BSC Exam 5 Neurons and CNS
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
337 Terms
Nervous System
Master controlling and communicating system of body.
Sensory Input
Information gathered by sensory receptors about changes.
Integration
Processing and interpretation of sensory input.
Motor Output
Activation of muscles and glands produces a response.
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Housing for neuron cell bodies in sensory input.
Afferent Neuron
Sensory neuron transmitting signals to CNS.
Integration Center
Brain and spinal cord process sensory information.
Efferent Fibers
Motor neurons transmitting impulses from CNS.
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
Involuntary control of smooth muscle and glands.
Effectors
Organs that perform actions in response.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord; control center.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nervous system portion outside CNS.
Sensory Division
Conveys impulses from sensory receptors to CNS.
Motor Division
Transmits impulses from CNS to effectors.
Visceral Sensory Fibers
Convey impulses from internal organs to CNS.
Somatic Sensory Fibers
Convey impulses from skin and muscles to CNS.
Sympathetic Division
Part of ANS; 'Fight or Flight' response.
Parasympathetic Division
Part of ANS; 'Rest and Digest' response.
Neuroglia
Supportive cells surrounding and protecting neurons.
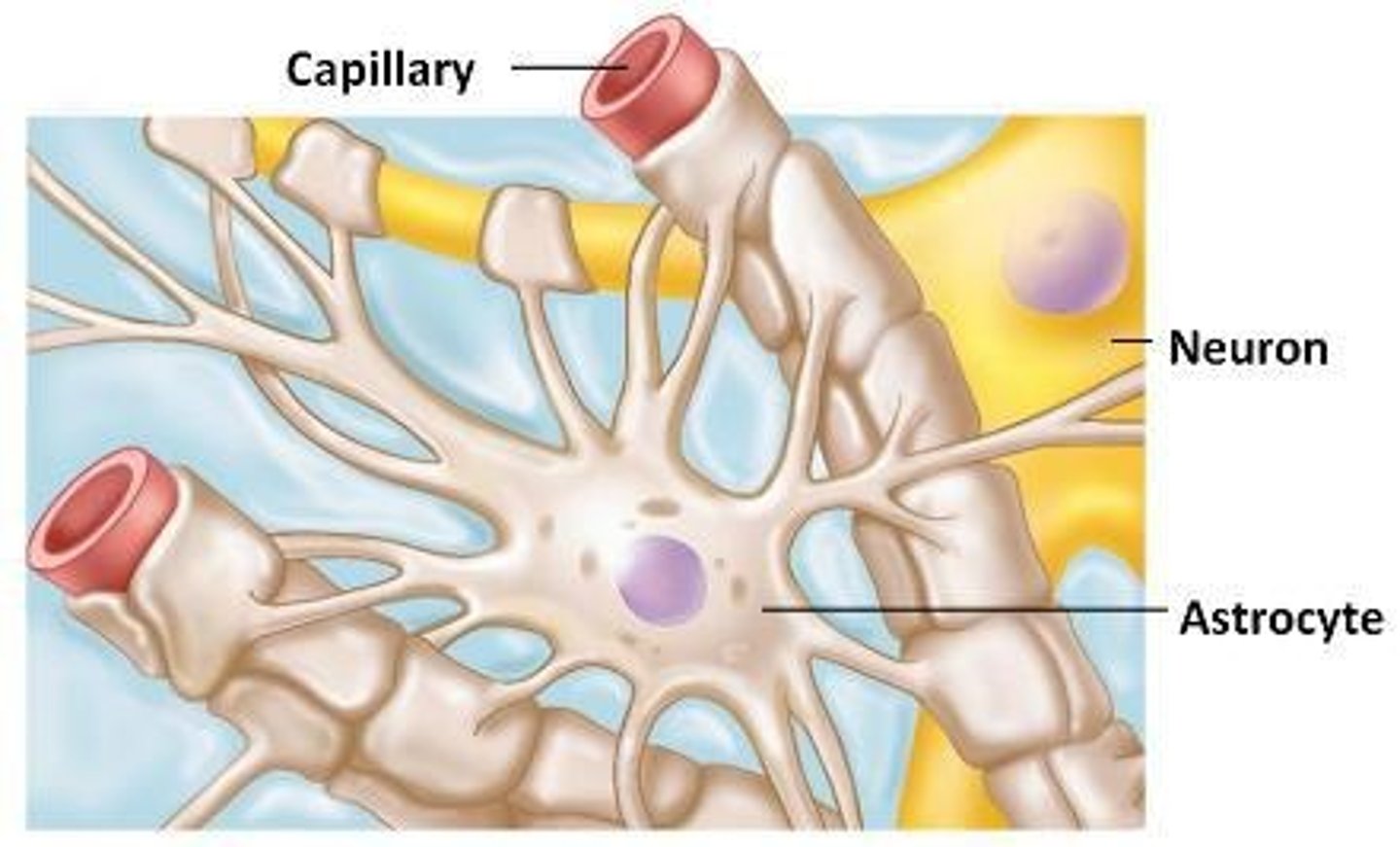
Astrocytes
Most abundant glial cells; support neurons.
