Unit 8: Discoveries About Stars
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
What is Earth’s orbit diameter?
2 astronomical units
What explains why stellar parallax can only be measured for nearby stars?
higher distance = lower stellar parallax
limited baseline
What is the largest stellar parallax?
1 arcsecond
1/3600 of a degree
What was incorrectly assumed about stars in the 17th & 18th centuries?
brighter star = nearer
What did Edmund Halley compare in 1718?
Almagest & current star catalog
What did Edmund Halley discover in 1718?
3 moving stars
What was the method of revealing moving stars in the early 1800s?
repeated star catalog
What did Edmund Halley discover about stellar motion?
stars have motion
What is the fastest star?
Barnard’s Star
What is a “pc?”
parsec
hypothetical star distance that has 1 arcsecond p shift
1 parsec = 206 235 astronomical units = 31 000 000 000 kilometres
What is a “ly?”
lightyear
light travel distance in 1 year
1 lightyear = 63 239 astronomical units = 9 500 000 000 kilometres ~ 1/3 parsecs
What did Von Struve find in 1837?
Vega parallax
1/8 arcseconds
8 parsecs
What explains why Von Struve measured Vega?
5th brightest star
moved 30 arcseconds in 100 years
What was assumed about the nearest stars in the 1830s?
brighter
larger motion
wider space binary
What did Bessel find in 1838?
61 Cygni parallax
1/3 arcsecond
3 parsecs
What explains why Bessel measured 61 Cygni?
moved 4 arcseconds in 1 year
widely spaced binary
What did Thomas Henderson find in 1838?
Alpha Centauri parallax
3/4 arcseconds
4/3 parsecs
What explains why Thomas Henderson measured Alpha Centauri?
1 of brightest southern stars
quickly moved across sky
widely spaced binary
triple star
What is the nearest star?
Alpha Centauri
What did the Hipparcos Space Telescope measure starting in 1989?
measure 100 000 star distances
What method did the Hipparcos Space Telescope use?
parallax method every 6 months above atmosphere
What is the number of Milky Way stars?
400 000 000 000
What did Gaia study starting in 2013?
400 000 000 (1%) Milky Way stars
What did Robert Hooke publish in 1665?
light textbook
light travels as wave
What did Christiaan Huygens publish a decade after Robert Hooke?
light textbook
light travels as electromagnetic radiation
What is “electromagnetic radiation?”
oscillating blue electric energy field & red magnetic energy field wave
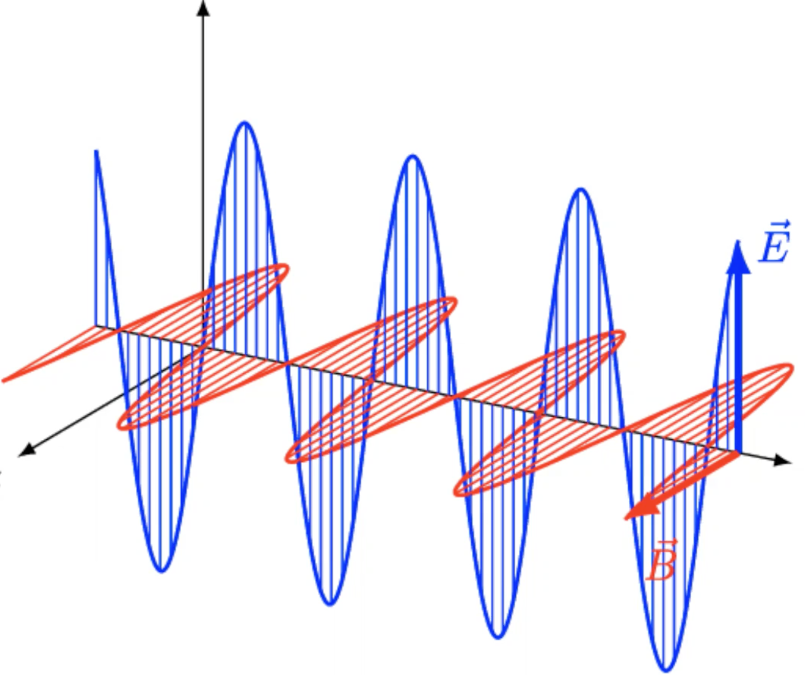
What characteristics differentiate light sources?
