Quality Management and Patient Safety
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
and the award for world's least student-friendly slides goes to...
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
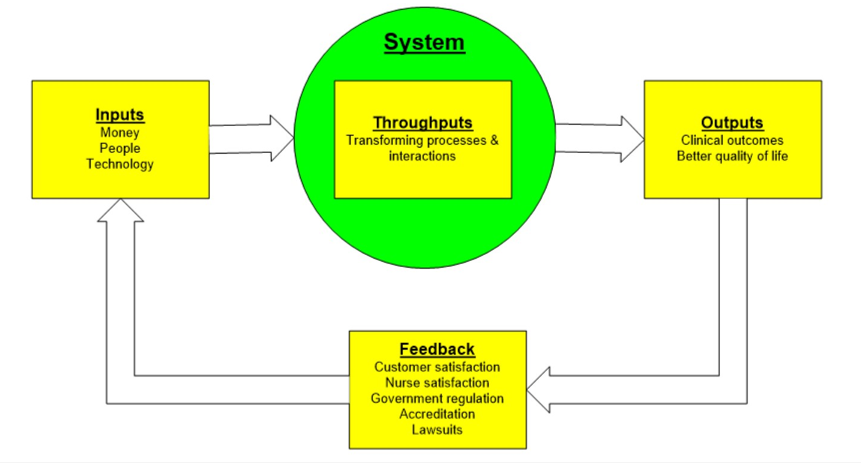
What is meant by throughput?
The things that pass through a system
Are transformed through processes and interactions
What was the call to action for developing the 6 aims for healthcare? Describe this.
1999 → “To Err is Human”
44000-98000 preventable deaths occur each year in hospitals due to medical errors and system failures
6 aims for Healthcare
STEEEP
Safe, timely, effective, efficient, equitable, and PT/person centered care
6 Aims for Healthcare Quality
Developed in response to high number of preventable hospital deaths.
STEEEP
Safe — Avoid injuries from care that is intended to help
Timely — Reducing wants and delays from pts and providers
Efficient — Provide appropriate level of services based on scientific knowledge (not giving too much but not too little)
Effective — Avoiding waste of equipment, supplies, ideas, and energy
Equitable — Care does not vary in quality due to personal characteristics
Pt/Person centered — Respectful and Responsive
STEEEP
6 Aims for Healthcare quality
Safe — Avoid injuries from care that is intended to help
Timely — Reducing wants and delays from pts and providers
Effective— Provide appropriate level of services based on scientific knowledge (not giving too much but not too little)
Efficient — Avoiding waste of equipment, supplies, ideas, and energy
Equitable — Care does not vary in quality due to personal characteristics
Pt/Person centered — Respectful and Responsive
One of the National Patient Safety Goals is to Improve the Accuracy of Patient Identification. What elements of performance can ensure this goal is met?
Use at least two patient identifiers when (The patient's room number or physical location is not used as an identifier.):
administering medications, blood, or blood components
collecting blood samples and other specimens for clinical testing
providing treatments or procedures.
Label containers used for blood and other specimens in the presence of the patient.
Use distinct methods of identification for newborn patients. Examples:
Distinct naming systems
Standardized practices for identification banding
Establish communication tools among staff
One of the National Patient Safety Goals is to Improve the Effectiveness of Communication among Caregivers. What elements of performance can ensure this goal is met?
I.E — Report critical results of tests and diagnostic procedures in a timely manner
Examples:
Written procedures for managing the critical results of tests and diagnostic procedures that address the following:
Definition of critical results of tests and diagnostic procedures
By and to who critical results of tests and diagnostic procedures are reported
Acceptable length of time between the availability and reporting of critical results of tests and diagnostic procedures
Evaluation of the timeliness of previous reports
One of the National Patient Safety Goals is to Use Medicines Safely. What elements of performance can ensure this goal is met?
Label all medications in an area where medicines and supplies are set up
Take extra care with patients who take blood thinners
Record and pass along correct information regarding a patient’s medications.
What meds are they taking?
