Foot Anatomy: Compartments, Arteries, Nerves, and Joints
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
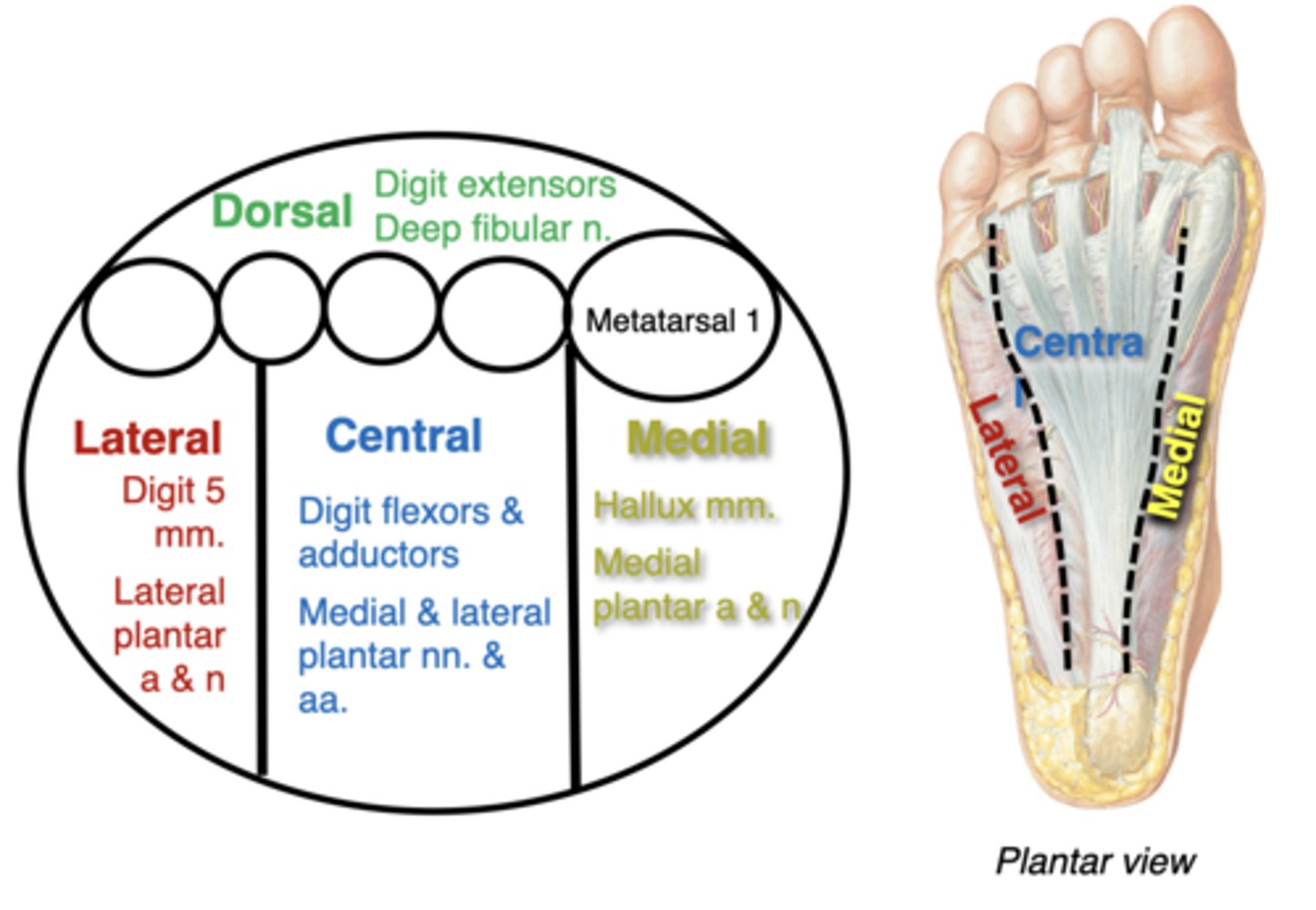
Compartments of the foot
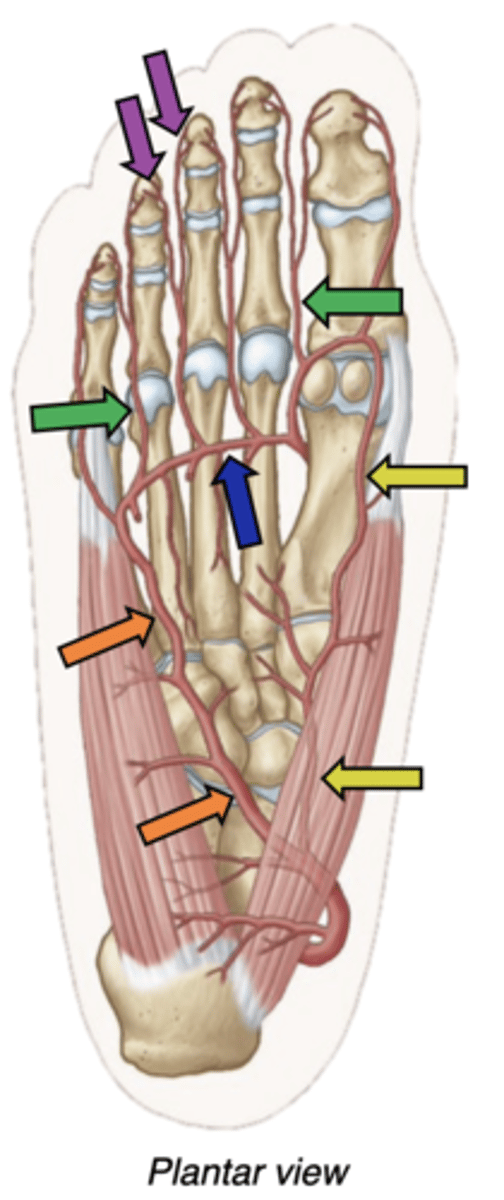
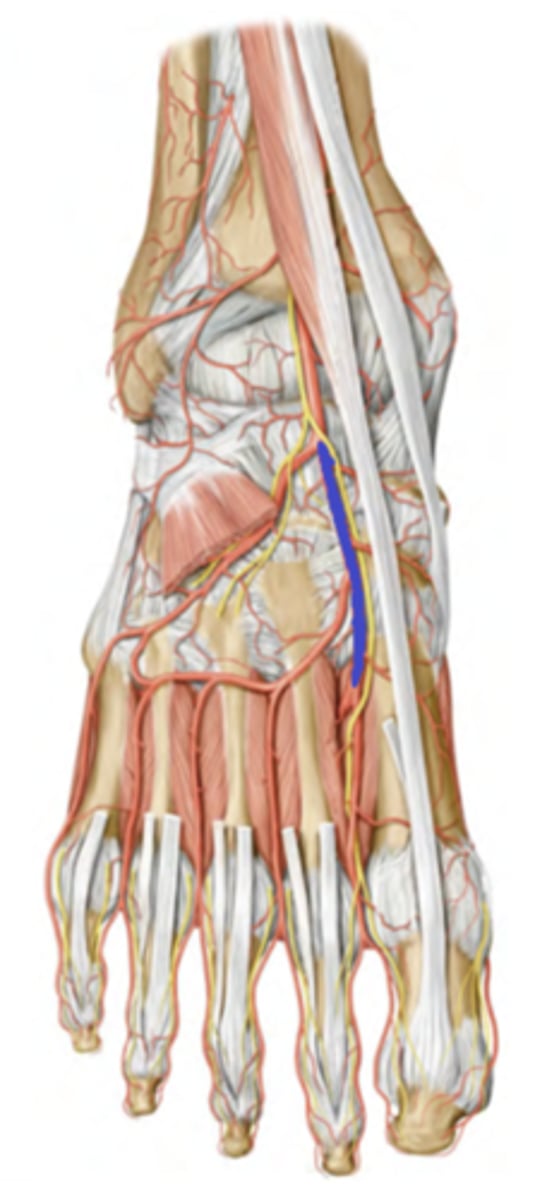
Arteries of the plantar foot
popliteal--> posterior tibial artery--> Crosses tarsal tunnel as “Bloody” --> Divides within foot to become the medial plantar and lateral plantar arteries.
-medial plantar artery -along digit 1 (yellow)
-lateral plantar artery (orange) heads laterally, then gives off the deep plantar arch (blue)
-Plantar metatarsal arteries (green) extend between digits, then split into proper digital arteries (purple) on the side of each toe.
medial foot compartment contents
Abductor hallucis
Flexor hallucis brevis
Flexor hallucis longus tendon [different n & a; tibial n & posterior tibial a]
medial foot compartment actions, innervation, artery
-Great toe flexion and abduction
-medial plantar nerve
-medial plantar artery
central foot compartment contents
Flexor digitorum brevis
Quadratus plantae
Lumbricals
Adductor hallucis
Plantar interossei
Dorsal interossei,
[Tendons of Flexors hallucis & digitorum longus]
central foot compartment actions, innervation, artery
-Digit flexion and adduction
-Lateral plantar nerve (except flexor digitorum
brevis & 1st lumbrical)
-lateral plantar artery
lateral foot compartment contents
Abductor digit minimi
Flexor digiti minimi brevis
lateral foot compartment actions, innervation, artery
-Fifth digit flexion and abduction
-lateral plantar nerve
-lateral plantar artery
dorsal foot compartment contents
Extensor hallucis brevis,
Extensor digitorum brevis,
[Tendons of Extensors hallucis & digitorum longus]
dorsal foot compartment actions, innervation, artery
-Digit extension
-Deep fibular nerve
-Dorsalis pedis artery
Medial plantar nerve innervates
-Flexor digitorum brevis, 1st lumbrical, abductor hallucis, flexor hallucis brevis
-cutaneous: Medial 3.5 digits, medial
sole
branches from tibial nerve
lateral plantar nerve innervates
-Lateral and central foot cmpts. (except
flexor digitorum brevis & 1st lumbrical)
-cutaneous: Lateral 1.5 digits, lateral
sole
