A&P: Structural Organization
1/64
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Structural Organization
Understanding the various primary tissue types in the human body is essential for understanding the structure and function of organs.
Four Basic Tissue Types
The four basic tissue types are nervous, muscular, epithelial, and connective, each with distinct functions and characteristics.
Connective Tissue
Provide structure and support, consisting of various cell types and extracellular fibers.
Loose, dense
The two connective tissue types.
Muscle Tissue Types
Classified into three subtypes: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth, each responsible for different types of movement.
Skeletal Muscle
Striated, multinucleated, and voluntarily controlled.
Cardiac Muscle
Striated, has intercalated discs, and no voluntary control.
Smooth Muscle
Nonstriated, unnucleated, and no voluntary control.
Nervous Tissue
Composed of neurons and glial cells, responsible for information processing and communication.
Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
Cellularity
Covers body surfaces
Have an exposed surface
Cellular organization
Cellular connections
Avascular
Innervated
Capable of Regeneration
Cellularity
Close-packed cells with limited extracellular material.
Have an exposed surface
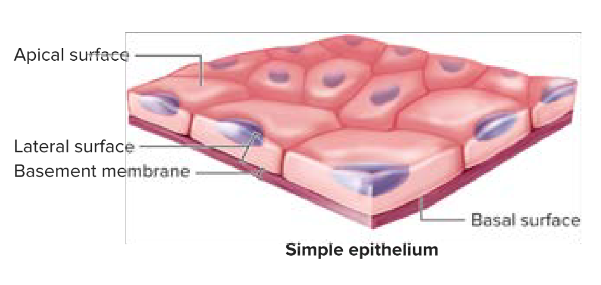
The surface that is exposed is called apical (free) surface. I.e, skin exposed to air; stomach lining exposed to food.
Cellular Organization
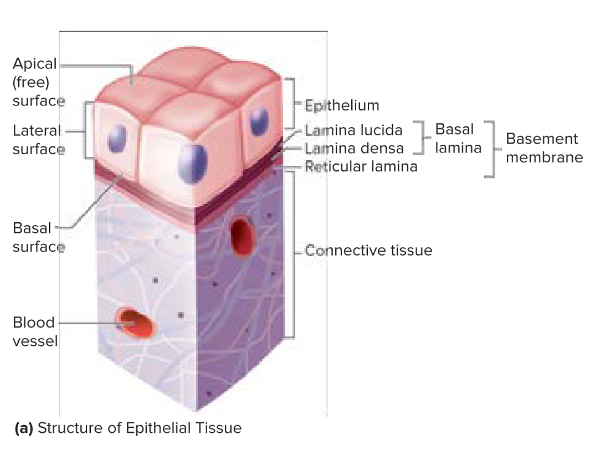
Epithelia tissue attaches at the basal surface— the surface of cells that are anchored in place. Material is called the basement membrane.
Made up of two layers: basal lamina and reticular lamina
Can be further divided into lamina lucia and lamina densa.
Deep to the basement membrane is the reticular lamina. Between the epithelial cells (where epithelial cells are connected to each other) is the lateral surface.
All epithelial tissue is supported by connective tissue.
Basal Surface
Epithelia tissue attaches at the __.
Basement Membrane
Made up of two layers: basal lamina and reticular lamina
Can be further divided into lamina lucia and lamina densa.
Made up of extracellular material secreted by epithelial cells— important role in supporting/guiding cell migration in tissue repair.
Reticular Lamina
Deep to the basement membrane.
Lamina Surface
Between epithelial cells.