Compare with new meds/prescriptions
Give pt written info regarding their meds
Tell the pt is important to give updated med info every time they visit a doctor
One of the National Patient Safety Goals is to Use Alarms Safely. What elements of performance can ensure this goal is met?
Ensure that alarms on medical equipment are heard and responded to on time
Determine which alarms are most important to manage immediately based on risk for patient harm if not responded to in a timely manner
Identify clear policies for whether alarms can be disabled or parameters changed
One of the National Patient Safety Goals is to Prevent infections. What elements of performance can ensure this goal is met?
Proper hand hygiene based on CDC and WHO guidelines
Set goals for improving hand cleaning
One of the National Patient Safety Goals is to Identify Patient Safety Risks. What elements of performance can ensure this goal is met?
Reduce the risk for suicide
Identify high risk patients with screening and assessment
Ensure environmental safety and safe discharges and counseling
One of the National Patient Safety Goals is to Improve Health Care Equity. What elements of performance can ensure this goal is met?
According to 2025 goals
One individual may be only in charge of ensuring equity for patients
Assess a patient’s health-related social needs
Identify health care disparities that a specific population faces
Written plan that describes how equity will be addressed
Include stakeholders to improve equity
One of the National Patient Safety Goals is to Prevent Mistakes in Surgery. What elements of performance can ensure this goal is met?
Ensure correct surgery on correct patient
Mark correct area on body where surgery is to be done
Have a “timeout” before surgery to ensure no mistake is being made
QSEN
Quality and safety education for nurses
Initiative to develop and implement competencies for safe and high-quality patient care
National quality strategy
Part of affordable care act
Goals:
Improve health of american public
Improve healthcare experiences
Make healthcare more affordable
Definition: Quality
How much health services (on individual and population level) increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes
Are they consistent with current professional knowledge (are they based on current evidence?)
True or false:
Total quality management is interchangeable with quality improvement
TRUE
Total Quality Management (TQM) = Quality Improvement (QI) = Process improvement (PI)
Definition: Quality improvement
Systematic process to improve outcomes
Uses data + scientific method to assess and problem solve
Based on customer needs
Proactive approach
Everyone has a responsibility in QI
Continuous process
Quality improvement:
______ process to improve outcomes
Uses ____ and _______ to assess and problem solve
Based on _______
(Reactive or proactive) approach
Who is responsible for quality improvement?
Is quality improvement a continuous process or in response to acute problems?
Systematic process to improve outcomes
Uses data + scientific method to assess and problem solve
Based on customer needs
Proactive approach
Everyone has a responsibility in QI
Continuous process
Quality improvement vs Quality Assurance
Quality Improvement:
Systematic process
Determining ways/methods to improve future quality
Continuous process
Prospective approach — looking to future
Everyone’s responsibility
Quality Assurance:
Investigative approach
Ensuring that current practices are compliant against standards
Is the quality produced good?
Reactive process
Retrospective — Looking at previous/current approaches, seeing if it’s good enough
Audits, incident reports, etc
Responsibility of a few — People who overlook to reports, look at data, etc
A plan is developed in order to decrease the number of CAUTIs developed on a unit. Would this be quality improvement or quality assurance?
Quality improvement
The incident reports on a particular unit are reviewed in order to identify any consistent issues present. Is this quality improvement or quality assurance?
Quality assurance
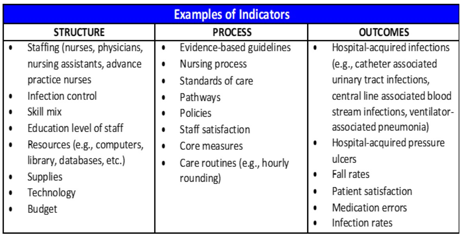
Donabedian model of quality
3 domains
Structure
Elements that make up health care system
Process
Interaction between patients and providers
Outcome
End results of health care practices/interventions
Domains of Donabedian Model of Quality
Structure
“How is care organized?”
Stable elements → Make up the healthcare system
Process
“What is done?”
Interactions between patients and providers
Outcome
“What happens to patient’s health?”
End results of healthcare practices/interventions
Structure domain of Donabedian Model of Quality
Structure
“How is care organized?”
