MOD 10 - General Inflammation, Osteomyelitis, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Osteoporosis & Positioning
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of Q&A flashcards covering inflammation, osteomyelitis, OA, RA, gout, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoporosis/osteopenia, and positioning considerations.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the difference between acute and chronic inflammation?
Acute inflammation is sudden and short-term; chronic inflammation is long-lasting.
Name four common causes of inflammation.
Infectious pathogens (bacteria); chemical exposure (allergens, bee stings); physical trauma (fractures, cuts); immune reactions.
What is the first defense mechanism of the body to injury?
Vascular changes — increased blood flow to the area causing redness and swelling.
List four visible signs of inflammation.
Tissue swelling, joint swelling, pus formation, ulceration/scarring.
How can mild inflammation heal?
Without intervention; acute inflammation may resolve or become chronic.
What is osteomyelitis and where does it most often occur?
A bone infection, usually in the metaphyseal area of long bones; common in lower extremities, vertebrae in adults.
What bacteria most often causes osteomyelitis?
Staphylococcus aureus.
What are the three stages of osteomyelitis pathogenesis?
Formation of sequestrum (necrotic bone), formation of involucrum (new bone with sinus tracts), irregular bone around abscess.
Radiographic signs of osteomyelitis?
Thickened bone, sclerosis, honeycomb appearance, periosteal elevation, deformities.
Treatment for osteomyelitis?
Early antibiotics; prognosis is good if treated early.
What are the two types of osteoarthritis (OA)?
Primary (degeneration of weight-bearing joints); Secondary (due to deformity or trauma).
Common age of onset for OA?
Over 40 years old.
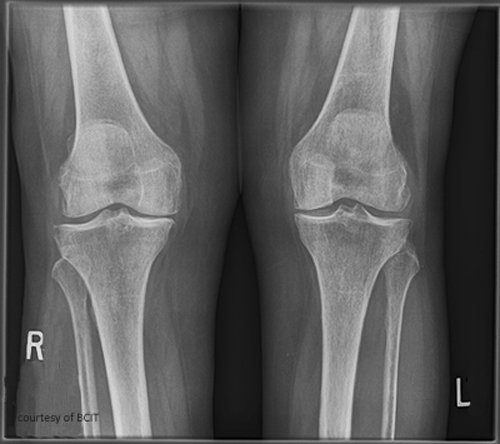
Pathogenesis of OA?
Cartilage wear → exposed bone (eburnation) → osteophyte formation → soft tissue damage.
Radiographic signs of OA?
Narrowed joint space, osteophytes.
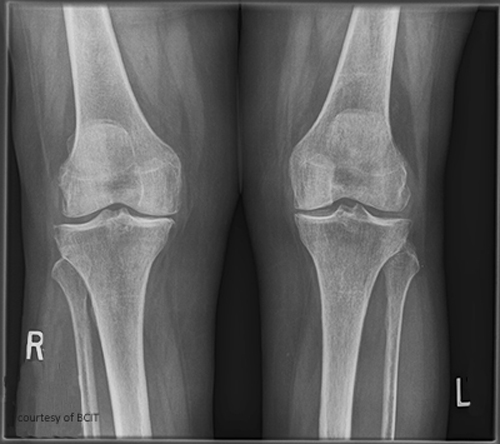
Treatment for OA?
Pain relief, lifestyle changes, joint replacement if severe.
Is RA more common in males or females?
Females (3:1).
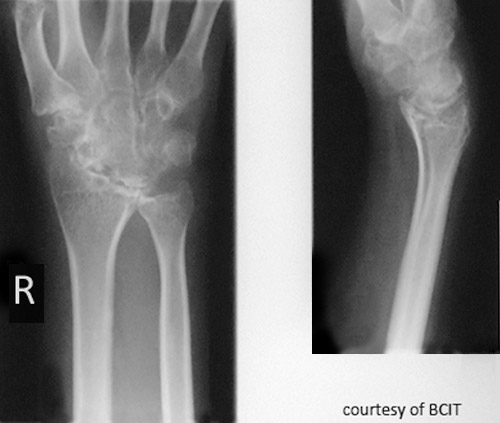
What is the typical age of onset for RA?
