Bot-Lab (Sem-1) - Chapter 14: The Leaf
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
leaf
main photosynthetic organ of plants; often described as flattened, laterally spread and green
xylem
water-conducting tissue
phloem
food-conducting tissue
chlorenchyma
photosynthetic parenchyma; strategically located within the blade in the mesophyll layer
mesophyll
the layer in which chlorenchyma cells can be found
dorsi-ventral leaf
leaves where stomata are confined to the lower epidermis
isobilateral leaf
leaves where stomata are on both the lower and upper epidermis
Poaceae
grass family
Fabaceae
legume family
Malvaceae
cotton family
leaf morphology
based on the foliage leaf; highly variable across major plant groups
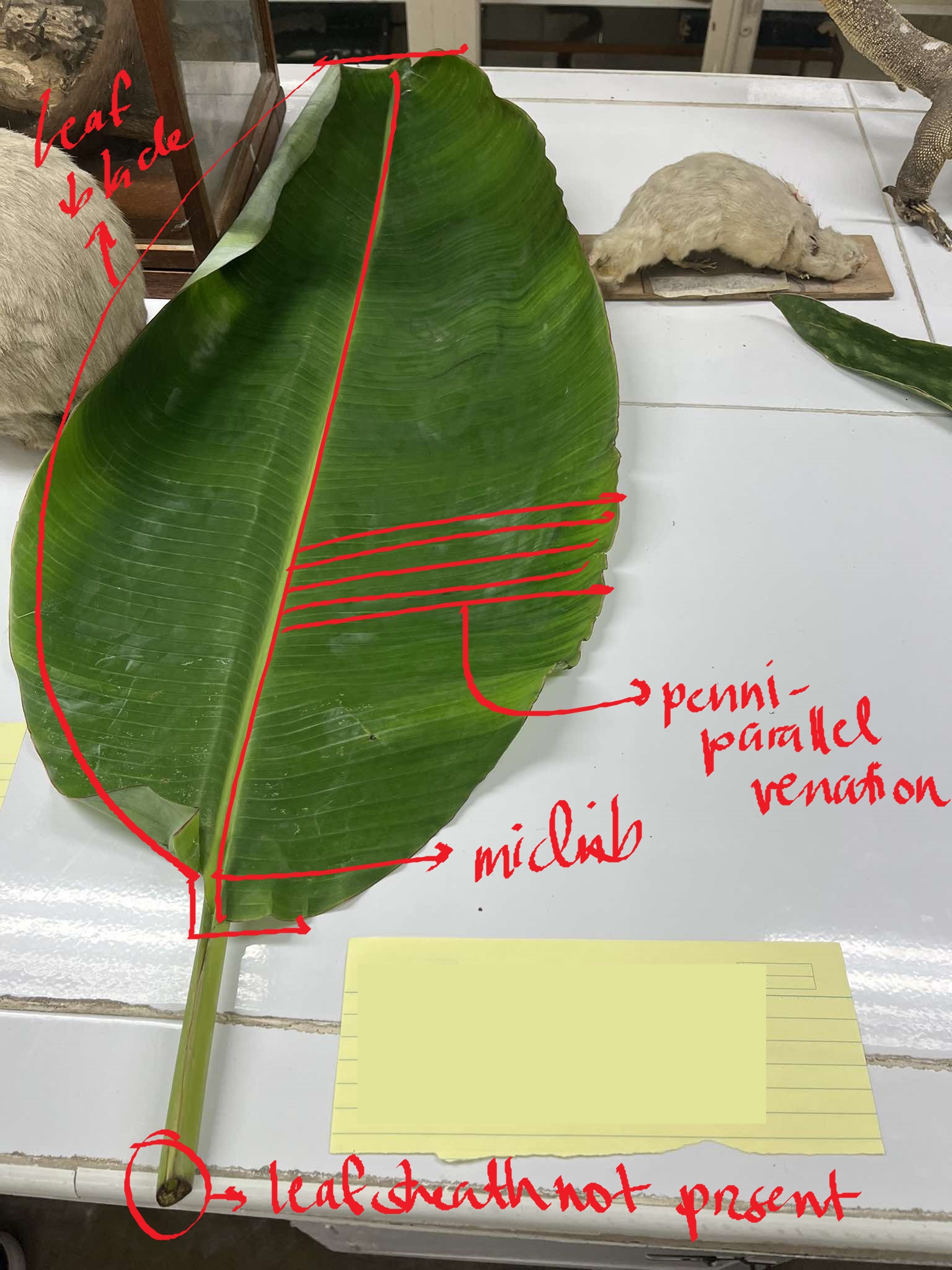
leaf blade/lamina
flat, light-harvesting portion of the leaf
abaxial surface
the blade’s lower side/dorsal surface
adaxial side
the blade’s upper side/ventral surface
midrib
the large central vascular tissue of the leaf
midvein
other term for midrib
veins
arise from the midrib and supply the blade
petiole
the stalk that attaches a leaf to the node of the stem
sessile
leaf without a petiole
monocot leaf
characterized by parallel venation
simple parallel venation
the veins run alongside each other from the base to the tip
leaf sheath
a clasping sheath that attaches the monocot leaf to the stem; base attachment encircles the whole stem, hence, ring-like nodes
Bambusa sp.
bamboo

penni-parallel venation
veins are arranged on both sides of the midrib in parallel direction like barbs of feathers
Musa sp.
banana
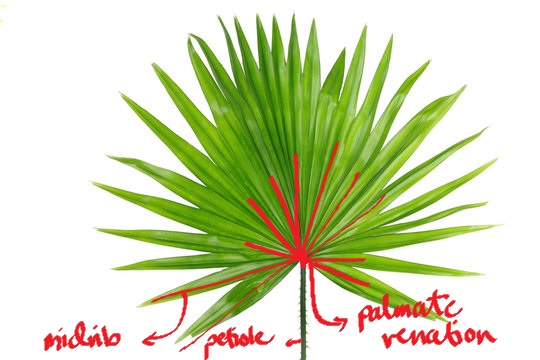
(parallel) palmate venation
veins arise from a common point and radiate in a parallel fan-shape fashion to the tip
Sanbus rotundifolius
anahaw
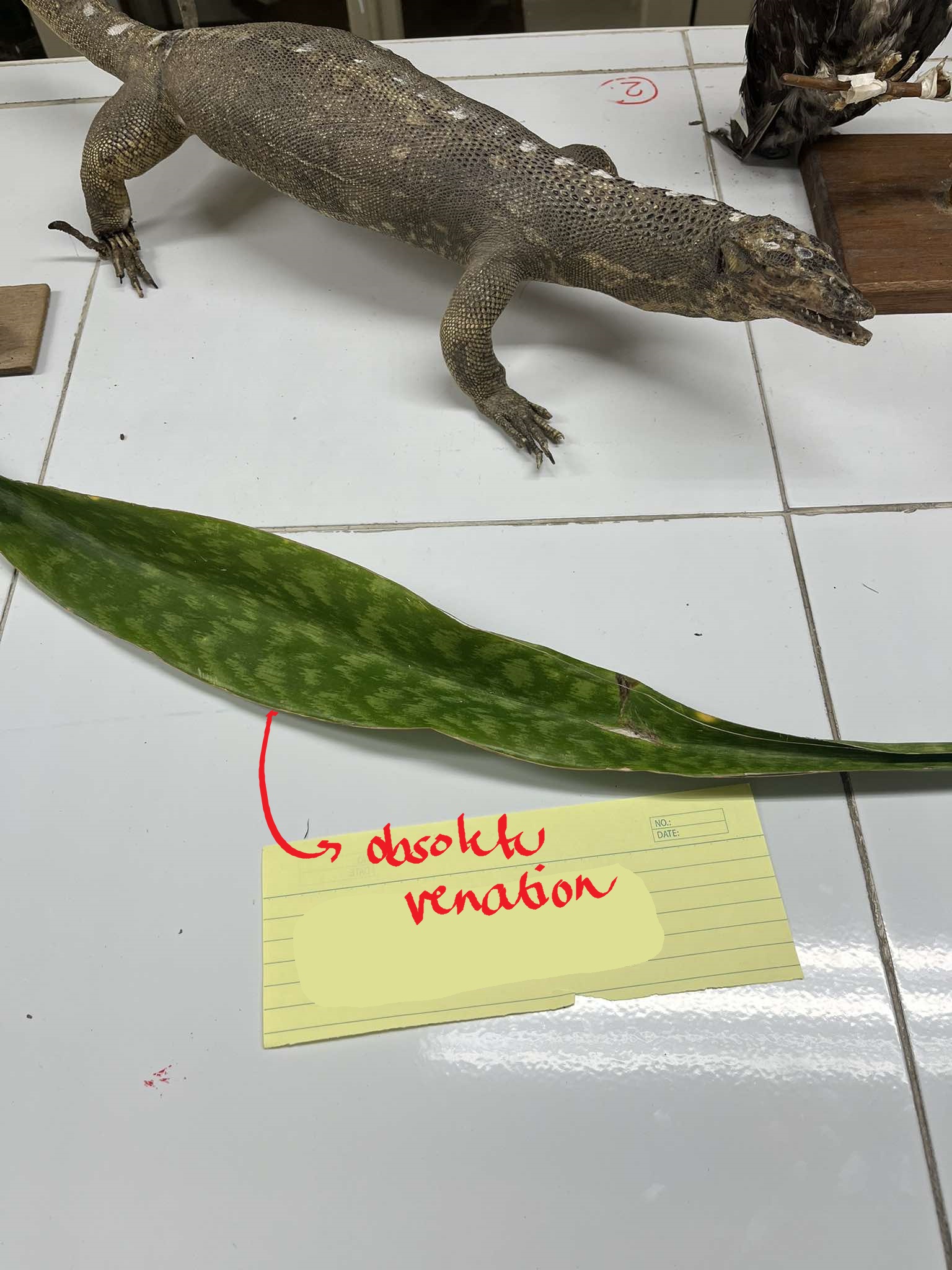
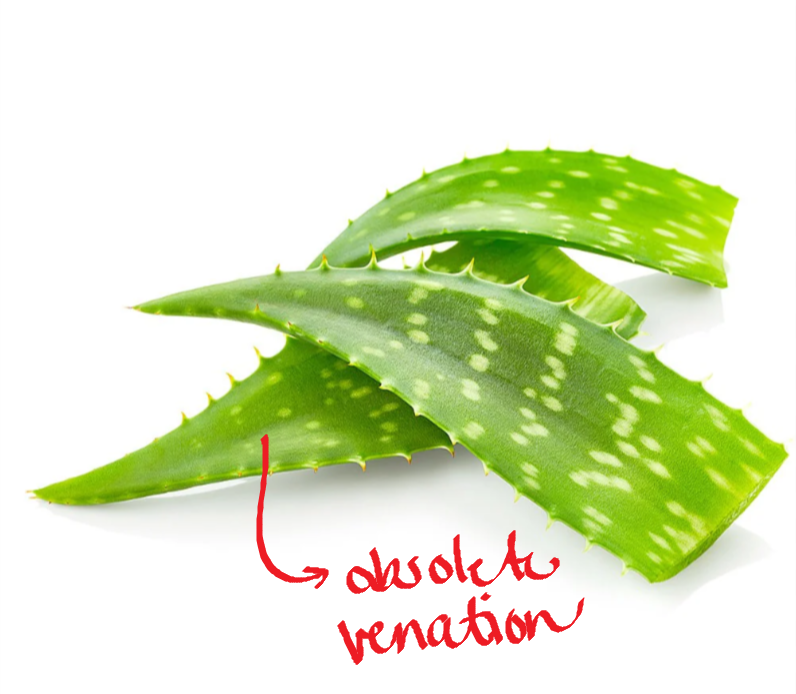
obsolete venation
mostly observed in succulents; veins are not visible
Sanseveria sp.
snake plant