branches from tibial nerve
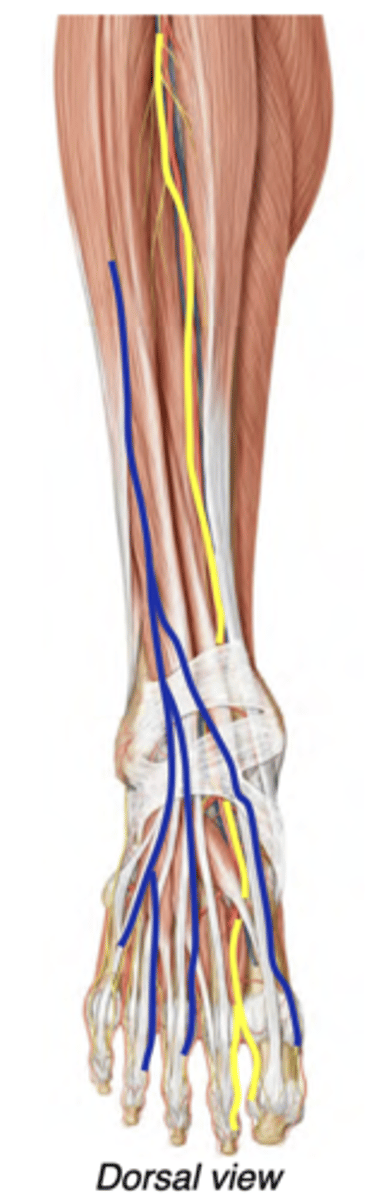
Nerves of the Dorsal Foot
The superficial fibular nerve (blue) continues into the skin of much of the dorsum of the foot--No motor innervation in foot
The deep fibular nerve (yellow) enters the foot deep to the extensor muscles --> Innervates extensors digitorum & hallucis brevis
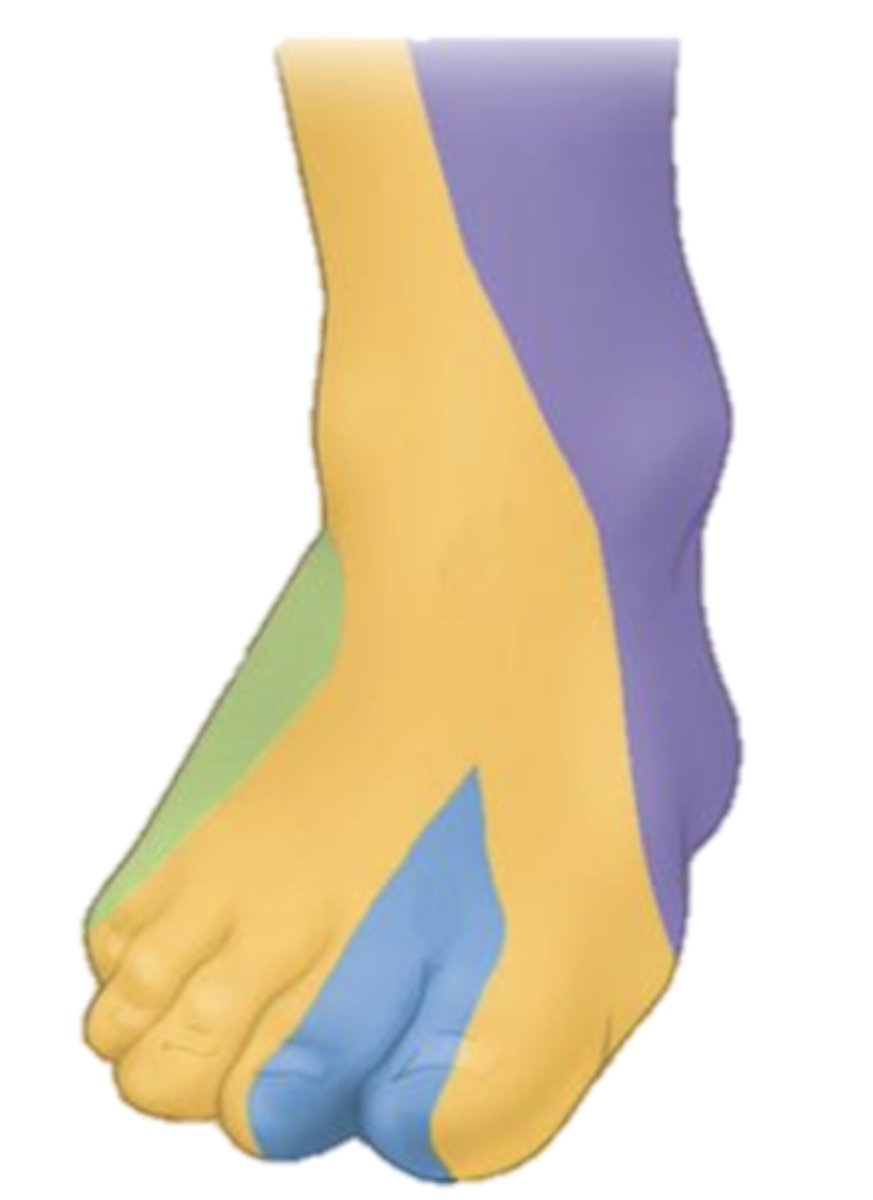
Cutaneous Innervation of the Dorsal Foot
-Superficial fibular nerve: most of the dorsal foot (yellow)
-Deep fibular nerve: first dorsal web space (blue)
-Saphenous nerve (from femoral): medial ankle & heel (purple)
Dermatome landmarks:
Big toe: L5
Little toe: S1
Arteries of the Dorsal Foot
The anterior tibial artery continues into the dorsum of the foot--> Name change to dorsalis pedis artery
Branches supply dorsal muscles, anastomose with plantar arteries
-Palpate for a distal pulse just lateral to extensor hallucis longus tendon
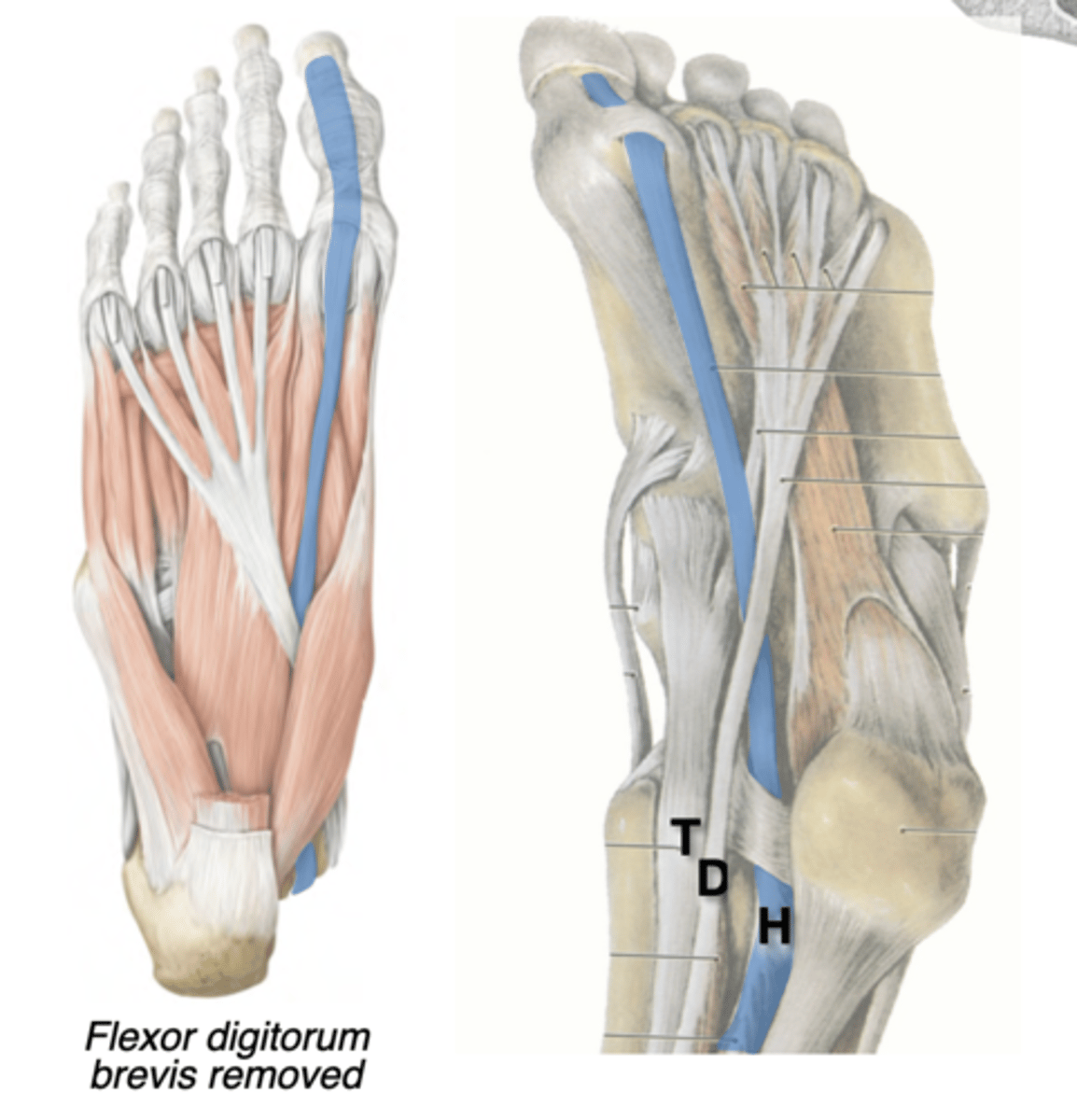
Tendon of Flexor Hallucis Longus
Central compartment
Posterior leg --> Tarsal tunnel (“Harry”) --> Distal phalanx of digit 1
-Actions Flexes digit 1
Tendon passes through a tunnel between the flexor hallucis brevis sesamoids
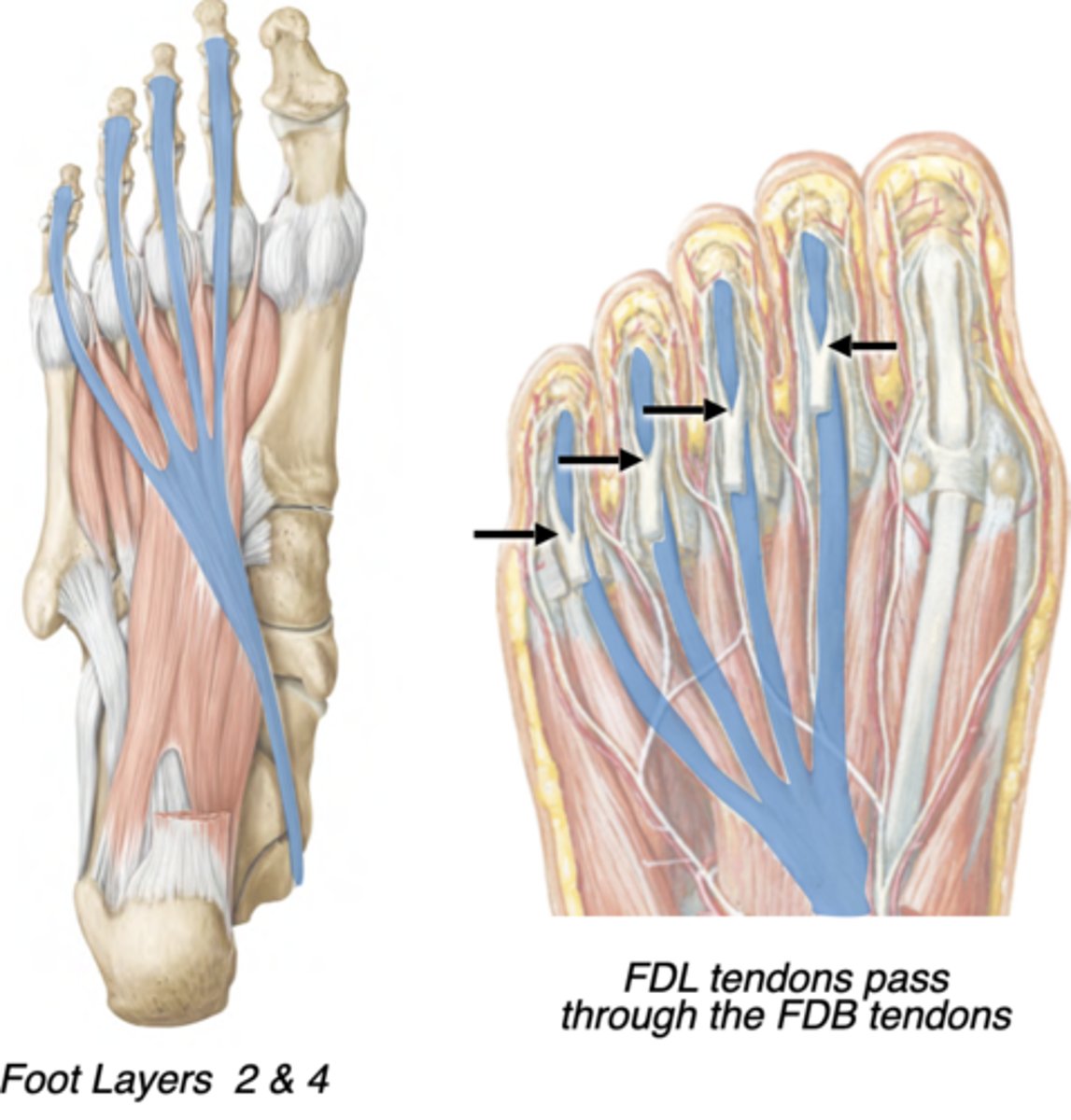
Tendon of Flexor Digitorum Longus
Central compartment
Posterior leg --> Tarsal tunnel (“Dick”) --> -Distal phalanges of digits 2-5
-Flexes lateral 4 digits
-tendons pass through the split in the flexor digitorum brevis tendons
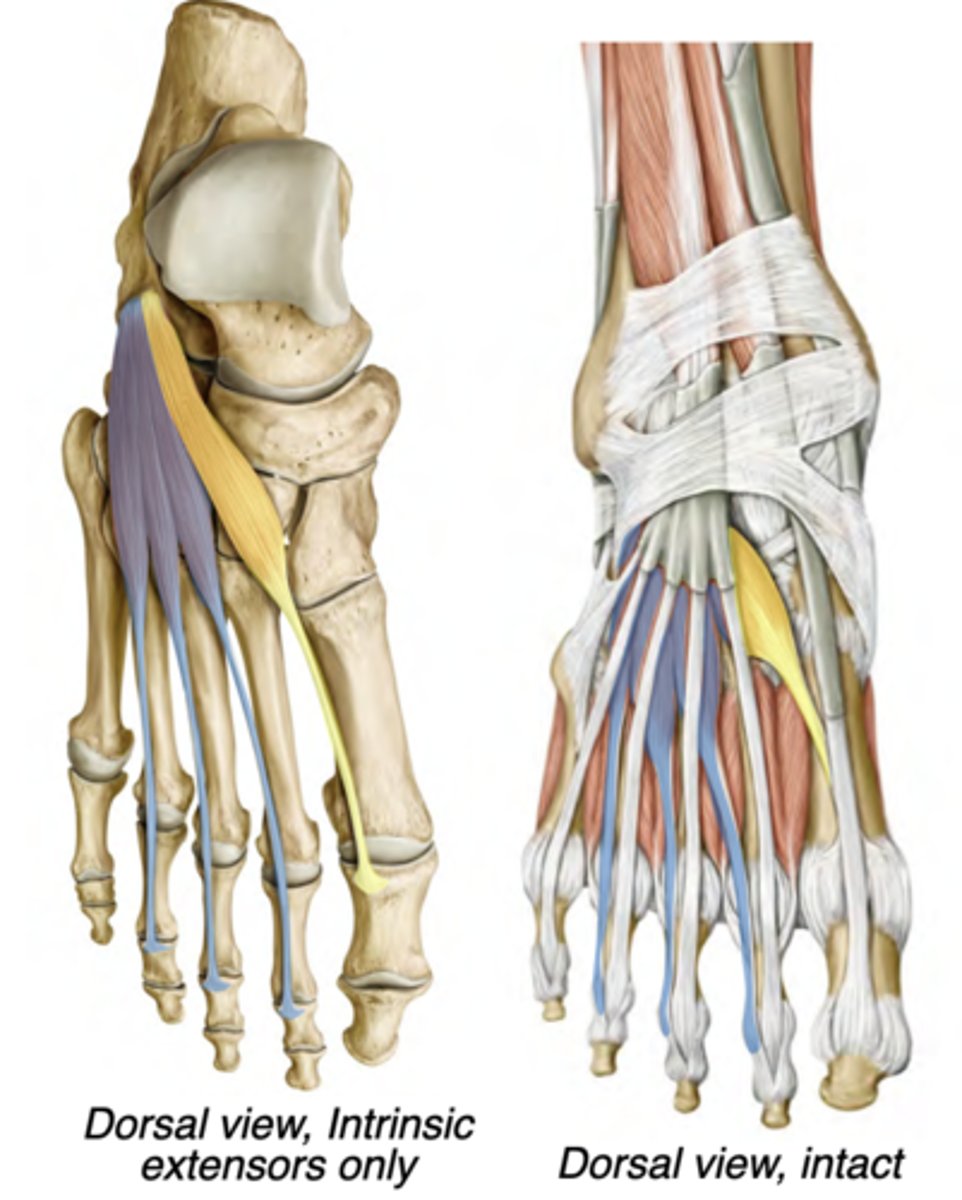
Extensor digitorum brevis
Dorsal compartment
-Deep fibular nerve
-Extends digits 2-4
-prox: Calcaneus
-distal: Tendons of extensor
digitorum longus
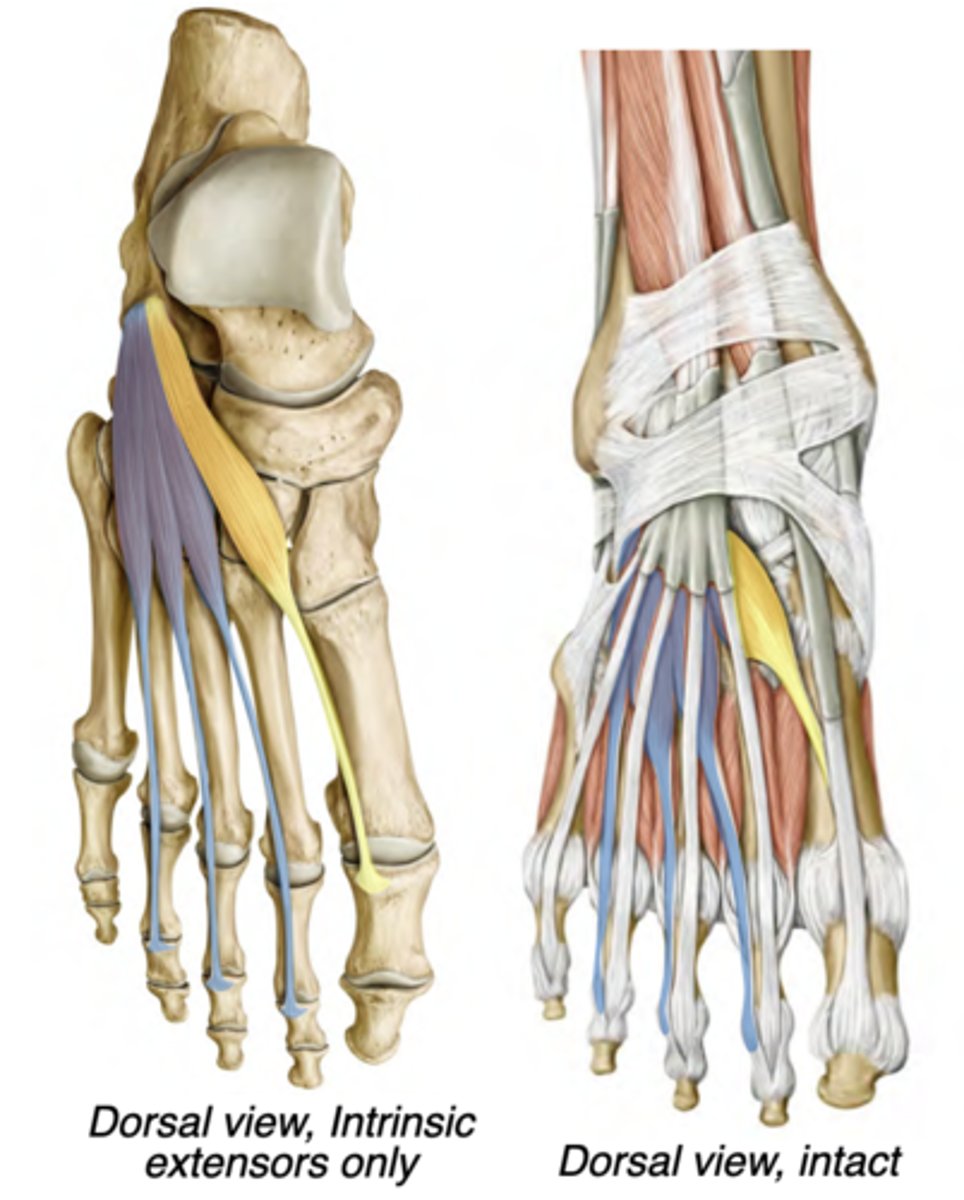
Extensor hallucis brevis
Dorsal compartment
-Deep fibular nerve
-Extends hallux
-prox: Calcaneus
-distal: Proximal phalanx of digit 1
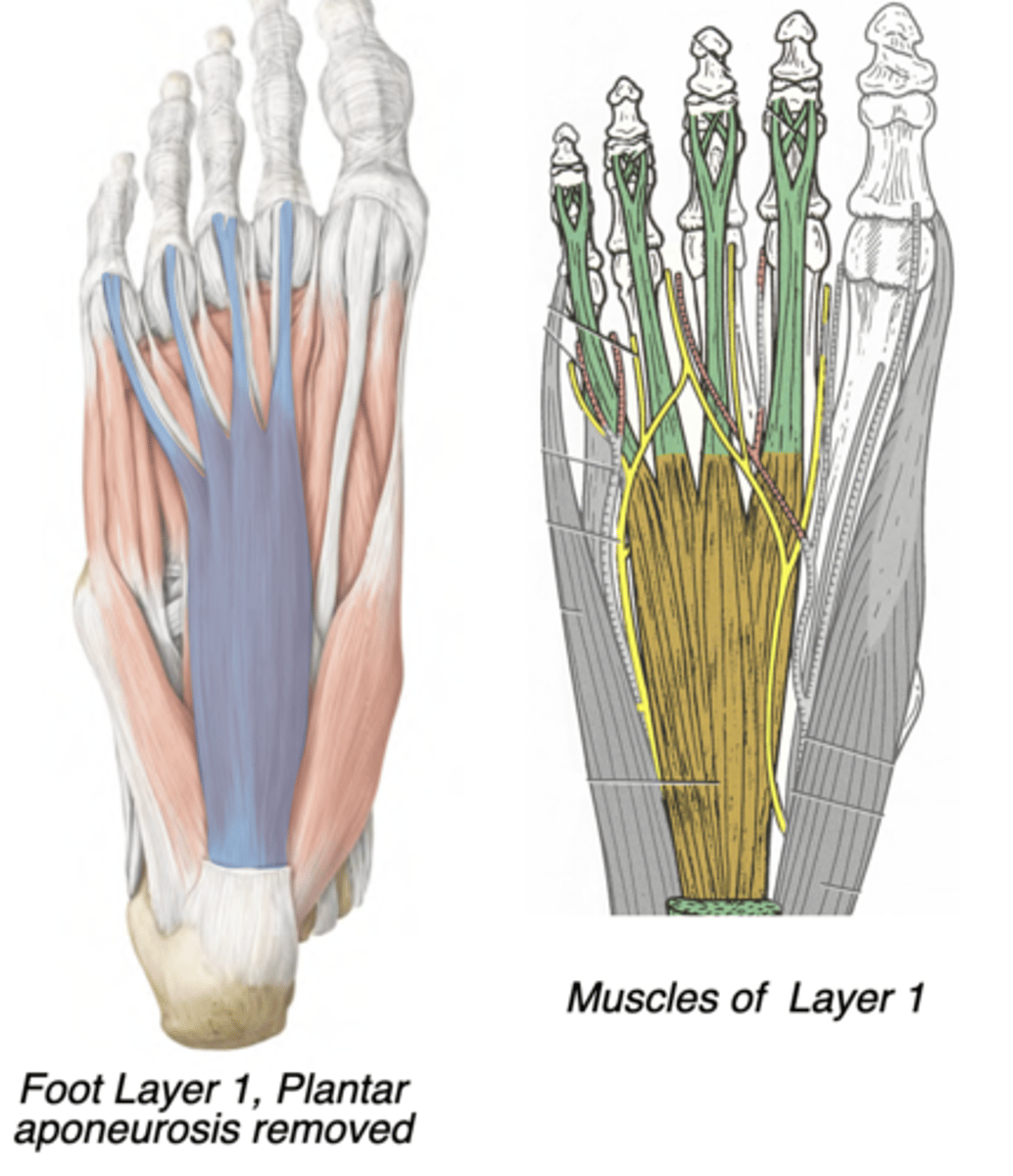
Flexor digitorum brevis
Central compartment
-Medial plantar nerve
-Flexes digits 2-5 (lateral 4 digits)
-prox: Calcaneus (tuberosity)
-distal: Intermediate phalanx of
digits 2-5
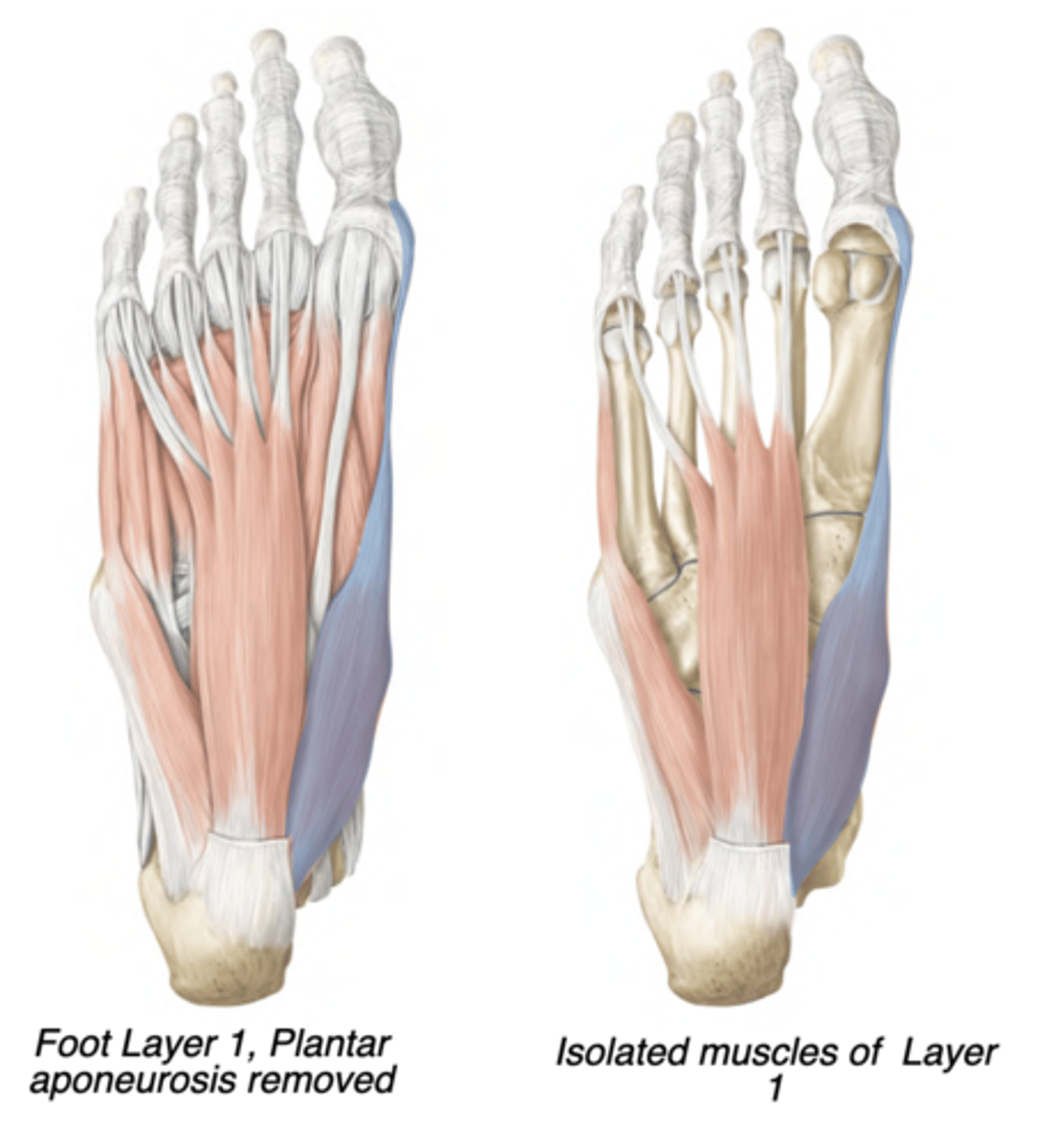
Abductor hallucis
Medial compartment
-Medial plantar nerve
-Abducts hallux
-prox: Calcaneus (tuberosity)
