Hosa Pharmacy Science: Identifying pharmacy equipment
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
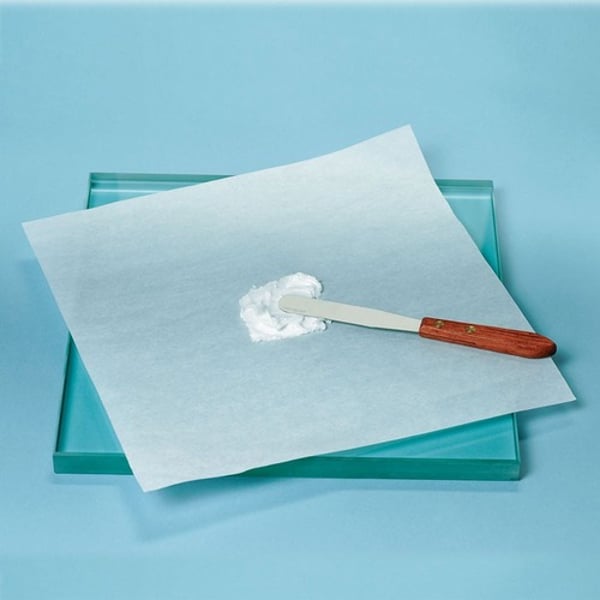
Compounding slab
Compound different substances together, usually ointments

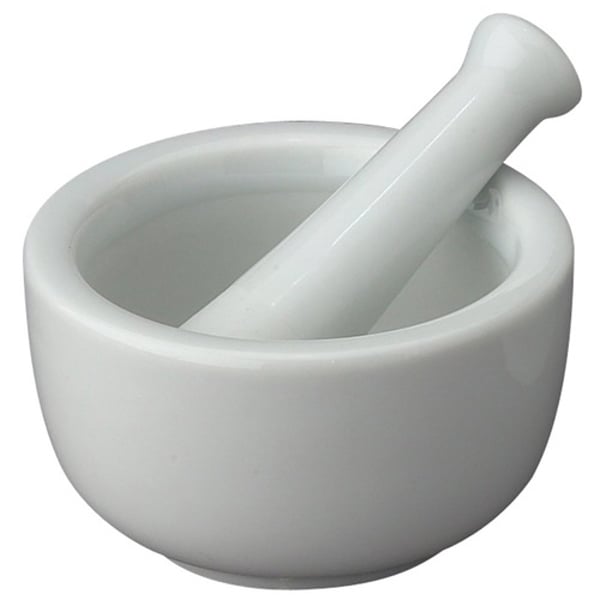
Mortar
Bowl: vessel in which substances are ground or crushed with a pestle
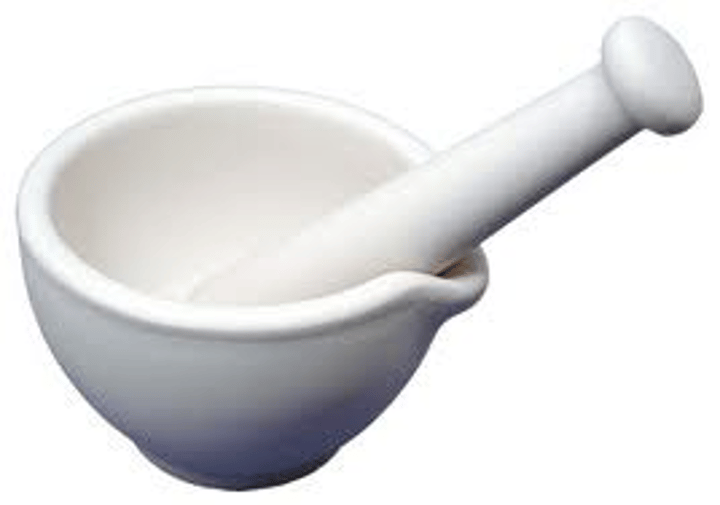

Pestle
Stick: used crush, mash or grind materials in a mortar

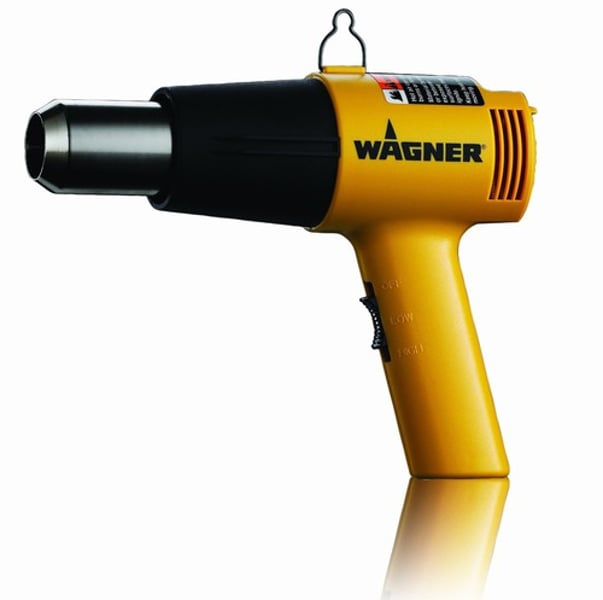
Heat Gun
Often used to shrink bands onto vials

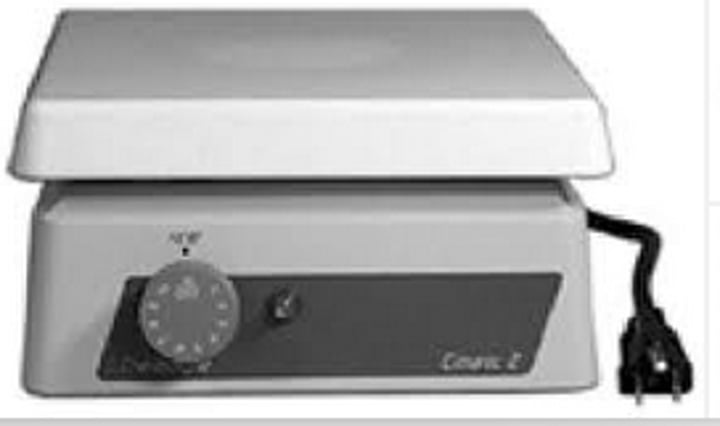
Hot plate
Used for fast heating

Crimper
Used to seal and close vials and other containers
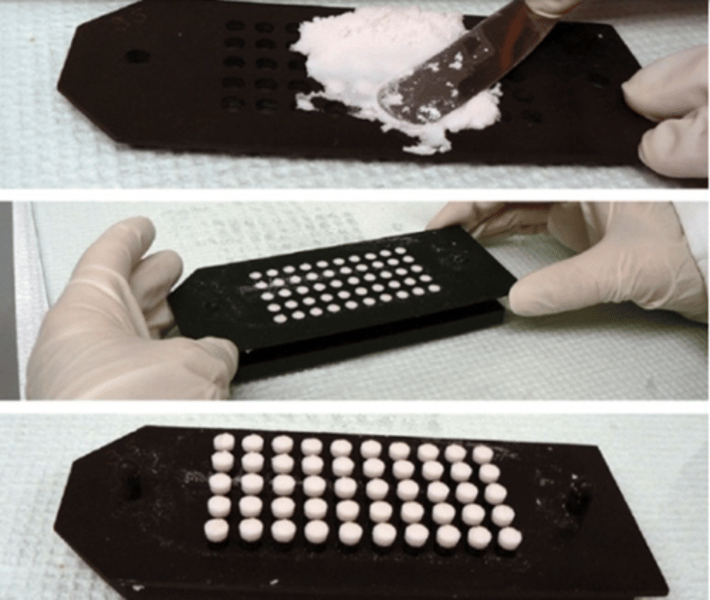
Tablet mold
used to mold compounds into single tablets

Suppository Mold
used to mold suppository capsules
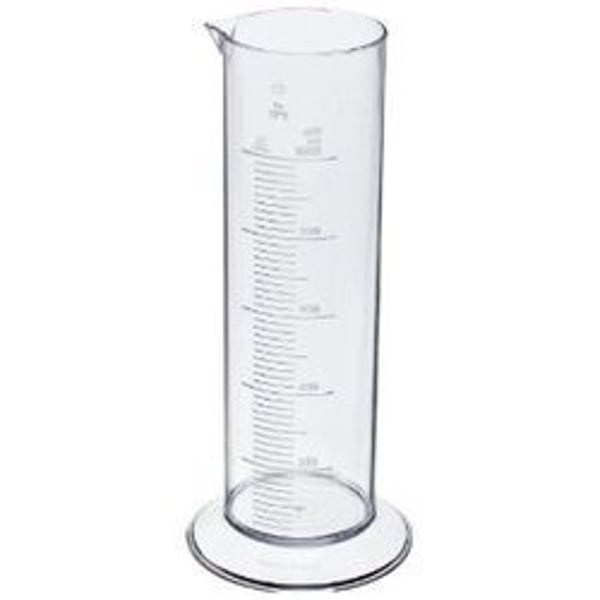
Cylindrical graduates
used to measure volumes of liquids