amplitude
wavelength & frequency
What does amplitude determine?
light intensity
What is “amplitude?”
peak height
What does wavelength determine?
light colour
What is “wavelength?”
peak distance
What is “frequency?”
wavelength number leaving light source per second
What is the wavelength & frequency relation?
higher frequency = shorter wavelength
What differentiates red & blue light wavelengths?
red > blue
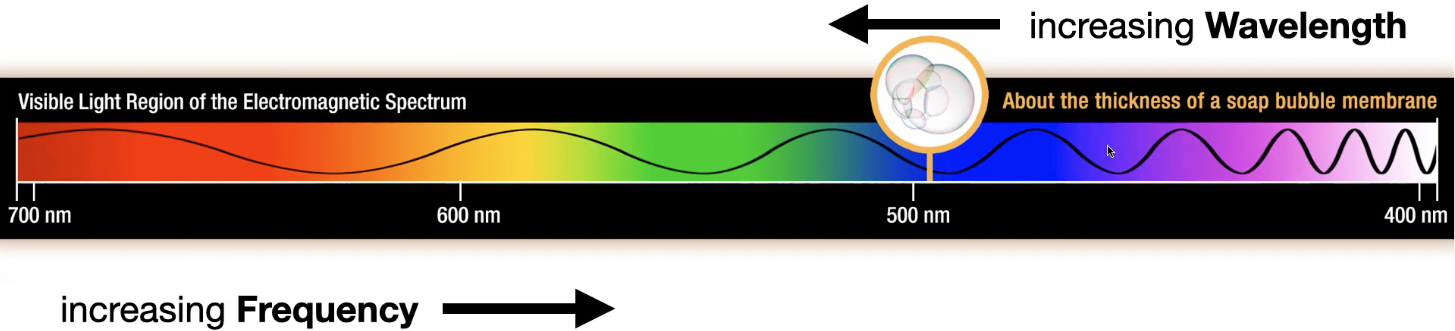
What are the wavelength units?
µm
nm
Å
What is a “µm?”
micron
1 000 000th of metre
What is a “nm?”
nanometre
1 000 000 000th of metre
What is an “Å?”
Angstrom
10 000 000 00th of metre
What is the electromagnetic spectrum appearance?
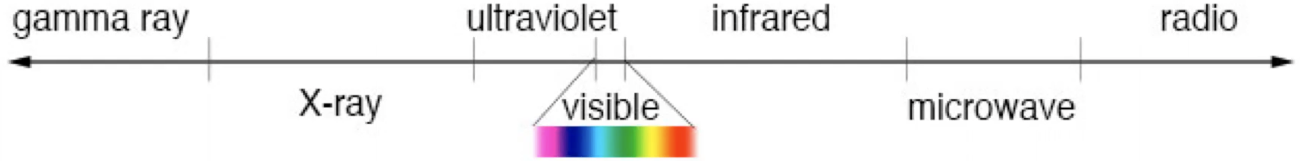
What are the electromagnetic spectrum left side’s properties?
short wavelength
high frequency
high energy
What are the electromagnetic spectrum right side’s properties?
long wavelength
low frequency
low energy
What is the longest & lowest-energy wave?
radio
What is the shortest & highest-energy wave?
gamma
What explains why Sun UV waves damage humans?
high amplitude
What are radio wave uses?
radio
TV
What are microwave wave uses?
cooking
communications
What are infrared wave uses?
heat
Sun
fire
radiator
What are visible light uses?
makes things able to be seen
What are UV wave uses?
