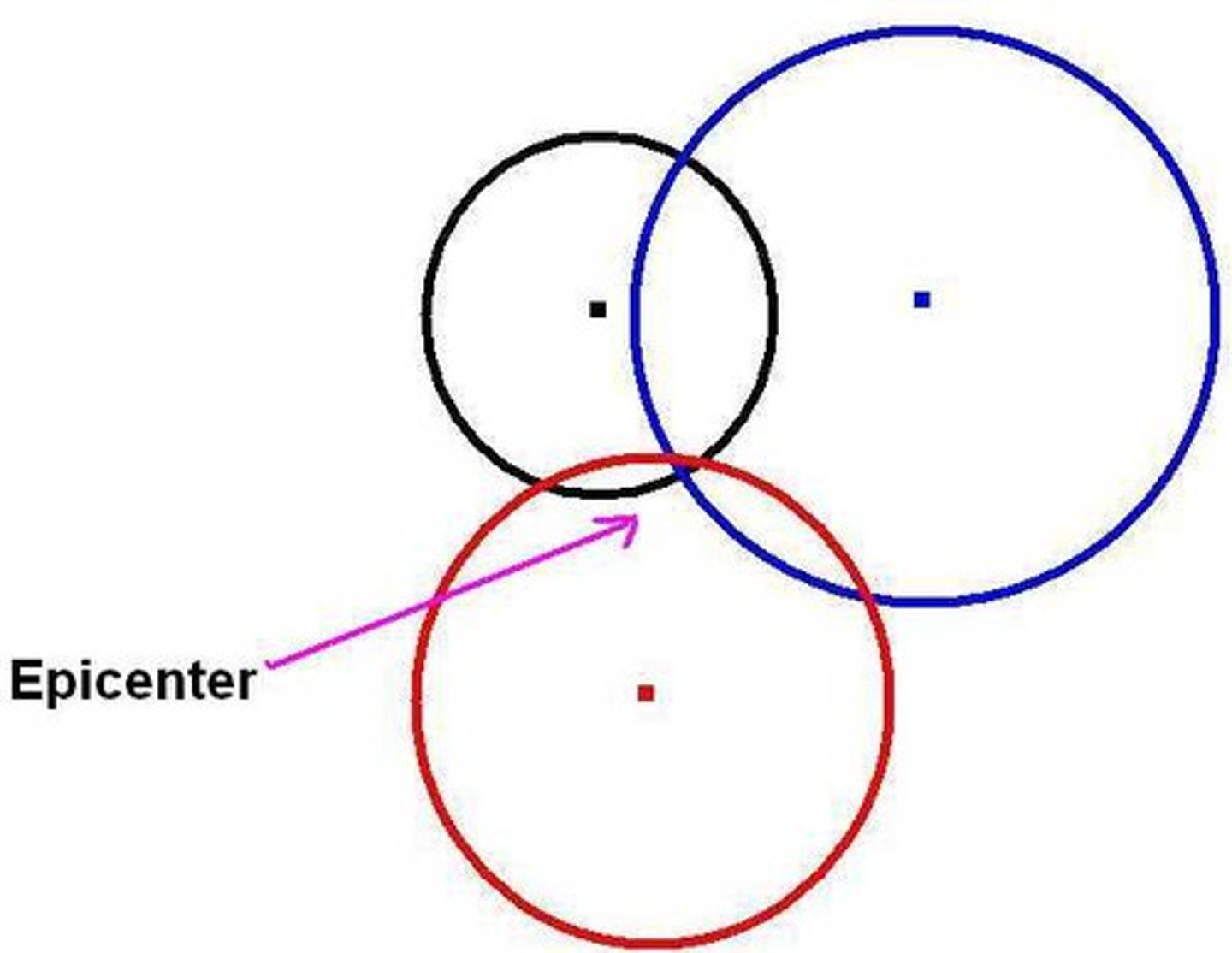
Triangulation
A method of indirectly measuring distance by creating an imaginary triangle between an observer and an object whose distance away is to be estimated.