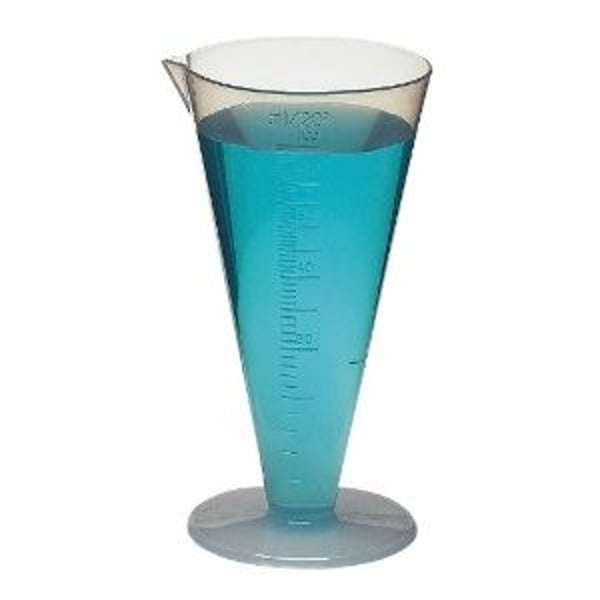
Conical Graduates
used to measure volumes of liquids; easier to clean

Pippettes
Long thin tubes made of glass and are used for measuring 1.5mL or less of liquids

Beakers
used to measure liquids or covered to store various liquids

Beaker tongs
Used to grab beakers when at an extreme temperature or when fumes are strong
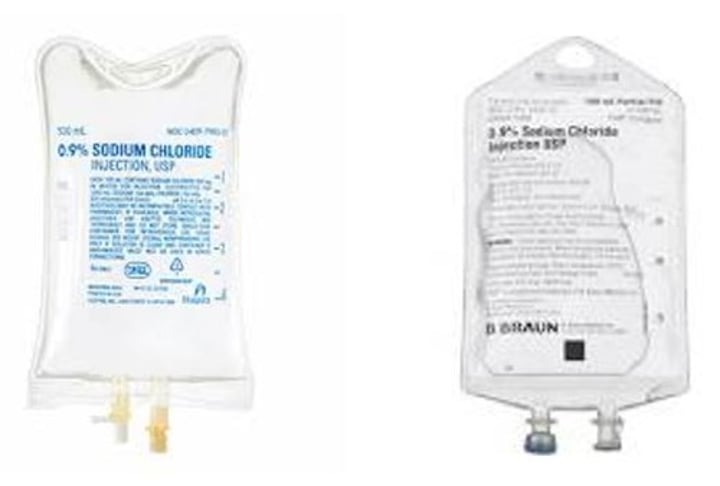
Intravenous System: IV solution bag
fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body, because the circulation carries them
Intravenous System: Injection port
where medicine or fluids other than those in the current IV bag can be injected so that they will infuse into the patient's vein through the IV tubing. The injection port on the actual IV bag is used if we want to mix some kind of medication with the fluid that is in the IV bag

Intravenous System: Drip chamber
inside this chamber we can see the fluid drip down from the bag into the IV tubing. This is where we measure the speed of a manual IV setup; we look at this chamber and count the number of drops we see per minute. The drip chamber must always be half full.
Intravenous System: Roller clamp
what we use to control the rate at which the IV fluid infuses

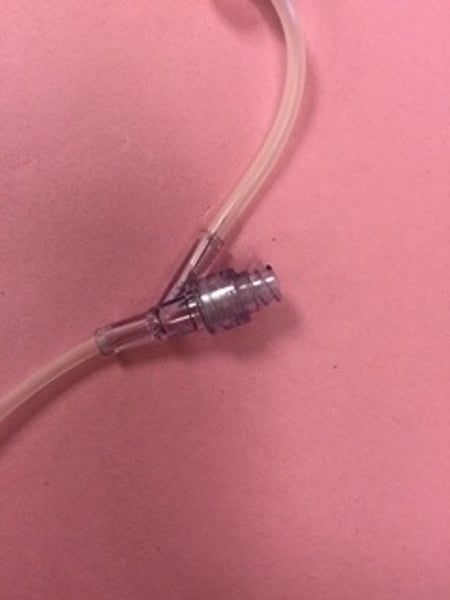
Intravenous System: Piggyback device
used to mix different iv bag contents
Syringes: Safety syringe
Safety syringes have a safety mechanism built into the syringe. The needle on a safety syringe can be detachable or permanently attached.
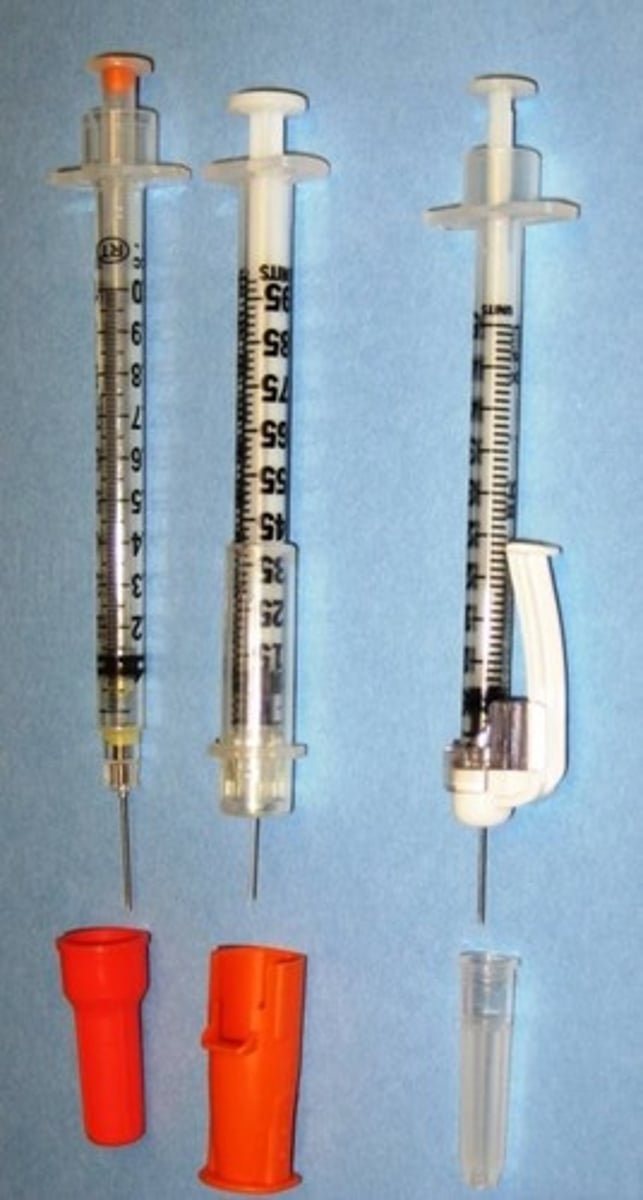
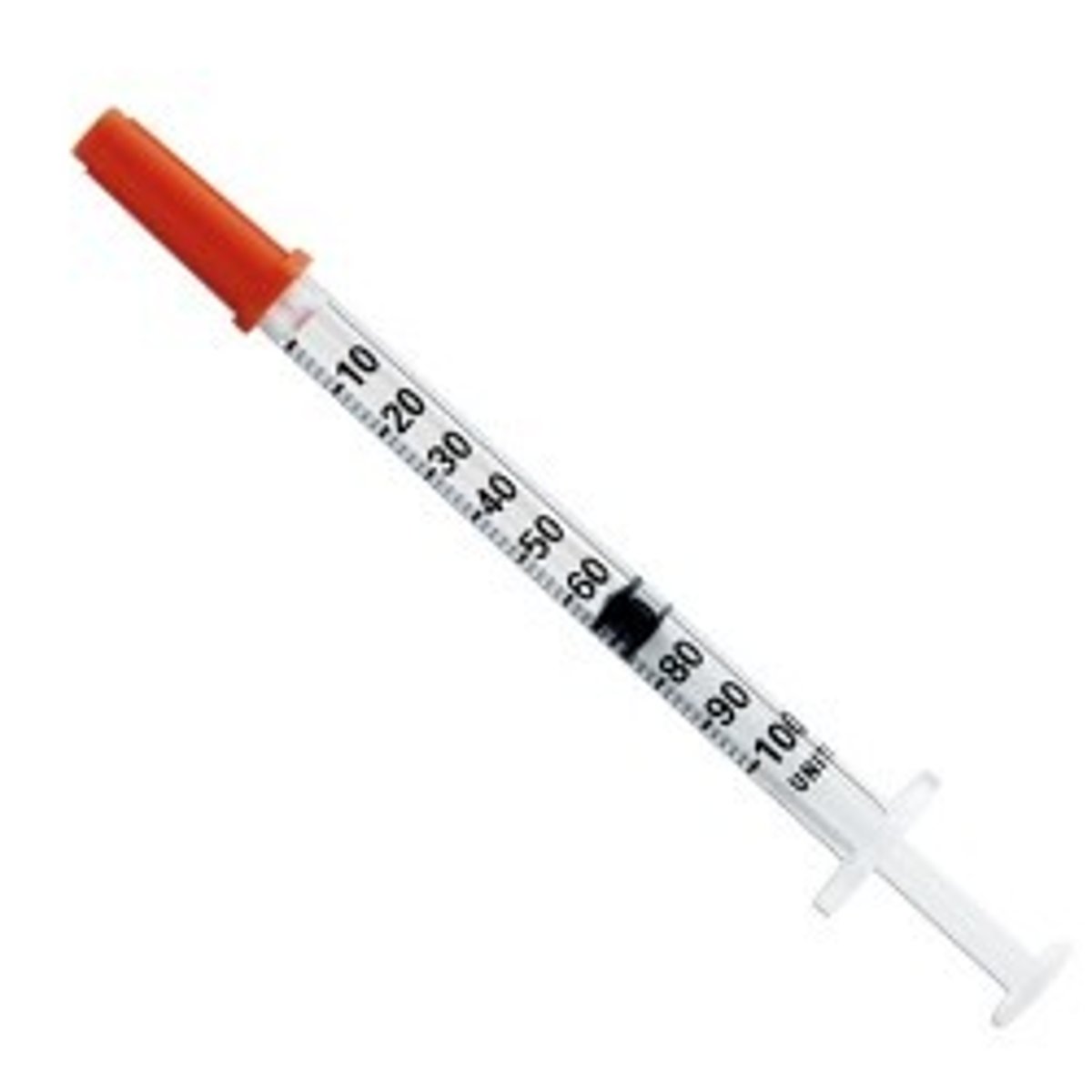
Syringes: Insulin Syringe
made specifically for self injections and have friendly features: shorter needles, as insulin injections are subcutaneous (under the skin) rather than intramuscular, finer gauge needles, for less pain, and. markings in insulin units to simplify drawing a measured dose of insulin.
Syringes: Tuberculin Syringe
are small syringes with fine needles that hold up to one half to one cubic centimeter of fluid, used to administer medication (antigen) under the skin and perform a tuberculosis test called PPD.
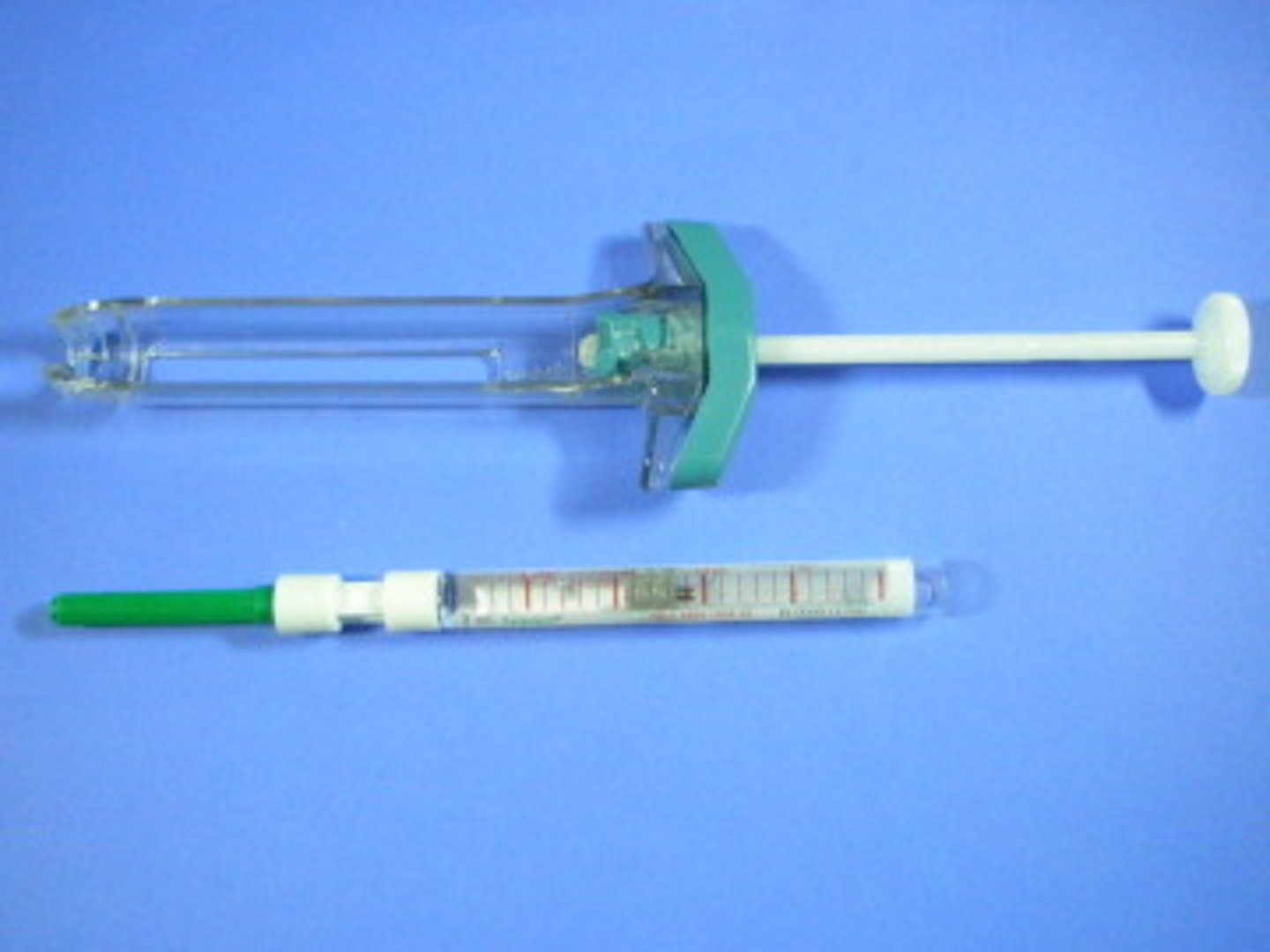
Syringes: Prefilled/ Single dose
is a disposable syringe that is supplied already loaded with the substance to be injected