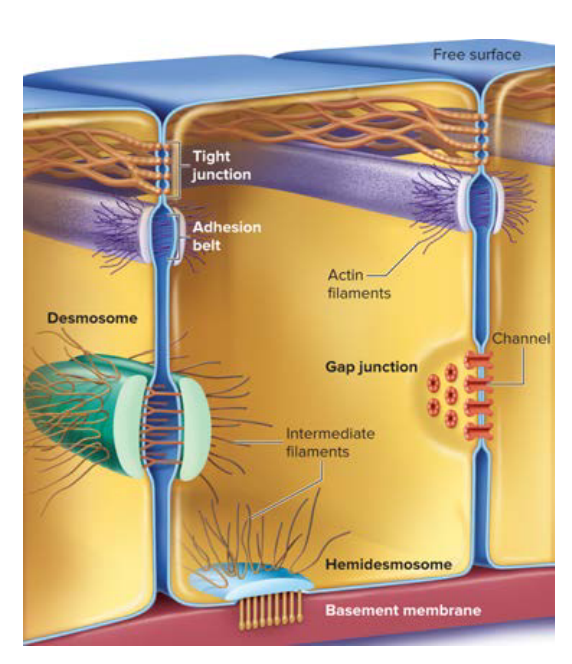
Cellular Connections
Between epithelia tissue are different cellular connections— tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions.
Avascular
Contains no blood vessels.
Innervated
Receives nervous innervation (includes nerves).
Regeneration
Epithelia tissue is replaced rapidly by cell division. Cell loss due to friction and contact with hostile environments.
Protection, absorption, filtration, and secretion
Functions of Epithelial Tissue.
Protection
Acts as a barrier and protects underlying structures from abrasion
Prevents substances from moving through it (toxic molecules and microorganisms).
Absorption
Contain carrier proteins which regulate the absorption of materials.
Filtration
Permits passage such as oxygen or carbon dioxide through.
Secretion
Epithelial tissue can secrete sweat or enzymes.
Simple Layers
Single cell layer, areas of absorption and filtration. Each cell extends from the basement membrane to the free surface. Facilitates absorption and filtration.
Stratified Layers
Two or more cell layers, areas of high abrasion.
Regenerate from below via mitotic division
Basal cell divide
Move apically to replace older surface cells
Durable
Provide protection
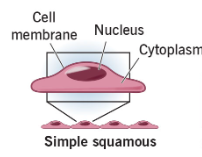
Squamous
Flattened, scale-like.