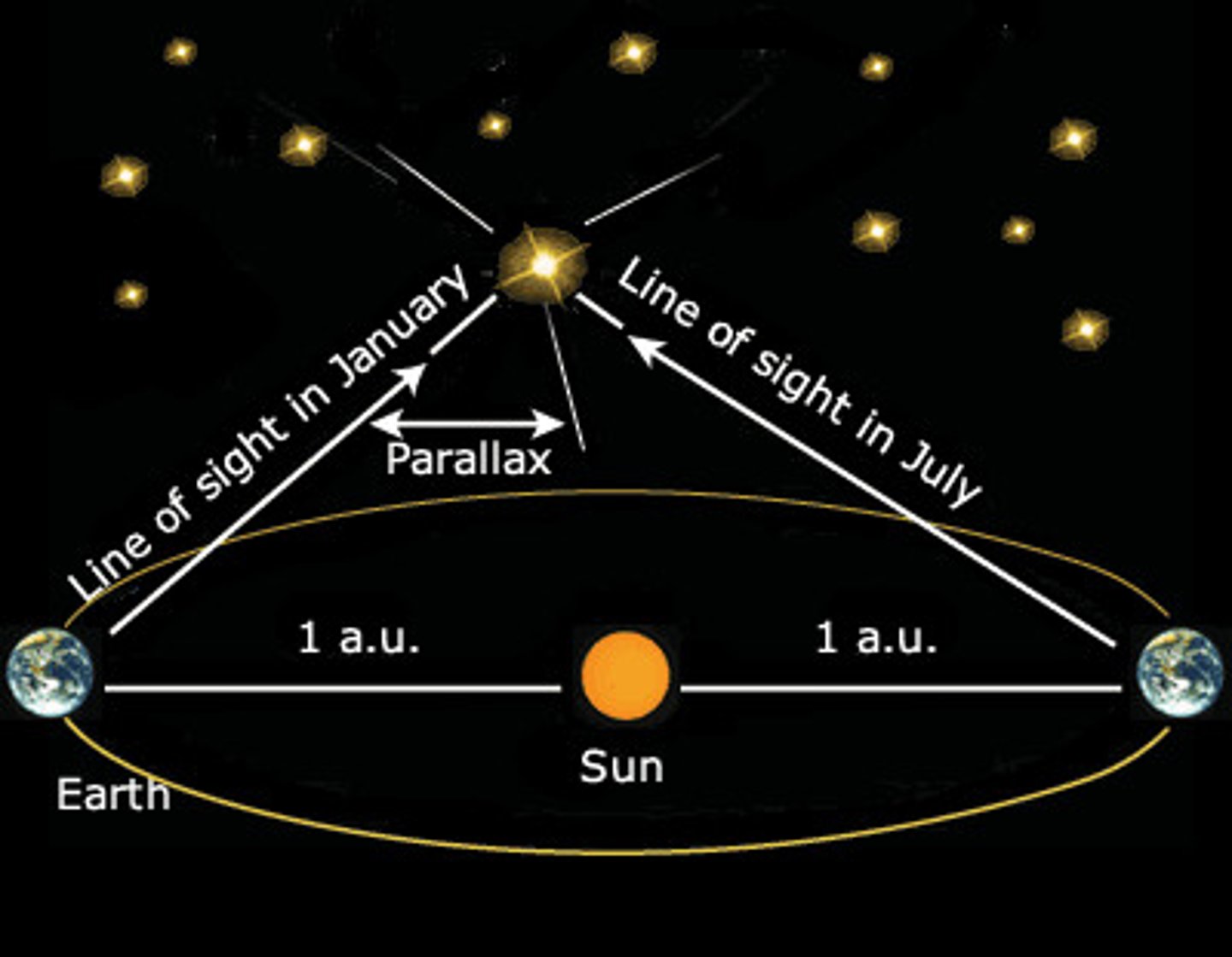
Parallax
The apparent shift in position of a nearby object against a distant background when the object is viewed from two different positions.