-distal: Proximal phalanx of digit 1
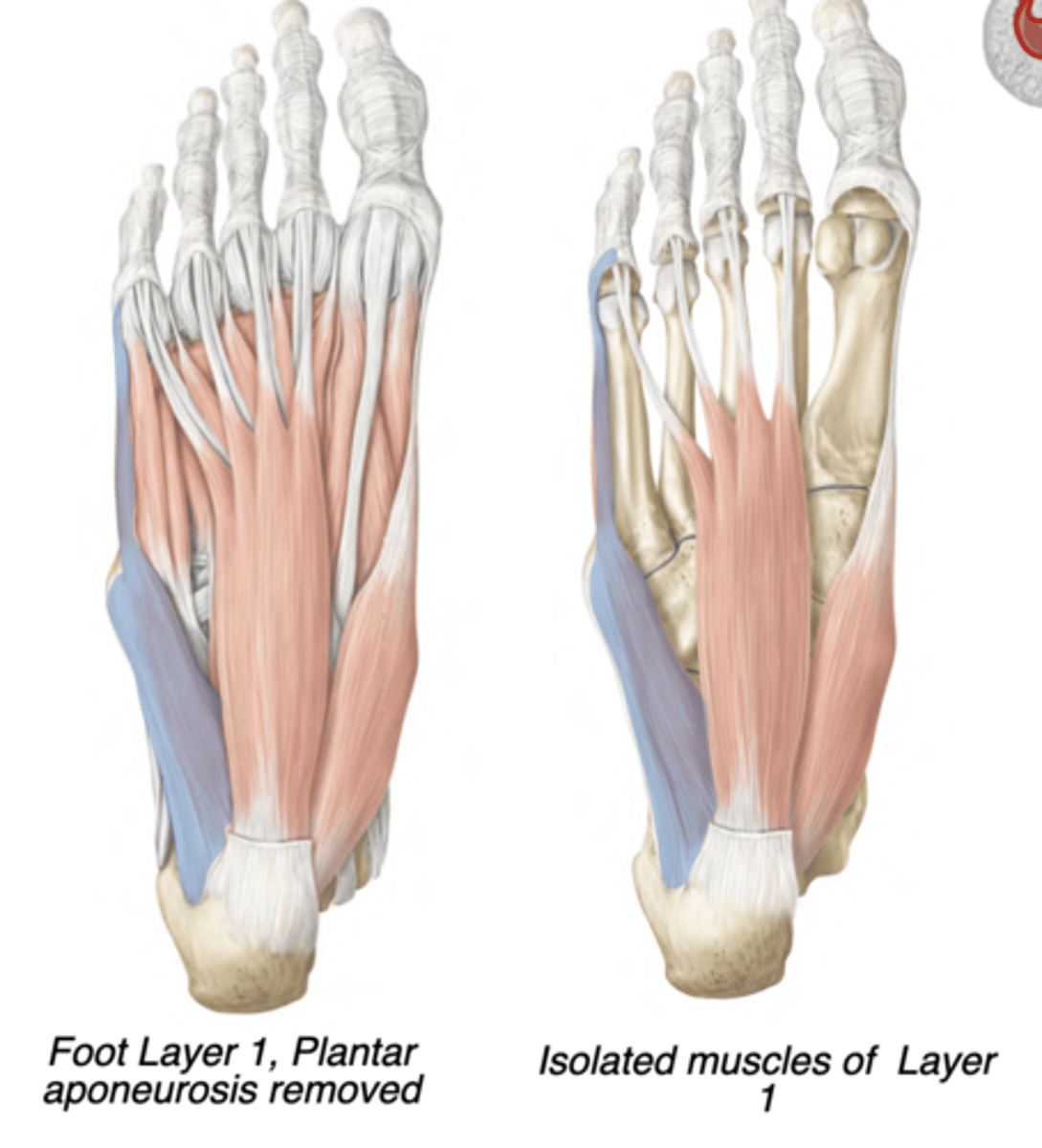
Abductor digiti minimi
Lateral compartment
-Lateral plantar nerve
-Abducts digit 5 (pinky)
-prox: Calcaneus (tuberosity)
-distal: Proximal phalanx of digit 5
Quadratus plantae
Central compartment
-Lateral plantar nerve
-Redirects pull of flexor digitorum longus
-prox: Calcaneus (tuberosity)
-distal: Tendon of flexor digitorum
longus
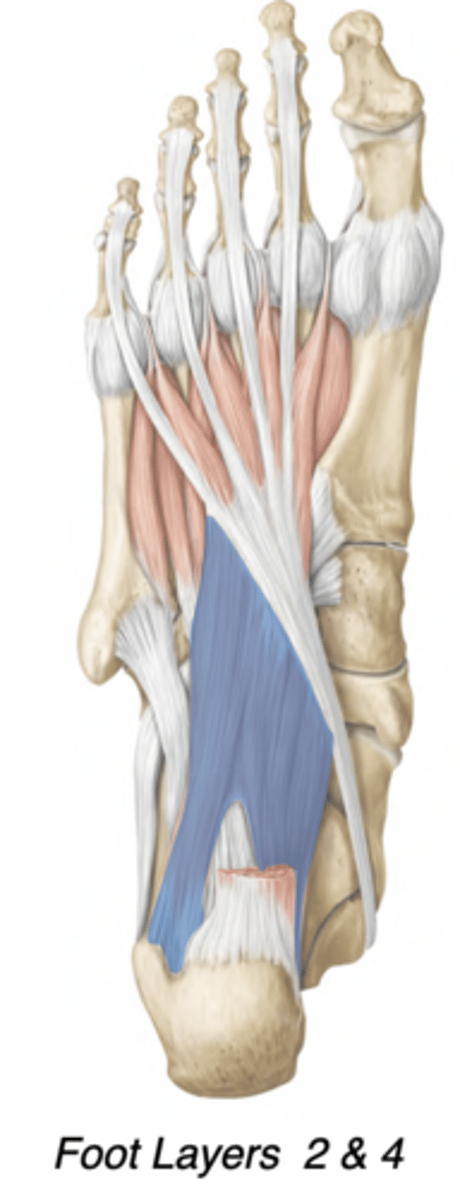
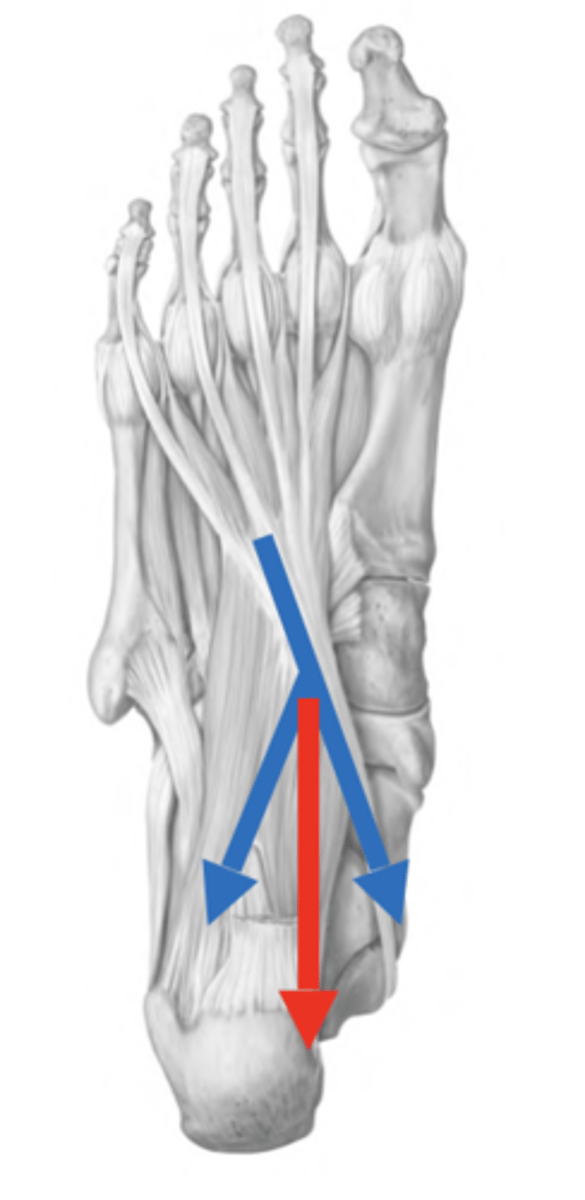
Quadratus plantae action
-It changes the direction of pull to ensure that the toes flex in the direction of the heel and not in the direction of the medial malleolus, by pulling on the lateral side of the tendon of flexor digitorum long
-counteracts the oblique pull of the flexor digitorum longus
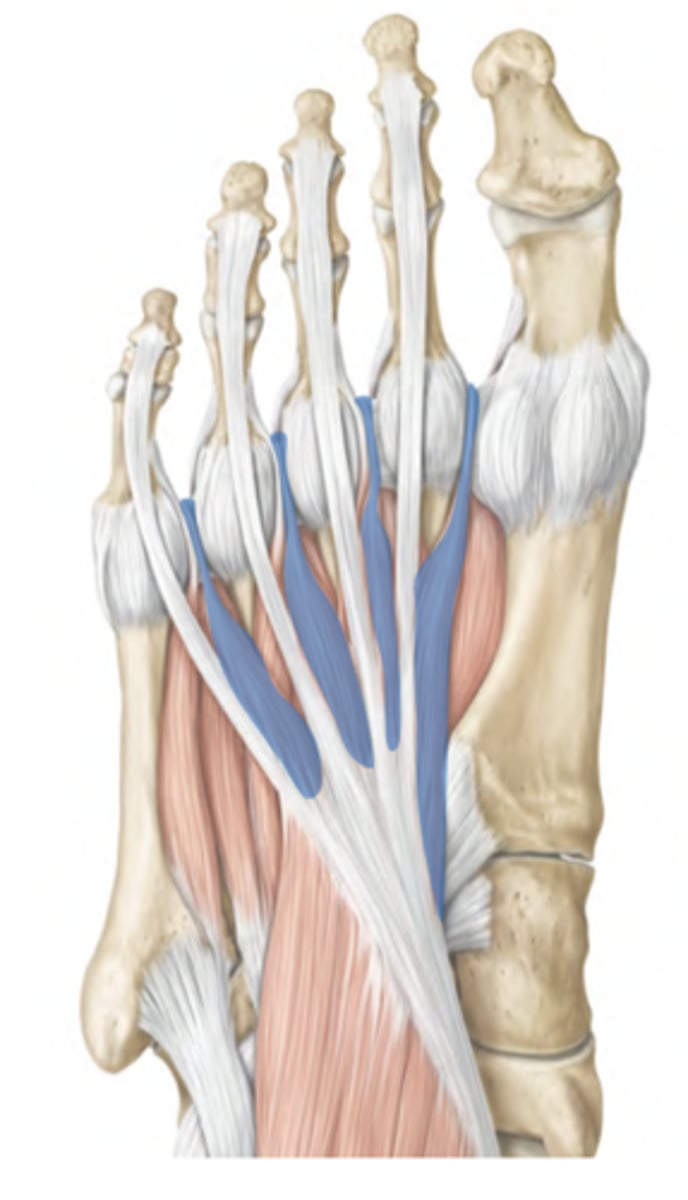
Lumbricals
Central compartment
-1st: medial plantar nerve
-2-4: lateral plantar nerve
-Flexes MTP joints, Extends PIP & DIP joints
-prox: Tendons of flexor digitorum longus
-distal: Extensor expansions of digits 2-5
Flexor hallucis brevis
Medial compartment
-Medial plantar nerve
-Flexes hallux
prox: Cuboid & Lateral cuneiform
distal: Base of 1st proximal phalanx
➢Two heads
➢Sesamoid bones form in its tendons
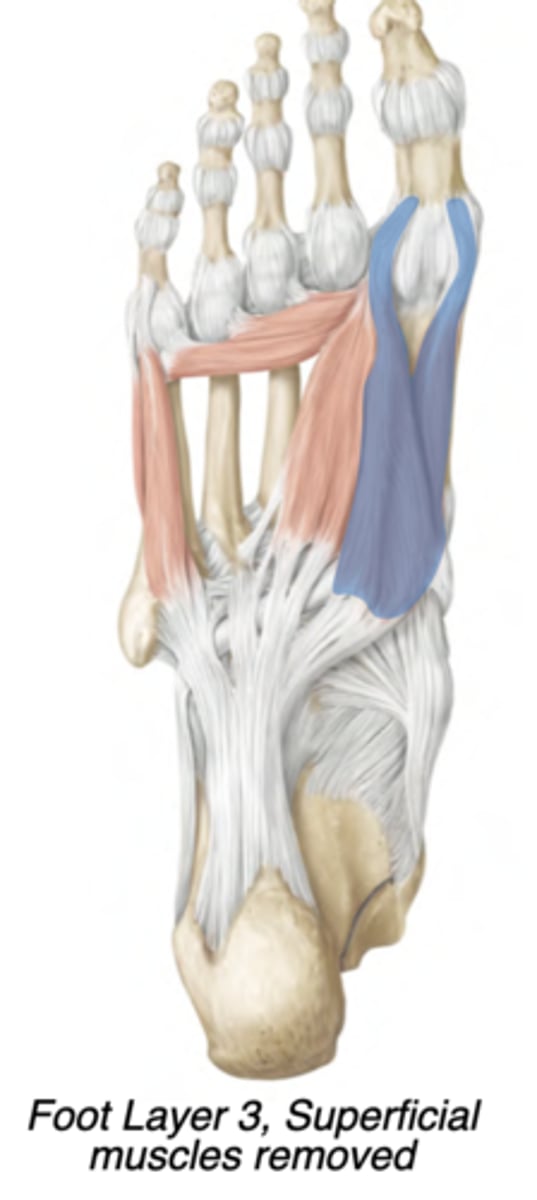
Adductor hallucis
Central compartment
-lateral plantar nerve
-Adducts hallux
-prox: Oblique head= bases of
metatarsals 2-4; Transverse head: ligaments of the MTP joints
-distal: Lateral base of 1st proximal phalanx
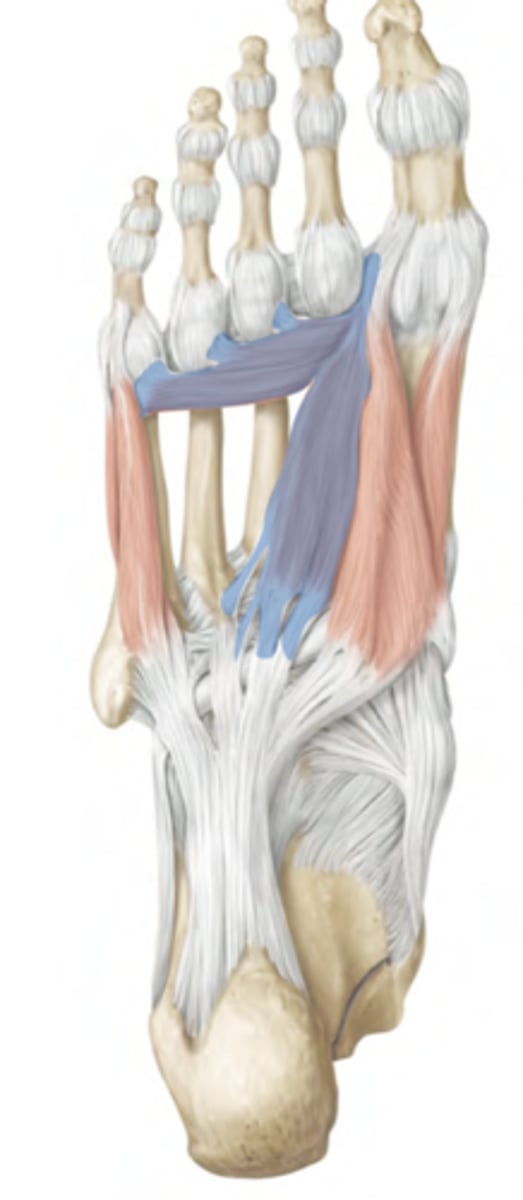
Flexor digiti minimi brevis
Lateral compartment
-lateral plantar nerve
-Flexes digit 5
-prox: Base of fifth metatarsal
-distal: Base of fifth proximal phalanx
Plantar interossei
Central compartment
-Lateral plantar nerve
-Adducts digits 3-5
Metatarsals to proximal phalanges 3-5
(Yellow)
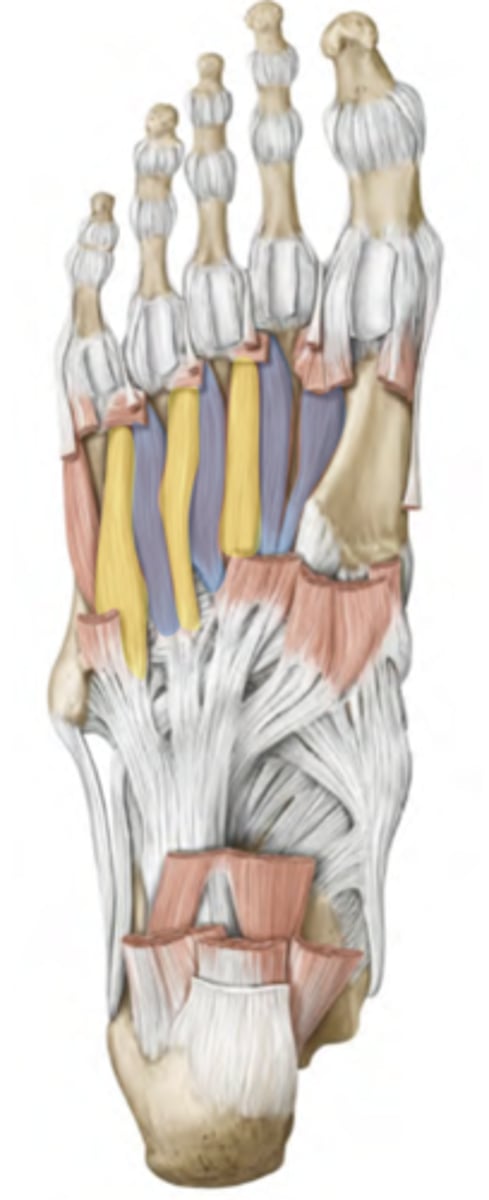
Dorsal interossei
Central compartment
-Lateral plantar nerve
-Abduct digits 2-4
All metatarsal shafts to proximal phalanges 2-4
(Blue)
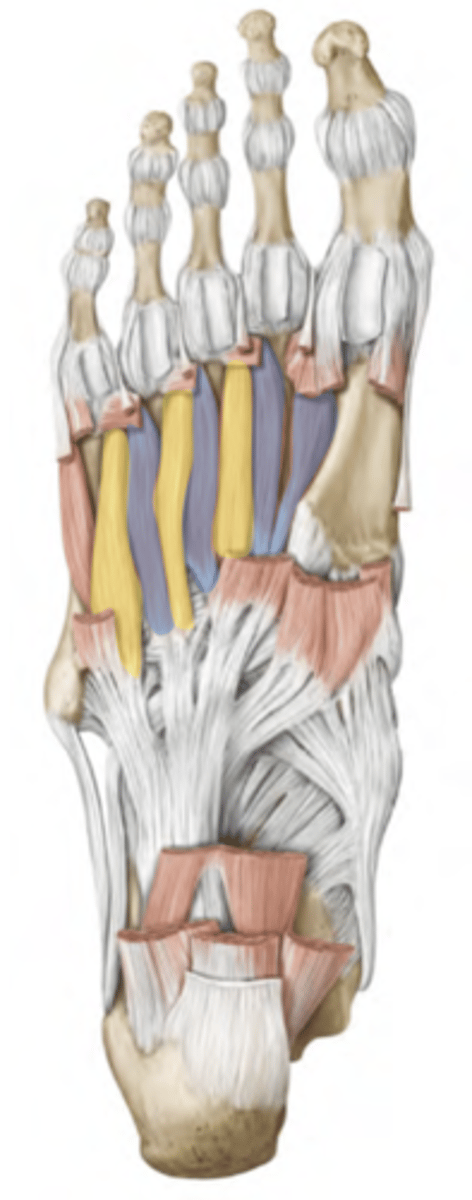
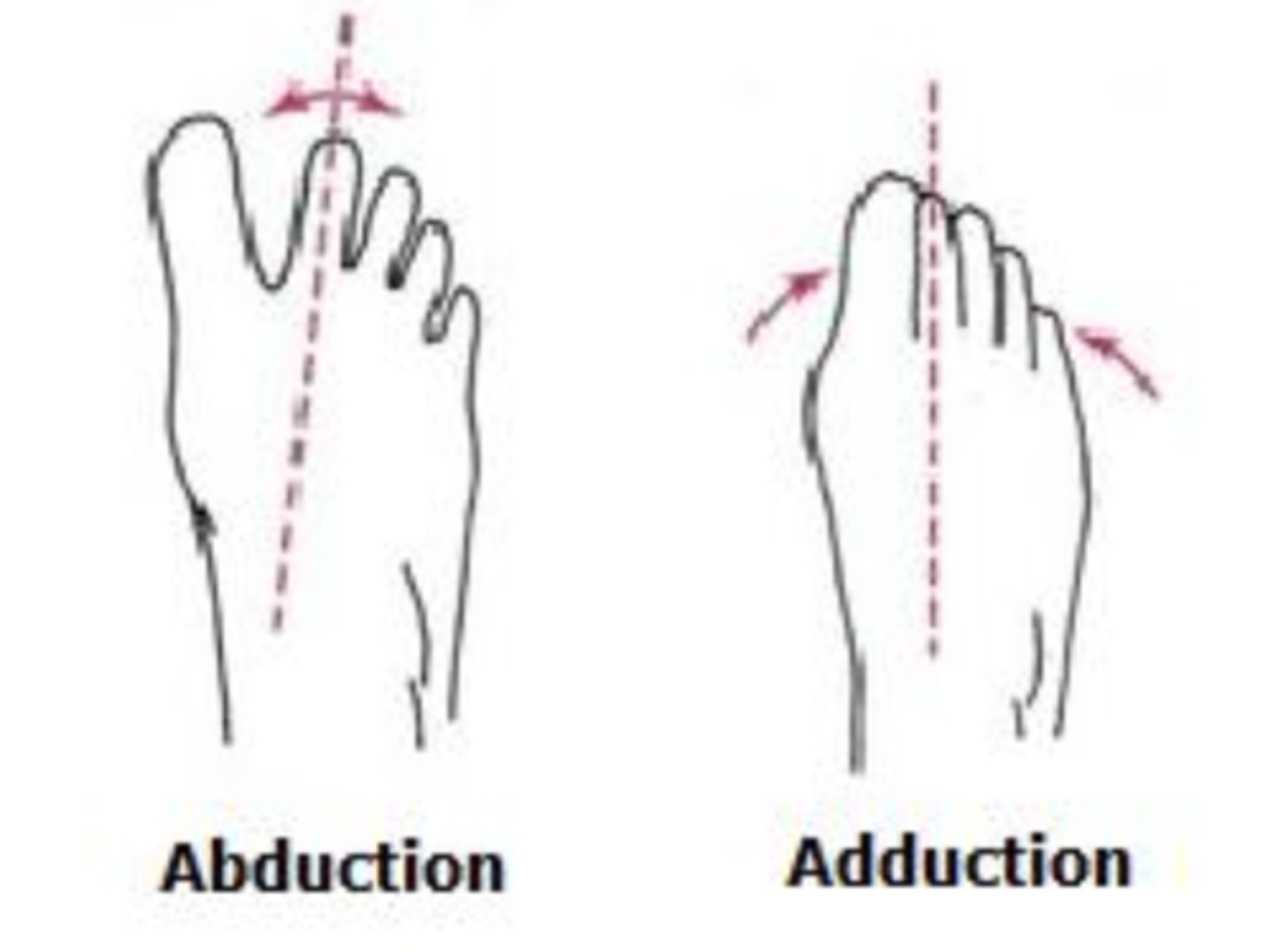
abduction and adduction of the foot
relative to the 2nd toe
--> the second toe can only abduct.
