IB BIO - Natural Selection
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Natural selection
- process by which organisms that are better adapted for the environment surrvive adn pass on their traits to offspring
- drives evolutionary change, resulting in biodiversity
- operates continuously and over billions of years
evolution
changes in the hertitable characteristics over generations
paradigm shift in evolution
- darwin's theory that natural selection drives evolution replaced lamarckism
lamarckism
thhhe idea that an organism could pass on physical characteristics it aquired during their lifetime to its offspring
what condition has to be present for natural selection to occur?
- variation
- otherwise if every organism in a population is identical then no individual will be favoured over another
what factors generates variation
1. mutations - generates new alleles
2. sexual reproduction - generates new combinations of alleles (via meiosis) - crossing over of non-sister chromatids and random orientation of homologous apirs
3. random fertilisation of gametes - any male gamete can fuse with any female gamete
what 2 factors promote natural selection
- Overproduction of offspring leads to competition for resources, such as food and light
- Happens because there are more offspring produced then can be supported by the surrrounding environment.
abiotic (non-living) factors as selection pressures
- some are density-indepdent: affects the size of the population regardless of the density of the population
- eg. temperature, rainfall, light intensity, soil pH
- can act as selection pressures affecting the surrvival of individuals within a population
intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species
basis for natural selection
- there are differences between indiividuals in adaptation, surrvival and reproduction
fitness in males (sexual selection)
- physical and behavorial traits which are visible to the female cohort
- these traits are viewed as indicators of overall fitness
- affect the individual's success attracting a mate, driving the evolution of the population
traits have to be what for evolutionary changes to occur
heritable
which traits are not heritable?
- traits that are acquired during an individual's life due to environmental factors
- because they are not encoded in the base sequence of genese and so do not get passed on as DNA
sexual selection
- occurs due to competion for mates
- results in animals with enhanced mating success and not in individuals that are well-adapted to their environment
sexual dimorphism
differences in size or appearance between sexes of an animal species
example of sexual dimorphism
- birds of paradise
- male birds are brightly coloured and perform intricate courtship displays which increase success of attracting a female mate
- female's plumuge is made up of grey and browns
John Endler's experiment with guppies (fish)
- observed that their colour patterning changed with predation pressure
- as predation increases the brightness of the spots decreases to help guppies camoflauge from predators - leads to selection for less spotted individuals
- when predation is low guppies have brighter spots to better attract mates, for sexual selection
gene pool
all the genes and different alleles present in an interbreeding population
why do multiple gene pools exsist for a single species?
if populations of the same species are geographically isolated from each other
what happens if the gene pool is stable?
- the population will not evolve
- each individual has an equal chance of mating
- instead matings are random
- no selection pressures acting upon individuals based on their phenotype
How do gene pools change as a consequence of natural selection?
- individuals have differences in heritable traits
- natural selection selects individuals with the most suitable traits for the environments so they pass on their genes
- as a result there are changes in allele frequency in the gene pool
Neo-Darwinism
Genetics integrated with natural selection
polymorphisms
many different forms of a gene, also known as alleles
hardy weinberg formula
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
how many alleles per gene
2
in a population of 100 individuals how many total alleles for 1 gene?