Spectroscope
An instrument used by astronomers to observe and measure the spectrum of a star.

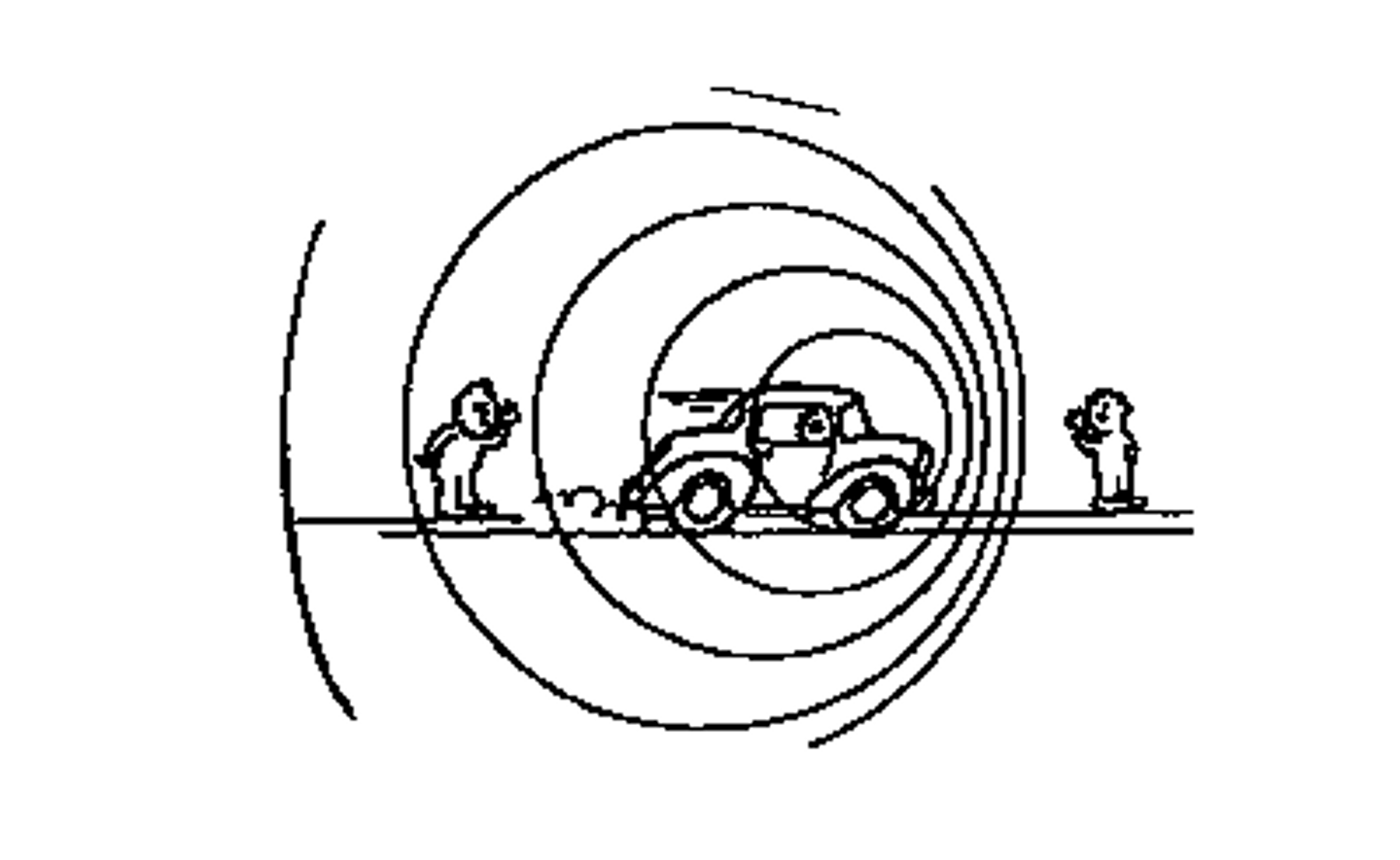
Doppler Effect
The apparent change in frequency of sound, light, and other waves as the observer and the wave source move towards or away from each other; also referred to as "Doppler shift".