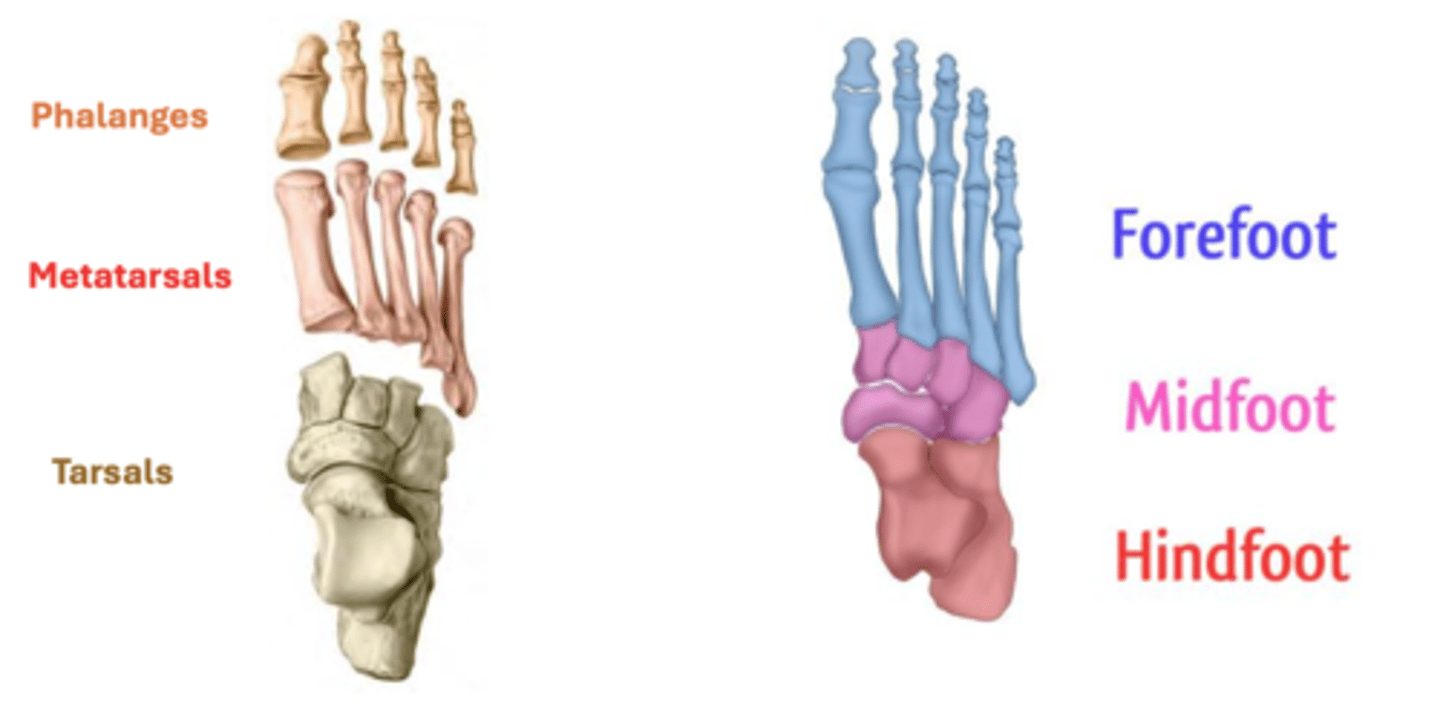
divisions of the foot
Tarsals
• Talus
• Calcaneus (has the sustentaculum tali)
• Navicular
• Cuboid
• Medial cuneiform
• Intermediate cuneiform
• Lateral cuneiform
Talus
ankle bone (articulates with tibia)
GREY
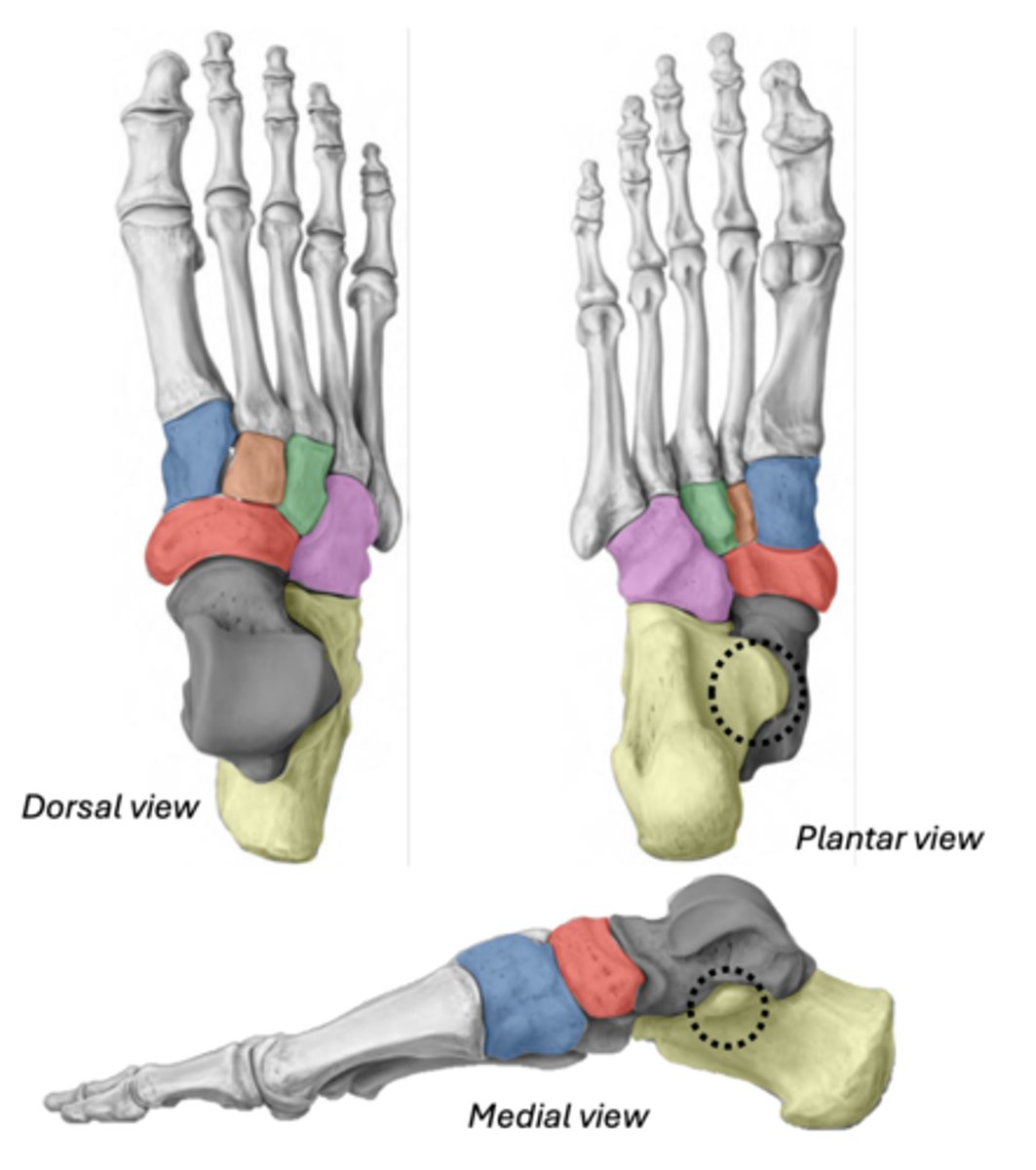
Calcaneus & Sustentaculum tali
YELLOW
BLACK (ST)
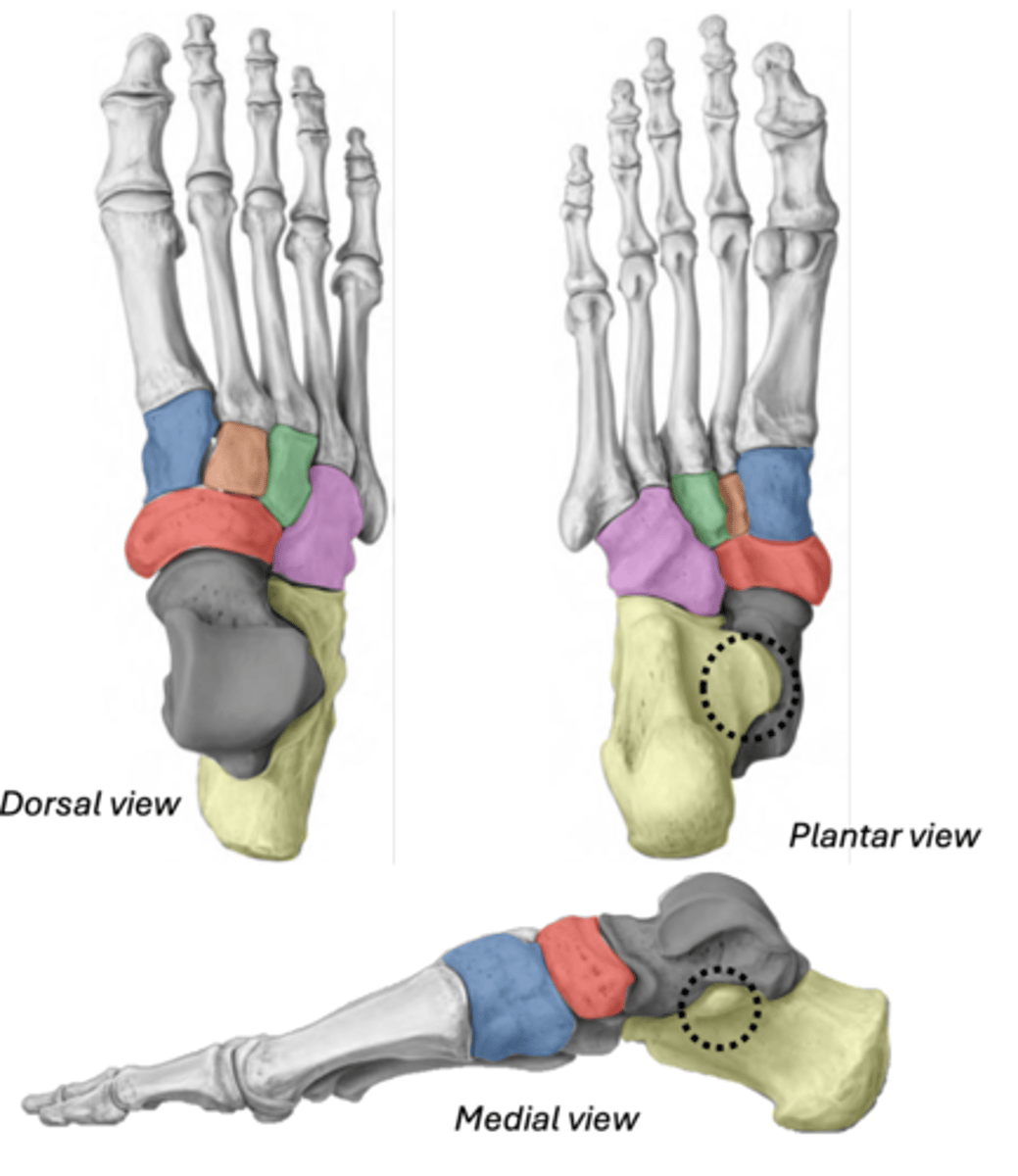
Navicular
between cuneiforms and talus
RED
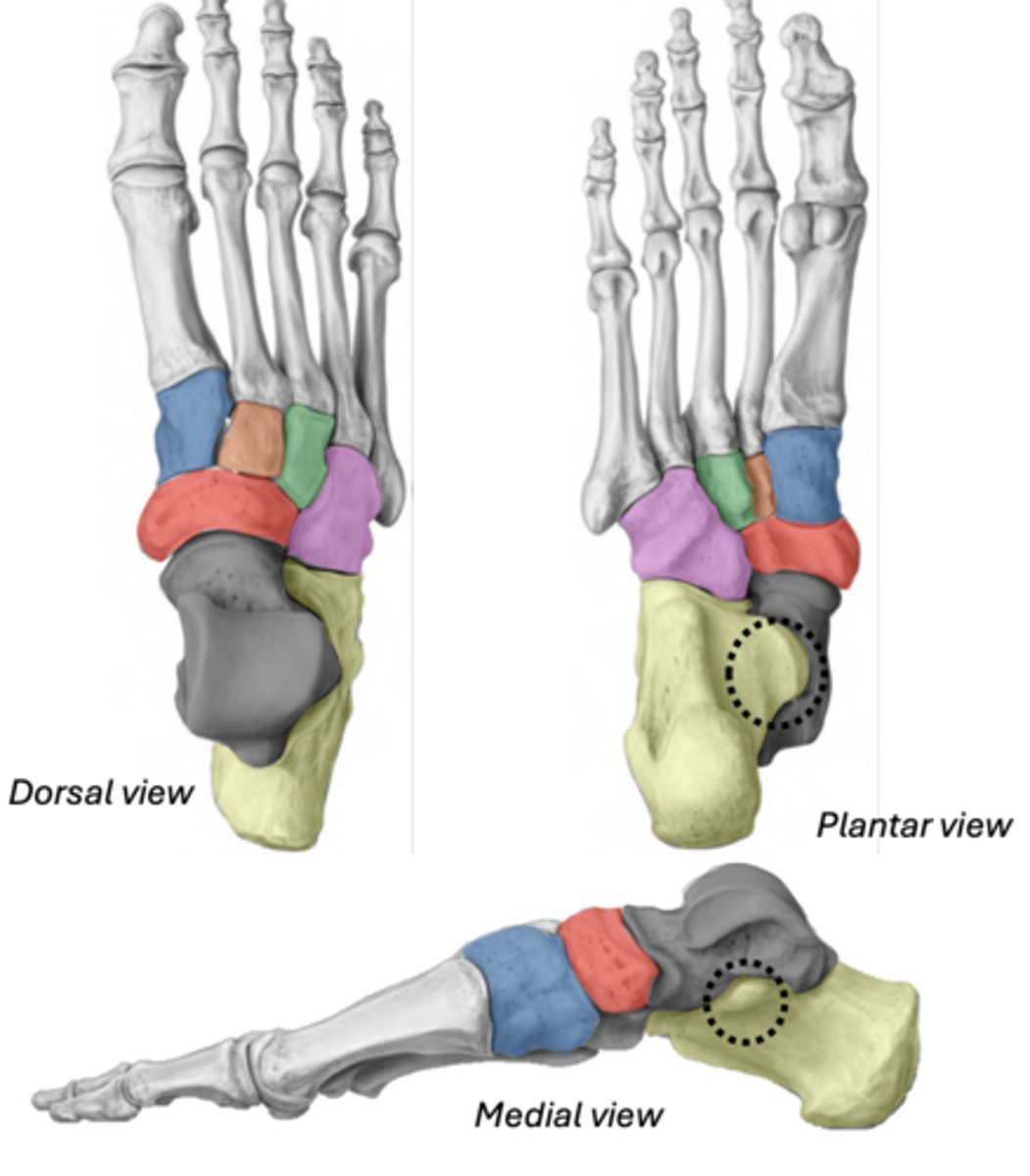
Cuboid
most lateral (articulates with 4th & 5th metatarsals)
PINK
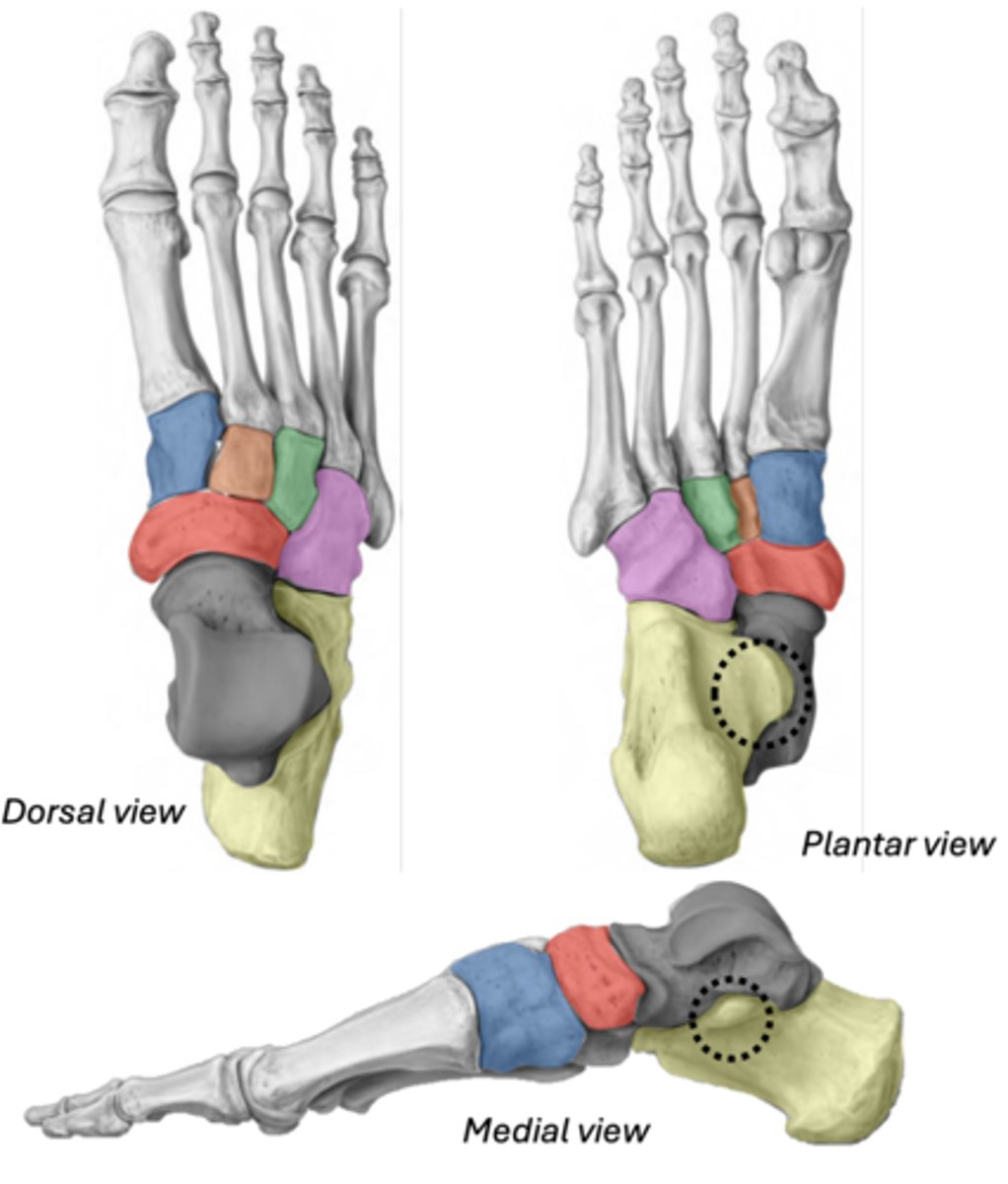
Medial cuneiform
BLUE
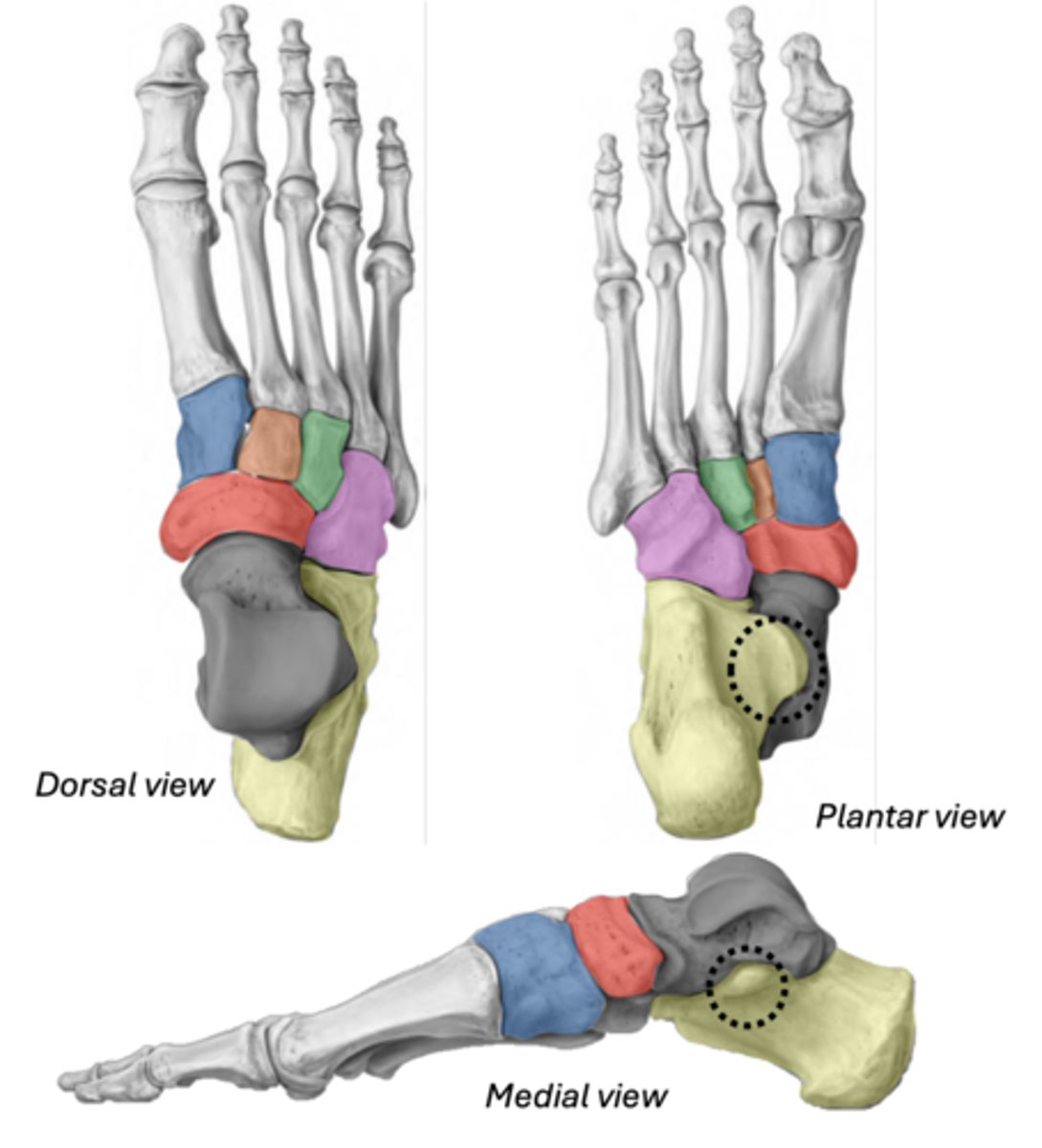
Intermediate cuneiform
ORANGE
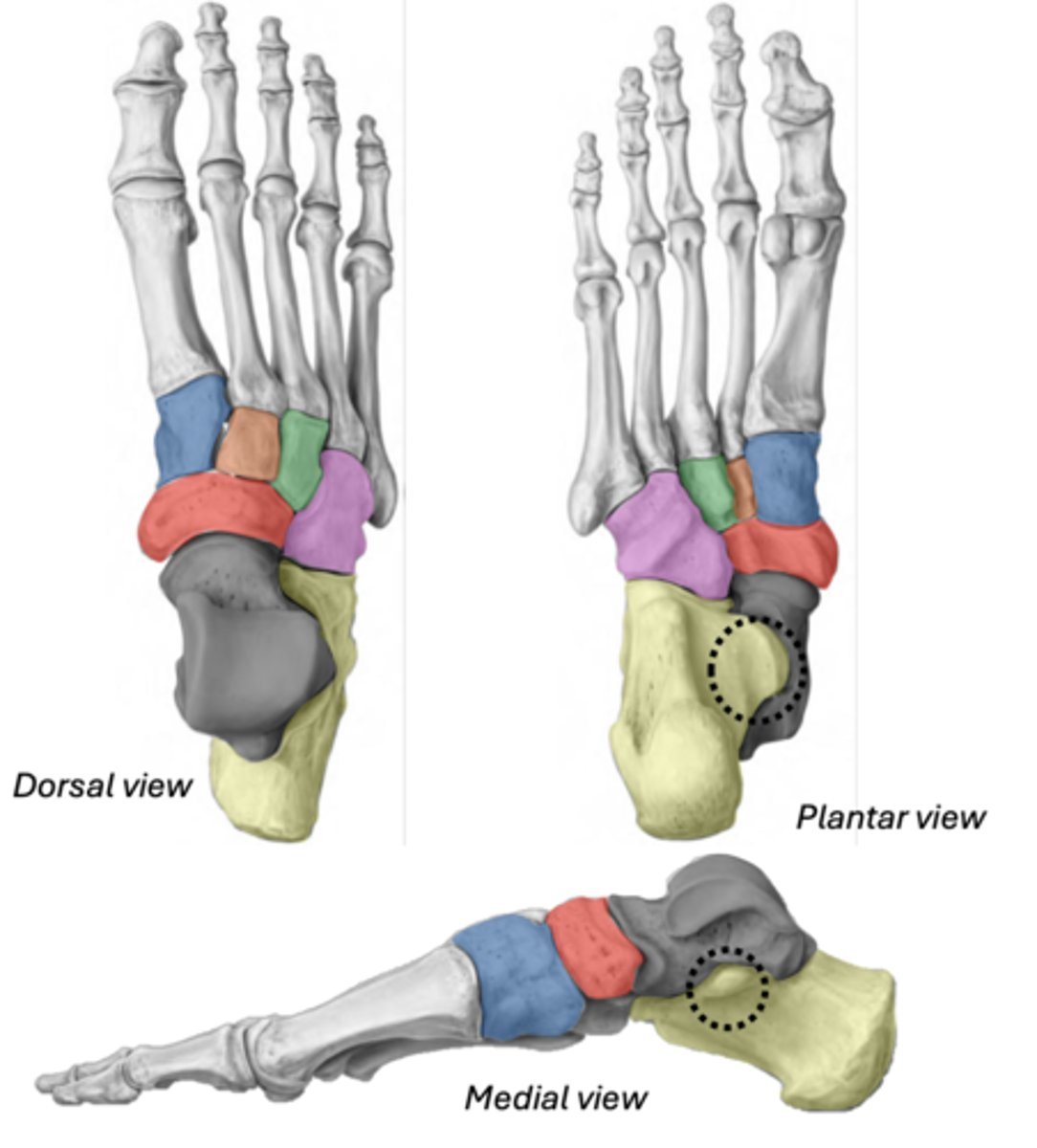
Lateral cuneiform
GREEN
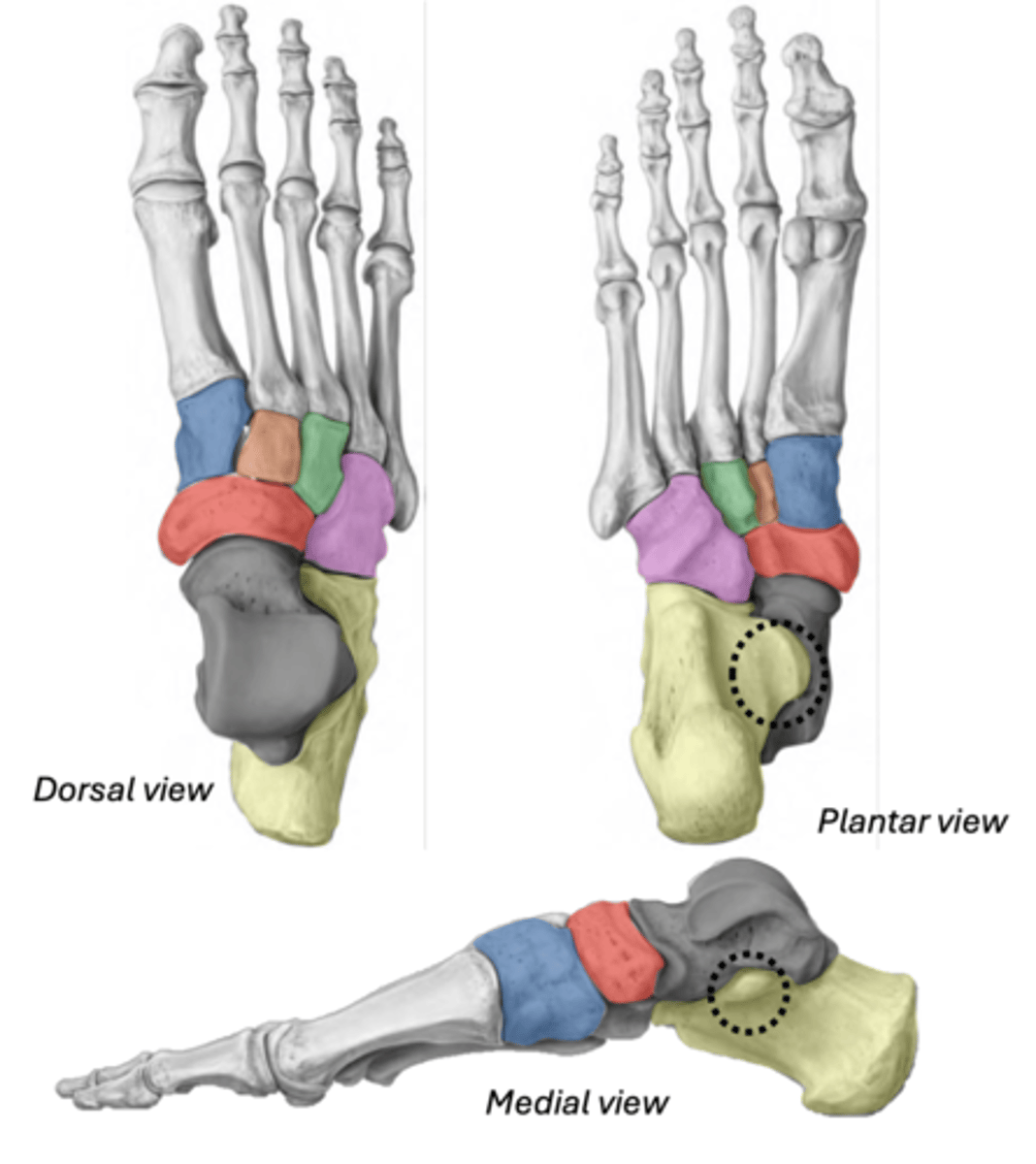
Metatarsals
base- orange
head- blue
