Chemistry - Greenhouse Effect and Fossil fuels
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is a fossil fuel/ types of fossil fuels
coal, (crude)oil and natural gas
how are fossil fuels formed?
slow and partial decomposition of plant and animal matter in the absence of oxygen
what do living matters contain that are useful? (they get reduced under pressure)
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen
what is crude oil
a complex mixture of different hydrocarbons including:
mainly saturated alkanes
straight-chained and branch chained hydrocarbons
cycloalkanes
why is sulfur dangerous?/why do we need to remove sulfur from crude oil?
it releases sulfur dioxide when combusted that can lead to acid rain
it can ‘clog up’ further reactions
how to remove sulfur?
desulfurisation
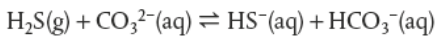
what are some disadvantages of coal
it contains a lot of extra pollutants
produces CO2 and SO2 particulates(electrostatic preceptors can remove these)
it is difficult to transport - solid
waste can lead to visual and chemical pollution
mining is dangerous
what are some advantages of coal?
cheap and plentiful
can be converted to synthetic liquid fuels and gases
ash produced can be used in making roads
what are some advantages of crude oil?
easily transported in pipelines or tankers
convenient fuel for use in cars as volatile and burns easily
sulfur impurities are easily removable
what are some disadvantages of crude oil?
limited lifespan and uneven world distribution
contributes to acid rain and global warming
transport can lead to pollution
carbon monoxide is a local pollutant produced by incomplete combustion of gasoline in internal combustion engines
photochemical smog produced as secondary pollutant due to reactions of primary pollutants(nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons) released from internal combustion engines
natural gas
produces fewer pollutants per unit energy
easily transported in pipelines and pressurised containers
does not contribute to acid rain
higher specific energy
what are some disadvantages of natural gas?
limited supply
contributes to global warming
risk of explosion due to leaks
whar are renewable energy sources?
naturally replenished on a human time scale - at a rate faster than it is used
what are non-renewable energy sources?
finite
how to choose the best energy source?
releases energy at a reasonable rate
produces minimal pollution
efficient conversion of energy
cheap, plentiful and readily available
what is a fuel?
a substance that can release energy by changing its chemical or nuclear structure
standard enthalpy change of combustion
enthalpy change when one mole of fuel is combusted completely in excess oxygen
what are the advantages of biofuels?
renewable
not a significant impact to pollution
safer to produce than coal
waste can be turned into biogas
what are the disadvantages of biofuels?
land could be used for other things
fertilisers may run off and pollute water
removes nutrients from soil and causes erosion
only occurs at a small scale at present time
why is change H = mcT/mol not good to use for fuel?
need to think about storage and transport - use mass instead of moles