ENTM midterm 2
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
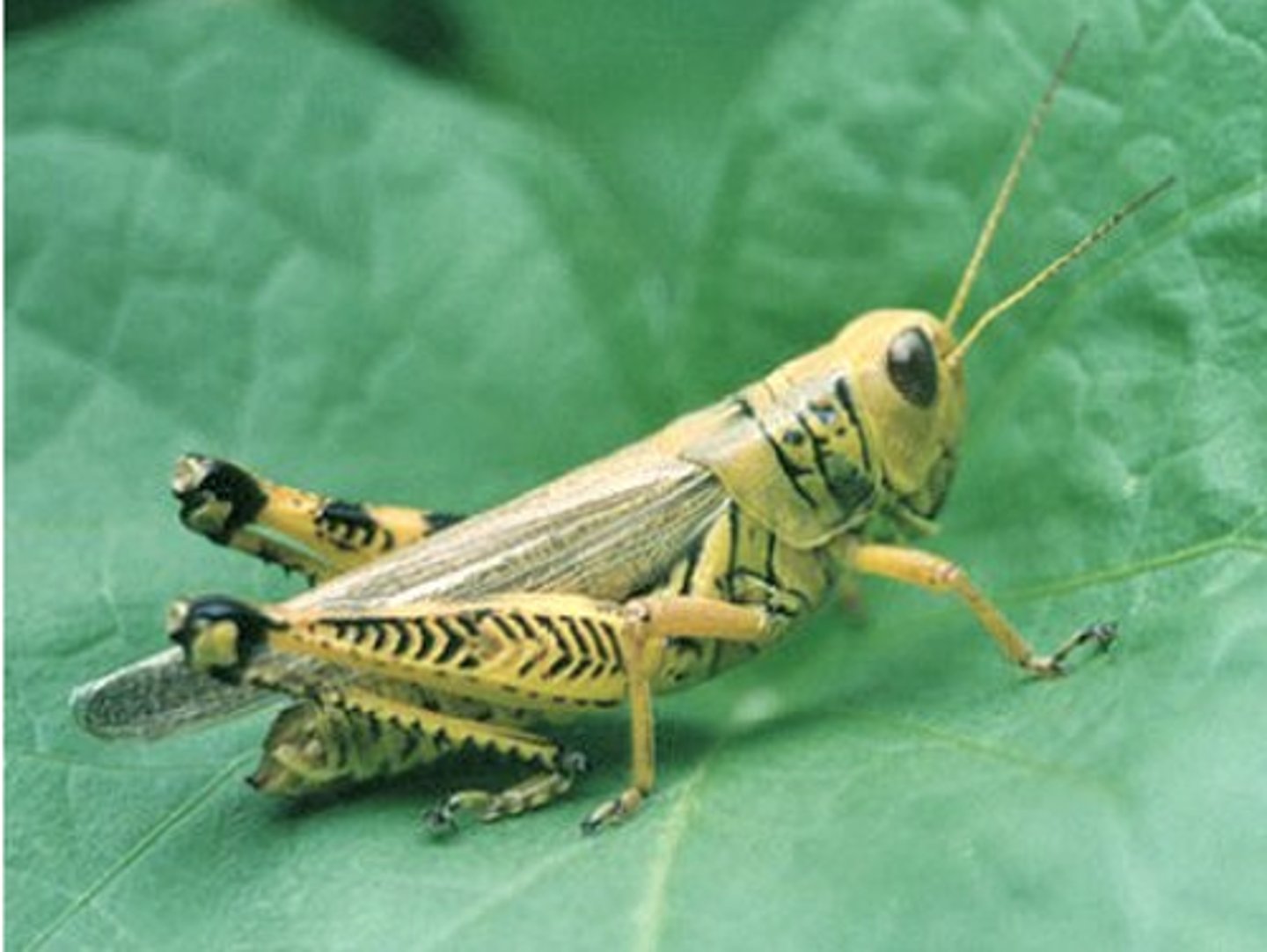
Acrididae
Family: Orthoptera
grasshoppers, locusts

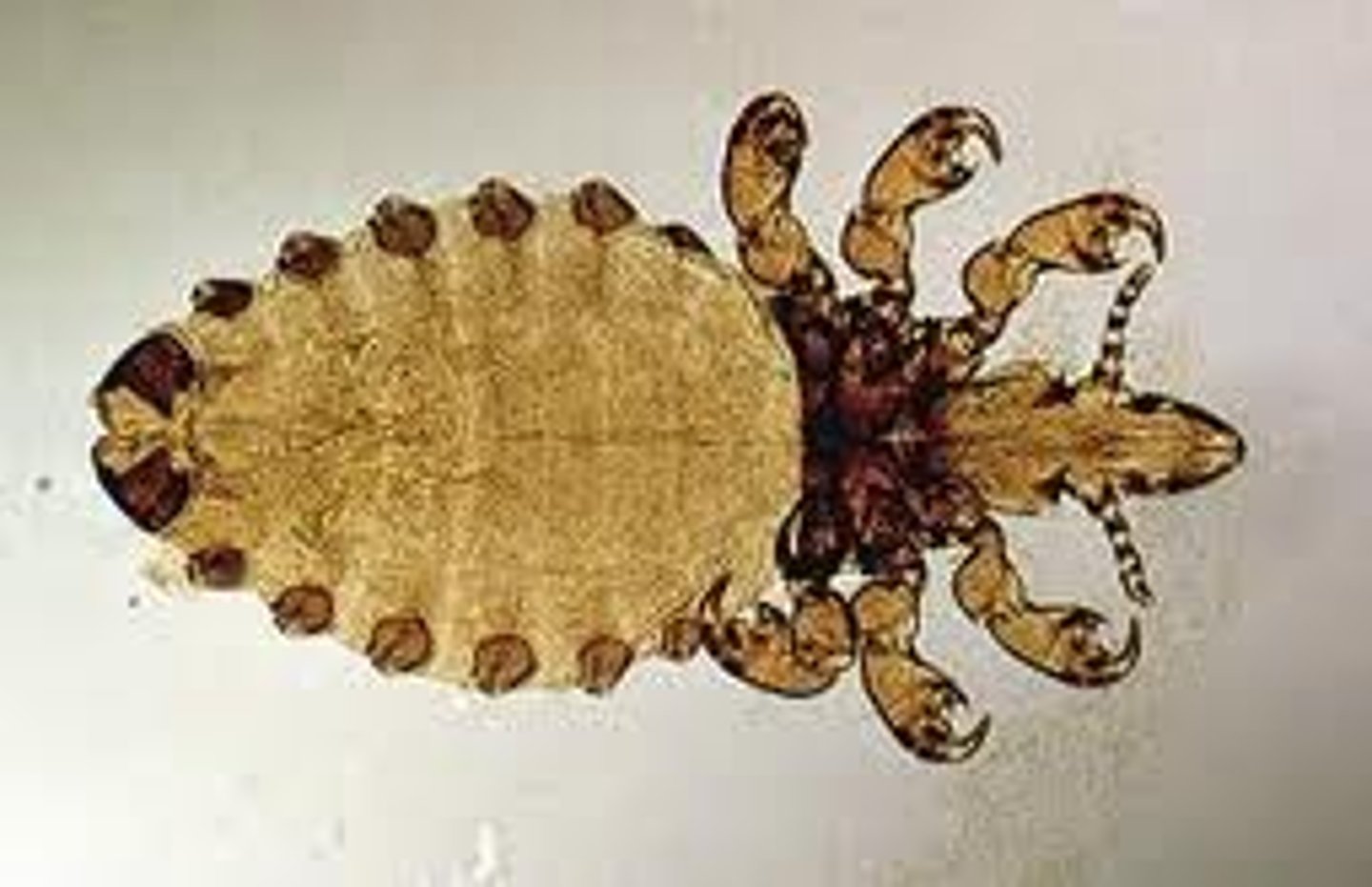
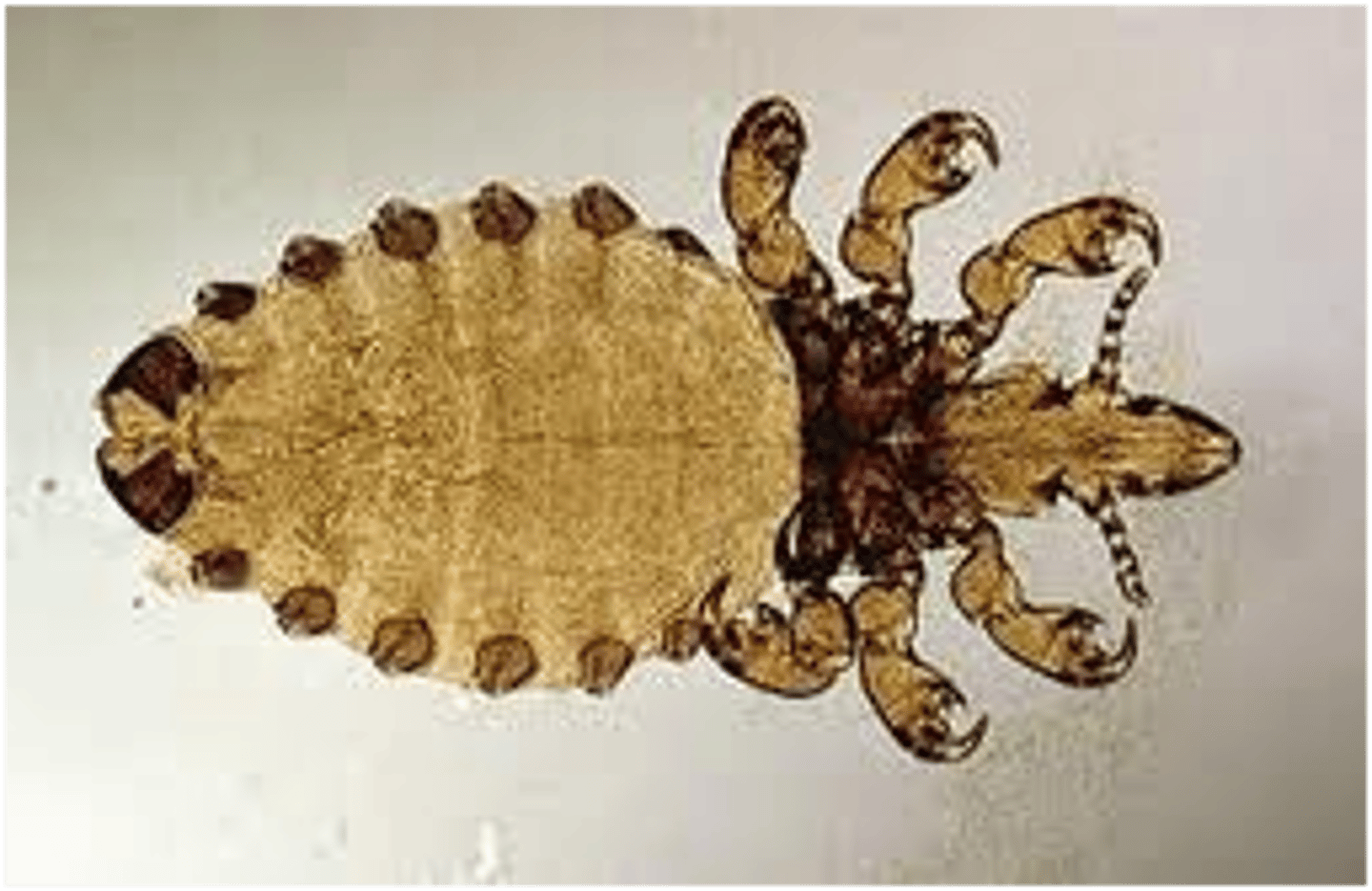
Anoplura
(sucking lice)
feeds on: blood, human disease vectors
Hosts: found on specific body parts of mammalian host
head is narrower than prothorax
consists of head lice + body lice

Ant-hemipteran mutualism
Both partners benefit (ants: gain carbohydrate-rich resource aphids: gain protection)
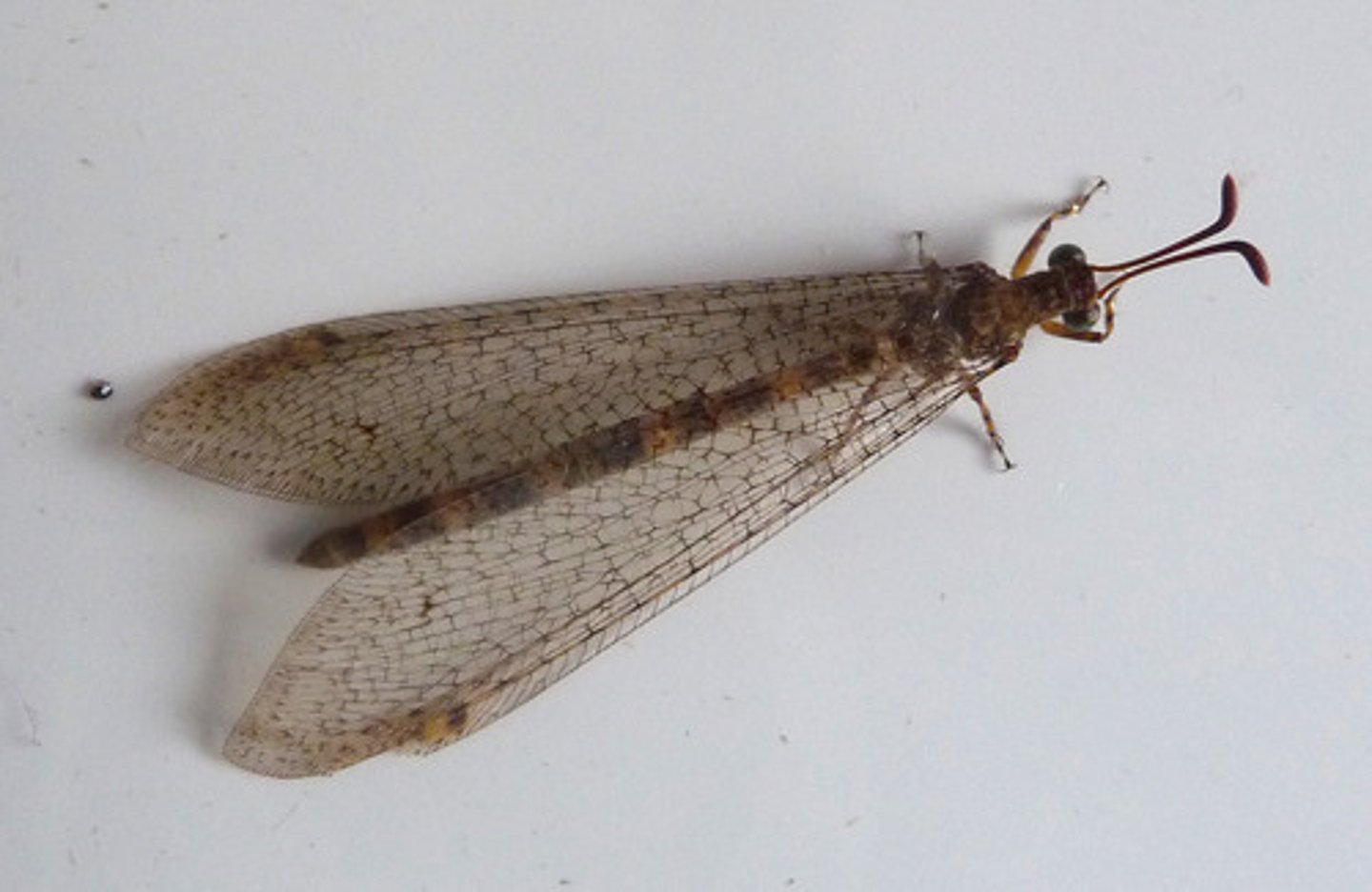
Antlion
(Family Myrmeleontidae)
Slender body, Weak flier, adult: nocturnal
larvae: predator
- require sandy soil/covered with something so they are protected from frequent /divert rain falls
- larvae: build funnel - like trap in sandy soil use to catch insect preys
convergent evolution: Worm lion (diptera)

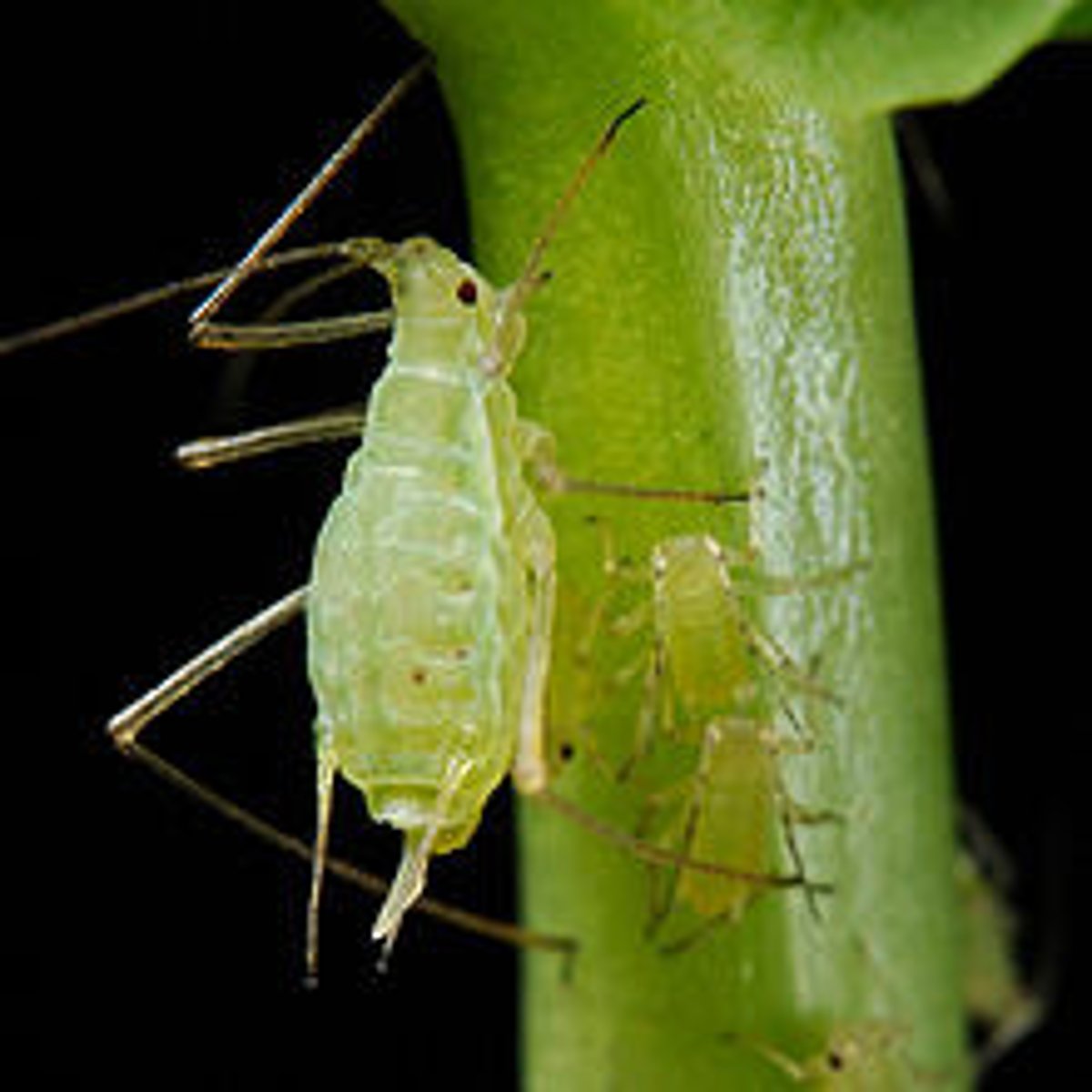
Aphididae / aphids
(Suborder Sternorrhyncha)
- Usually wingless during cloning phases
- Alates: winged reproductives during sexual reproduction phase
- Transmit plant diseases
- Ant-aphid mutualism

Beetles vectoring plant diseases
Pierce's disease transmitted by leafhopper beetle
Chestnut blight: bark beetles
Dutch elm disease transmitted thru fungus by bark beetles
Emerald ash borer attacks ash trees
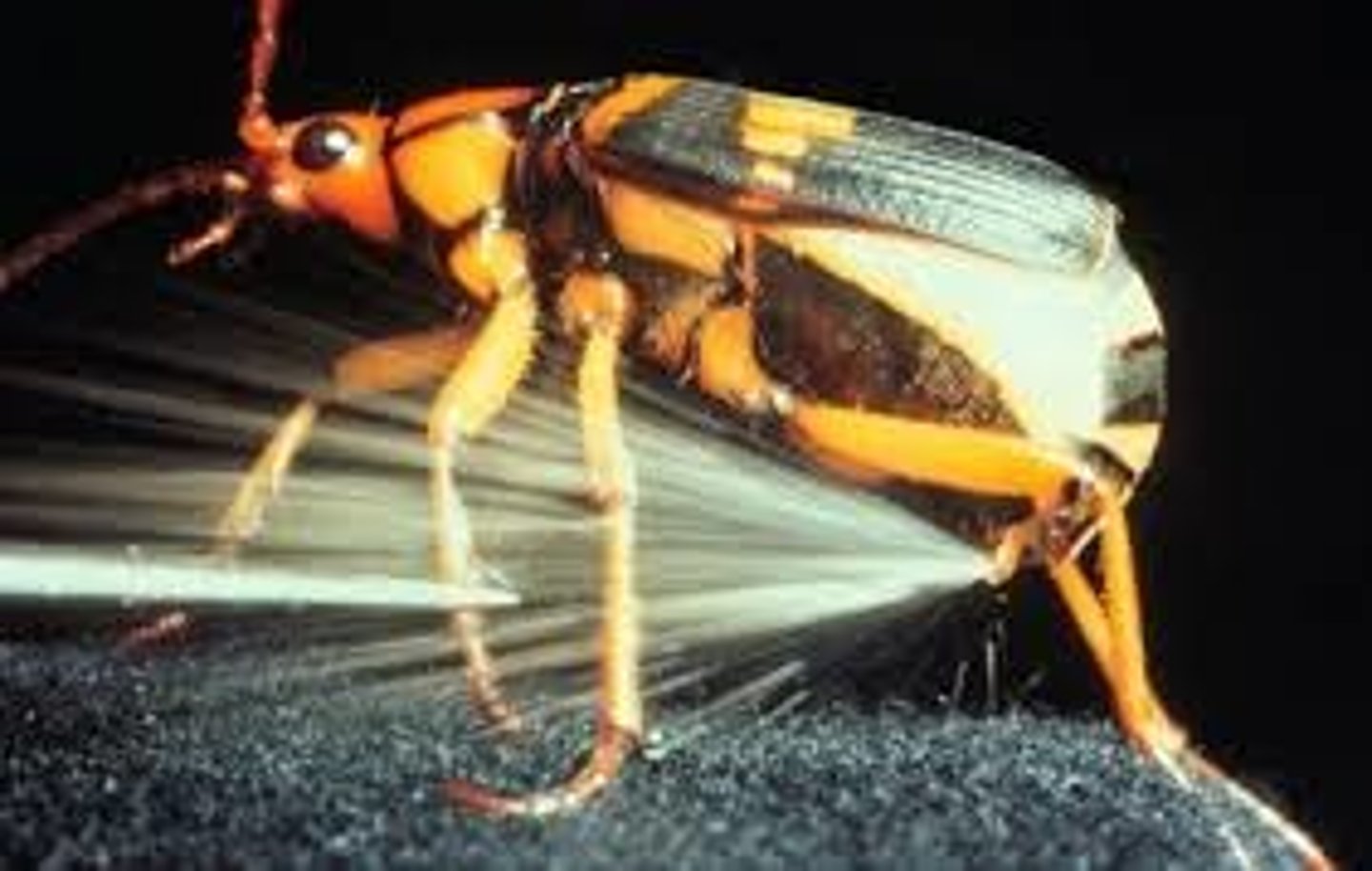
Bombardier beetle
Family Carabidae / ground beetle
chemical weapon gas against predator