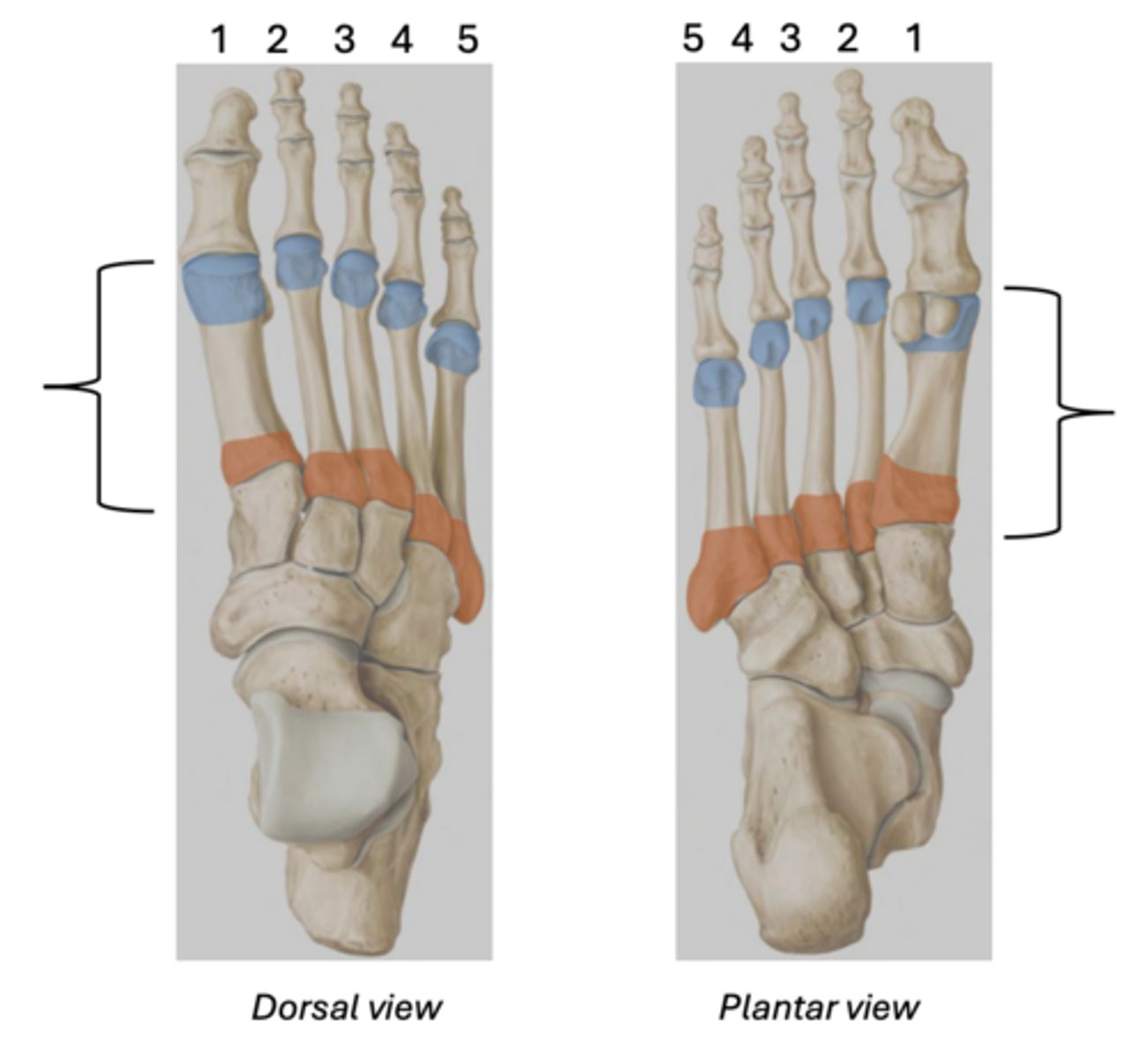
Phalanges
Proximal - blue
Intermediate - red
Distal - yellow
(The hallux only has 2 phalanges)
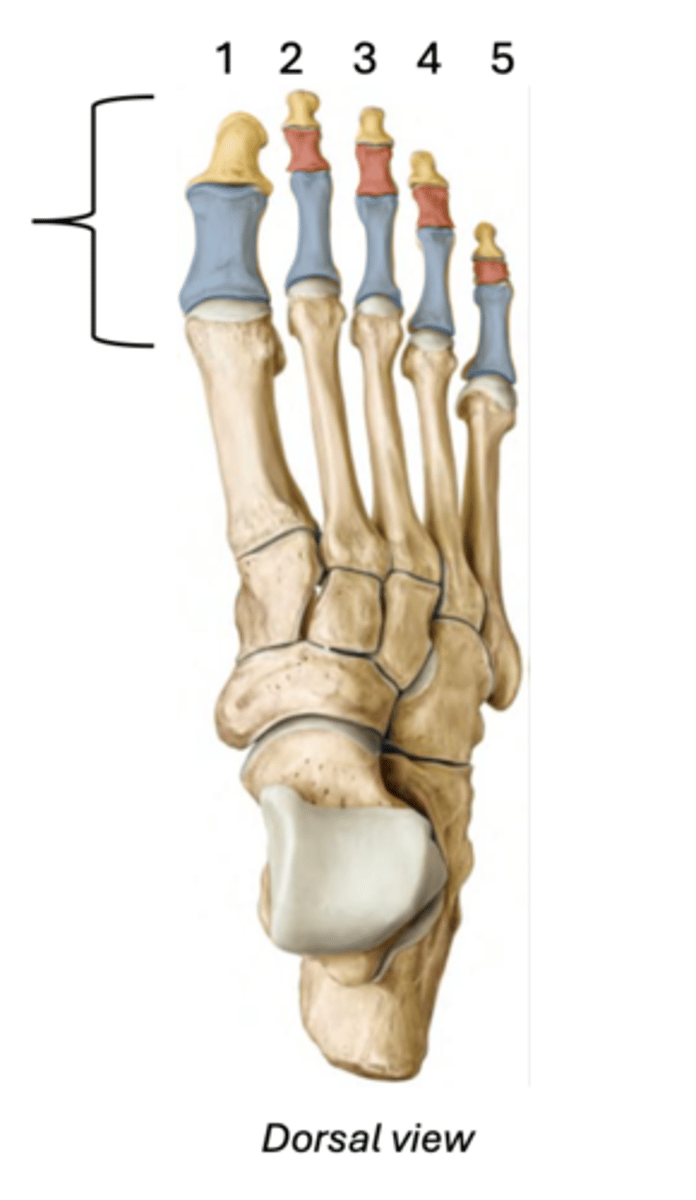
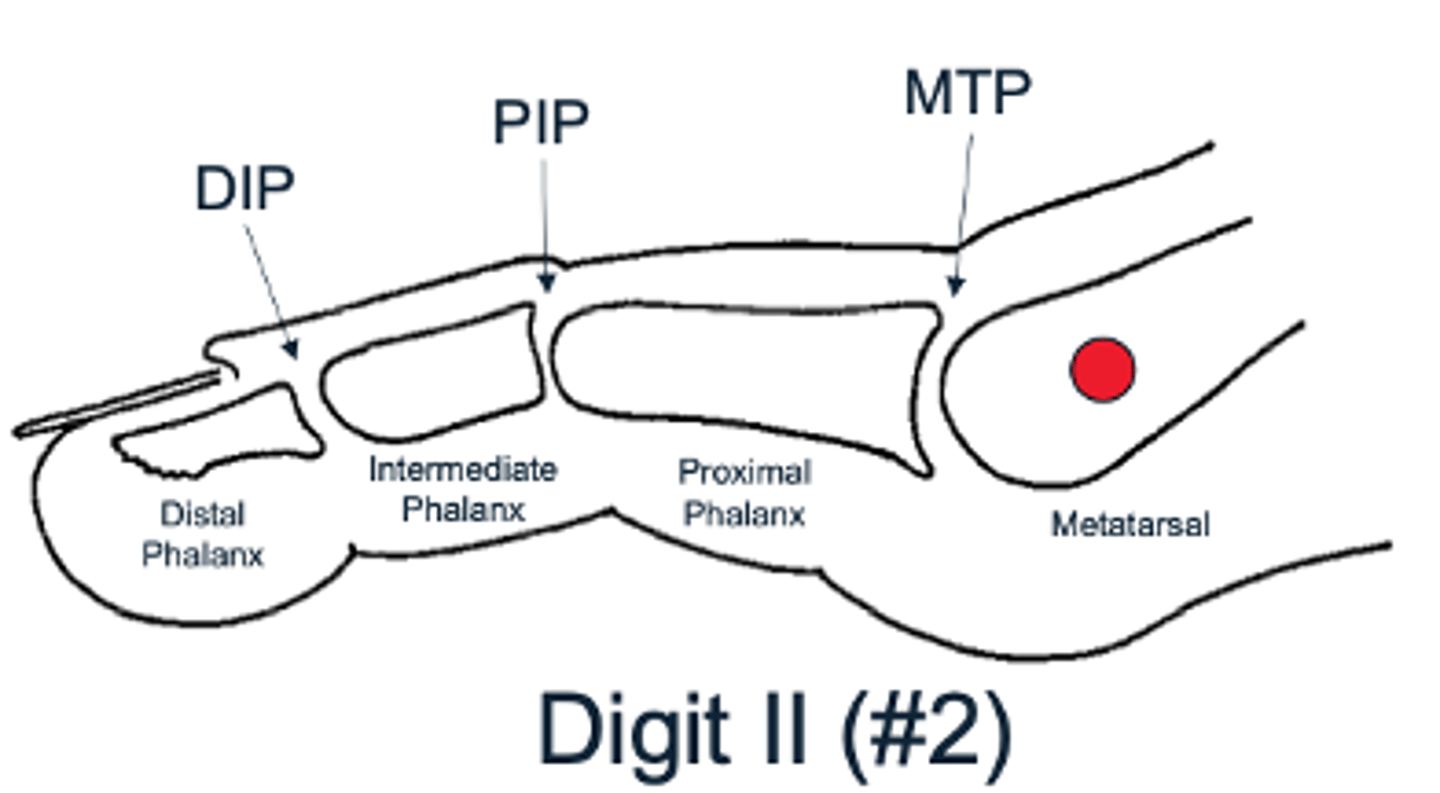
Toe joints
Metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP) found at the base of the toe
Proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) found in the middle of the toe
Distal interphalangeal joint (DIP) found near the tip of the toe (not found in the big toe)
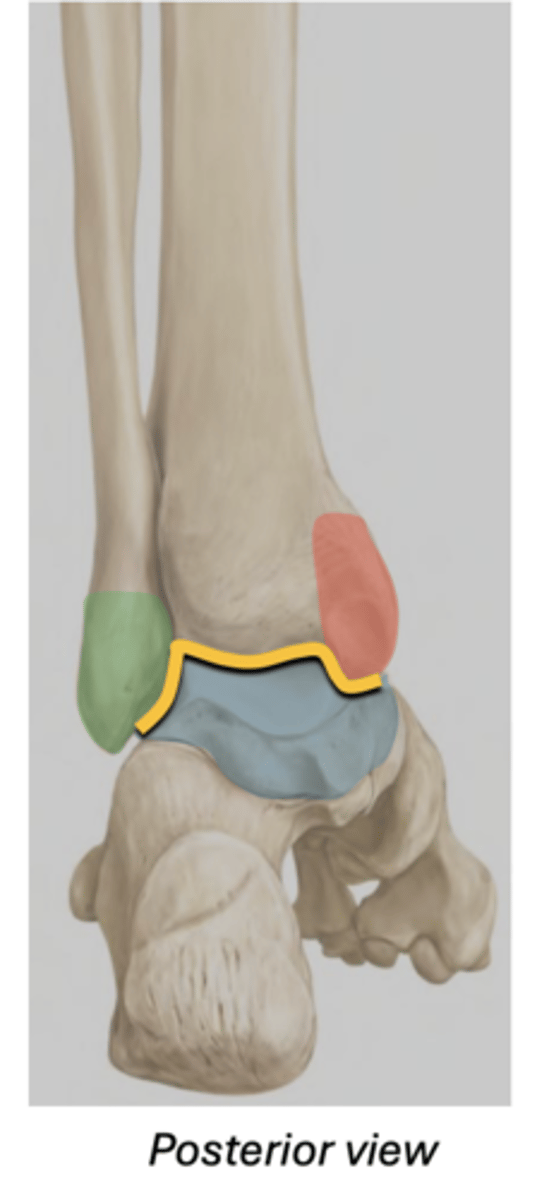
Talocrural Joint (ankle joint)
Hinge joint between the talus and
leg (crus) -- Yellow
Medial malleolus (RED), inferior tibia, and lateral malleolus (GREEN) --> create a bracket shaped around the talus (BLUE)
Permits dorsiflexion and plantarflexion; No inversion/eversion here!
