Male Reproductive System: Part 2
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam #3: disease and disorder terms, surgical terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
erectile dysfunction (ED)
the inability of the male to attain or maintain an erection sufficient to perform sexual intercourse
(formerly called impotence)
Tx: meds to increase blood flow (1st line), injectable drugs + vacuum devices (2nd), prosthesis
hydrocele
fluid-filled sac around the testicle; causes scrotal swelling
infertility
reduced or absent ability to achieve pregnancy; generally defined after 1 yr of frequent, unprotected sex (M/F)
phimosis
tightness of the prepuce (foreskin of the penis) that prevents its retraction over the glans penis; may be congenital or a result of balanitis
Tx: circumcision
priapism
persistent abn erection of the penis accompanied by pain and tenderness
prostate cancer
cancer of the prostate gland, usually occurring in men middle-aged and older
most common diagnosed cancer in Men, 2nd most common cause of cancer death for Men (95% are adenocarcinomas, arising from epithelial cells)
spermatocele
distention of the epididymis containing an abn cyst-like collection of fluid and sperm cells; may cause scrotal swelling
testicular cancer
cancer of the testicle, usually occurring in men 15 - 35 yrs of age
testicular torsion
twisting of the spermatic cord causing decr. blood flow to the testis;
(occurs most often during puberty and often presents w. a sudden onset of severe testicular or scrotal pain. Because of lack of blood flow, it is considered a surgical emergency)
varicocele
enlarged veins of the spermatic cord; may cause scrotal swelling
balanoplasty
surgical repair of the glans penis
epididymectomy
excision of the epididymis
orchiectomy (aka orchidectomy)
excision of the testis
(bilateral orchiectomy = castration)
orchiopexy (aka orchidopexy)
surgical fixation of the testicle (performed to bring undescended testicle(s) into the scrotum)
orchioplasty
surgical repair of the testis
orchiotomy (aka orchidotomy)
incision into the testis
prostatectomy
excision of the prostate gland
prostatocystotomy
incision into the prostate gland and the (urinary) bladder
prostatolithotomy
incision into the prostate gland to remove stone(s)
prostatovesiculectomy
excision of the prostate gland and the seminal vesicles
vasectomy
excision of a duct (partial excision of vas deferens bilaterally, resulting in male sterilization)
vasovasostomy
creation of artificial openings btw ducts
(the severed ends of the vas deferens are reconnected in an attempt to restore fertility in men who have had a vasectomy)
vesiculectomy
excision of the seminal vesicle(s)
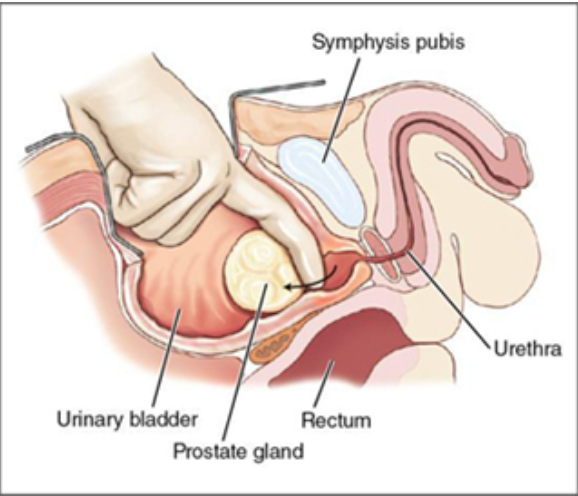
Simple prostatectomy
the inside portion of the prostate gland is excised through an abdominal incision made above the pubic bone and through an incision in the bladder and prostate capsule
surgeon uses a finger to remove the hyperplasticity tissue
used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) when prostate is very large and meds haven’t worked
aka open prostatectomy
Simple terms: procedure to remove the inside part of the prostate gland to treat an enlarged prostate
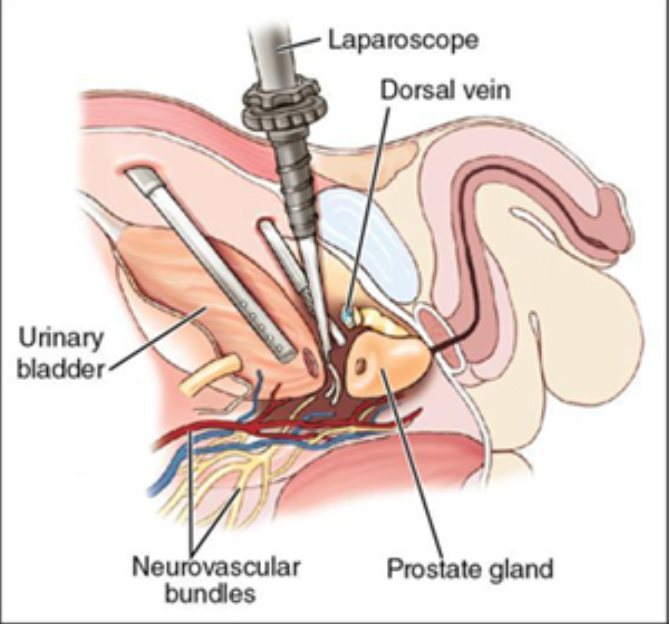
Radical prostatectomy
the prostate gland w. capsule, seminal vesicles, vas deferens, and pelvic lymph nodes are excised. Laparoscopic or robotic-assisted.