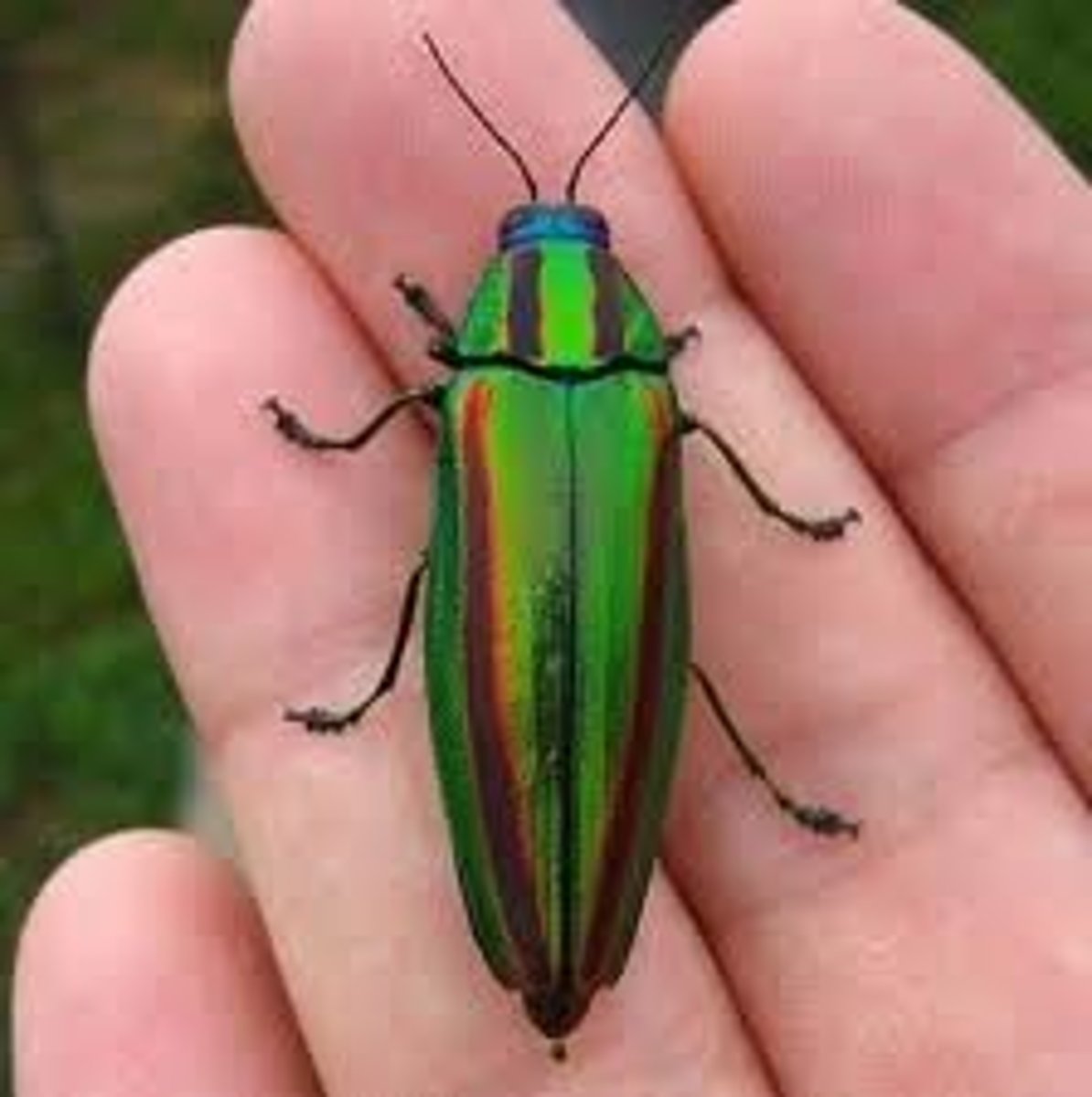
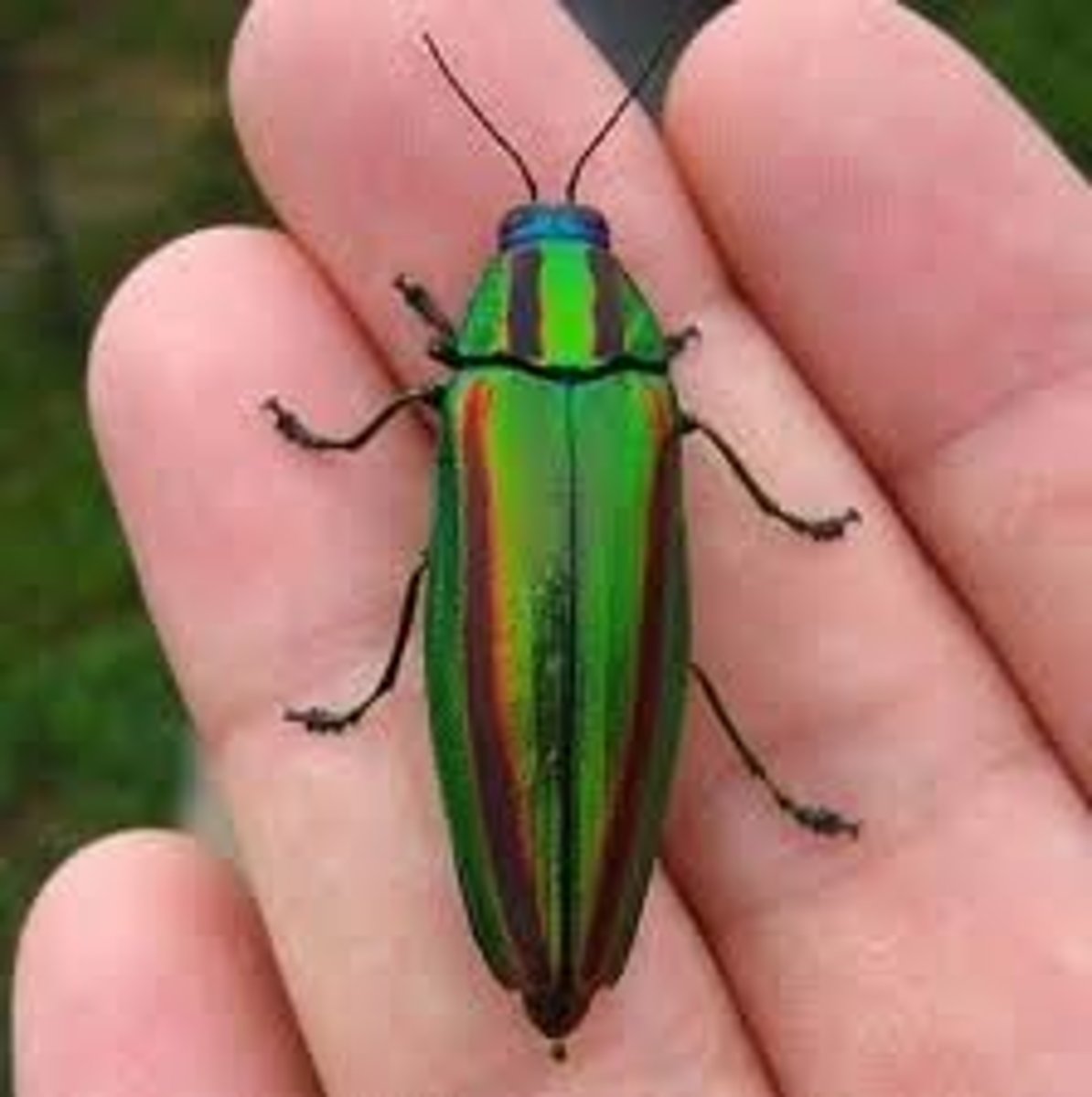
Buprestidae
Jewel beetles
- Shiny/metallic
- textured cuticle
- thin film interference
- prefer wood (from dying or weakened trees)
- bore tunnels in wood (larvae)

Capitulum
a swollen, fatty extension of the stick insect eggs -> facilitate ants' carrying of eggs to their nest (diversify survival of phasmida)
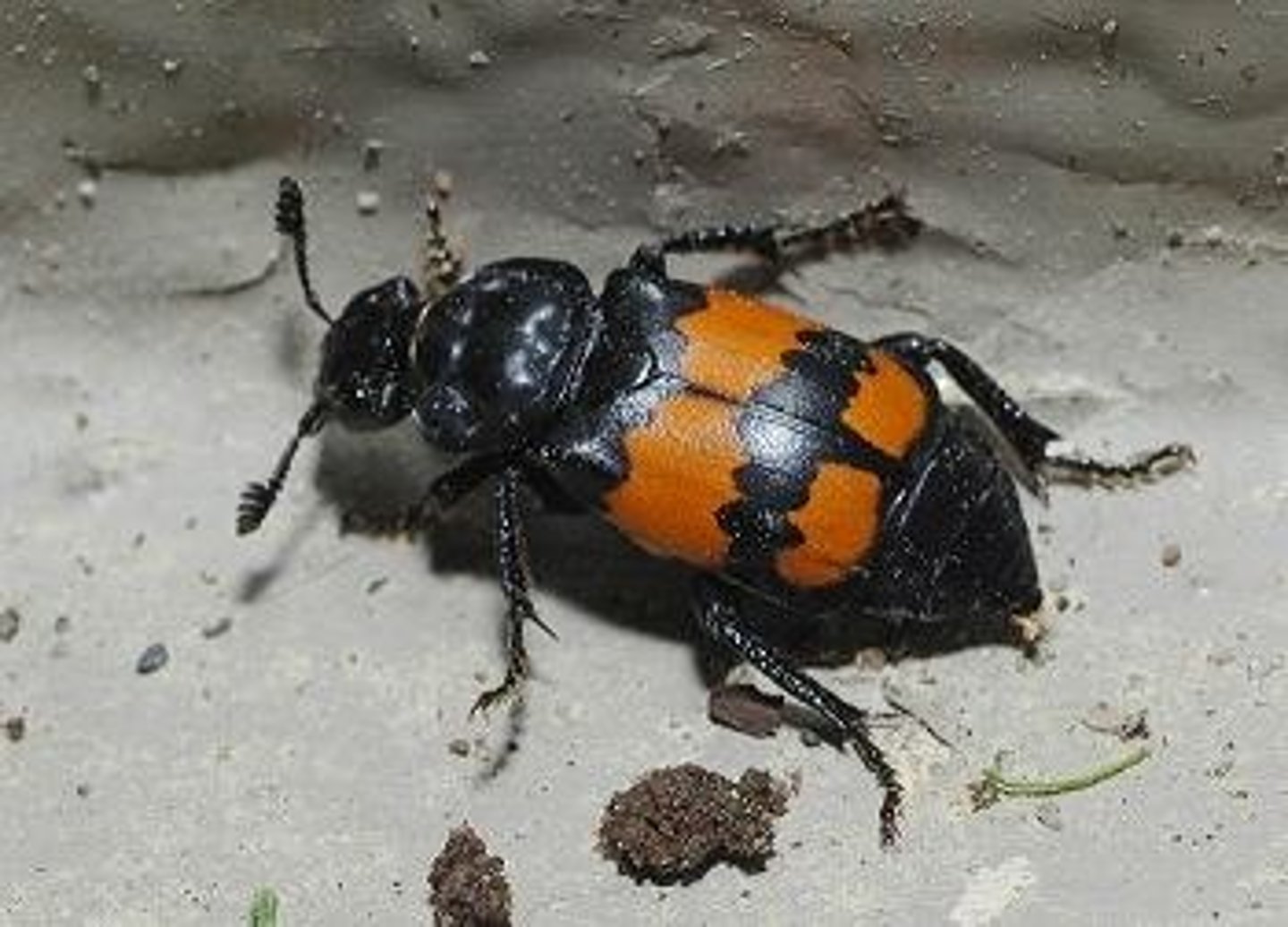
Carrion beetles
(Family Silphidae)

Chagas disease
disease is caused by parasite Trypanosoma cruzi
- transmitted thru fecal pellets of kissing bugs
Characteristics of thrips
- short legs, narrow wings w/ long fringe of hairs
- Asymmetrical mouthparts - only left mandible involved in forming a stylet along with maxillae (right mandible is reduced & non-functional)
- Occasionally parthenogenetic
- Leaves small scar on fruits
- 2 feeding nymphal then 2 non-feeding stage; winged adult stage
Chewing lice vs. sucking lice
Chewing lice (Mallophaga)
Feeds on dead skin cells, hair, or feathers
90% feed on birds; remainder species feed on mammals
head wider than prothorax
Sucking lice (Anoplura)
Feeds on blood, human disease vectors
found on specific body parts of mammalian host
head is narrower than prothorax
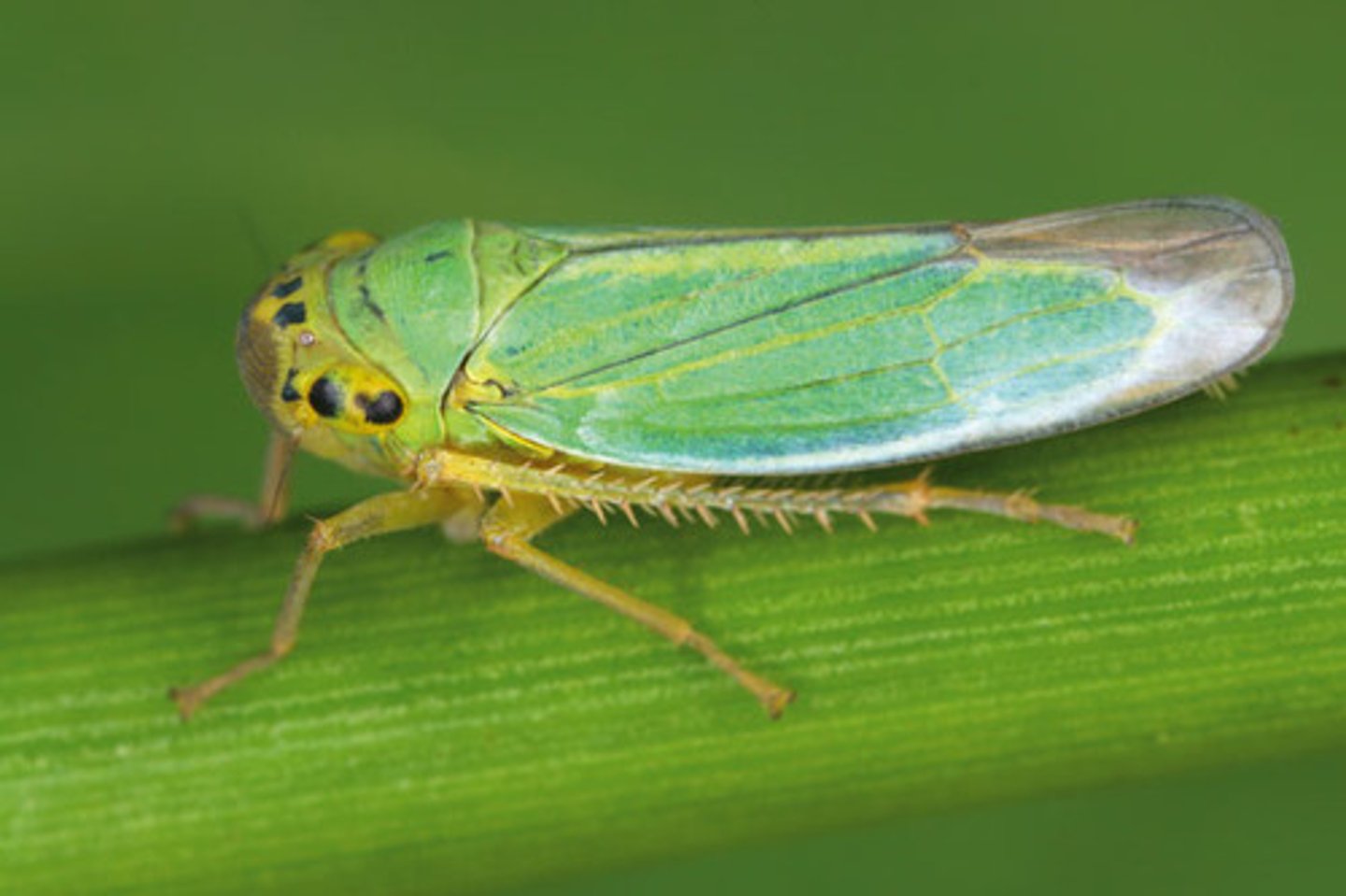
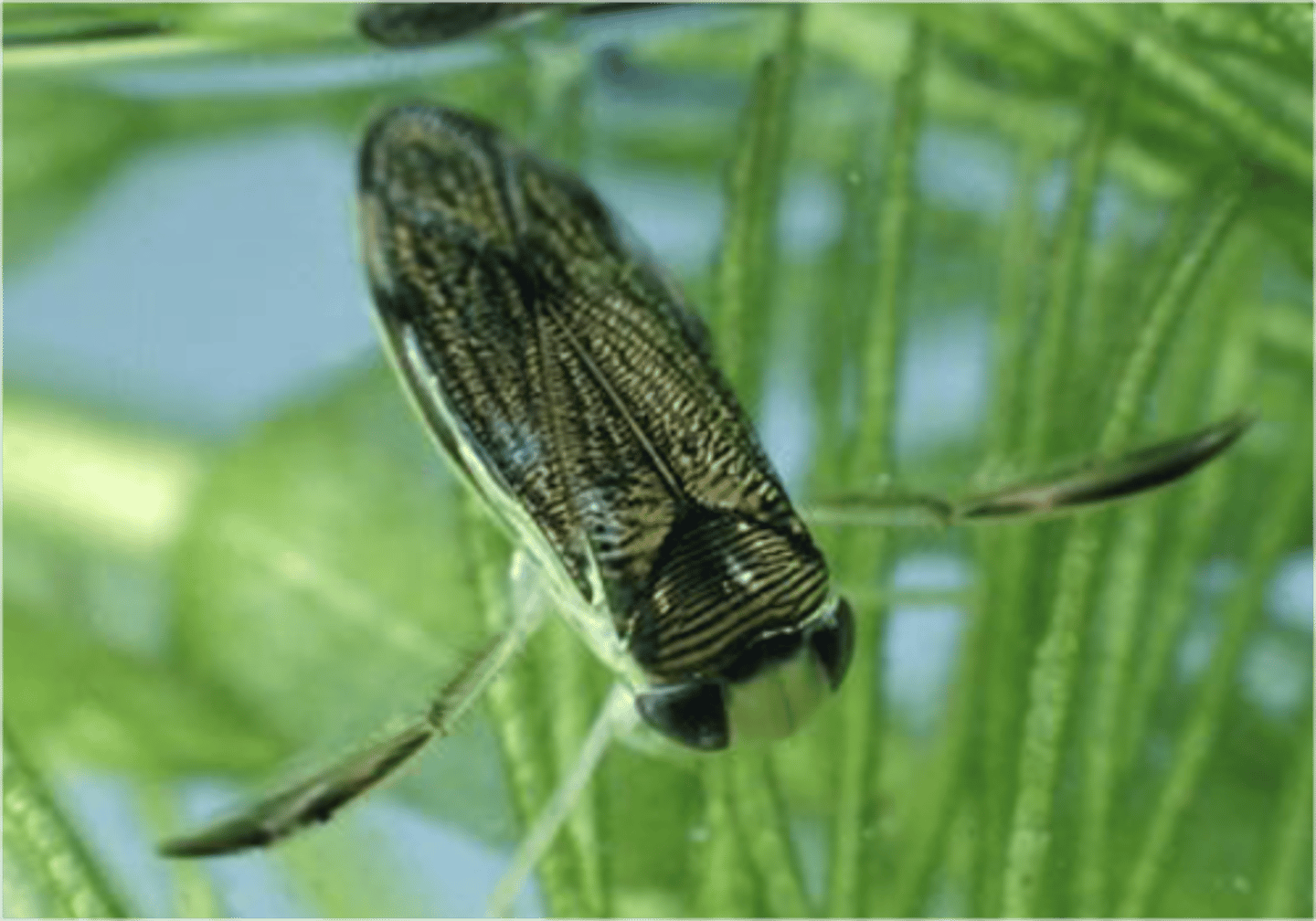
Cicadellidae
(leafhoppers and sharpshooters)
- Can be very damaging (Feeding)
Disease transmission (Pierce's disease)
- Excessive honeydew production
- Some have extraordinary jumping mechanism: "gear-like" structure on base of hind legs, keeping legs synchronized when insect jumps