30–58 years (can occur at any age).
What antibody is associated with RA?
Rheumatoid Factor (R-factor).
Describe the pathogenesis of RA.
Synovial inflammation → pannus → cartilage erosion → bone fusion (ankylosis) → muscle atrophy and fibrous tissue replacement.
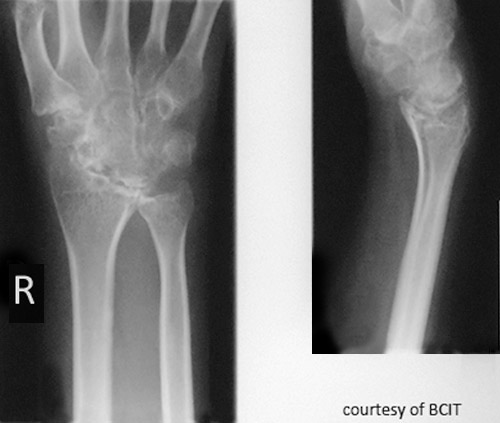
Symptoms of RA?
Painful swollen joints, fatigue, fever, anemia, weight loss, chronic pain, periods of remission and flare-ups.
Radiographic signs of RA?
Early: minimal bony change; later: osteoporosis/rarefaction, deformities.
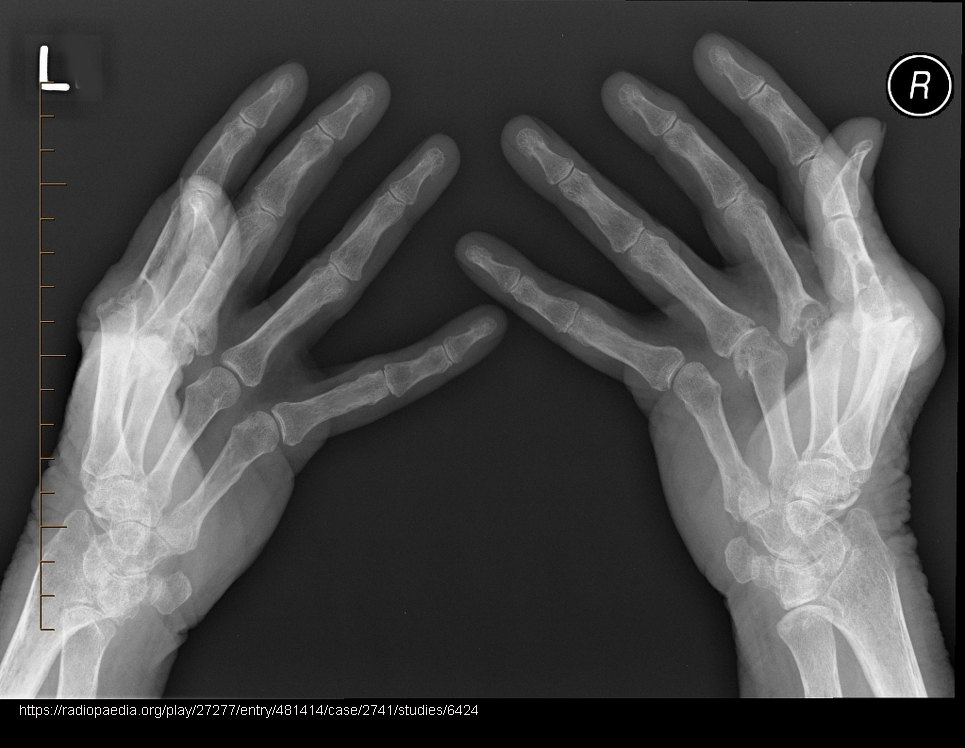
Treatments for RA?
EORA: joint reconstruction, arthrodesis, tendon repair. YORA: DMARDs. JIA: medication to reduce bone destruction.
What causes gout?
Inherited metabolic disorder → excess uric acid → crystal deposits (tophi) in joints.