Oligodendrocytes
CNS glial cells that insulate axons.
Schwann Cells
PNS glial cells that form myelin sheath.
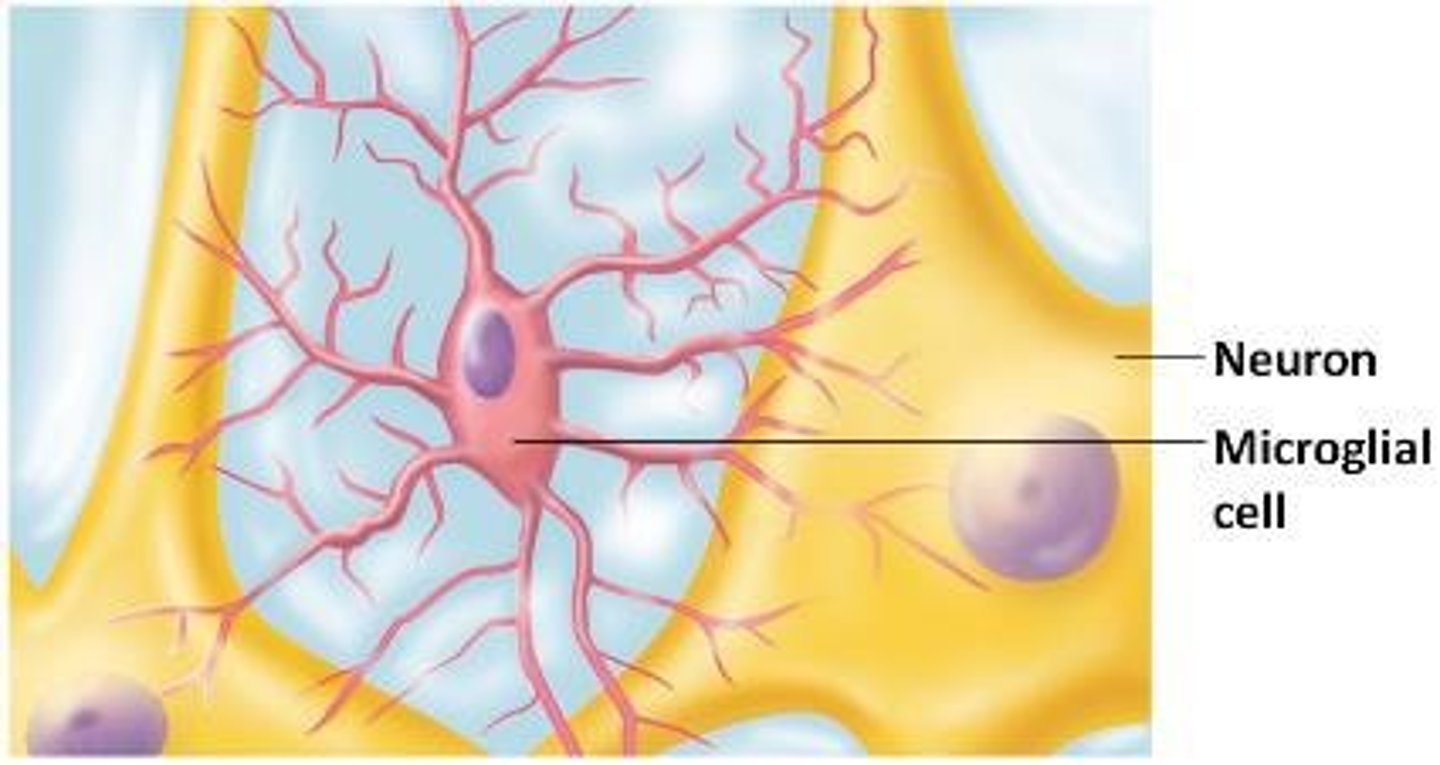
Microglial Cells
Small cells that monitor and support neurons.