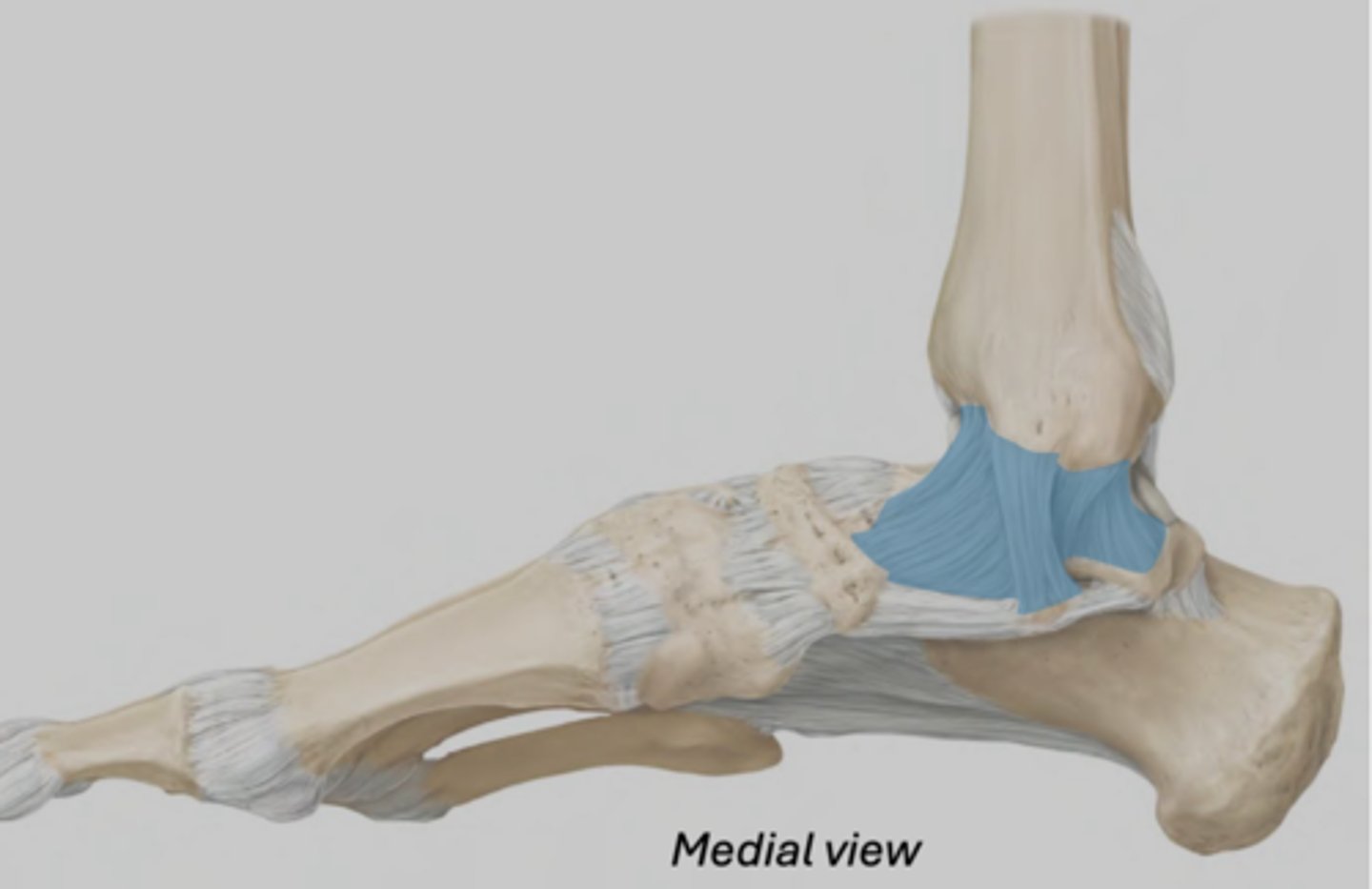
Medial collateral ligament (ankle)
Series of 4 ligaments attaching the medial malleolus to the talus, calcaneus, and navicular.
• Relatively strong
• Limits foot eversion
referred to as deltoid- triangle shape
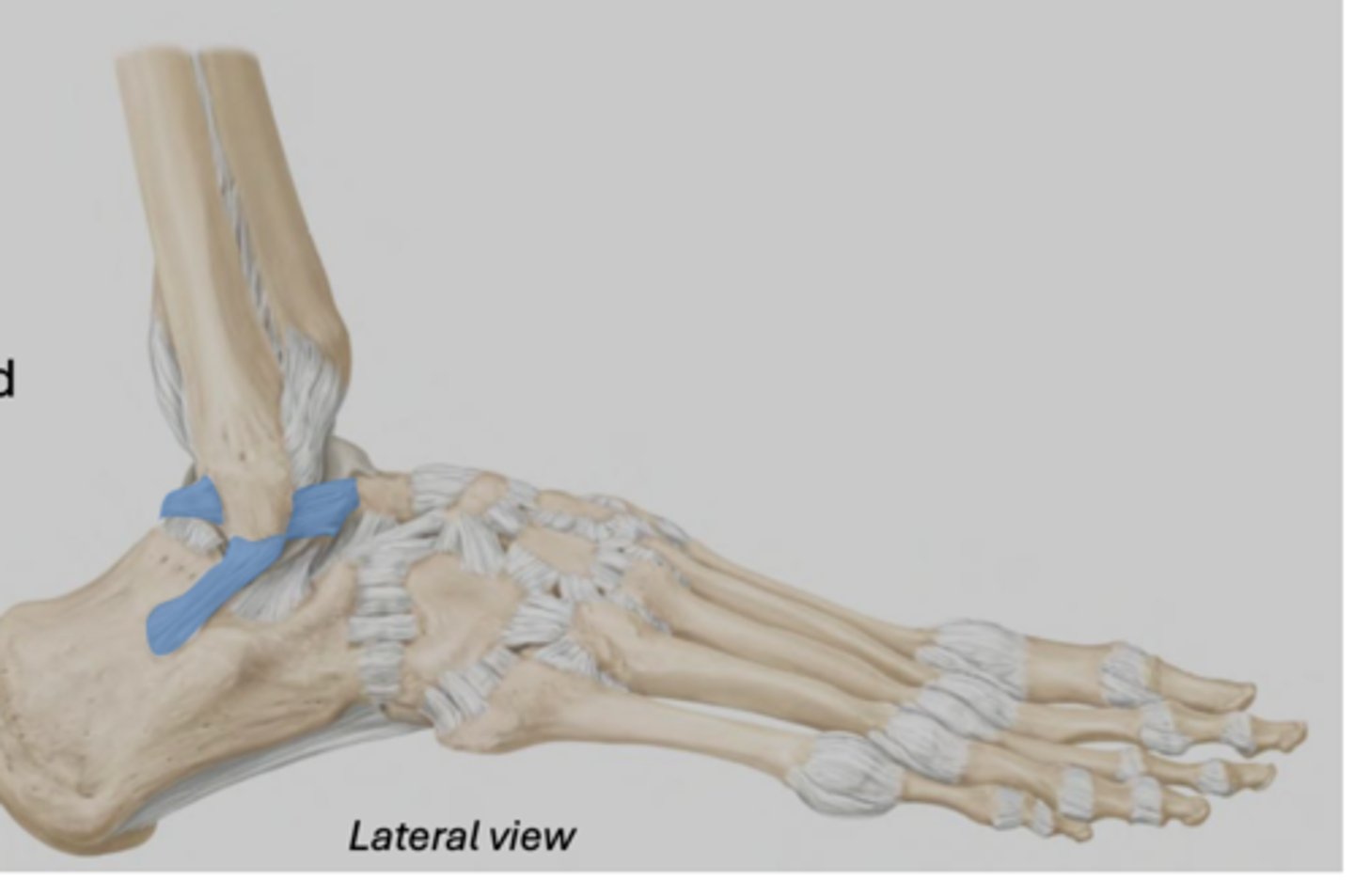
Lateral collateral ligaments (ankle)
Series of three ligaments connecting the lateral malleolus to the talus and calcaneus
• Relatively weak (more prone to sprain)
• Limits inversion of the foot
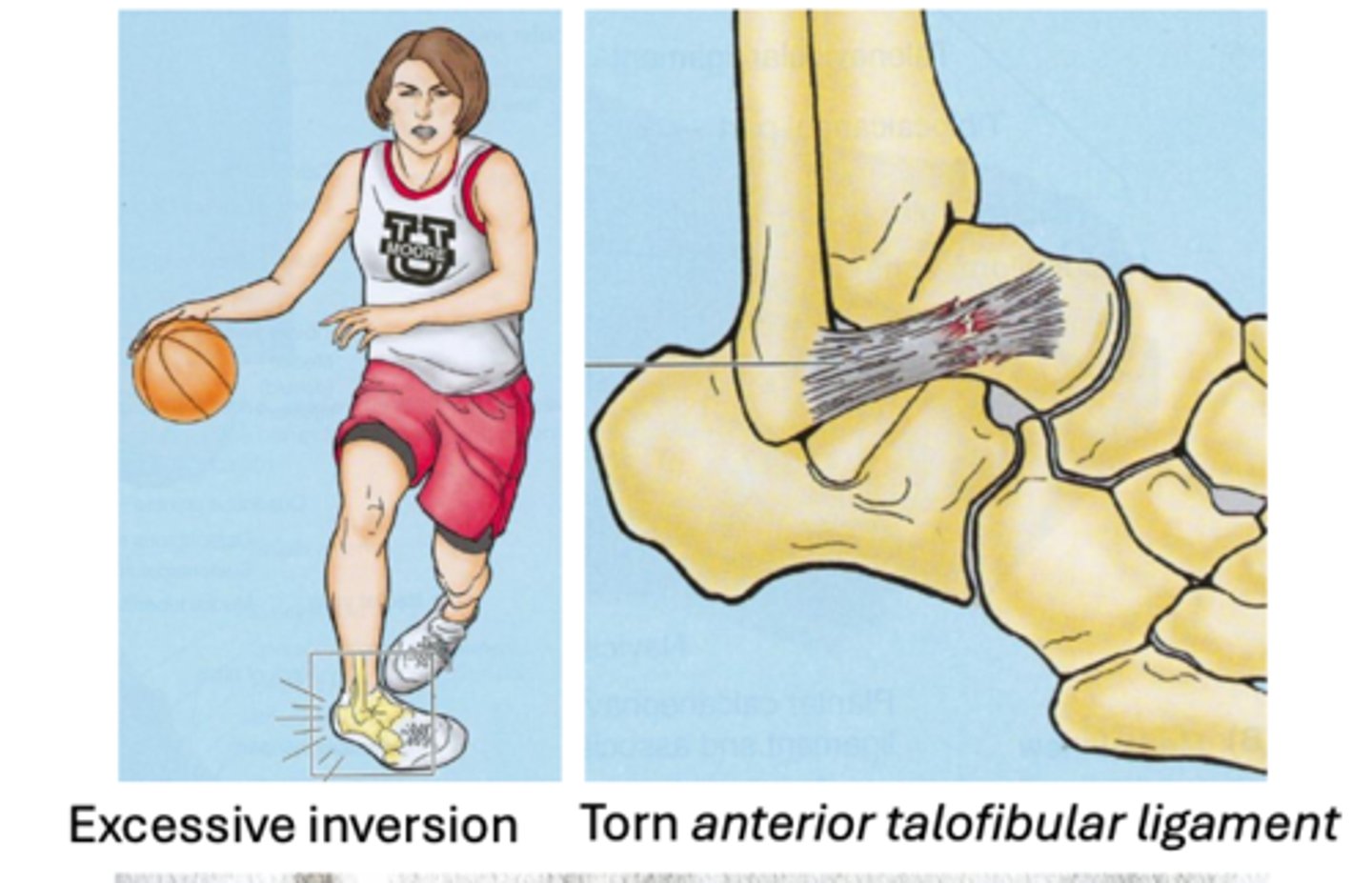
Ankle Sprains
-stretching or tearing of ligament(s)
-Inversion injuries more common (~80%)
-Anterior talofibular ligament: most commonly injured ligament, usually due to inversion injuries
-Eversion injuries less common = damage to the deltoid ligaments
Bimalleolar Fracture
- Both the medial and lateral malleoli are fractured
~60% of ankle fractures, often due to eversion or rotational trauma to ligaments
-surgery to fix
Subtalar joint
Main joint for inversion/eversion
• Between: talus & calcaneus
BLUE
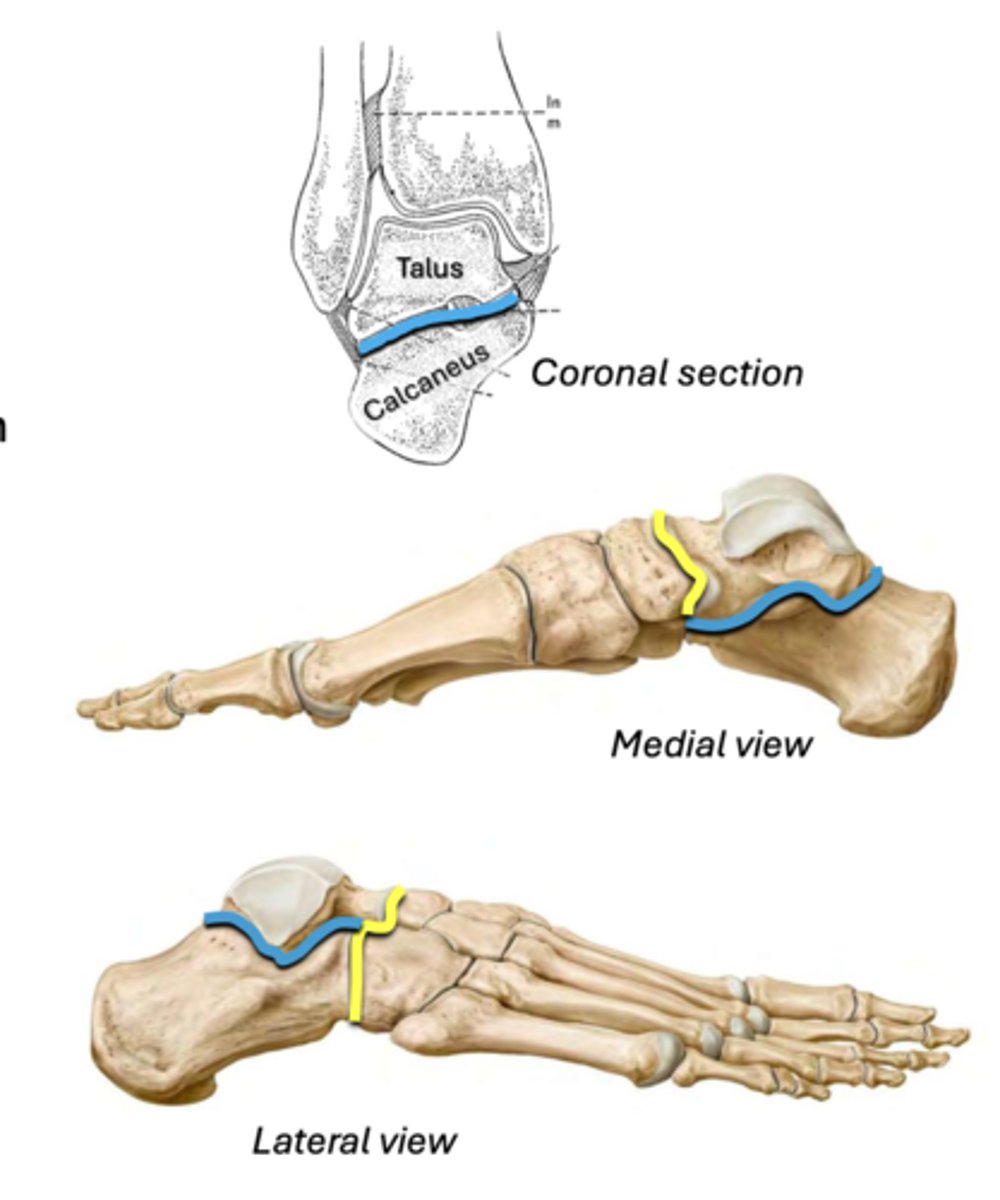
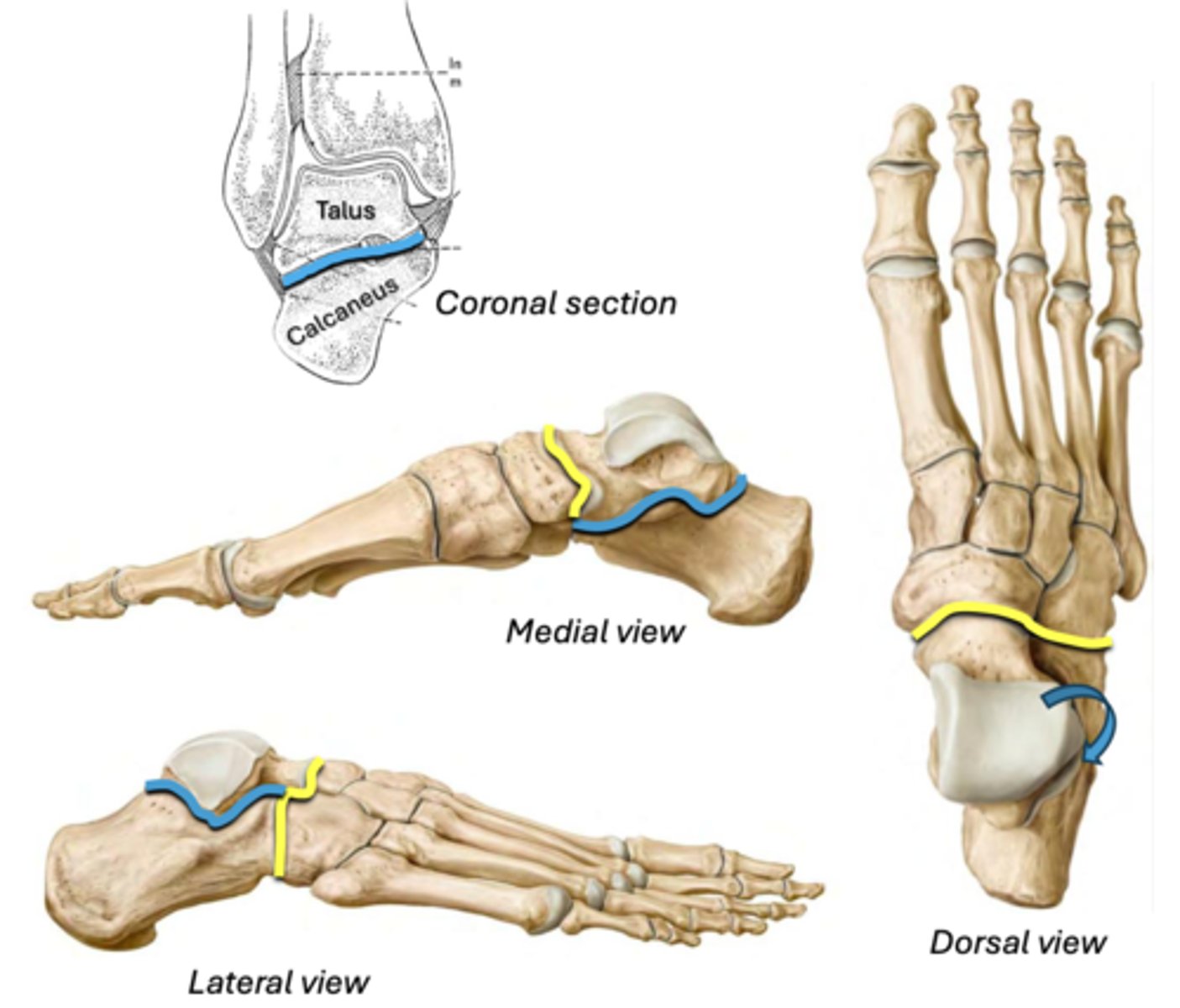
Transverse tarsal joint
Assists inversion/eversion
• Between: talus & navicular + calcaneus & cuboid
YELLOW
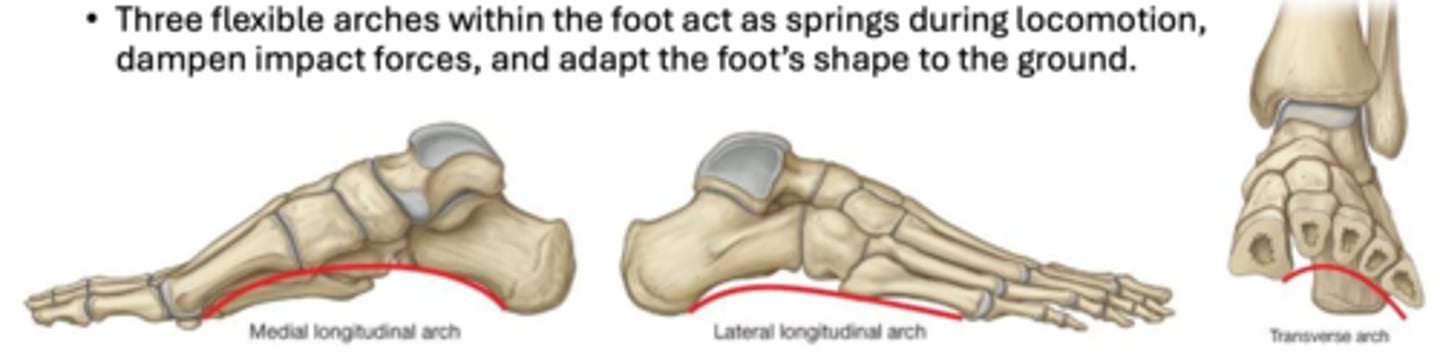
Arches of the Foot
Medial longitudinal, lateral longitudinal, transverse
Fallen arch= Flat feet (pes planus) can result in foot pain, eversion injuries, and pain in structures compensating for altered gait
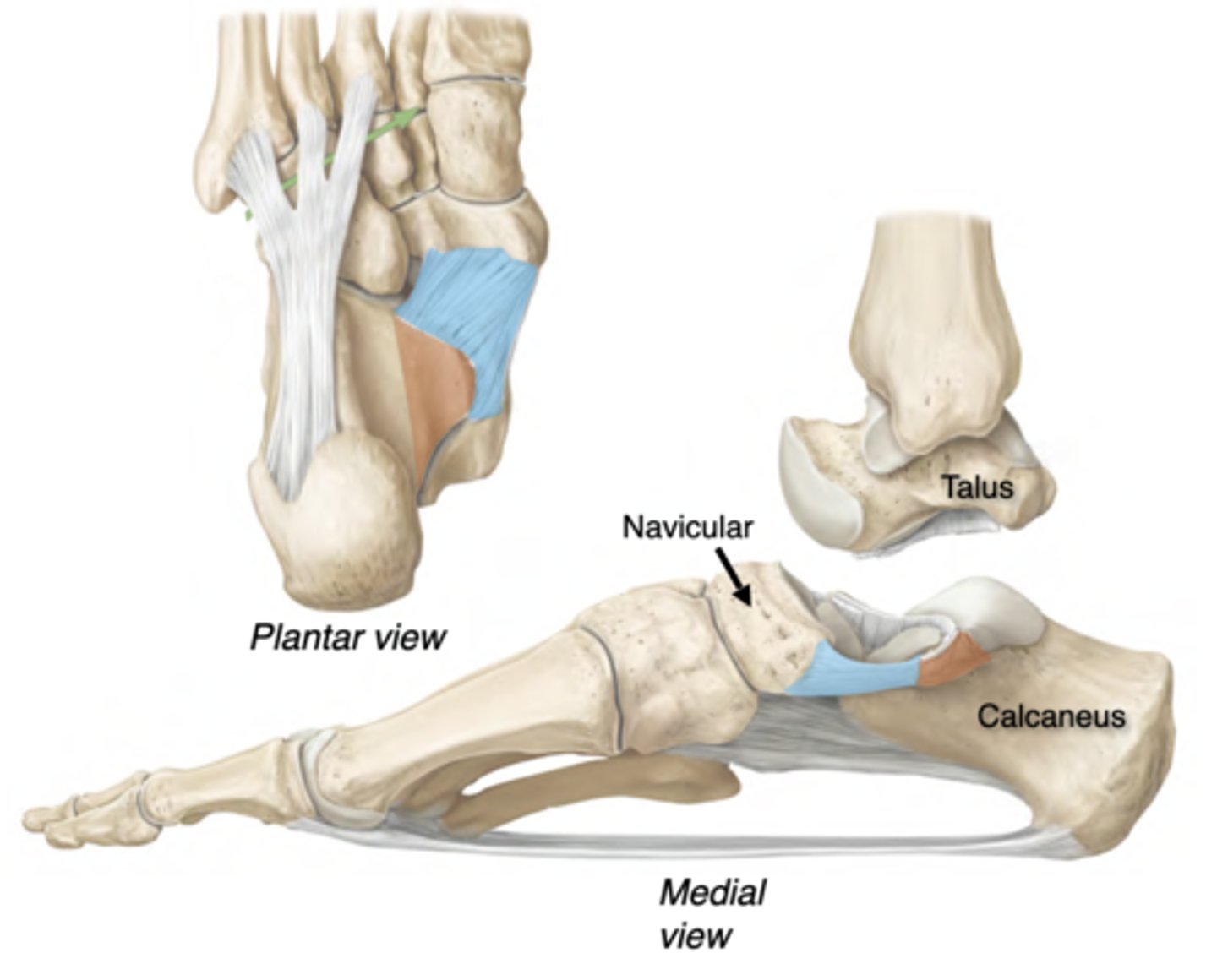
Arch Support: Spring Ligament
aka Plantar Calcaneonavicular ligament (BLUE)
• Connects the sustentaculum tali (ORANGE) of the calcaneus to the navicular.
Strongest supporter of the medial longitudinal arch
• Helps support the talus
• Injury can lead to talus displacement & fallen arches
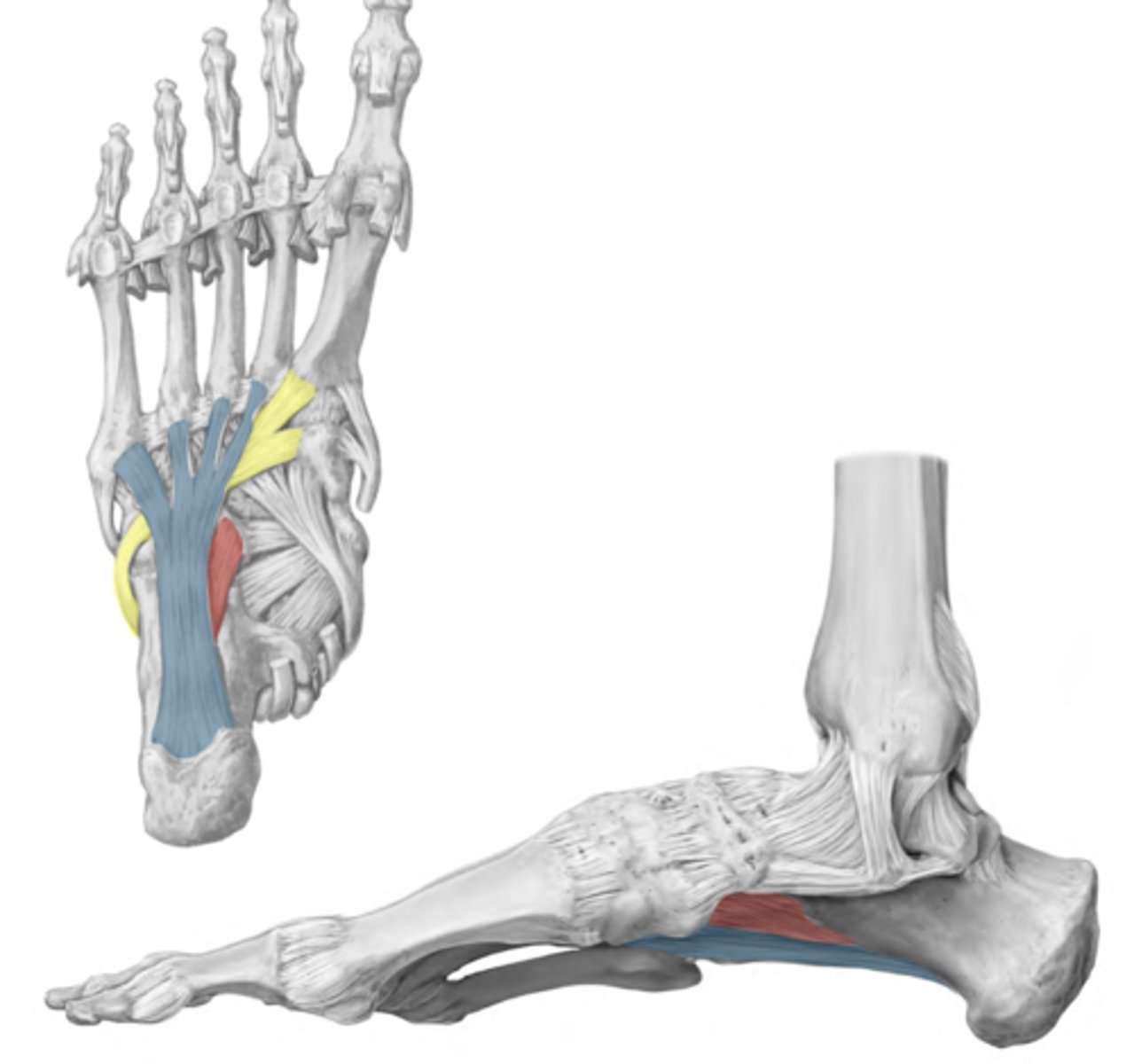
Arch Support: Long plantar ligament
BLUE
-Calcaneus to cuboid and lateral 4 metatarsal bases
-Supports longitudinal arches
-Creates a tunnel for the tendon of fibularis longus (yellow)
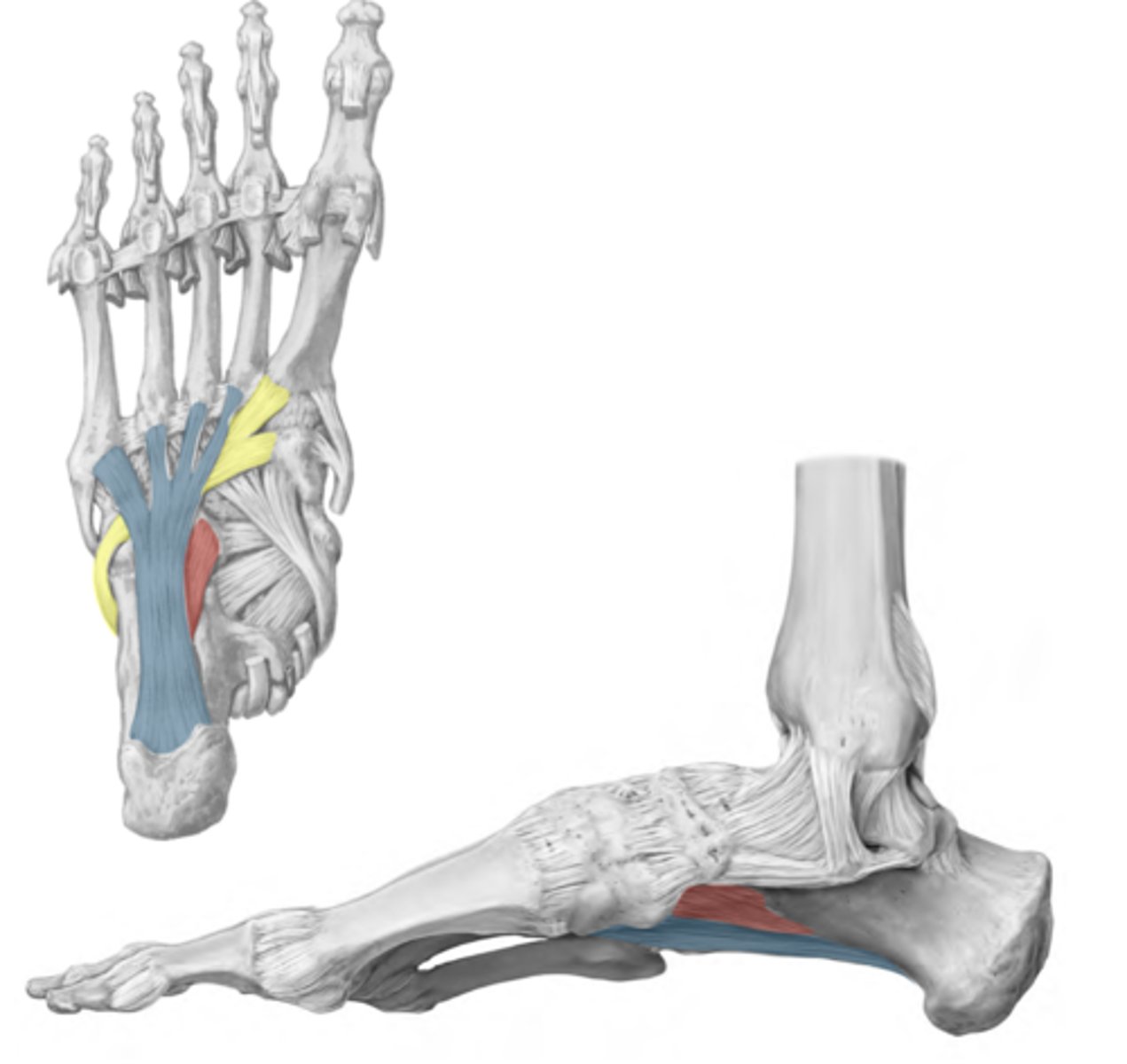
