Ecology Exam #2 Review
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
population
a group of interbreeding individuals of the same species occupying a particular space at the same time
density
the number of individuals per unit area
growth rate
= (B + I) – (D + E)
immigration
an animal establishes a home in a habitat because it has resources it can utilize or because the habitat is ideal for them; and animal enters an area
emigration
an animal leaves its home because the habitat is no longer ideal for them and they need to find a more suitable environment
size
the total number of individuals in the population
age structure
the number of individuals in each age group
distribution pattern
how individuals are distributed in space
random
clustered (clumped)
regular (uniform)
modules
clones (groups of ramets)
genet
derived from individual zygote; difficult to age
ramets
disconnect over time; each asexually originating part of the genet
crude
___________ density ecompasses all land
ecological
_____________ density ecompasses the land that can actually be colonized by the organism
true
(true or false) population density tends to be greater for smaller organisms
density dependent
those factors limiting population growth which express themselves as a function of population size (disease, predation, competition)
density independent
those factors limiting population growth which are independent of population size (fire, earthquake, habitat fragmentation)
range
The sum of the tolerance limits for each environmental factor determines the ________ of habitats that a species can grow in.
niche
the multidimensional description of species with all aspects of its biotic and abiotic environmental requirements
range
the geographic extent over which a population exists
subpopulation
a local population of a species
metapopulation
a collection of local subpopulations
fundamental niche
a physical condtion under which a species might live
realized niche
a condition in which we actually see an organism live
random
a type of distribution pattern in which individuals have an equal probability of occuring anywhere in an area; they have neutral interactions
regular
a type of distribution pattern in which individuals are uniformly spaced through the environment; antagonistic interactions and compete for resources
clumped
a type of distribution pattern in which individuals live in areas of high local abundance, which are separated by areas of low abundance; individuals are attracted to a common resource
variance
mean used to indicate distribution type
clumped/clustered - variance > mean
random - variance = mean
regular/uniform - variance < mean
regular
variance < mean
clumped
variance > mean
random
variance = mean
population size
the following equation measures ___________ _____
M/N = m/n
M: number of marked individuals (=size of the first sampling)
m: number of marked individuals recaptured in a second sample
N: estimate of population size
n: total number of individuals captured in a second sample (=size of the second sample)
correction factor
Since mark-recapture assumptions are not always met, there is bias in estimates… this requires a __________ ______.
correction factor
the equation that measures ________ _______ is:
M/N = (m+1)/(n+1)
mark-recapture technique
Animals are captured and marked/photographed
animals are released
subsequent samples are taken
number originally seen (marked) are noted
equation is used to estimate population size
false
(true or false) all individuals in a population do not have an equal and independent chance of being captured (mark-recapture assumption)
true
(true or false) immigration, emigration, births and deaths should NOT significantly alter the proportion of marked and unmarked individuals in the population (mark-recapture assumption)
true
(true or false) marked animals behave in the same way, have an equal chance of being captured, and are not subject to more/less mortality than unmarked individuals (mark-recapture assumption)
false
(true or false) marked animals do not distribute themselves randomly among unmarked animals (mark-recapture assumption)
true
(true or false) animals that are marked will retain their marks (mark-recapture assumption)
100
approximately ______ (number) species go extinct each day
deterministic extinction
change occurs within an environment and organisms cannot escape
stochastic extinction
random fluctuations in population size or environment severely reduce population size; a process with random elements and thus not predictable with complete accuracy
generalist
an organism with a broad habitat tolerance
specialist
an organism with a narrow habitat tolerance
population status
______________ ________ can be interpreted through geographic range, habitat tolerance, and local population size
passenger pigeon
The __________ _________ had numbers in the billions, a notoriously narrow habitat tolerance, was common to the Eastern US, and was made extinct within 9 years.
immigration
movement into an area, increases population
emigration
movement out of an area, decreases population
population equation
N(t+1) = Nt + B + I – D - E (note that italics should be subscripts)
N(t+1) : population density at time t+1
Nt : population density at time t
B: births
I: immigration
D: death
E: emigration
food
Numbers of kestrels and owls seeem to closely track vole populations. This is an example of ______ induced dispersal.
climate
Following glaciation, North American trees dispersed north. This is an example of ________ induced dispersal.
adaptations
Many invertebrates that use dispersal by drift in streams employ __________ to resist downstream displacement.