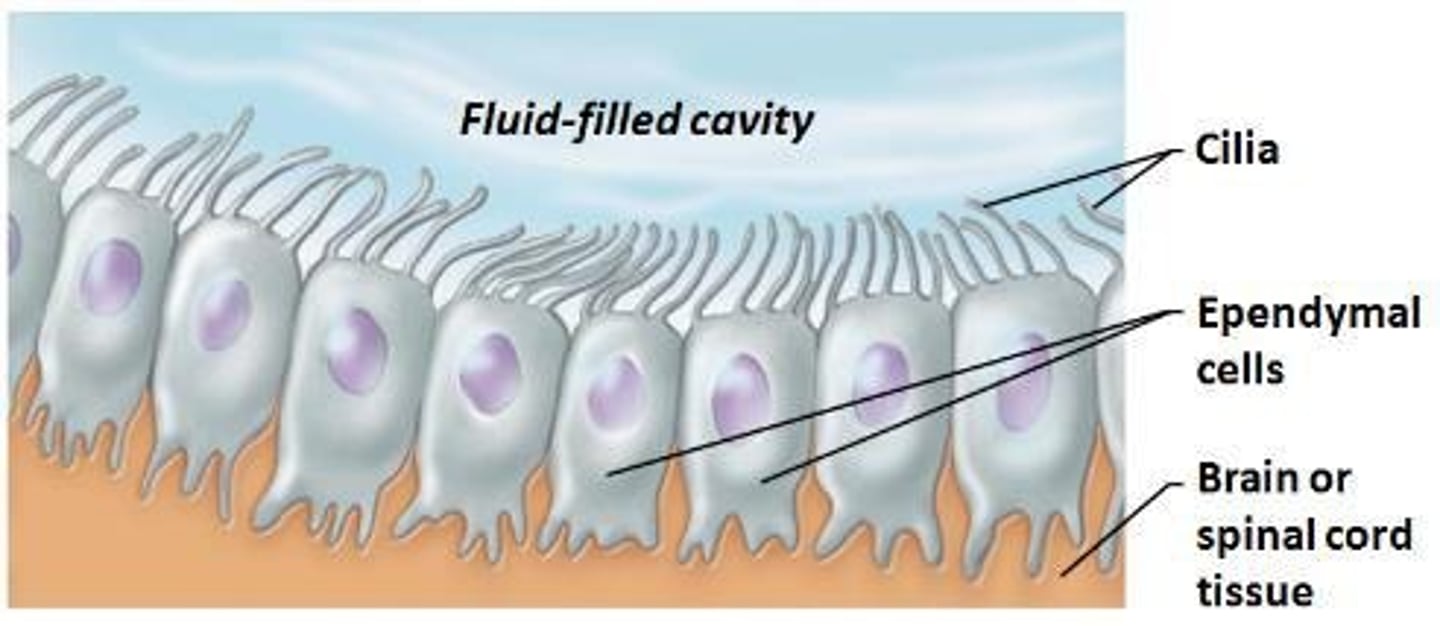
Ependymal Cells
Line brain cavities; circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
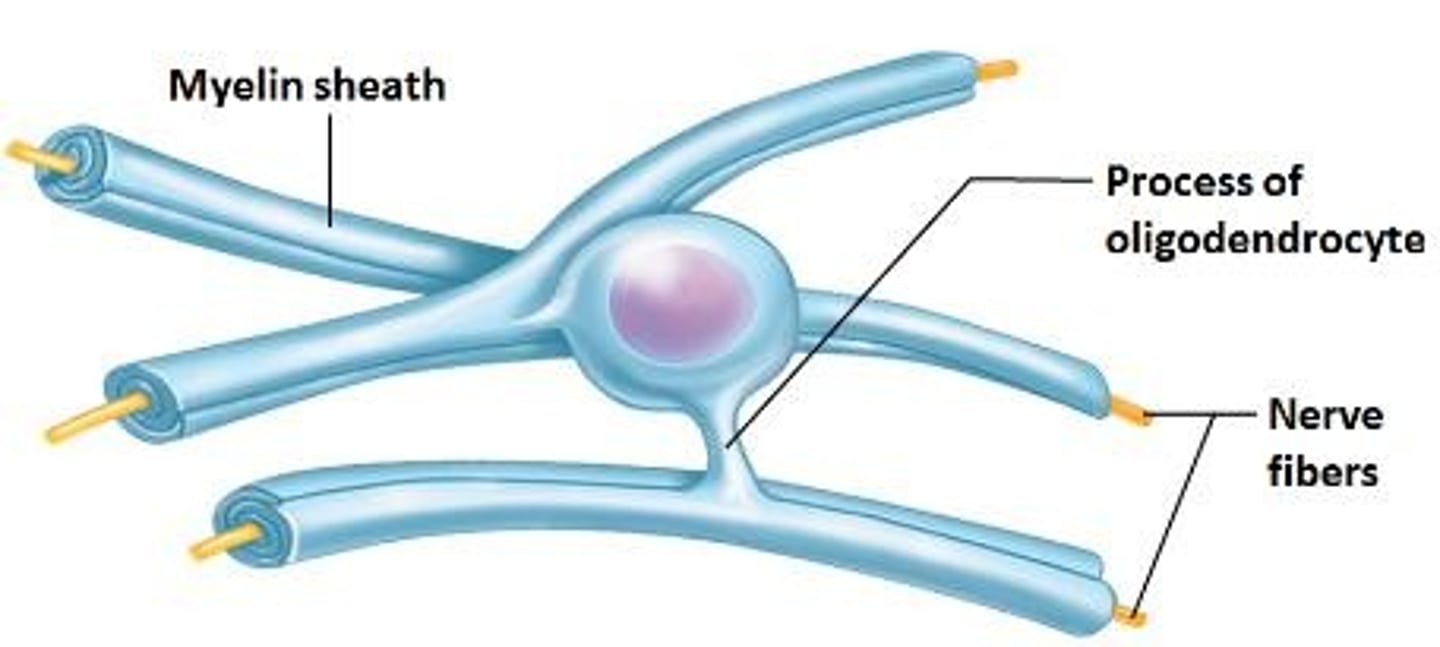
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheaths