Module 6 Electrophilic substitution reactions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
why does benzene not undergo electrophilic addition
the delocalised ring of electrons is too stable and would be disrupted
what substitution reactions does benzene undergo
reactions in which a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring is replaced by another atom. the delocalised ring is briefly disrupted and then restored during the process
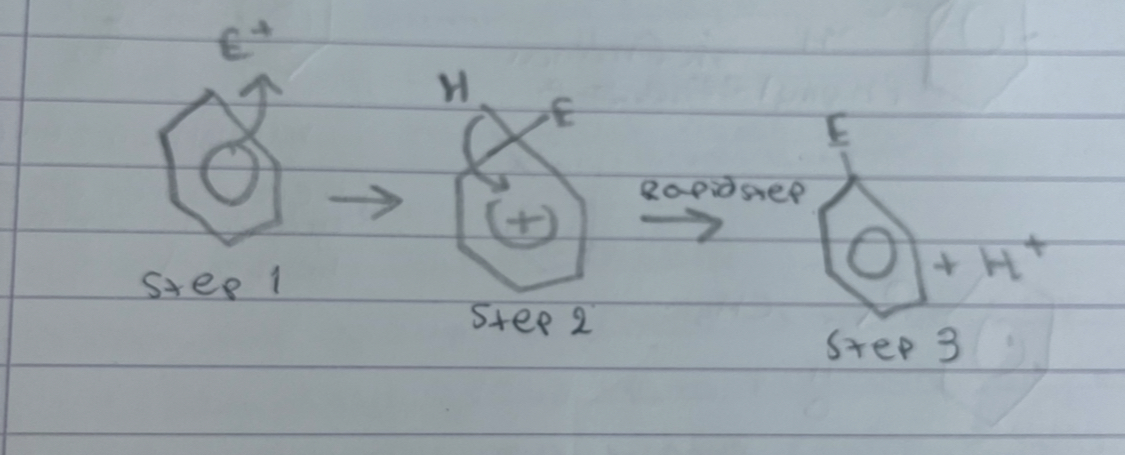
what is this
electrophilic substitution of benzene
what is the reaction rate increased by in nitration of benzene
heating to 50 degree, using a sulfuric acid catalyst
what will benzene do in nitration of benzene
react slowly with nitric acid to form nitro benzene
what happens to one of the hydrogen atoms around the benzene ring in nitration of benzene
it is replaced by a nitro group NO2
what happens at higher temps in the nitration of benzene
further substitutions around the ring producing dinitrobenzene
what is nitrobenzene used in
dyes, pharmaceuticals, pesticides
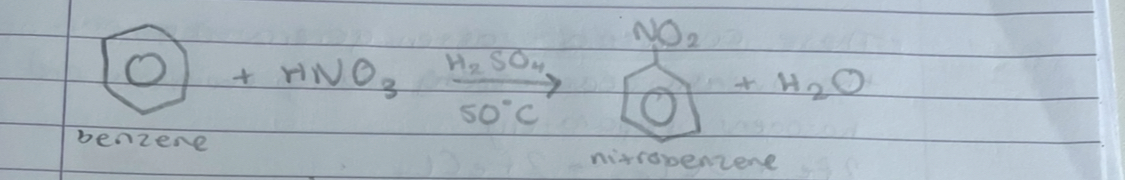
what is this
nitration of benzene
what happens in step one of nitration of benzene
nitric acid reacts with sulfuric acid to produce the electrophile nitronium ions NO2+. HNO3 + H2SO4 -> NO2+ + HSO4- + H2O
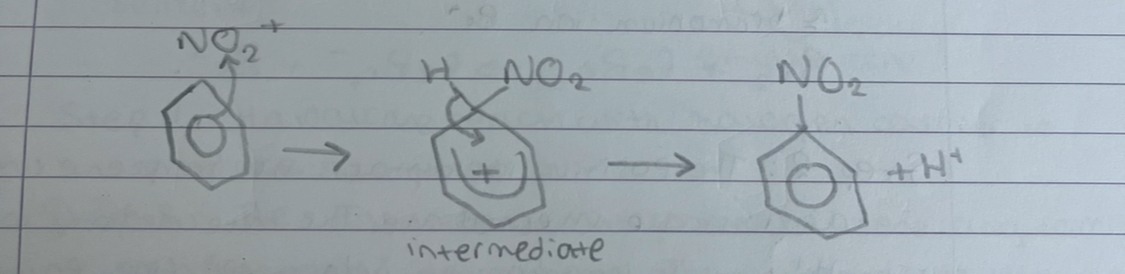
what happens in step 2 of nitration of benzene
nitronium ions attack the benzene ring forming an unstable intermediate. the intermediate loses and H+ ion to restore the delocalised ring forming nitrobenzene
