ANSC 1401 - Growth and Development: Key Terms and Definitions
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Growth
result of many physiological processes that produce meat
Meat
most important source of high quality protein in human diet
Growth rate of animals
important factor determining the economic return from an animal enterprise
Scientists growing understanding
have been able to successfully alter and improve development, boosting efficiency and profit margins.
True growth
net increase in body protein, amount synthesized over that lost
Fat, bone, water
can be increased or decreased any time in animals life, not included in growth definition
True growth definition
definition of true growth does not fit everyday usage of term growth
Typical growth curve for population/individual (early)
increase in cell numbers, little increase in weight
Typical growth curve for population/individual (later)
greater increase in weight and then maturity. Could be bacterial or animal numbers.
Measuring growth in layman terms
Growth=Weight/time or W2-W1/T2-T1
Cattle: A steer was 265 days old and weighed 650 lb when put on feed. In the feedlot, it gained 350 lb in 120 days. It then weighed 1,000 lb and was 385 days old.
ADG= 1000-650lb/120d= 2.92 lb.
WDA=1000lb/365 days= 2.60 lbs
ADG
average daily gain
WDA
weight per day of age, includes birth weight
Swine- 231st day of year a feeder pig weight 40lb, it was fed until 326th day of the year when it weighed 230lb. ADG?
ADG=(230-40)/326-231= 2.00 lb
Are higher or lower ADG's and WDA's more desirable?
if an animal gains faster, it goes to market sooner
Facility use (ADG, WDA)
Higher= using facilities over a shorter time, less overhead expenses
Profit (WDA and ADG)
higher is more profitable
compensatory gain period
happens after dieting
Growth of cells
hyperplasia, hypertrophy
hyperplasia
increase in number of cells, mainly prenatal
Hypertrophy
increase in size of cells, fattening, weight lifter, callipyge sheep
Periods or phases of growth
Prenatal, postnatal
Prenatal
in uterus between fertilization of ovum and birth
Prenatal (Litter weight)
lower birth weights are caused by larger litters, smaller younger mothers, and nutrition of mother.
Who profits from compensatory gain?
cow producer-running yearlings- feedlot operator-slaughterer
Feedlot buyers
pay more per pound for thin calves than those showing bloom
Hyperplasia occurs?
almost always prenatally
Postnatal growth
all hypertrophy
Exceptions of growth
rodents, much less developed at birth than farm animal babies
Preweaning
still getting mothers milk
Post weaning
fending for self
Being in larger litter
less space and nutrients
Small uterus and small mother
less space to grow and less uterine space
younger mother
is still growing
Stages of development
Egg+sperm-> fertilized ovum-> Morula-> Blastocyst-> embryo-> fetus
Blastocyst
fluid filled cavity
Morula
16-32 cells-
Which trimester does the most fetal weight growth occcur?
3rd Trimester
Postnatal
after birth, relative growth rate declines with age, but accelerates after puberty begins
Stages of postnatal
preweaning and post weaning
Preweaning (Calves, pigs, lambs)
Calves:7mnths, Pigs: 3-5 wks, Lambs:2-6mnths
Preweaning weight
weaning weight affected by mothers milk, creep feed, pasture, genetics, age of dam, sex, castration, diet.
Sow diet
expensive, early weaning of pigs may be practiced
Post weaning (Postnatal)
from weaning to slaughter or to entry into breeding herd
Post weaning market weights (steers and heifers)
Steers:1,300lb avg, heifers:1,200 lb avg.
Post weaning market weights (barrows and gilts)
both 270lb avg
Post weaning market weights (lambs)
135lb avg
Factors affecting post weaning gain
amount and type of feed, genetics, sex, age, climate
what declines after puberty?
ADG
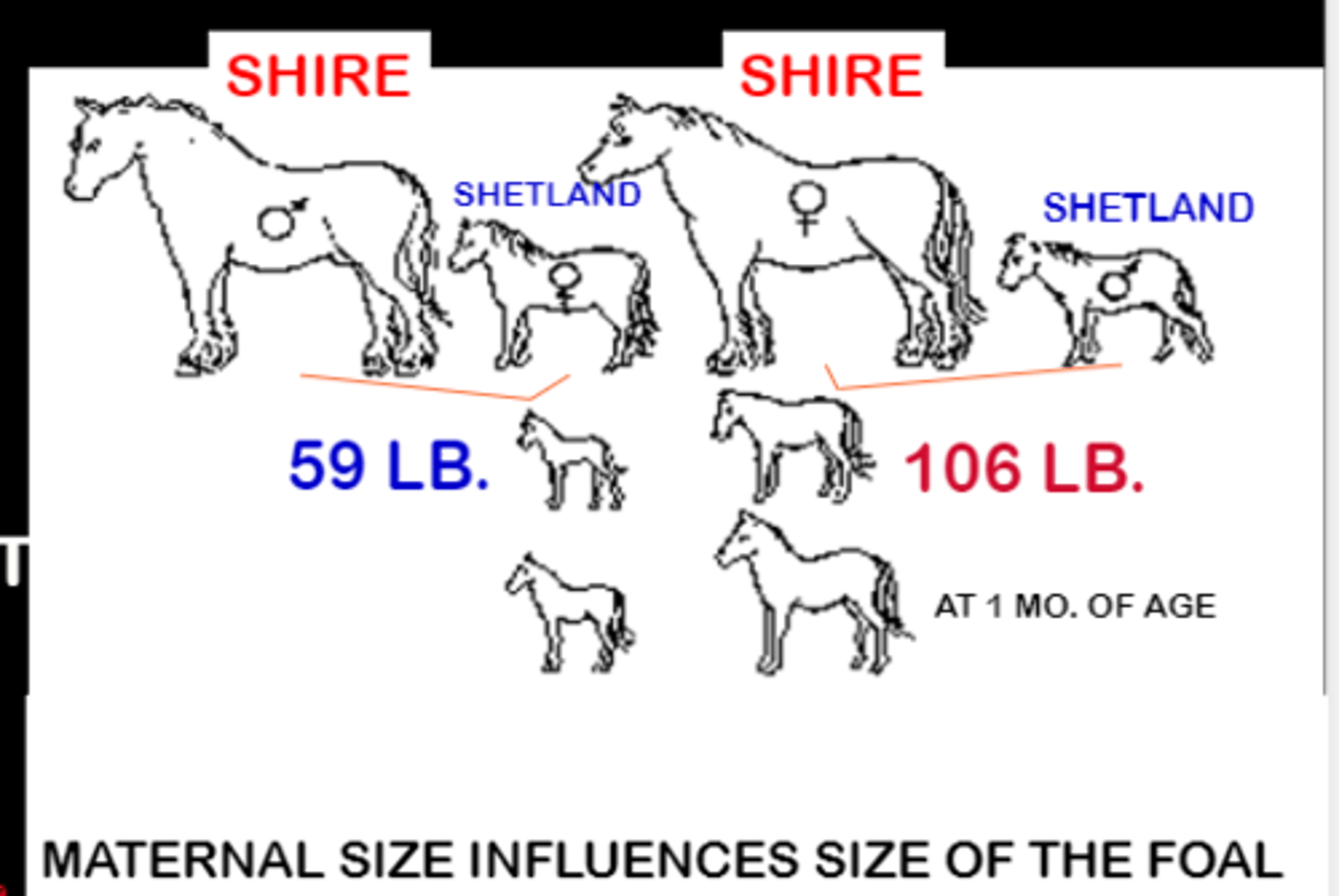
Effect of uterine size on offspring
similar genetic makeup but vastly different birth weights