around CNS nerve fibers.
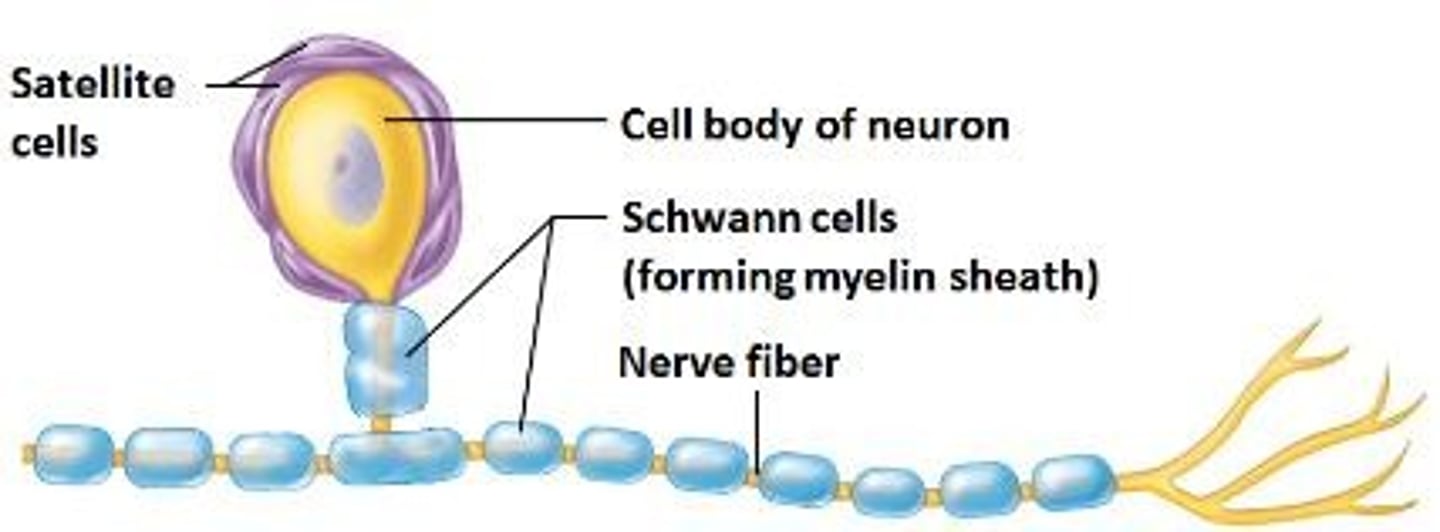
Satellite Cells
Surround neuron cell bodies in the PNS.
Schwann Cells
Myelinate peripheral nerve fibers; aid regeneration.