Aloe vera
leaf spines; succulent leaves; sabila
eudicot leaf
a type of leaf with netted venation
stipules
two small flaps of tissue at the base of the petiole
netted venation
branching/reticulate veins arise from one large midrib
Psidium guajava
opposite phyllotaxy; guava

(netted) palmate venation
netted veins that arise from the base of the midrib
Carica papaya
papaya

simple leaf
consists of a single unincised blade/incised incision does not reach up to the midrib
compound leaf
made up of several leaflets; incisions reach up to the midrib or to the tip of the petiole; leaflets are ALWAYS arranged in two rows and never in spiral, whorled, or decussate phyllotaxy
petiolule
the “stem” that attaches the leaflet to the primary rachis
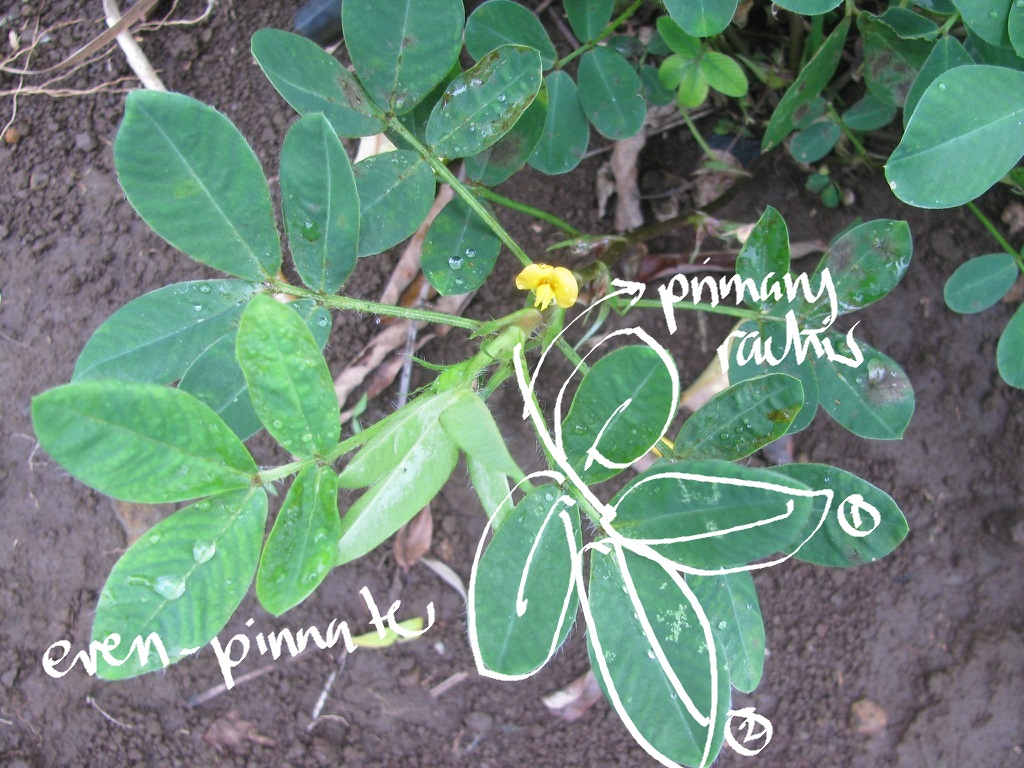
primary rachis
an extension of the petiole of a compound leaf that bears the leaflets; never have a terminal bud
secondary rachis
branches of the primary rachis
tertiary rachis
branches of the secondary rachis
pinnately compound; palmately compound
types of compound leaf
pinnately-compound leaf
the lamina is incised up to the midrib which gets modified into a rachis bearing leaflets laterally
unipinnate; bipinnate; tripinnate
types of pinnately compound leaves
unipinnate
leaflets arise on the primary rachis; even-pinnate if the number of leaflets is in even number; odd pinnate if the number of leaflets is odd
even-pinnate
a unipinnate leaf with 2 terminal leaflets
Cassia alata
candle bush; asunting

Arachis hypogea
peanut
odd-pinnate
a unipinnate leaf with 1 terminal leaflet
Rosa sp.
rose

bipinnate
type of pinnately compound leaf when the primary rachis branch one and leaflets arise from the secondary rachis
Delonix regia
firetree
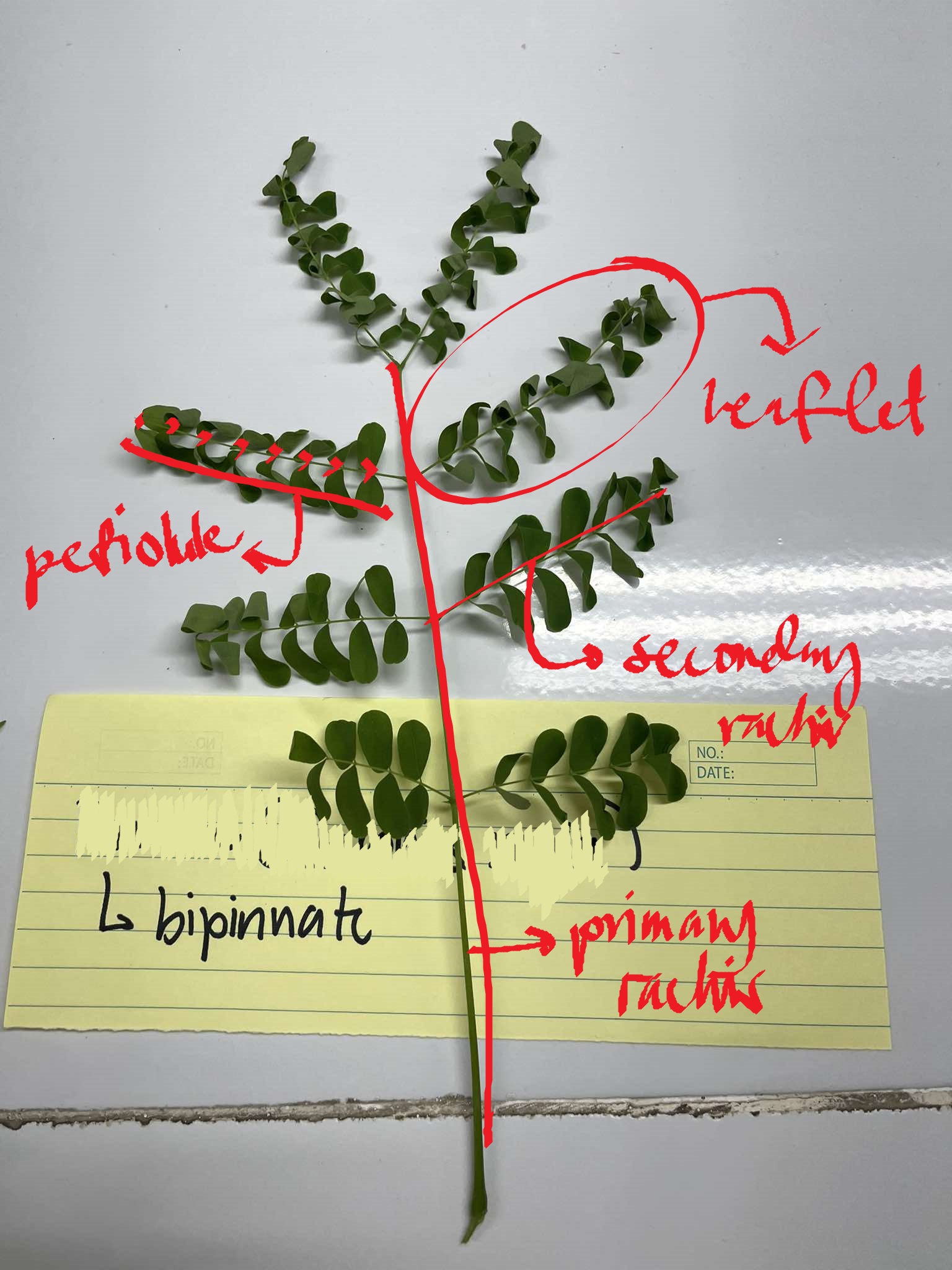
Leucaena leucocephala
ipil-ipil
tripinnnate
type of pinnately compound leaf when the secondary rachis branches and the leaflets arise from the tertiary rachis
Moringa oliefera
malunggay

