Biology - The Chemical Basis of Life
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Last updated 12:01 PM on 11/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
Chemicals that serve as stimuli to other individuals of the same species for varied behavioral responses are ...
Pheromones
2
New cards
Matter is anything that ...
occupies space and has mass
3
New cards
Matter is composed of ...
chemical elements
4
New cards
An element is a substance that ...
can not be broken down into other substances
5
New cards
How many elements occur in nature?
92
6
New cards
How many chemical elements are essential to life?
Around 25
7
New cards
__% of the human body (the bulk) is made up of _____, ______, _______, and _______.
96, carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
8
New cards
Trace elements are _____ to the body even though they are found in _____ quantities.
vital, small
9
New cards
A deficiency in this trace element causes the thyroid gland to grow to an abnormal size (goiter).
Iodine
10
New cards
A deficiency in this trace element causes anemia.
Iron
11
New cards
A deficiency in this trace element causes tooth decay.
Fluoride
12
New cards
True or False: all atoms in an element are similar
True
13
New cards
Formed when 2 or more atoms combine (same or different elements):
molecule
14
New cards
Formed when 2 or more atoms from different elements combine:
compound
15
New cards
NaCl is:
Sodium Chloride
16
New cards
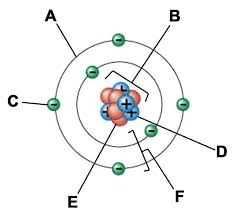
A:
Electron cloud
17
New cards
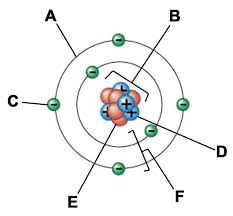
B:
Nucleus
18
New cards
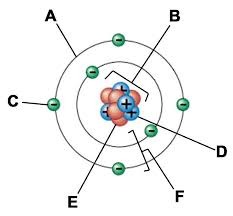
C:
Electron
19
New cards
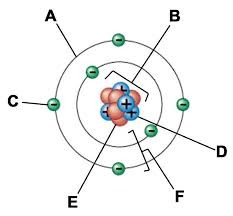
D:
Proton
20
New cards
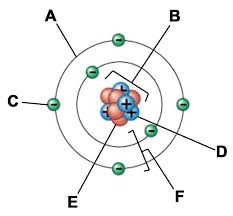
E:
Neutron
21
New cards
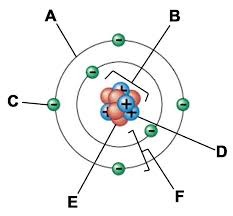
F:
Electron shells
22
New cards
The smallest particle of matter is:
Atom
23
New cards
Protons are _____ charged, _____ ______ in the center of the atom
positively, tightly, packed
24
New cards
Neutrons have ___ charge, ______ ______ in the center of the atom.
no, tightly, packed
25
New cards
Electrons are _____ charged, more at the speed of ______, form a ____ around the atom.
negatively, light, cloud
26
New cards
Atomic number =
number of protons in an atom
27
New cards
In a neutral atom, atomic number = number of ______ = number of _____
protons, electrons
28
New cards
All atoms of the same element have the same ____ but different ____.
atomic number, atomic mass
29
New cards
Atomic mass =
number of protons + number of neutrons
30
New cards
1 electron = ______ the mass of a proton
1/2000
31
New cards
Isotopes are atoms of the same ______ with a different atomic _____.
element, mass
32
New cards
Stable isotopes have intact _____
nuclei
33
New cards
Unstable isotopes are _______. Their _____ decays and gives off particles and energy
radioactive, nuclei
34
New cards
Radioactive isotopes work as markers for ...
their nonradioactive counterparts
35
New cards
Radioactive isotopes can work as a treatment for this illness ...
cancer
36
New cards
Radioactive isotopes also help _____ with instruments
diagnosis
37
New cards
Radiation can cause _____.
cancer
38
New cards
Electron arrangement determines the _____ _____ of an atom.
chemical, properties
39
New cards
The farther an electron is from the nucleus, the _____ its energy.
greater
40
New cards
Electron shells are:
electron energy levels
41
New cards
The first shell is full with ____ electrons
2
42
New cards
The second shell is full with ____ electrons
8
43
New cards
The third shell is happy with ___ electrons
8
44
New cards
The fourth shell is satisfied with _____ electrons
18
45
New cards
Electron capacity:
2n^2
46
New cards
Energy levels _-_ are happy with less than the maximum amount of electrons they can hold
3,7
47
New cards
This is the outermost electron shell of an atom:
Valence shell
48
New cards
Electrons in the valence shell are called:
Valence electrons
49
New cards
Valence electrons determine the _____ _____ of an atom
chemical, properties
50
New cards
Atoms with valence shells that are not full tend to do what?