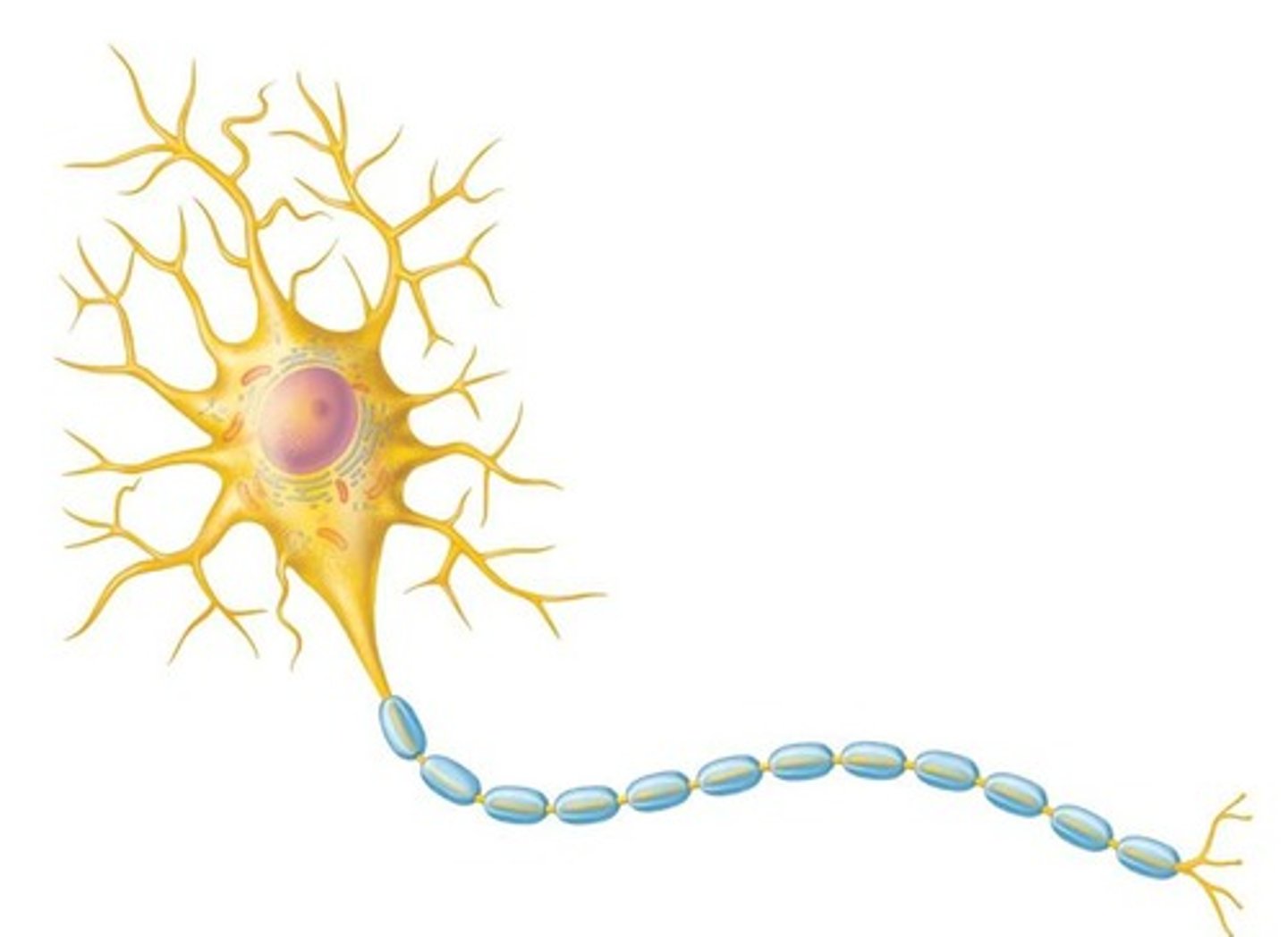
Neuron
Specialized cell conducting impulses in nervous system.
Neuron Cell Body
Biosynthetic center synthesizing proteins and chemicals.
Soma
Another term for neuron cell body.
Nissl Bodies
Rough ER in neuron; synthesizes proteins.
Ganglia
Clusters of neuron cell bodies in PNS.
Tracts
Bundles of neuron processes in CNS.
Nerves
Bundles of neuron processes in PNS.
Dendrites
Short branches receiving signals toward cell body.
Axon
Long extension transmitting impulses away from soma.
Axon Hillock
Cone-shaped area where axon originates.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in myelin sheath along axon.
Axon Terminals
Distal endings of axon; release neurotransmitters.
Myelin Sheath
Insulating layer increasing impulse transmission speed.
Myelination
Process of forming myelin around nerve fibers.
Action Potentials
Electrical impulses transmitted along axon.
Graded Potentials
Short-distance signals in dendrites.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals released to communicate between neurons.