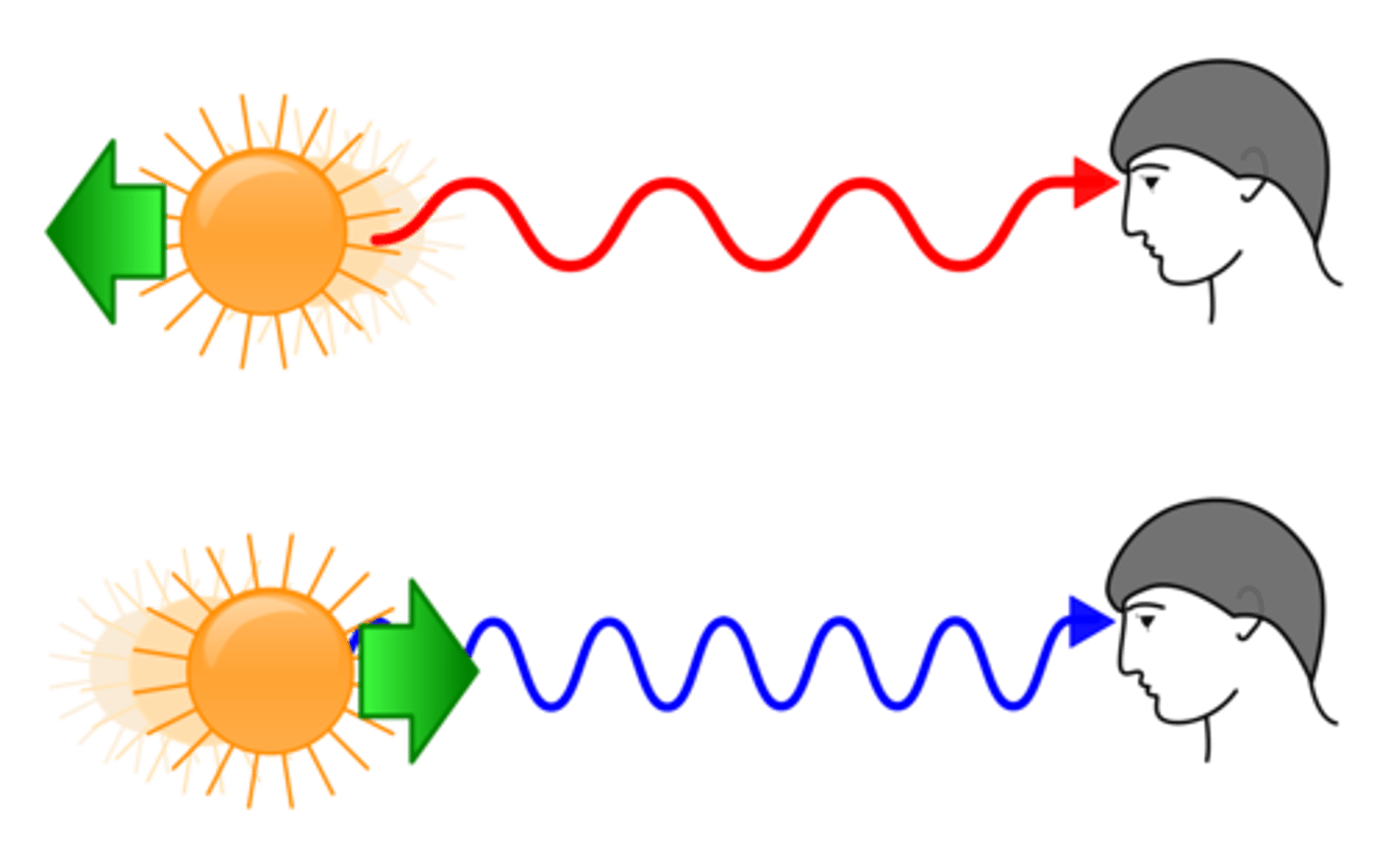
Redshift
When an object moves away, the light is shifted to the red end of the spectrum, as its wavelengths get longer.
