PSYCH: Cognitive approach definitions
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Cognition
Refers to all mental structures and processes involved in the reception, storage, and use of knowledge
Cognitive schema
A network of knowledge, beliefs, and expectations about particular aspects of the world, used as a means of simplifying reality
Model
A visual representation of a theory designed to explain it. Helps us to understand how something works
Multi-store memory model
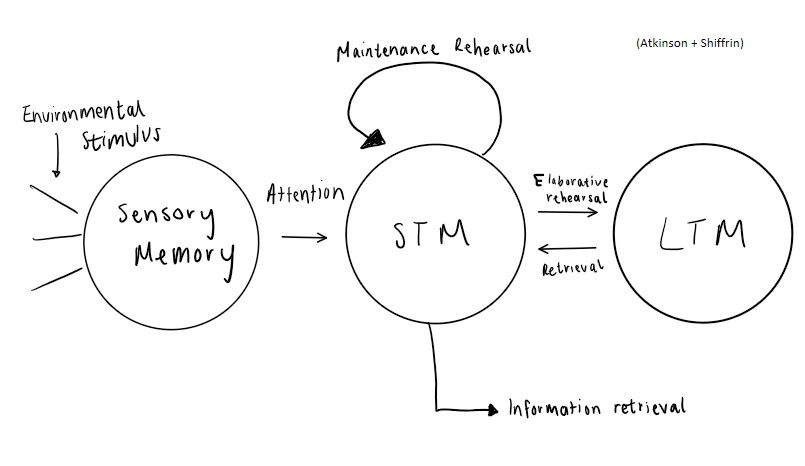
Sensory memory
Takes information from one of the sense organs and hold it in the same form (iconic or echoic)
Iconic memory
Visual information from the eyes (stored as images
Iconic memory duration
0.2-0.4 seconds
Echoic memory
Auditory input from the ears, stored as sounds
Echoic memory duration
3-4 seconds
Short term memory
Capacity: 7±2 items
Duration: 20 seconds
Long-term memory
Capacity: unlimited
Duration: lifetime
Working memory model
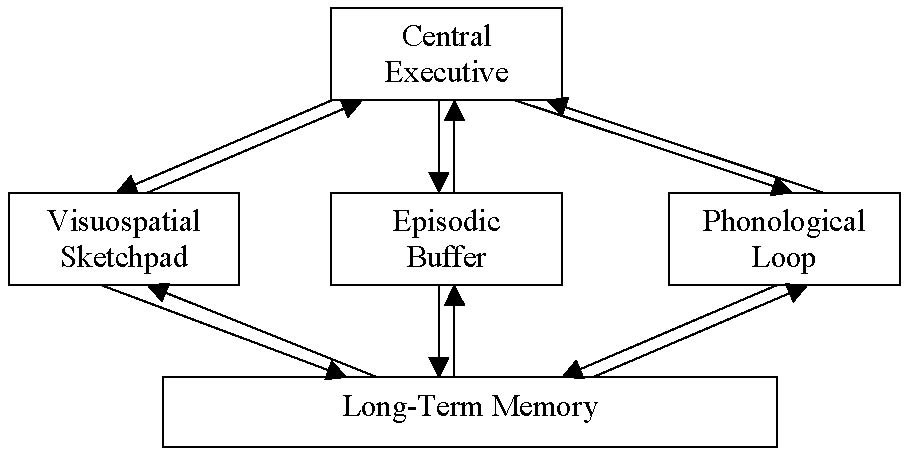
Working memory
The small amount of information that can be held in the mind and during the execution of cognitive tasks. It is information that is held and manipulated in conscious attention
Central executive
In control of the working memory, allowing concentration to be regulated
Phonological loop
Holds and manipulates auditory information in the working memory
Visuospatial sketchpad
Holds and manipulates visual information in the working memory
Episodic buffer
Temporary store that connects LTM to be ready for use when needed
System 1 thinking
Relies on LTM
Fast, automatic & effortless
intuitive
employs heuristics
little concentration required
not linked to cognitive ability or intelligence
System 2 thinking
Relies on Working memory
Slow, conscious, requires effort
rational thinking
logical
reliable
strongly linked to cognitive ability and intelligence
Thinking
The process of using knowledge and information to makes plans, interpret the world, and make predictions about the world in general
Decision-making
A component of thinking defined as the process of identifying and choosing alternative based on the values and preferences of the decision-maker
Heuristics
Mental shortcuts that allow people to solve problems and make judgements quickly and efficiently
Bias
Heuristic that affects out ability to make a rational decison
Anchoring bias
A heuristic describing the human tendency to rely too heavily on the first piece of information offered (the anchor) when making decisions.
Reconstructive memory
Human memory is not an exact copy of events but rather a reconstruction that may be altered over time. MEMORY IS MALLEABLE
Memory may be changed during storage, processing and retrieval due to schema processing.
Leading questions
Questions that have content or are phrased in a way to suggest a certain answer.
Flashbulb memory
A highly detailed, exceptionally vivid snapshot of the moment when a surprising and emotionally arousing event happened.