4.3 Chordates
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Deuterostomia
blastopore becomes anus
radial cleavage
indeterminate cleavage
primitiive dorsal nervous system
primitive central circulatory system
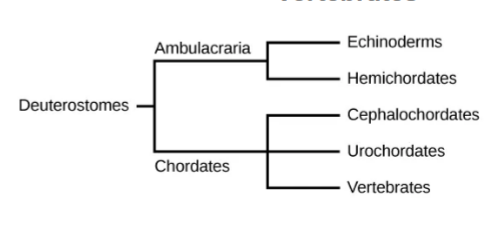
Chordates characteristics
Notochord: flexible rod shaped structure that runs along nerve chord
Dorsal hollow nerve chord: parallel to notochord
pharyngeal slits: gills, parts of ear and tonsils
Post-anal tail
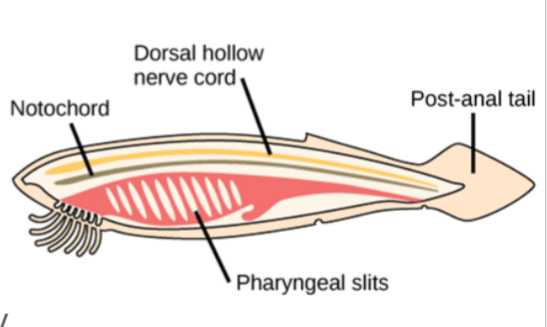
Phylum Chordata Subgroups
cephalochordata (invertebrates)
Urochordata (invertebrates)
Vertebrata
Urochordata
all 4 chordate features
adults have pharyngeal slits
tunicates: sea squirts
Cephlachordata
“head cord”
all 4 chordate features
Lancelets: filter feeders in mud
Vertebrata
largest group of chordates
cranium
all 4 chordate features
vertebrae
Fish
jawless fish
jawed fish
Chordate Jawless Fishes
Hagfish: poorly developed cranium and notochord
transitional group
have gills
scavengers and parasites
Vertebrate Jawless fishes
lampreys: possess a skull
parasitic
Gnathostomata- jaw mouth
jaw derived from gill arches
2 sets of fins
Chondrichthyes
cartilagionous fishes
oldest group
sharks rays
jaws/skeleton made of cartilage
evolution of teeth (modified scales)
gill slits lack hard covering
Osteichthyes- boney fishes
ossified skeleton
largest class of vertebrates
gills covered by operculum
swim bladder
1. gills
2. lungs -in bony fishes
3. swim bladder
Actinopterygii- ray finned fishes
slender bones in fin
gills are most common
bichirs- gills and lungs
Sarcopterygii- lobed finned fishes
lobed fins supported by arrangment of bones similar to tetrapods
lungfish and coelacanths- gills and lungs
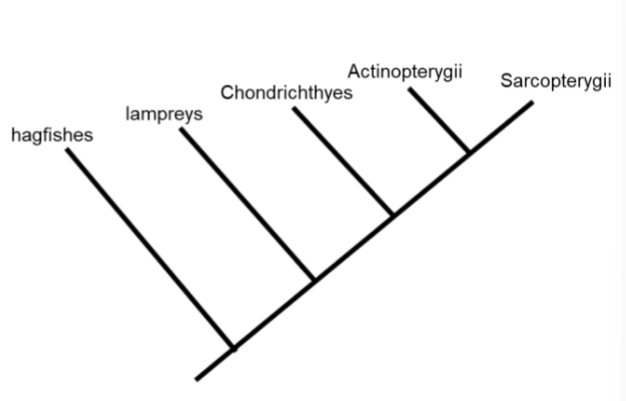
Practice: 2-3 defining characteristics for each group