forces and elasticity
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
what does the term ‘deformation’ mean?
deformation refers to the change in the shape of an object, as a result of forces being applied to it.
what is elastic deformation?
elastic deformation is a change in the shape of an object, which can be reversed once the forces causing it have been removed.
so the object will return to its original shape.
what is inelastic deformation?
inelastic deformation is a change in the shape of an object, which cannot be reversed once the forces causing it have been removed.
so the object will not return to its original shape.
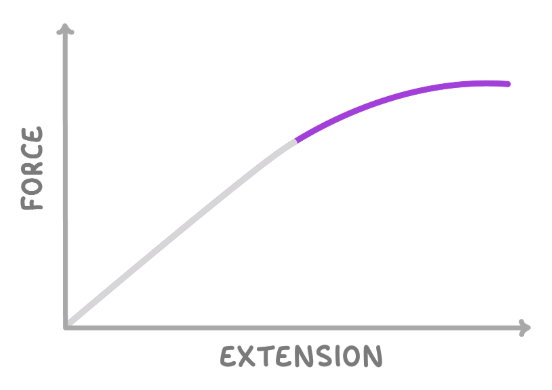
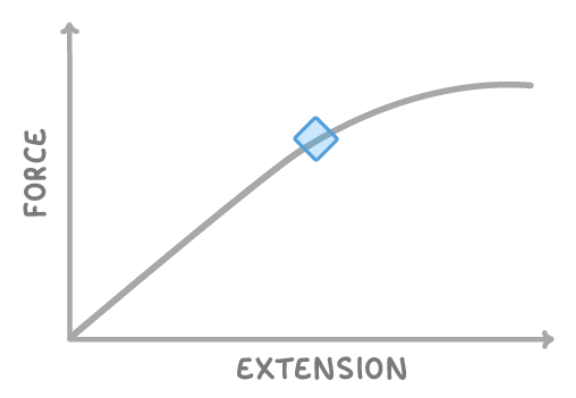
on the graph above, what sort of deformation occurs in the highlighted part of the line?
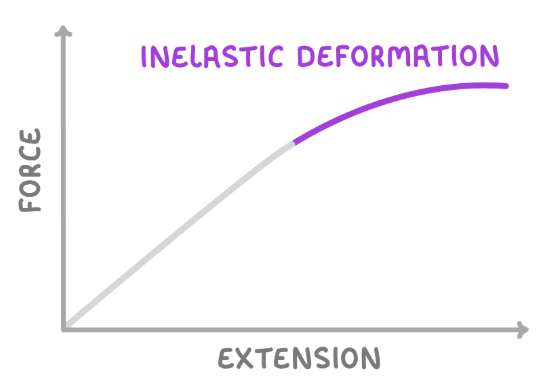
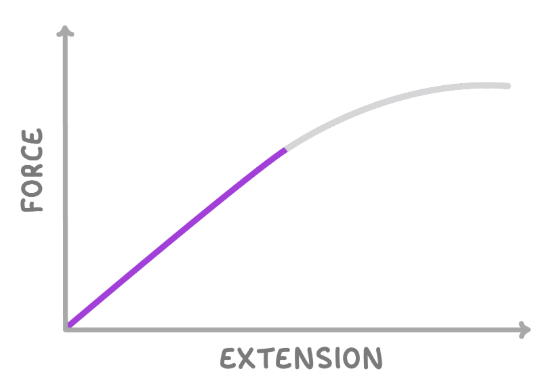
on the graph above, what sort of deformation occurs in the highlighted part of the line?
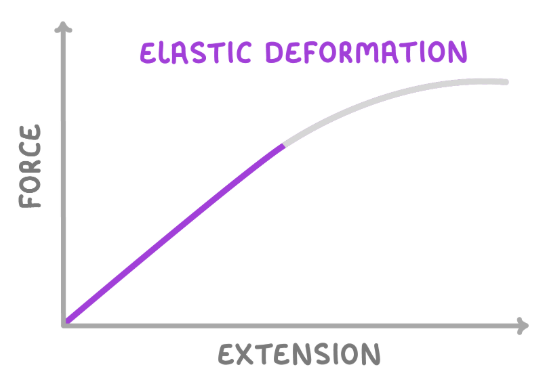
what is the minimum number of forces required to stretch, compress, or bend an object?
two forces.
if only one force is applied then it would cause the object to accelerate instead.
what does the term ‘spring constant’ mean?
an object’s spring constant is a measure of how many newtons of force it would require to stretch (or compress) the object by 1 metre. it has the units n/m. it’s basically a measure of how firm (or stiff) the spring is.
a higher spring constant means the spring is more firm (harder to stretch).
a lower spring constant means the spring is less firm (easier to stretch).
which would have a higher spring constant, an elastic band, or a hosepipe?
a hosepipe would have a much higher spring constant as it would require much more force to stretch.
what is hooke’s law?
hooke’s law states that the extension of an object is directly proportional to the force applied. it can be described by the formula F = ke.
what is the ‘elastic limit’?
the point at which an object being stretched stops deforming elastically, and starts deforming inelastically.