Syringes: Intravenous Injection
Some medications must be given by an intravenous (IV) injection or infusion. This means they're sent directly into your vein using a needle or tube. In fact, the term "intravenous" means "into the vein."
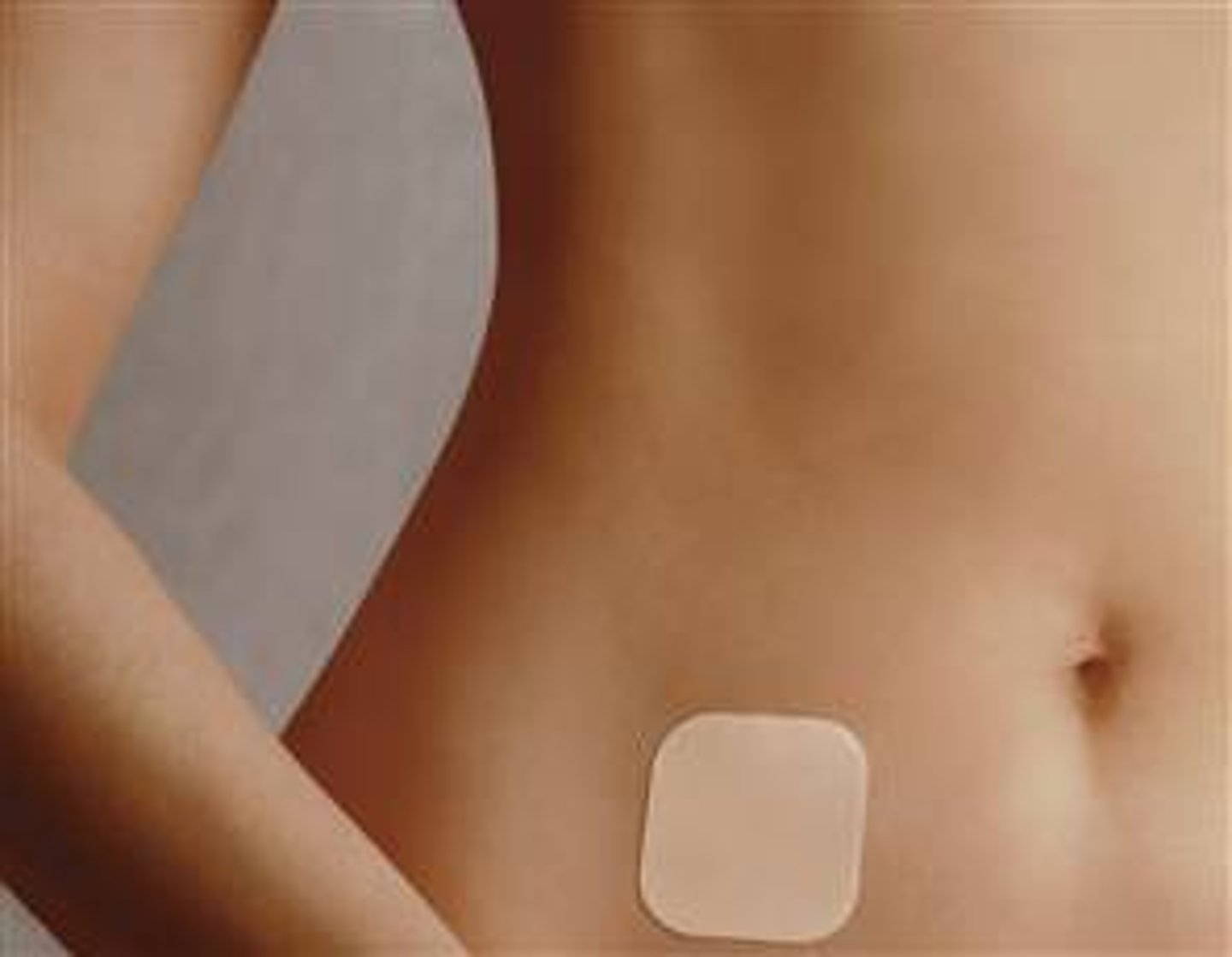
Transdermal Patch
a small patch with medication placed on the skin
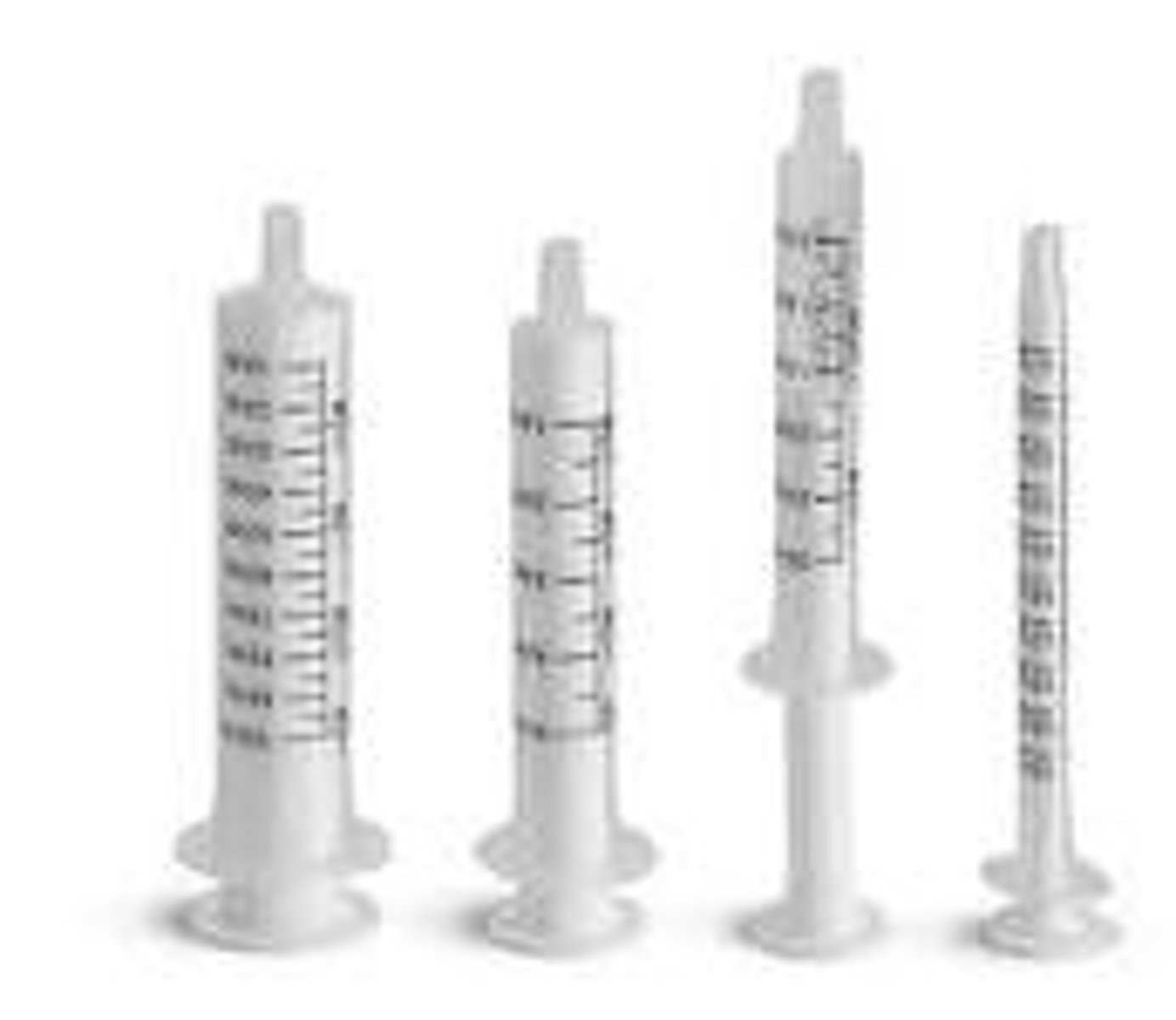
Liquid Oral Syringe
used to dispense liquid solutions and suspensions
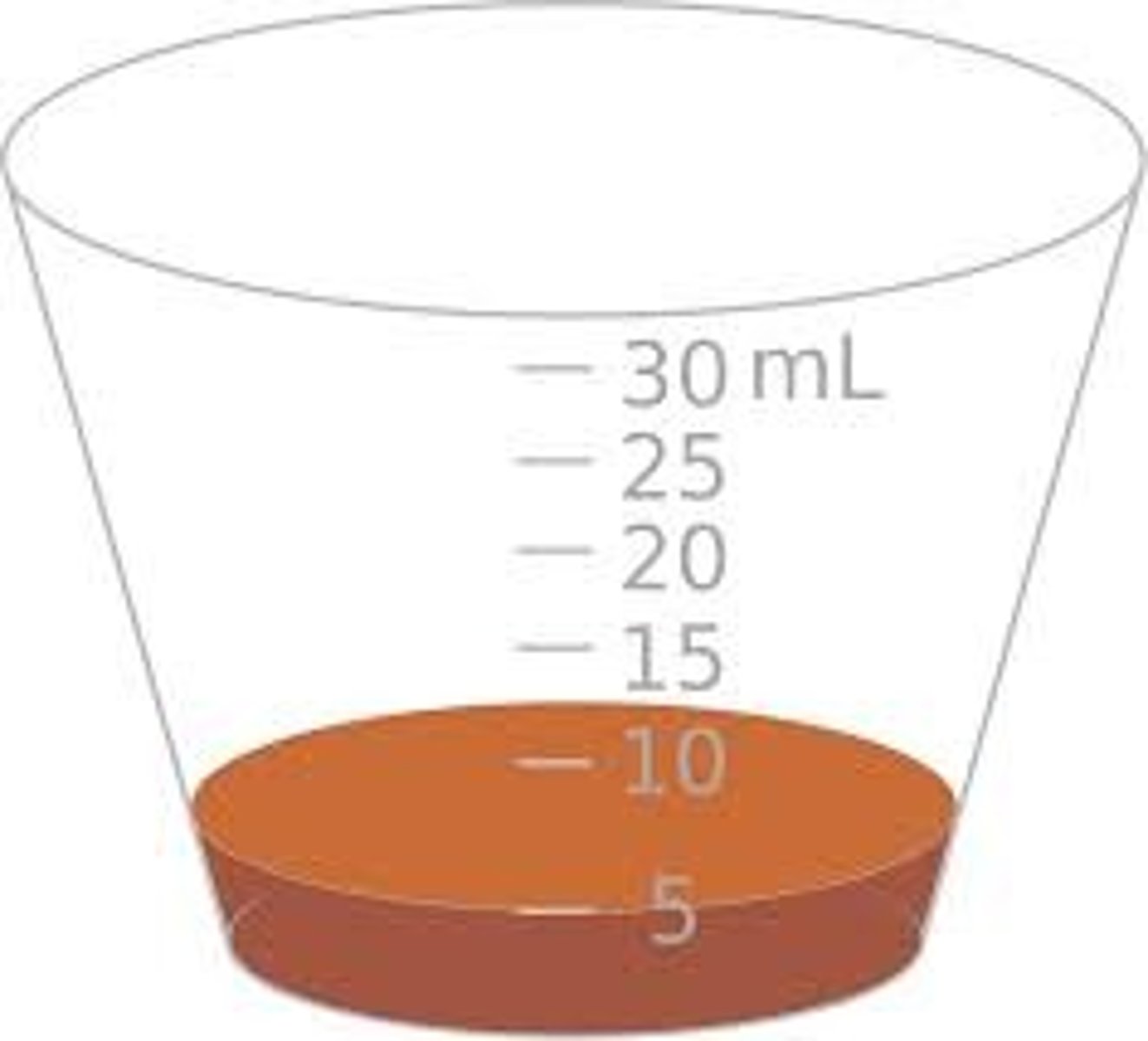
Medicine Cup
small plastic measuring cup