Squished

Cuboidal
Boxlike, as tall as wide.
Cube
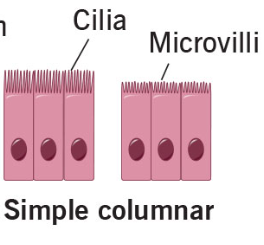
Columnar
Tall
Column
Simple Epithelia
This kind of epithelia consists of a single layer of cells, facilitating absorption and filtration.

Stratified Epithelia
This kind of epithelia have two or more layers, providing protection in areas of high abrasion.
Transitional Epithelium
This type of epithelium accommodates fluctuations in fluid volume and changes shape to increase surface area.
Pseudostratified Epithelium
One layer, but looks like more due to different sizes of cells. Has cilia on apical side.
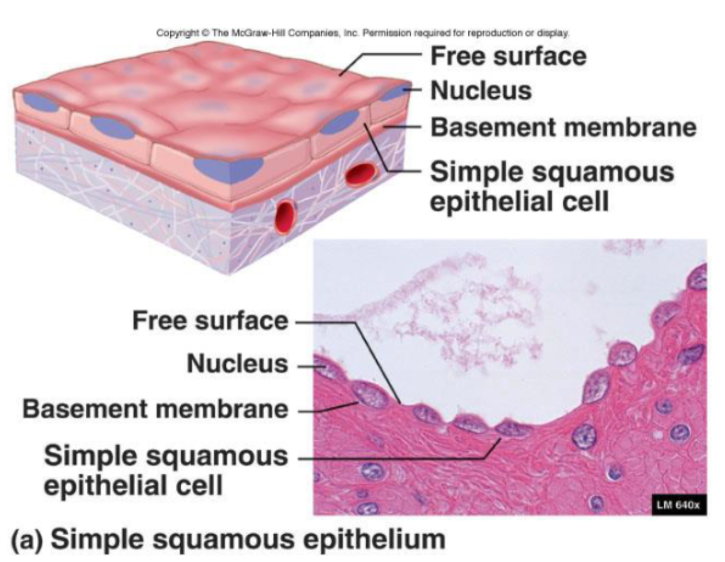
Simple Squamous Epithelia
Function:
Diffusion, secretion, and filtration
Needed when fluids or air must readily travel for diffusion
Location:
Endothelium
Lining of the lymphatic system
Lining of all organs in cardiovascular system
Mesothelium
Serous membrane linings of ventral body cavity
Alveoli or capillary beds
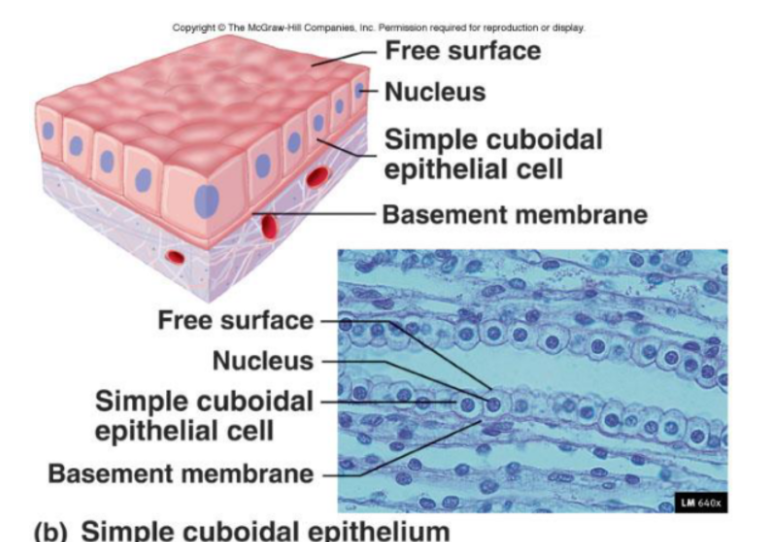
Simple Cuboidal Epithelia
Function:
Secretion and absorption
Location:
Kidneys (nephron cells)
Plexus of the brain
Lining of lung bronchioles
Surfaces of ovaries
Microvilli may be present to increase surface area.
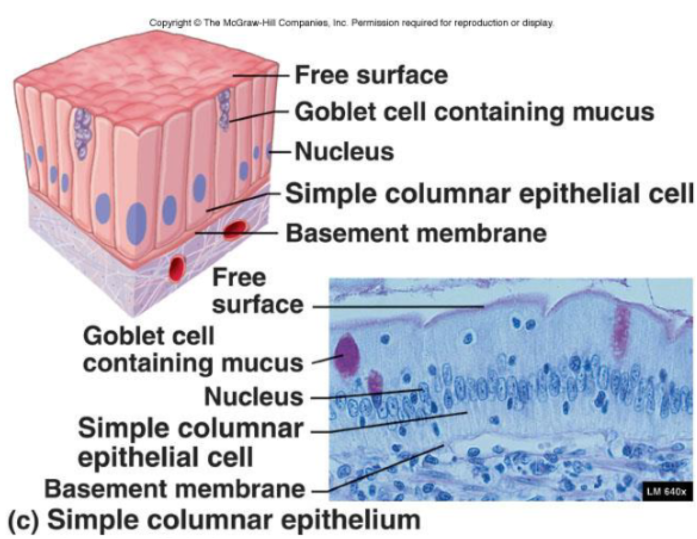
Simple Columnar Epithelia
Function:
Absorption (specifically pinocytosis), protection, and secretion
Location:
Digestive tract, GI tract
Modifications:
Dense microvilli on apical surface
Goblet cells that secret protective lubricant
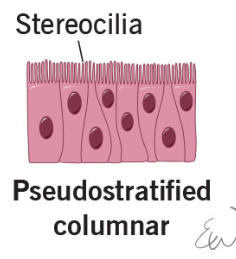
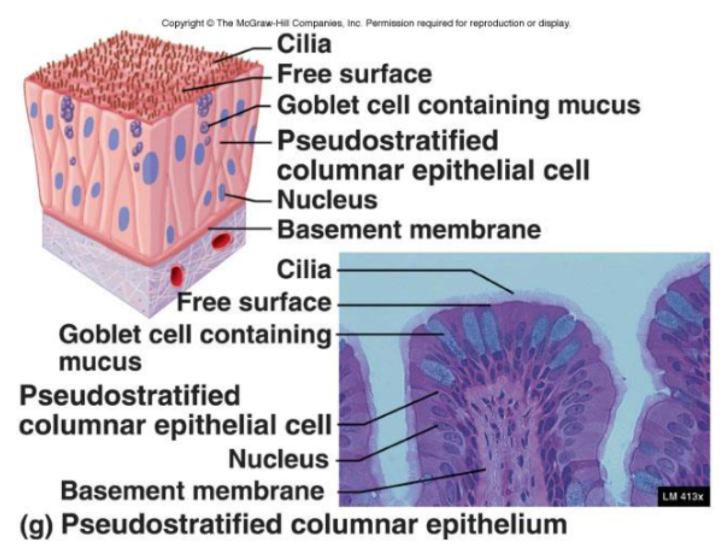
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelia
Single layer of cells that vary in height
Only tallest reach apical surface
Always ciliated
Cilia propel trapped matter out
Goblet cells secrete mucus
Mucus traps particulate matter
Nuclei are located at different heights
Function:
Absorption and secretion
Location:
Respiratory system (nasal cavities)
Reproduction
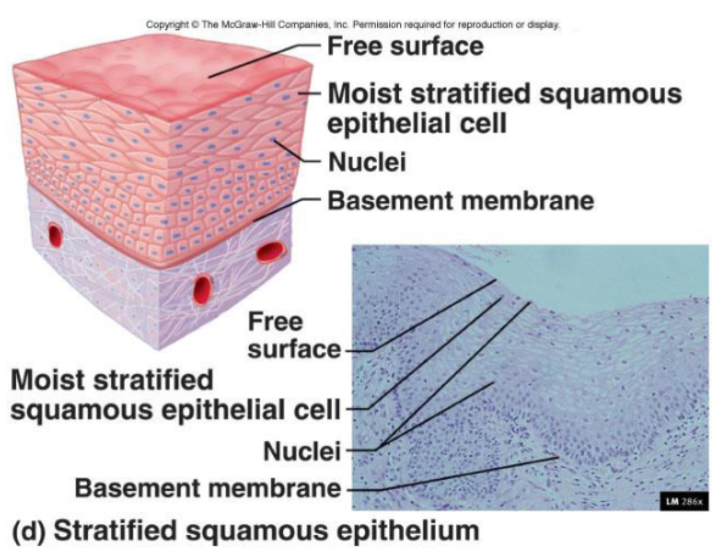
Stratified Squamous Epithelia
Surface cells are squamous
Deep layers consist most often of cuboidal
Stratified squamous is categorized as non keratinized (moist) or keratinized.
Non keratinized are living cells in the deepest and superficial layers— a layer of fluid covers superficial layers, making them moist
Keratinized are living cells only in the deepest levels, and the superficial layers are composed of dead cells
Function:
Protects against abrasion; mechanical protection wherever there is friction
Location:
Areas of abrasion
I;e, tongue or epidermis
Forms external surface of the body
Extends into all body openings