Arch Support: Short plantar ligament
RED
-Calcaneus to cuboid
-Helps maintain longitudinal arches
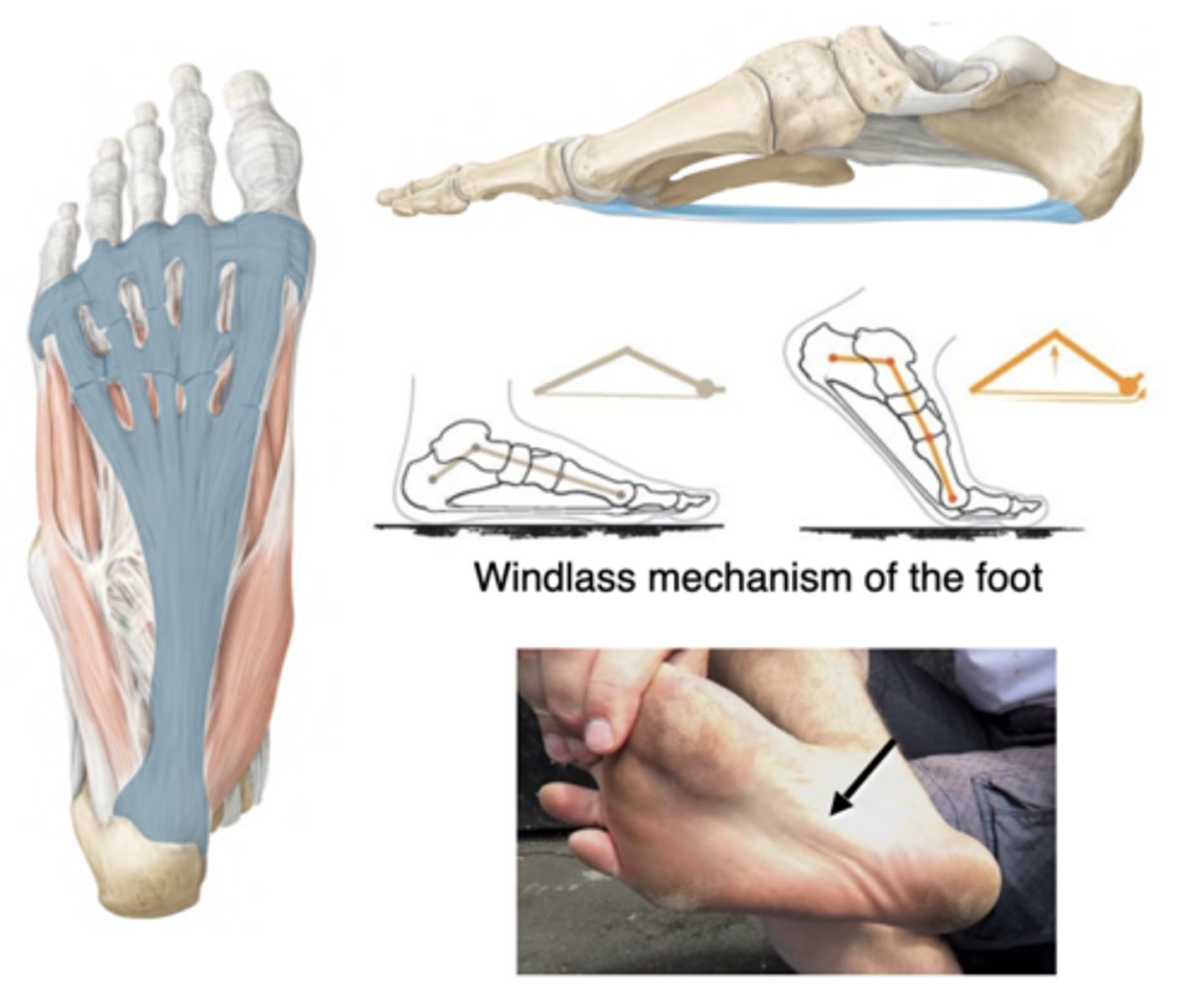
Arch Support: Plantar Aponeurosis
-Calcaneus to the metatarsal heads & digital flexor tendon sheaths
-Supports longitudinal arches
-Dorsiflexing the toes tenses the plantar aponeurosis, raising & stiffening the longitudinal arches --> Less foot flexibility = more efficient propulsion
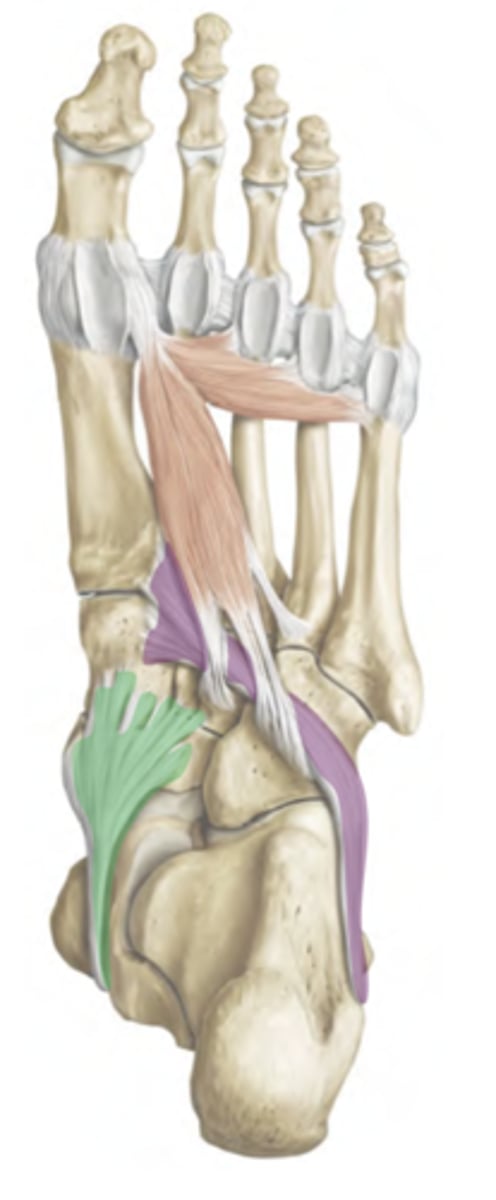
Arch Support: Muscles
-Tendons of fibularis longus and tibialis posterior insert on the plantar surface of the foot
-Muscle tension provides support of the transverse arch
-Injury of tibialis posterior can overload the spring ligament, resulting in collapsed arches
Tendons Continuing from the Leg
Tibialis anterior (blue)
Extensor hallucis longus (yellow)
Extensor digitorum longus (green)
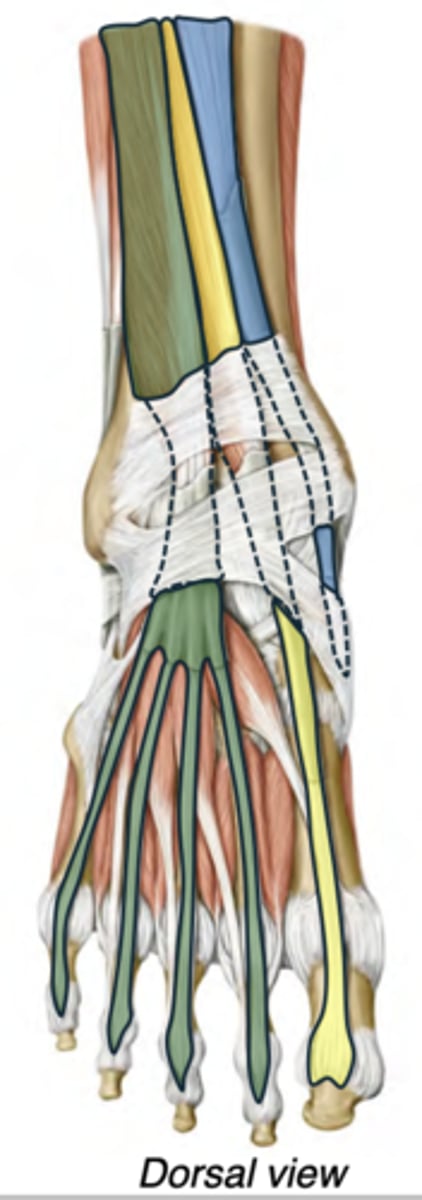
The Gait Cycle
Stance phase: Foot is in contact with the ground; from foot strike to toe off
Swing phase: Foot is off the ground; from toe off to foot strike
Gait with Hip flexors damage
Anterior thigh; rectus femoris, sartorius, iliopsoas
Lumbar nerve
-Weakness initiating swing phase with hip flexors (Light Blue)
-Compensate by circumducting the affected limb using hip abductors and adductors (Lean to contralateral side to create space for the limb to swing)
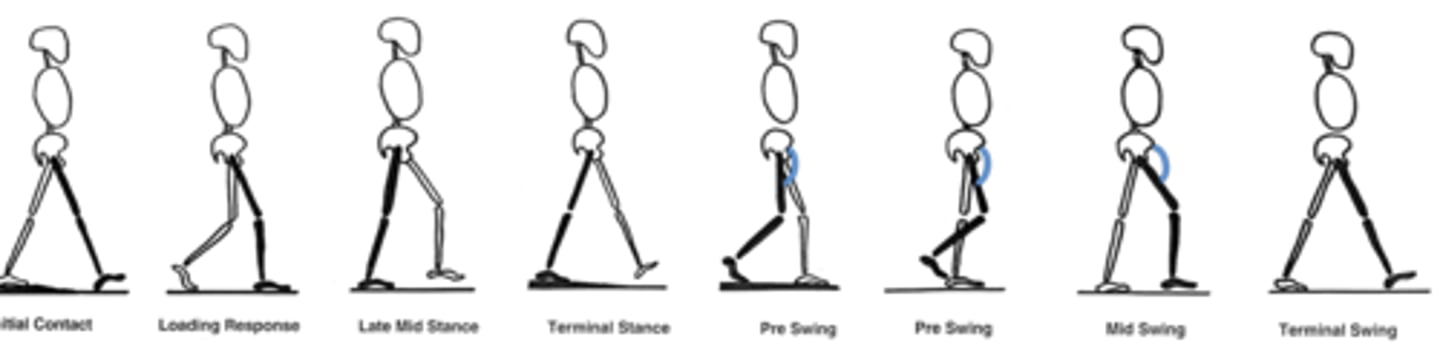
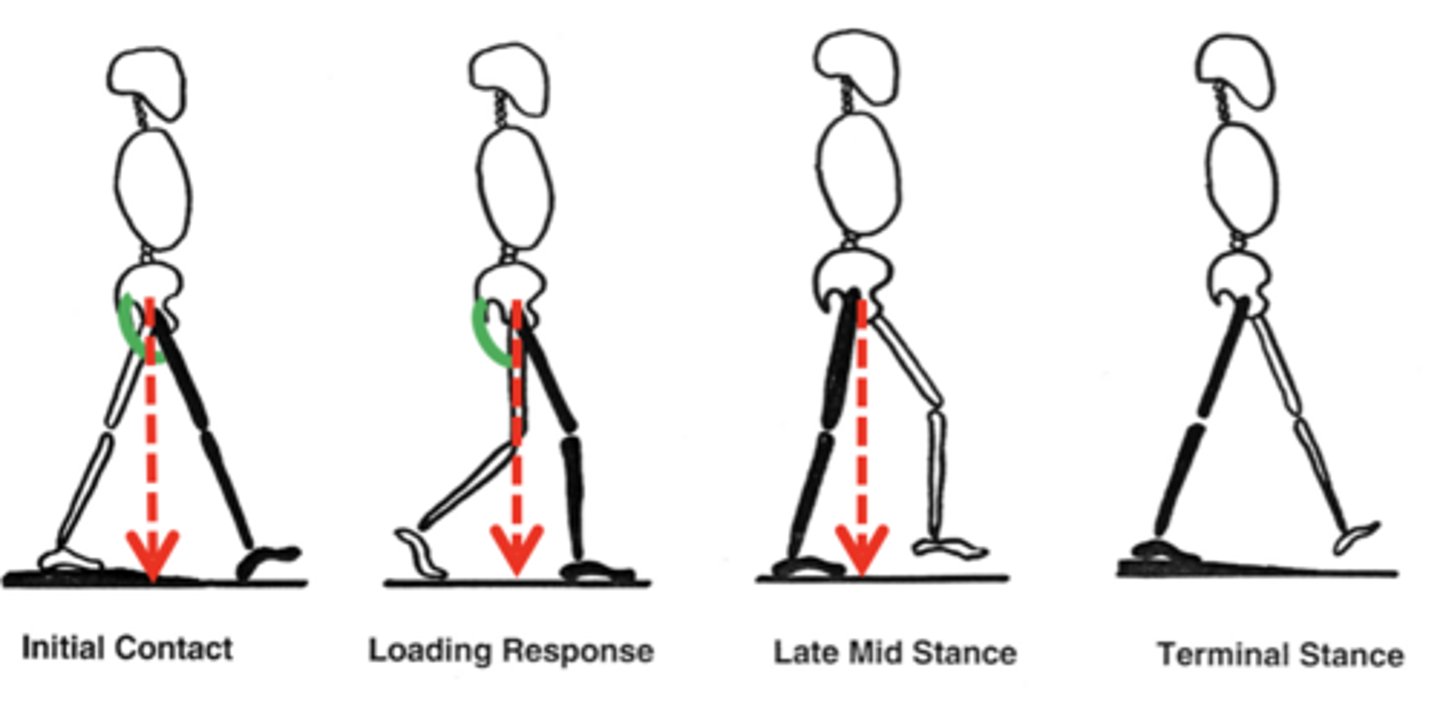
Gait with Hip extensors damage
Gluteus maximus
Inferior gluteal n.
-Hip extensors (GREEN) prevent hip buckling while center of mass is behind the hip.
-Inability to resist gravity while weight is behind hip joint
-Leaning back at initial foot contact shifts center of mass behind hip, passively stabilizes hip joint
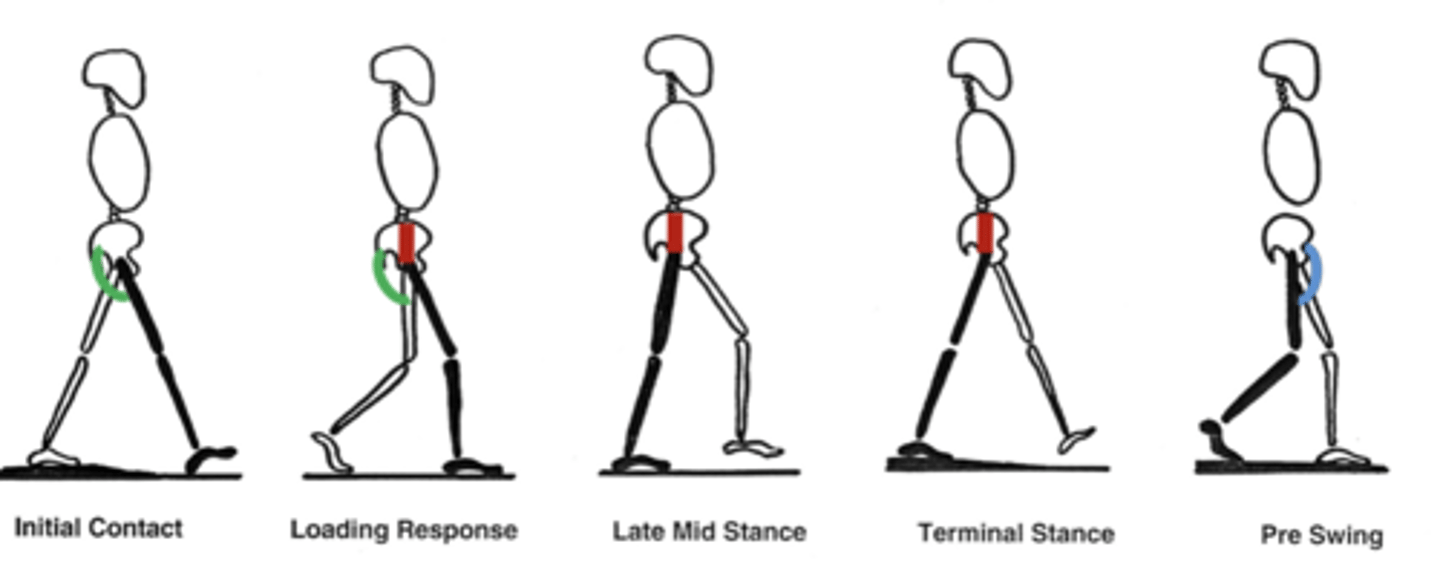
Gait with Hip abductors damage
Lateral thigh/deep gluteal
Superior gluteal n.
-Hip abductors (RED) keep the pelvis level during stance phase, while weight is on one limb.
-Trendelenburg gait: Inability to resist gravity causes pelvis to drop to the contralateral side