palmately compound leaf
all the leaflets arise from a common point; becomes incised up to the petiole; leaflets appear like articulated fingers
unifoliolate; bifoliolate; trifoliolate; quadrifoliolate; pentafoliolate; multifoliolate
types of palmately compound leaf
unifoliolate
palmately compound; a single leaflet; two lateral leaflets are suppressed and only the central leaflet becomes functional
Citrus sp.
pomelo

bifoliolate
palmately compound; with double leaflet
Pyrostegia venusta
flametree
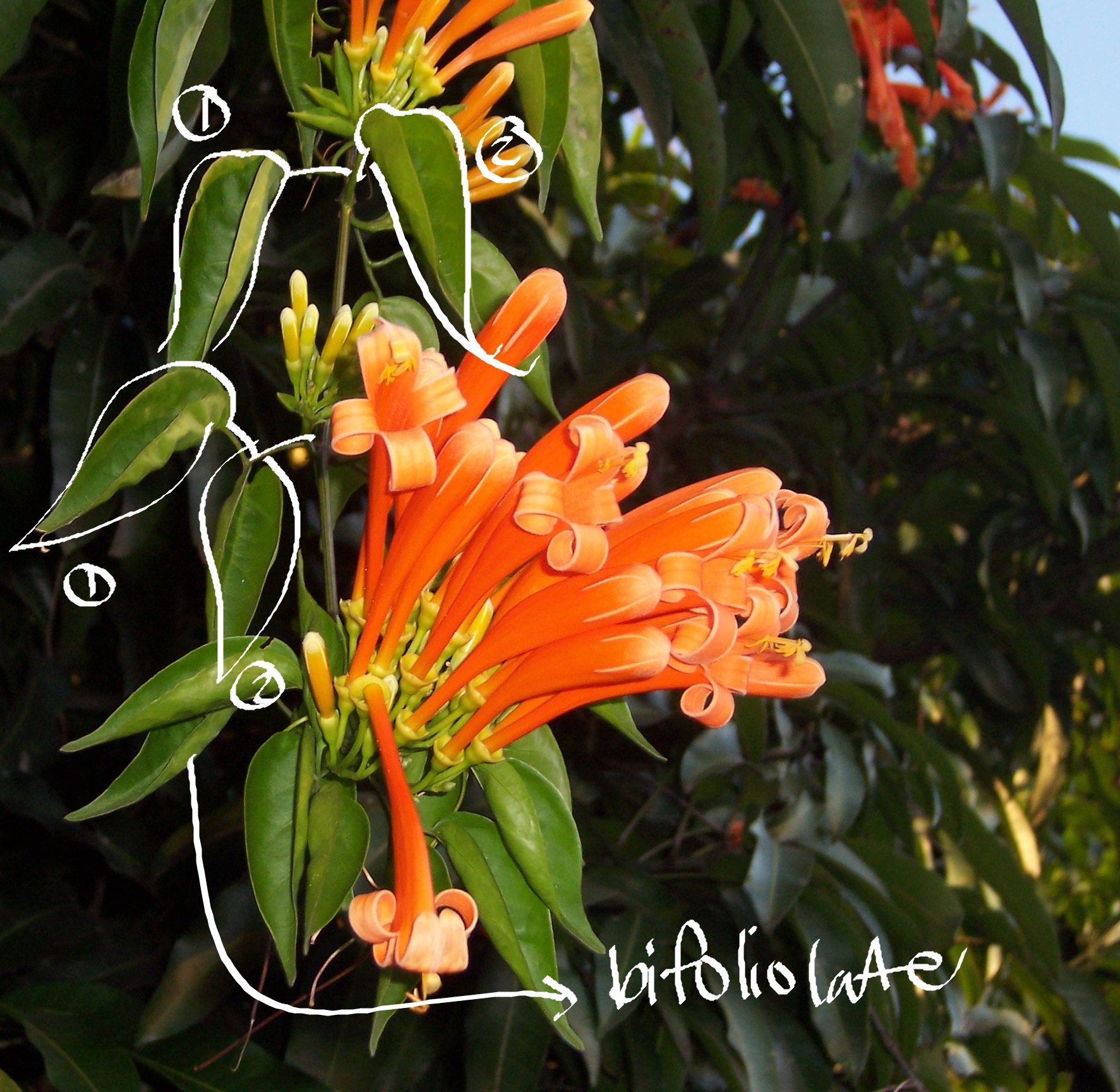
Phaseolus sp.
bean
trifoliolate
palmately compound; with triple leaflets
Erythrina variegata
dapdap

