NEU 201 Lecture 6: Dendritic Intergration
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
How many muscle fibers are connected to a motor neuron
one muscle fiber per motor neuron
Why does the Nerve-Muscle Synapse always fire?
huge synapse
alot of vesicles ~200
many postsynaptic receptors
How many inputs does a CNS receive?
thousands
How many outputs are made by most CNS neurons
one (excitatory or inhibitory PSP)
How do CNS neurons receive multiple inputs
with multiple neurotransmitters (1 vesicle per AP)
ionotropic and metabotropic receptors
diverse ion flow
What is dendritic intergration?
the spatial and temporal summation of inputs
What effects the size of PSP
the number of channels open during dendritic integration
What is at a dendrite synapse?
neurotransmitter molecules
vesicles
postsynaptic receptors
Types of dendritic input summation
single channel currents become EPSP or IPSP
EPSP and ISPS are integrated
Spatial summation
What determines if an action potential threshold is crossed in Dendritic integration
number, amplitude (stronger vs weaker) , and timing (did they fire close to each other) of EPSP and IPSP
location of axon inputs
Spatial Summation
inputs that arrive at different synapses can sum to a larger EPSP or IPSP
How does EPSP and IPSP spread in Dendrites?
passively but voltage-gated channels can boost signals
How does location affect Spatial Summation
inputs closer to axon initial segment are more effective to trigger AP
Temporal Summation
when 2 inputs at the same synapse sum within 1-15 miliseconds
What happens to EPSP and IPSP over time
they spread out as they trave; which helps temporal integration
What affects Action Potential Propogation Speed?
time constant and length constant
What is time constant?
time to charge membrane

What is the relationship between time constant and charging speed?
smaller time constant = faster charging speed
What is length constant?
distance where graded potential decays to 37% of original amplitude
What is the relationship between length constant and propagation of action potentials?
larger length constant = more effective propagation
What are the two types of resistance that oppose current spread?
membrane resistance and axial (internal) resistance
What is membrane resistance (Rm)?
the opposition to ion flow across the membrane
subject to change
What causes membrane resistance?
less open channels (less conductance)
constant in mature neurons
What is Axial( (internal) resistance?
opposition to the flow of ions down the inside of neurites
What affects Axial resistance?
larger axons =less resistance
What is the length constant formula?

Length constant depends on what?
axon diameter , internal resistance, membrane resistance
How can you reduce axial resistance?
widen the axon and close channels
How are length constant and membrane resistance related?
increased membrane resistance = increased length constant= faster conduction = higher time constant (slow conduction)
What is the relationship between Myelin and Conduction
Myelin increase specific membrane resistance and decreases membrane capacitance
What effect does Myelination have on the time constant?
no effect

what effect does myelination have on the length constant
myelination increases the length constant

Impact of Length constant on spatial summation
larger length constant: action potential travels farther
smaller length constant: decays fast
same for EPSP and IPSP
affects how much inputs is need to make postsynaptic cell fire
What does Lidocaine do to Voltage-gated Sodium Channels?
it blocks open, inactivated channel ONLY
Why are small axons like pain fibers sensitive to Lidocaine?
smaller axons have high internal resistance and low length constant so they require more depolarization and are more sensitive to lidocaine

What is the relationship between Neuromodulators and Length constant?
neuromodulators regulate the efficiency of distant synapse through length constant because less current leaks during transmission