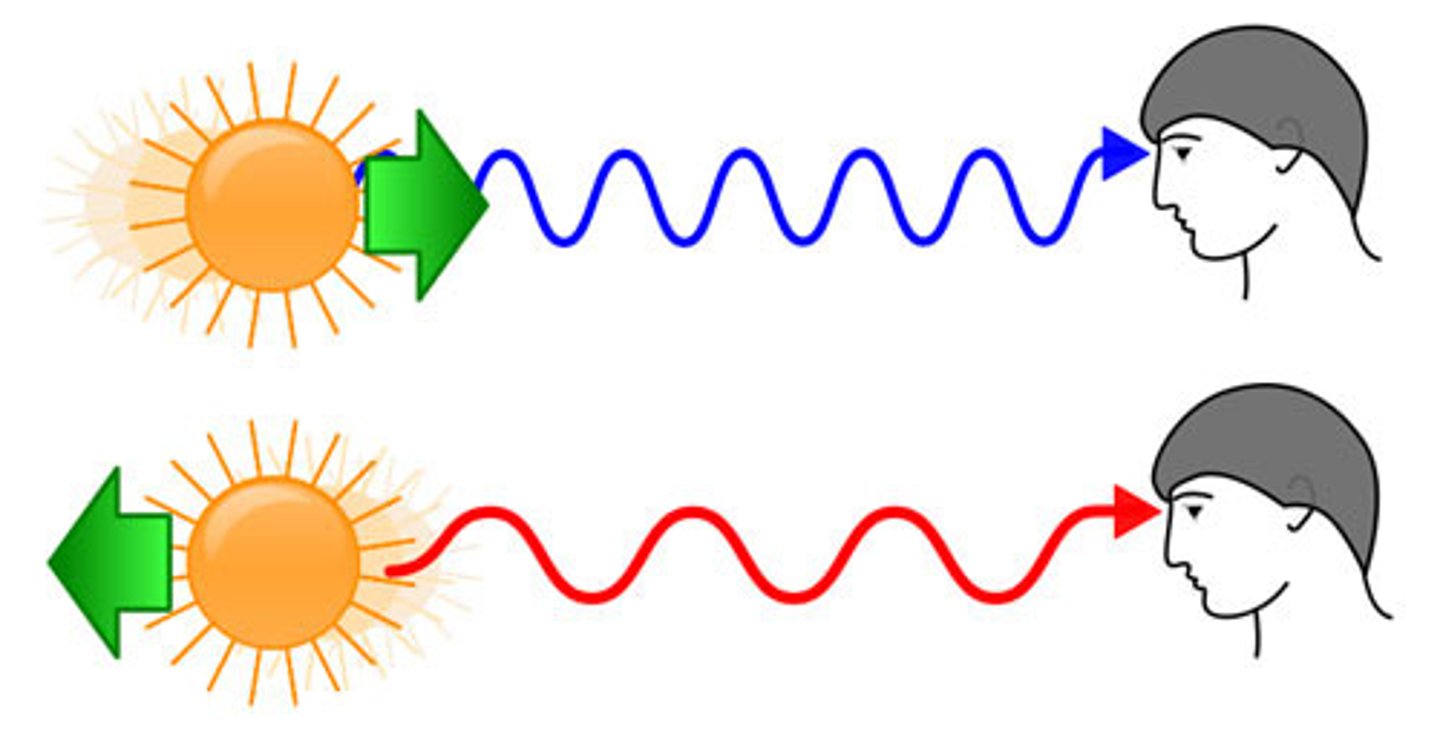
Blueshift
When an object moves closer, the light moves to the blue end of the spectrum, as its wavelengths get shorter.