quadrifoliolate
palmately compound; with four leaflets
Marsilea sp.
water clover

pentafoliolate
palmately compound; with five leaflets
Schefflera sp.
lima-lima

multifoliolate
palmately compound; more than five leaflets
Ceiba pentandra
kapok

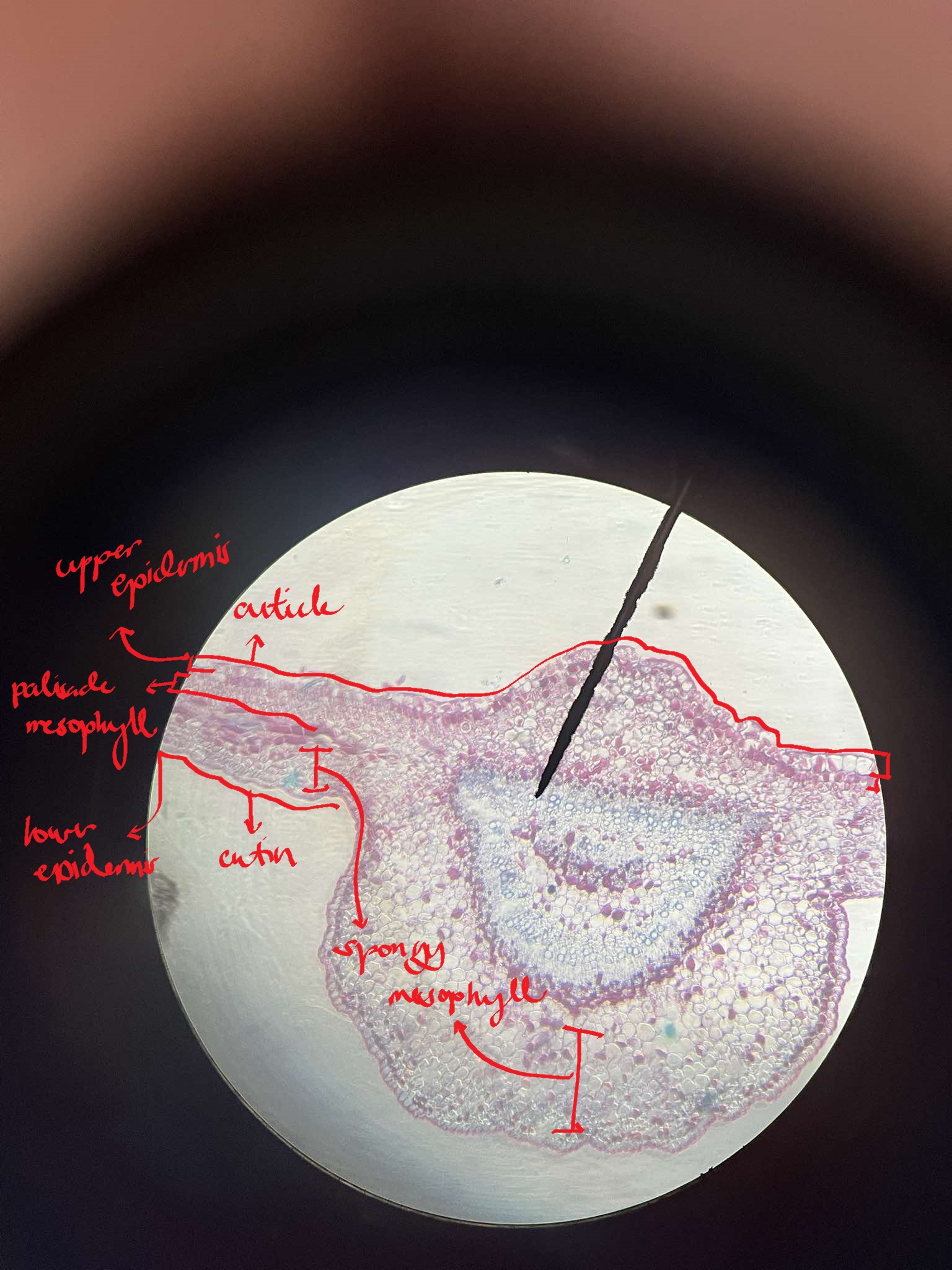
dorsi-ventral/bifacial leaf
a feature of most eudicots; horizontal in orientation; a distinct upper and lower surface
mesophyll
distinctly divided into a palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll
palisade mesophyll
composed of tall cells vertically oriented to the leaf surface
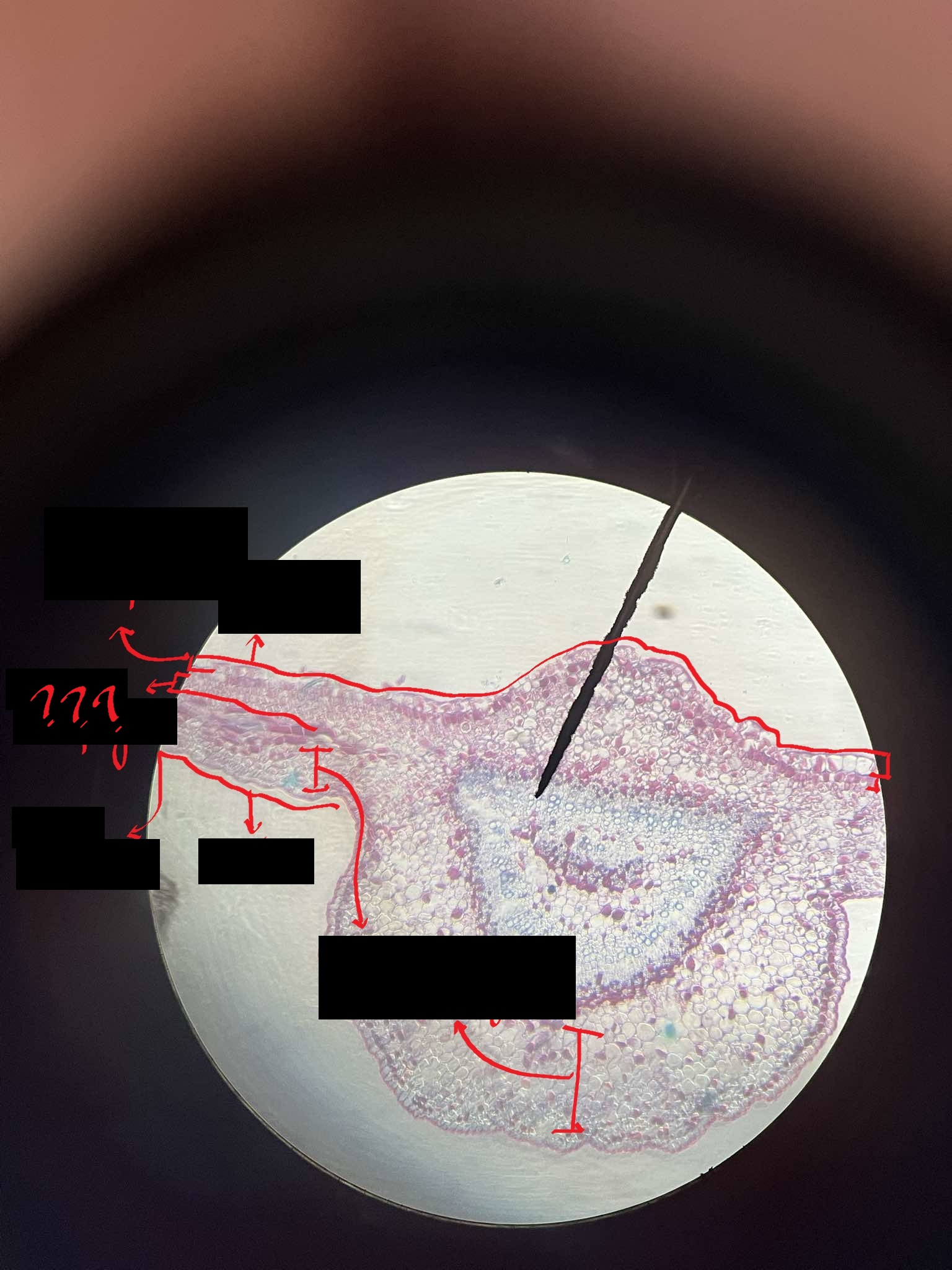
spongy mesophyll
composed of irregular parenchyma with a lot of intercellular spaces; where the stomata are confined
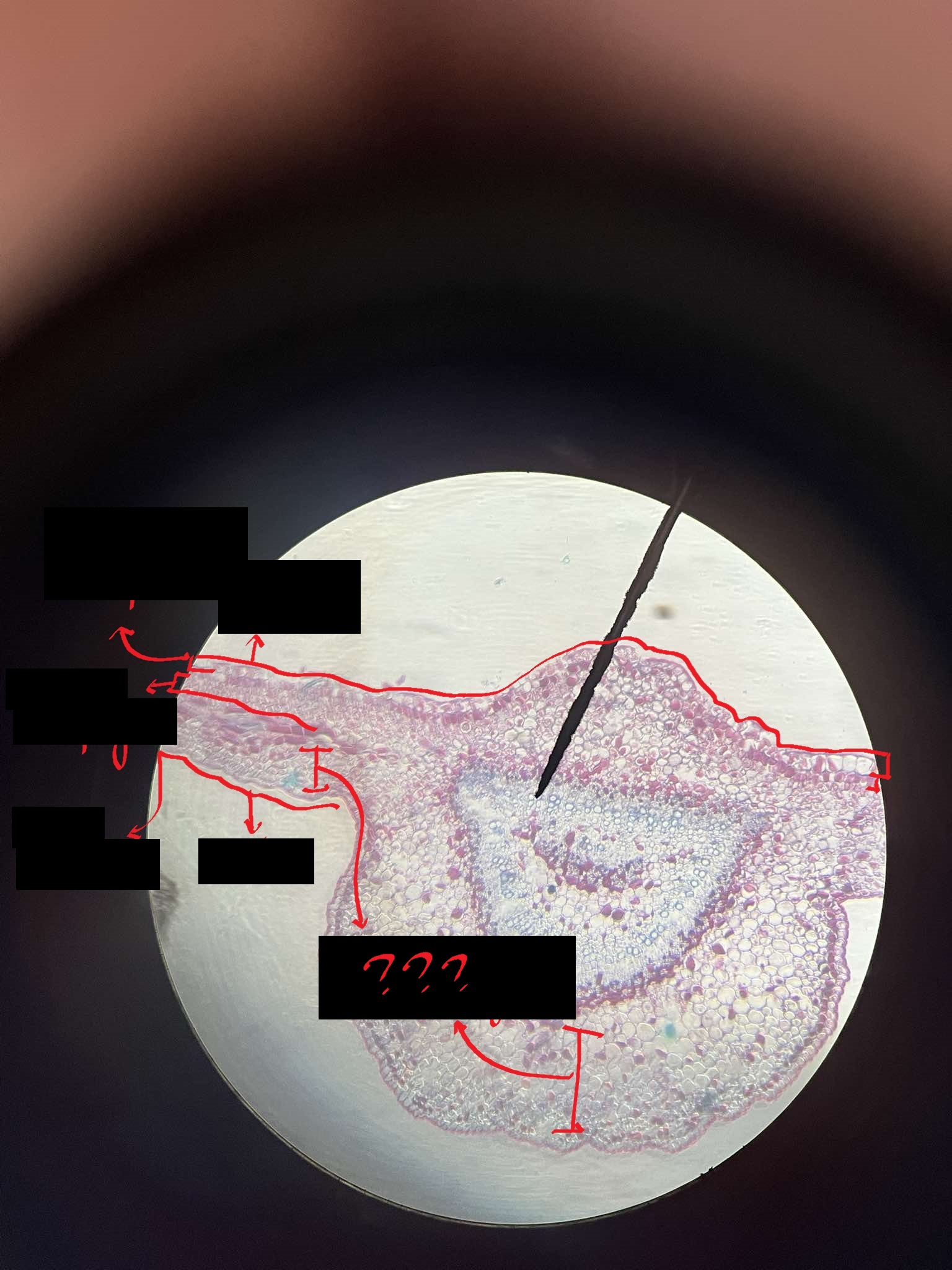
guard cells
cells that regulate the opening and closing of the stomatal pores
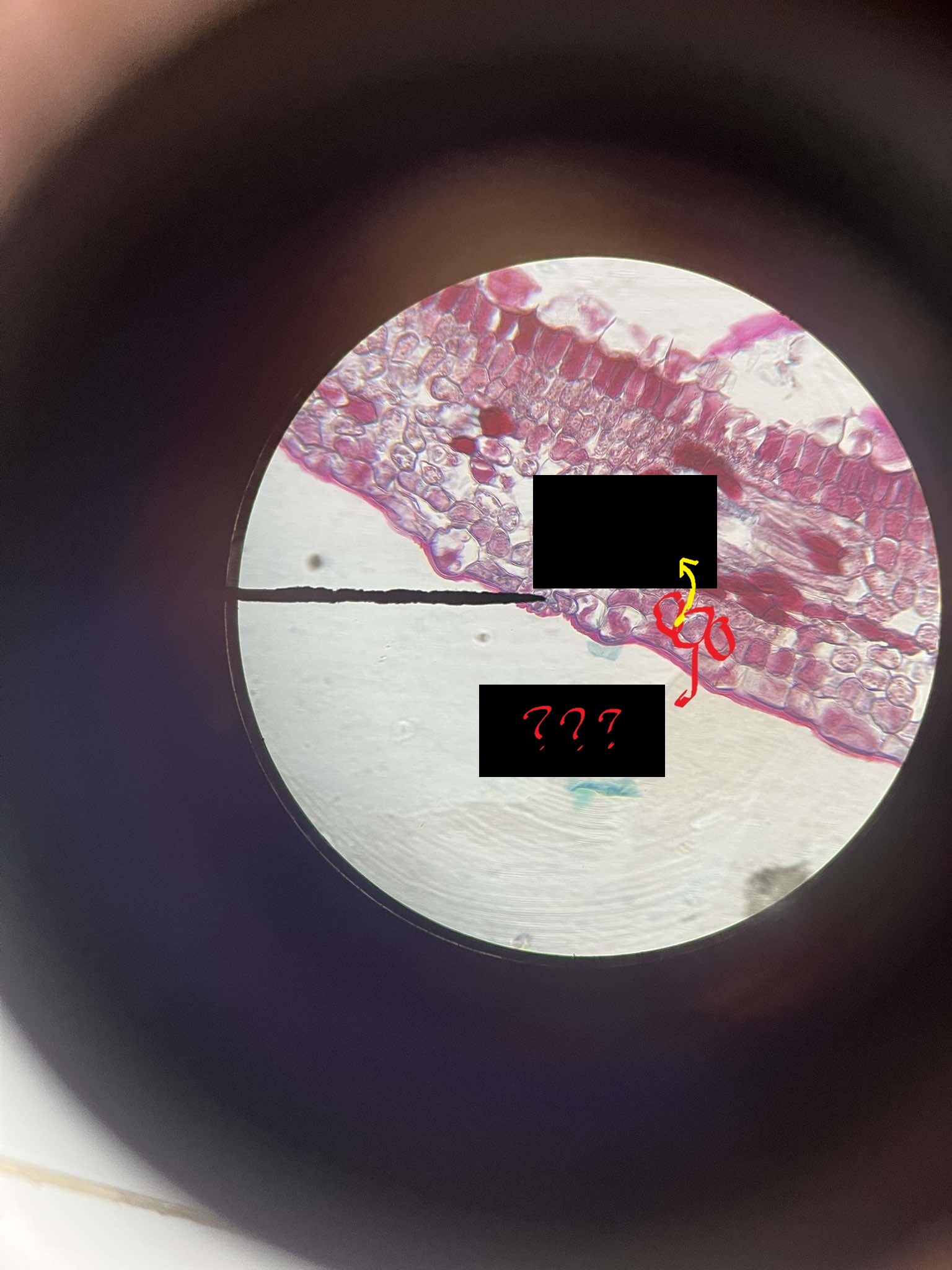