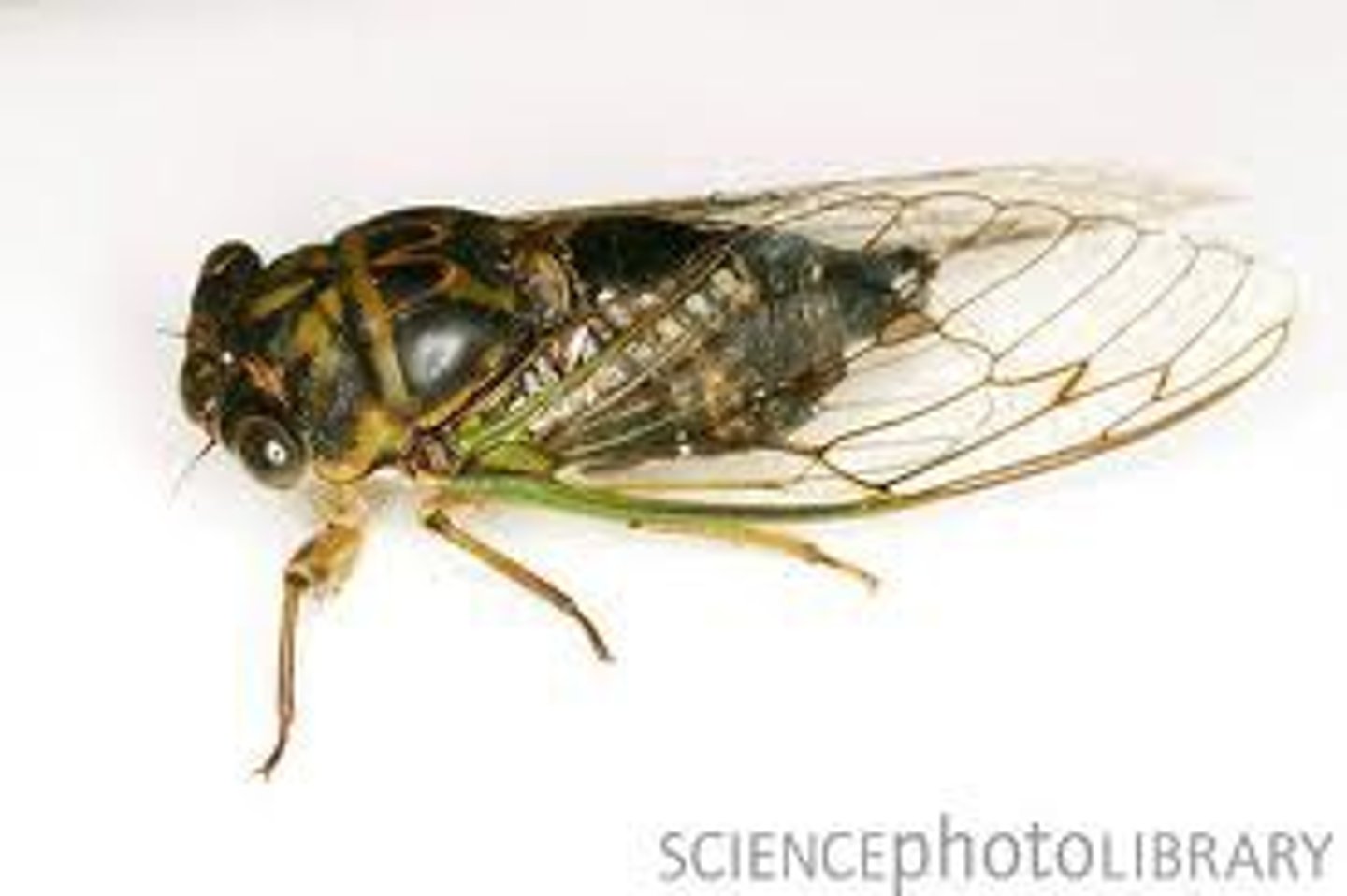
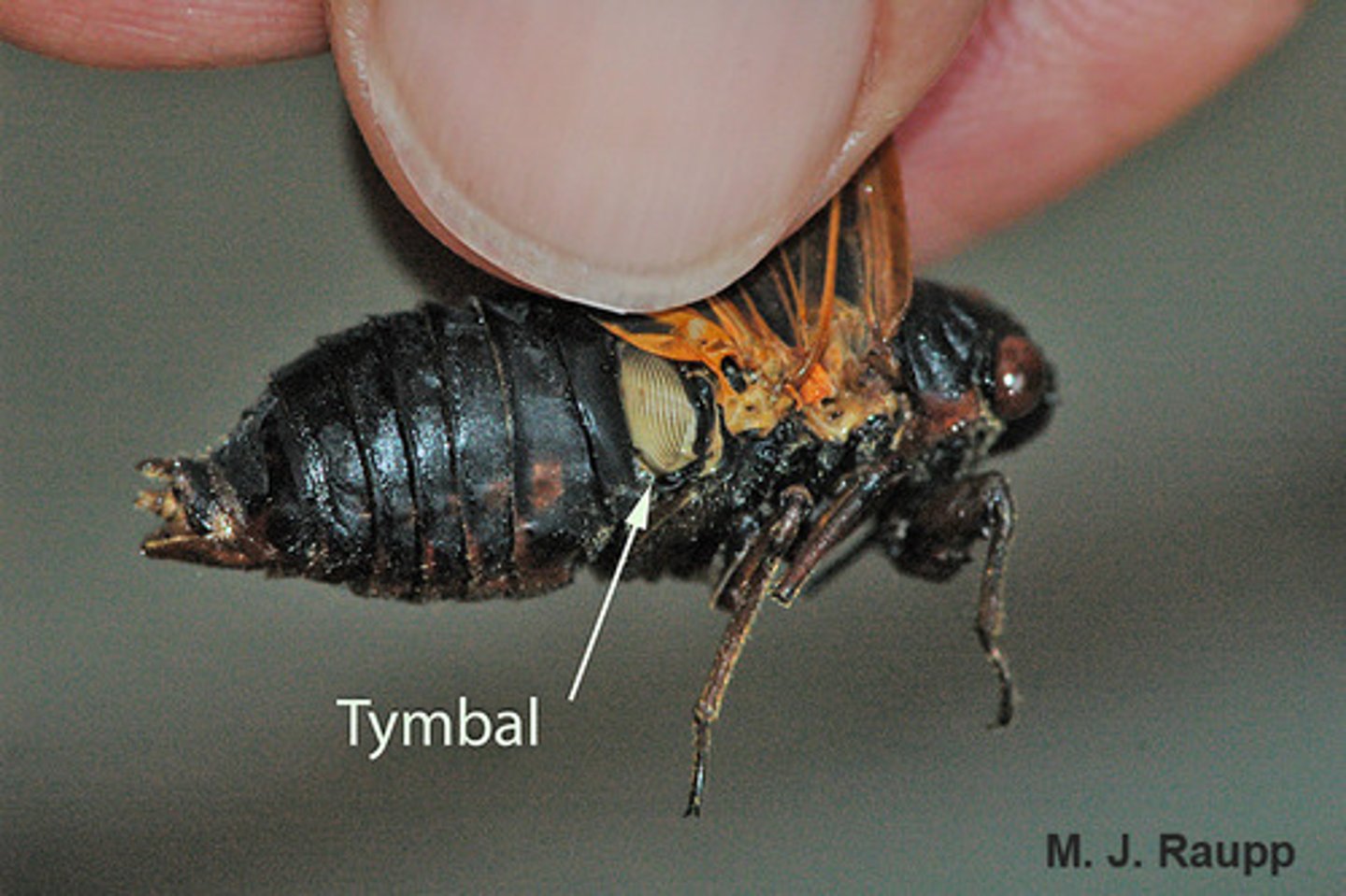
Cicadidae
Cicadas
- Produce very loud sounds (tymbals)
- Fossorial front legs in nymphs (digging tunnel)
- Synchronous emergence
- 4 species live on a 13-year cycle, and 3 for 17 years
- Predator avoidance strategy: eliminate possibility of potential predators receiving periodic population boosts by synchronizing their own generations to divisors of cicada emergence period
- Lay eggs in tree

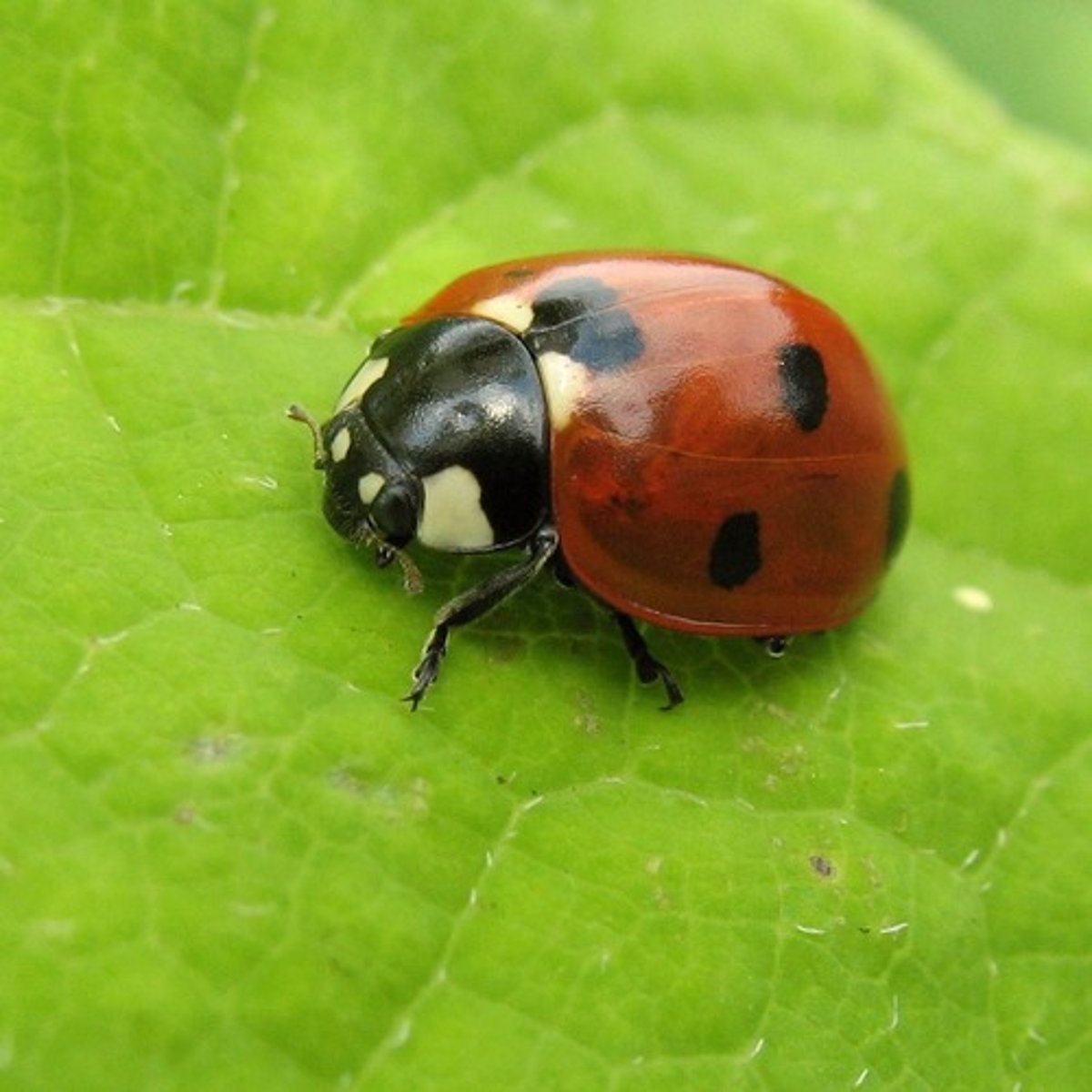
Coccinellidae
Lady bird beetles
- Larvae spotted or banded, with minute spines
- Adults with oval body shapes, bright coloration
- Feed on other plant pests (ex: aphids)
- Aposematic coloration (reflex bleeding)
- Noxious chemical
- Some ladybugs "migrate" to specific overwintering spots

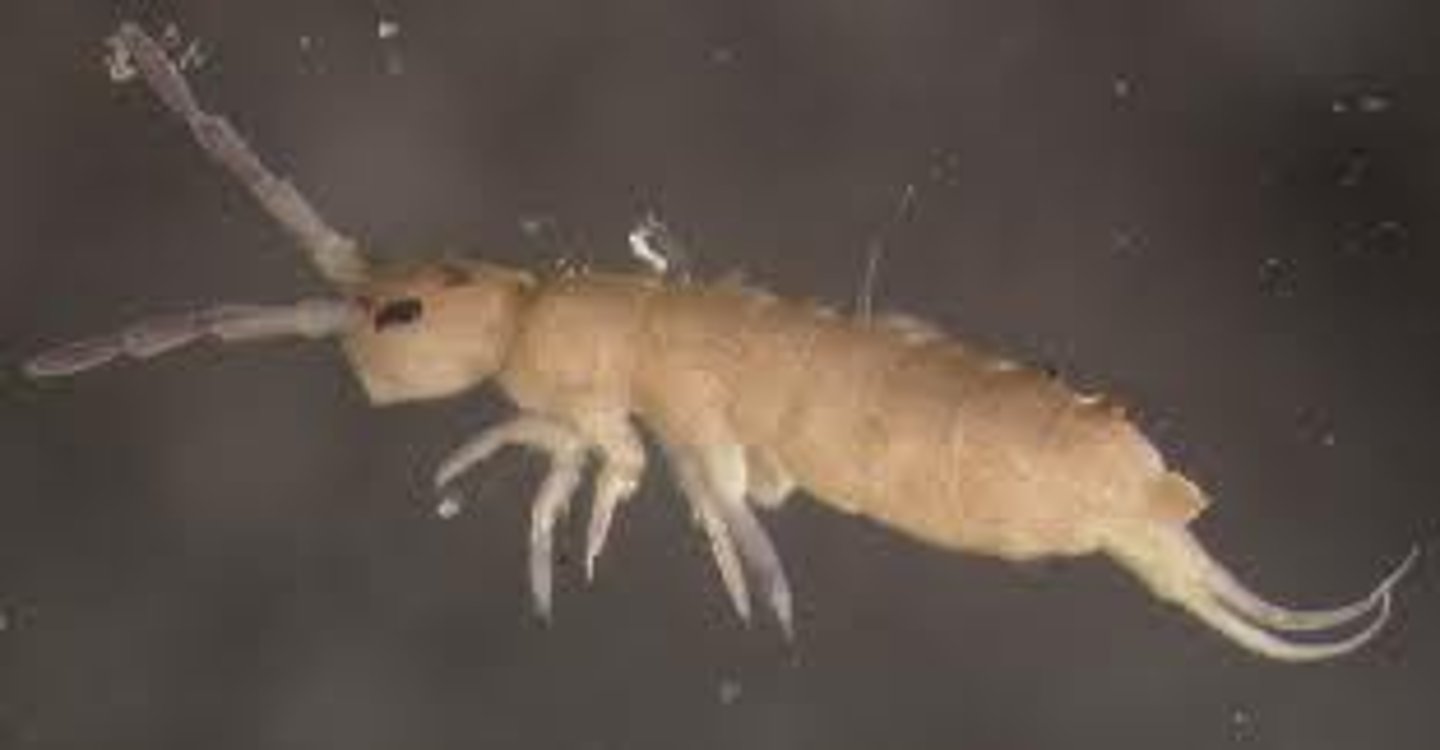
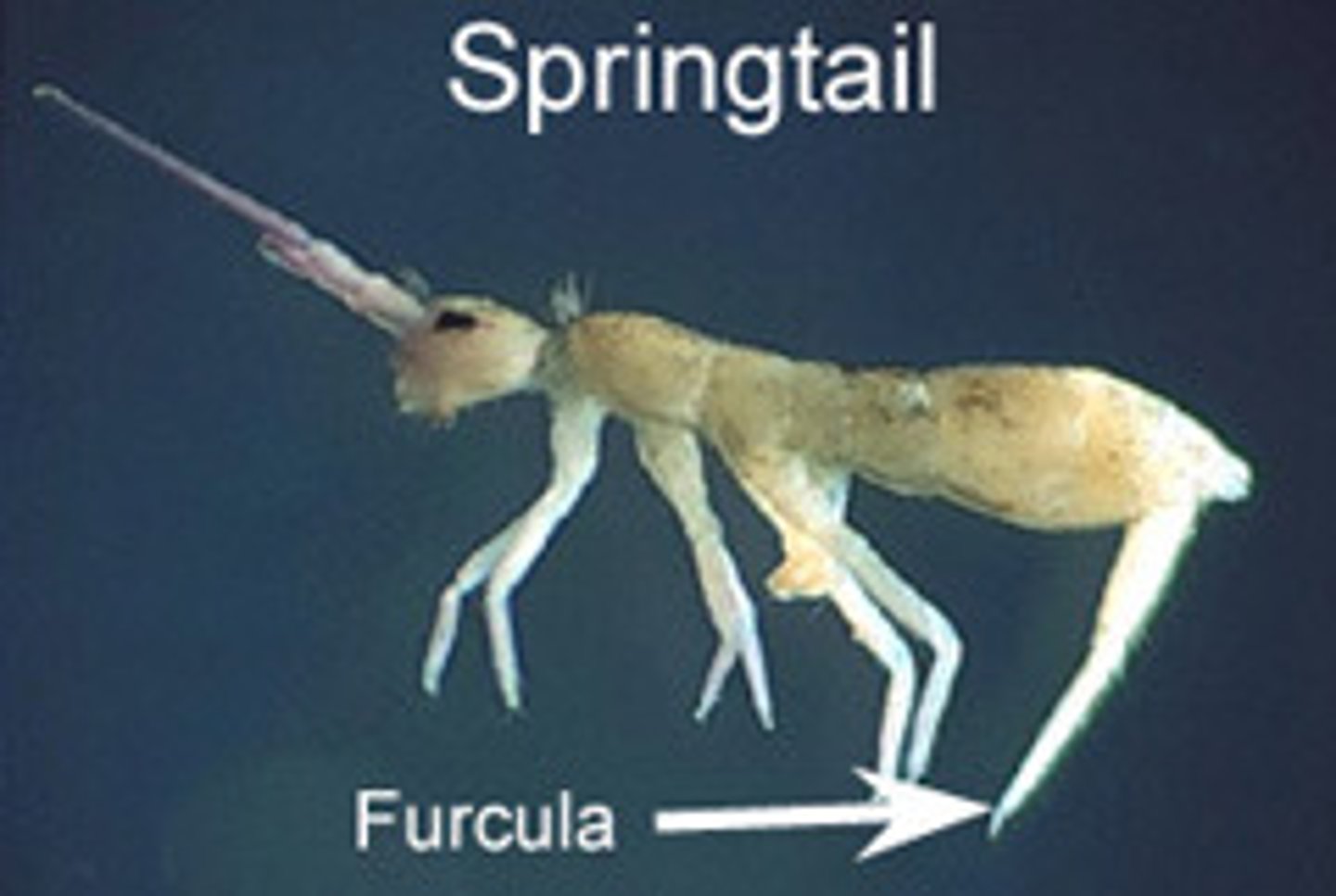
Collembola
Springtails
- Collophore (peg-like structure on 1st abdominal segment)
- Primitive compound eye
- Furcula (jumping fork) -> end of abdomen
- Live in moist environment (even water surface); soil/ bark/ freshwater ponds
- Dense populations
- Indirect sperm transfer

Common cockroach pests
Brown-banded (warm dry areas near appliances)
German (homes)
American (basement/damp areas)
Oriental (basement/damp areas)
- causes asthma
Convergent evolution
independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages
Worm lion (diptera) - ant lion (myrmeleontidae)
Mantid (mantodea) - mantidfly (mantispidae)
Corixidae
(water boatmen)
- Freshwater aquatic
- Lack gills, carry air bubble down into the water to take oxygen from water
- Natatorial legs
- Mostly herbivores, eat algae

Courtship behaviors in hexapods
Calling (katydids / crickets)
pheromones
Nuptial gifts
Fighting
Visual displays
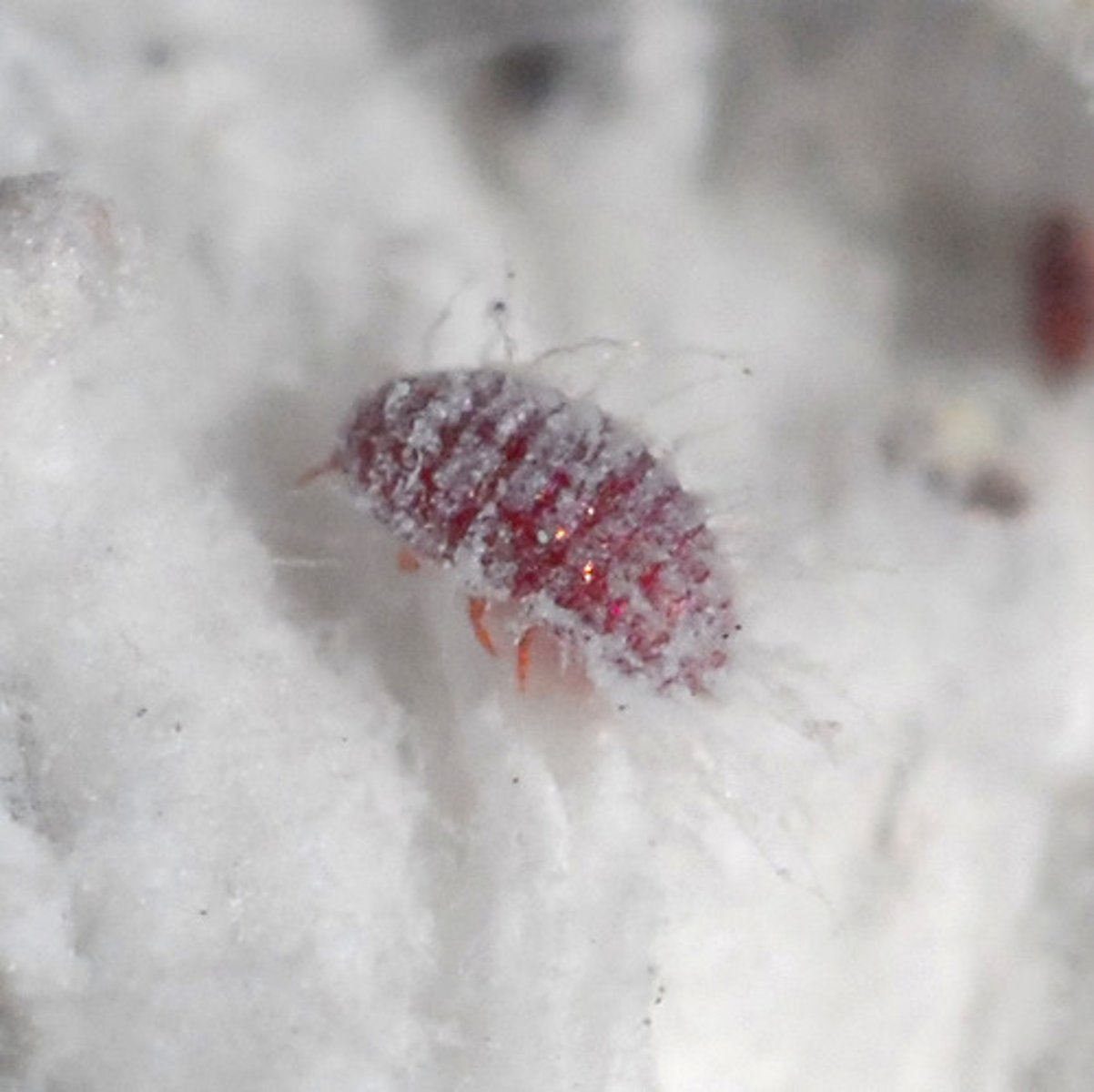
Dactylopiidae
Cochineals (Suborder Sternorrhyncha)
- Sessile parasites on plants
- Lives on cacti in genus Opuntia
- Natural dye carmine is derived