what happens in step 3 of nitration of benzene
the hydrogen ion reacts with the HSO4- ions from step 1 to reform the catalyst H2SO4. H+ + HSO4- -> H2SO4
when will the halogen not react with benzene in halogenation of benzene
if there is no halogen carrier catalyst used
what are the common halogen carriers especially for halogenation of benzene
AlCl3, FeCl3, AlBr3, FeBr3
where are the halogen carriers often generated
as part of the overall reaction by adding the metal and halogens separately. 2Fe + 3Cl2 -> 2FeCl3
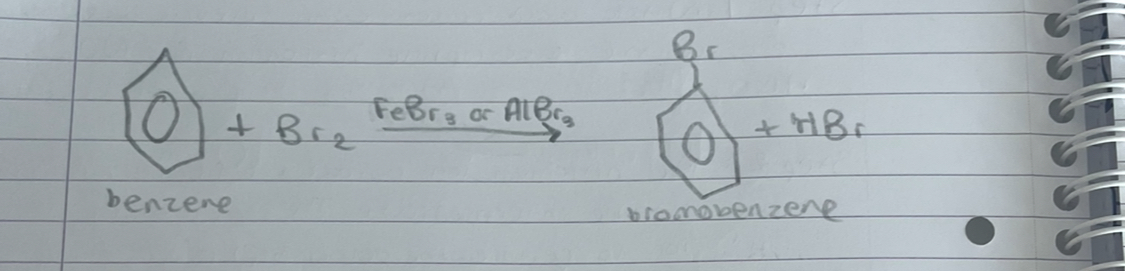
what is this
halogenation of benzene
what happens in step one of halogenation of benzene
halogen reacts with halogen carrier to produce a bromonium ion Br+. Br2 + FeBr3 -> FeBr4- + Br+
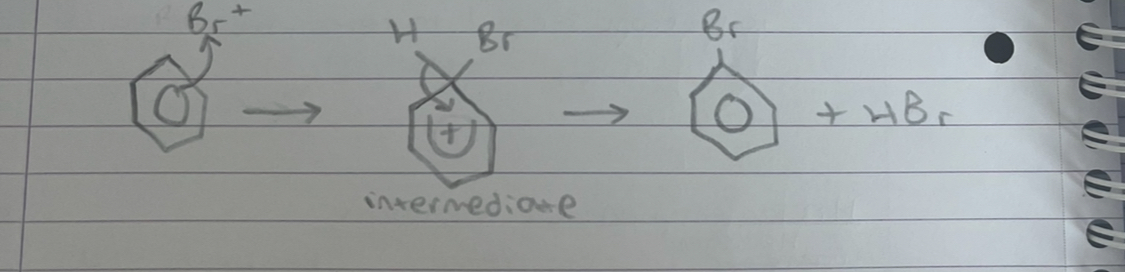
what happens in step 2 of halogenation of benzene
the positive ion attacks the benzene ring forming unstable intermediate. the intermediate loses a H+ ion to restore the delocalised ring forming bromobenzene
what happens in step 3 of halogenation of benzene
the hydrogen ion reacts with the halogen carrier ion from step 1 to reform the carrier and hydrogen bromide. H+ + FeBr4- -> FeBr3 + HBr
why is the intermediate unstable
because electrons have been removed from the benzene ring
what is alkylation of benzene
reacting a haloalkane with benzene in the presence of a halogen carrier. nearly always doe with chloroalkanes and AlCl3
