7 reflexes
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pgy 452 exam2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what can a spinal cord do?
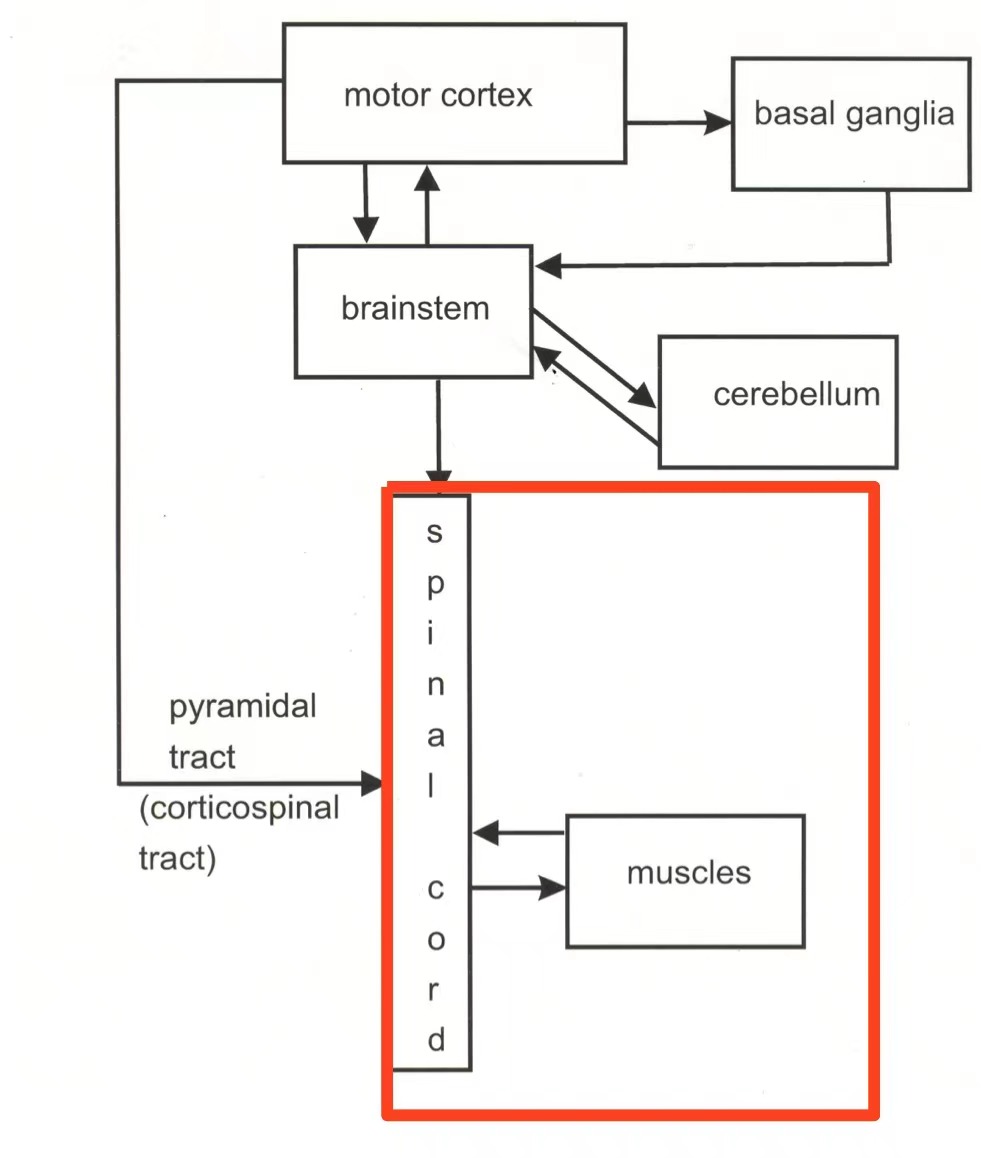
spinal reflexes
unlearned motor response to sensory stimulus
spinal transection
lose sensation and voluntary movement below the cut
spinal reflexes components
muscles
motoneurons
sensory input from the body
spinal interneurons
abnormal reflex
a reflection of the dysfunction of some component of the motor system
because circuitry电路 for a reflex may be present in the spinal cord, but reflex strength or gain may be modulated by descending pathways - stronger, weaker, suppresses
stimulus
stretch of a muscle
response
contraction of the same muscle, clinically tested by tendon tap which stretches the muscles
afferent (sensory input)
1A fiber from muscle spindle
efferent
α motoneuron to same muscle, short latency延迟 reflex
monosynaptic reflex
the stretch reflex underlies muscle tone, resistance to passive stretch of a muscle
reciprocal innervation
as the agonist contracts, its antagonist relaxes, circuit branch of 1A synapses on inhibitory interneuron in spinal cord that inhibits motoneuron innervating the antagonist muscle
flexion reflex
stimulusL noxious (damaging, painful) stimulus to skin
response: contraction of flexor and relaxation of extensors at every joint in the limb
not get into the stimulus but to spinal cord, still feel the pain
flexion crossed-extension reflex
leg on the other side extends to increase postural support
double reciprocal innervation
pattern of innervation
head up
forelimbs extend, hindlimbs flex
head down
forelimbs flex, hindlimbs extend
head to side
ipsilateral limb extend, contraclateral limb flexes
descending control of reflexes
under the control of higher levels of the motor system
ex: flexion flex modulation屈区反射调节 - abnormal reflexes
spinal shock
absence of reflexes followed by spinal transection
reflexes gradually return
more complex the CNS the longer period of spinal shock
endpoint may be hyperreflexia反射亢进
unknown mechanism
Babinski sign巴宾斯基征
damage to motor cortex or PT
normal in newborns
low descending control
flaccidity松弛
hypotonnia肌张力低下
down syndrome
too high descending control
rigidity刚性
hypertonia肌张力亢进
cerebral palsy (CP)脑瘫
solution: cut dorsal roots, to eliminate excess sensory input
decorticate rigidity-seen
lesions of motor cortex:
increase tone - flexors of arms and extensors of legs
clonus阵挛 - more than one contraction for a single stretch
rigidity in cerebral palsy
results from damage to any component or combination of components of the motor system, and it reflects the degree of involvement of cortex or cerebellum or basal ganglia
shortening of tendons so the limbs become immobile, and lead to arthritis关节炎
treatment for cerebral palsy
surgical: selective dorsal rhizotomy
medical: injection of baclofen into spinal cord to inhibit the stretch reflex