200
state 3 types of natural selection
1. directional
2. stabilising
3. disruptive
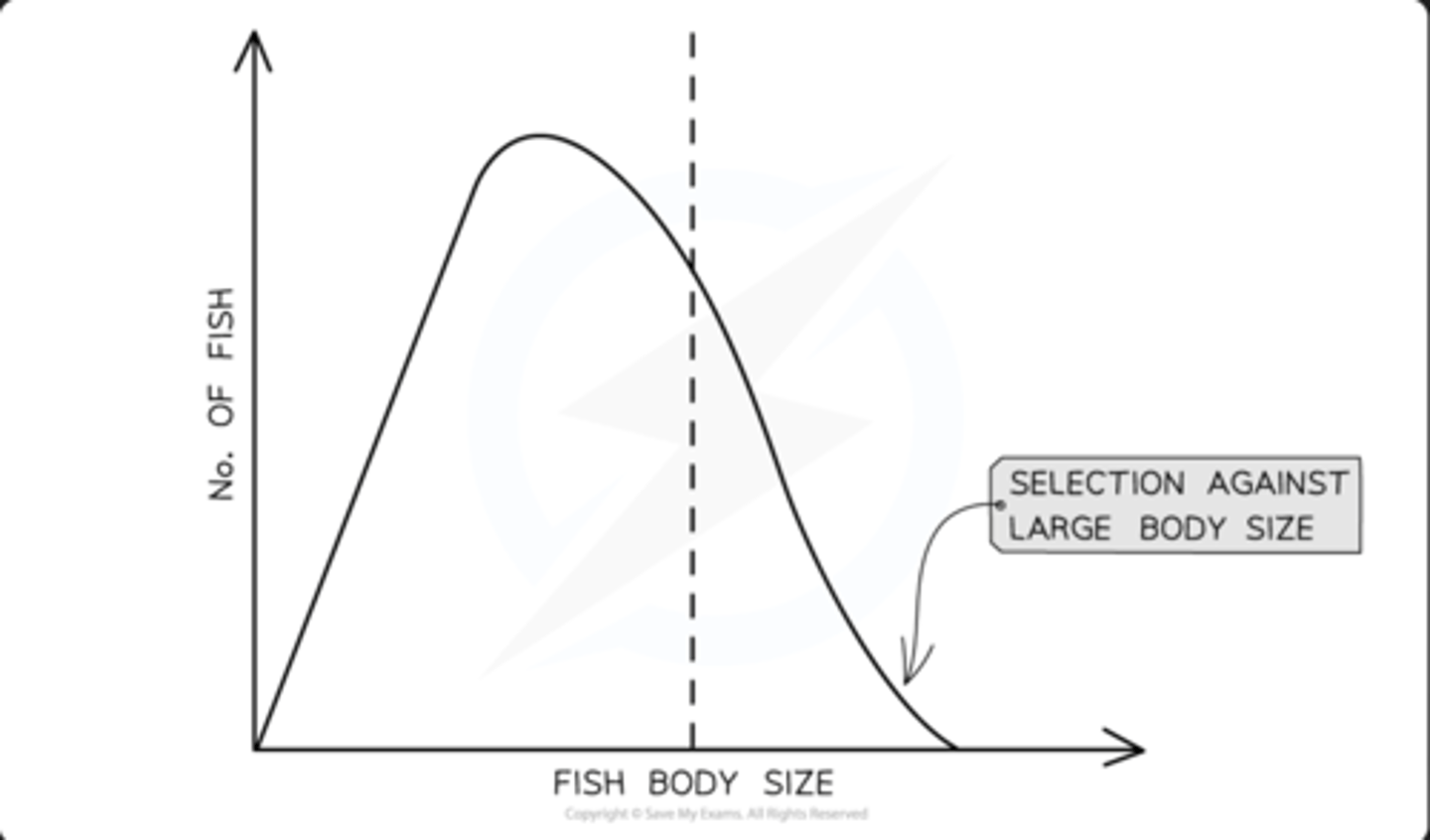
directional selection
- when the population changes towards one extreme range of variation
- as that extreme is better adapted
- usually happens when environmental conditions change, eg, a rise in temperature
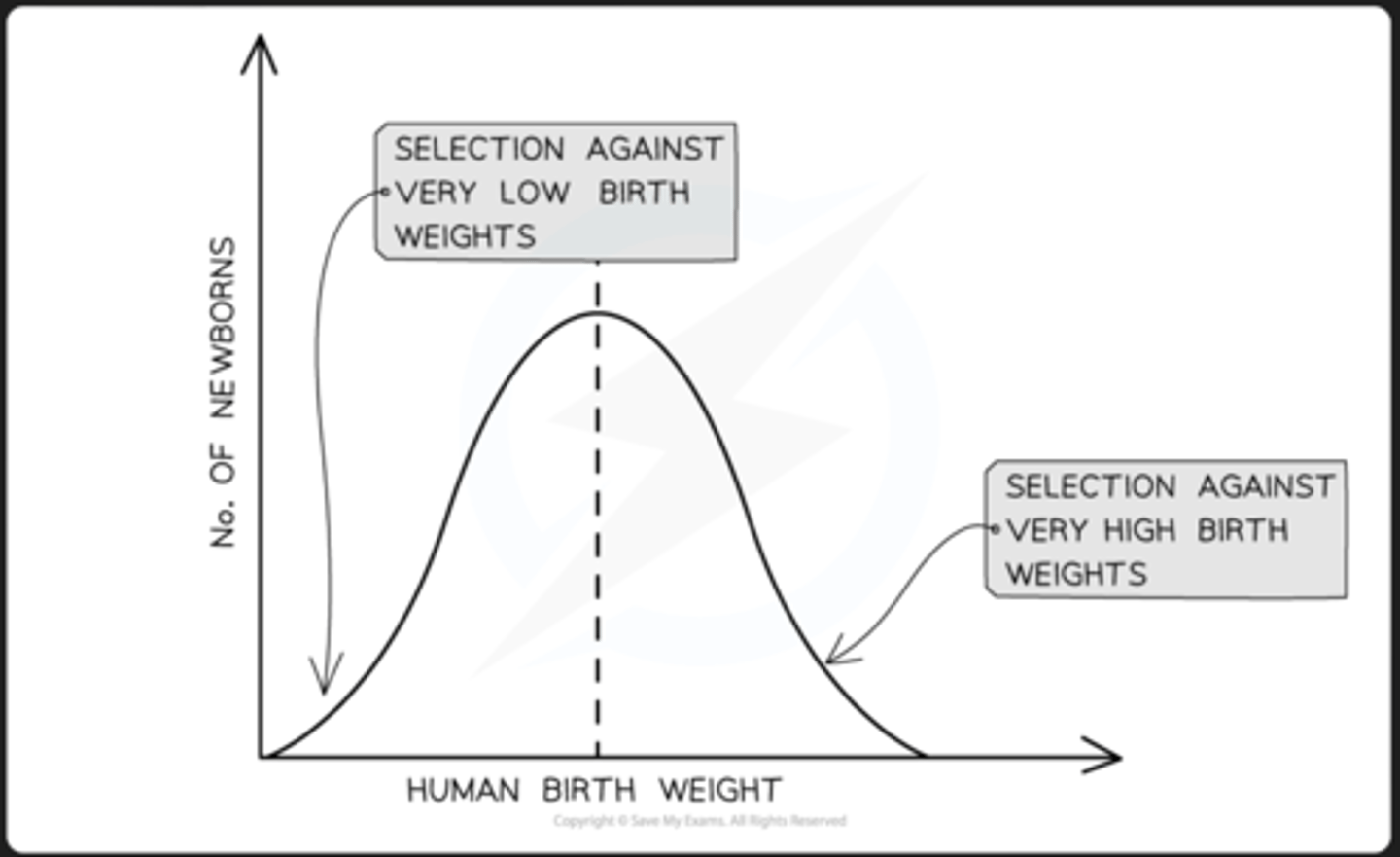
stabilising selection
- selects in favour of the average individual in a population
- occurs when environmental conditions are stable
- most common form of selection
- bell shaped curve