Stable elements → Make up the healthcare system
Process domain of Donabedian Model of Quality
Process
“What is done?”
Interactions between patients and providers
Outcome domain of Donabedian Model of Quality
Outcome
“What happens to patient’s health?”
End results of healthcare practices/interventions
What are examples of nursing indicators representing the Structure domain in Donabedian’s Model of Quality?
Supply of nursing staff
Skill levels
Education/certification of staff
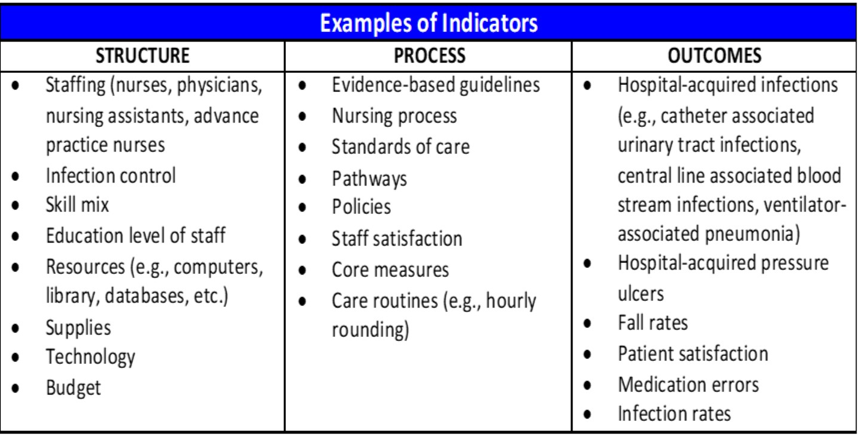
What are examples of nursing indicators representing the Process domain in Donabedian’s Model of Quality?
Assessments
Interventions (meds given, nursing actions, etc)
RN job satisfaction (?)
Are nursing activities/care being done appropriately, effectively, and efficiently?
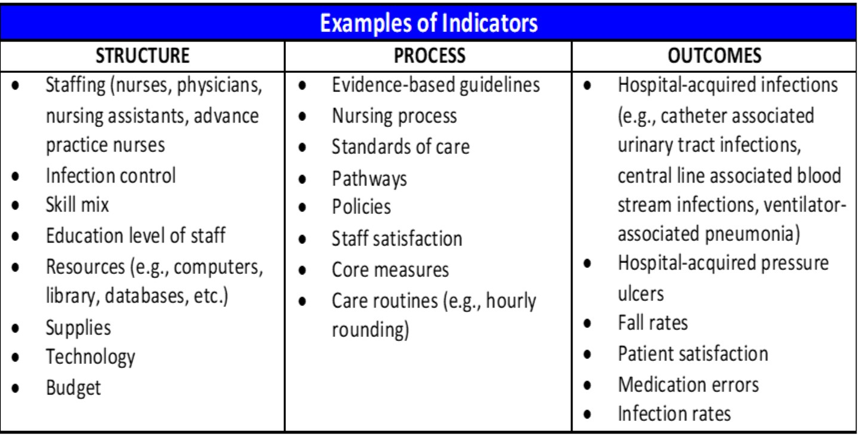
What are example of nursing indicators representing the Outcomes domain in Donabedian’s Model of Quality?
Falls
Pressure ulcers
IV infiltrations
Did the services provided make a difference (good or bad)?