stomatal pores
openings on the leaf’s surface flanked by guard cells that regulate moisture
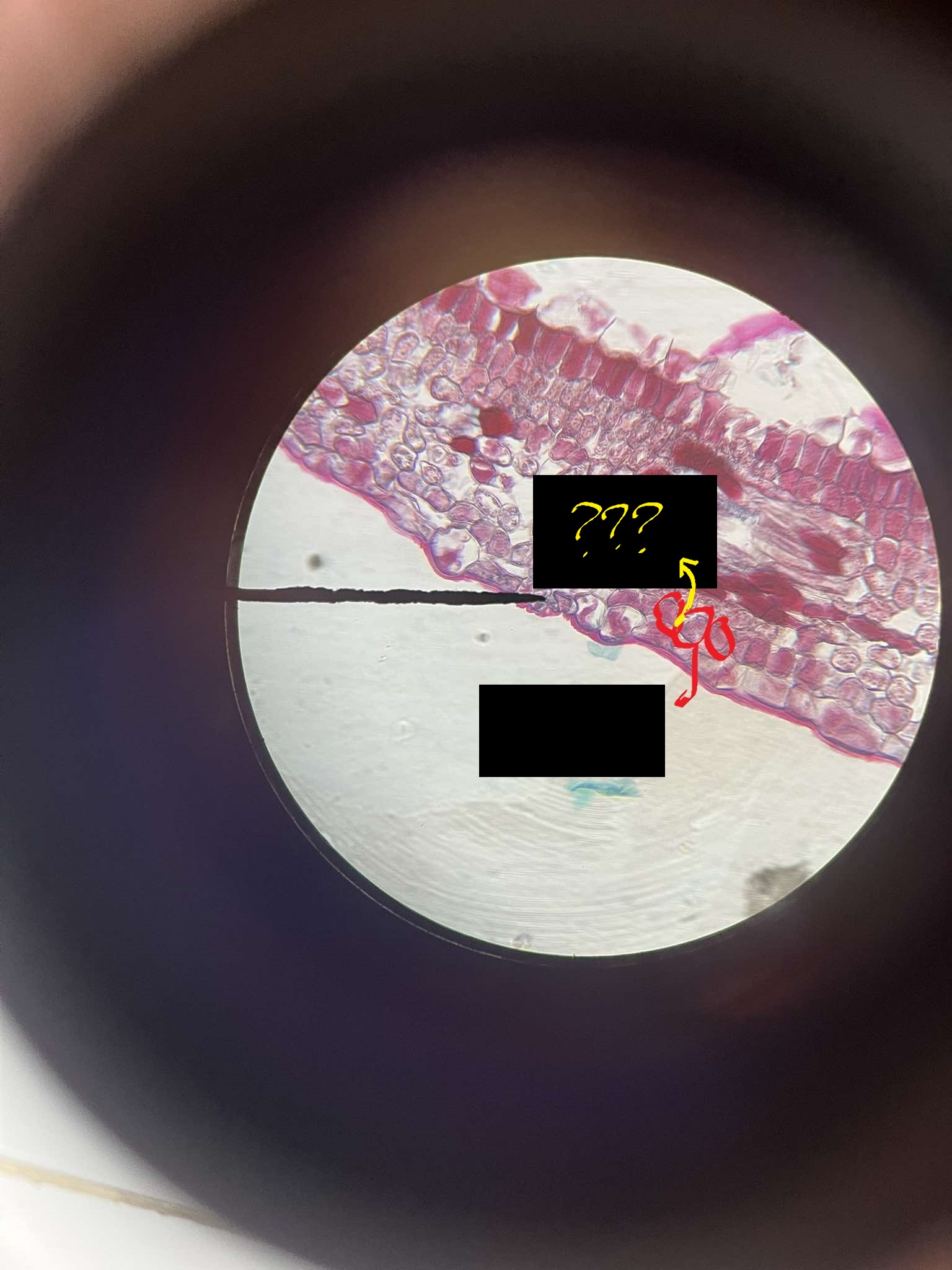