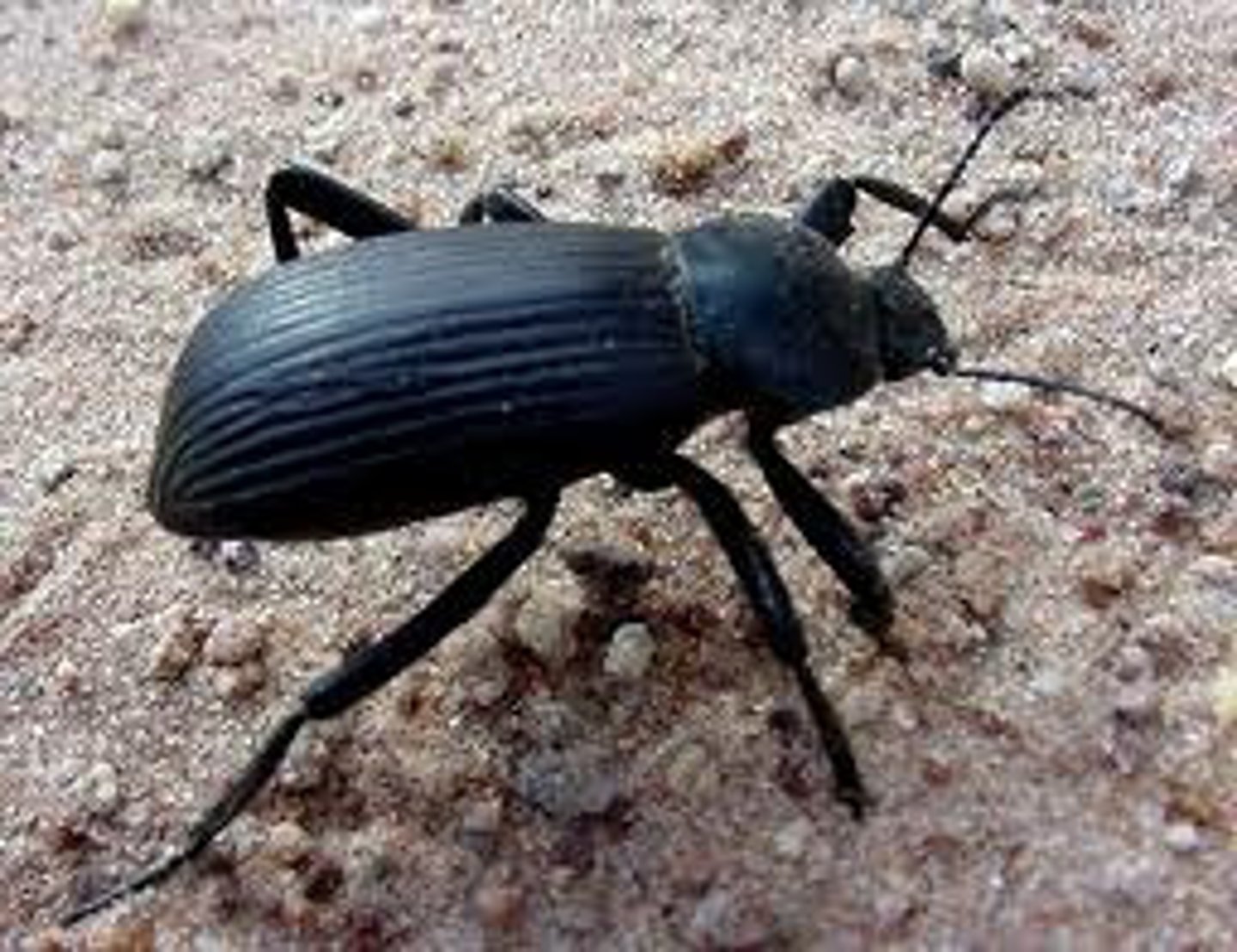
Darkling beetle
Order Coleoptera
Fused Elytra
Flightless

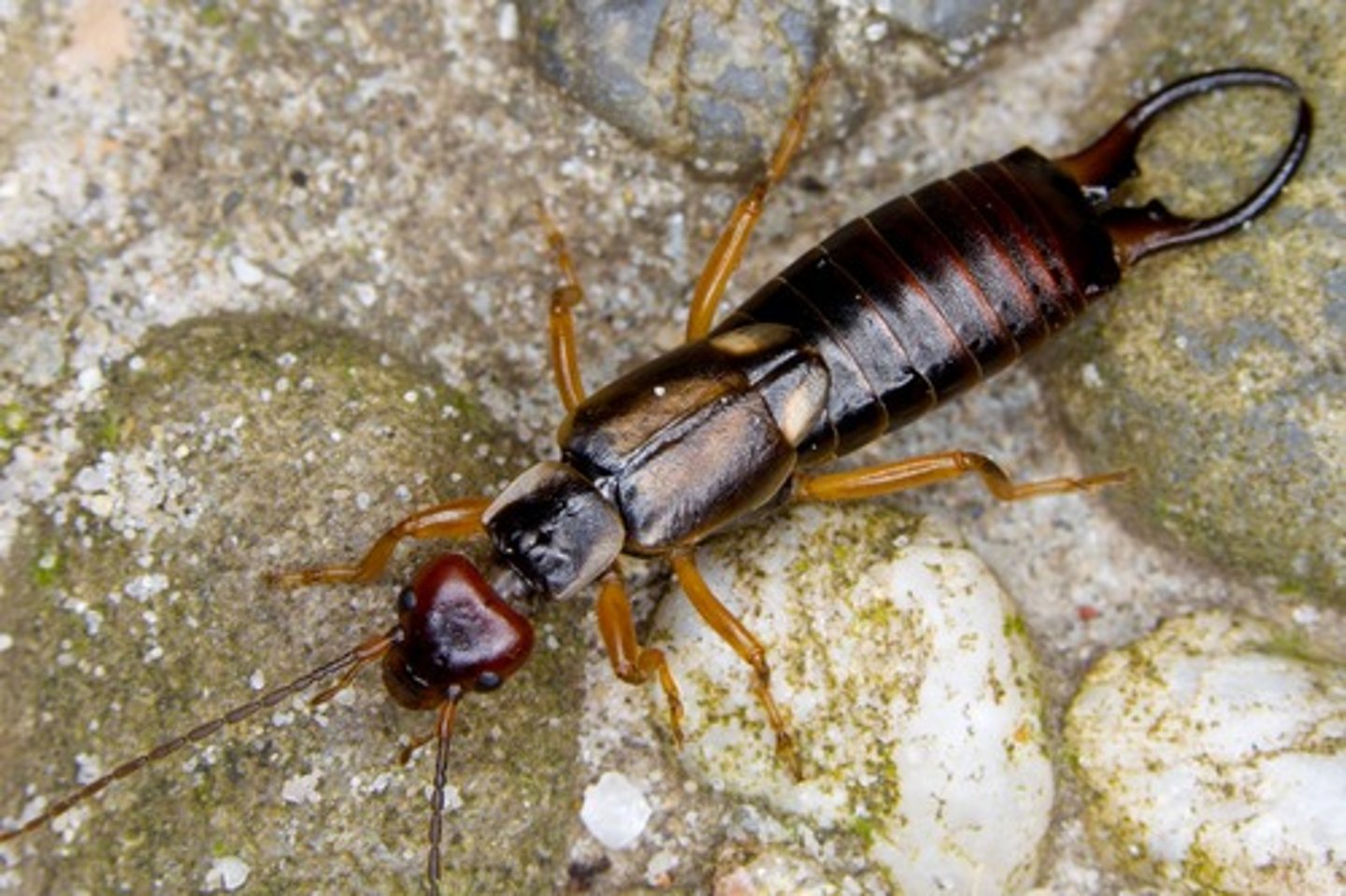
Dermaptera
Earwigs
- Chewing mouthparts
= Short leathery forewings
- Large cerci on abdomen (for mating & defense)
- Nocturnal
- Feed on plant materials, young citrus fruit
- Maternal care of brood / Not cooperative
- Females cleans and re-piles the eggs
- Chemical defense (doru taeniatum) in the glands when attacked (pinched body parts to squirt opposite way)

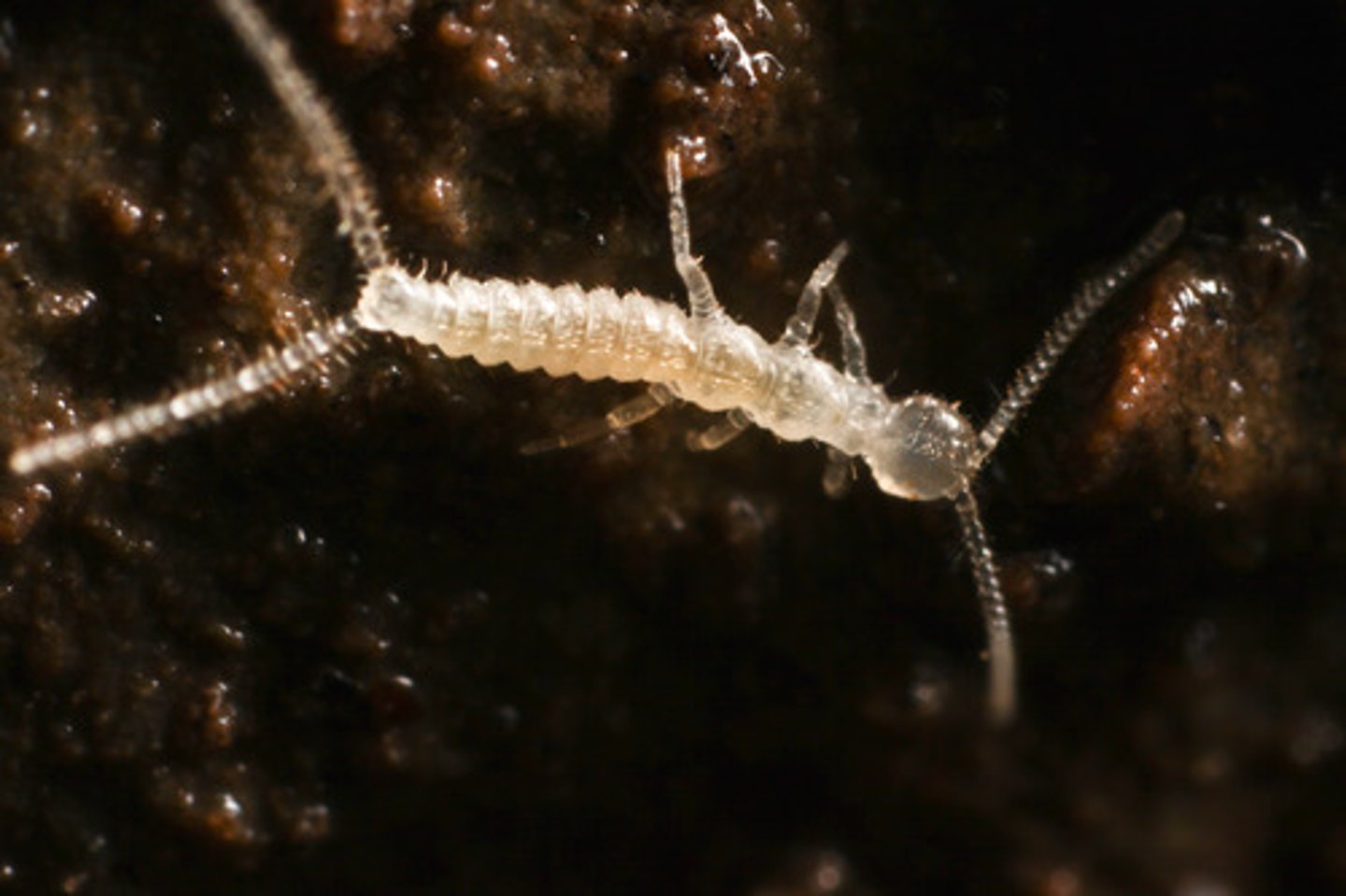
Diplura
"two-pronged tails" "forked tails"
- Narrow, elongate body, usually colorless
- Lacks eyes
- 2 abdominal cerci
- Similar to collembolans, indirect sperm transfer (spermatophore in the environment)

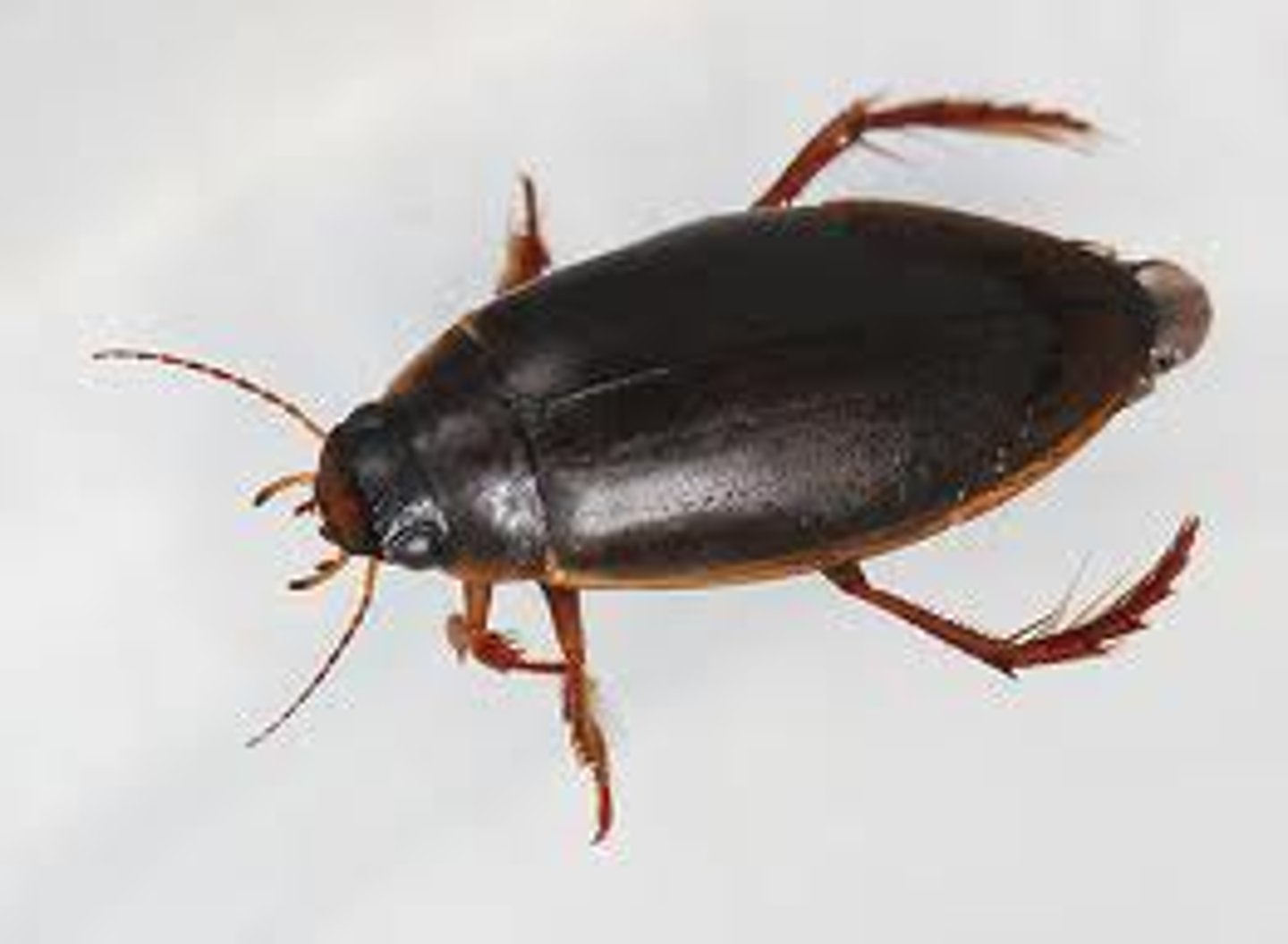
Diving beetle
Order Coleoptera (Family Dytiscidae)
- Can dive
- Predaceous
- Pupate in mud
Larvae -> spiracle at end of abdomen
Adult -> air bubble, natatorial leg

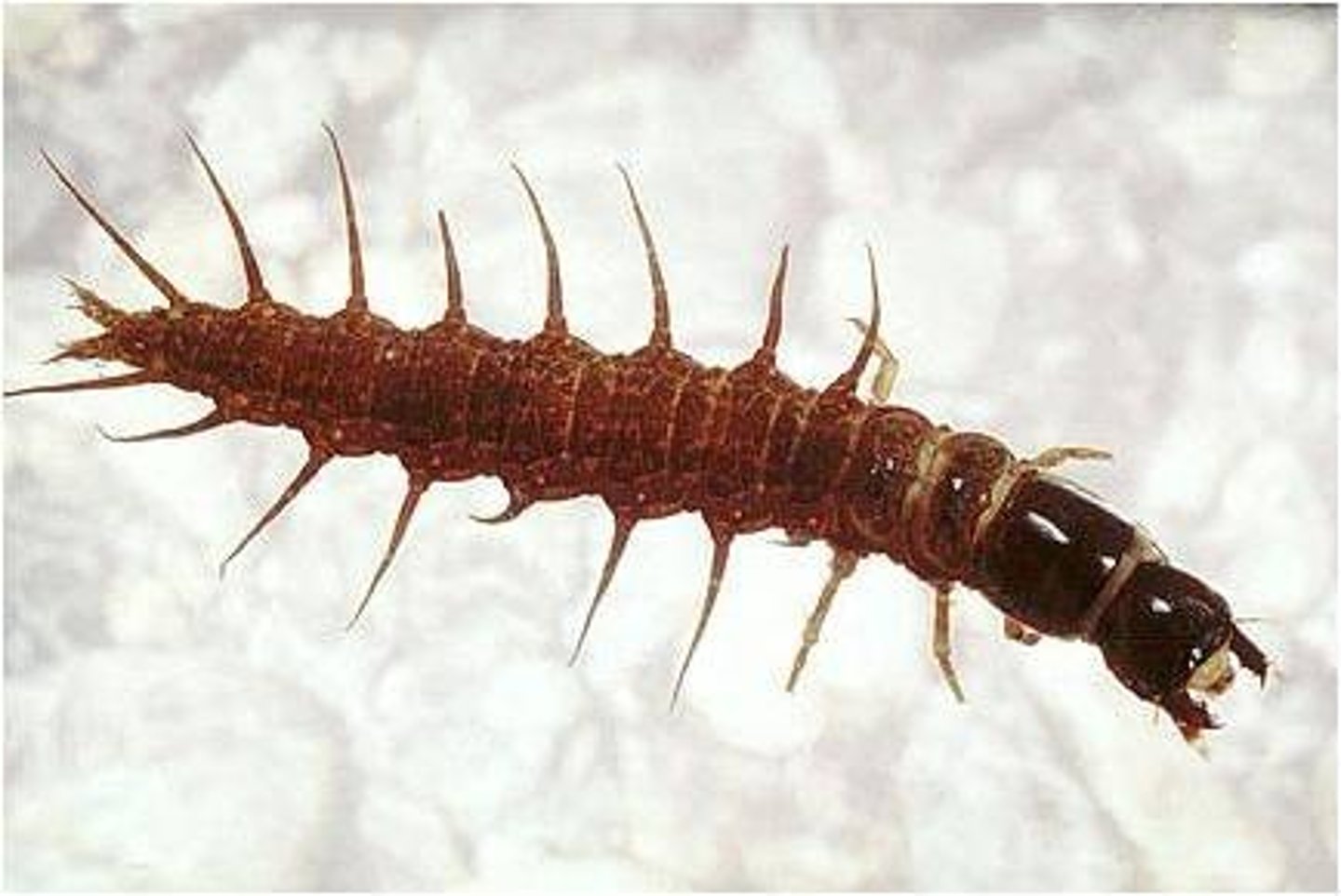
Dobsonflies
Family Corydalidae / Holometabolous
- Larvae are aquatic (aka hellgrammites)
- Huge male mandibles
- Good fishing bait
- Voracious predator (as larvae)
- Pupate in soil
- Adult: terrestrial