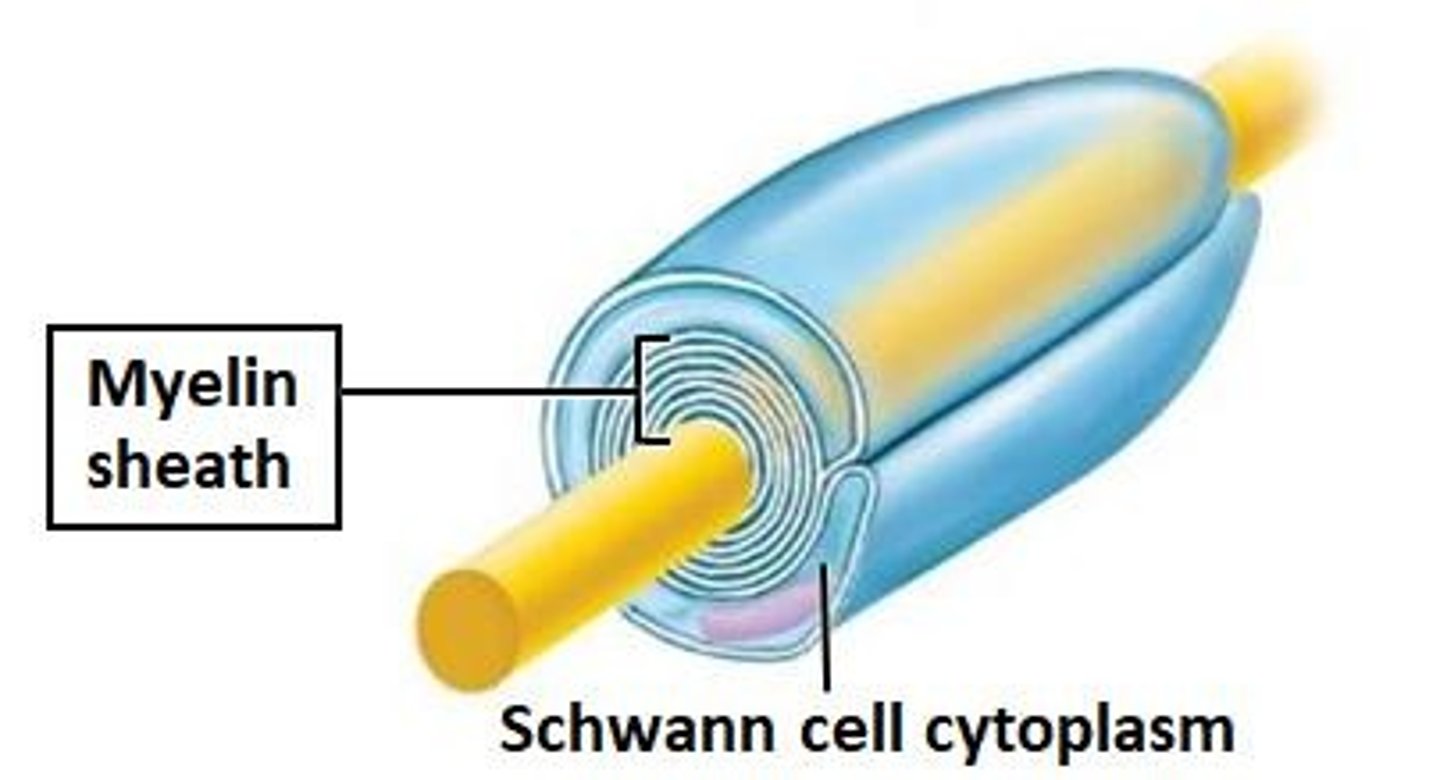
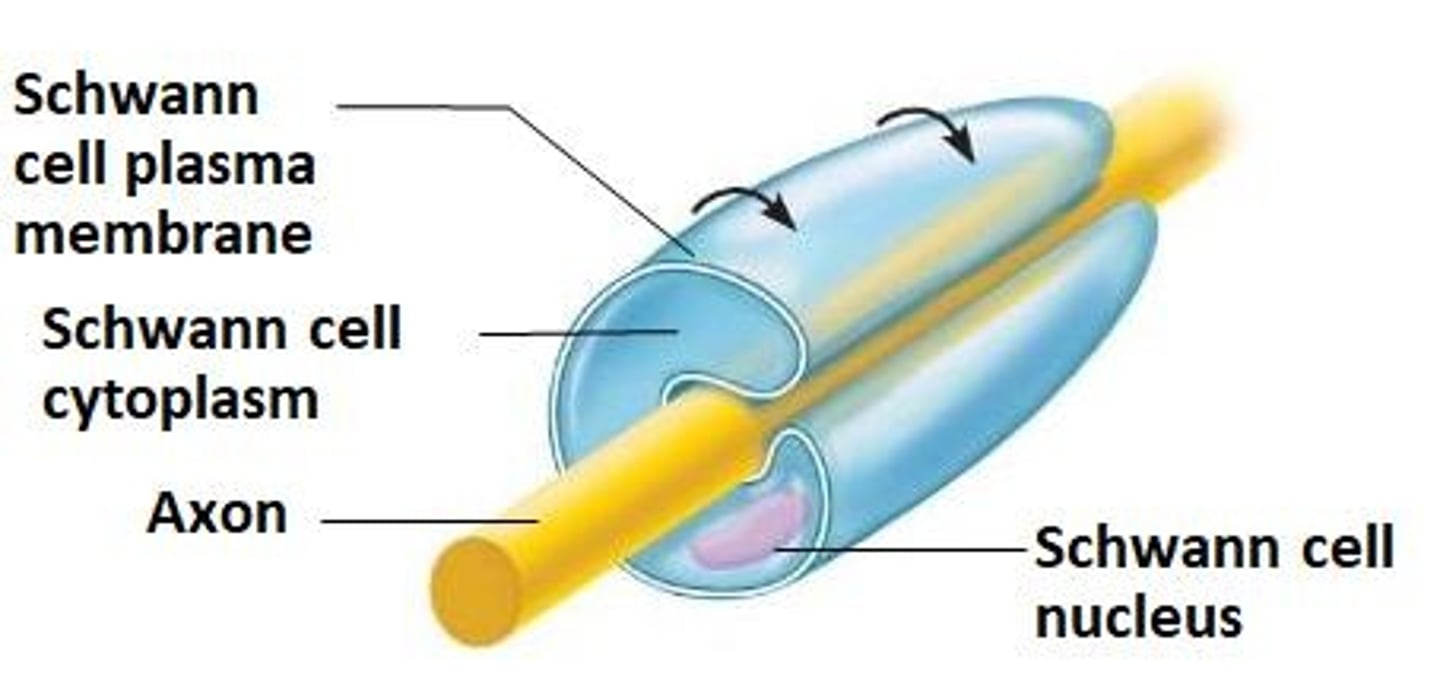
Schwann Cell
Glial cell forming myelin sheath in PNS.
Myelin Sheath
Insulating layer around axons formed by Schwann cells.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in myelin sheath between Schwann cells.
Nonmyelinated Fibers
Fibers not wrapped in myelin, surrounded by Schwann cells.
Oligodendrocytes
CNS cells forming myelin sheaths from flat processes.
White Matter
Brain regions with dense myelinated fiber tracts.
Gray Matter
Regions with neuron cell bodies and nonmyelinated fibers.
Multipolar Neurons
Neurons with three or more processes; most common.
Bipolar Neurons
Neurons with two processes; rare in retina.
Unipolar Neurons
Neurons with one short process; sensory receptors.
Sensory Neurons
Transmit impulses from receptors to CNS; mostly unipolar.
Motor Neurons
Carry impulses from CNS to effectors; mostly multipolar.
Interneurons
Connect motor and sensory neurons; mostly multipolar.
Membrane Potentials
Electrical differences across neuron membranes.
Action Potential
Nerve impulse generated by adequate stimulus.
Ion Channels
Proteins allowing ions to cross neuron membranes.
Leakage Channels
Always open ion channels allowing passive ion flow.
Gated Channels
Ion channels that open/close in response to stimuli.
Chemically Gated Channels
Open when neurotransmitters bind to them.
Voltage-Gated Channels
Open/close based on membrane potential changes.
Mechanically Gated Channels
Open/close due to physical deformation of receptors.