crypts
areas where the epidermis is depressed

x-s of Ixora finalysoniana leaf
identify the specimen
x-s Adelfa (Nerium oleander) leaf
identify the specimen
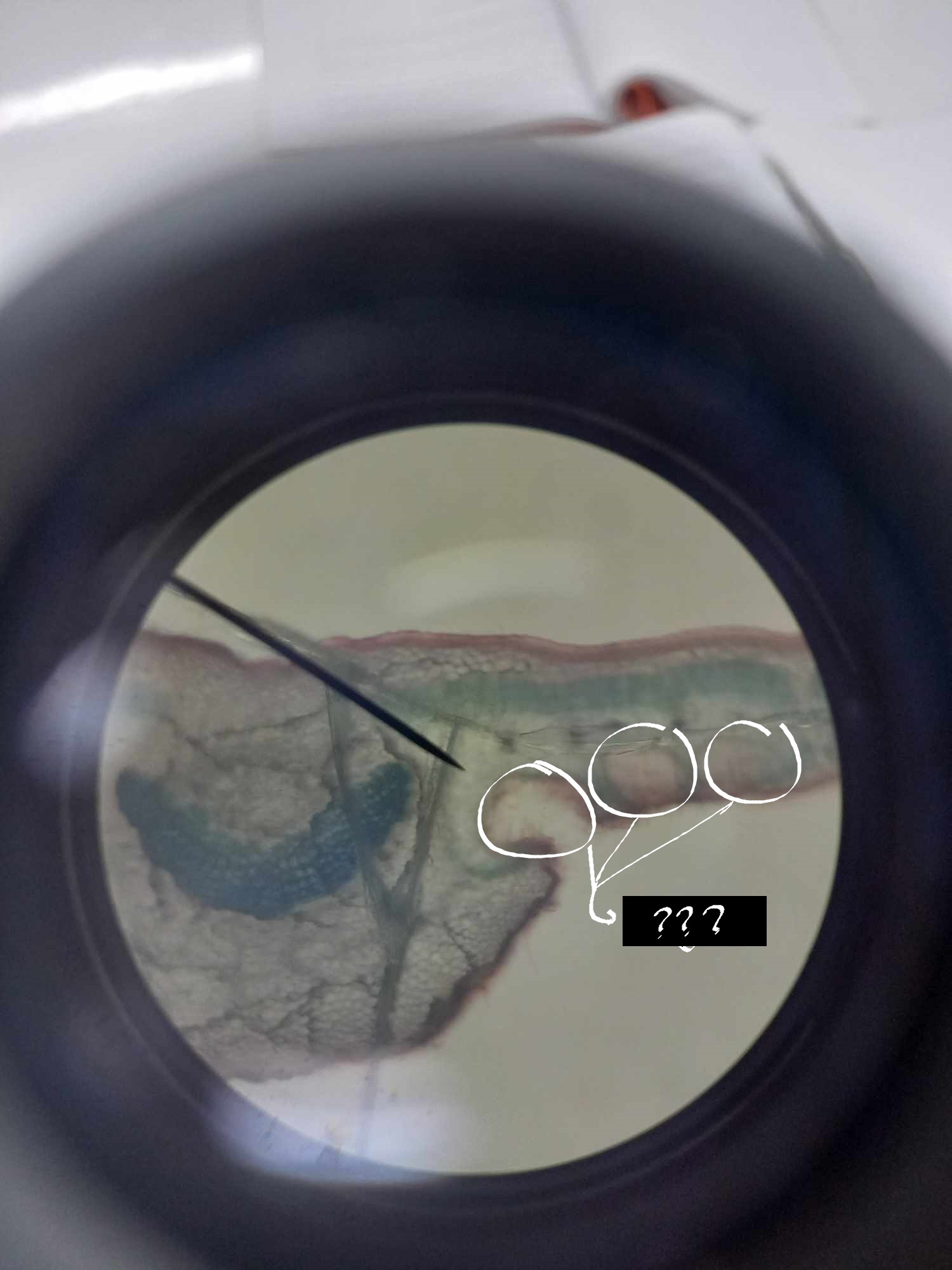
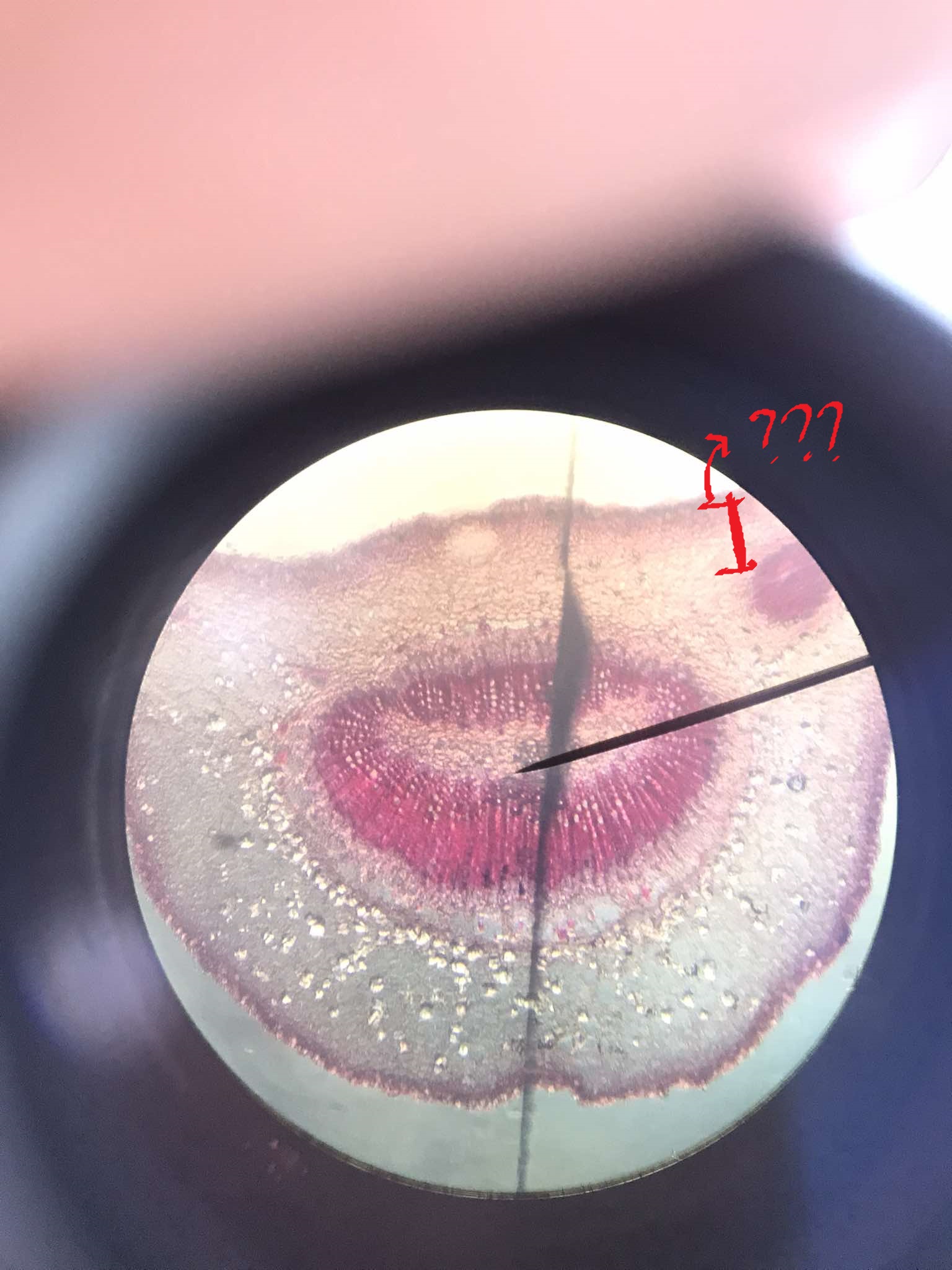
petiole
considered as transition between the stem and the lamina (leaf blade); epidermis contain fewer stomata and trichomes than lamina; non-aerenchymatous mesophyll
leaf traces
the convergence of the stem and petiole
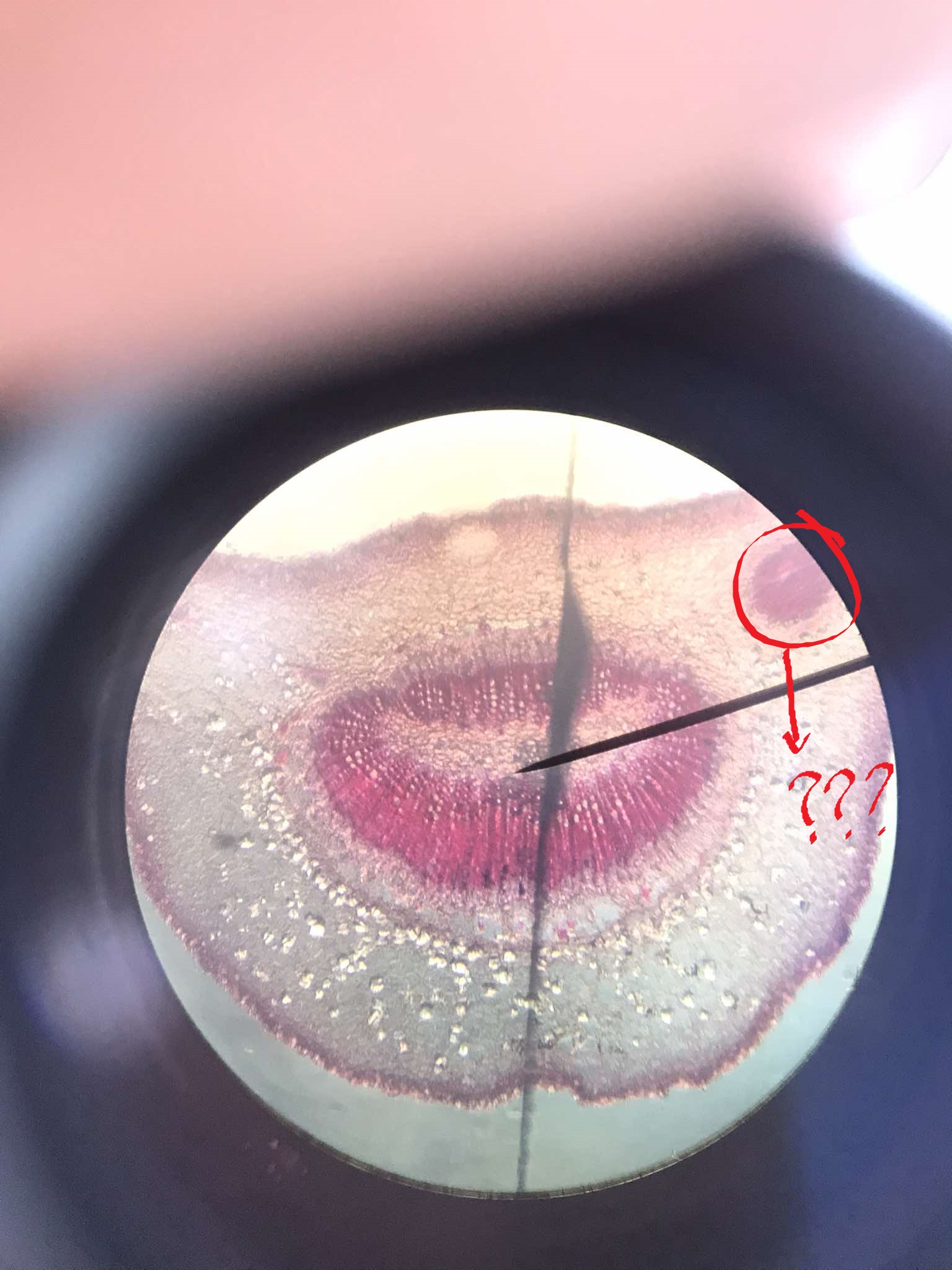
leaf gaps
parenchymatous regions located adaxially from the diverging leaf traces
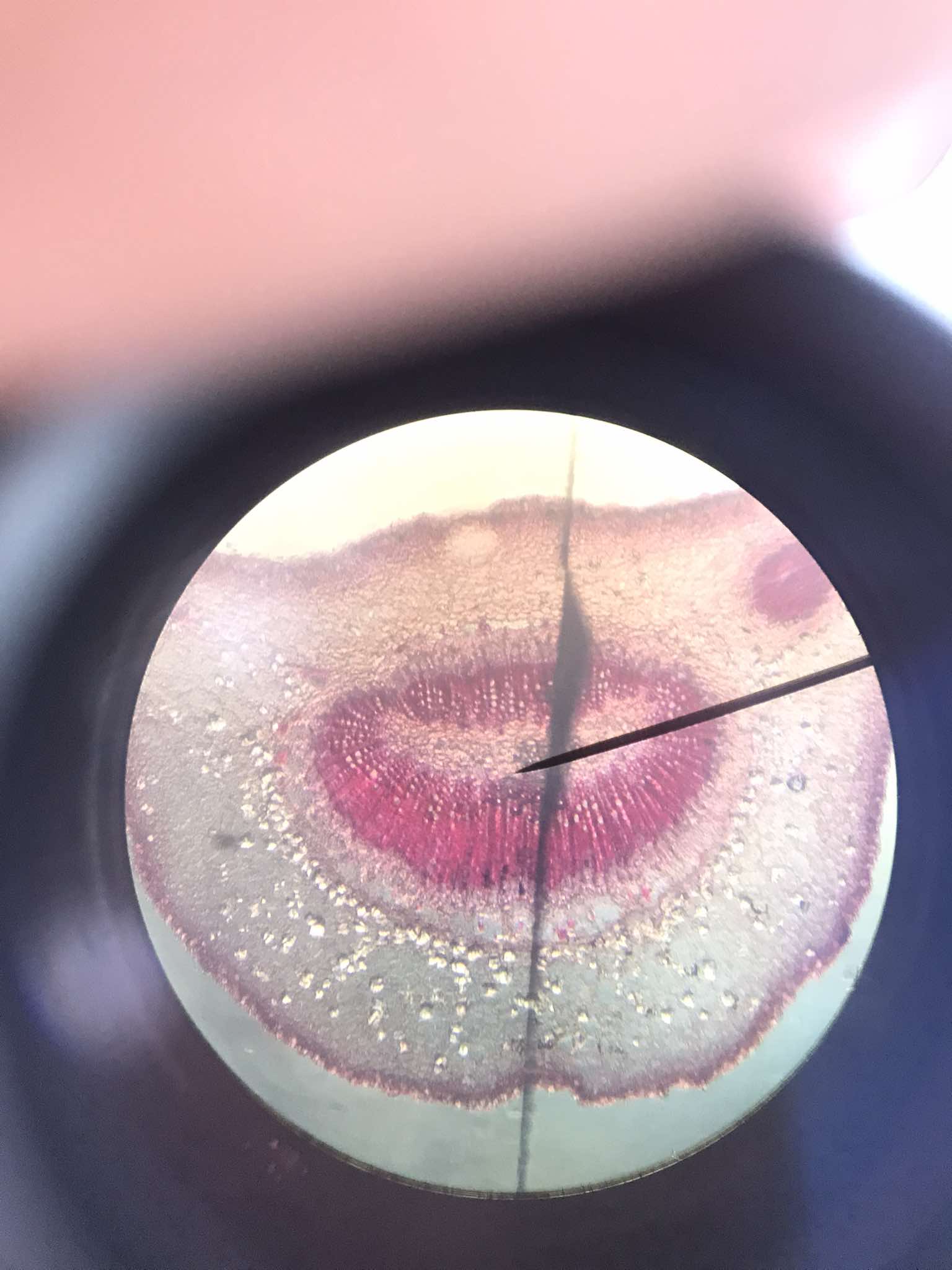
x-s petiole of Schefflera
identify the specimen
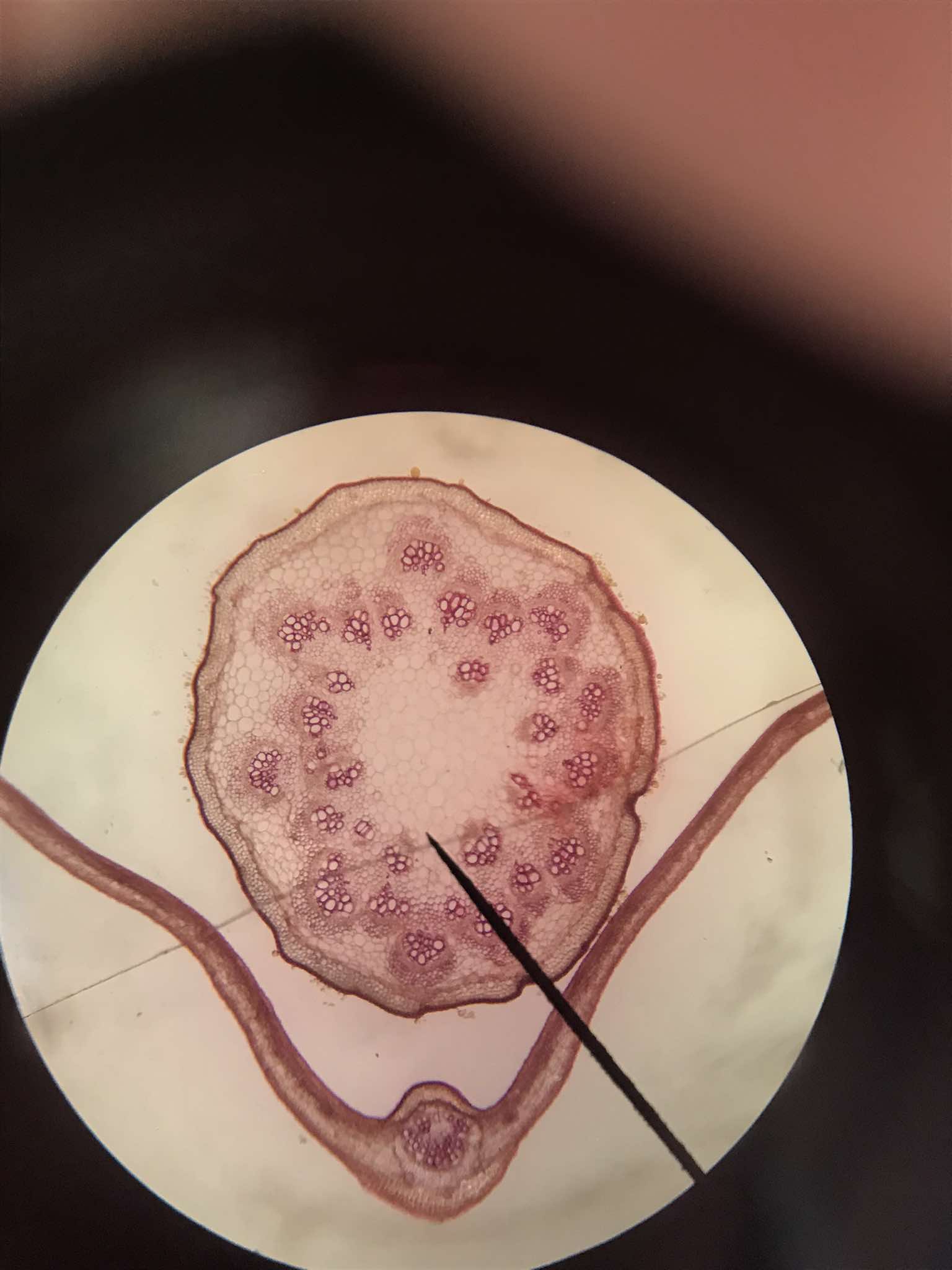
x-s petiole of Citrus
identify the specimen
isobilateral/equifacial leaf
vertically-oriented leaf; distinction between upper and lower surfaces of the leaf is absent; mesophyll is usually indistinguishable
amphistomatic
having stomata on both sides of the blade
x-s of Eucalyptus leaf or Callistemon
identify the specimen