Outer layer (epidermis) is keratinized
Surface cells are flattened and atrophied
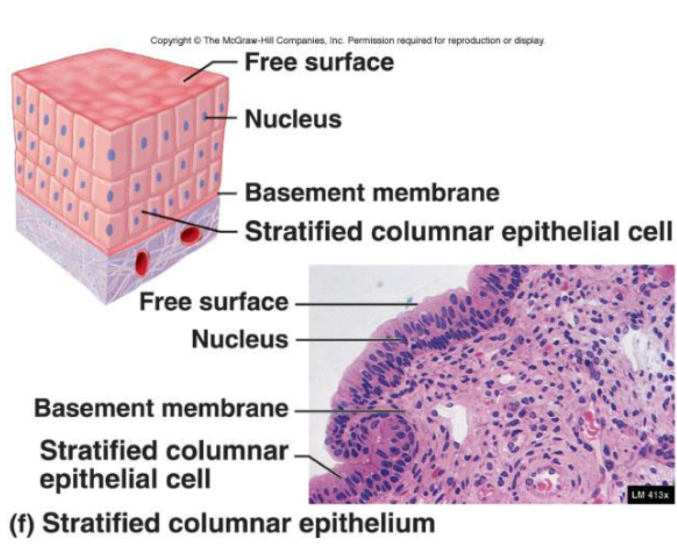
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelia
Rare
Function:
Movement and secretion
Location:
Glands (mammary, sweat)
Ureter
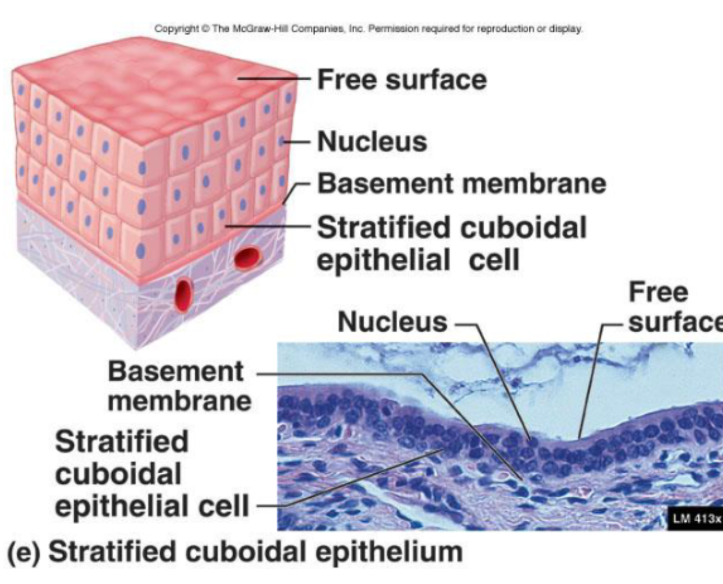
Stratified Columnar Epithelia
Rare
Function:
Protective and secretion
Location:
Location of eyelids
Urethra
Pharynx
Anus
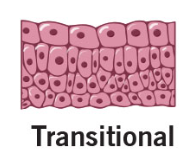
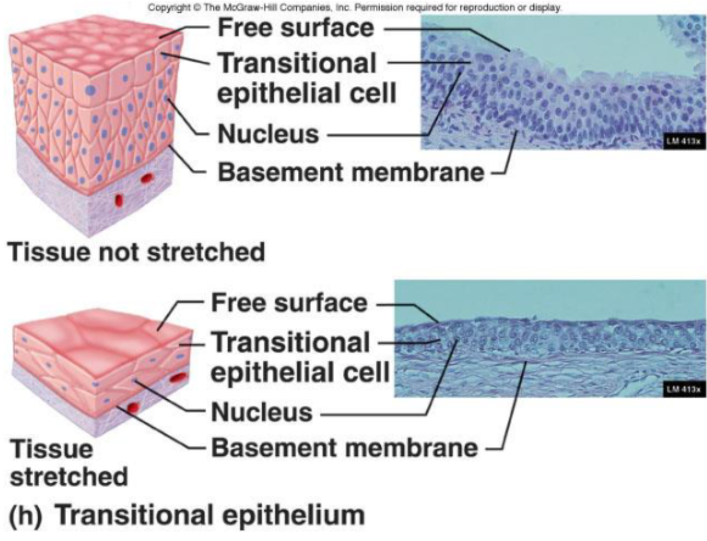
Transitional Epithelia
Function:
Accommodates fluctuations in the volume of fluid in an organ/tube
Need for more surface area
Location:
Lining of urinary organs
Apical cells can change shape to accommodate stretching
Glandular Epithelium
Consists of specialized cells that secrete products, classified into exocrine and endocrine glands.
Classification of Glandular Epithelia
There are three specific distinctions of glands— duct structure, secretory structure, and mode of secretion.
Glands
They consist of one or more cells that make/secrete a product.
Secretion refers to the aqueous product of glandular cells and the process of making that product.
Formation involves active processes.
Made in ER, packed in Golgi, and secreted by exocytosis
Exocrine Glands
Secrete products via ducts onto body surfaces or cavities.
