Microbiology Midterm 1 (Week 1/2 Stuff)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Paramecium
An example of a fungi
Incubation Period
The length of time it takes between being exposed to a disease and showing the symptoms
Yeast
The most common microbe used in food production
Units in which microorganisms are often measured
micrometers µm (10^-6 m)
“W” Shaped Mortality Curve
Caused by certain generations have immune protection from previous exposures that other generations didn’t have (Black Death/Bubonic Plague)
Microorganism
Organism too small to be seen with the naked eye
Prokaryote/Prokaryotic (he hates this word)
Cells lacking a membrane-bound nucleus
Eukaryote/Eukaryotic
Cells with a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles
Old 5-Kingdom Tree of Life
Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists, Monera
Bacteria Characteristics
Nucleiod, Free-Floating Circular DNA, No organelles, 0.02 to 2 µm in diameter, Binary Fission, 70s ribosome
Eukaryotes Characteristics
Nucleus, Linear DNA, Membrane-Bound organelles, 10 to 100 µm in diameter, Mitosis and Meiosis, 80s ribosomes
Species
Individuals that are able to reproduce and produce fertile offspring
Phenotype
Physical Characteristics of the organism
Genotype
Genetics/DNA
Phylogenetics
Evolutionary relationships, sequence-based, 16s rRNA
Polyphasic Taxonomy
Using phenotype, genotype, and phylogenetics to classify organisms
Dr. Claire Fraiser
First to sequence the complete genome of a free-living organism
16s rRNA
universally conserved in all bacterial life, used in molecular-based classification
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
Amplify fragments by PCR and digest with restriction enzymes. Pattern is characteristic in certain groups of microbes.
Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (MLST)
Expansion of the rRNA sequencing. Instead of comparing the sequences of one gene, compare the sequences of five to seven genes. Identical sequences in multiple different genes is more stringent criteria and can distinguish between strains within a given species.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