How can length constant change?
locally (neuromodulators)
rapidly
Shunting Inhibition
lowering of the length constant to prevent action potentials
How do ions affect shunting inhibition?
Inhibitory Cl- influx holds membrane potential at 65mV
Open channels reduce the membrane resistance and length constant because depolarization is leaking out
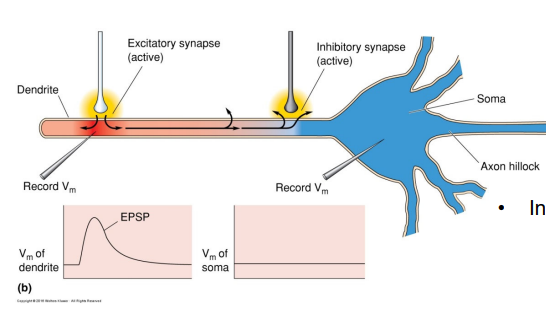
What is counterbalance excitation in Spatial Summation
inhibitory neurons can influence which EPSP trigger action potential
What is Microcephaly
to have reduced brain size (~400cm)
average adult ~1200-1600cm
What is cerebral rubicon
human behavior result of human brain organization rather than brain size
Common features of the Nervous system
the neuron
the synapse
neural circuits
Similarities in rat and human brain
two cerebral hemispheres
relative locations of brain regions ventricles
complexity of cerebellum
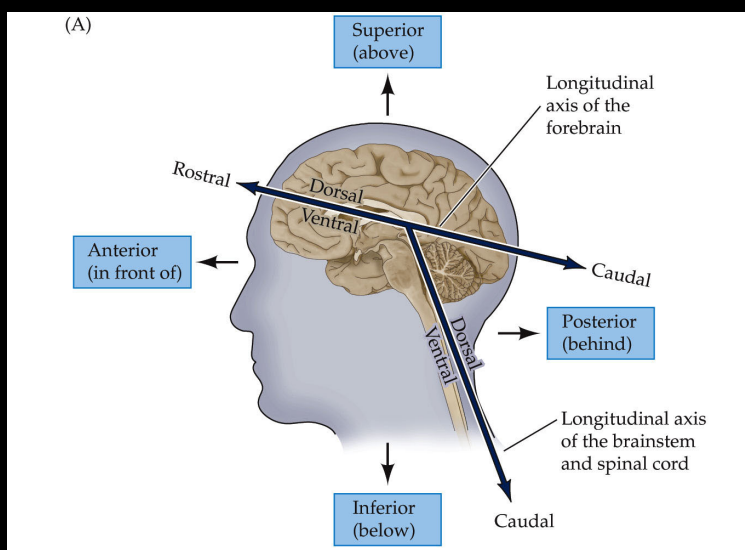
Ipsilateral
from brain to tail
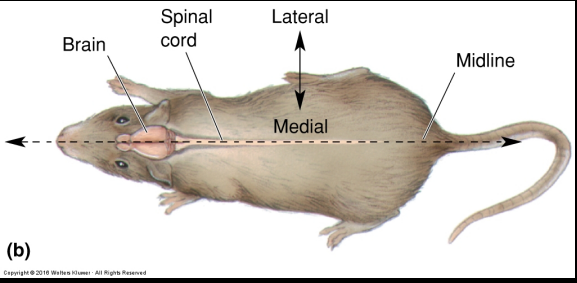
Contralateral
from side to midline
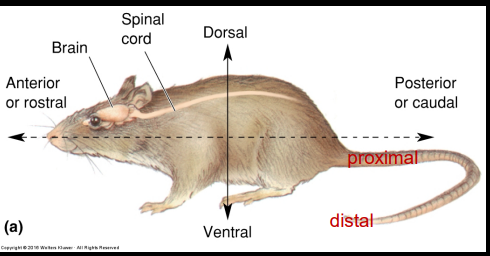
Superior
Above
Posterior
behind
Anterior
in front of (toward the eyes)
Inferior
below (toward spine)
Rostral
toward eyes on longitudinal axes
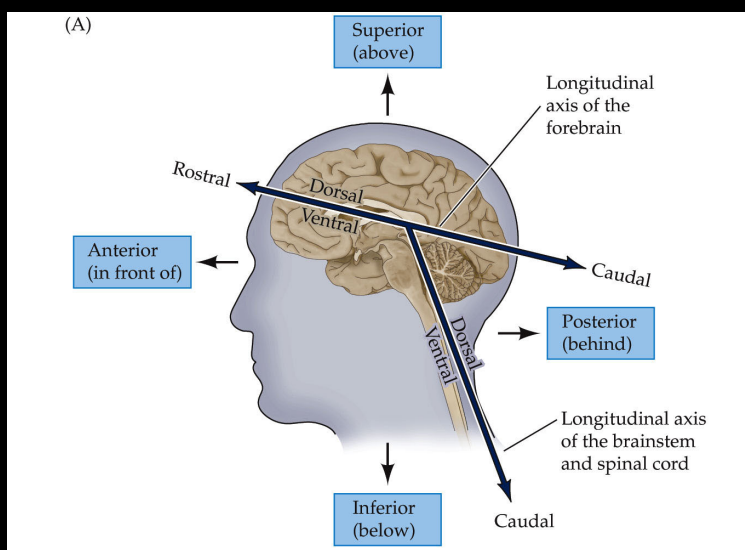
Caudal
toward back of brain on longitudinal axis
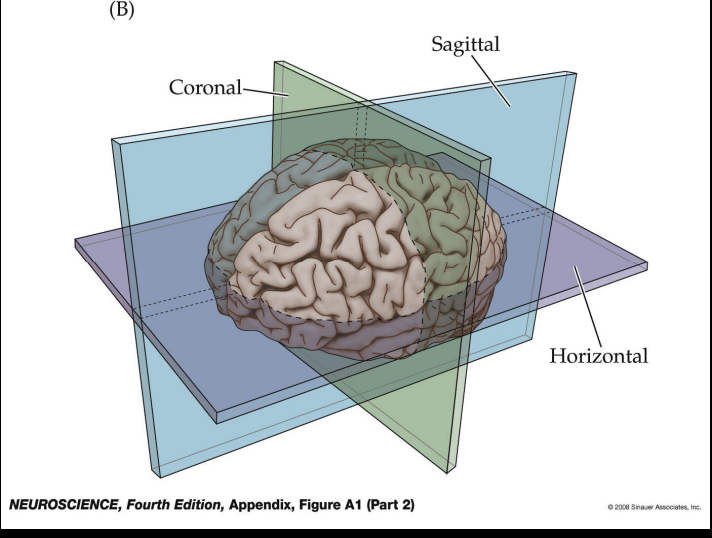
Coronal
cut the brain like a guillotine
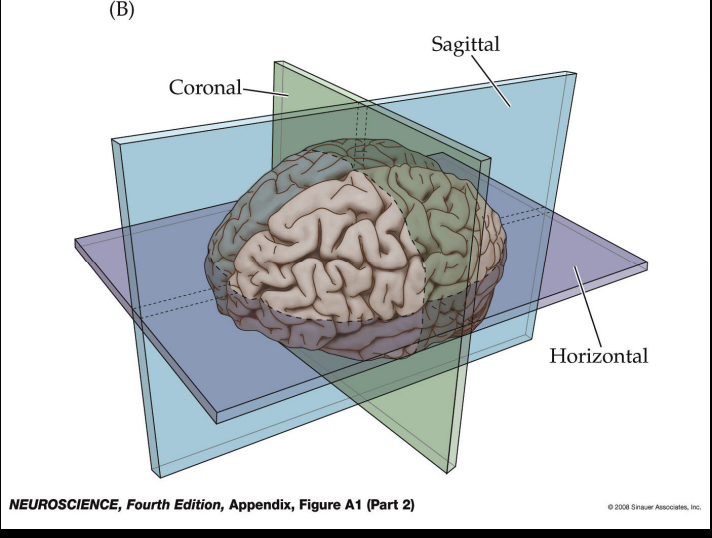
Horizonal Slice
like a pencil held horizontally
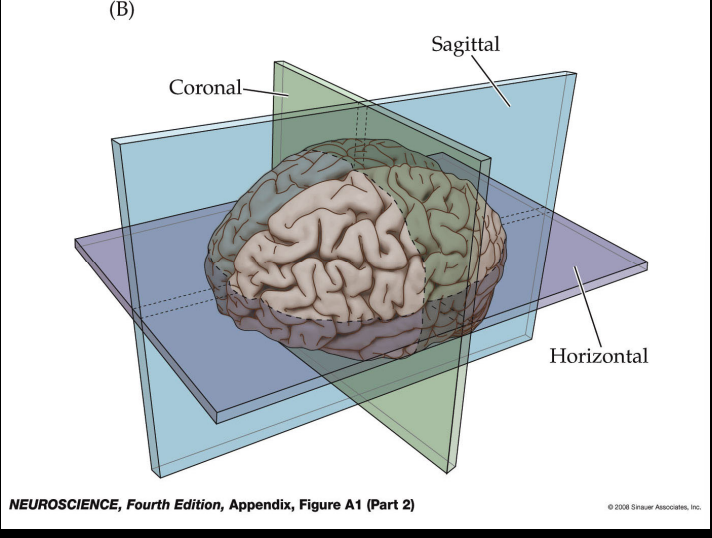
Sagittal Slice
like a cut forward and back
What are the two types of nervous systems
Central and Peripheral Nervous System
What makes up the central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
Which neurons cross the midline
most sensory and motor neurons
Which brain regions are in all mammals?
cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem (CNS)
Which layers protect the brain?
Dura mater, Arachnoid Membrane, Pia mater
What is Dura Mater?
the most external covering of the brain under the skull
What is the arachnoid membrane?
series of spiderweb like connects that connect the dura mater to the pia mater