fluorescent tubes
skin absorbs
purifies water
What are x-ray wave uses?
view inside of body & object
What are gamma wave uses?
kill cancer cell
What method produces gamma waves?
nuclear reaction
What was 1 method Joseph Fraunhofer used to test glass?
pass sunlight through lenses & ensure no colour separation
What process did Joseph Fraunhofer use to discover Fraunhofer’s spectrum in 1814?
passed sunlight through prism
placed spectrum on white screen
looked at spectrum through telescope
saw 600 thin dark lines
labeled with letters → designated wavelength
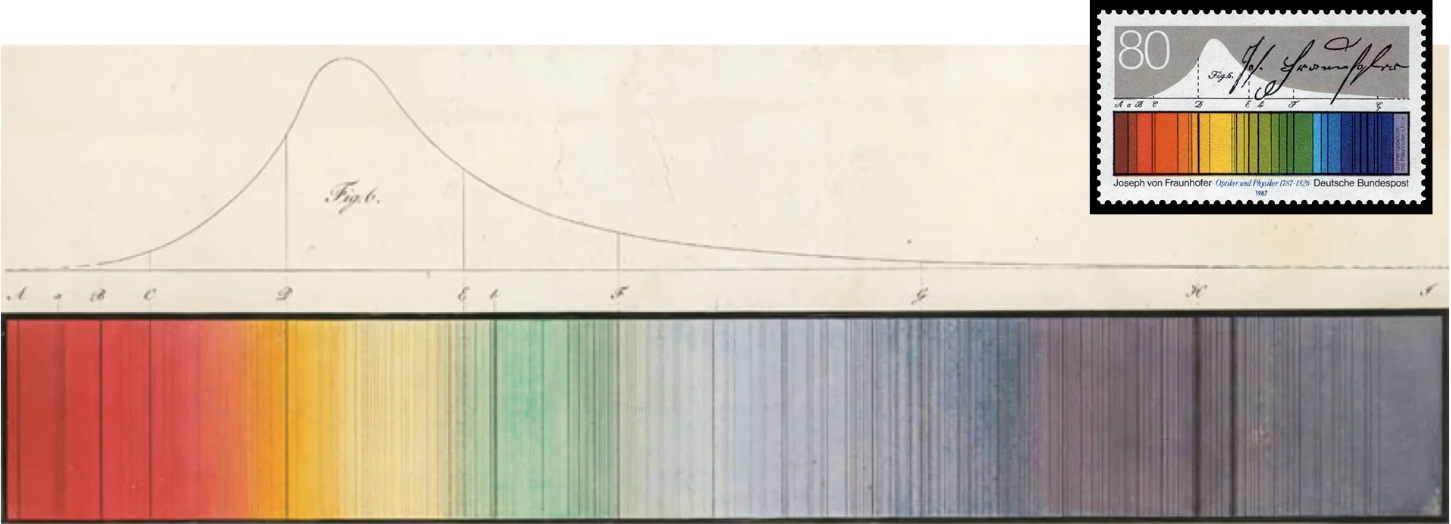
What was “Fraunhofer’s spectrum?”
1st dark Sun line visible light map
What did German chemist Robert Bunsen & physicist Gustav Kirchhoff produce in 1859?
heated gas spectra
What did Robert Bunsen & physicist Gustav Kirchhoff conclude in 1859?
gas spectra contains unique bright coloured line sequence
What explains why Robert Bunsen & physicist Gustav Kirchhoff were interested in Fraunhofer’s spectrum?
Fraunhofer passed flame light through prism
What did Joseph Fraunhofer see in his other expriment?
mostly dark area with few bright coloured lines
What was Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff’s response to Joseph Fraunhofer’s other experiment?
built apparatus (spectroscope) & placed chemical metals
What is “spectroscopy?”
light source spectrum analysis to determine chemical composition
What did Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff realize about the Sun spectrum & gas spectra?