Similar concept to MLST, but instead searching for SNPs that are characteristic indicators of a given microbe
G/C Content
Higher G/C content = higher melting temps
Varies 25 to 80%
Related microbes have similar G/C content
Molecular ID Tools
Genome Sequencing, 16s rRNA sequencing, Mol% G/C, DNA-DNA Hybridization, MLST, SNP, Genomic Fingerprinting
Carl Woese
Divided prokaryotes into bacteria and archaea and replaced five-kingdoms system with three domain system: eukaryotes, bacteria, and archaea
Eukaryotes Examples
Protists: Algae, Protozoa, Slime molds, Water molds
Fungi: yeasts, molds, mushroom
Microbes not in 3 Domains
Viruses and Prions
Virus
Not alive, acellular, cannot replication without a host cell, include viroids, satellites, and bateri0phages
Dr. Jillian Banfield
Leveraged genomics to describe microbial diversity and build microbe tree of life
Archaeal Membranes
Ether Linkages, Isoprene-derived hydrocarbon
More resistant to chemical/heat stress
Bacterial Membranes
Ester Linkages, Fatty Acid
Glycerol Diether Lipids
Archaeal Lipid: Two hydrocarbons (~20 C long) attached to glycerol
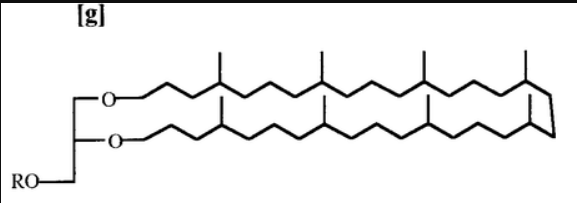
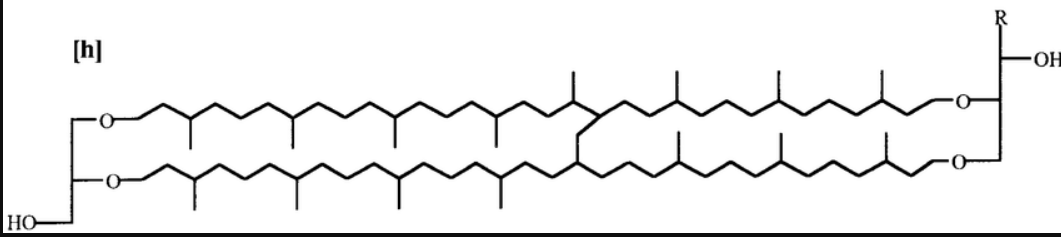
Diglycerol Tetraether Lipids
Archaeal Lipid: Two glycerol molecules linked by 2 hydrocarbons (~40 C long)
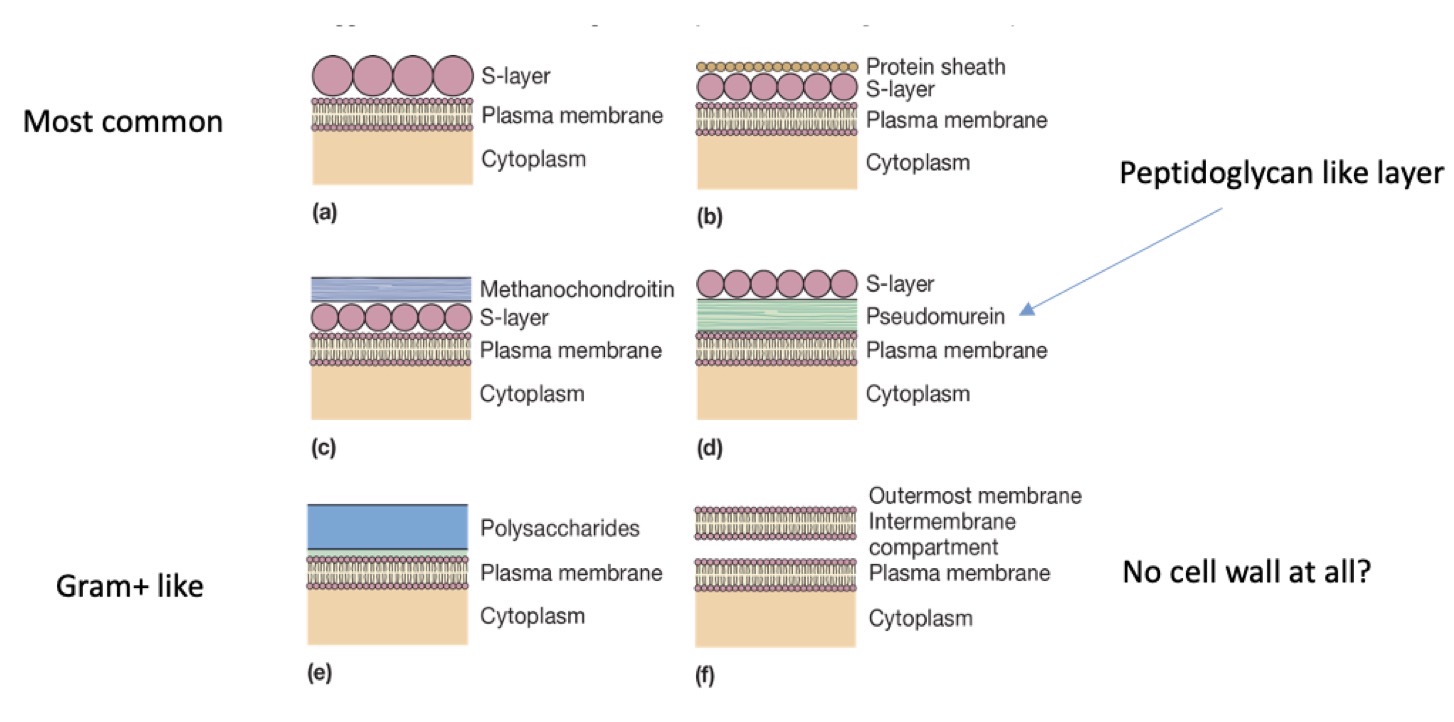
Archaea Cell Walls
Highly Variable sometimes with protein s-layer, peptidoglycan-like layer, gram positive-like structure, no cell wall
Archaea Ribosomes
Have some similarities to both eukaryotic and bacterial ribosomes, but most bacterial-targeted antibiotics don’t work against it (intermediate between bacteria and eukaryotes)
Archaea DNA Packaging
Have histone proteins that form nucleosomes homologous to eukaryotic nucleosomes, except, only 4 histones vs. 8 in eukaryotes with less DNA
Purpose of Microscopy
Our eyes can only seem up to 0.1 mm (10^-1 m) and bacteria are usually in μm range (10^-6 m)
Magnification
Making an object bigger
Resolution