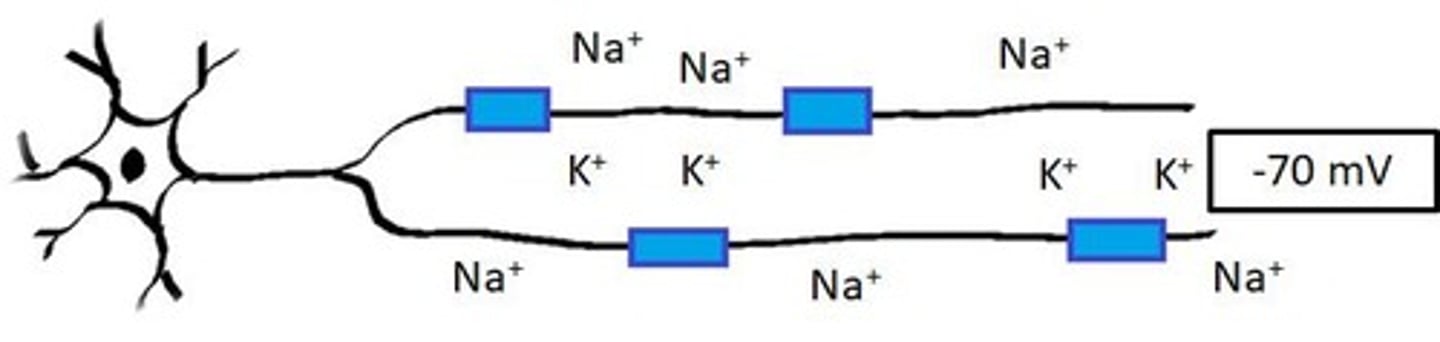
Resting Membrane Potential
Potential difference of approximately -70 mV in neurons.
Multipolar Neuron
Neuron with three or more processes; common in CNS.
Bipolar Neuron
Neuron with one axon and one dendrite; rare.
Unipolar Neuron
Neuron with one short process; T-like division.
Interneurons
Connect sensory and motor neurons; mostly multipolar.
Afferent Neurons
Sensory neurons that approach the CNS.
Efferent Neurons
Motor neurons that exit the CNS.
Membrane Ion Channels
Proteins that regulate ion flow across membranes.
Leakage Channels
Ion channels that are always open.
Chemically Gated Channels
Open when neurotransmitter binds to them.
Action Potential
Nerve impulse generated by neuron response.
Resting Membrane Potential
Potential difference across a resting neuron's membrane.
Polarized Membrane
State of membrane at approximately -70 mV.
Effectors
Muscles or glands that respond to motor neuron signals.
CNS
Central nervous system; includes brain and spinal cord.
PNS
Peripheral nervous system; includes all other nerves.
Neuron Cell Body
Contains nucleus and organelles; integrates signals.
Resting Membrane Potential
Electrical charge difference across a neuron's membrane.
Ionic Composition
Concentration of ions inside vs. outside cell.
Na+ Concentration
Higher outside the cell than inside.
K+ Concentration
Higher inside the cell than outside.
Potassium's Role
Most significant in establishing membrane potential.
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Maintains Na+ and K+ concentration gradients.
Membrane Potential Changes
Alterations in ion concentrations and permeability.
Action Potentials
Long-distance signals along axons.
Depolarization
Decrease in membrane potential, less negative inside.
Polarized State
Positive outside, negative inside the membrane.
Hyperpolarization
Increase in membrane potential, more negative inside.
Nerve Impulse Probability
Increased by depolarization, decreased by hyperpolarization.
Current Flow
Varies with stimulus strength in graded potentials.
Decay of Graded Potentials
Signal diminishes quickly over distance.
Action Potential Voltage Change
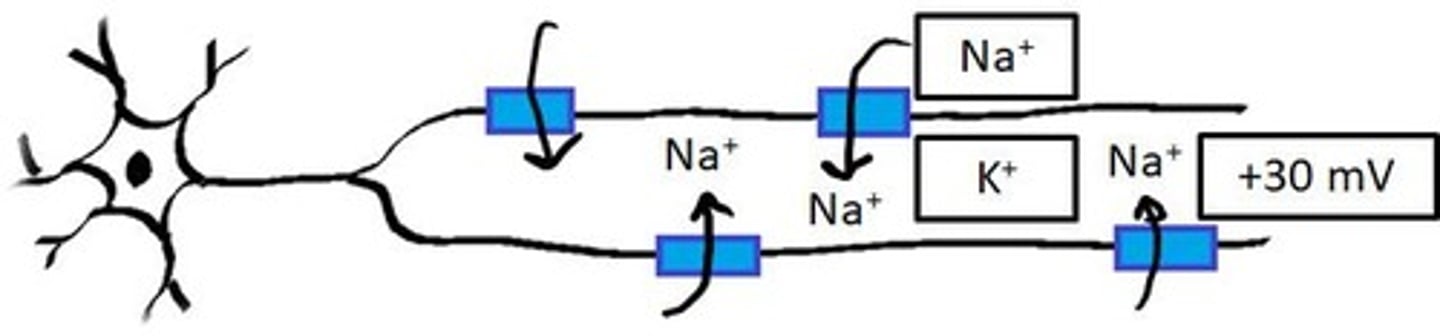
Brief change of ~100 mV during signal.
Positive Inside During AP
Inside becomes positive, reaching +30 mV.
Resting Membrane Value
Typically around -70 mV in neurons.