Sun dark lines = gas bright lines
What was Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff’s response to Sun’s dark lines matching the gases’ bright lines?
produced sunlight spectrum passing through gas flame
What did Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff initially believe by producing a sunlight spectrum passing through a gas flame?
no more dark line
What did Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff finally believe by producing a sunlight spectrum passing through a gas flame?
thicker dark line
What did Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff correctly conclude about the Sun core?
produces full light spectrum

What did Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff correctly conclude about the Sun core’s surroundings?
atmosphere
What did Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff correctly conclude about the dark line?
Sun atmosphere’s molecules absorb light at signature wavelengths equal to ones the gas emits on its own

What did Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff correctly conclude about the thicker dark line?
also passes sodium flame that absorbs more light
What was Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff’s process of correctly concluding the thicker dark line?
looked at atmosphere alone
heated it up
→ glowed
got emission line on spectrum

What’s an “absorption line?”
light absorbed on its way to Earth
What’s an “emission line?”
light emitted by atoms
What reveals Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff’s emission lines in the 1860s & 1870s?
Sun atmosphere spectra was collected during solar eclipses
What do Robert Bunsen & Gustav Kirchhoff conclude about the Sun atmosphere chemical composition?
match spectra to known substances
What is the Sun’s “lower atmosphere?”
layer containing elements for most absorption lines
What is the Sun’s hottest layer?
lower atmosphere
What is the Sun’s “upper atmosphere?”
hydrogen & helium layer
What is the Sun’s coolest layer?
upper atmosphere
What explains why people were able to measure the Sun layers at the same time?
as telescope moved across atmosphere, emission lines changed
What gas spectrum was produced in the 1860s?
hydrogen
matched with dark lines
What was concluded by producing hydrogen spectra?
in Sun atmosphere
What was the identity of the person that produced the 1st hydrogen spectra in the 1860s?
Julis Plücker
What was Julius Plücker’s method of producing gas spectra in the 1860s?
constructed vacuum tube
heated up
What did Norman Lockyer & Pierre Janssen discover in 1868?
yellow emission line in Sun upper atmosphere spectra during solar eclipse
What was concluded about the yellow emission line in the Sun upper atmosphere spectra?
helium
What are the word origins of “helium?”
Helios
Greek sun god
What explains why the yellow emission line hadn’t been seen by others?
close in wavelength to thick sodium line
What are the 2 spectra types?
visual
graphical
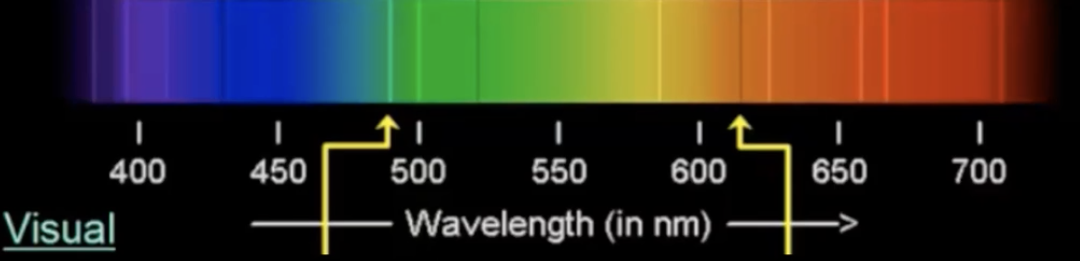
What is a “visual spectrum?”