Calf weaning weight peak
cow age of 6 years with little difference at 5,6, and 7. Mainly a milk yield affect.
Climate
can have a large effect on post weaning gain
Sex factor (Post weaning)
male: castrates, Female: hormones
External factors affecting growth
nutrition and environment
internal factors affecting growth
genes, hormones
Hereditary factors
genetic constitution of individual
Hereditary factor weight
Mature weight vs growth rate vs birth weight
Hereditary factor (uterine space)
Differences are not as large for other large animal species, can be partially influenced by external factors.
Hereditary factors (list)
weight, growth rate, uterine space, sex
Nutrition (nutrient priorities)
nervous, skeletal, muscular and adipose tissues.
Flow of blood containing nutrients
Nerves, Bones, Muscles, Fats
Fat deposition priorities
internal fat>subq fat>intermuscular fat>
Genetic potential
cannot be achieved with inadequate nutrition
Hormones
Secretions of endocrine glands that are carried in blood to sites where the are used.
Adrenaline
fight or flight, get them on the truck before they get their tails up
growth hormone (GH)
somatotropin, from anterior pituitary, can be made by genetically engineered microbes.
GH
species specific, affects CHO and fat metabolism, stimulates N retention and protein synthesis
GH shortage
dwarfism
GH oversupply
acromegaly (giantism)
GH in dairy cows
can use to increase milk production, increases stress and shortens time in herd.
Thyroxin
Thyroid gland, regulates BMR. Under control of thyrotropic hormone of anterior pituitary
Hypothyroidsm
Too little, causes our motors to run too slowly. early in embryonic life causes disproportionate dwarfism.
Hypothryoidism symptoms
reduced BMR, lethargy, low blood sugar, lowered N retention, fattening, dull hair coat, less cold tolerance.
Hyperthyroidism
too much, causes motors to run too fast. Pop eyed condition.
Iodine and temperature effects
iodized salt, goiter
Gonadal hormones
from ovaries or testes
Estrogens
from ovaries and adrenals, close epiphyseal plates and slow growth.
Estrogen variable effects across species
reduce rat growth, fatten chicks, increase growth and decrease fat of sheep and cattle. Increase protein synthesis
Implant compounds
DES, MGA, prevent estrus and increase ADG about 10% in heifers
Androgens
from testes and adrenals, increase growth and decrease fattening.
Androgen effect
greater effect on females than castrates
Castration effects
behavior change, fattening, lower gain, less lean, higher meat quality, more long bone growth
Progesterone
from corpus luteum on ovary, growth stimulant
Heifers
fatten faster than steers and steers faster than bulls
Swine
barrows are fatter than gilts
Environment
heat, cold, humidity, elevation
Diseases
death loss and reduced productivity
Maturity
fattening, muscle deposition ceases except when muscles are loaded such as in weight lifting.
What closes at maturity?
epiphyseal diaphyseal junction on long bones, break or spool joints on lamb carcasses
What happens at maturity?
No more increase in height, slow daily gain, decrease in body functions and metabolic rate
Hens
lay the most eggs first year and steadily decline each year after
Body weight vs metabolic rate
Heavier weight= lower MR
Senescense
process of growing old, onset of old age
life span vs growth rate
shorter growth period=shorter life span and vice versa
Calories expended during lifetime
nearly same for all animals except man. Larger size= lower BMR
BMR
basal metabolic rate
Aging
less hormone secretion, reaction time slows, strength and speed decline, recovery time increase, skin less elastic, body wears out.
Theories of aging
genetic mutations, immunological, developmental, biochemical
Genetic mutation aging
mutations accumulate and interfere with body functions
Immunological aging
reduction in AB production= older more prone to disease condtions