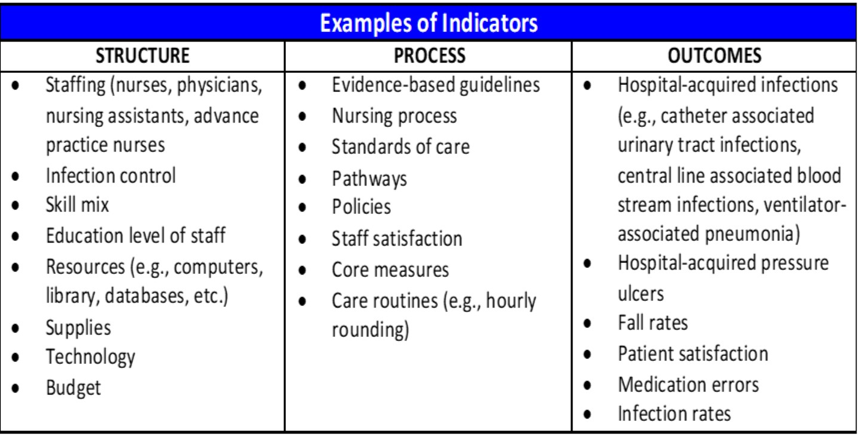
Patient safety indicators
Set of measures that screen for adverse events
Pressure ulcers
“Failure to rescue”
Foreign body left during procedures
Transfusion reactions
Post-op sepsis
Post-op wound dehiscence
What empowers the public to seek quality healthcare services?
Core measures — Methods of tracking the quality of healthcare provided from various hospitals
Core measures —> Strokes, VTE, etc
Quality measures
Efficiency of care
Structure of the care
Process of the care
Outcomes of care
The patient’s experience/perception of the care they received
Core measure: Efficiency of care
Resources needed to provide quality care VS the actual quality of the healthcare
Example: cost of care
Core measure: Structure of care
The presence of a mechanism/system that supports the delivery of quality health care
Example:
Electronic health records
Participation in quality measures databases
Core measure: Process of care
Whether the patient received elements of care that are evidence-based
Example:
Documentation that aspirin was given to pts with MI
Core measure: Intermediate outcomes
Result of health care processes
Example:
Mortality rates
Patient safety indicators
How is patient-centered care measured?
Surveys
Standards of care
Minimum acceptable nursing care → Scope, function, and role of a nurse in practice
Reflect the knowledge and skill possessed by active nurses
Developed by the ANA (american nurses association)
Used to determine the presence of malpractice
What organization develops the standards of care by which active nurses practice?
American nurses association (i think this is the main source?)

What outlines the scope, function, and role of actively practicing nurses?
Standards of care from ANA
What is compared to a nurse’s actions in order to determine the presence of malpractice?
ANA Standards of care
How is a nursing intervention evaluated according to the Standards of Care?
2 factors: appropriateness of the intervention + correct application of the intervention
Standards of care —→ Determine whether the intervention was appropriate or whether additional interventions need to be taken
Basic steps in quality improvement (check lippincott, i think it’s organized better lmaoo)
Identify the problem
Identify the metric associated with the problem
Assemble evidence that the problem is legitimate
Align with Donabedian Model of quality (Structure, Process, or Outcome problem)
Assemble an improvement team
Determine extent of problem with analysis tools and data collection
Consider financial aspect
Determine evidence-based interventions
Testing of evidence-based interventions
Develop a plan to sustain the interventions
Put the steps of quality improvement in order
Assemble an improvement team
Determine evidence-based interventions
Identify the problem
Align with Donabedian Model of quality
Assemble evidence that the problem is legitimate
Identify the metric associated with the problem
Develop a plan to sustain the interventions
Determine extent of problem with data collection
Consider financial aspect
Testing of evidence-based interventions
Identify the problem
Identify the metric associated with the problem
Assemble evidence that the problem is legitimate
Align with Donabedian Model of quality (Structure, Process, or Outcome problem)
Assemble an improvement team
Determine extent of problem with analysis tools and data collection
Consider financial aspect
Determine evidence-based interventions
Testing of evidence-based interventions
Develop a plan to sustain the interventions
You notice that on your floor, there are a high amount of pressure ulcers.
What step in quality improvement would this be?
Identify the problem/opportunity for improvement
Noticing a gap between what organization desires vs actual performance
Is it possible to obtain data that proves the problem exists?
Is this issue important to patient care, goals, and/or team?
You identify that the frequency of pressure ulcers on your floor aligns with AHRQ Patient Safety Indicator #3: Pressure ulcer rates.
What step in the quality improvement process is this?
Identify metric associated with the problem
What measure/data and/or indicator is associated with the problem?
