Other Systems 2 Pt. 1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Pregnancy Questions/Themes - What are things to consider with:
system interactions in pregnancy
sidelying in pregnancy
pregnancy complications
other conditions?
pregnancy exercises
system interactions in pregnancy
postural changes
HR and BP changes
sidelying in pregnancy
left sidelying
avoid supine hypotensive syndrome
pregnancy complications
preeclampsia vs. eclampsia
pregnancy exercises
posture
precautions
Changes with pregnancy:
What is essential weight gain and for what?
25-35 lbs. essential for baby’s nourishment
Changes with pregnancy - MSK System:
postural changes? (4)
how long does postural stress continue for and due to what?
postural changes
forward head, kyphosis, increased lordosis, anterior pelvic tilt - COM goes anterior
postural stress continues even postpartum due to lifting and carrying of baby
Treatment for MSK changes (4)
postural education
stretching of tight muscles and strengthening of weaker ones
pelvic stabilization exercises - bc increase in relaxin = ligamentous laxity
pelvic tilts
Cardiovascular changes in pregnancy:
what happens to the blood pressure and when?
what happens to cardiac output?
after 4 months, what complications can be caused with supine lying after 5 minutes?
this declines CO and may cause what?
therefore, no supine lying when?
both systolic and diastolic BP is low/reduces in the first and second trimesters, increases in the last trimester
CO increases due to increased blood volume
supine-lying after 4 months = compression of inferior vena cava
Cardiovascular changes in pregnancy:
what happens to resting HR? what is the change during exercise?
resting HR increases by 10-20 bpm, but max HR does not increase proportionally with exercise
since resting HR is high, it does not increase more like the general population with exercise
What is the best position for pregnancy?
this position:
decreases compression of what?
maximizes what?
decreases GERD how?
improves what circulation?
decreases compression of inferior vena cava
maximizes cardiac output
decreases GERD as internal organs are relaxed
improves maternal and fetal circulation
Recap of changes or system interactions during pregnancy:
MSK
CV
pulmonary
depth of respiration, respiration rate, tidal volume, work of breathing
metabolism
MSK
changes in posture (kyphosis), ligamentous laxity, LBP, teach stabilization and postural education
CV
changes in blood volume, HR, CO
pulmonary
increased depth of respiration, respiration rate stays the same, tidal volume increases, work of breathing increases (diaphragm is elevated, changes of rib position)
metabolism
increases bc of the fetus

Practice Question 1.1 – Previous Class Warm Up!
What is the BEST initial physical therapy intervention?
A. Supine and perform contractions held for 3 seconds each
B. Left side lying and perform contractions held for 5 seconds each
C. Right side lying and perform contractions held for 5 seconds each
D. Sitting and perform contractions held for 10 seconds each
B. Left side lying and perform contractions held for 5 seconds each
RATIONALE: Left side lying is the most appropriate position to start pelvic floor muscle strengthening as the patient is pregnant. Supine position causes compression of Inferior vena cava causing supine hypotensive syndrome. Sitting is anti gravity, and not recommended initially.
strengthen levator ani
supine increases inferior vena cava compression
Practice Question 1.2 – System Interactions
Which of the following is MOST APPROPRIATE regarding physiological changes related to pregnancy?
A. Blood pressure increases in first and second trimester, and then decreases in the third trimester
B. Cardiac output is decreased in pregnancy
C. Resting heart rate is decreased during pregnancy
D. Metabolic rate and heat production increases during pregnancy
D. Metabolic rate and heat production increases during pregnancy
RATIONALE: Resting HR is increased during pregnancy. Blood pressure decreases in first and second trimester and then increases in the third trimester. Metabolic rate and heat production increases during pregnancy. Cardiac output is increased in pregnancy.
for pregnant women, usually fasting blood glucose decreases so when they wake up, FBG drops and fetus needs nourishment too
both eclampsia and preeclampsia are considered 911 situations right? Yes
Describe what and when preeclampsia takes place.
what changes in urine, reflexes, fluid, and 2 other symptoms?
what value is the BP reading?
what would confirm the diagnosis?
how severe is this?
pregnancy induced hypertension after the 20th week of gestation (bc BP normally increases in third trimester)
increase in protein in urine, hyperreflexia, edema, headache, sudden weight gain
a blood pressure reading more than 140/90 mmHg
second abnormal blood pressure reading four hours after the first confirms the diagnosis
EMERGENCY
Practice Question 1.3 – Pregnancy Complications
After an uncomplicated vaginal delivery of her child, patient is seen again for physical therapy. During the treatment, the patient begins to report headache with visual disturbances then suddenly develops a seizure. Which condition is MOST LIKELY seen in this patient?