Bond with other atoms and share valence electrons
51
New cards
Both major chemical bonds share two rules: the resulting compound is ____, and the outer orbits are ____.
neutral, full
52
New cards
This bond is attractions between ions of opposite charges:
Ionic bond
53
New cards
The steps to an ionic bond: 1. atoms share ____ until both atoms have _____ electron shells 2. This causes an attraction because the atoms have _____ charges.
electrons, full, opposite
54
New cards
Atom that loses an electron:
cation (positive)
55
New cards
Atom that gains an electron:
anion (negative)
56
New cards
This chemical bond involves atoms sharing electrons:
Covalent bond
57
New cards
Covalent nonpolar molecules share electrons _____
equally
58
New cards
Covalent polar molecules share electrons _____
unequally
59
New cards
These bonds are attractions between oppositely charged parts of polar molecules
Hydrogen bonds
60
New cards
Each water molecule is bonded to ____ other water molecules
4
61
New cards
The 2 strands in a DNA molecule are held together with:
hydrogen bonds
62
New cards
The property by which water molecules stick TO EACH OTHER:
cohesion
63
New cards
Cohesion helps water molecules move from a plant's _____ to its ______
roots, leaves
64
New cards
The property by which water molecules stick TO OTHER SUBSTANCES:
adhesion
65
New cards
The rising of liquids through a small tube with adhesion and cohesion is called:
Capillary Action
66
New cards
How difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid:
Surface tension
67
New cards
When heat is ______, hydrogen bonds break
absorbed
68
New cards
When hydrogen bonds assemble, heat is ________
released
69
New cards
a small amount of heat only _____ the hydrogen bonds, but a large amount will _____ them.
disrupts, breaks
70
New cards
When a liquid evaporates, only the molecules with ______ kinetic energy are left. This is called ________ ________
less, evaporative, cooling
71
New cards
Evaporative cooling ______ temperature of lakes and ponds, prevents ______ tissue from becoming too warm, and cools down the _____ body by releasing ______.
regulates, plant, human, sweat
72
New cards
Why is ice less dense than water?
Its hydrogen bonds hold the molecules farther apart
73
New cards
Generally, liquids become _____ denser when they cool
more
74
New cards
Water is densest at what temperature? (Celcius)
4
75
New cards
When water reaches this temperature, its molecules spread apart and form a crystal lattice
0
76
New cards
True or False: Ice sinks under water.
False
77
New cards
If ice sank, what would happen?
Aquatic life would be trapped, ponds and lakes would fully freeze
78
New cards
When water turns to ____, it absorbs heat and _____ hydrogen bonds.
vapor, breaks
79
New cards
When vapor turns to ______, it releases heat and ______ hydrogen bonds
water, creates
80
New cards
Anything dissolved in water:
Aqueous solution
81
New cards
Water dissolves what:
ionic compounds and polar molecules
82
New cards
To dissolve molecules, water molecules ____ apart the solvent molecules and _____ them from one another
break, seperate
83
New cards
Sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion:
hydration shell
84
New cards
These substances like water, are ionic, and are polar:
hydrophilic substances
85
New cards
These substances are scared of water, are non-ionic, and are non-polar:
hydrophobic substances
86
New cards
Hydrogen forms _____ bonds with other elements, while all other group _____ elements form ____ bonds with other elements.
covalent, 1A, ionic
87
New cards
This happens when a small percentage of water molecules break apart into ions in an aqueous solution:
Dissociation of water
88
New cards
What ions are formed in the dissociation of water?
Hydronium ions (H3O+) and Hydroxide ions (OH-)
89
New cards
Synonym for hydronium ions:
Hydrogen ion (H+)
90
New cards
2____ -> ____ + _____
H2O, H3O+, OH-
91
New cards
Acids
A compound that releases H+ ions in a solution
92
New cards
An acidic solution has a higher concentration of _ ions than _ ions.
H+, OH-
93
New cards
Base/Alkaline substance
A compound that accepts H+ ions or releases OH- ions in a solution
94
New cards
A basic solution has a higher concentration of _ ions than _ ions
OH-, H+
95
New cards
The pH of a solution is the negative logarithm of the _____ ions concentration in _____ per ______.
hydrogen, moles, liter
96
New cards
Each pH unit has what change?
10x
97
New cards
What pH level is neutral?
7
98
New cards
Solutions below 7 are:
acidic
99
New cards
Solutions above 7 are:
basic
100
New cards
What do buffers do?
They maintain large fluctuations in pH levels that could damage living tissues