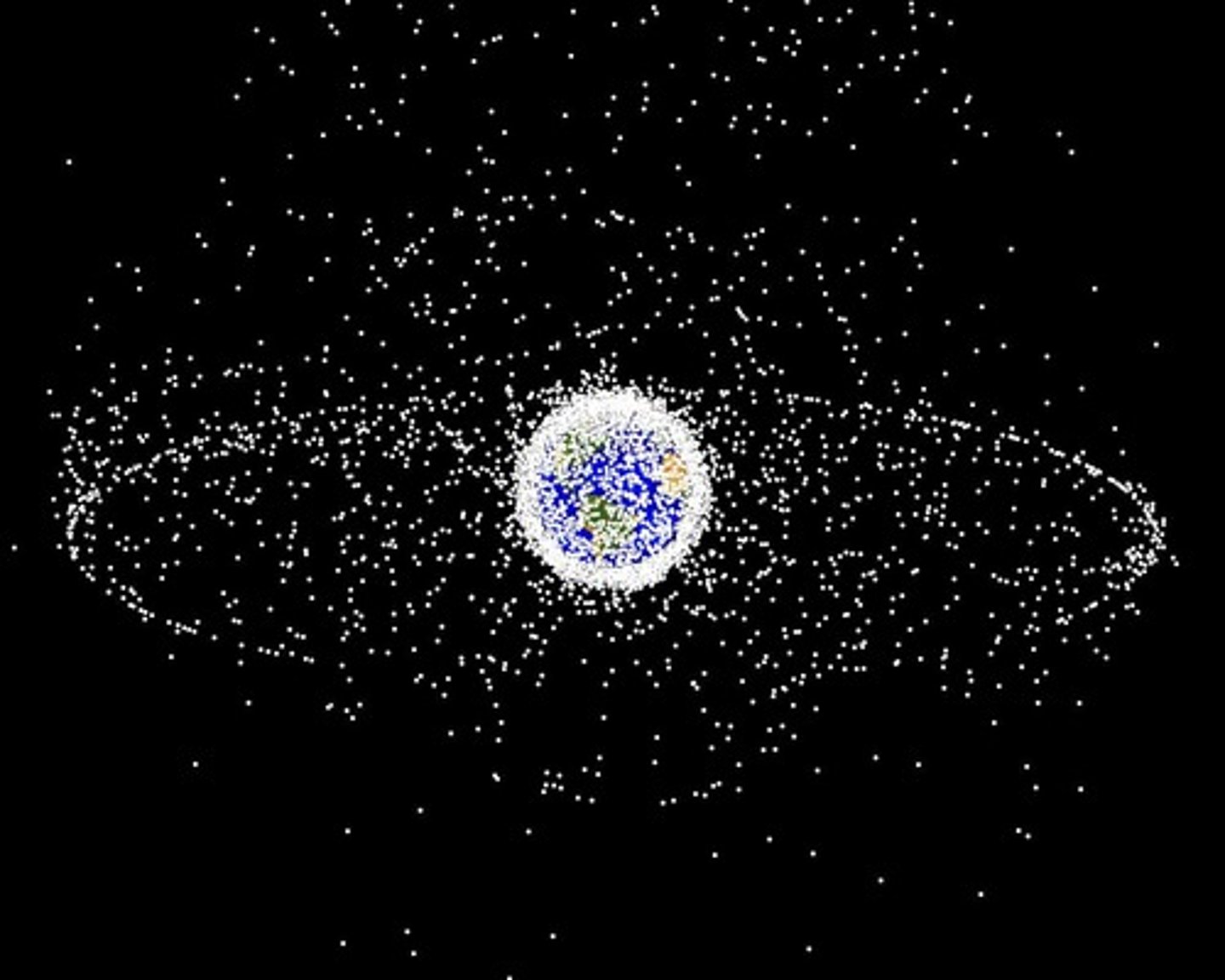
Space Junk
Refers to all the pieces of debris that have fallen off rockets, satellites, space shuttles, and space stations and remain floating in space.