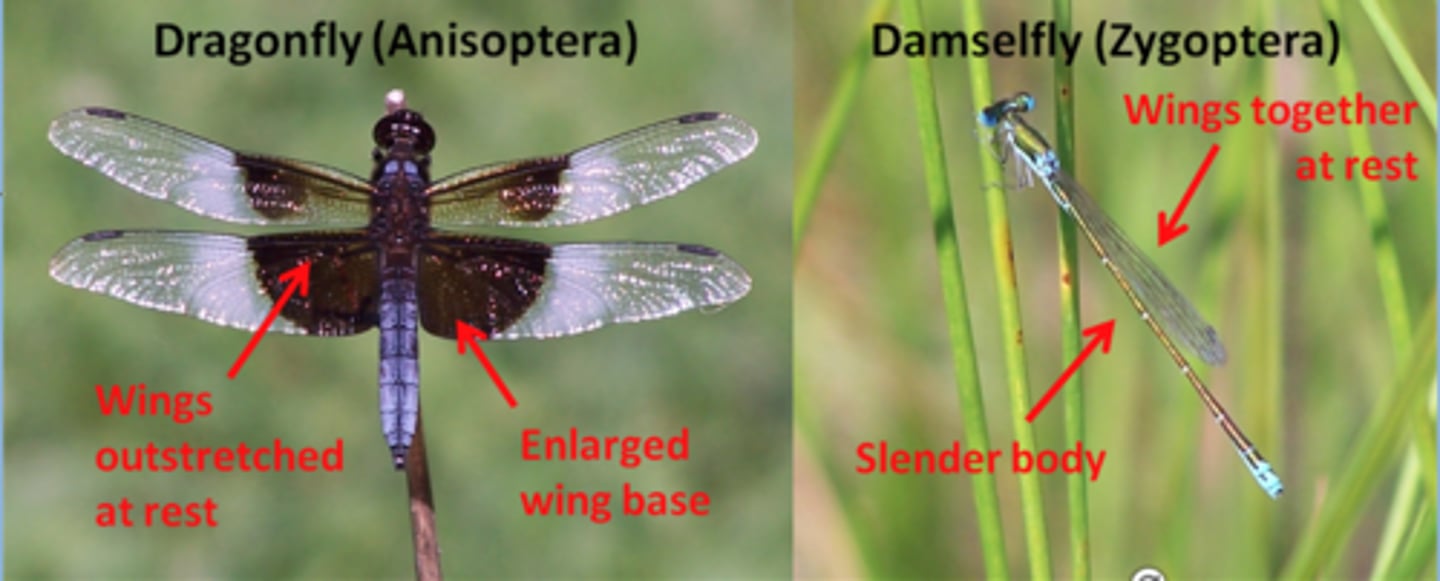
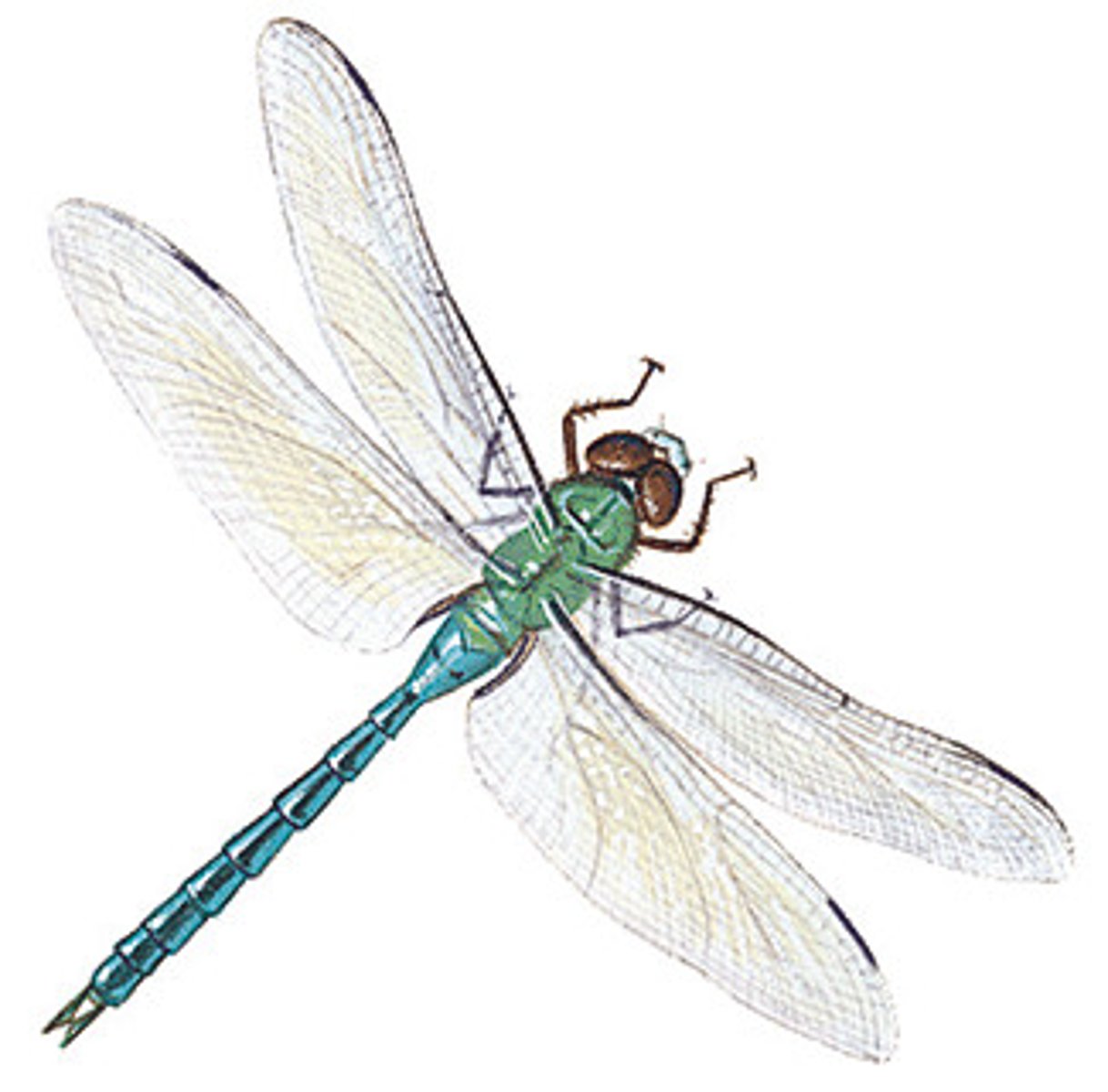
Dragonflies vs. damselflies
Odonata Suborder
Dragonfly: wings broad at base and held horizontally at rest; no external gills (rectal gill)
Damselflies: wings narrow at base and held over back at rest
has external gills
Drywood termites vs. subterraneantermites
Drywood termites: live in colonies above ground directly in dry wood; produce holes where fecal pellets are pushed out from wood (small piles on floor)
Subterranean termites: live in soil and feed on wood in contact w/ soil; construct tubes for shelter as they travel b/w underground colonies and structure
Different habitat + behavior
Dung beetles
(Family Scarabaeidae): Adults eat soft dung
rollers & tunnelers & dwellers
Dung as provision for: developing larvae
- Recyclers of animal dung
- associated with Re, supreme being and sun god in Egyptian culture

Elateridae
click beetles
ability to produce a clicking sound as a means of self-defense

Elytra
"Kolean": sheath
- protection of hindwings
- armor
- retention of water
- stabilization during flight
Entognatha
Subphylum Hexapoda w/ Collembola, Diplura and Protura
Mouthparts are large (concealed in head capsule); wingless; indirect sperm transfer
Ephemeroptera
Mayflies (remember adults are short-lived)
- adults do not feed, only disperse, mate, and die
- Large triangular front wings
- 1 median caudal filament and 2 cerci (long)
- Adults terrestrial, nymphs aquatic (respire thru abdominal gills)
- Relatively long life cycles (live as nymphs for months to years)
- Subimago stage - final stage before molting to adult (imago)
Mass emergence swarms, lay eggs in water
Very important in food webs

Epidemic typhus fever
Transmission of disease by human body lice
Caused by bacterium Rickettsia prowazekii
Symptom: sudden headache, chills, high fever, protration, coughing and severe muscular pain, skin rash
- Typically occurs in conditions of overcrowding and poor hygiene aka prisons and refugee camps
- Common in concentration camps in WWII

Feeding habit of neuropterans
- Lacewings (family Chrysopidae) and antlions (family Myrmeleontidae), are predatory and feed on other insects
- mantispids (family Mantispidae), feed on nectar and pollen as adults
Filter chamber
Modification in a gut
"filter chamber" separates excess fluid from plant sap for rapid removal "honeydew"
Furcula
(jumping fork) -> end of abdomen

Gregarious vs. solitary phases in locusts
Solitary phase: low density, low reproductive rate, short flights, lighter green in color
Gregarious phase: high density, high reproductive rate, flies far,
darker in color
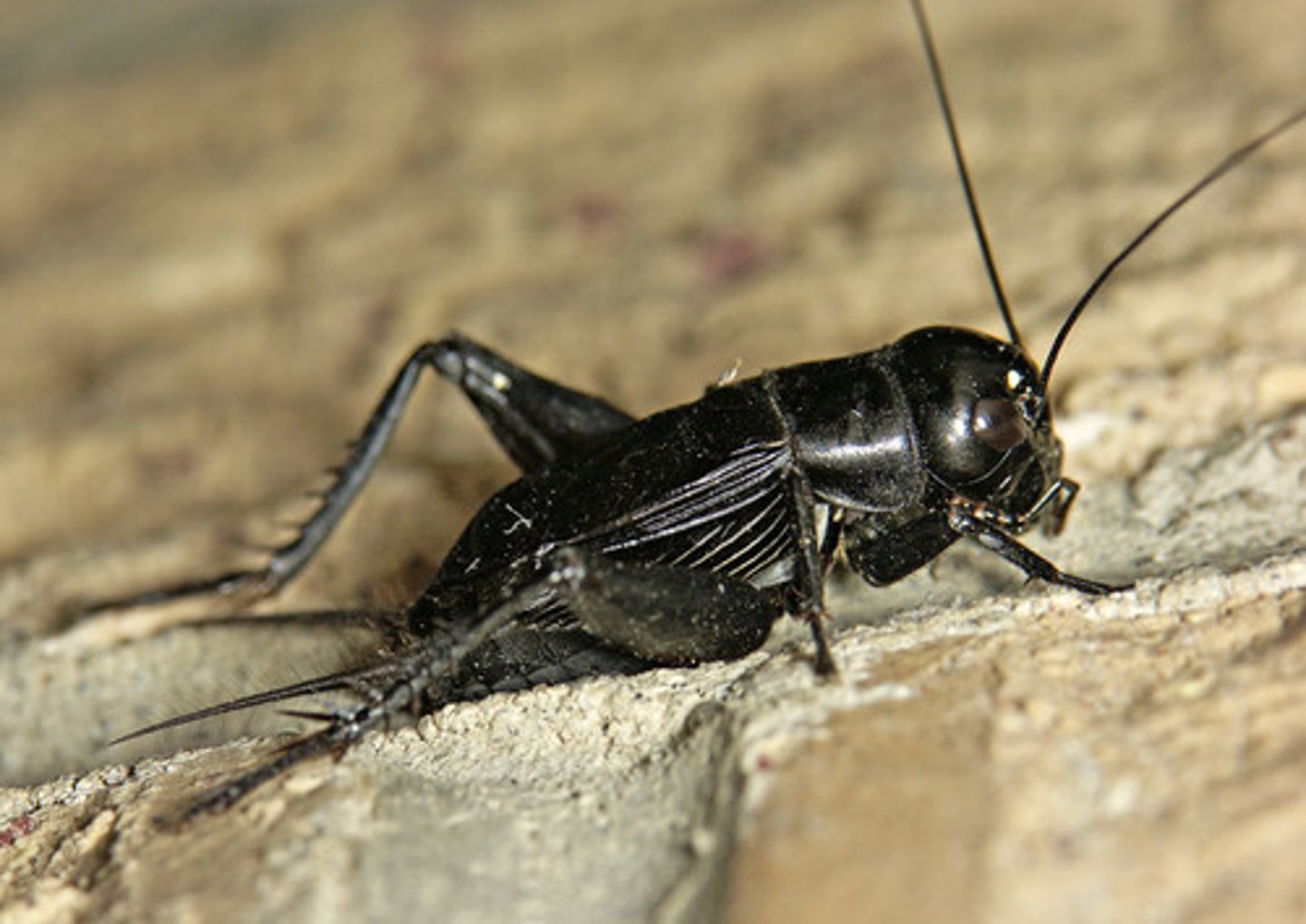
Gryllidae
crickets (Suborder Orthoptera)

Head lice vs. body lice
Head lice (Pediculus humanus capitis): mostly found on hair on head; Eggs (nits) of head lice attached to hair
Body lice (Pediculus humanus humanus): mostly found in pubic region, hygiene DOES affect likelihood of getting body lice
; can cause intense itching and rash
- prefer to develop off human body; eggs are laid on clothes, and , when not feeding, adults and nymphs reside in the clothing
Hemimetabolous development
incomplete metamorphosis; egg, nymph, adult
Hemipteran feeding habit
- piercing and sucking plant or animal fluids
- Proboscis
Plant-feeding hemipterans: aphids and whiteflies
Blood-feeding hemipterans: kissing bugs and bed bugs
- transmits disease (Chagas disease)
Hemipteran mouthparts
- sucking mouthparts (proboscis)
- mandibles and maxillae: sheathed within a modified labium to form a proboscis
Pierce tissues and sucking out the liquids
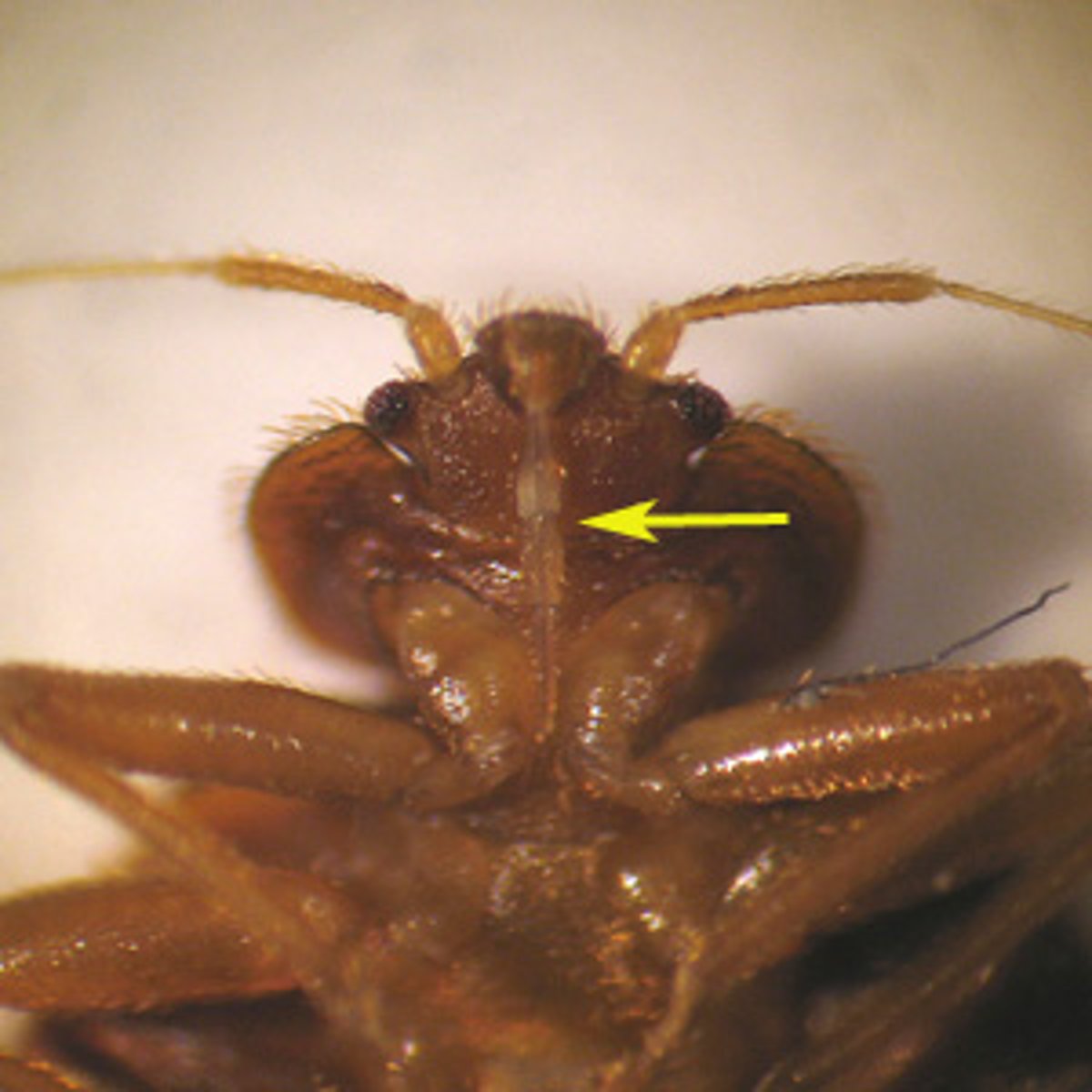

Heteroptera mouthpart
piercing-sucking mouthparts, labium folds

Holometabolous development
Complete metamorphosis; egg, larva, pupa, adult
Honeydew
weet, sticky substance excreted by sap-sucking insects
Cicadellidae (leafhoppers and sharpshooters)
Suborder Sternorrhyncha (aphids, scale insects, and whiteflies)
How do insects breathe underwater
- air bubble (water striders)
- gills (larvae of dragonflies, damselflies, and mayflies, diving and Whirligig beetles)
Hydrogen peroxide
Chemical compound of hydrogen and oxygen; a colorless liquid with a characteristic odor and slightly acid taste.
- Defensive strategy of bombardier beetles
Hydroquinone
Defensive strategy of bombardier beetles
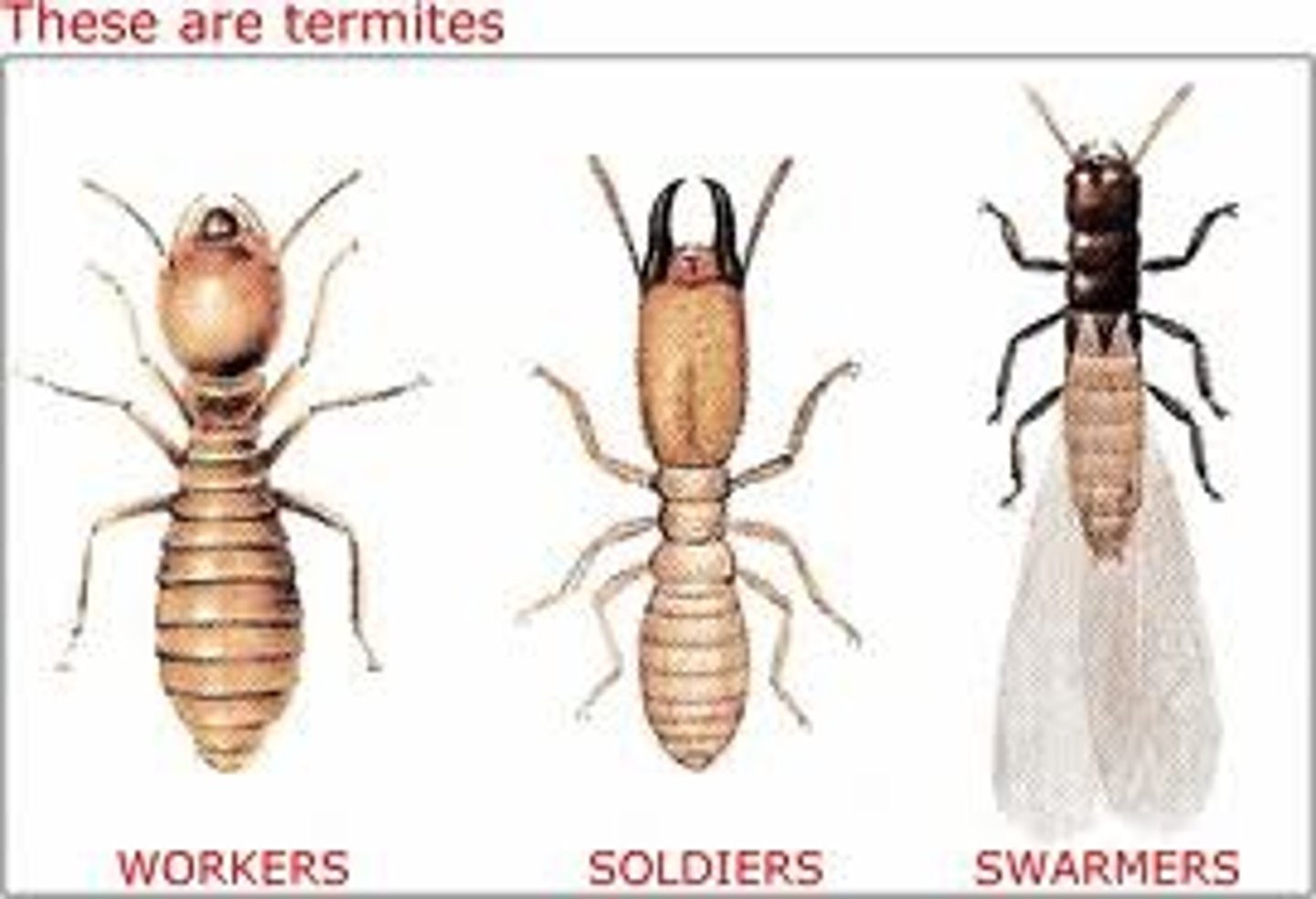
Isoptera
(member of Order Blattodea): Termites
2 pair of similarly sized wings (winged reproductive only)
Abdomen broadly joined to thorax
Differential caste morphology: Reproductives: king & queen
Workers
Soldiers - Nasute & Mandibulate
- Feed on dead plant material (leaves, twigs, wood, lumber,
feces) - cellulose
Some are able to digest cellulose thru a mutualistic
relationship with microbial symbionts in their gut
Some will maintain specific fungus garden and feed
on it
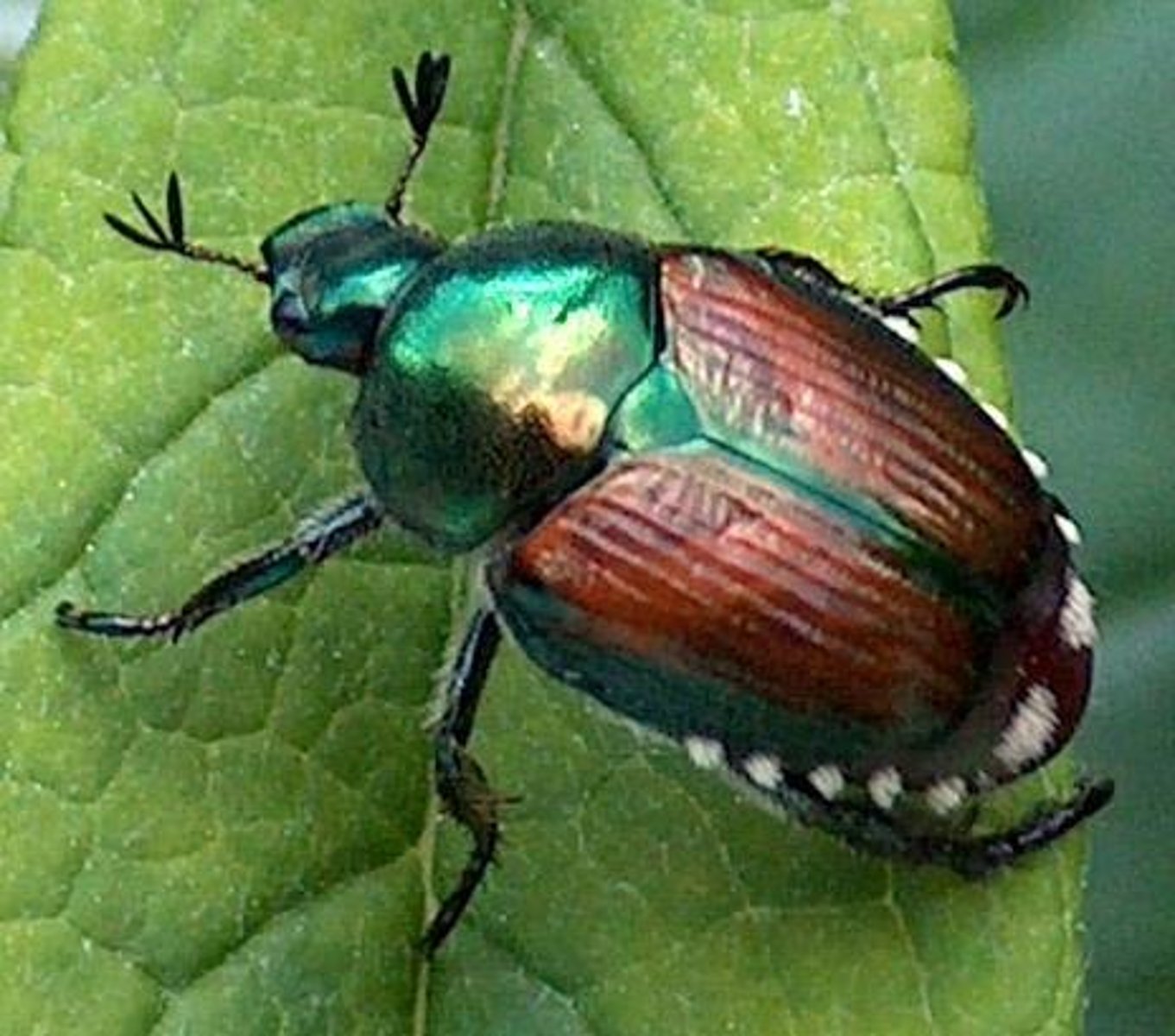
Japanese beetle
Scarab beetles (Superfamily Scarabaeoidea)
- Popillia japonica
- Serious agricultural pest in US
Adults - Skeletonize leaves of trees and shrubs (feed on tissues between veins)
Larva - Attack root system of grass (important pest in lawn, golf courses)