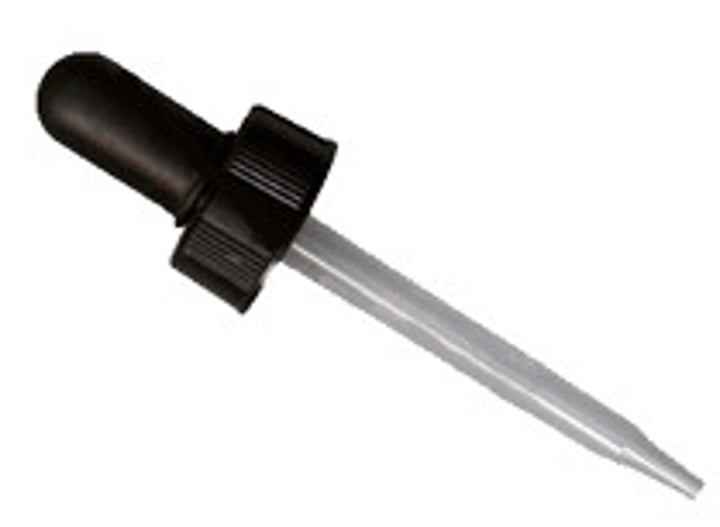
Medicine Dropper
used to transfer small amounts of liquid