A. Preeclampsia
B. Gestational diabetes
C. Eclampsia
D. Ectopic pregnancy
C. Eclampsia
RATIONALE: Eclampsia is a characterized by seizures, headaches, visual disturbances after pregnancy. more severe
Preeclampsia can progress to eclampsia, but eclampsia does not need preeclampsia to occur. preeclampsia does NOT have seizures
gestational diabetes = increased BG during pregnancy
during pregnancy, for some people, the body stops producing insulin so blood glucose increases
resolves after delivery
ectopic pregnancy = fertilization of the egg outside of the uterus/uterine cavity
can happen in fallopian tubes - not safe for pt due to LBP/pelvic pain, discomfort, vaginal bleeding
Contraindications to exercise pt. 1:
hemodynamically significant heart disease, meaning?
cardiopulm disease?
incompetent cervix meaning?
vaginal bleeding especially when?
placentia previa when? (explain this)
hemodynamically significant heart disease, meaning?
acute signs of significant heart failure / irregular pulse
cardiopulm disease?
restrictive lung disease
incompetent cervix meaning?
early dilation of cervix before full term
vaginal bleeding especially when?
second or third trimester
placentia previa when? (explain this)
after 26 weeks gestation
placenta is located on the uterus position in which it may detach before the baby is delivered
Contraindications to exercise pt. 2:
which pregnancy condition?
if they had rupture of membranes why?
premature labor when?
pancreas disease?
blood cell issue?
recall what is the safe range for RPE
which pregnancy condition?
preeclampsia/pregnancy-induced hypertension
if they had rupture of membranes why?
loss of amniotic fluid before the onset of labor
this fluid is important for nourishing the baby
premature labor when?
labor before 37th week of pregnancy
pancreas disease?
maternal type I diabetes
blood cell issue?
severe anemia
RPE 11-13; during pregnancy exercise as tolerated
Practice Question 2 – Pregnancy Exercises
A patient, after an uncomplicated delivery, has a 3-cm diastasis recti and weak abdominal muscles. Which of the following exercises is MOST APPROPRIATE for initial phase of rehabilitation?
A. Modified Plank exercises on forearms and knees
B. Head lifts with arms bracing the abdomen
C. Curl-ups with hands behind the head
D. Deep breathing exercises in bridging position
B. Head lifts with arms bracing the abdomen
RATIONALE: A split >2 cm requires bracing/ splinting of the abdomen while performing the head lift exercises. Once the patient has improved core stability and the diastasis recti has begun to heal, more challenging exercises such as modified plank exercises or curl-ups can be introduced, but initially, exercises should prioritize safety and gentle engagement of the core muscles.
review: diastasis recti = separation of rectus abdominis muscle from the linea alba
assess this by positioning them hooklying, keep fingers horizontally over the umbilicus - ask the pt to perform a curl up with clearance of the scapula then see how many fingers go inside the umbilicus
2 fingers = 2 cm
significant = diastasis recti > 2cm
Treatment for diastasis recti pt. 1:
head lift
pt is in what position and does what for support?
have pt exhale and lift what? while at the same time, using their hands to gently approximate what?
then lower the head slowly and?
head lift
pt is in hooklying position and crosses arms around the stomach area for support
have pt exhale and lift only the head off the floor, while at the same time, using their hands to gently approximate the rectus muscles toward midline
then lower the head slowly and relax
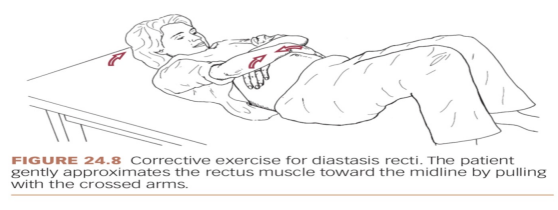
Treatment for diastasis recti pt. 2:
head lift with pelvic tilt
pt is in what position?
how do they self-support their body?
have patient slowly lift what while approximating the rectus muscles and perform what?
then lastly slowly do what?