what is alkylation of benzene nearly always done with
chloroalkanes and AlCl3
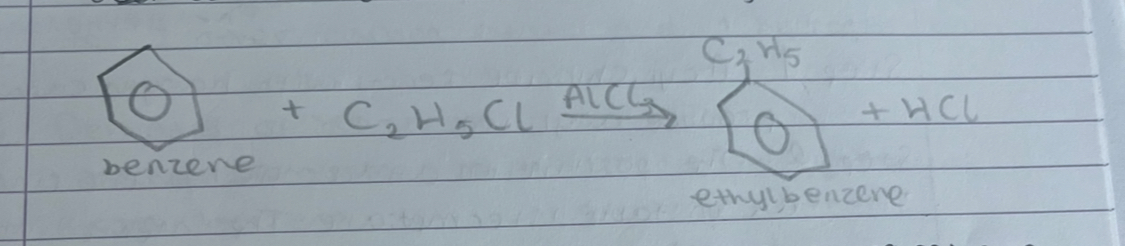
what is this
alkylation of benzene
what is step 1 in alkylation of benzene
haloalkane reacts with halogen carrier to produce alkyl ion
what is step 2 in alkylation of benzene
the positive ion attacks the benzene ring forming an unstable intermediate. the intermediate loses an H+ ion to restore the delocalised ring forming alylbenzene
what is step 3 in alkylation of benzene
the hydrogen ion reacts with the halogen carrier ion from step 1 to reform the carrier and a hydrogen halide
what is acylation of benzene
reacting an acyl chloride with benzene in the presence of a halogen carrier. this is almost always done with an acyl chloride and AlCl3
what is acylation of benzene almost always done with
acyl chloride and AlCl3
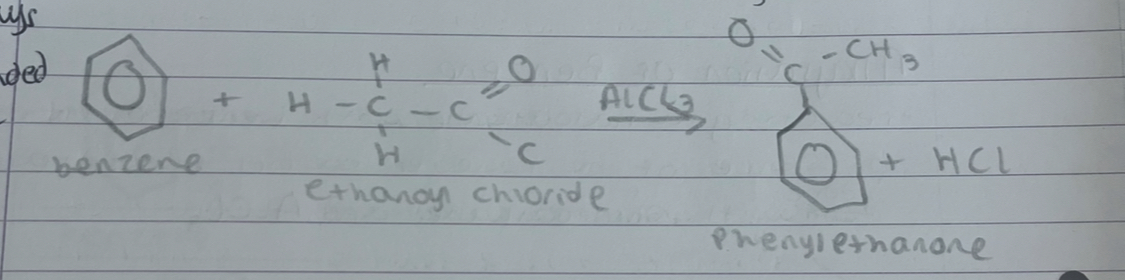
what is this
acylation of benzene
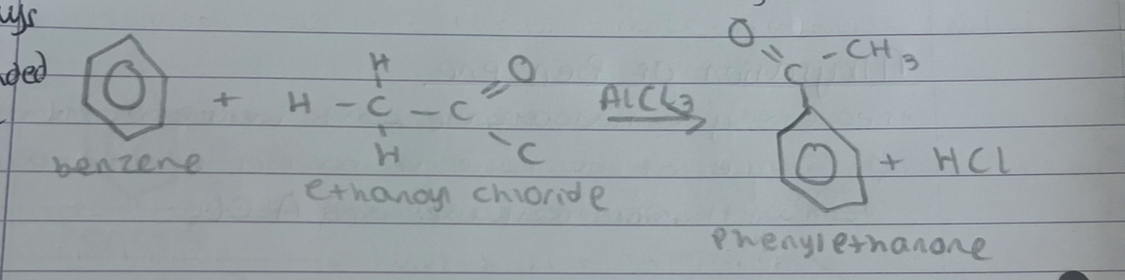
what always has to happen to the O
always has to be double bonded to first C
what is step 1 in acylation of benzene
acyl chloride reacts with halogen carrier to produce acyl ion
what is step 2 in acylation of benzene
the positive ion attacks the benzene ring forming an unstable intermediate. the intermediate loses an H+ ion to restore the delocalised ring forming alkylbenzene
what is step 3 in acylation of benzene
the hydrogen ion reacts with the halogen carrier ion from step 1 to reform the carrier and a hydrogen halide