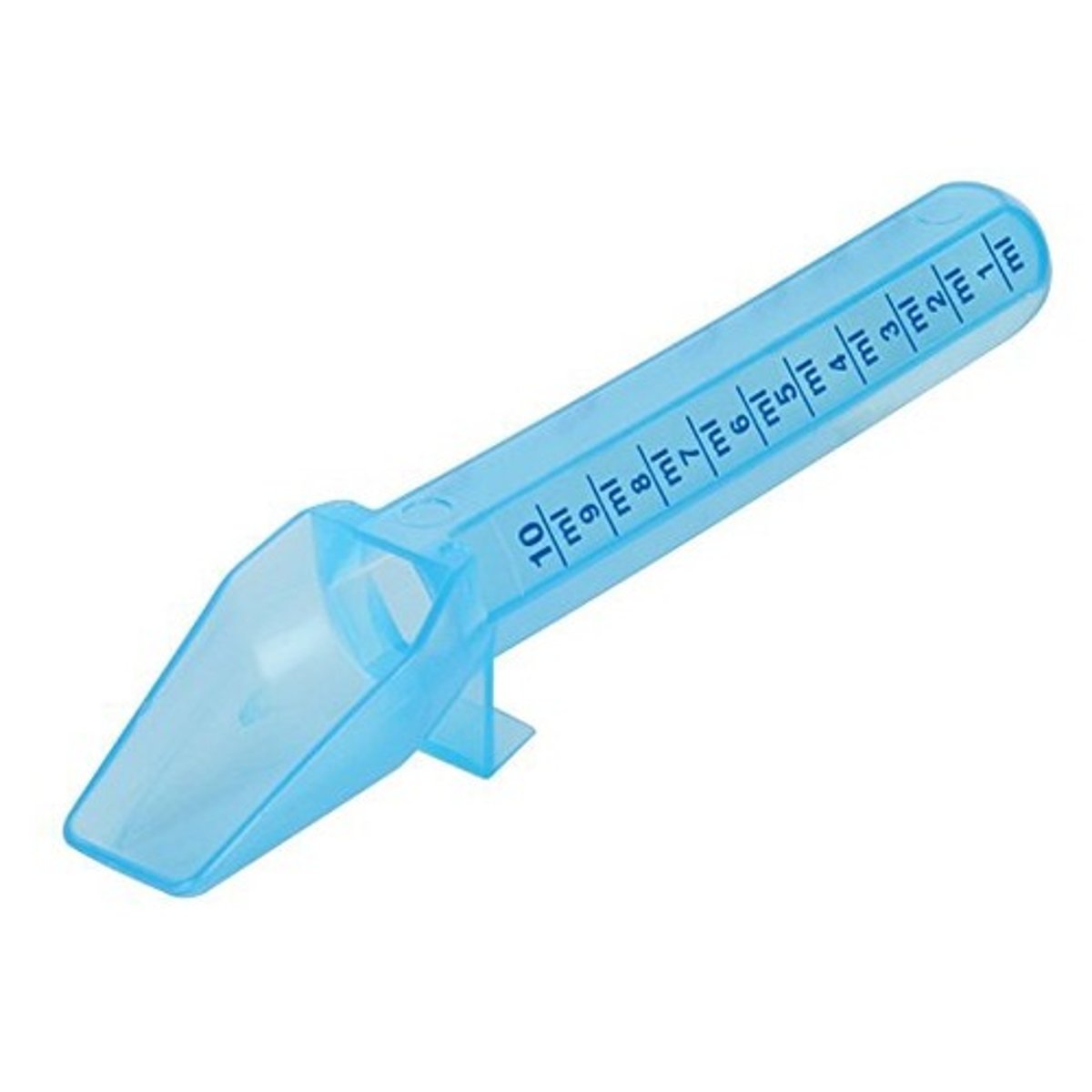
Calibrated Spoon
A spoon that has special markings, or calibrations, that allow you to measure a dose of liquid medication

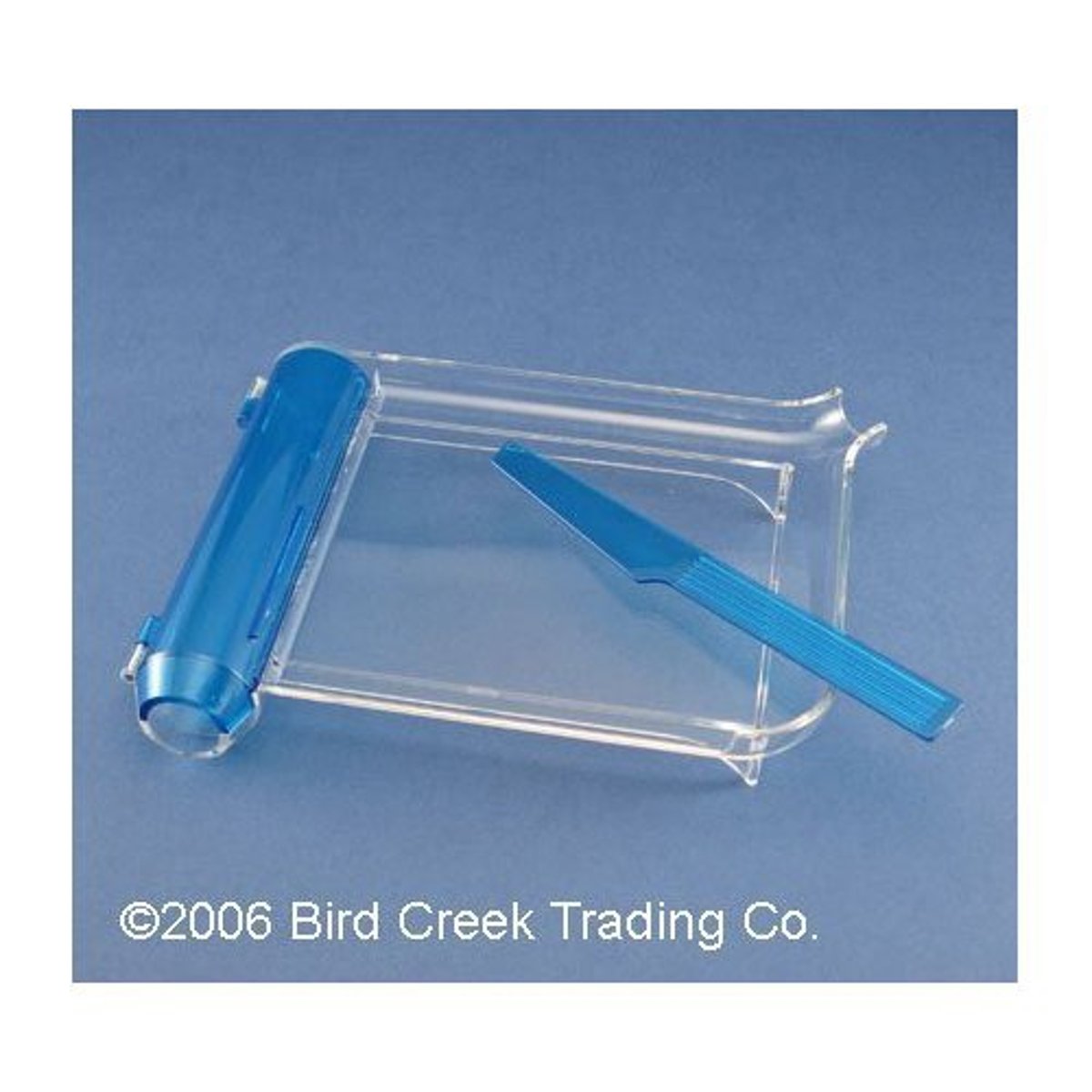
Counting Tray
a tray designed for counting pills from a stock bottle into a prescription vial

Medication Containers
prescription bottles
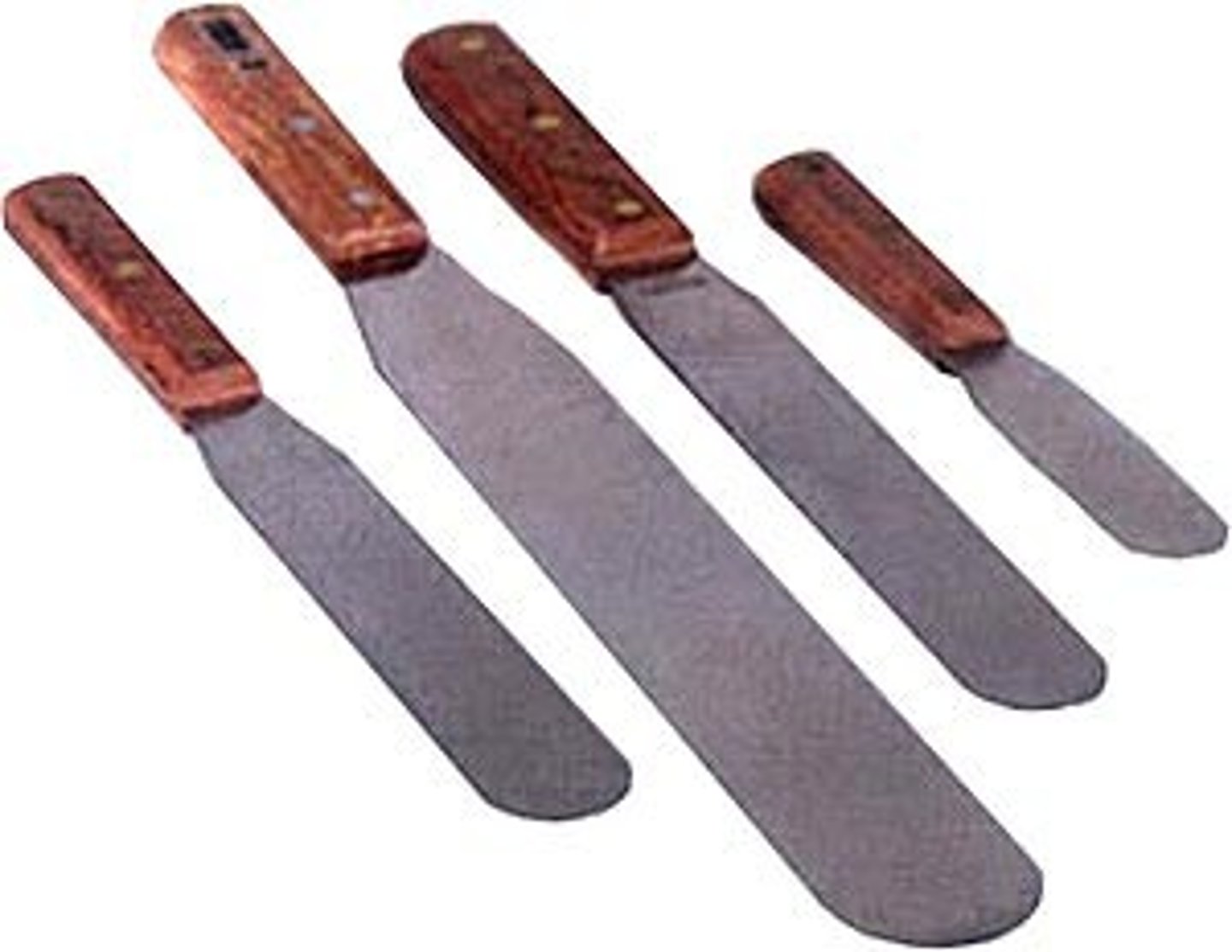
Spatula
broad-bladed instrument used for spreading or mixing