head lift with pelvic tilt
pt is in hooklying
arms are crossed over the diastasis for support as described in head lift exercise
have patient slowly lift only the head off the floor while approximating the rectus muscles and perform a posterior pelvic tilt
then lastly slowly lower the head and relax
Treatment for diastasis recti:
how should all abdominal contractions be performed?
what is the progression of treatment?
what is the FF tip to remember?
what if 3-4 cm?
what if it is >4cm?
if >6cm?
perform all abdominal contractions with an exhalation (during concentric) to minimize intra-abdominal pressure
abdominal bracing —> + head lifts —> + posterior pelvic tilt
3-4 cm = bracing + head lifts
if >4cm, no head lift, just bracing and breathing
>6cm refer pt and physician will decide if they want to do surgery or conservative

NPTE vs. treatment now for diastasis recti
NPTE
diastasis recti
avoid crunches, double leg lifts, fire hydrant (dog peeing), avoid valsava maneuver
clinical research
can do some advanced exercises
Genitourinary Quick Recap!
Treatment for functional incontinence?
What type of incontinence is seen with diabetes mellitus?
Blood pressure changes in pregnancy?
Exercises to avoid with diastasis recti?
Treatment for functional incontinence?
clear the clutter
if pt has cognitive problem then prompt with post-its
if they have weakness, do strengthening
gait problems, do gait training
What type of incontinence is seen with diabetes mellitus?
overflow
Blood pressure changes in pregnancy?
decreases first/second trimester
increases third trimester
Exercises to avoid with diastasis recti?
crunches, double leg lifts, fire hydrants, valsava maneuver
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): reflux of gastric content from where into where?
what are 3 complications?
reflux of gastric content from gastroduodenal contents into the esophagus
aka lower esophageal dysfunction because it does not stay closed so gastric contents comes up
complications (if GERD is not taken care of)
aspiration pneumonia, asthma
esophagitis (can be pre-cancer)
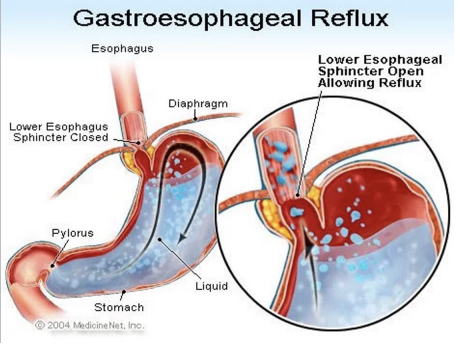
GERD symptoms:
heart burn occurring when? (2)
swallowing?
sour taste from what?
voice?
atypical pain where? (2)
what is this confused with?
heart burn
30 minutes after eating
at night lying down
dysphagia
sour taste
from regurgitation of acids
hoarseness of voice
atypical pain
head and neck, chest
confused with angina when they have chest pain
How would you differentiate whether GERD symptoms is a GI or cardiac issue?
position of pt
GI = improves with change of position
cardiac = worsen with activity
antacids
GI = improves
cardiac = does not relieve
Practice Question 3 – GERD
Which of the following guidelines is MOST APPROPRIATE in treating patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease?
A. Exercises should be performed in supine position
B. Encourage the patient to sleep on right side to prevent nocturnal reflex
C. Instruct the patient to perform Valsalva maneuvers during exercise
D. Encourage the patient to elevate the head of the bed while lying down
D. Encourage the patient to elevate the head of the bed while lying down
RATIONALE: Elevating the head of the bed reduces nocturnal reflux by using gravity to minimize backflow of gastric contents into the esophagus. Sleep on left side is encouraged to prevent nocturnal reflex, L side relaxes internal organs. Exercise must be completed 2-3 hours after eating. Valsalva maneuver increases intra-abdominal pressure, which worsens reflux symptoms.
when should the patient perform valsalva maneuver? if they are a spinal cord injury and need help fully voiding
Treatment of GERD:
maintain what positions?
eat meals how much longer before sleep?
avoid what position and why?
sleep on what side and why?
maintain upright positions
eat meals at least 3-4 hours before sleep
avoid supine - tends to straighten the esophagus
sleep on L side to prevent nocturnal reflex
Treatment of GERD pt. 2:
exercise when before or after meals?
avoid what 4 types of food?
3 types of drugs?
exercise must be completed 2-3 hours after eating or before meals
avoid spicy, chocolate, fatty food, peppermint
drugs
antacids
H2 receptor blockers
protein pump inhibitors