You gather information on the rate of pressure injuries on your floor from every month in the past year. You determine that your floor is not meeting current standards.
What step in quality improvement process is this?
Examine historical data to assemble evidence that the problem actually exists
You determine that the high frequency of pressure injuries on your floor is indicative of an issue with patient outcomes, according to the Model of Quality.
What step in quality improvement process is this?
4. Align the problem/indicator with Donabedian’s Framework
You speak to the manager on your floor regarding the high frequency of pressure injuries on your floor. You get permission to assemble a team to address this issue.
What step in the quality improvement process is this?
Notify the chain of command, assemble the improvement team
“Know your stakeholders”??
Seek support in addressing the problem
Time, money, supplies, personnel
Assemble the team
Project goals — SMART format
You compare the rates of pressure injuries on your floor with the rates of pressure injuries in the same unit at a neighboring hospital (that has overall better outcomes).
What step in the quality improvement process is this?
Determine the extent of the problem
Benchmarking: Comparison against other organizations that have better outcomes/results. Determine how those results are achieved, and use this info to improve our own operations.
Other methods of collecting/comparing data
Gap analysis, fishbone
Surveys, interviews
Qualtiy metrics
Etc
Benchmarking
improvement process
Comparison of results with those of another organization with better results
Determine how this performance is achieved —→ Used to improve its own performance
Internal vs external
Internal - using data from within the organization
External - comparing with other hospitals/organizations (nationwide or worldwide or whatever)
You determine that addressing the high frequency of pressure injuries on your unit would save your hospital a large amount of money and resources.
Which step in the quality improvement process is this?
Consider the financial aspect of the problem
Does the problem impact you financially?
Will there be a return on investment into fixing the problem?
You and your team research and determine based on previous research studies strategies that can reduce the frequency of pressure injuries on your floor.
What step in the quality improvement process is this?
Search the literature for interventions that are evidence-based
Create evidence table with interventions
Use this to determine the best intervention(s)
What are often components of a sustainment plan in the quality improvement process?
Champions - encouraging staff to maintain gains, continue to improve
Quality Assurance Monitoring
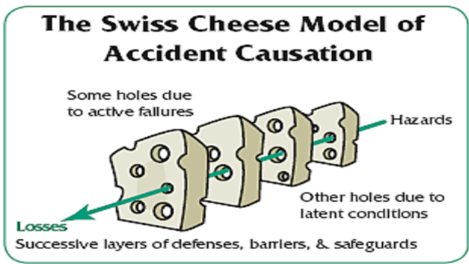
Error definition
Error of execution: Failure to complete a planned action as intended
Error in Planning: Use of the wrong plan to achieve an aim
Directly related to outcomes
Active (you messed up directly) vs latent (the system itself is effed up)
Active error vs Latent error
Active error
“Incident that is non-compliant with procedure”
The nurse makes a mistake on their own
Latent error
The incident involves problems within the system
“May lie dormant in a system”
When they both occur —→ They can bypass multiple safeguards
Definition: Misuse
Avoidable event — prevents patient from receiving the full benefits of a service
Examples:
Incorrect diagnoses
Medication errors
Avoidable complications
Definition: Overuse
Occurs when the potential for harm from a service exceeds the possible benefits
“Risks outweigh the benefits”
Examples:
Overtesting, overdiagnoses, overtreatment → May increase risk for complications, errors, and healthcare costs
Definition: Adverse event
Injury resulting from medical intervention
Not due to the patient’s underlying conditions
Example:
Falls, pressure injuries, cautis, etc
Definition: Never Event
“particularly shocking medical errors—such as wrong-site surgery—that should never occur.”
“adverse events that are unambiguous (clearly identifiable and measurable), serious (resulting in death or significant disability), and usually preventable.”
I’m pretty sure it’s the same as a never event. They literally have the same definitions.
Examples:
Surgical
Wrong site, foreign body,wrong pt
Devices
Contamination leading to death/impairment
Air embolisms
Death from medication error
Etc
Failure to Rescue
Deterioration (death or permanent disability) that occurs from a complication from illness or medical care
The degree to which providers responded to adverse occurrences that developed under their care that lead up to the deterioration
Not inherently due to negligence. It describes when a pt dies/is disabled due to a complication.