Tissue Forceps
tweezer-like, non-locking instruments used to grasp tissue
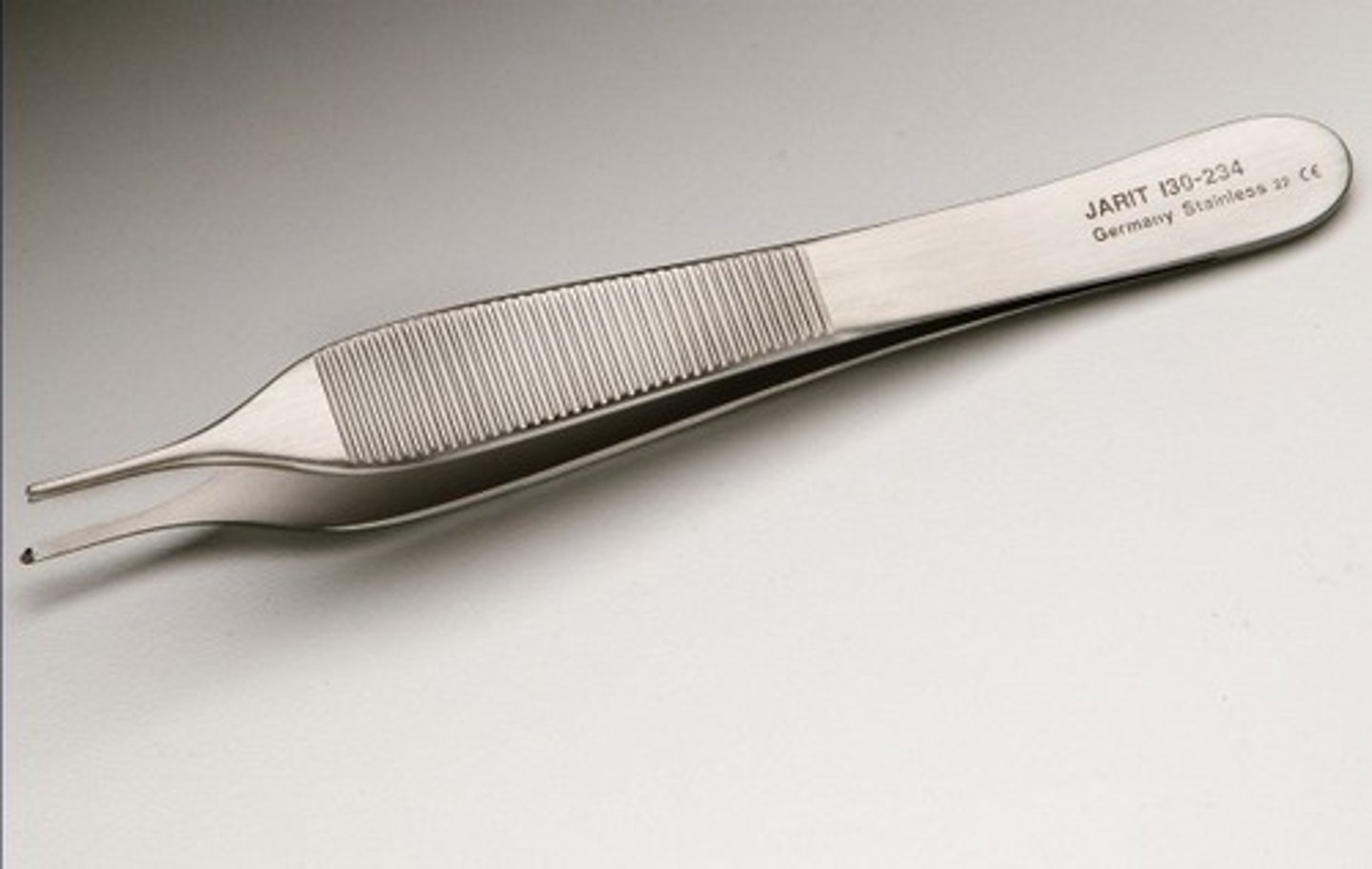

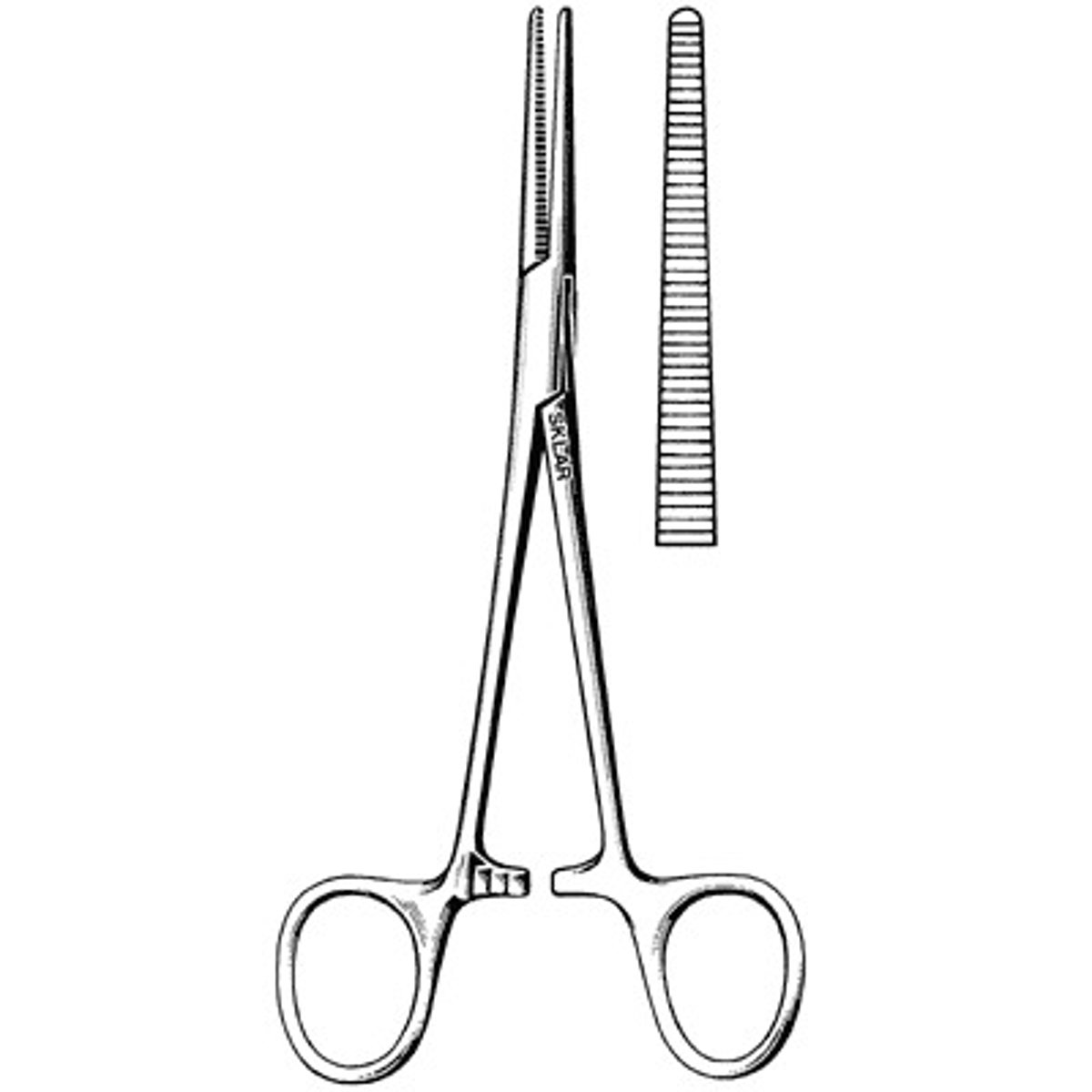
Hemostatic Forceps
Surgical instruments used to control flow of blood
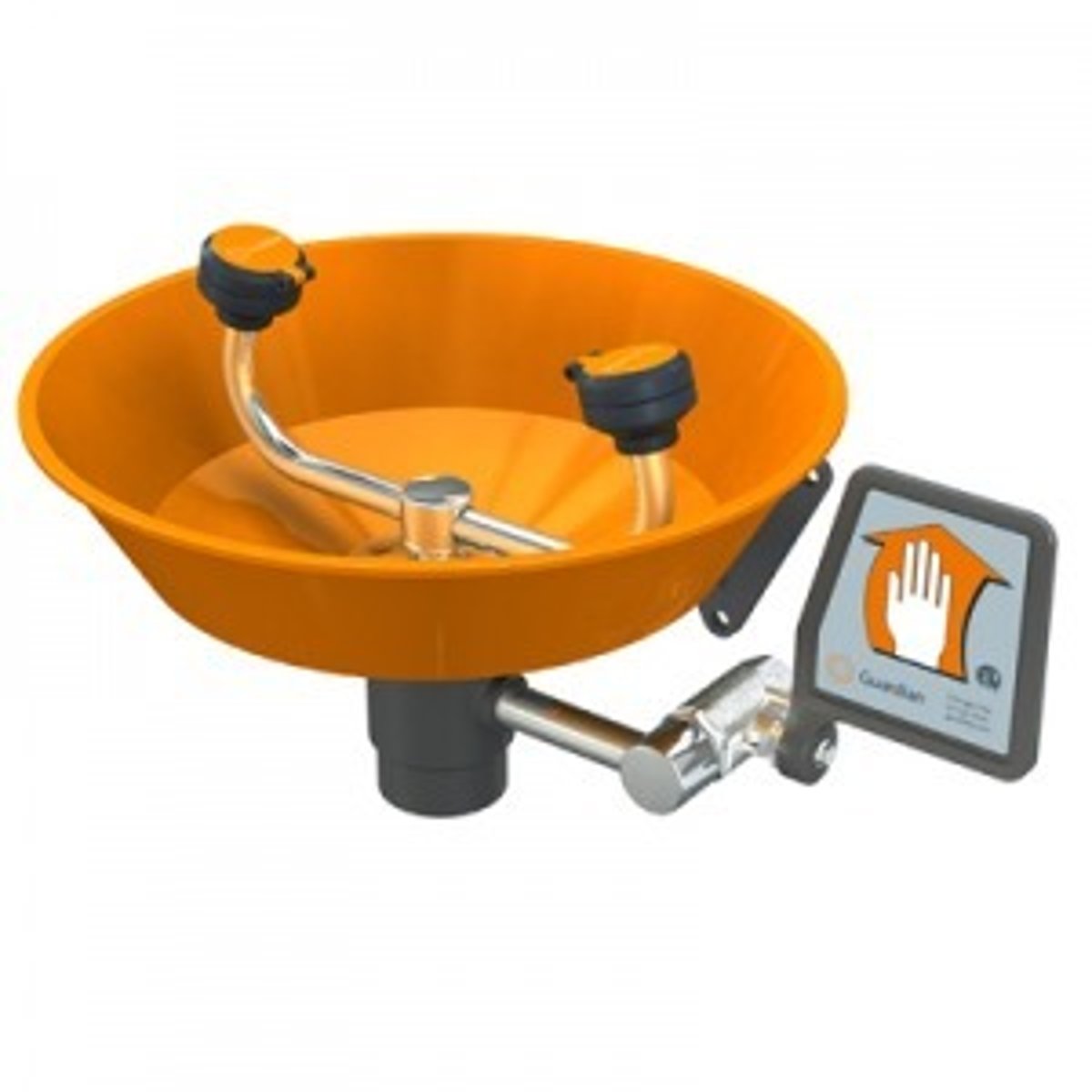
Eyewash Station
used to rinse the eyes when they have contacted a chemical