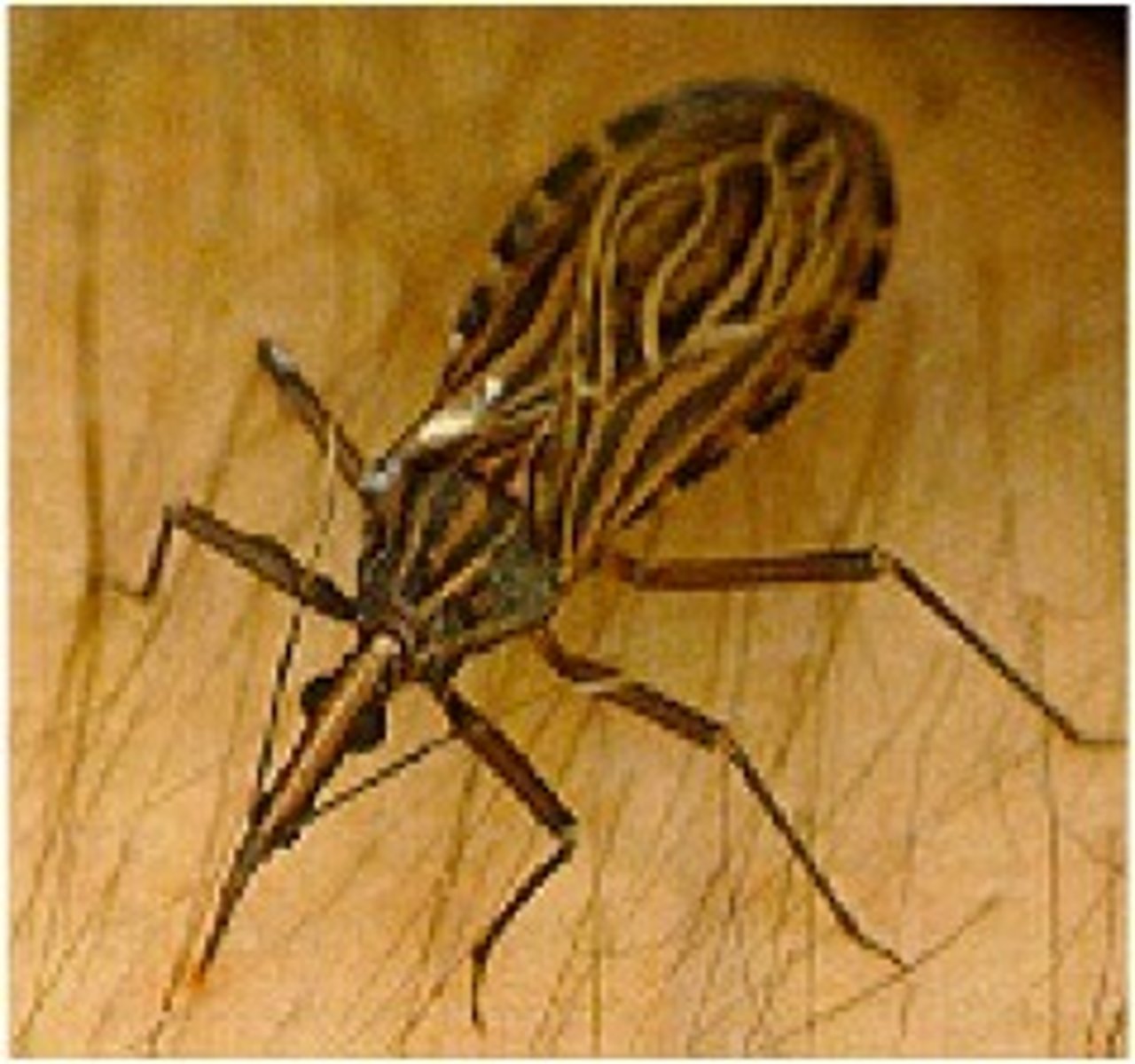
Kissing bug
(Subfamily triatominae)
- Nocturnal
- Use heat and odor to locate hosts
- Transmits Chagas disease (disease is caused by parasite Trypanosoma cruzi)
- transferred thru fecal pellets
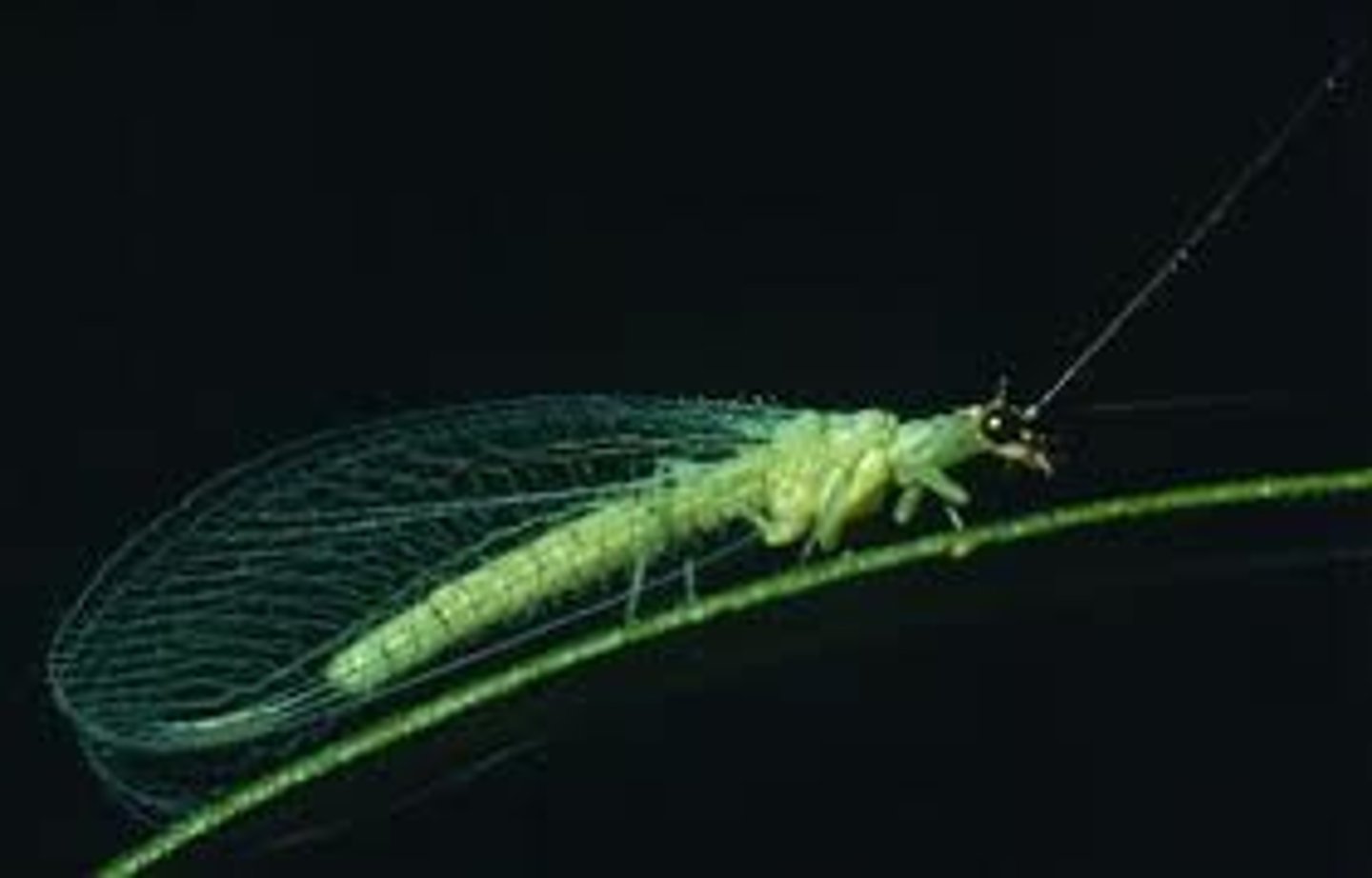
Lacewings
(Family Chrysopidae)
- Adult, eggs on stalks, cocoon (pupa inside) w/ silk on plant , larvae w/ sickle-like mouthparts (predator)
- Voracious chrysopids are reared for sale as biological control agents of insect and mite pests in agriculture and gardens
- Larvae -> voracious predator biological control agent
- Can hear bat sounds and closes its wings and free falls to avoid capture (Chrysopidae insects have ears near the bases of forewings)

Lampyridae
- fireflies/lightning bugs
- seen near water, as their larvae live in damp soil or in the water
- Luminescent organ on abdomen (involves specialized cells, photocytes)
- Luciferin, luciferase, energy, and oxygen
Adult: attract mate
Larvae: aposematic signal
Luminescent mechanism in fireflies
- bioluminescence, which they use to attract mates or to communicate with other fireflies
- produced by a chemical reaction in their bodies that involves the enzyme luciferase and a substrate called luciferin
Mallophaga characteristics
Chewing lice
- Feeds on: dead skin cells, hair, or feathers
- Hosts: 90% feed on birds; remainder species feed on mammals
- head wider than prothorax
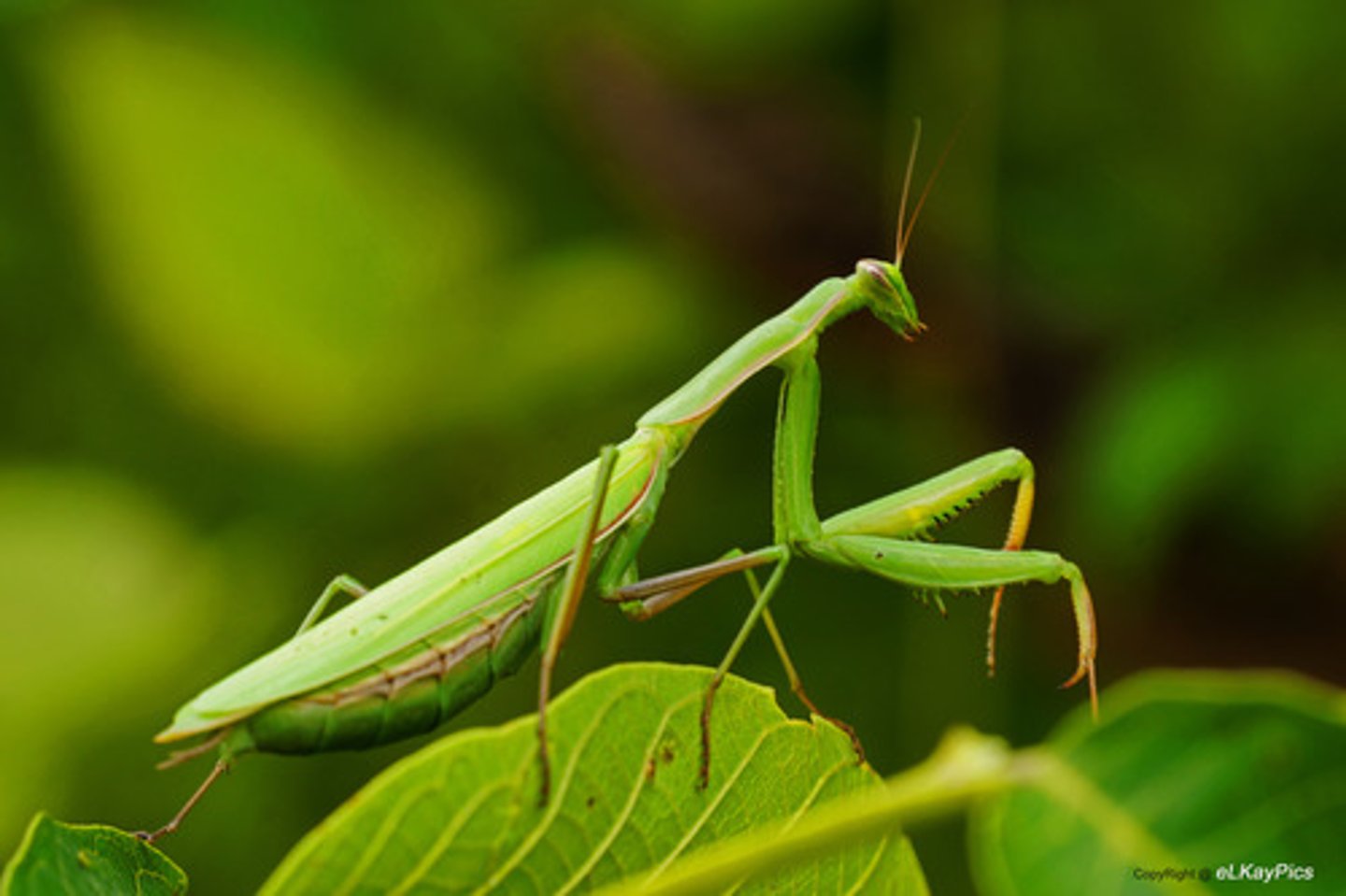
Mantodea
(soothsayer): praying mantids
- Large raptorial front legs
- Triangular hand
- Large compound eye
- Chewing mouthparts
- Masters of camouflage
- Ambush predators
Produce ootheca (foamy egg sac -> harderns)
Unusual mating (sexual cannibalism)

Maternal care of eggs in earwigs
- Females cleans and re-piles the eggs
tending increases survival rate
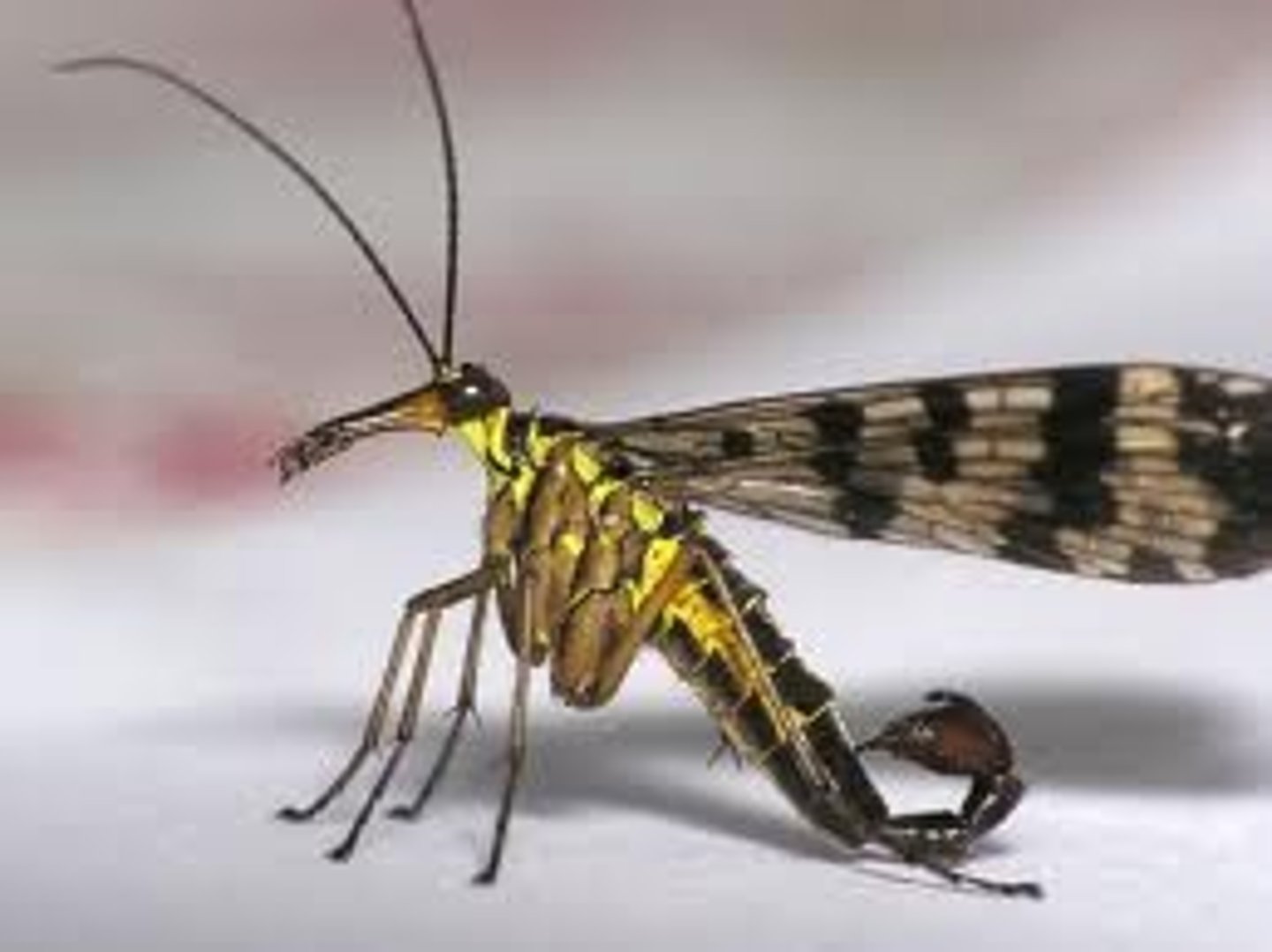
Mecoptera
Scorpionflies
- Male "scorpion" tail - enlarged genitalia
- Female lacks "scorpion" tail
- Nuptial gift by male -> in some species
- Hangingfly (mecoptera) -> resemble crane fly (absence of halteres)

Neuroptera
lacewings, mantidflies, antlions
- With numerous cross veins
- 4 wings same size
- Adult neuropterans feed on nectar, pollen, and aphid honeydew, while the larvae are voracious predators
Odonata
dragonflies & damselflies (Hemimetabolous)
- Large, many-veined, membranous wings
- Chewing mouthparts in adults & nymphs
- Adult cerci function as claspers while mating (male)
- Adults terrestrial, nymphs aquatic with rectal gill pads

Pheromone use in beetles
- Carpet beetle use pheromones to locate mates
- communication, aggregation, and mate attraction
Phthiraptera
("true" lice)
- scansorial leg (for clinging)
- feed on fur, feathers, skin debris, secretions
- chewing and sucking lice
- Ectoparasites of mammals and birds
- Wingless