What is the pia mater?
the layer that directly covers the brain
Ventricular System
CSF is made in ventricles
flows to subarachnoid
leaves via blood vessels
What happens when the CSF flow is disrupted
the CSF continues to flow in but cannot flow out, so it presses on the brain and causes swelling
What makes up white matter
mylination
What makes up gray matter
neurons
Anatomy of cerebral hemisphere
Frontal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Frontal Lobe
reasoning, speech, problem solving, movement, emotions
Parietal Lobe
movement, orientation, perception of stimuli
Occipital Lobe
visual processing
Temporal Lobe
perception and recognition of audio, memory, speech
Spinal Cord
get signals to and from body
has white and gray matter
Somatic PNS
spinal nerves that control voluntary behaviors
Dorsal Roots
incoming sensory
Ventral Roots
outgoing motor
Somatic Motor Neurons are in which nervous systems
cell bodies : CNS (spinal cord)
axons: in PNS
Visceral PNS (autonomic nervous system)
involuntary reactions (organs, blood, rate of heart)
How many cranial nerves?
12
How to define a brain area
lesions studies
stimulate and monitor responses
image cytoarchitecture
trace connections
record responses properties
wiring diagram/ map
Which staining technique absorbs light?
lipids replaced by water-soluble gel
Types of brain imaging
CT , MRI, fMRI, PET
What do fMRI and PET measure?
blood flow
good spatial bad temporal resolution
shows activity
What does MRI measure?
changes in the H atom energy state in response to magnetic fields
Common organization of cerebral cortex
outer layer (layer I) no neuronal cell bodies
1 or more layer of pyramidal neurons with large dendrites in layer 1
Does the amygdala is made of layers or nuclei?
nuclei
How to identify receptive fields
with single unit electrophysiological recording from cortical pyramidal neuron
Which cortex are organized into maps
sensory and motor cortices
What is the sensory map called
somatosensory map
What does the homunculus tell us about brain organization
more area dedicated to finer precepting body movement and regions