Endocrine Glands
Ductless and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
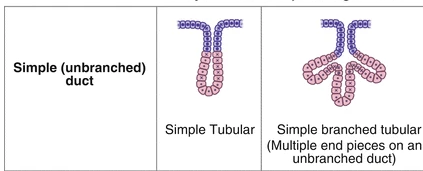
Duct Structure
The duct is the tube in contact with the epithelial tissue free surface, which transports secreted material.
The duct can be:
Simple— single, unbranched duct
Compound— branched duct
Secretory Portion
Found deeper within the epithelium, composed of cells responsible for producing the secreted material (secretory cells).
The secretory portions of the glands can be:
Tubular— straight, narrow tube with the same width as the duct
Acinar— a saclike structure whose width is greater than the width of the duct
They both are supported by connective tissue, which supplies blood and nervous fibers.
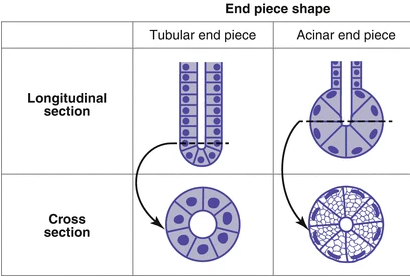
Unicellular, simple, and compound
Three Categories of Exocrine Glands
Unicellular Glands
Goblet cells that secrete mucus.
Simple Glands
Multicellular glands with a single, unbranched duct.
Compound Glands
Multicellular glands that have several branched ducts. The secretory portions can be tubular or acinar, or a mixture of both.
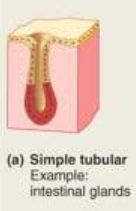
Simple Tubular
Glands forming a straight tube with no branching.
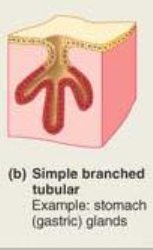
Single Branched Tubular
Glands with several tubular secretory portions branching from single duct.
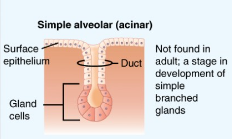
Simple Acinar
Glands with a single saclike secretory portion.
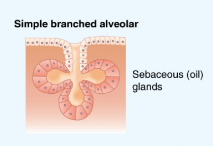
Simple Branched Acinar
Several acinar secretory proportions branching from single duct.
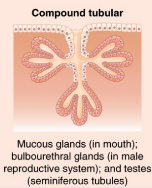
Compound Tubular
Glands with multiple ducts, each with a narrow tubular secretory portion.
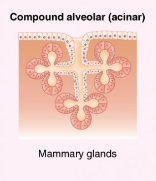
Compound Acinar
Glands with multiple ducts, each with several saclike secretory portions.
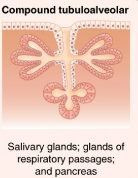
Compound Tubuloalveolar
Glands with multiple ducts, each with several tubular and acinar secretory portions.
Modes of Secretion
Exocrine glands can secrete via merocrine, apocrine, or holocrine modes, each with distinct mechanisms.
Merocrine Glands
Secrete via exocytosis without altering secretory cell. It is the most common gland.
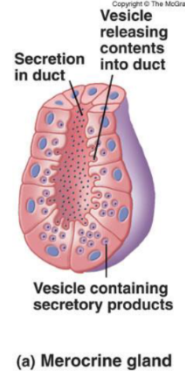
Apocrine Glands
Accumulate products just beneath the free surface.
Top of the cell is removed, and products are released.
The cell is then repaired
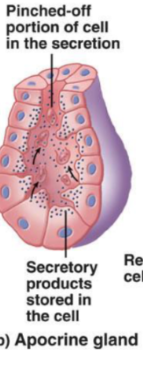
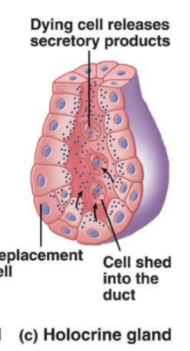
Holocrine Glands
Accumulate products until the cell bursts— releases secretory products, and then dies.