Psychology Exam 2
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Dreaming: Freud Theory
dreams stem from unconscious thoughts
Freud: Manifest content
the actual images in the dream
Freud: Latent content
the unconscious thoughts, feelings, and wishes behind the manifest content
Dreaming: Activation synthesis
brain’s internally generated signals form dreams
Dreaming: Information processing
memories of events form dreams
Dreaming: Preserving neural pathways
purpose of dreaming is to provide brain stimulation
Adoption studies
compare adopted children to adoptive families and biological families
Twin studies
compare pairs of monozygotic and same-sex dizygotic twins
Monozygotic twins
share 100% of genes
Dizygotic twins
share 50% genes
Adoption twin studies
compare MZ twins separated in infancy and MZ twins reared together
Primitive reflexes
Sucking, Rooting, Moro, Grasping, Babinski
Piaget: Assimilation
fitting new information into present system of knowledge (schema)
Piaget: Accommodation
as a result of new information, changes existing schema
Sensorimotor Stage
birth to 2 years
looking, sucking, touching
develop object permanence
Preoperational Stage
age 2 to 7
Egocentric
Animistic thinking
Can’t grasp concept of conservation
Concrete Operations Stage
age 7 to 11
Can understand conservation
Can understand reversibility
Can understand transitivity
Concrete Operations: Reversibility
the idea that a stimulus that has been changed can return to its original state
Concrete Operations: Transitivity
understanding how components in a series are related
Preoperational: Egocentric
only use own frame of reference
Preoperational: Animistic thinking
attribute life to objects
Preoperational: Conservation
understanding that physical properties do not change when its appearance changes
Sensorimotor: Object Permanence
understanding that something continues to exists when it is not seen
Formal Operations Stage
age 11 to adulthood
abstract and systematic reasoning
thinking about future possibilities
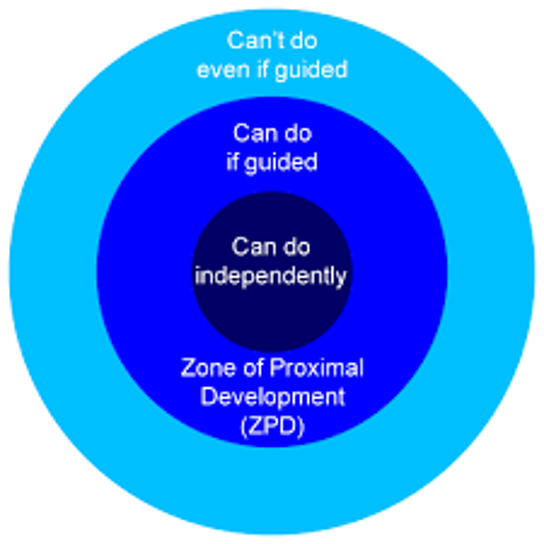
Vygotsky: Zone of Proximal Development
level at which a child can almost perform a task independently; difference between what the child can do alone and with assistance
Vygotsky: Scaffolding
teacher adjusts amount of support to child’s level of development
Theory of Mind
understanding of how other people think
Band-Aid Box Study
Kids shown Band-Aid box, asked what was inside
Kids were surprised to find pencils in box
Erikson: Trust vs. Mistrust
infancy
if needs are dependably met, infants develop sense of basic trust
develops when caregiving is sensitive, responsive, and consistent
Issue: Who can i trust?
Erikson: Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
toddlerhood
toddlers learn to exercise their will and do things for themselves, or they doubt their abilities
autonomy - independence, self-control
Issue: How can I do what I want without feeling bad about myself?
Erikson: Initiative vs. Guilt
preschool
preschoolers learn to initiate tasks and carry out plans, or they feel guilt about their efforts to be independent
Issue: What can I do without causing trouble?
Erikson: Competence vs. Inferiority
elementary school
children learn the pleasure of applying themselves to tasks, or they feel inferior
sense of competence or inadequacy
Issue: What activities am I good at? How do I compare with other?
Harlow’s Studies of Infant Attachment
soft contact is important
Rhesus Monkeys - cloth (no food) vs. wire (food) mother
Ainsworth: Secure
Adult as secure base from which to explore
Secure Base
Provided through a relationship with one or more caregivers offer a reliable base to explore and for a safe haven for reassurance during difficulties
Causes of Attachment Styles
temperament, stressful home life, parenting
Long Term Effects of Attachment
size of vocabulary, interpersonal interaction, emotions
Langlois’s Study of Attachment
infants gain attachment due to attractiveness
Mothers observed interacting with infants and behavior rated
Results: attractiveness —> affection, attention
Baumrind’s 2 Dimensions of Parenting
warmth (responsiveness) and control (demandingness)
Baumrind’s 4 Parenting Styles
authoritarian, permissive, uninvolved, authoritative
Parenting Style: Authoritarian
low warmth, high control
controlling, demanding, high emphasis on obedience
very restrictive, lots of rules
Outcome (most optimal) - higher grade, cooperative
Parenting Style: Permissive
high warmth, low control
very few rules or restrictions
Outcome: easily frustrated, low self-control
Parenting Style: Uninvolved (neglectful)
low warmth, high control
least effective, most detrimental
Outcome: low self-esteem, emotionally detached
Parenting Style: Authoritative
high warmth, high control
not overly demanding or hostile
child-centered
Outcome: lower grades, lower self-esteem
Kohlberg’s 3 Stages of Moral Development
Preconventional morality
Conventional morality
Postconventional morality
Kohlberg: Preconventional Morality
ages 4-10
avoid punishment or gain reward
Kohlberg: Conventional Morality
after age 10
“law and order”
Kohlberg: Postconventional Morality
early adolescence/young adulthood
individual principles and conscience
Heinz Dilemma
Heinz needs a particular expensive drug to help his dying wife. The pharmacist who discovered and controls the supply of the drug has refused Heinz’s offer to give him all the money he now has, which would be about half the necessary sum, and to pay the rest later. Heinz must now decide whether or not to steal the drug to save his wife; that is, whether to obey the rules and laws of society or to violate them to respond to the needs of his wife. What should Heinz do, and why?