continuum light
emission line
absorption line
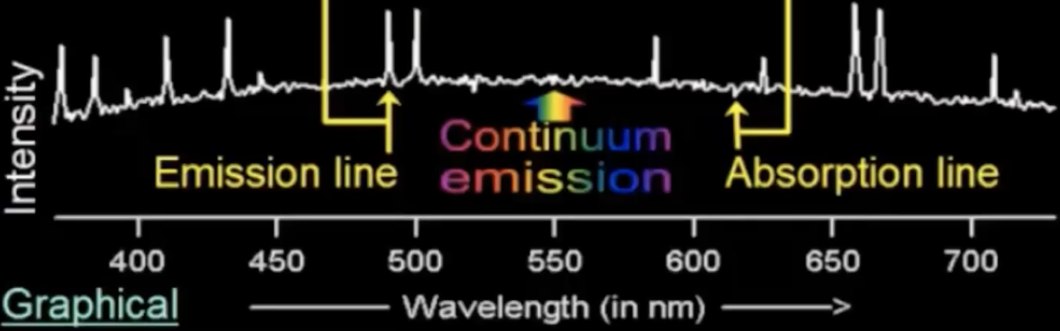
What is a “graphical spectrum?”
intensity at each wavelength
continuum emission
dip = absorption line
peak = emission line
What spectrum did English astronomers William Huggins & Margaret Lindsay Huggins produce in 1864?
planetary nebula
What are “Nebulium?”
unidentified emission lines on planetary nebula spectrum
What was discovered to be Nebulium?
oxygen
What was the Huggins’ 1st reported nebula?
Cat’s Eye Nebula
What was the Huggins’ Cat’s Eye Nebula spectrum appearance?
1 strong green line
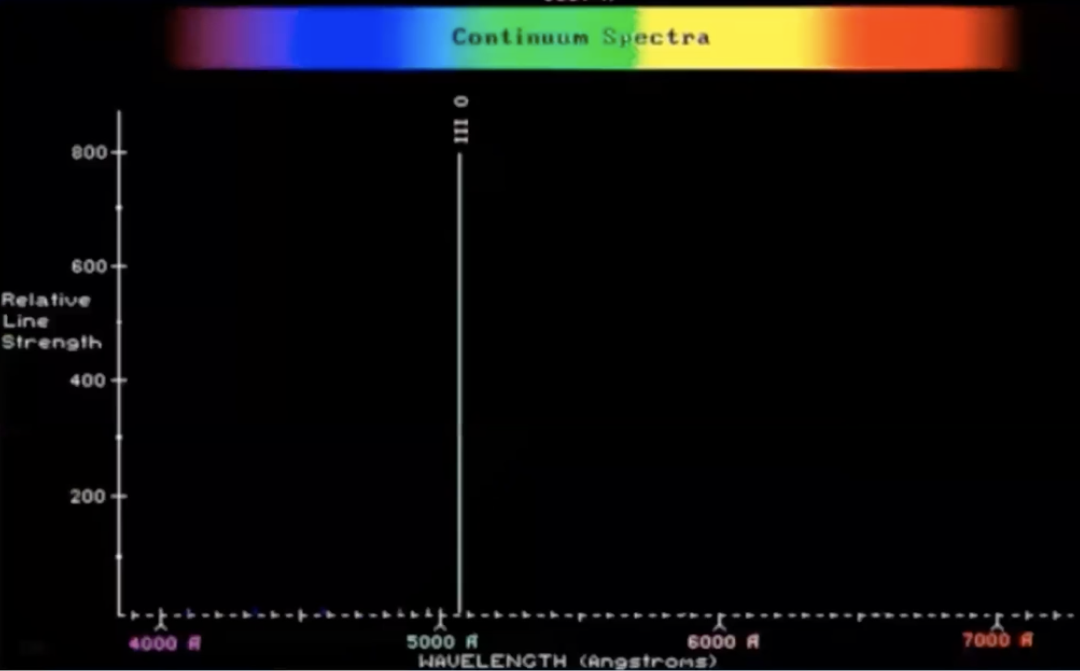
What explains the Cat’s Eye Nebula strong bright line?
highly excited oxygen
What did the complete Cat’s Eye Nebula spectrum reveal?
emission-line nebula
hot gas cloud
What nebula types did Huggins find?
emission-line
continuum
absorption-line
What nebula types are actually star clusters?
continuum
absorption-line
What are a continuum nebula’s properties?
continuous emission
absorption line
no emission line