Making two adjacent objects appear distinct and separate
Defines smallest object that can clearly be seen
Limiting Factor for Resolution
The wavelength of the light used for detection (nothing smaller than the wavelength of light used can be seen)
Types of Light Microscopy
Bright Field, Dark Field, Phase Contrast, DI-M, Fluorescence
Total Magnification
ocular magnification * objective magnification
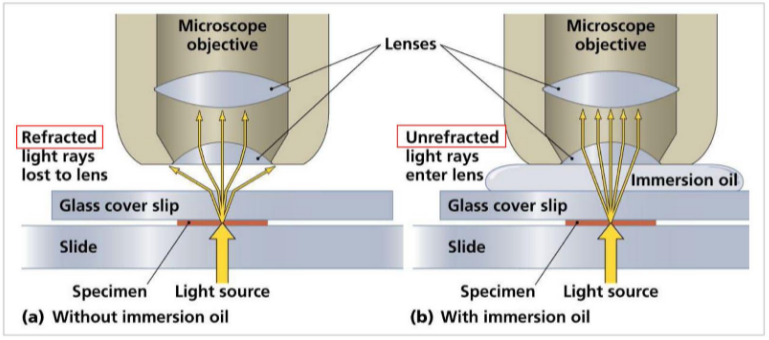
Oil Immersion Objection
A technique in light microscopy where immersion oil is used to match the refractive index of glass to prevent refraction of light rays
Dark Field Microscopy
Inversion of the image so cells appear bright on a dark background, using a dark field stop that creates a hollow cone of light that only magnifies the sample
Best For: Small/Thin cells at limit of resolution of light microscopes (~0.2 μm)
Phase Contrast Microscopy
Boosts contrast between sample and surrounding medium via destructive interference which exploits differences in refractive index
Best For: Not having to stain cells (stain can kill cells) and seeing internal structures
Differential Interference Microscopy (DI-M)
Uses prisms to make 3D-like image with enhanced contrast
Simple Stains
Provide coloration to cells indiscriminately for easy viewing. Usually charged molecules
Differential Stains
Provide coloration to some cells but not others
Examples: Gram Stain, Acid-Fast Stain, Endospore Stains
Gram Stain
Gram Positive-like turn purple and Gram Negative-like turn pink
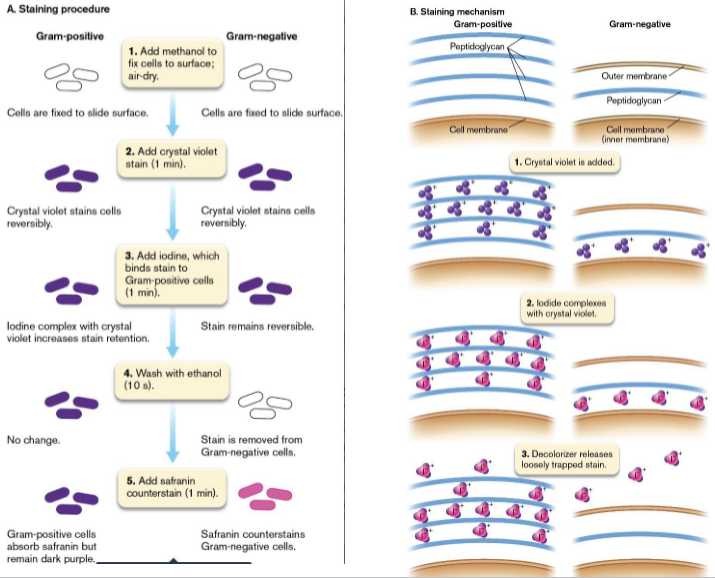
Fluorescence Microscopy
Fluorescent molecules detect cells/cellular structures (specific targeting utilizes proteins and antibodies)
Super Resolution Microscopy
Computers predict peak location to allow resolution beyond wavelength threshold
Electron Microscopy
Electrons detect instead of light which leads to much higher resolution (0.2 nm limit vs. light’s μm limit). However, cells must be dead since it is done in a vacuum
Atomic Force Microscopy
0.2 nm resolution like electron microscopy but done on alive cells using topographical (surface) map