8 - Graphical User Interface (GUI) Applications
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
AWT
Single Windowing Interface on Multiple Platforms
Supports functions common to all window systems
Uses Underlying Native Window system
Abstract Windowing Toolkit
What does AWT stand for?
GUI widgets
Event Handling
Containers for widgets
Layout managers
Graphic operations
AWT provides…
Portable GUI
preserves native look and feel
Standard GUI Components
Buttons, menus, checkboxes, etc.
Containers
Panels, Frames, Designs
BorderLayout, GridLayout, FlowLayout, Null layout
Layouts responsible for actual positioning of components:
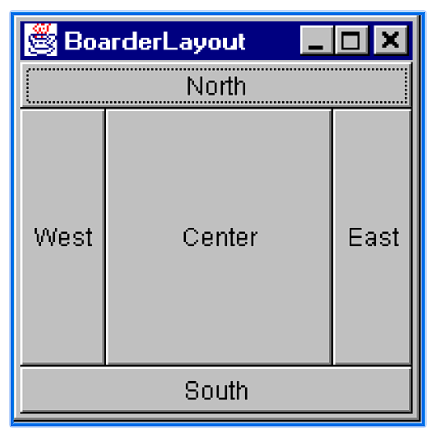
What do adding components via the BoarderLayout look like?

What do adding components via the GridLayout look like?
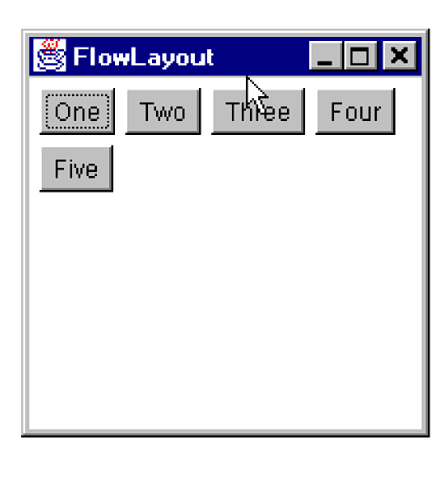
What do adding components via the FlowLayout look like?
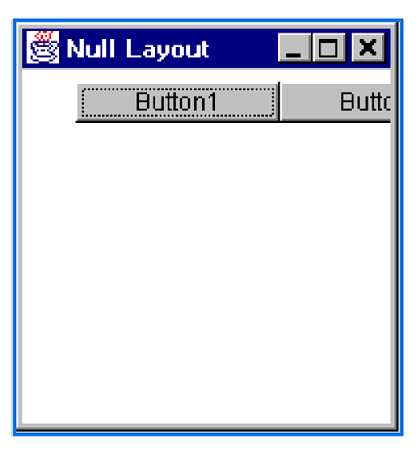
What do adding components via the Null Layout look like?
import java.awt.*;
Assemble the GUI
use GUI components,
basic components (e.g., Button, TextField)
containers (Frame, Panel)
set the positioning of the components
use Layout Managers
Attach events
Steps to building Graphical User Interfaces
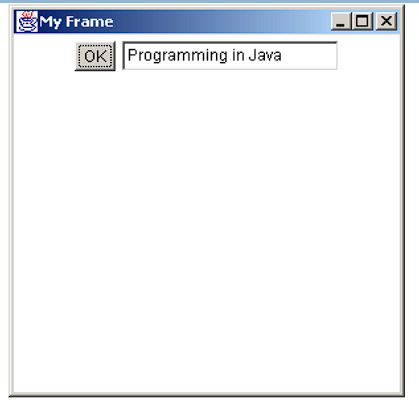
What is the output of the following?
import java.awt.*;
public class MyGui
{
public static void main(String args[] )
{
Frame f = new Frame ("My Frame");
Button b = new Button("OK");
TextField tf = new TextField("Programming in Java", 20);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
f.add(b);
f.add(tf);
f.setSize(300, 300);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
Listener
Each GUI component (e.g., a Button) that wishes to respond to an event type (e.g., click), must register an event handler, called a?
an object of a "Listener" interface.
The listener is an object of?
A Listener class can be created by subclassing (through "implements") one of Listener interfaces (all listener inrefaces are in the java.awt.event package = > must import java.awt.event.*; )
A Listener class can be created by?
The registration of the listener is done by a call to a method such as:
addActionListener(<Listener Object>).
How to register the listener?
[1] ActionListener
[2] ItemListener
[3] MouseMotionListener
[4] MouseListener
[5] KeyListener
[6] FocusListener
[7] AdjustmentListener
[8] ComponentListener
[9] WindowListener
[10] ContainerListener
[11] TextListener
Listener Interfaces in java.awt.event.*
Each listener interface has methods that need to be implemented for handling different kinds of events.
How do you handle different kinds of events and listeners?