Work-around
When one doesn’t follow the rules or works around the rules/correct actions of a process in order to save time
“Cutting corners” (especially in an unsafe way)
Can lead to error and/or adverse events!
Near-Miss
Recognition that an event occurred that might have led to an adverse event
Sentinel event
Event that had a negative patient outcome (unexpected death, serious physical/psychological injury, serious risk)
I’m pretty sure it’s the same as a never event. They literally have the same definitions.
Root Cause Analysis
In-depth analysis of an error to assess the event and identify causes and possible solutions
Incident/Variance Report
Confidential document
Describes any patient or staff accident/incident while on premises
What conditions might serve as a barrier to creating an incident report?
Inability to recognize errors
Documentation suckss
Lack of anonymity
Hesitancy
Unclear reporting requirements for errors without an adverse outcome
Fear of lawsuits
Feeling like it won’t make a difference
What is a Root Cause Analysis?
Interdisciplinary and full of experts - meant to be impartial
Involves those who are most familiar with the situation
“Why why why”
Trying to determine why an adverse event/near miss/error or whatever the frick occurred
Identifies changes that need to be made
Goals:
What happened, why did it happen, and how to prevent it from happening
A thorough Root Cause Analysis will include:
Determination of contributing _____
Determination of the related _____ and ______
Analysis of underlying _____ and ______
Identification of ____ and their potential contributions
Determination of potential _______ in processes or systems
Determination of contributing factors
Determination of the related processes and systems
Analysis of underlying causes and effects
Identification of risks and their potential contributions
Determination of potential improvement in processes or systems
Culture of Safety
Blame-free environment in which staff can practice and openly discuss potential errors or near-misses and actual errors
“Prevention, NOT punishment!”
A culture of safety allows a just culture to exist
Just Culture
Staff are willing to come forward with info about errors so people can learn from mistakes
Recognition of need for accountability and at times, disciplinary actions
“No shame, no blame”
A happy medium between punishment for every mistake vs letting everybody get off scott free.
People shouldn’t be afraid to speak up - However, accountability still needs to exist at some capacity
5 Characteristics of High-Reliability Organizations
Preoccupation with failure
Be alert to near-misses, recognize weaknesses in systems early
Basically be like me — always prepare for and expect the worst
Reluctance to simplify
Recognize the complexity of the work
Easy-fix causes may not be enough to prevent a failure
(note to self - don’t think of it as complicating things. think of it as not expecting an easy simple magic fix for a problem, and that it will likely require a lot of effort to address the causes of a failure")
Sensitivity to operations
Recognize complexity of healthcare processes
Situational awareness of environment, distractions, resources, supplies, and relationships
Resilience
Anticipate failure
Determine how to diminish risk of harm
Identify strategies to recover when an adverse event occurs
Deference to expertise
Teamwork
Active participation from other professionals
Share information
Deemphasize hierarchys
Basically = bitch be humble
List the 5 characteristics of high-reliability organizations
Preoccupation with failure
Reluctance to simplify
Sensitivity to operations
Resilience
Deference to expertise
Safe Harbor
protects a nurse from employer retaliation, suspension, termination, etc when a nurse makes a good faith request for peer review of an assignment
Nurse must believe it could result in violation of NPA or board rules
MUST be invoked PRIOR to engaging in the assignment in question
May be invoked at anytime should the assignment change
A nurse has been given an assignment of 6 patients. Midway through her shift, she receives another patient with a relatively high acuity. She tries to continue caring for all 7 of her patients, however, she becomes overwhelmed due to the new pts acuity. She invokes safe harbor.
Is she allowed to do this?
If she had invoked it prior to starting patient care then maybe.
However, at this point, she may be unable to invoke it.
“Must be invoked prior to engaging in assignment in question”
Requirements for invoking safe harbor?
“Good faith”
Orally invoke safe harbor
Invoke PRIOR to accepting an assignment
Nurse supervisor must complete the Safe Harbor form