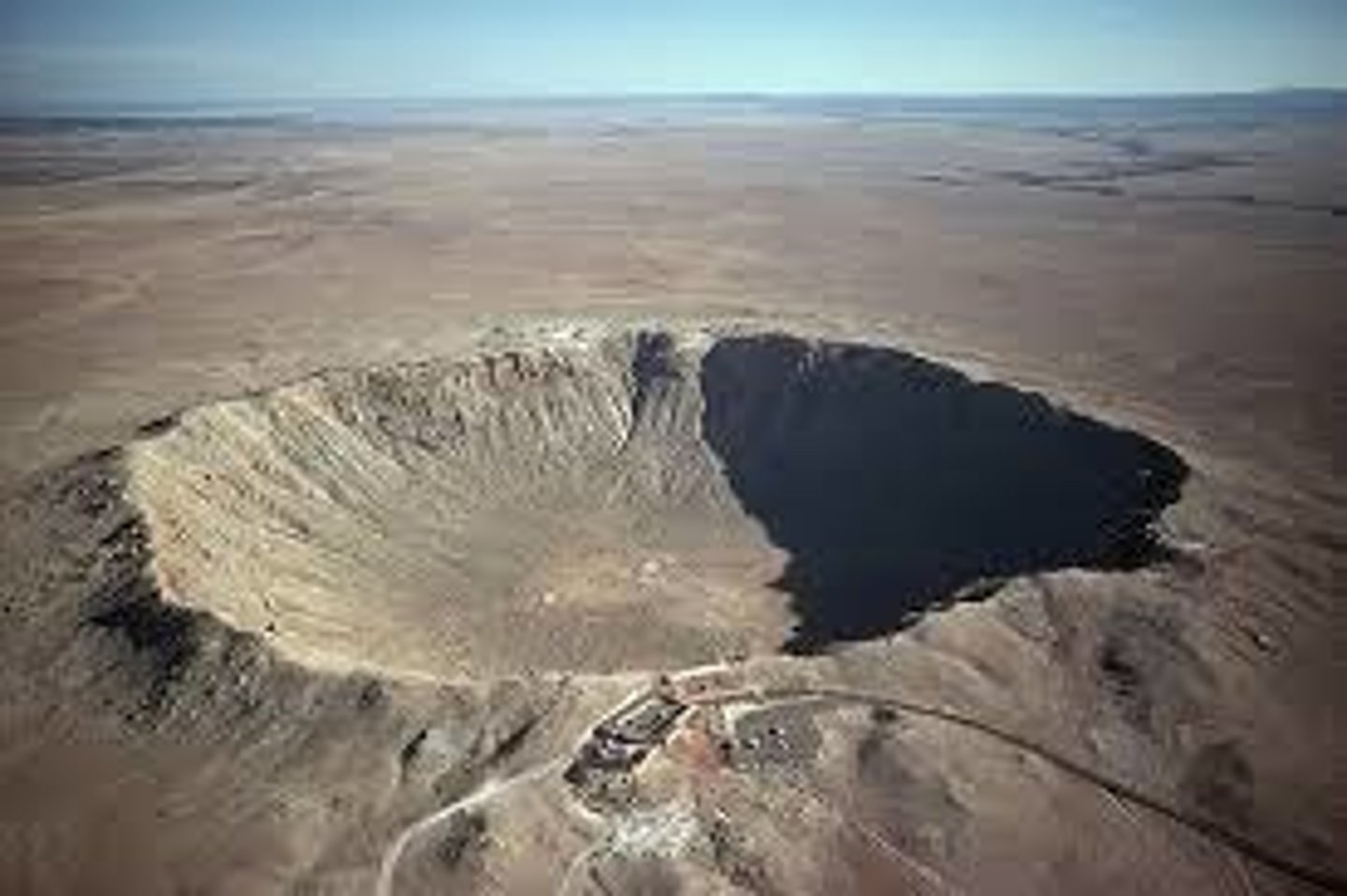
Impact Crater
A crater on a planet or moon caused by the impact of a meteorite or other object, typically circular with a raised rim.