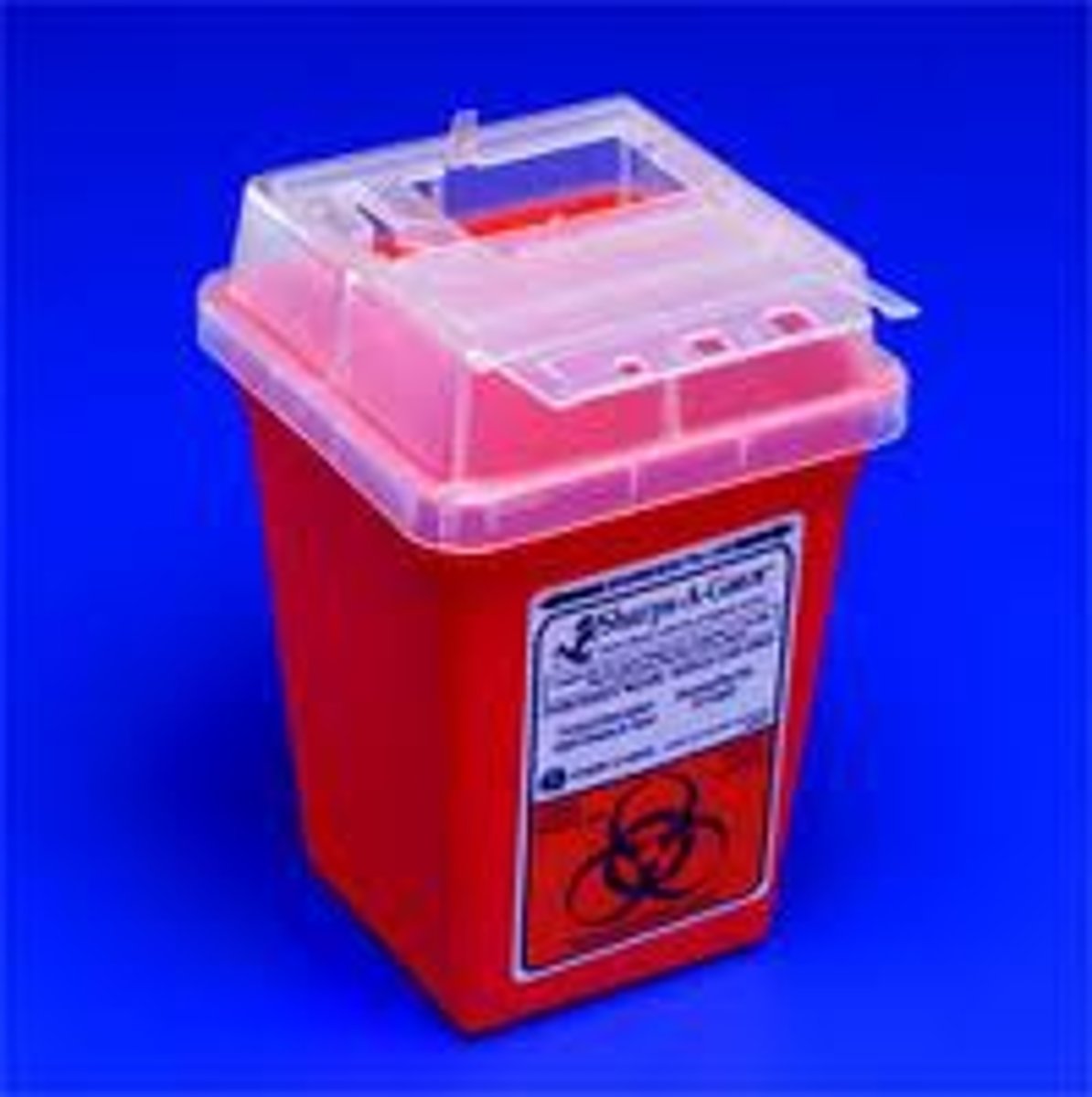
Sharps Container
a puncture resistant container used to dispose of contaminated needles and other sharp medical objects

Auxiliary Labels
labels regarding specific warnings, foods or medications to avoid, potential side effects, and other cautionary interactions

Indicator Strip (for sterilization)
Indicator strips verify that steam sterilization parameters of time and temperature have been met

