Geology
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Property - Colour
Is a guide to identifying - not reliable because impurities, can be same colour, same mineral can be different colours
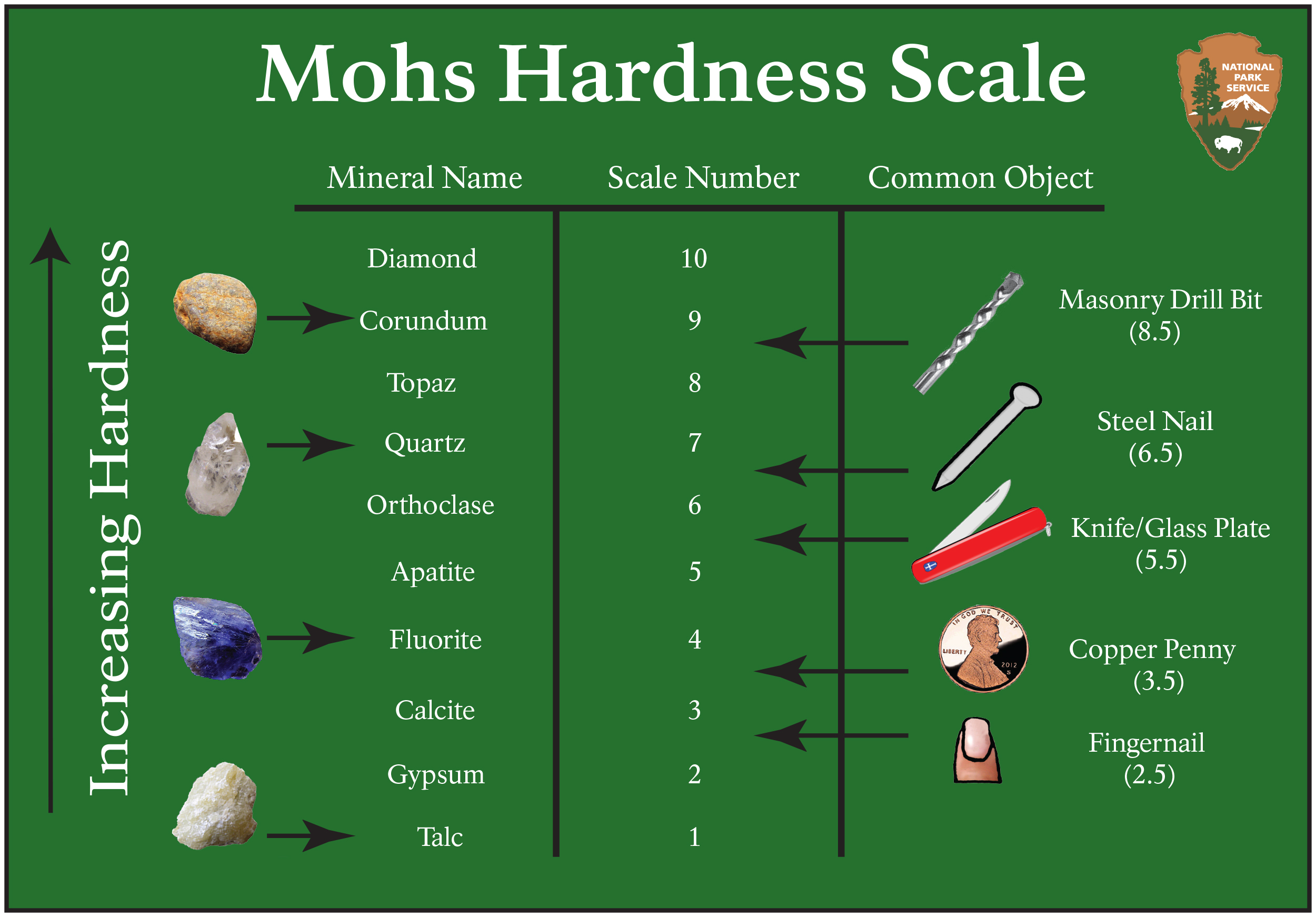
Property - Hardness
Is a measure of a rocks ability to scratch other minerals, Mohs scale measures hardness
Property - Lustre
Shininess of a material, can be earthy, vitreous, brilliant, pearly, metallic
Property - Streak
Colour of minerals powdered form - not always the same as mineral
To get powder mineral is rubbed against hard surface
Property - Cleavage/Fracture
Is how a mineral break up into pieces - thin sheets, small pieces
What is a mineral
Chemicals (elements or compounds) that occur naturally in the Earth’s crust. They are the basic building blocks of rocks.