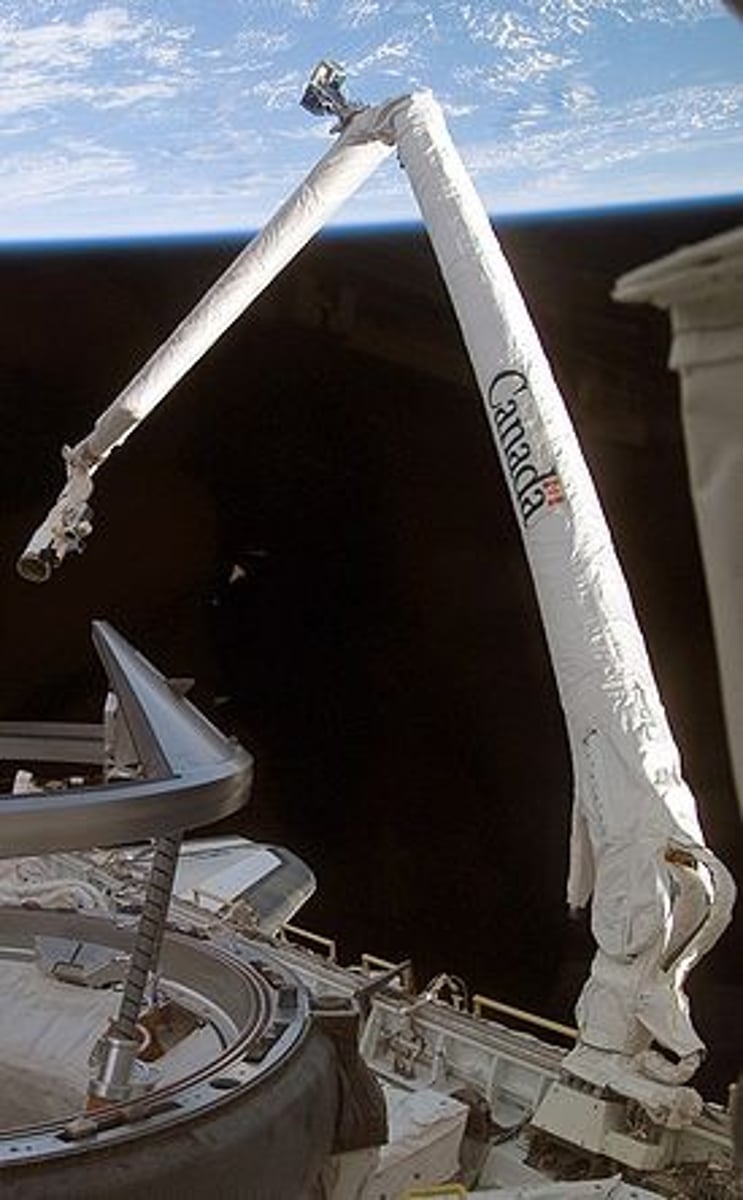
Canadarm
A Canadian robotic arm controlled by remote control that has launched and retrieved satellites, helped fix optical apparatus on the HST, and put together modules for the ISS.

Ethical Issue
Occur when a given decision, scenario or activity creates a conflict with a society's moral principles. Is it right to spend money on space exploration rather than on solving problems on Earth? Do we have a right to alter materials in space to meet our needs? How can we ensure that space resources will be used for the good of humans and not to further the interests of only one nation or group?

Political Issue
Any event or action that is in the arena of state power and its maintenance. Who owns space? Who has the right to use the resources in space? Who will determine how space will be used?
Environmental Issue
Problems with the planet's systems that have developed as a result of human interference or mistreatment of the planet. Who is responsible for protecting space environments from alteration? Who is responsible for cleaning up space junk, and who should pay for doing it?