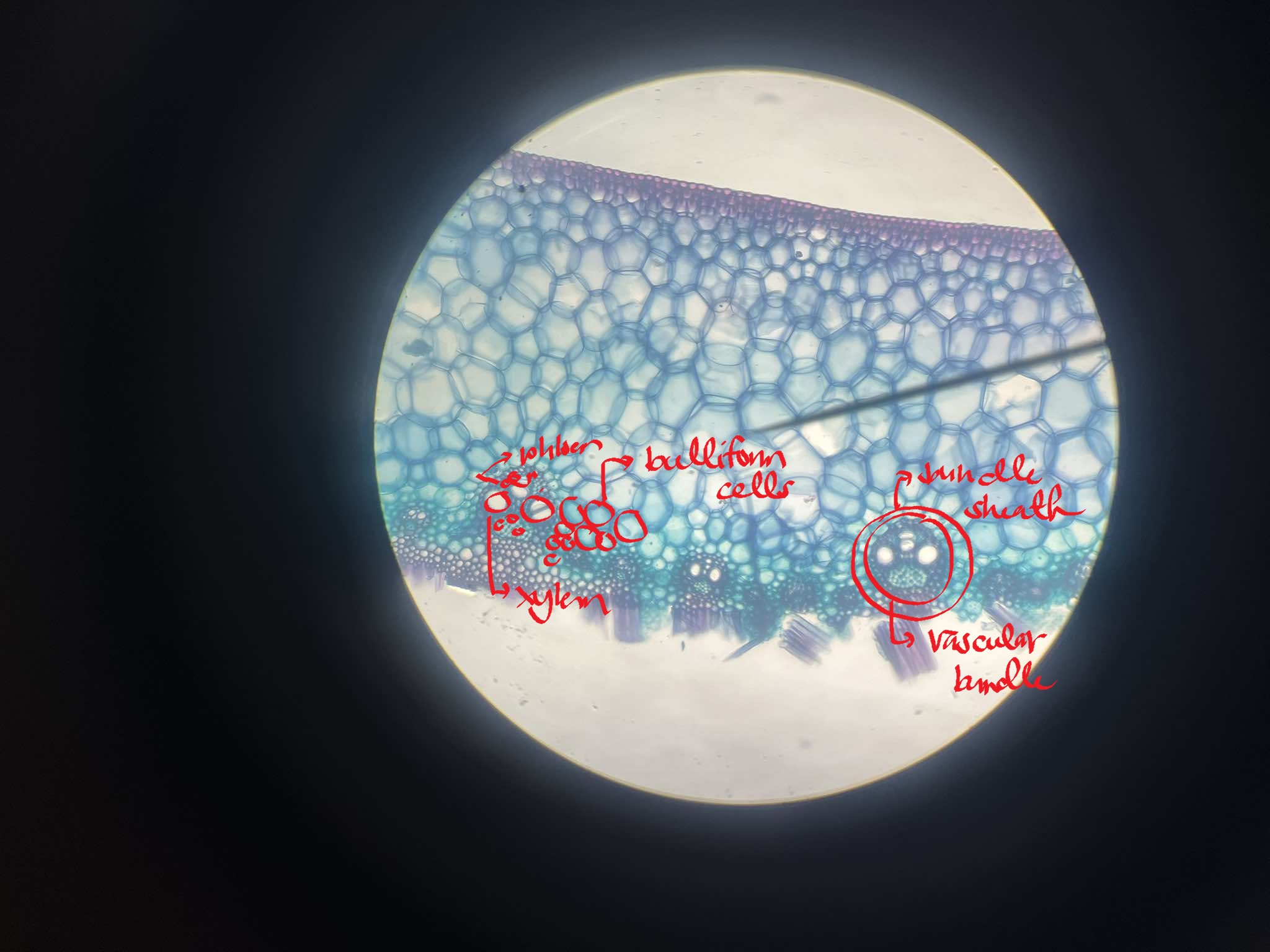
x-s of the corn (Zea mays) leaf
identify the specimen
phyllotaxy
the arrangement of leaves on stem; important in positioning leaves so that they will not shade each other
alternate; opposite; whorled
three types of phyllotaxy
alternate phyllotaxy
only one leaf attached to the node, alternating up the stem
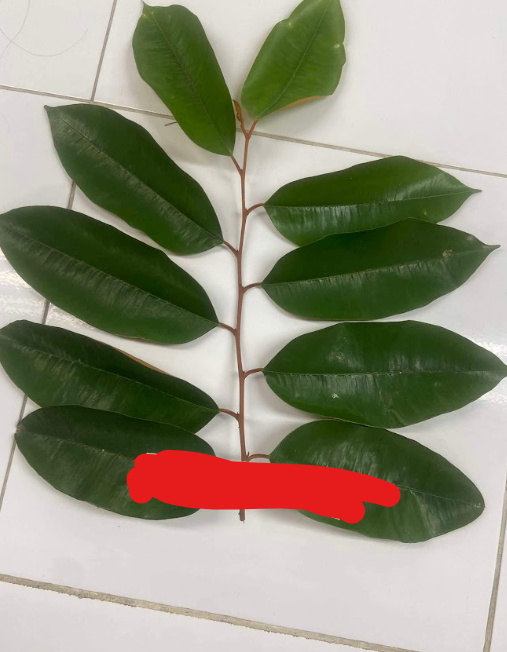