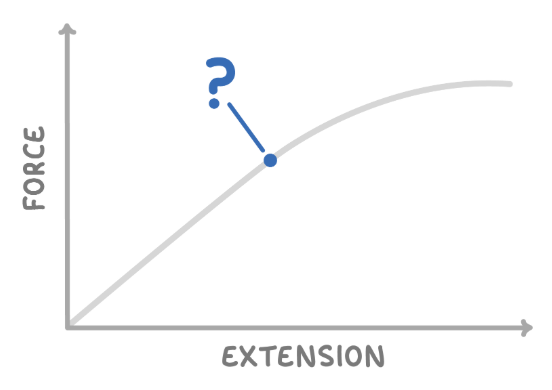
what name is given to the point where extension is no longer proportional to force applied?
limit of proportionality.
what is elastic potential energy?
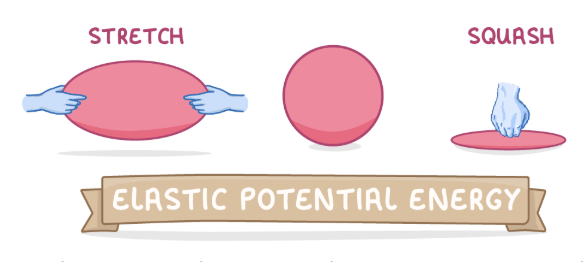
the energy stored in an object when it is stretched or squashed.
when discussing elastic potential energy, what does extension (e) mean?
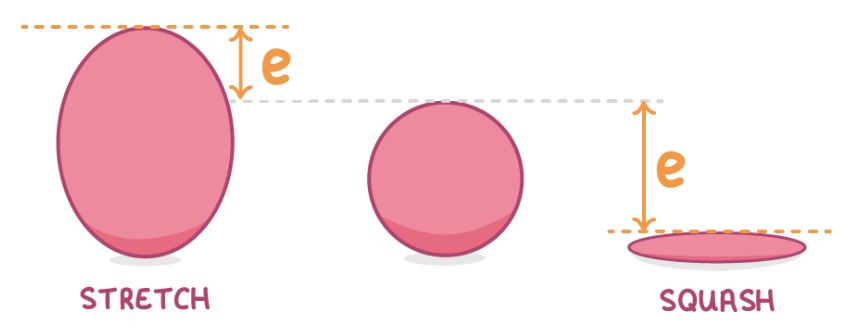
the extension (e) of an object is how much longer or shorter it is, due to being stretched or squashed.
when discussing elastic potential energy, what units should extension (e) be in?
metres (m)
what is the formula for elastic potential energy?
elastic potential energy = 0.5 × spring constant × (extension)2
Ee = ½ k e2
what is the formula that links force, spring constant and extension?
force = spring constant × extension
F = k e
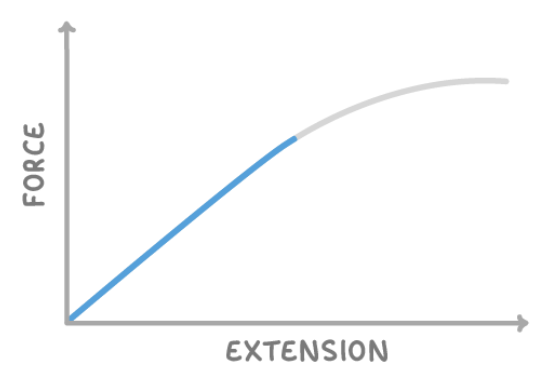
above is a force-extension graph. what does the gradient of the straight part of the line tell you?
that straight part of the line tells you the spring constant.
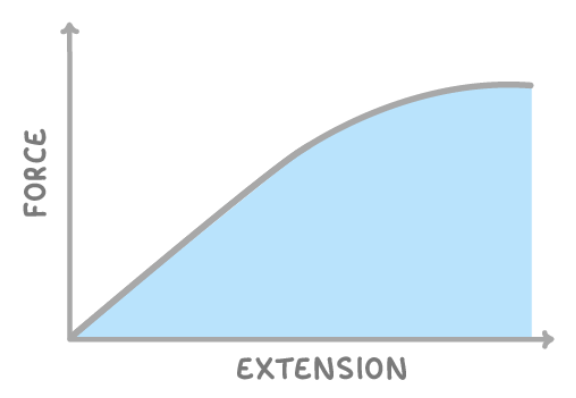
above is a force-extension graph. what does the area under the curve tell us?
elastic potential energy.
above is a force-extension graph. what do we call the point where the line transitions from straight to curved?
the limit or proportionality or the elastic limit
what is the aim of the hooke’s law practical investigation?
to determine the relationship between force and extension for a spring.
what is the independent variable in the hooke’s law practical?
applied force
what is the dependent variable in the hooke’s law practical?
extension of the spring
what is the control variable in the hooke’s law practical?
using the same spring
how is the extension of the spring calculated?
extension = new length - original length