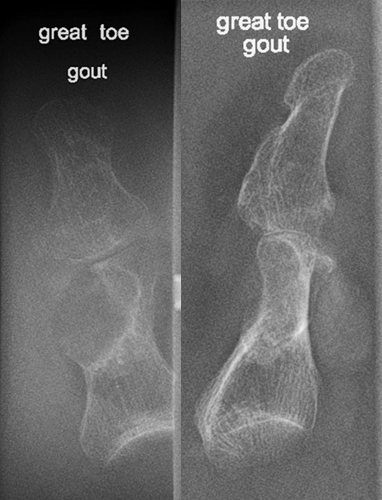
Who is most at risk for gout?
Males 30–50, post-menopausal females, patients on diuretics.
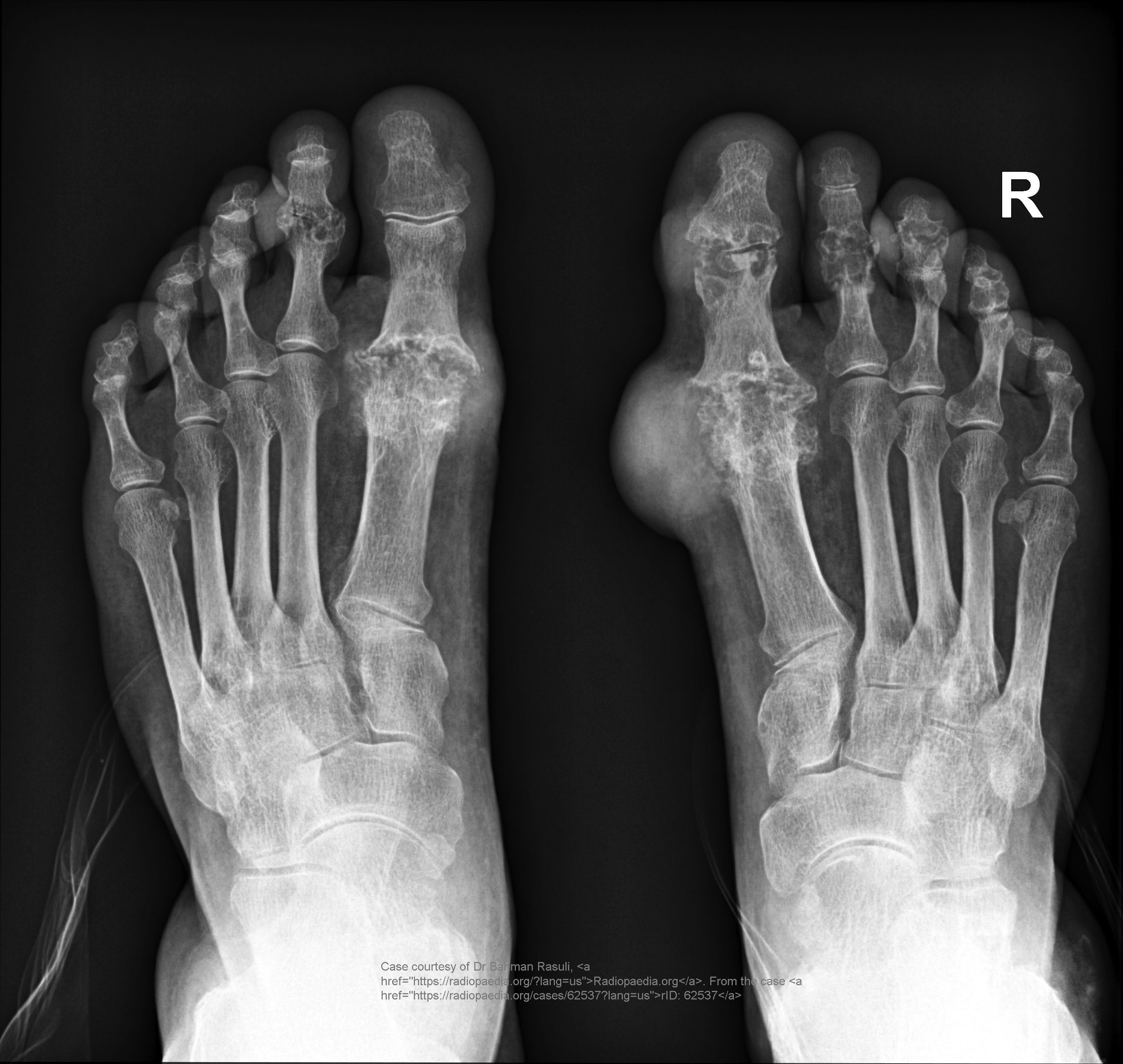
Common site for gout?