Used to treat prostate cancer
ablation
destruction of abnormal or excessive tissue by melting, vaporizing, or eroding
circumcision
surgical removal of the prepuce (foreskin); all or part of the foreskin may be removed
enucleation
excision of a whole organ or mass w/o cutting into it
hydrocelectomy
surgical removal of a fluid-filled sac around the testicle causing scrotal swelling (hydrocele)
laser surgery
use of a focused beam of light to excise or vaporize abnormal tissue and to control bleeding; uses variety of non-invasive and minimally invasive procedures
commonly used to treat BPH
morcellation
cutting or grinding solid tissue into smaller pieces for removal
robotic surgery
use of small surgical instruments attached to a computer and operated by the surgeon from a console several ft from the operating table
sterilization
surgical procedure that prevents pregnancy, either the ability of the F to conceive or of the M to induce conception
transurethral incision of the prostate gland (TUIP)
surgical procedure that widens the urethra by making a few small incisions in the bladder neck and the prostate gland. No prostate tissue is removed
TURP used when the prostate gland is less enlarged
transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT)
treatment that eliminates excess tissue present in benign prostatic hyperplasia by using heat generated by microwave
transurethral resection of the prostate gland (TURP)
surgical removal of pieces of the prostate gland tissue by using an instrument inserted through the urethra. The capsule is left intact; usually performed when the enlarged prostate gland interferes with urination
Photoselective vaporization of the prostate gland (PVP)
uses a laser system operated through a cystoscope inserted through the urethra to the prostate gland. Overgrown prostate tissue is vaporized using heat generated by the laser.
MRI ultrasound fusion biopsy
combination of magnetic resonance imaging w. transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) to obtain a tissue from a prostate lesion. Software merges an existing MR image w. live ultrasound images
multi parametric MRI
magnetic resonance imaging procedure providing information of anatomical structure and physiology for the staging of prostate cancer
transrectal ultrasound
ultrasound procedure used to diagnose prostate cancer. Sound waves are sent and received by a transducer probe that is placed into the rectum
prostate specific antigen (PSA)
blood test that measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood
(elevated test results may indicated the presence of prostate cancer, urinary or prostatic infection)
semen analysis
microscopic observation of ejaculated semen, revealing the size, structure, and movement of sperm; used to evaluate male infertility and to determine the effectiveness of a vasectomy
(aka sperm count/ sperm test)
total testosterone
blood test to measure the level of testosterone; used to detect multiple conditions in M/F including infertility
digital rectal examination (DRE)
physical examination in which the healthcare provider inserts a gloved finger into the rectum and palpates the prostate through the rectal wall to determine the size, shape, and consistency of the gland
(used to screen for BPH and prostate cancer)
aspermia
condition of w/o sperm (characterized by absence of semen or ejaculation)
may indicate the lack of production of spermatozoa, the lack of production of semen, or the lack of ejaculation of semen
oligospermia
condition of scanty sperm
(may contribute to infertility)
orchialgia
pain in the testis (aka testalgia)
chlamydia
sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by C. trachomatis (bact.)
sometimes referred to as a silent STI — because many people are not aware they have the disease
Sx: painful urination and discharge from penis, itching, vaginal discharge, bleeding btw menstrual periods in women
genital herpes
STI caused by herpes simplex virus type 2
gonorrhea
STI caused by a bact. organism that inflames the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
STI caused by a retrovirus that infects T-helper cells of the immune system; may also be acquired in utero or transmitted through infected blood via needle sharing
advanced infection progresses to AIDS
human papillomavirus (HPV)
STI caused by viral infection; more than 40 types of ___ that cause benign or cancerous growths in M/F genitals (aka genital warts)
cause of most cervical cancers
sexually transmitted infection (STI)
infection spread through sexual contact; affect both M/F, causing damage to repro organs and potentially serious health consequences if left untreated (aka STD)
syphilis
infection caused by bact. Treponema pallidum. Rapidly spreads through the body, and if untreated becomes systemic and can progress through 3 stages separated by latent periods
Usually sexually transmitted, but may be acquired in utero and by direct contact w. infected skin
trichomoniasis
STI caused by a one-cell organism Trichomonas — infects genitourinary tract
Men may be asymptomatic or may develop urethritis, an enlarged prostate gland, or epididymitis
Women may have vaginal itching, dysuria, and vaginal or urethral discharge
artificial insemination
introduction of washed and concentrated sperm into the F reproductive tract; used as a tx for infertility
condom
cover for the penis worn to prevent conception and the spread of STIs
spermicide
an agent that destroys spermatozoa; used to prevent conception
azoospermia
lack of live sperm in the semen (characterized by absence of semen or ejaculation)
obstructive — caused by blocked vessels or ducts
nonobstructive — caused by infection, lack of production of sperm, or retrograde ejaculation (sperm travels into bladder rather than out through urethra)
ejaculation
ejection of semen from the male urethra
orgasm
climax of sexual stimulation
puberty
period when 2ndary sex characteristics (ex: pubic and arm hair, voice depends, etc) develop and the ability to reproduce sexually begins