Criteria to be Mineral
Solid - at normal temp
Naturally occurring - occur in nature, not lab
Inorganic - Don’t come from living things
Fixed chemical structure - will always have the same formula
Crystal Structure - repeating arrangement of atoms
Mohs Hardness Scale
The higher on the scale the harder it is. The lowest can have everything above it scratch it, but the highest thing can’t have anything below it scratch it.
Igneous Rock
Rocks that form from the cooling of lava or magma
Extrusive Igneous Rocks
Cool quickly and as a result these rocks are fine grained or has lack of crystal growth.
Intrusive Igneous Rocks
Formed from magma that cools slowly and as a result these rocks are coarse graine
Sedimentary Rocks
They are compacted sediment
Lava
molten rock at or above earths surface
Magma
is molten rock below the earths surface
Weathering
Breaking down of rock
Erosion
is the moving of that rock/sediments
How are sedimentary rocks formed
Sediments are deposited in layers
The grains of lower layers begin being forced together
Chemicals that are dissolved in the water can soak into the sediments
The chemicals help cement the grains together once the water has evaporated
Sedimentary Type - Biological
Are formed when the remains of living things break down and are deposited as sediments
Sedimentary Type - Chemical
Are formed when water evaporates, leaving behind a solid substance
Metamorphic Rocks
Are rocks formed when other types of rocks are changed by heat and pressure inside the Earth
Metamorphic Rock Uses
they can be used for building materials
Metamorphic compared to parent rock
Metamorphic rocks, their crystals can become bigger, change shape, new texture and appearance, their chemicals can change
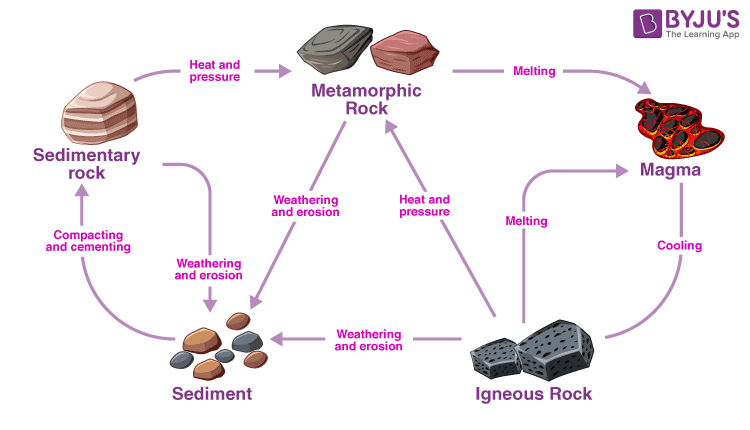
The Rock cycle
Rocks can and will change over time due to pressure, weathering, compaction and cementation, erosion or temp changes
Body Fossils
are the fossils of bones, teeth, and shells
Trace Fossils
are rocks that have preserved evidence of biological activity
How fossils are made
Animal dies
Soft parts rot away or eaten
Before body rots away, buried by sediment
More layers build, putting weight and pressure, making them sedimentary rock
Water seeps into bone and teeth, turning them to stone as it leaves behind minerals
Fossils
are remains and traces of organisms preserved in rocks
Relative dating
Does not give exact age, compares with ages of other things, (older or younger)
Absolute Dating
Actual number of years
Cast fossil
a fossilized copy of an organism, formed when an impression, or mold fossil, is filled with minerals or sediment
Mould Fossil
An empty space left in a rock after an organism’s remains have dissolved
Why are fossils found in sedimentary rocks
because of the process of their formation
Convection Currents
drive movement of magma through mantle which causes tectonic plates to shift
Continental drift
the idea that the continents are continually moving and were once joined together to form a supercontinent called Pangaea
Sea-floor spreading
This theory says that the middle of the ocean is spreading apart because tectonic plates are moving very slowly in opposite directions
How many major plates are there
12
Movement because of heat energy
convection currents in the earths mantle which are driven by heat energy from the earths
Divergent boundaries
are where plates move away from each other
Convergent boundaries
are where the plates move towards each other
Transform boundaries
are where the plates slide past each other
Crust
thinnest layer
between 5-70km thick
temp between 20-500C
thinner under oceans
Mantle
2900 km thick (thickest layer)
Temp between 500-2000C
Made of solid rock that flows
Moves in big circles called convection currents
Outer core
2300km thick
temp 3000C
made of mainly iron and nickel
is liquid
generates magnetic field
Inner core
1200 km thick
temp 4000C
Metals are solid
made of iron
Rock cycle
magma - cool -igneous rock - weathering erosion - sediment - compacting and cementing - sedimentary rock - heat and pressure - metamorphic rock