Delay of Gratification
ability to forego smaller, immediate rewards for greater rewards later
The Marshmallow Test
choice of 1 marshmallow now or 2 marshmallows in a few minutes
ability to delay gratification —> positive social and academic outcomes
Erikson: Identity vs. Role Confusion
adolescent
stable sense of who one is and what one’s values are or identity confusion
Issue: Of all the social roles, which ones fit me and how can I develop a role that is uniquely my own?
Erikson: Intimacy vs. Isolation
young adult
establish enduring, committed relationships
Issue: Whom can I trust with intimacy and love?
Erikson: Generativity vs. Stagnation
middle adult
generativity - generate things that contribute to the future of society
stagnation - see life as meaningless
Issue: How can I continue to grow as a person?
Erikson: Integrity vs. Despair
elder
Ego Integrity - feeling that one’s life has coherence and purpose
Despair - disappointment, regret
Issue: How can I feel content with my life, so I can face death calmly?
Socioemotional Selectivity Theory
model of social activity; old age - smaller social network; very close relationships maintained, superficial relationships
Sensation
process by which sensory organs obtain information about the environment and transmit it to the brain
Perception
the organization of sensations into interpretations
Transduction
translation of physical energy into electrical signals
Bottom-up Processing
starts with raw sensory data that gets communicated to the brain
Top-down Processing
starts with observer’s expectations and knowledge
Absolute Threshold
minimal amount of stimulation that can be detected half of the time; occurs when person can detect signal 50% of the time
Difference Thresholds (The JND)
smallest difference in intensity between 2 stimuli that a person can detect
Weber’s Law (fraction)
for 2 stimuli to be perceived as different in intensity, the second must differ from the first by a constant proportion
Signal Detection Theory
perception results from both sensory information, and making a judgement
detection (perception of stimulus) depends on sensitivity of sensory systems and response bias
Response Bias
person’s readiness to report detecting a stimulus
Signal Detection Theory: Hits, Misses, False Alarms, Correct Rejections
Hits - signal present, response given
Misses- signal present, no response given
False Alarm: no signal present, response given
Correct Rejection: no signal present, no response given
Factors Affecting Response Bias
expectations and motivation (history of signal detection errors may affect future response bias)
Gestalt Approach
we perceive objects as whole rather than as sum of the individual parts
Figure-Ground Perception
we inherently distinguish between object and background
Grouping Principles
proximity, similarity, continuity, closure
Proximity
we tend to group together objects that are close to one another
Similarity
we tend to group together objects that are similar to one another
Continuity
brain organizes stimuli into continuous lines or patterns
Closure
we tend to perceive incomplete figures as complete
2 Kinds of Visual Information for Depth
binocular and monocular cues
Retinal (Binocular) Disparity
images produce different image on each retina - greater disparity —> less depth
Binocular Cues: Convergence
turning inward of eyes towards nearby object; closer object —> greater convergence
Monocular Cues
can use only 1 eye; when objects are far away —> relative size, relative clarity, linear perspective
Perceptual Constancy
interpretation of changing sensations as perception that is relatively consistent
Color Constancy
consistent perception of color of objects although the amount of light changes
Lightness Constancy
consistent perception of shade of objects although the amount of light changes
Shape Constancy
perception that object’s shape remains constant despite changing shape of retinal image
Size Constancy
perception that the size of objects remains constant despite different sizes of images on retina
Classical Conditioning
learning to respond to new stimulus that has been associated with another stimulus that normally produces the response
Pavlov’s Study of Classical Conditioning
studied digestion
noticed that dogs salivated at mere sight of food dish - learning to associate dish with food
presented food with neutral stimulus (bell) & measured salivation in response to neutral stimulus (bell) presented alone
Unconditioned Stimulus
stimulus that automatically elicits response without prior conditioning
Unconditioned Response
innate response to unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned Stimulus
previously neutral stimulus; elicits a conditioned response due to its association with unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned Response
learned response to a stimulus that did not originally elicit response