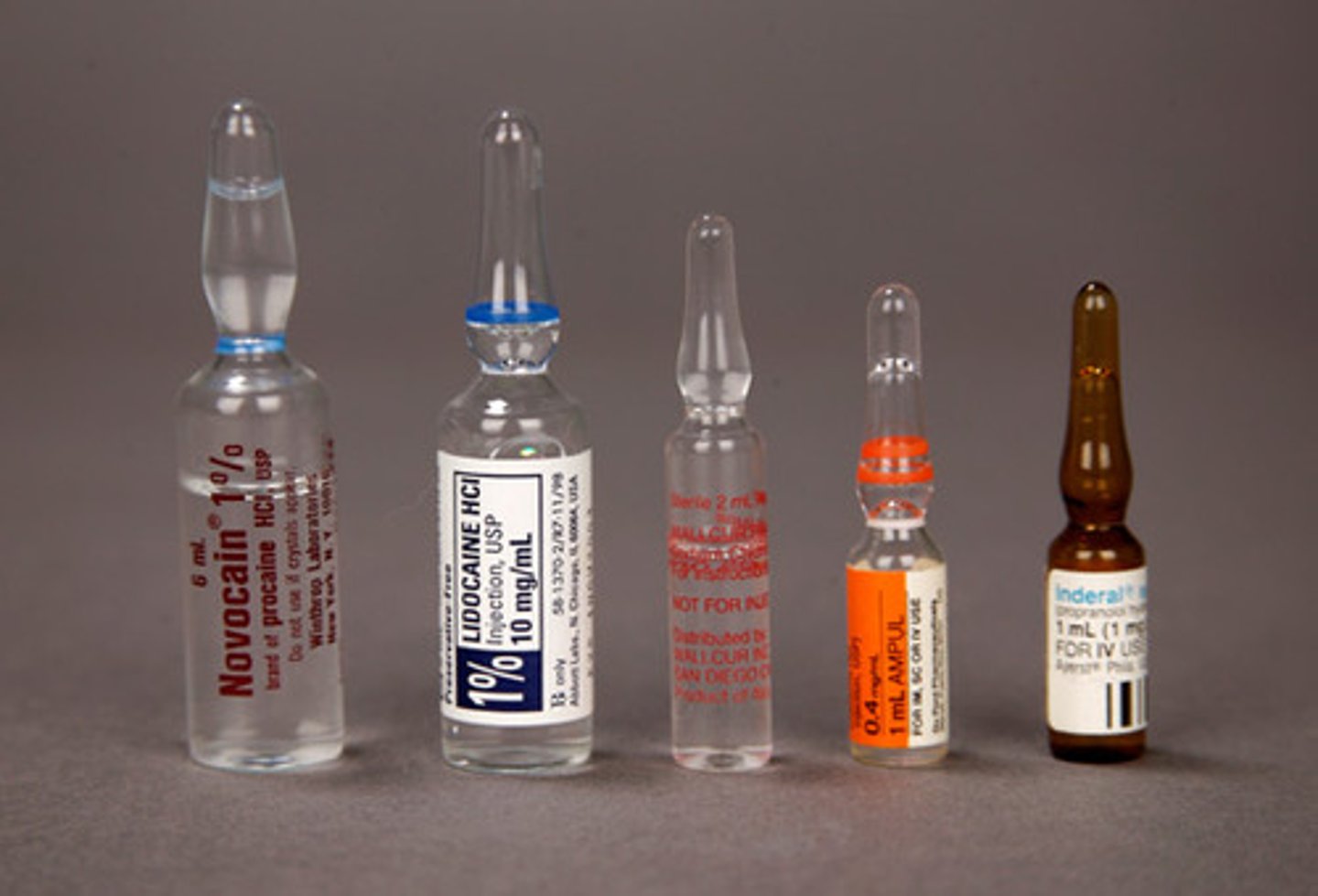
Ampules
a sealed glass capsule containing a liquid, especially a measured quantity ready for injecting
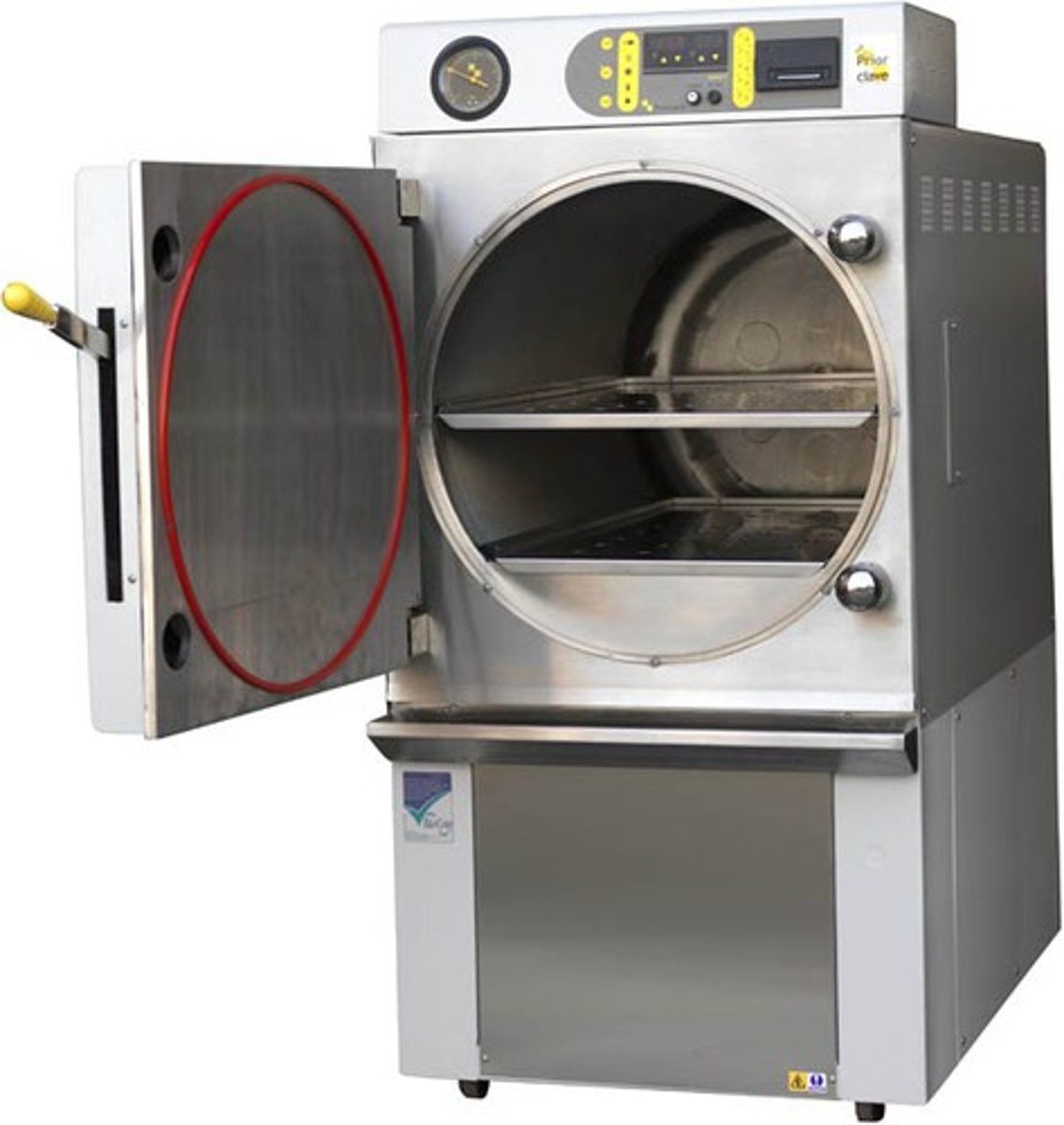
Autoclave
A chamber for sterilizing with steam under pressure. The original autoclave was essentially a pressure cooker in which steam tightened the lid.

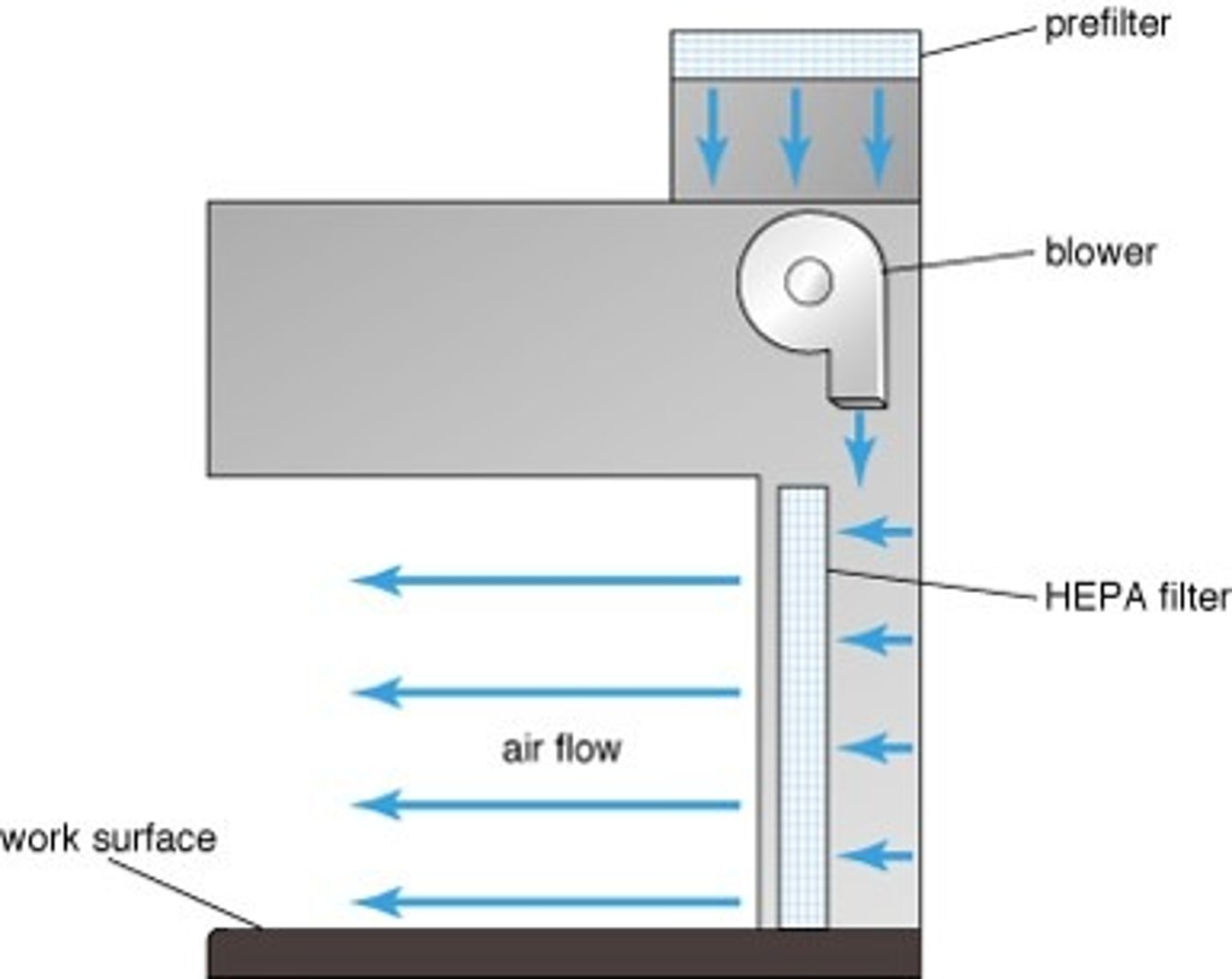
Laminar Airflow Hood
a system of circulating filtered air in parallel-flowing planes in hospitals or other health care facilities. The system reduces the risk of airborne contamination and exposure to chemical pollutants in surgical theaters, food preparation areas, hospital pharmacies and laboratories