-Abductor lurch/Compensated Trendelenburg: shifting weight over the affected side reduces contralateral hip drop
Gait with Knee extensor damage
Anterior thigh
Femoral nerve
Knee extensors (BLUE) straighten the knee at the end of swing
Also prevent knee buckling while center of mass is behind the knee
Inability to extend and lock the knee causes knee to buckle. Patient shift weight anterior to knee and use hand to force the knee into extension.
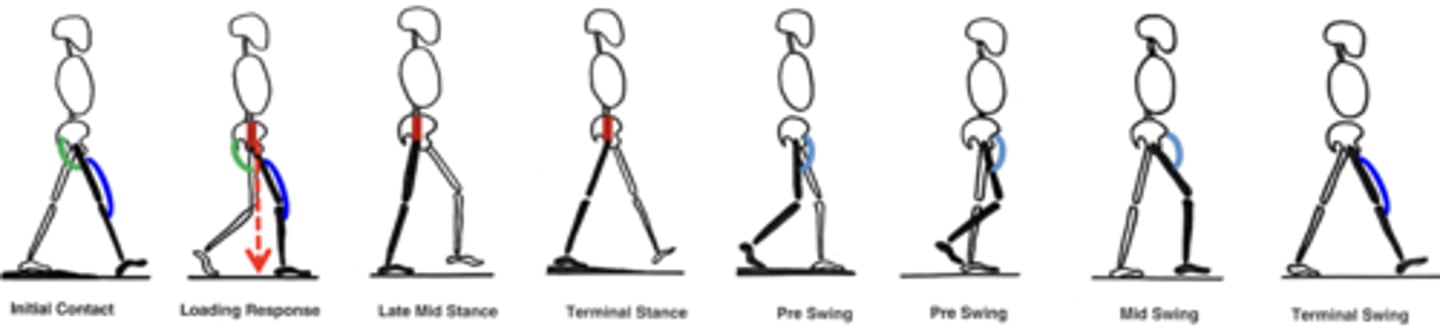
Gait with ankle plantarflexor damage
Posterior leg
Tibial n.
Plantarflexors (PURPLE) stabilize the tibia while center of gravity is ahead of the ankle & provide forward propulsion and stride length
Flat-footed gait/ Lack of toe-off. Loss of propulsion leads to shortened stride length, slower walking speed. May compensate by using hip flexors to propel swing phase.
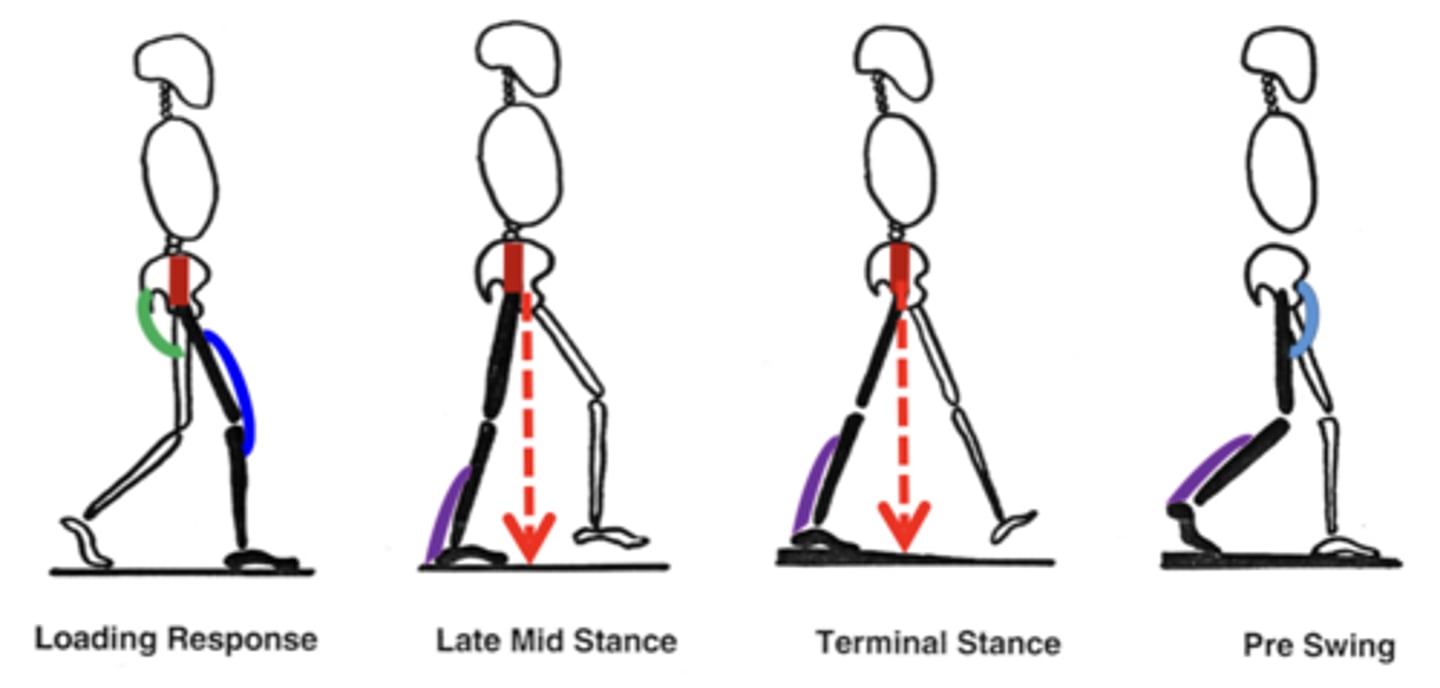
Gait with ankle dorsiflexor damage
Anterior leg
Deep fibular n.
Dorsiflexors (ORANGE) allow the toes to clear the ground during swing phase
Foot drop: toes drop with gravity. Toes drag during swing phase. May compensate by increasing hip flexion, "high knees" or "steppage gait".
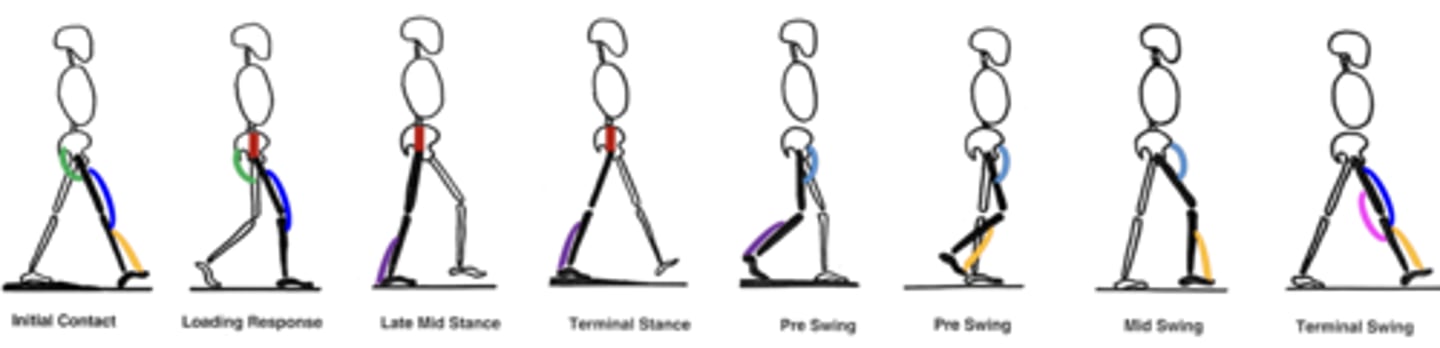
Ankle everters in Gait
Lateral leg
Superficial fibular n.
-Ankle everters help transition weight medially onto ball of foot for toe-off. Also help foot adapt to uneven surfaces. Weak ankle everters or superficial fibular nerve damage can result in walking on the lateral side of the foot
-->Tension in from inverters overpowers, pulls foot into inversion
Lateral thigh sensation
lateral femoral cutaneous n.
medial thigh and medial leg sensation
femoral n.
very medial thigh sensation
obturator n.
lateral leg sensation
lateral sural cutaneous n. (common fib. n)
most of dorsum of foot sensation
superficial fibular n.
flip flop sensation
deep fibular n.
medial side and medial 3.5 digits of plantar surface sensation
medial plantar n.
lateral side and later 1.5 digits plantar sensation
lateral plantar n
medial ankle and heel sensation
saphenous n.