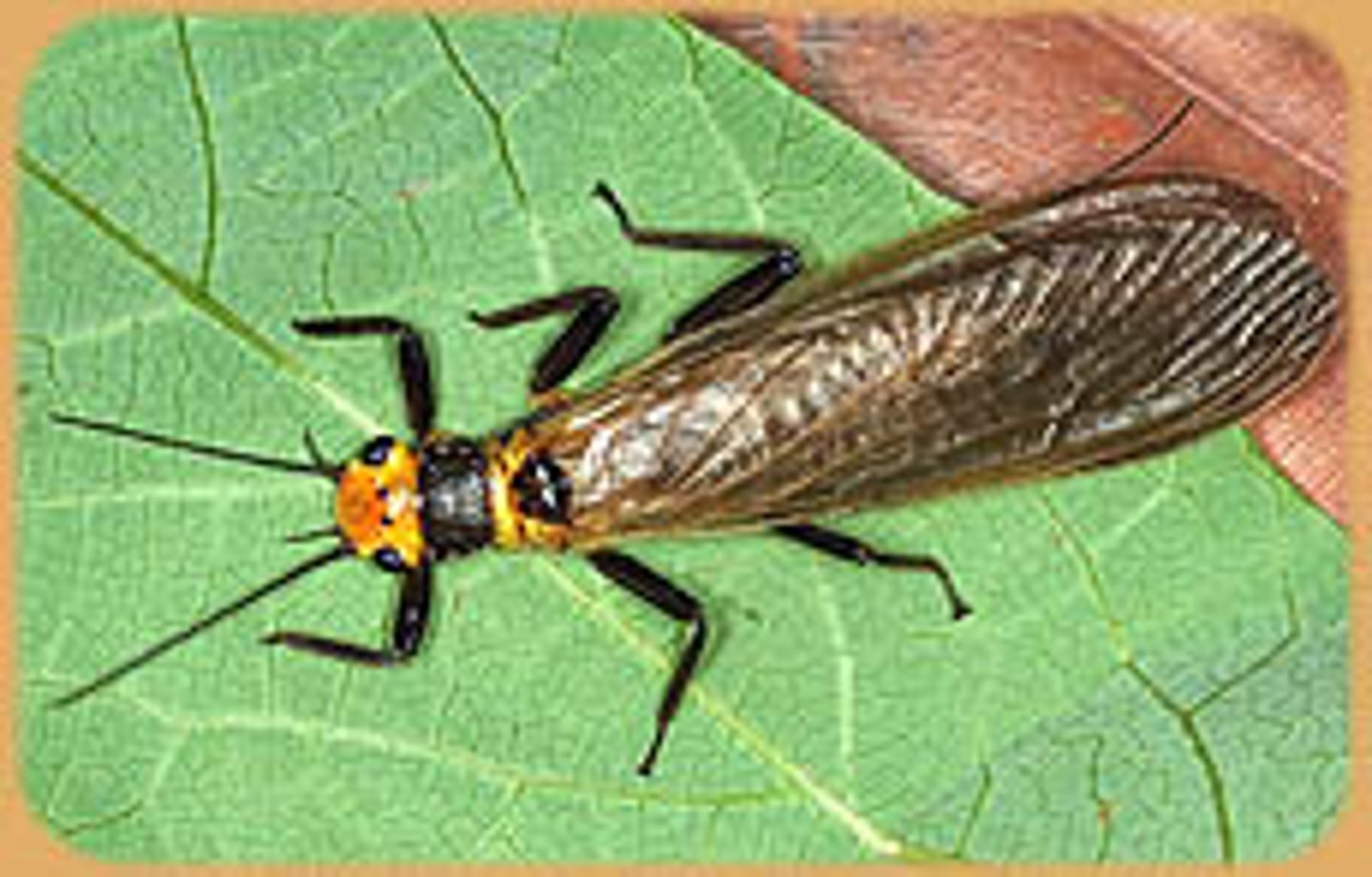
Plecoptera habitat
(stoneflies)
- nymphs are aquatic, prefer clean, cold water
- grazers or predators
- tracheal gills
- Prefer well-oxygenated / fast flowing water

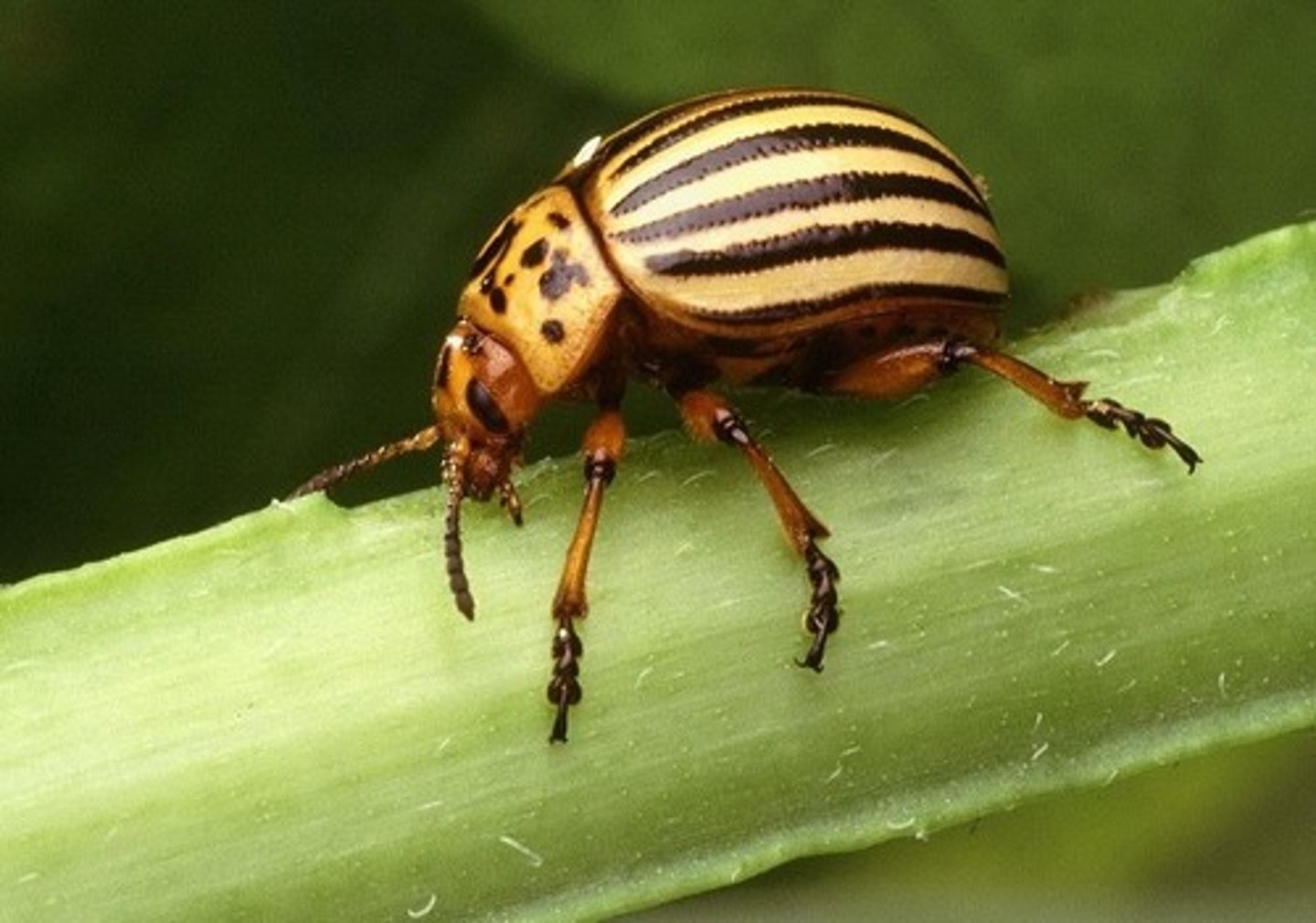
Potato beetle
Leaf Beetles (Family Chrysomelidae)
- Major Crop pests
- feed on several different plants within nightshade family
- Quickly develops resistance to insecticides

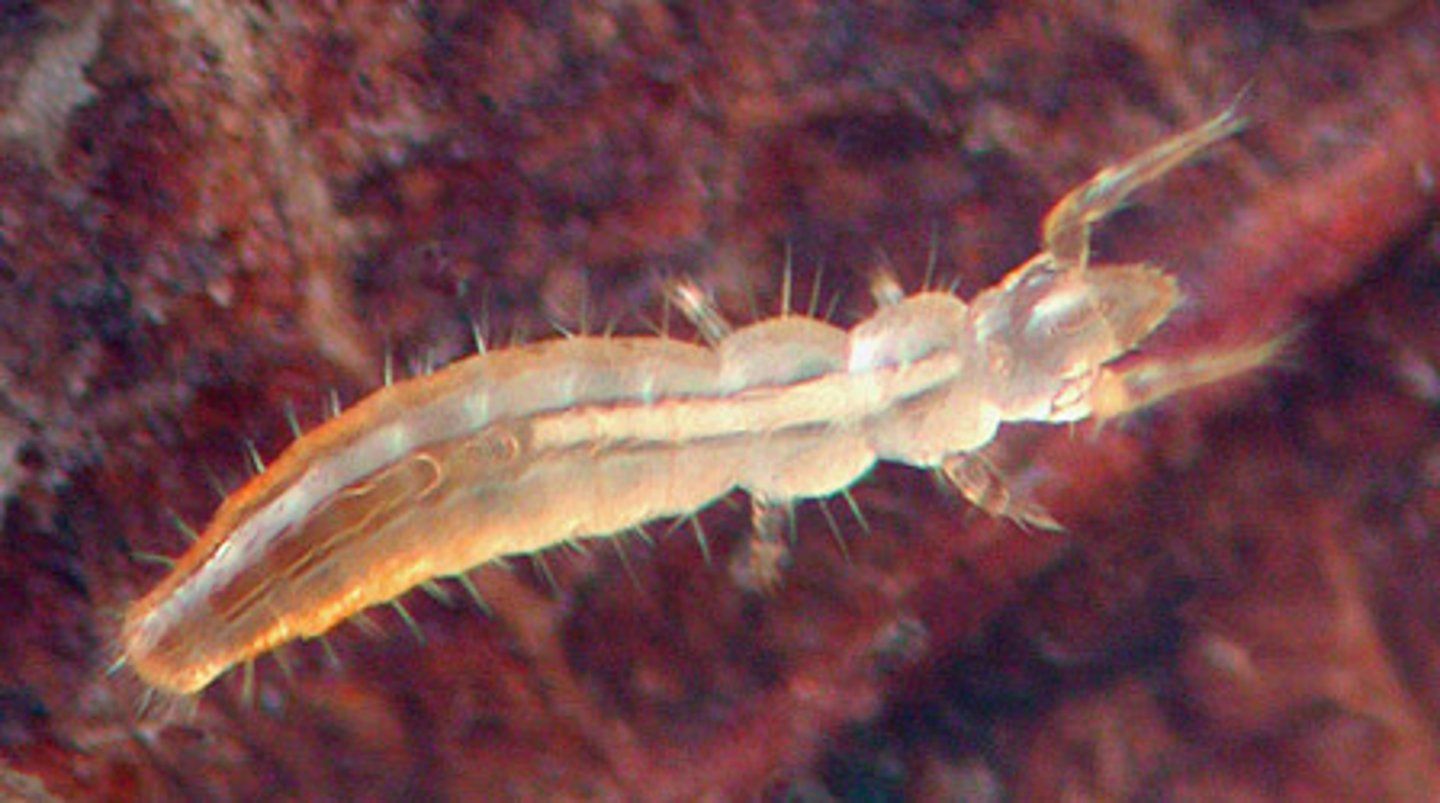
Protura
Entognatha hexapods
- very small (about 1mm long)
- "proto" (first, original), "ura" (tail): a name implying they have primitive physical features
- lacks antennae (unique among hexapods)
- first pair of legs are sensory
- eyes absent
- live in moist soil
- detritivores - feed on dead organisms material

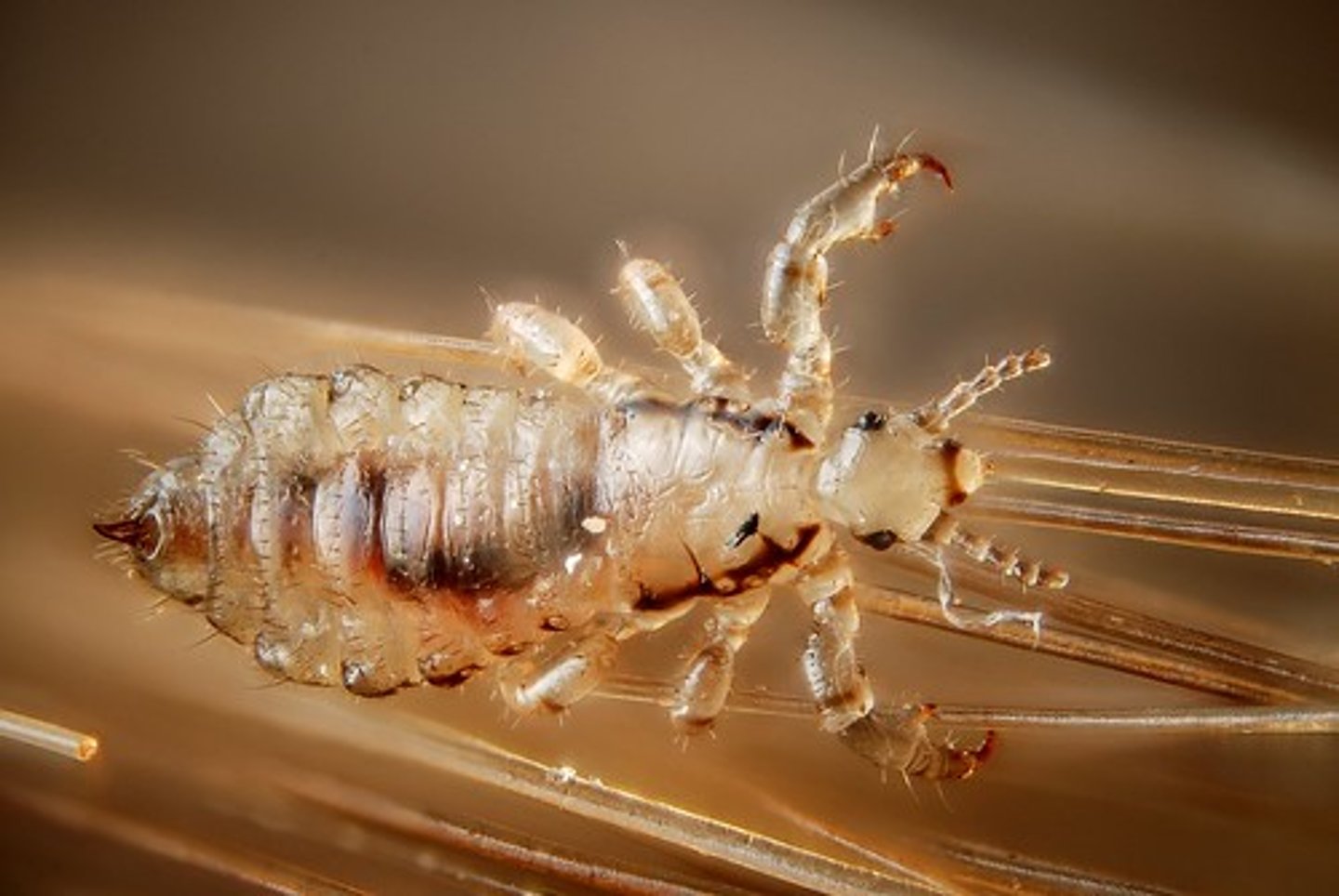
Psocodea
booklice, barklice
- feed primarily on fungi, algae, lichen, and organic debris in nature but also feed on starch-based household items like grains, wallpaper glue and book bindings
- generally prefer humid conditions
- chewing mouthparts

Pyrophilous
Loving fire; thriving in a habitat that recently has been burnt or attracted to recently burnet forests.
ex: Jewel Beetle Melanophila species
Scansorial leg
for clinging found on true lice Suborder Phthiraptera
Scarabaeoidea
Scarab beetles
- Brightly colored/metallic
- Mostly scavengers (as immatures)
- Distinctive antennae
lamellate antennae (layers of thin plates)

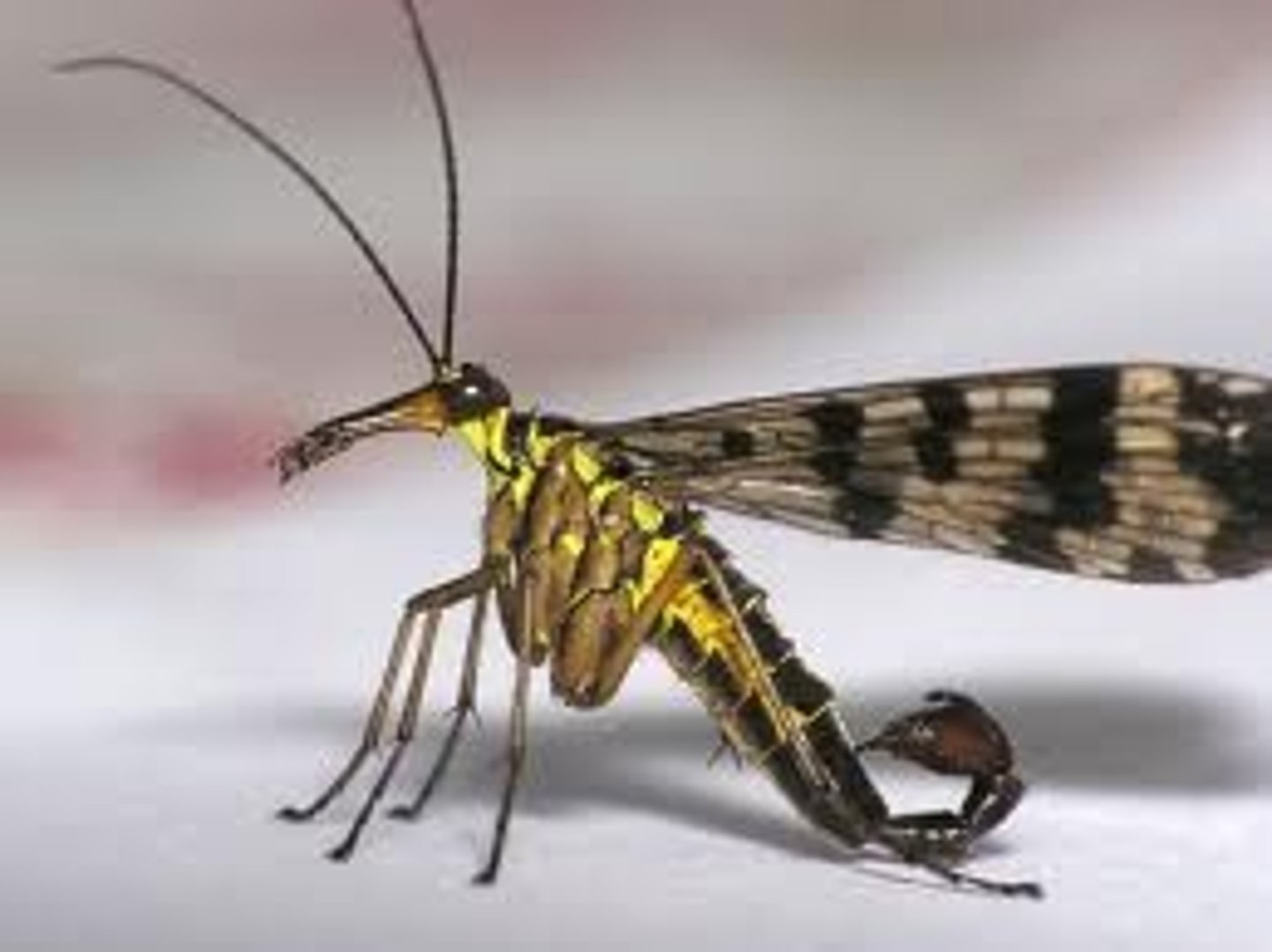
Scorpionflies
Mecoptera
- Male "scorpion" tail - enlarged genitalia
- Female lacks "scorpion" tail
- Nuptial gift by male -> in some species
- Hangingfly (mecoptera) -> resemble crane fly (absence of halteres)

Sound perception / production insects
Stridulation: katydids/crickets (wings) & grasshoppers (rub hind legs against edge of closed wings)
tymbals: cicadas
moths and beetles can detect the ultrasonic calls of bats
Crucial in courtship and most have distinct songs
Stridulation in Orthoptera
Grasshoppers rub hind legs against edge of closed wings
Katydids and crickets stridulate with wings only — can move while making sound
- Tympanal organ in katydid and cricket: front tibia
- Tympanal organ in grasshopper: first abdominal segment
Subimago
a stage in the development of some insects (such as the mayflies) between the nymph and imago in which the insect is able to fly but becomes mature only after a further molt
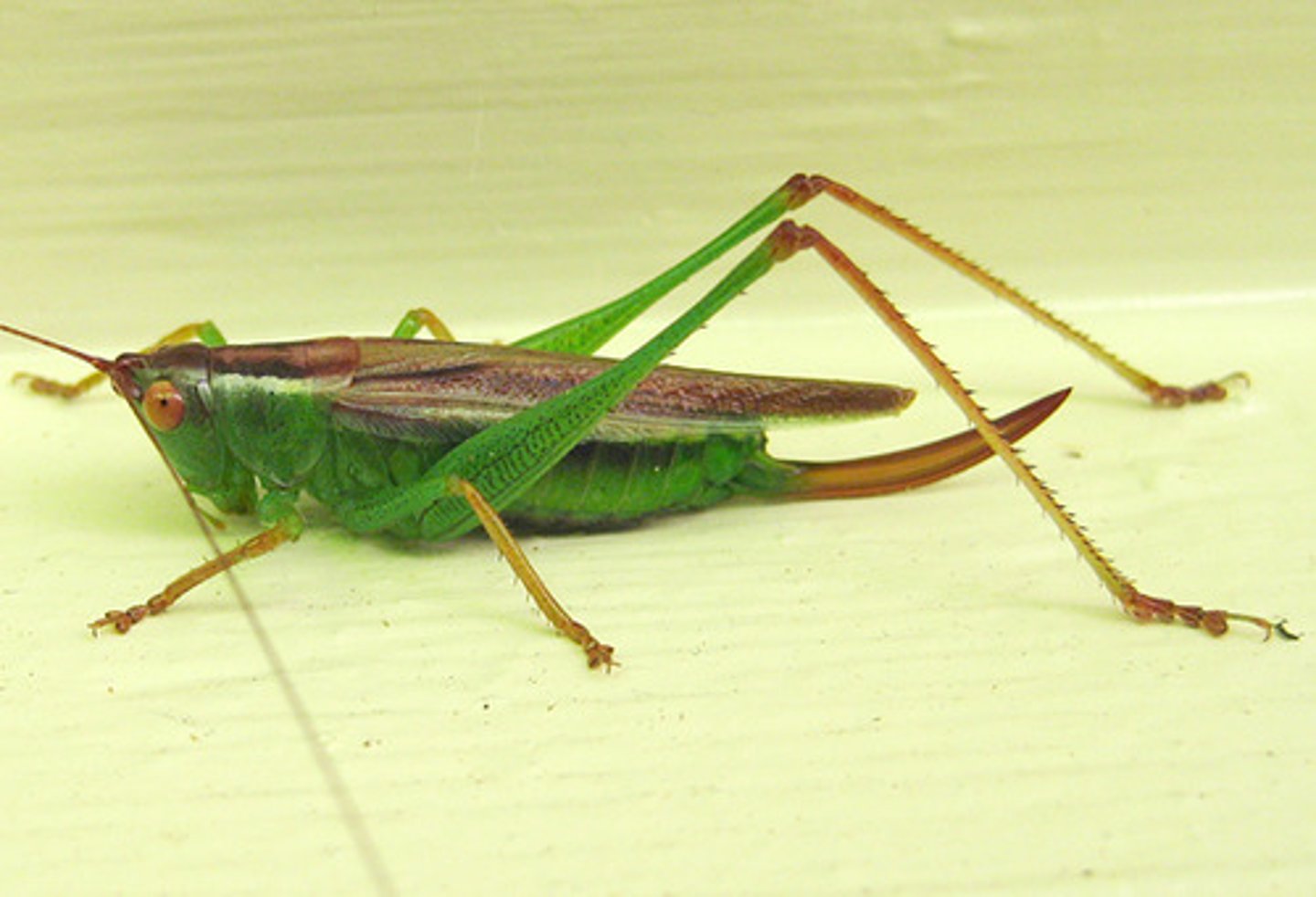
Tettigoniidae
Katydids