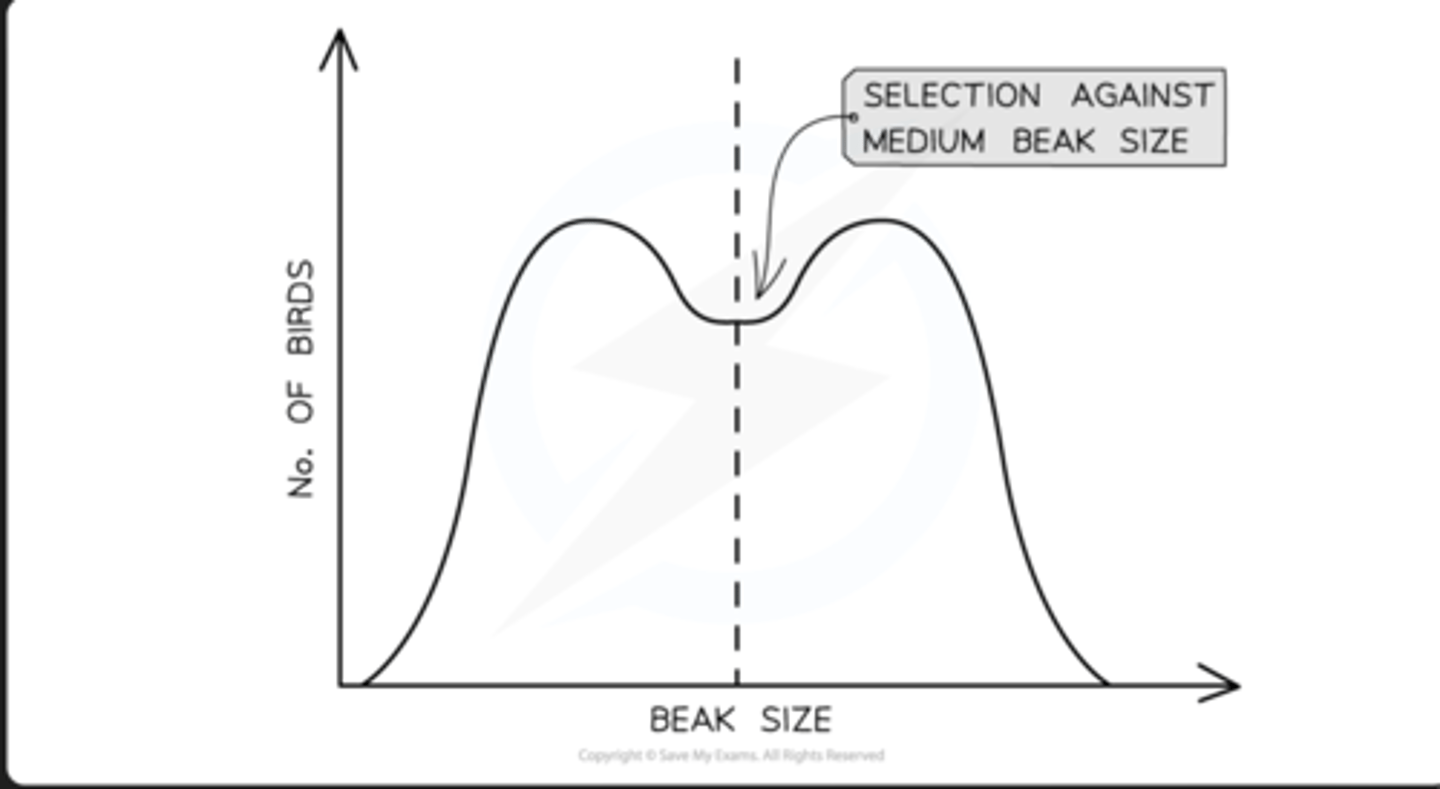
disruptive selection
- selects against the average individual in a population
- happens when habitats/resources undergo a change
- can result in the formation of an entirely new species (speciation)
what conditions must be met for the hardy-weinberg equation to work?
- organisms are diploid
- sexual reproduction ONLY
- no overlap between generations - parents do not mate with offspring
- mating is random
- population is large
- no migration, mutation or selection
- surrvival rates do not vary between genotype
If the genotype frequencies in a population do not meet the hardy-weinberg equation, one of the condtions is not being met
artificial selection
- process carried out in domesticated animals and crop plants by choosing individuals with desirable traits and selectively breeding them together to enhance the expression of desirable traits over time and many generations
what is the evolution of resistant bacteria from the overuse of antibiotics due to?
- natural selection rather than artifical selection
- uninted consequence of antibiotic use