Examples:
streamline body
sticky secretions
ballast and retreats
burrowing
oviposition behavior
metapopulations
__________________ arise through dispersal of individuals among subpopulations
cohort life table
indentifies individuals born at the same time and keep records from birth
static life table
records the age at death of individuals
age distribution
calculates the difference in proportion of individuals in each age class; assumes difference from mortality
life table
analyzing a _________ ________ provides a means to study probabilities of survival, ages most vulnerable, and population growth
cohort
a group of individuals born at the same time
natality
birth of new individuals = birth rate
physiological natality
maximum possible under ideal conditions, biological limit
realized natality
the actual rate of births
crude birth rate
#1000/time (in terms of births)
specific birth rate
# of births for specific age group of females
crude death rate
# dying/1000/time
probability of dying
# dying / # beginning
probability of survival
# survival / # beginning
life expectancy
the average number of years a newborn is expected to live
true
(true or false) assessing tooth wear, plumage changes, growth rings in teeth, horns, otoliths, & shells, DBH of tees and shrubs, and annual rings on trees and shrubs are all ways of measuring the age of individuals
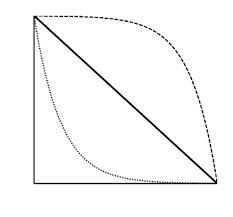
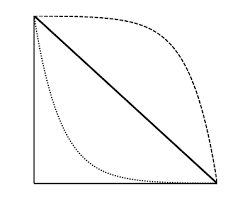
type I
the top line is an example of ________ ___ survivorship; this is consistent with high juvenile survival and th emost mortality occurs among older individuals
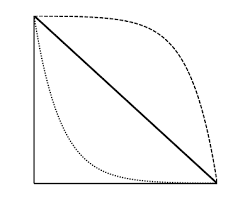
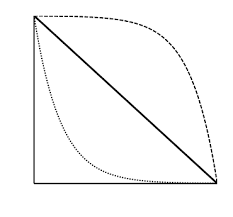
type II
the middle line is an example of ________ ____ survivorship; organisms with this survivorship die at equal rates regardless of age
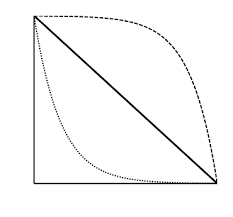
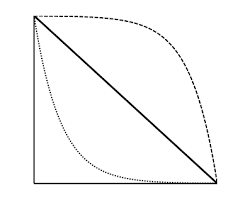
type III
the bottom line is an example of _______ ____ survivorship; high juvenile mortality rate, but much lower death rates later in life
stable
_________ age distribution is when the ratio of each age group is approximately the same
stationary
_____________ age distribution is when a population is not growing
x
age class (in life table analysis)
nx
number of surviving to age class x (life table analysis); “x” should be a subscript
Ix
survivorship, proportion surviving to age class x (life table analysis); “x” should be subscript
bx
also mx, birth rate, the average number of offspring produced per individual in age x (life table analysis); “x” should be subscript
dx
number of dying within each age class x (life table analysis); “x” should be subscript
qx
age specific mortality rate (life table analysis), percent of dying between age x and age x+1; “x” should be subscript
sx
proportion surviving to the next age class (life table analysis); “x” should be subscript
Lx
average number alive during the interval (life table analysis); “x” should be subscript
Tx
the total years all individuals live into future (life table analysis); “x” should be subscript
ex
life expectancy for each age class (life table analysis); “x” should be subscript
R0
net reproductive rate (life table analysis); the average lifetime number of female offspring produced by an individual female in population in her lifetime; “0” should be subscript
generation time
average time from fertilized egg to fertilized egg/seed to seed
r
per capita rate of increase or intrinsic rate of increase; equals per capita birthrate minus per capita death rate (b-d) or (lnR0)/T for life table
geometric rate of increase
λ; the ratio of the population size at two points in time
stable population
for net reproductive rate, values = 1.0, indicates a __________ ____________
growing population
for net reproductive rate, values > 1.0, indicate a __________ ____________
decreasing population
for net reproductive rate, values < 1.0, indicates a __________ ____________
stable
if r = (b-d) = 0, population is _____________
increasing
if r = (b-d) > 0, population is ____________
decreasing
if r = (b-d) < 0, population is ________________
per capita rate of increase
( r ) when reproduction is continuous and generations overlap
Where:
r<0 : population decreases
r=0 : population stable
r>0 : population increases
geometric increase
(λ) when reproduction is discontinuous and generations do not overlap
Where:
λ < 1 : population decreases
λ = 1 : population stable
λ > 1 : population increases
generation time
(Σ x lxmx)/Ro
geometric
_____________ population growth; generations do not overlap and the ratio of number of individuals at time (t+1) to the number of individuals at time (t) is always that same; abundant resources
exponential
_____________ population growth; j-shaped pattern is produced, very rapid growth (unrestricted growth)
logistic
____________ population growth; produces sigmoidal or s-shaped growth (restricted growth)
carrying capacity
K, the number of individuals of a population the environment can support