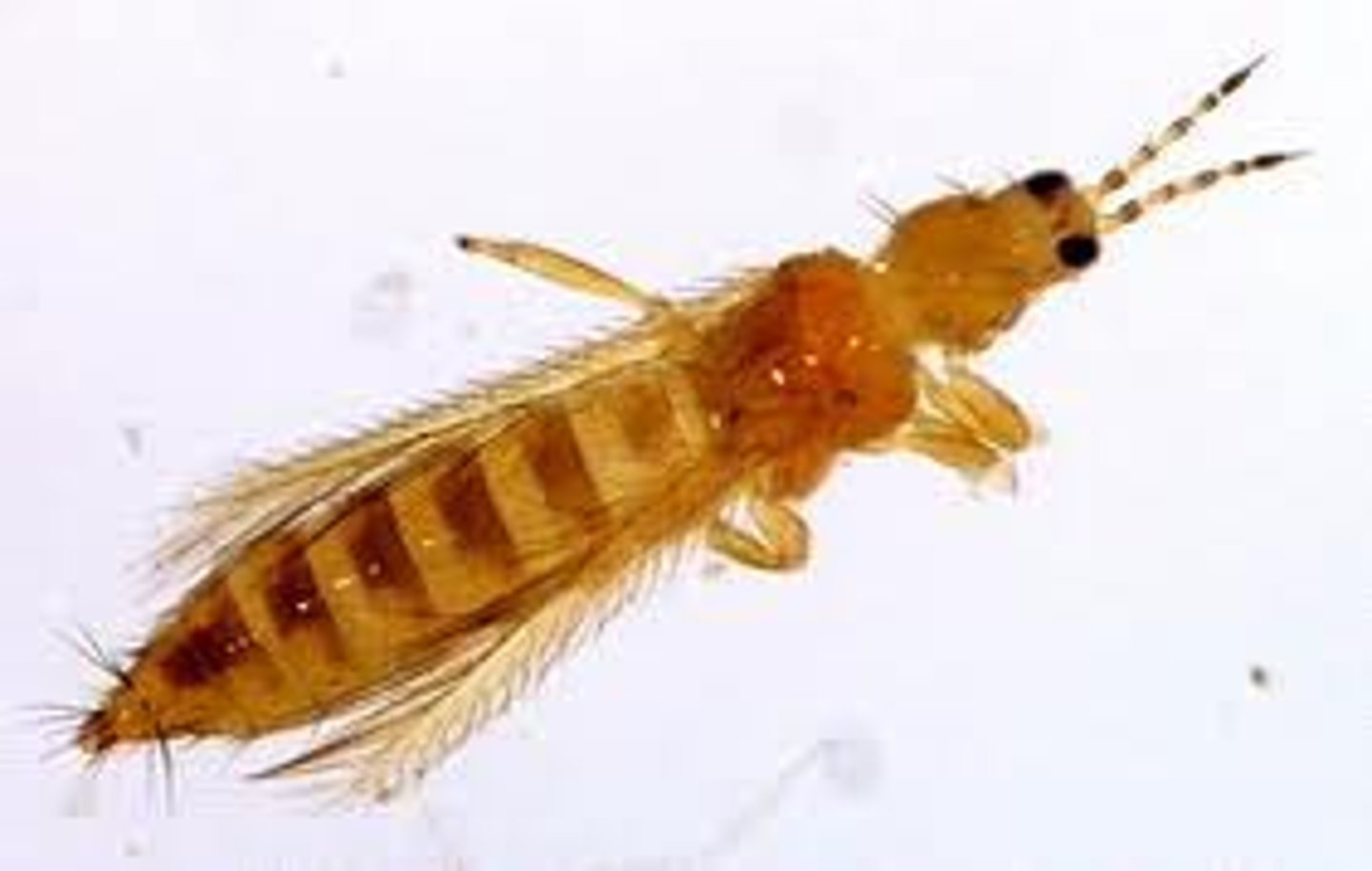
Thysanoptera
fringe (thysanos) wings (ptera) Thrips
short legs, narrow wings w/ long fringe of hairs
Asymmetrical mouthparts - only left mandible involved in forming a stylet along with maxillae (right mandible is reduced & non-functional)
Occasionally parthenogenetic
- Leaves small scar on fruits
- 2 nymphal stages and 2 non-feeding stages

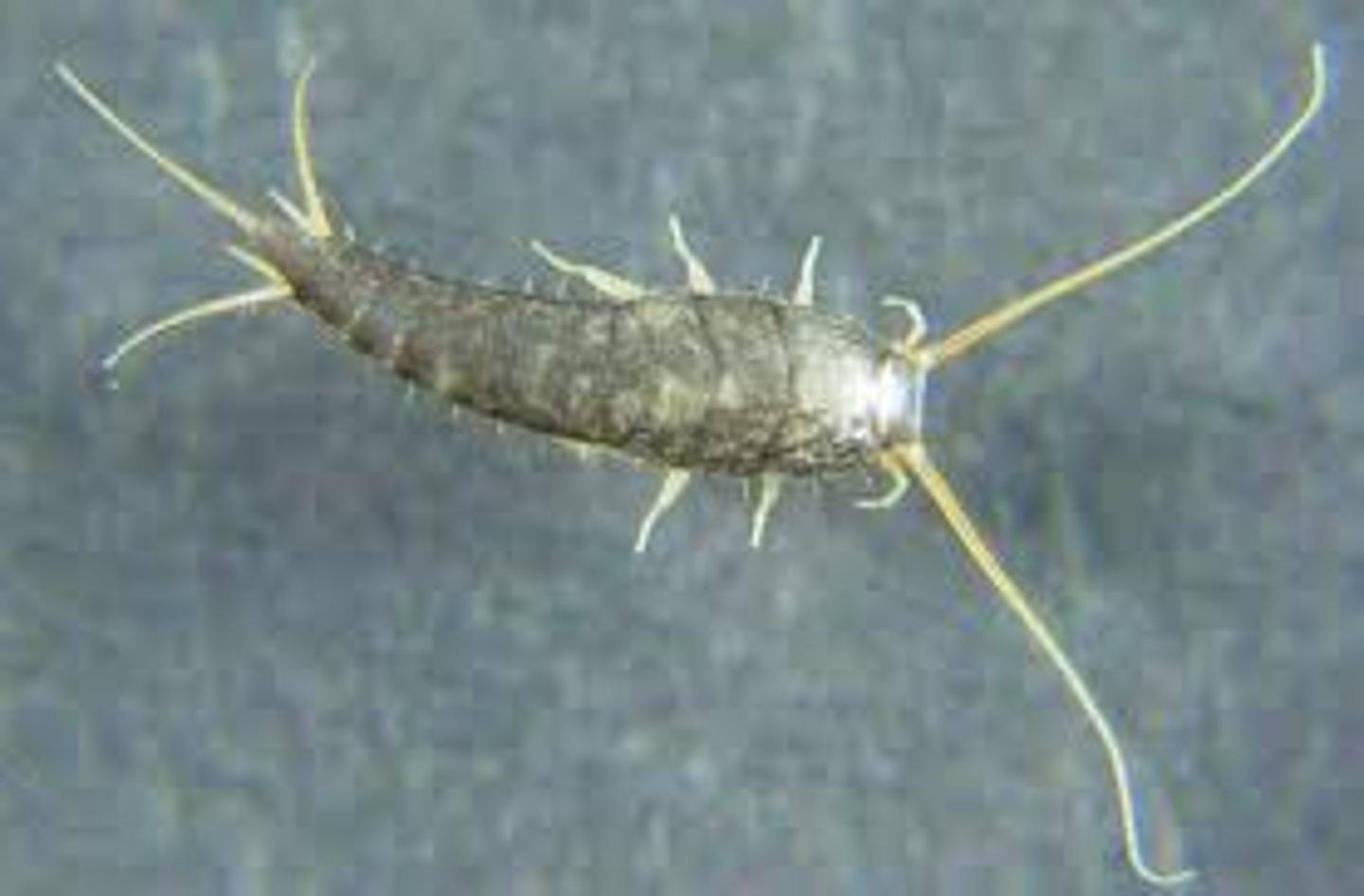
Thysanura
Silverfish
- Wingless
- Ametabolous development
- Long, paired abdominal cerci and a single median, tail-like caudal filament
- Compound eyes
- Indirect sperm transfer
- Found in decaying vegetation
- Some live inside of ant nest, probably scavenging the seeds collected by ants
- Can be household pests (eats paper)

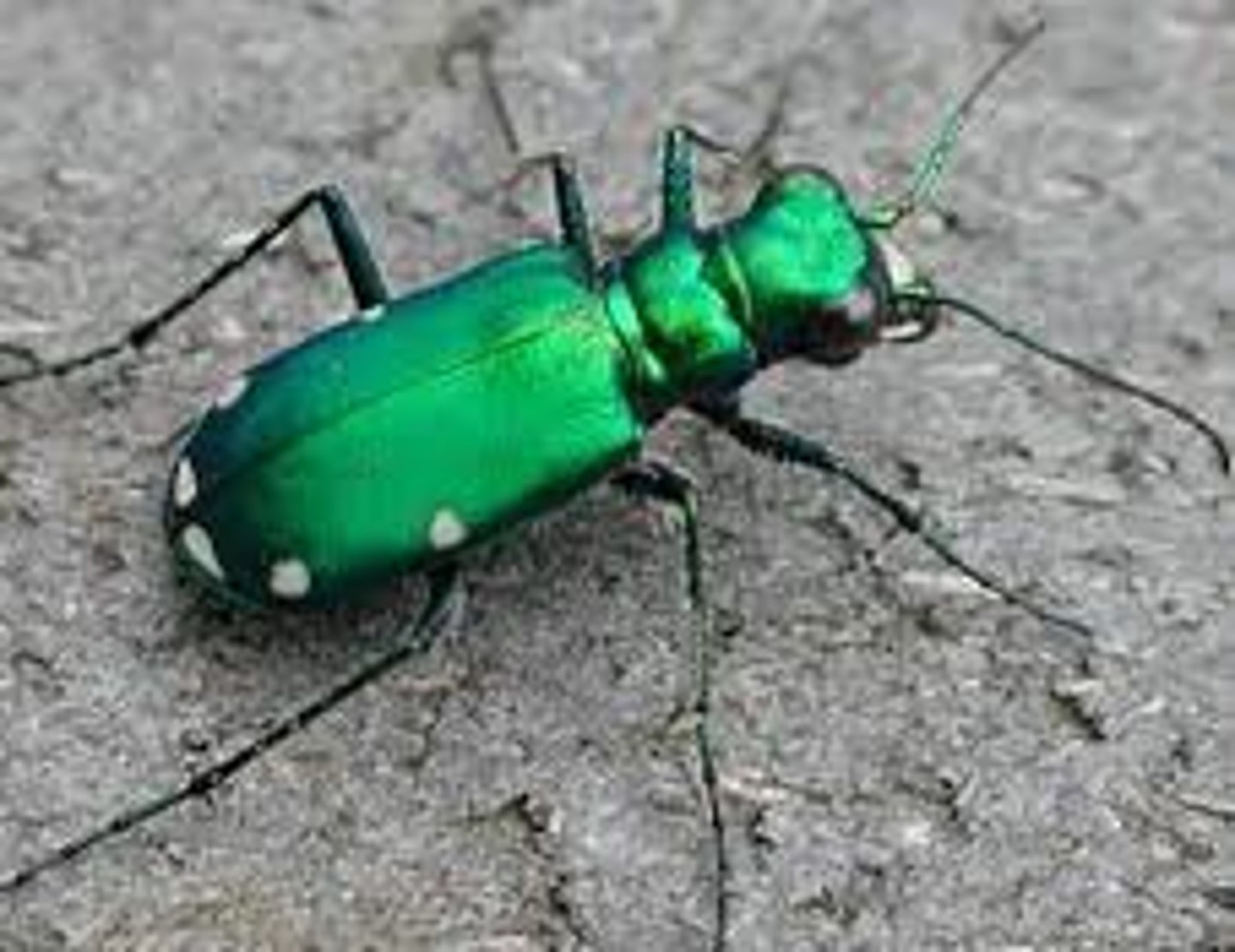
Tiger beetles
Family Carabidae
- Some are brightly colored
- Fast! up to 5.6 mph
- Hiding in tunnel in ground they built and wait for prey
- Anchored inside tunnel by their tail / visual hunter
- Secrete hot, noxious gas/liquid to deter predators

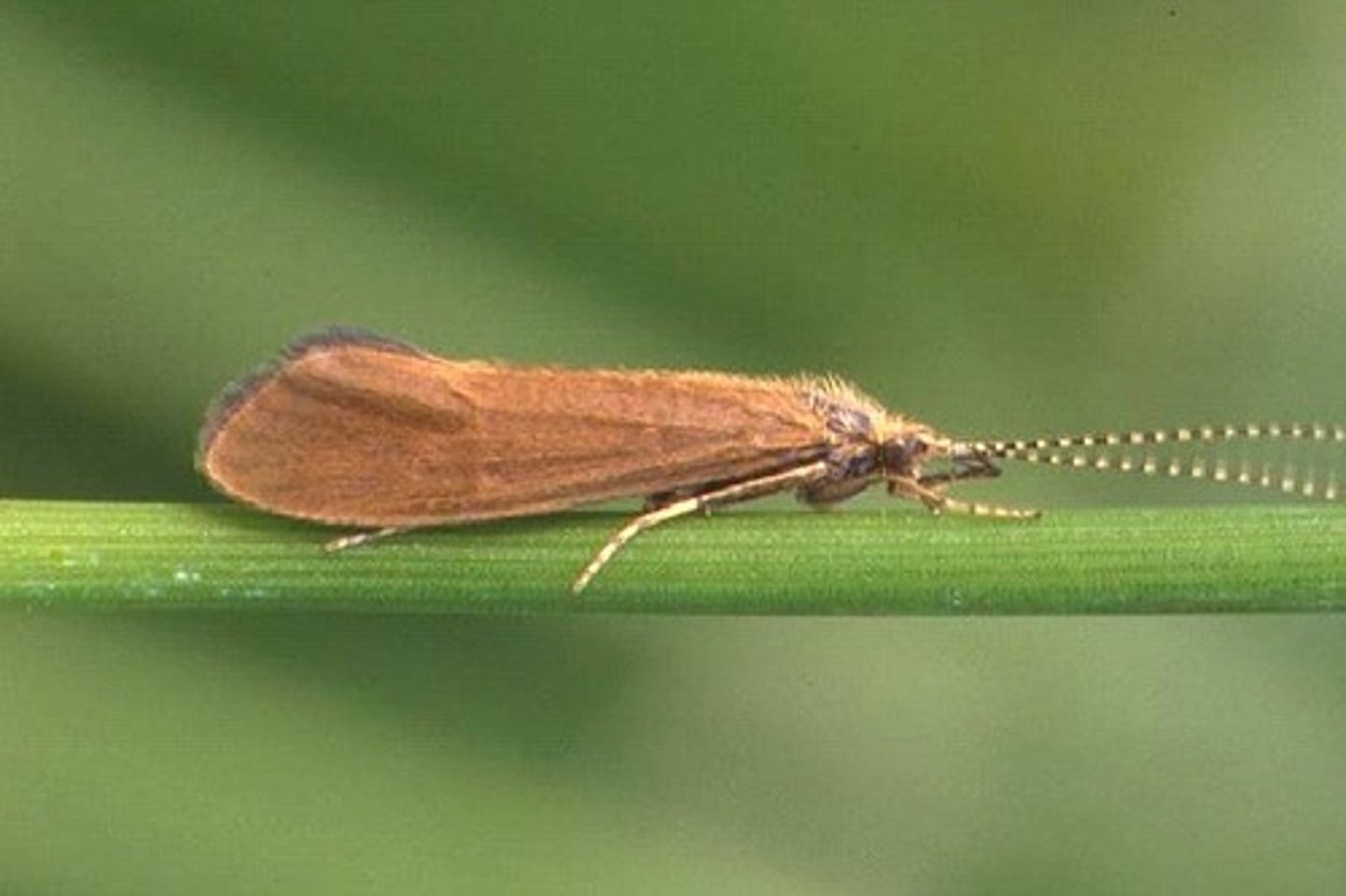
Trichoptera
Caddisflies
- Related to butterflies & moths (lepidoptera)
- Larvae have various feeding habits depending upon species (larval variability)
- Shredders/scrapers/collectors - larvae mostly feed on periphyton (layer of algae)

True bugs
Phylum Arthropoda
Subphylum Hexapoda
Class Insecta
Order Hemiptera
Tympanal organs of insects
Tympanal organ in katydid and cricket: front tibia
Tympanal organ in grasshopper: first abdominal segment
Moths and beetles: on the thorax or abdomen
Tymbals in cicada
- on sides of the abdominal segments
- found in males to attract mates

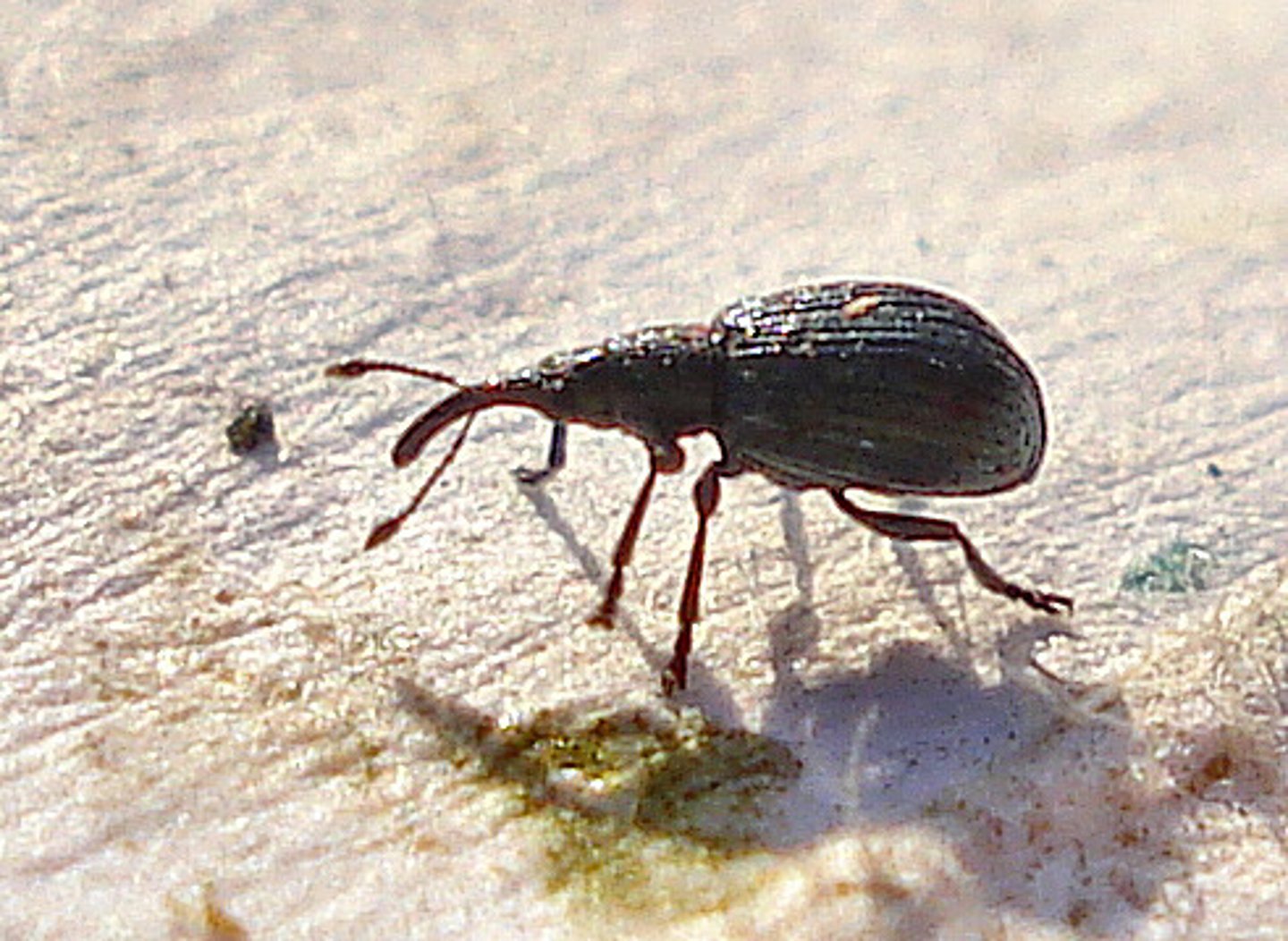
Weevils
Family Curculionidae
- One of the largest animal families in existence (>80K species)
- Distinctive morphology!
- Long snout and geniculate antennae
- Serious pests w/ narrow host range
Boll Weevil: Major pest of cotton

Whirligig beetle
Family Gyrinidae
Gregarious aquatic beetles
"two pairs" of eyes : above + below water
Good fliers
Keep air bubble under elytra for aquatic respiration
Larvae and adults predacious

Wood boring beetles
Many families eat and destroy wood - either as larvae or adults (xylophagous)
- Consume wood (cellulose)
Ecological roles: forest turnover, nutrient recycling