Chrysophyllum cainito
alternate phyllotaxy; caimito
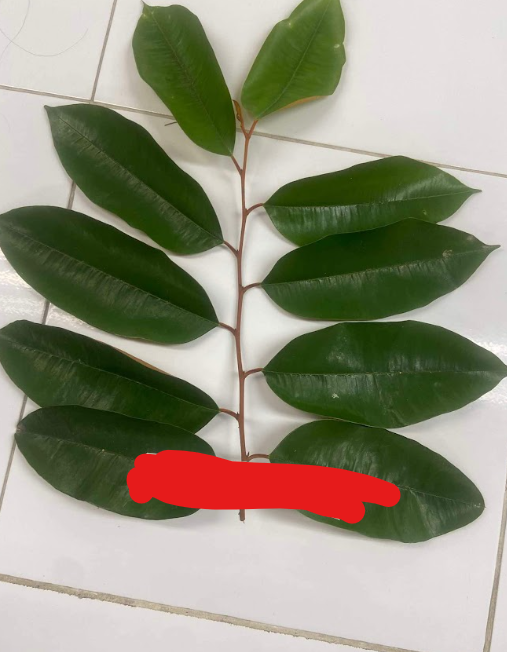

opposite phyllotaxy
two leaves attached per node

whorled phyllotaxy
three or more leaves per node
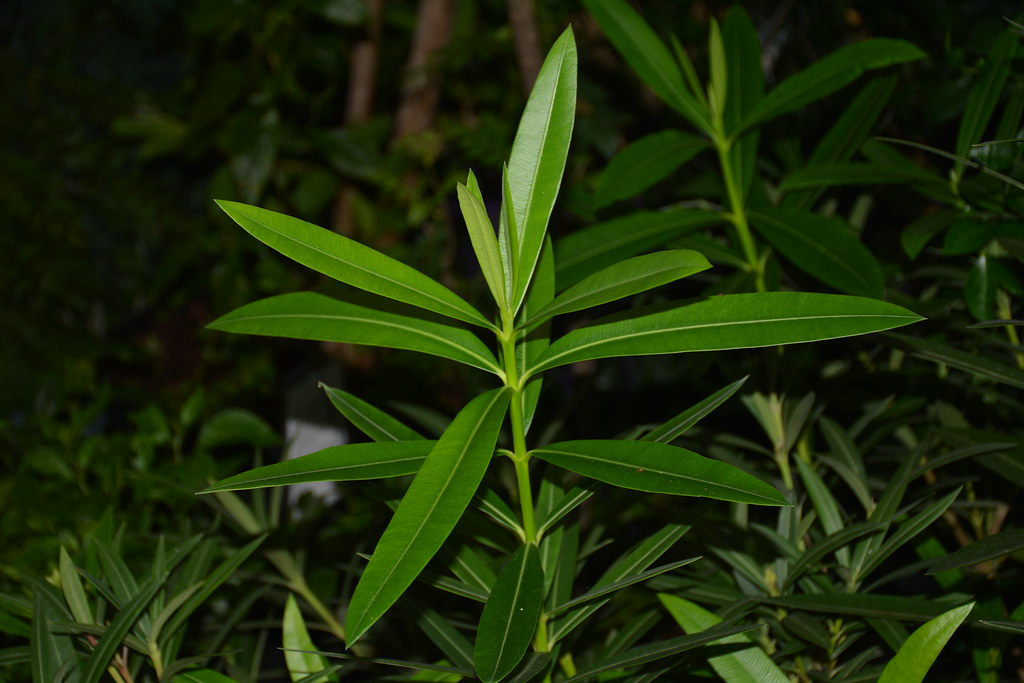

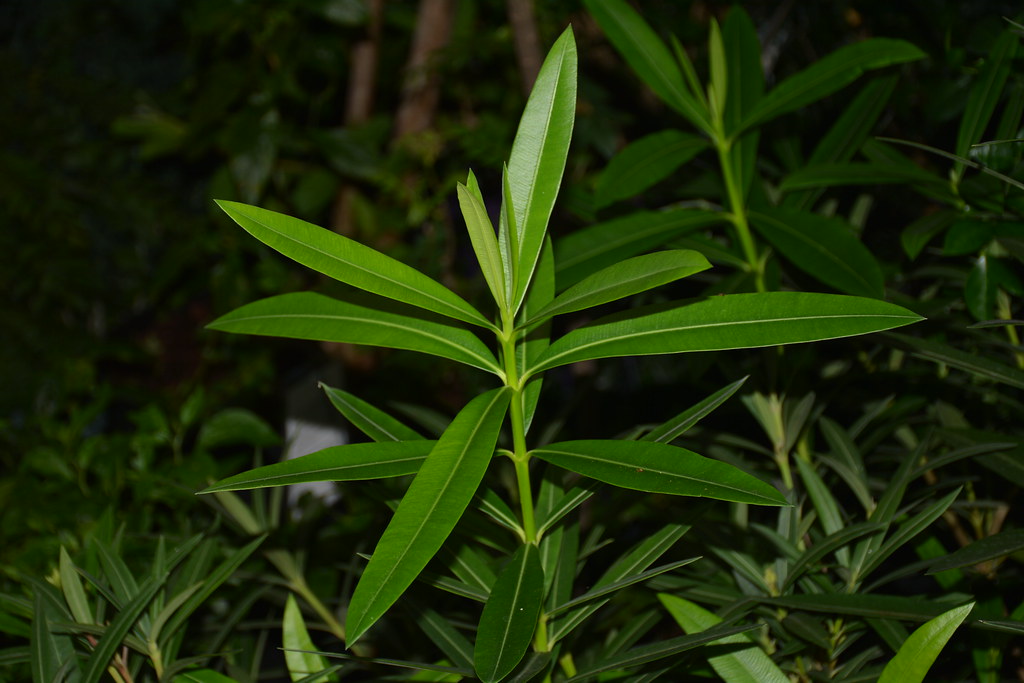
Nerium oleander
whorled phyllotaxy; adelfa

specialized leaves
leaves that become modified and perform other functions
tendrils
threadlike sensitive structures that coils on a surface and gives support to the plant

Ipomoea cairica
tendrils; morning glory

Clitoria ternatea
tendrils; butterfly pea