First MTP joint of the big toe.
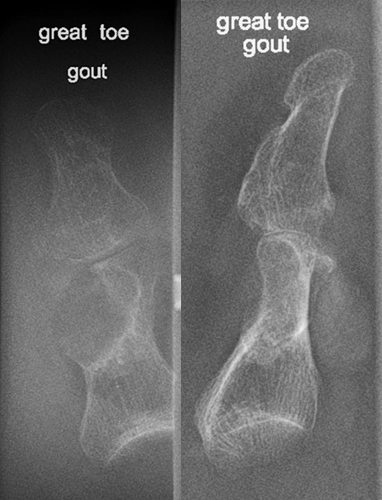
Radiographic signs of gout?
Late changes: “mouse-bitten” erosions, overhanging edges, possible calcified tophi; no osteopenia.
Treatment for gout?
Lower uric acid production or increase excretion.
Possible complication of gout?
Joint damage, uric acid kidney stones (radiolucent).
Which joints does AS (Ankylosing spondylitis) affect first?
Sacroiliac joints.
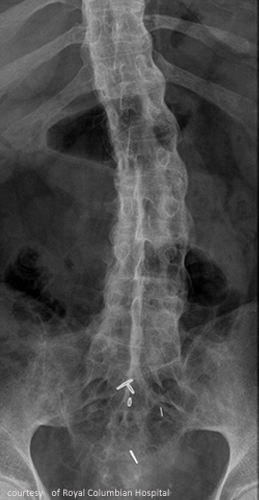
Who is most affected by AS?
Males 16–30 years old.
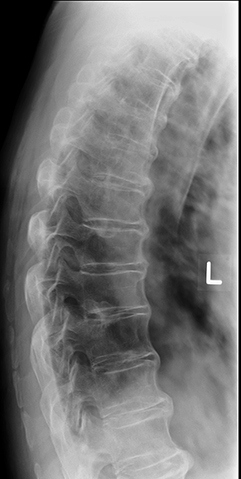
Describe AS progression.
SI joint inflammation → fusion → ascends spine → complete spinal fusion (“bamboo spine”).
Radiographic signs of AS?
Early: SI joint blurring, narrowing; Late: “bamboo spine,” squared vertebrae.
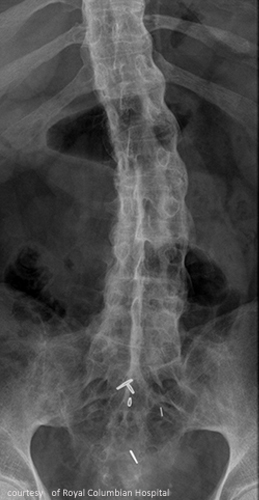
Treatment for AS?
No cure; anti-inflammatories, exercise to maintain mobility.
Difference between osteoporosis and osteopenia?
Osteoporosis = significant bone density loss; osteopenia = early/milder loss.
Name 3 risk factors for osteoporosis.
Post-menopause, inactivity, corticosteroid use.
Symptoms of osteoporosis?
Loss of height (kyphosis), back pain, spontaneous fractures.
Radiographic signs of osteoporosis?
Thinned cortex, enlarged medullary cavity, “picture frame pattern.”
What imaging test is used to diagnose osteoporosis?
DEXA scan (T-score < -2.5).
Treatment for osteoporosis?
Calcium, vitamin D, magnesium supplements, weight-bearing exercise, hormone therapy, kyphoplasty/vertebroplasty.
What should be considered when positioning patients with inflammatory/metabolic bone disorders?
Avoid pain-inducing positions; support joints with limited mobility; protect fragile bones from fracture; minimize movement for swelling/tenderness; use lowest kVp for osteopenic bones.